Business frameworks and methodologies are structured tools to approach complex, but common business challenges. They allow us to cut through noise, zero in on the key issues, and facilitate the development of insightful recommendations.
Business frameworks and methodologies are structured tools to approach complex, but common business challenges. They allow us to cut through noise, zero in on the key issues, and facilitate the development of insightful recommendations.
The importance and usefulness of business frameworks in the consulting world—especially among the global strategy firms—cannot be overstated. For consulting firms, these frameworks are part of the bread and butter that enable them to consistently deliver value to client organizations across industries and geographies.
Frameworks are helpful for several reasons:
- They provide structured and detailed process for addressing the business challenge at hand.
- They help ensure that the analysis is comprehensive and that critical aspects of a problem are thoroughly examined.
- They accelerate the problem-solving process, as they allow consultants to apply proven methods and best practices, rather than reinventing the wheel each time or wasting time and effort pursuing dead ends.
Consulting firms with extensive resources pioneer their own consulting frameworks through a combination of research, years of accumulated project experience, as well as subject matter expertise gathered from working across different sectors and functional areas. This development process is iterative and ongoing, with frameworks being continuously refined and updated to reflect new business realities and emerging best practices. Each global consulting firm maintains an internal knowledge management library of consulting framework presentations.
At FlevyPro, our team of former McKinsey and Big 4 consultants with several decades of combined experience have developed the largest publicly available knowledge base of consulting framework presentations, known as the FlevyPro Library. Each FlevyPro consulting framework presentation follows the standard “headline-body-bumper” design structure that is utilized by all the global strategy consulting firms.
FlevyPro is currently used by 100s of consultants and business executives. Based on sales and downloads of the FlevyPro frameworks, here is what we found to be the top 10 Organizational Design frameworks used by management consultants.
1. Organizational Design and Capability Analysis
The Organizational Design and Capability Analysis framework offers a strategic approach to structuring an organization in a way that aligns with its goals and enhances its operational efficiency. By focusing on the creation of roles, processes, and structures, this framework ensures that the foundational elements of the organization are optimally designed to meet current and future challenges.
This framework not only addresses the initial stages of Organizational Design, but also incorporates a thorough analysis of organizational capabilities, providing a deep understanding of the organization’s strengths and areas for improvement. The framework emphasizes 3 critical initial steps in a comprehensive 10-step Organizational Design process:
- Vision and Business Architecture: Establishing a clear vision and understanding of the business architecture is crucial. This step involves aligning the organization’s structure with its strategic objectives and ensuring that the overall design supports the achievement of these goals.
- Clarifying Design Criteria: This step involves defining the criteria that will guide the design process. These criteria ensure that the Organizational Design aligns with the strategic vision and operational requirements, facilitating decision-making throughout the design process.
- Defining Capabilities and Competencies: Identifying the key capabilities and competencies required to achieve strategic objectives is essential. This step ensures that the organization has, or plans to develop, the necessary skills, knowledge, and abilities to execute its strategy effectively.
Capability Analysis is a critical component of this framework, offering strategic insights into the organization’s ability to pursue or implement strategic options. This analysis helps identify gaps in capabilities and competencies, guiding strategic planning and investment in areas critical for success.
The Organizational Design and Capability Analysis framework provides several benefits:
- Strategic Alignment: Ensures that the organization’s design is fully aligned with its strategic goals, enhancing the likelihood of achieving these objectives.
- Operational Efficiency: By optimizing roles, processes, and structures, the organization can operate more efficiently, reducing redundancies and improving performance.
- Informed Decision-Making: Capability Analysis offers valuable insights into the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, informing strategic decisions and investments.
- Future Readiness: The framework facilitates an organization’s ability to adapt to future challenges by ensuring that capabilities and competencies are continually assessed and developed.
Incorporating this framework into Organizational Design efforts provides a structured approach to creating a robust, efficient, and strategically aligned organization. By emphasizing both the structural aspects of Organizational Design and the critical role of capability analysis, management consultants can guide organizations towards achieving operational excellence and strategic success.
2. Smart Organizational Design
The concept of Smart Organizational Design, pioneered by BCG, addresses the need for a contemporary approach to restructuring organizations in today’s complex and rapidly changing business environment.
As organizations face unprecedented challenges from competition, disruptive technologies, globalization, and evolving legal landscapes, the demand for enhanced performance to meet customer needs and outperform rivals has never been higher. The shift from manual and clerical work to knowledge-based experiential work underscores the transformation of the workforce, which is now more empowered and innovative.
Traditional reorganization methods are often inadequate in this digital age, leading to a high failure rate of transformation and change programs.
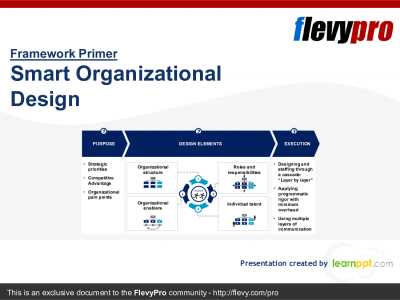
This Smart OD framework introduces a new paradigm for reorganization, focusing on three critical steps to ensure successful implementation:
- Purpose: Clearly defining the rationale behind the reorganization is crucial. This involves articulating why the change is necessary and what it aims to achieve, ensuring alignment with the organization’s strategic goals.
- Design Elements: Identifying and determining the behaviors, structures, and processes critical to supporting the reorganization. This step involves a deep understanding of the desired outcomes and how different elements of the organization can be aligned to facilitate these changes.
- Execution: Outlining a clear and actionable plan for executing the Smart Organizational Design. This includes identifying key milestones, resources required, and mechanisms for monitoring progress and adjusting the approach as needed.
The framework also highlights Critical Success Factors that significantly improve the likelihood of success for reorganization initiatives:
- Strong Leadership Commitment: Leadership must be fully committed to the reorganization, providing clear direction and support throughout the process.
- Effective Communication: Open and transparent communication is essential to manage expectations, mitigate resistance, and foster a culture of inclusion and collaboration.
- Agility and Flexibility: The ability to adapt to unforeseen challenges and feedback during the reorganization process is critical for maintaining momentum and achieving objectives.
- Employee Engagement and Participation: Actively involving employees in the reorganization process helps to harness their insights, increase buy-in, and encourage innovation.
The Smart Organizational Design framework offers several advantages:
- Strategic Alignment: Ensures that reorganization efforts are closely aligned with the organization’s overarching strategic objectives, enhancing the likelihood of achieving desired outcomes.
- Increased Competitiveness: By focusing on critical behaviors and designing for agility, organizations can better respond to market changes and competitive pressures.
- Higher Success Rate of Transformation Programs: Addressing the shortcomings of traditional reorganization approaches increases the chances of success in transformation and change initiatives.
- Enhanced Organizational Performance: A smart approach to Organizational Design can lead to improved efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction.
Adopting the Smart OD approach provides organizations with a modern, strategic approach to reorganization, enabling them to navigate the complexities of the digital age and achieve sustainable competitive advantage.
3. 9 Principles of Organizational Design
The 9 principles of Organizational Design, compiled by McKinsey, is a comprehensive approach that addresses the challenges and complexities inherent in structuring or restructuring organizations. With the business environment experiencing rapid and continuous change due to technological advancements, regulatory shifts, and global events, organizations find themselves in a near-constant state of flux.
McKinsey’s research underscores the prevalence of Organizational Design efforts, yet also highlights a concerning statistic: less than 25% of these redesign efforts meet their intended objectives. This framework aims to significantly improve the success rate of Organizational Design initiatives by providing a structured, principle-guided approach.
While the detailed content of each principle, including current practices, principle-guided approaches, case examples, and impacts, is explored within the framework, the overarching principles focus on ensuring that Organizational Design efforts are strategic, evidence-based, and aligned with long-term goals. These principles encompass:
- Alignment with Strategy: Ensuring the OD directly supports the strategic objectives of the organization.
- Customer Centricity: Structuring the organization to effectively meet customer needs and drive customer satisfaction.
- Simplicity: Striving for simplicity in processes and structures to enhance efficiency and clarity.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Designing an organization that can adapt to changes and scale as needed.
- Empowerment and Accountability: Establishing clear roles and responsibilities that empower employees and ensure accountability.
- Culture and Leadership Alignment: Aligning the OD with the company’s culture and leadership vision.
- Communication and Collaboration: Facilitating effective communication and collaboration within and across teams.
- Talent and Competencies: Aligning organizational roles with the talents and competencies needed to execute the strategy.
- Technology and Innovation: Incorporating technology and innovation into the OD to drive future growth.
By adhering to these principles, organizations can significantly improve the likelihood of a successful redesign. The benefits include:
- Strategic Coherence: Aligning the structure with strategic goals ensures that organizational efforts are focused and effective.
- Increased Agility: A principle-guided approach to Organizational Design fosters an agile organization capable of responding to external changes.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: When roles and processes are clear, and the organization’s design aligns with its culture, employee engagement and satisfaction are likely to increase.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Simplification and clarity in OD can lead to more efficient operations and reduced costs.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that effectively implement these principles are better positioned to capitalize on new opportunities and navigate challenges.
The 9 principles of Organizational Design offers a roadmap for companies seeking to undertake Organizational Design (or Redesign) efforts. By moving away from intuition-based decision-making to a more structured, principle-guided approach, organizations can achieve not only the desired outcomes from their redesign efforts but also establish a resilient and dynamic organizational structure equipped for the demands of the modern business environment.
4. Organizational Design: 10 Leadership Questions
The “Organizational Design: 10 Leadership Questions” framework emphasizes the role of strategic questioning in guiding a company through a successful organizational restructuring process.
The framework underscores that while the path to successful Organizational Design is complex, focusing on key leadership questions can significantly clarify the direction and ensure alignment with the organization’s core objectives and capabilities.
Recognizing that alignment between an organization’s structure, its strategy, and the customer experience is crucial for performance enhancement, this framework distills the process into 3 simplified steps:
- Decide: The initial step involves making strategic decisions about the direction of the OD. This includes defining the purpose and objectives of the redesign effort.
- Design: This step focuses on crafting the structure of the organization in a way that aligns with the strategic decisions made in the first step. It involves detailed planning of roles, processes, and interactions within the organization.
- Deliver: The final step is the implementation of the designed organizational structure. This includes managing the transition, communicating changes, and ensuring the organization is equipped to operate effectively in the new structure.
While the framework suggests a structured approach through its 3 steps, it also posits that leaders should ponder 10 critical questions to navigate the Organizational Design Journey effectively.
Thoroughly addressing these integral Leadership questions provides several benefits:
- Strategic Clarity: Helps ensure that the organizational redesign is fully aligned with the strategic goals of the company, enhancing the likelihood of achieving these objectives.
- Enhanced Performance and Competitiveness: By focusing on alignment and efficiency, organizations can improve performance and gain a competitive edge.
- Improved Decision-Making: The framework encourages a thoughtful and strategic approach to decision-making, ensuring that changes are well-considered and based on a solid understanding of the organization’s goals and capabilities.
- Successful Transformation: By focusing on the right questions and following a structured process, companies can increase the chances of a successful organizational transformation.
This framework provides leaders with a strategic approach to restructuring, ensuring that the process is aligned with the organization’s purpose, strategy, and operational needs. By focusing on these critical questions, organizations can navigate the complexities of design and transformation, leading to improved performance and long-term success.
5. Digital Organizational Design
The Digital Organizational Design framework addresses the evolving requirements of the modern workplace, profoundly influenced by digital technologies. This transformation necessitates a shift from traditional, hierarchical structures to more agile, flat, and decentralized models that foster open culture and candid communication. As digital technologies continue to reshape business landscapes, organizations are exploring innovative structures to enhance agility, improve decision-making, and better respond to customer needs.
This framework discusses 4 specific operating models of Digital Organizations:
- The Tactical Model: Focuses on specific digital initiatives and projects with the aim of achieving immediate operational improvements or addressing particular challenges.
- The Centralization Model: Involves centralizing digital functions within the organization to ensure consistency, leverage synergies, and optimize the use of digital technologies across different departments.
- The Champion Model: Empowers leaders within various departments to drive digital initiatives, encouraging innovation and digital thinking throughout the organization.
- The Business As Usual (BUA) Model: Integrates digital technologies and practices into all aspects of the organization’s operations, making digital proficiency and innovation part of the everyday workflow and culture.
To complement the operating models, the Digital Readiness Diagnostic Framework aids organizations in assessing their digital maturity across 5 critical areas:
- Strategy and Leadership: Evaluates the alignment of digital strategies with overall business objectives and the effectiveness of leadership in driving digital transformation.
- Customer Engagement: Assesses how well the organization uses digital channels and technologies to engage with customers and meet their expectations.
- Products and Services: Looks at the organization’s capability to innovate and offer digital or digitally enhanced products and services.
- Organization and Talent: Examines the organization’s structure, culture, and talent management practices to support digital initiatives.
- Digital Operations: Reviews the efficiency and effectiveness of digital processes and operational models within the organization.
Utilizing the Digital Organizational Design framework provides several benefits:
- Enhanced Agility and Innovation: By adopting more flexible and decentralized organizational models, companies can respond more rapidly to market changes and foster a culture of innovation.
- Improved Customer Experience: A focus on digital readiness enables organizations to better understand and engage with customers through digital channels, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlining operations through digital technologies and models can significantly reduce costs and improve service delivery.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that effectively implement digital organizational models and assess their digital readiness are better positioned to capitalize on new opportunities and gain a competitive edge in the digital age.
Digital Organizational Design offers a roadmap for traditional organizations to navigate the complexities of Digital Transformation, ensuring they are equipped to thrive in an increasingly digital world. By embracing these models and conducting a thorough digital readiness assessment, organizations can unlock their digital potential and achieve sustained success.
6. Galbraith Star Model
The Galbraith Star Model™ is a renowned framework for Organizational Design that provides a holistic approach to structuring a company. This framework is pivotal for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of creating an organization that is both effective and adaptable.
By considering a series of design policies that management can control, the Star Model™ aids in shaping employee behavior in a way that aligns with the company’s overarching goals.
The framework is structured around 5 key components (forming the points of a star), each of which plays a critical role in the overall effectiveness of the organization:
- Strategy: This component defines the company’s direction and goals. It outlines what the business aims to achieve and sets the foundation for the other elements of the model.
- Structure: Refers to how the organization is arranged, including the division of tasks, coordination, and allocation of responsibilities. The structure should support the execution of the strategy.
- Processes: This encompasses the flow of information, decision-making mechanisms, and daily operations that enable the organization to function efficiently and effectively.
- Rewards: Systems put in place to motivate and reward employees. These should be aligned with the company’s goals, encouraging behaviors that support the achievement of those objectives.
- People: Focuses on the human resources policies related to recruitment, development, and retention of employees. This component ensures that the organization has the skills and capabilities required to execute its strategy.
A key premise of the Star Model™ is its recognition that every organizational structure comes with inherent positives and negatives. By identifying the drawbacks of a chosen structural design, management can intentionally design the other elements of the Star Model™ to mitigate these negatives while capitalizing on the positives. This balanced approach allows for a more nuanced and effective Organizational Design.
Implementing the Galbraith Star Model™ offers several advantages:
- Holistic Design: Offers a comprehensive view of OD, ensuring that all critical aspects are considered and aligned.
- Strategic Alignment: Ensures that the structure, processes, rewards, and people policies are all aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Adaptability: Facilitates the identification and mitigation of potential drawbacks in OD, allowing for greater flexibility and adaptability in changing markets.
- Enhanced Performance: By aligning rewards and people policies with organizational goals, companies can foster a culture of high performance and achievement.
The Galbraith Star Model™ serves as a powerful tool for organizations aiming to design or redesign their structure in a manner that is cohesive, strategic, and capable of adapting to market demands. By thoughtfully considering each of the five components, companies can build a solid foundation for sustained success.
7. Five Pillars of Agile Organizations
The Five Pillars of Agile Organizations framework provides a structured approach for transforming traditional, hierarchical organizations into Agile entities capable of quick execution, rapid decision-making, and heightened responsiveness to market changes. This shift from a static, siloed structure to an Agile framework is essential for organizations looking to thrive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
By focusing on 5 foundational pillars, organizations can redesign their operations to be more flexible, collaborative, and driven by a shared purpose to create value for stakeholders:
- Strategy: Agile organizations adopt a flexible strategy that allows them to quickly respond to changing market conditions. This involves setting a clear vision and allowing teams the autonomy to pursue objectives that align with the overarching goals.
- Structure: Instead of rigid hierarchies, Agile organizations favor flat structures that promote open communication and collaboration. Teams are cross-functional and empowered to make decisions, reducing bottlenecks and enhancing responsiveness.
- Process: Processes in Agile organizations are streamlined and designed for speed. Decision-making is decentralized, and there is a strong focus on continuous improvement, learning from successes and failures alike.
- People: The focus is on building a culture where employees are empowered, engaged, and committed to the organization’s purpose. This involves fostering a mindset of collaboration, innovation, and accountability.
- Technology: Leveraging technology to enable agility, Agile organizations use digital tools to facilitate communication, automate processes, and provide real-time data to support decision-making.
The transition to an Agile organization requires significant shifts in thinking and behavior. Traditional command-and-control approaches give way to leadership styles that prioritize empowerment, trust, and a focus on enabling teams to deliver value efficiently. Core Agile practices such as iterative development, continuous feedback, and a strong emphasis on customer-centricity become central to the organization’s way of operating.
Implementing the Five Pillars of Agile Organizations framework offers numerous benefits:
- Increased Flexibility: Organizations can more effectively adapt to market changes and emerging opportunities.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined processes and empowered teams reduce delays in decision-making and execution.
- Greater Employee Satisfaction: A culture of empowerment and accountability leads to higher levels of employee engagement and job satisfaction.
- Improved Customer Experience: A focus on agility and customer-centricity ensures that organizations can quickly respond to customer needs and preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
By understanding and incorporating these five pillars, traditional organizations can undertake a successful Agile Transformation, positioning themselves to not only adapt to the demands of the modern business landscape but to lead and innovate within it.
8. 4 Building Blocks of Organizational DNA
The 4 Building Blocks of Organizational DNA framework presents a foundational approach for companies aiming to excel in execution and secure a competitive advantage. It suggests that true effectiveness in execution is achieved not by mastering a set of processes, but by embedding intelligence, decision-making capabilities, and a focus on common goals throughout the organization’s very fabric. This integration ensures that every employee and unit operates efficiently and collaboratively towards shared objectives.
These 4 building blocks of Organizational DNA are defined as:
- Structure: This refers to how the organization is arranged, including its hierarchy, team configurations, and division of roles and responsibilities. An optimal structure facilitates clear communication and efficient workflow.
- Decision Rights: Clearly defined decision rights ensure that employees at all levels understand their authority and the scope of decisions they can make, leading to faster and more effective decision-making processes.
- Motivators: These include the systems and incentives in place to encourage desired behaviors and outcomes. Effective motivators align individual goals with the organization’s objectives, driving performance and innovation.
- Information: The flow and accessibility of information within the organization are crucial for informed decision-making and action. Ensuring that the right people have access to relevant, timely information is key to the organization’s success.
While the presentation further delves into the 8 core elements of Organizational Design, these elements likely expand upon the 4 building blocks, offering a more detailed blueprint for crafting organizations that are adaptable, self-correcting, and robust. These elements encompass aspects such as leadership, culture, processes, and technology, each contributing to the organization’s ability to execute its strategy effectively.
A lack of operational understanding of these building blocks can be a major obstacle to achieving excellence. By focusing on these foundational aspects, organizations can address common challenges that hinder execution and performance.
The journey to refining these building blocks and aligning the core elements of OD with the company’s strategic goals is iterative and may take several years, but it is essential for building a resilient and successful organization.
Implementing the 4 building blocks of Organizational DNA provides several benefits:
- Enhanced Execution and Performance: By integrating decision-making capabilities and a focus on common goals into the organization’s DNA, companies can significantly improve their execution effectiveness.
- Increased Agility: An optimal OD allows companies to adapt more quickly to changes in the environment or strategy.
- Stronger Alignment: Aligning structure, decision rights, motivators, and information with the organization’s goals ensures that all efforts contribute to the desired outcomes.
- Greater Cohesion and Collaboration: A well-designed organizational DNA fosters a culture of collaboration, where teams and individuals work together seamlessly towards common objectives.
This framework offers a strategic foundation for companies looking to achieve not just operational efficiency, but a sustainable competitive advantage through superior execution and organizational cohesion.
9. Removing Organizational Silos
This framework on removing Organizational Silos provides a strategic approach to fostering collaboration and unity across different parts of an organization, especially crucial during periods of transformation.
In the modern, knowledge-based economy, while silos can enhance productivity by grouping similar skills and functions together, they can become a significant impediment during organizational transformation efforts. Silos can lead to cultural misalignment, communication breakdowns, and a lack of cooperation, which in turn can stall or derail transformative initiatives.
This framework outlines 7 critical strategies to dismantle these barriers and promote a more integrated and cohesive organizational environment:
- Align Leaders: Ensuring that leaders across the organization are on the same page regarding the goals and processes of the transformation. Leadership alignment is critical to setting a unified direction for the company.
- Create Cross-Functional Teams: Establishing teams composed of members from various departments or functions to work on specific transformation initiatives. This promotes knowledge sharing and breaks down traditional departmental barriers.
- Create Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Defining and communicating the roles and responsibilities clearly to avoid overlaps and conflicts, ensuring everyone knows their part in the transformation effort.
- Co-locate Teams: Physically situating cross-functional teams together can enhance communication and collaboration among team members who might otherwise not interact frequently.
- Create Joint Incentives: Developing incentive structures that reward collaborative success rather than individual departmental achievements can motivate teams to work together towards common goals.
- Create a “Two in a Box” Leadership: Implementing a leadership approach where two leaders from different parts of the organization share responsibility for a project can foster mutual understanding and shared accountability.
- Clarify Decision Rights: Making sure that it is clear who has the authority to make decisions on various aspects of the transformation initiatives. Clear decision rights prevent bottlenecks and ensure swift action.
Removing Organizational Silos can lead to several benefits:
- Enhanced Collaboration and Unity: By breaking down silos, organizations can foster a culture of collaboration and unity, essential for successful transformation.
- Increased Agility: A more interconnected and less siloed organization can respond more quickly to changes and challenges, enhancing its agility.
- Improved Communication: The framework encourages open lines of communication across different parts of the organization, which is vital for the successful execution of transformation initiatives.
- Higher Employee Engagement: Employees who feel they are part of a cohesive, united effort are more likely to be engaged and motivated.
- Successful Transformation: Ultimately, by addressing the challenges posed by silos, organizations can significantly increase the likelihood of successful business transformation.
Following this framework’s approach allows organizations to overcome the barriers posed by siloed structures, paving the way for more effective collaboration and successful pursuit of the organization’s objectives.
10. The Strategic Functional Organization
The Strategic Functional Organization framework addresses the evolving role of functional organizations in today’s dynamic business landscape, where Agility, Flexibility, and Operational Excellence are paramount.
As organizations increasingly focus on capabilities, functional leaders are called upon to play a more strategic role, balancing day-to-day operational demands with the development of distinctive capabilities that drive competitive advantage. This shift necessitates a new functional agenda that enables leaders to elevate their contributions and align more closely with the company’s strategic objectives.
There are 3 core elements of the Strategic Functional Organization:
- Priorities: Functional leaders must identify and focus on a set of clear priorities that support the organization’s overall strategy. This involves distinguishing between critical strategic initiatives and day-to-day operational tasks, ensuring resources are allocated effectively to drive strategic outcomes.
- Fit-for-Purpose Operating Model: Developing an operating model that is tailored to the unique needs and strategic goals of the function. This includes structuring the organization, defining roles and responsibilities, and establishing processes that enable agility and efficiency.
- Execution and Resource Allocation: Effective execution of the strategic plan requires meticulous resource allocation and a focus on achieving results. Functional leaders must ensure that their teams have the necessary resources, including talent, technology, and capital, to implement strategic initiatives successfully.
Functional leaders who successfully transition to their new strategic role can significantly impact the organization, bringing the company’s strategy to life and delivering substantial value. To do this, leaders must excel in several key areas:
- Interpersonal Skills: Building strong relationships within and outside the function is crucial for fostering collaboration, influencing stakeholders, and driving change.
- Strategic Insight: Leaders must develop a deep understanding of the broader business landscape, including market trends, competitive dynamics, and internal strategic objectives, to guide their functional strategy.
- Operational Excellence: While focusing on strategic objectives, leaders cannot overlook the importance of operational efficiency. Balancing long-term strategic goals with the need for cost reduction and operational improvements is essential.
Becoming a Strategic Functional Organization offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Strategic Alignment: Functional strategies that are closely aligned with the organization’s overall goals can drive more impactful outcomes.
- Increased Agility and Flexibility: A fit-for-purpose operating model enables the function to adapt more readily to changes in the business environment.
- Improved Performance Results: Focusing on execution and strategic resource allocation helps ensure that functional initiatives contribute to the organization’s success.
- Elevated Role of Functional Leaders: As functional leaders take on a more strategic role, they can contribute more significantly to the company’s strategic direction and competitive positioning.
By adopting this framework, functional organizations can navigate the challenges of the modern business environment, transitioning from traditional operational roles to becoming key drivers of strategic success.
Additional Consulting Tools for Organizational Design
Here are links to additional consulting resources related to Business Transformation available through Flevy:
Organizational (re-)designs are becoming more and more common. In fact, most organizations have undertaken an Organizational Redesign within the past 3 years.
The OD consulting frameworks discussed provide critical insights and methodologies for navigating these frequent redesign efforts effectively. By grounding organizational changes in structured approaches, these frameworks help ensure that redesigns are not just reactive measures, but strategic initiatives that enhance alignment with business goals, improve operational efficiency, and foster a culture conducive to innovation and agility.
 Business frameworks and methodologies are structured tools to approach complex, but common business challenges. They allow us to cut through noise, zero in on the key issues, and facilitate the development of insightful recommendations.
Business frameworks and methodologies are structured tools to approach complex, but common business challenges. They allow us to cut through noise, zero in on the key issues, and facilitate the development of insightful recommendations.