Editor's Note: Take a look at our featured best practice, Pricing Strategy (38-slide PowerPoint presentation). Pricing Strategy is a core pillar of Marketing and Product Strategy. It is 1 of the 4 Ps of Marketing (also known as the Marketing Mix - Product, Price, Placement, and Promotion). As such, knowing how to properly price your product is extremely important to the commercial success and viability of [read more]
Also, if you are interested in becoming an expert on Strategy Development, take a look at Flevy's Strategy Development Frameworks offering here. This is a curated collection of best practice frameworks based on the thought leadership of leading consulting firms, academics, and recognized subject matter experts. By learning and applying these concepts, you can you stay ahead of the curve. Full details here.
* * * *
So, you have a robust product roadmap, covering all product features from the most basic to the most innovative. Now, how did you prioritize these features? Did you prioritize things correctly?
 With limited resources, all organizations strive to prioritize those activities that drive the most value. This is particularly true in product development. Focusing on the right or wrong set of features can make or break your product (or even company).
With limited resources, all organizations strive to prioritize those activities that drive the most value. This is particularly true in product development. Focusing on the right or wrong set of features can make or break your product (or even company).
The Kano Customer Satisfaction Model is a theory of product development and customer satisfaction developed by Professor Noriaki Kano. This framework provides a rational, structured approach to product development, offering tremendous insight into the product attributes that are perceived to be important to customers.
The Kano Customer Satisfaction Model focuses on differentiating product features, as opposed to focusing initially on customer needs.
To understand this model, first, we must define the concepts of Satisfaction and Functionality–the 2 dimensions that form the basis of the Kano Model.
Satisfaction
- Our goal is to achieve Satisfaction. In the Kano model, the Satisfaction dimension can be evaluated on a 5-level scale, that goes from total satisfaction (i.e. customer is “Delighted”) to total dissatisfaction (i.e. customer is “Frustrated”).
Functionality
- Functionality represents how much of a given feature the customer receives, how well we’ve implemented it, or how much we’ve invested in its development. This dimension ranges from no functionality at all to the best possible implementation.
Remember, there is a cost to developing functionality, which is why proper prioritization is so critical.
Kano classifies product features into 4 categories, driven by how customers react to the level of Functionality:
Performance
- Sometimes also referred to as Linear or One-Dimensional, because the relationship between Satisfaction and Functionality is linear—i.e., as Functionality increases, so does Satisfaction.
- Examples of Performance features include gas mileage (of your car), internet connection speed, laptop battery life.
Must-Be
- Must-Be features a “must have” features—if our product doesn’t have them, the product will be considered incomplete
- We must have these features, but they won’t make the customer satisfied nor dissatisfied.
- Examples include: product receipts, apartment windows, hotel towels.
Attractive
- These features, also called Exciters or Delighters, are unexpected features that produce a positive reaction—our reaction can range from mild delight to absolute mind-blown
- An example could be the first you used a smartphone and were surprised by the ease of use
Indifferent
- These are features that don’t make a real difference in our reaction to the product
- We should avoid spending any time and effort developing these features
- An example if thickness of wax coating on the milk carton—this may be key to the design and manufacturing of the carton, but customers are not even aware of the distinction
To better grasp what these categories represent, lets map these 4 categories against the axes of Satisfaction (y-axis) and Functionality (x-axis). See the diagram below.
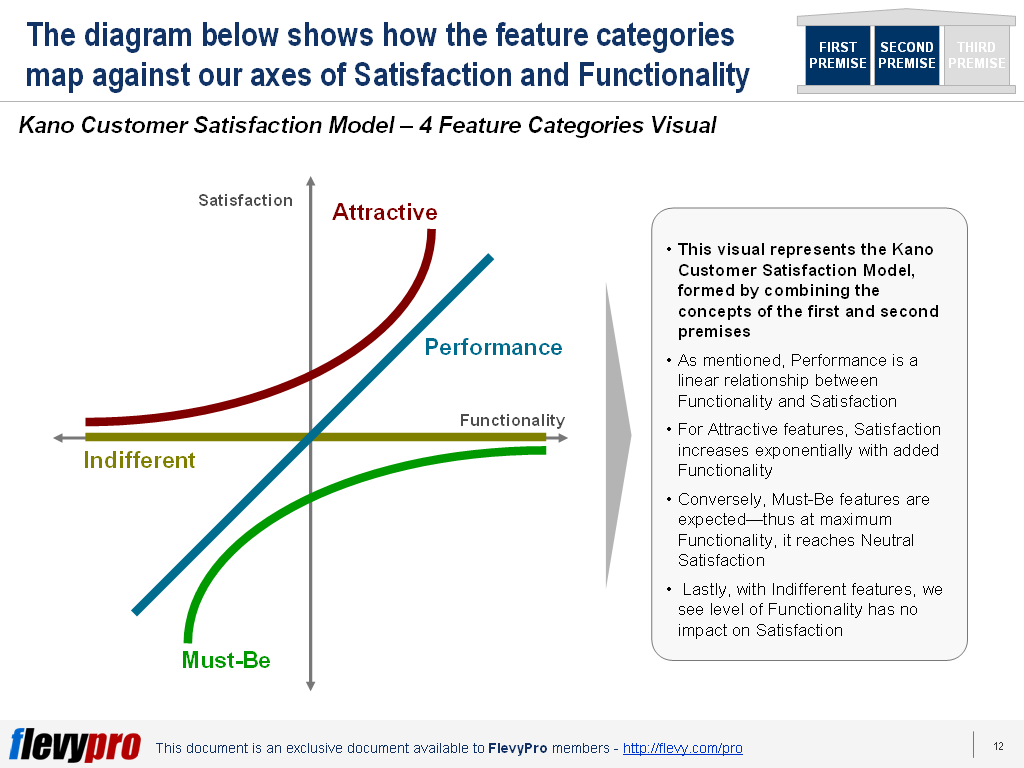
Here are the immediate take-aways:
- As mentioned, Performance is a linear relationship between Functionality and Satisfaction.
- For Attractive features, Satisfaction increases exponentially with added Functionality.
- Conversely, Must-Be features are expected—thus at maximum Functionality, it reaches Neutral Satisfaction.
- Lastly, with Indifferent features, we see level of Functionality has no impact on Satisfaction. Why develop these features at all? Remove them from the roadmap, as they will only waste our resources.
Kano also noted that, customers get spoiled over time, as they get used to features. Thus, features once deemed Attractive, over time become Performance features and eventually become Must-Be features. This disenchantment is driven by many factors, including technology evolution and the emergence of competitors who all bring the same functionality as incumbents. Therefore, any analysis done using this model is only a current snapshot. It needs to be updated regularly to keep up with changing customer expectations.
How do you product features map against Satisfaction and Functionality? What other insights can you gather from the Kano Customer Satisfaction Model?
You can download an editable PowerPoint about the Kano Customer Satisfaction Model here on the Flevy documents marketplace.

29-slide PowerPoint presentation
Launching a new product or venturing into a new market is a significant endeavor. The Ultimate Go-To-Market (GTM) Strategy Framework, developed by seasoned consultants from BCG and EY, is your robust action plan ensuring a well-coordinated and potent market entry. This framework aids in
[read more]
Want to Achieve Excellence in Strategy Development?
Gain the knowledge and develop the expertise to become an expert in Strategy Development. Our frameworks are based on the thought leadership of leading consulting firms, academics, and recognized subject matter experts. Click here for full details.
"Strategy without Tactics is the slowest route to victory. Tactics without Strategy is the noise before defeat." - Sun Tzu
For effective Strategy Development and Strategic Planning, we must master both Strategy and Tactics. Our frameworks cover all phases of Strategy, from Strategy Design and Formulation to Strategy Deployment and Execution; as well as all levels of Strategy, from Corporate Strategy to Business Strategy to "Tactical" Strategy. Many of these methodologies are authored by global strategy consulting firms and have been successfully implemented at their Fortune 100 client organizations.
These frameworks include Porter's Five Forces, BCG Growth-Share Matrix, Greiner's Growth Model, Capabilities-driven Strategy (CDS), Business Model Innovation (BMI), Value Chain Analysis (VCA), Endgame Niche Strategies, Value Patterns, Integrated Strategy Model for Value Creation, Scenario Planning, to name a few.
Learn about our Strategy Development Best Practice Frameworks here.
Readers of This Article Are Interested in These Resources
34-slide PowerPoint presentation
Product Lifecycle Analysis is an invaluable tool for developing a robust product marketing strategy. Marketers and strategists can use this analysis to predict sales growth, associated customer and competitor behaviors, and, in turn, devise the appropriate product marketing strategy.
The Product
[read more]

46-slide PowerPoint presentation
Some innovations are truly spectacular, but consumers are slow or just refuse to adopt. In fact, over 70% of all new products fail in the marketplace--and innovative, new products fail at an even higher rate.
Why is this the case? And, how do companies overcome this?
This document discusses
[read more]

29-slide PowerPoint presentation
This document discusses Rogers' Five Factors, framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations.
Businesses are interested in understanding how innovations diffuse, so that they can better predict and manage this consumer adoption. A popular framework
[read more]

121-slide PowerPoint presentation
Curated by McKinsey-trained Executives
Unlock the Power of Your Brand with the Ultimate Brand Equity Strategy Business Toolkit!
In the dynamic realm of business, where competition is intense and consumer preferences shift rapidly, establishing and maintaining a robust brand is the linchpin
[read more]
 With limited resources, all organizations strive to prioritize those activities that drive the most value. This is particularly true in product development. Focusing on the right or wrong set of features can make or break your product (or even company).
With limited resources, all organizations strive to prioritize those activities that drive the most value. This is particularly true in product development. Focusing on the right or wrong set of features can make or break your product (or even company).




