Editor's Note: Take a look at our featured best practice, IT Strategy (30-slide PowerPoint presentation). The key drivers of Information Technology (IT) or Management Information Systems (MIS) value are an organization's IT mindset and its ability to execute. Today’s best practices show that IT value can be maximized when enterprise IT investments are aligned with business goals and IT execution is [read more]
* * * *
The Business Relationship Management (BRM) process was introduced into the Service Strategy element of the ITIL Service Lifecycle in 2011, but you’d be forgiven for not being aware of this. BRM is perhaps a little ambiguous, and the line between it and its better-known cousin, Service Level Management (SLM), is certainly blurred.
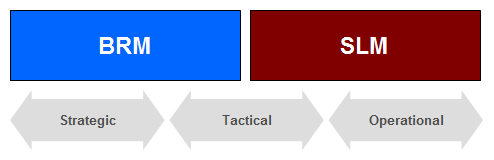
To better understand the BRM process, it is important to first acknowledge the differences in focus between BRM and SLM:
- SLM Focus – Tactical and Operational
- BRM Focus – Strategic and Tactical
The purpose of the BRM role is to establish and maintain positive relationships with the Business, providing input and guidance into the design and delivery of services that exist solely as a means to provide the desired Business outcomes.
A key element of the BRM role is the need to become aware of and understand any factors that may influence a change in the services that are required. A change in the desired Business outcomes, almost certainly means a change to service provision. As such the balancing act of ‘Supply & Demand’ falls squarely at the feet of the BRM. Equally, the pace of technological change must also be considered as an external factor that could influence service utilization.
In contrast, the SLM role is predominantly about the ‘here and now’ (Service Reviews) and the short-term future (Service Improvement Plans). To use PRINCE2 parlance, the Planning Horizon is never far away.
This author offers a number of documents related to IT management, project management, and other related concepts on
Flevy here.
This BRM activity of looking ahead is crucial for both the Business and the Service Provider. If we do not know what’s changing in the Business then how can we plan for it?
The BRM is responsible for the Customer Portfolio. This is a database or structured document used to record the details of all of the Customers of the Service Provider. In addition, the BRM is responsible for the Customer Agreement Portfolio, in which all contractual arrangements between Service Provider & Customer are recorded.
From the Business point of view, the Critical Success Factor (CSF) that provides the measure of the Business Relationship Manager is the level of Customer Satisfaction (are we delivering value to the Business?). For the Service Level Manager, the measurement is all about the whether or not the SLA’s are being met.
So we have explored what the BRM role does for the Business, what about the Service Provider?
The level of engagement with the Business that is required from the Business Relationship Manager is such that one could be forgiven for wondering where the reporting line actually is. Indeed, this thinking often manifests itself in the more technical resources of the Service Provider (whose side is he/she on? etc.). We must remember therefore that while the BRM must focus on delivering value to the Business, and continually improving Customer Satisfaction, he/she is also the marketing agent of the Service Provider, ever on the lookout for ways in which to sell new or improved services.
While the BRM process is tucked away in Service Strategy, it should be clearly understood that BRM activities occur all across the ITIL Service Lifecycle. BRM must stay close to the progression of services through Service Design and Service Transition (testing, evaluation, and finally acceptance) all the time engaging with the Business, and ensuring that the service remains on track towards meeting the desired outcome. Once into Service Operation, the BRM role is involved in managing customer expectation through any Major Incidents that may occur, and ensuring that any planned service outages do not have a detrimental effect on the Business.
You can learn more about ITIL Service Management in this 129-slide PowerPoint, which covers the whole of the Service Lifecycle (Service Strategy, Service Design, Service Transition, Service Operation and Continual Service Improvement).

170-slide PowerPoint presentation
This presentation is a collection of PowerPoint diagrams and templates used to convey 30 different IT-related frameworks, models, standards and methodologies. The list is compiled based on recent trends in agile methodologies, cybersecurity, project management, and risk management, reflecting their
[read more]
Do You Want to Implement Business Best Practices?
You can download in-depth presentations on MIS and 100s of management topics from the FlevyPro Library. FlevyPro is trusted and utilized by 1000s of management consultants and corporate executives.
For even more best practices available on Flevy, have a look at our top 100 lists:
These best practices are of the same as those leveraged by top-tier management consulting firms, like McKinsey, BCG, Bain, and Accenture. Improve the growth and efficiency of your organization by utilizing these best practice frameworks, templates, and tools. Most were developed by seasoned executives and consultants with over 20+ years of experience.
Readers of This Article Are Interested in These Resources

41-slide PowerPoint presentation
A management consulting framework for establishing IT operating model in the organization (ITOM). The framework consist of blueprint documents and tools for the following dimensions; IT processes (including process descriptions), organizational setup of IT (including organizational
[read more]

24-slide PowerPoint presentation
The Capability Maturity Model (CMM) is an organizational model that describes 5 evolutionary stages (or levels), in which the business processes in an organization are managed. The term "maturity" relates to the degree of formality and optimization of processes, from ad hoc practices, to formally
[read more]

116-slide PowerPoint presentation
This document provides a collection of 100+ Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) related to the Information Technology functions listed further below.
Keeping in mind that each organization is different, the enclosed KPIs are intended as a general reference and their relevance depends on the
[read more]

21-slide PowerPoint presentation
An integrated framework for evaluating IT from both an IT as well as a business perspective is a necessity for CIOs and other technology leadership. This presentation focuses on the IT Capability Maturity Framework (IT-CMF) developed by the Innovation Value Institute (IVI), geared towards
[read more]






