Editor's Note: Take a look at our featured best practice, Business Model Innovation (30-slide PowerPoint presentation). Innovative business models can reshape industries and drive tremendous growth. However, many organization find business model innovation difficult. The framework outlined in this presentation is based on the HBR article "Reinventing Your Business Model," authored by Clayton Christensen, Mark [read more]
Also, if you are interested in becoming an expert on Innovation Management, take a look at Flevy's Innovation Management Frameworks offering here. This is a curated collection of best practice frameworks based on the thought leadership of leading consulting firms, academics, and recognized subject matter experts. By learning and applying these concepts, you can you stay ahead of the curve. Full details here.
* * * *
 In this article, we will go on a journey… a journey for your Business Model.
In this article, we will go on a journey… a journey for your Business Model.
As we all know, innovative Business Models can reshape industries and drive tremendous growth. In fact, if executed successfully, Business Model Transformation can make organizations resilient in the face of Disruption and create Growth unbounded by the limitations of its businesses.
However, Corporate Renewal and Business Model Innovation (BMI) are difficult to achieve, as many executives do not understand what truly drives BMI.
To begin, let’s first breakdown–what is a Business Model? As defined by Clayton Christensen, author of the Innovator’s Dilemma, a Business Model consists of 4 elements:
- Customer Value Proposition – The Customer Value Proposition is the “job to be done.” In other words, it is our offering that helps customers to more effectively, conveniently, and/or affordably do a job they’ve been trying to do. The most important attribute of a Customer Value Proposition is precision—how perfectly it addresses the customer to be done and nothing else.
- Profit Formula – For a business model to be viable, it must be able to make the company money. The profit formula dictates the margins, asset velocity, and scale requires to achieve an attractive return for the company.
- Key Resources – Key Resources captures the people, technology, products, facilities, equipment, brands, and cash necessary to deliver on our Customer Value Proposition. The focus is on the key elements that create value for the customer and the company.
- Key Processes – The Key Business Processes are ways of working together to address recurring tasks in a consistent way. These processes include training, development, manufacturing, budgeting, planning, sourcing, service delivery, etc. Key processes also include the organization’s rules, metrics, and norms.
Many high-tech startups have figured out the Customer Value Proposition, but not the Profit Formula and thus do not have a viable Business Model.
As an organization matures, its Business Model evolves naturally through a predictable 3-phase journey, what we call the Business Model Journey. It begins with the creation of the Business Unit and its Business Model, followed by sustaining and growing the business, and ultimately later to driving efficiencies from it. This is depicted on the slide below.
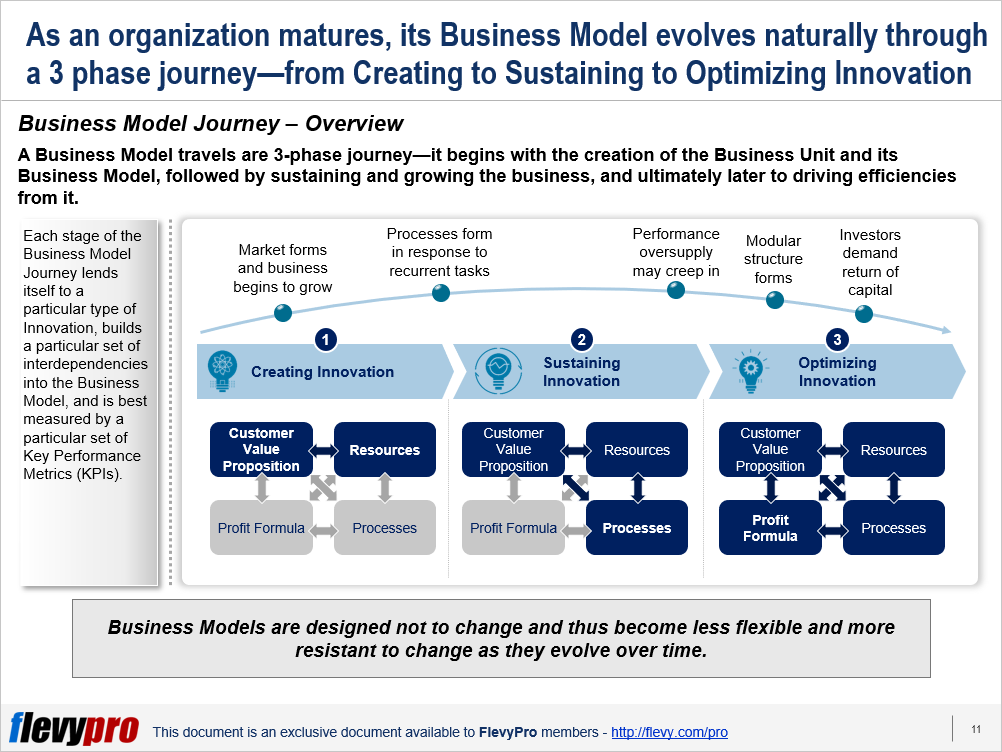
Each stage of the Business Model Journey lends itself to a particular type of Innovation, builds a particular set of interdependencies into the Business Model, and is best measured by a particular set of Key Performance Metrics (KPIs).
Let’s take a closer look at each of these 3 phases.
Phase 1. Creating Innovation
 The focus of this inception phase is for the business to find a product-market fit. In doing so, it is searching for a meaningful Customer Value Proposition, which it can design initial offerings to fulfill. There is limited data, as the market is typically still very new and unproven.
The focus of this inception phase is for the business to find a product-market fit. In doing so, it is searching for a meaningful Customer Value Proposition, which it can design initial offerings to fulfill. There is limited data, as the market is typically still very new and unproven.
At this point, resources are very limited, typically comprised of a founding team, some funding and ambition, and sometimes also a technology or intellectual property.
The link between the Value Proposition and Key Resources is forming, but the rest of the Business Model is unformed. The Profit Formula is nascent and exploratory. This allows the organization to operate with great flexibility.
Phase 2. Sustaining Innovation
The second phase, Sustaining Innovation, the business has already successfully achieved product-market fit. The next challenge is to scale operations to meet growing customer demand.
We also focus on improving and innovating on our offerings to make them better, which can be sold at higher prices to the current target market. The organization is also building out structured, repeatable business processes.
Phase 3. Optimizing Innovation
At a certain point of business maturity, investments in product performance will no longer yield incremental profitability. At that point, we enter the final, most mature phase of the Business Model Journey, Optimizing Innovation, which focuses on driving process efficiencies and cost savings.
Examples can include process changes to eliminate labor costs, reduce components in product design, replace of components with lower-cost alternatives, outsource of certain activities, restructure, add financial leverage, consolidate operations to leverage economics of scale, etc.
Are you interested in digging deeper into the Business Model Journey, as well as better understanding the interrelationships and dynamics of the 4 elements of the Business Model? We have developed a framework presentation on the Business Model Journey, which elaborates on all these concepts highlighted in this article.
27-slide PowerPoint presentation
As core markets become saturated with new entrants and products, we find it more and more difficult to grow the core. We find traditional approaches that have successfully driven growth historically are also reaching points of diminishing returns.
Business Model Innovation (BMI) is a powerful,
[read more]
Want to Achieve Excellence in Innovation Management?
Gain the knowledge and develop the expertise to become an expert in Innovation Management. Our frameworks are based on the thought leadership of leading consulting firms, academics, and recognized subject matter experts. Click here for full details.
To be competitive and sustain growth, we need to constantly develop new products, services, processes, technologies, and business models. In other words, we need to constantly innovate.
Ironically, the more we grow, the harder it becomes to innovate. Large organizations tend to be far better executors than they are innovators. To effectively manage the Innovation process, we need to master both the art and science of Innovation. Only then can we leverage Innovation as a Competitive Advantage, instead of viewing Innovation as a potential disruptive threat.
Learn about our Innovation Management Best Practice Frameworks here.
Readers of This Article Are Interested in These Resources

27-slide PowerPoint presentation
The Innovation Sandbox is an approach to Innovation that promotes exploration and experimentation, while under extreme constraints. These constraints are industry or market requirements that are extremely fixed.
Through the Innovation Sandbox approach, industries and organizations can achieve
[read more]
39-slide PowerPoint presentation
Organizations across industries face unprecedented challenges as markets evolve rapidly and innovation disrupts established norms. Even organizations with cutting-edge technological products struggle to sustain long-term success.
Notable examples include Kodak, Agfa, and other once-dominant
[read more]

29-slide PowerPoint presentation
Innovative Business Models can reshape industries and drive tremendous growth. In fact, if executed successfully, Business Model Transformation can make organizations resilient in the face of Disruption and create Growth unbounded by the limitations of its businesses.
However, Corporate
[read more]

23-slide PowerPoint presentation
Today's volatile business environment challenges archaic businesses models more so than ever before. Business Model Innovation (BMI) provides a means for organizations to either defend against receding competitiveness or grab new opportunities.
This presentation discusses the 4 distinct
[read more]
 In this article, we will go on a journey… a journey for your Business Model.
In this article, we will go on a journey… a journey for your Business Model.
 The focus of this inception phase is for the business to find a product-market fit. In doing so, it is searching for a meaningful Customer Value Proposition, which it can design initial offerings to fulfill. There is limited data, as the market is typically still very new and unproven.
The focus of this inception phase is for the business to find a product-market fit. In doing so, it is searching for a meaningful Customer Value Proposition, which it can design initial offerings to fulfill. There is limited data, as the market is typically still very new and unproven.



