Value-Driven Boards - Frameworks, Models and Tools (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + Excel (XLSX) 53 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Includes frameworks, models and tools to help build an effective, strategic and value-driven board
- Illustrates to measure current board engagement against a desired level
- Includes steps for developing an effective board evaluation
VALUE CREATION PPT DESCRIPTION
Boards often focus their most of their time and efforts on activities related to regulatory compliance and risk oversight, which helps preserve existing shareholder value. Increasingly, however, shareholders expect CEOs and boards to spend more time on long-term value creation activities.
This document explores select frameworks, models and tools that can help:
• build an effective, strategic and value-driven board
• measure current board engagement against a desired level, and
• develop an effective board evaluation
A supplementary self-explanatory Excel worksheet to help graph current and desired board engagement levels is also included. Only the "Current Level" and "Desired Level" columns need to be filled using the drop down list, with cells left blank for "Not applicable/Don't know".
Contents
1. Context and overview
• Context
• Primary parties to corporate relations
• Corporate governance stakeholders
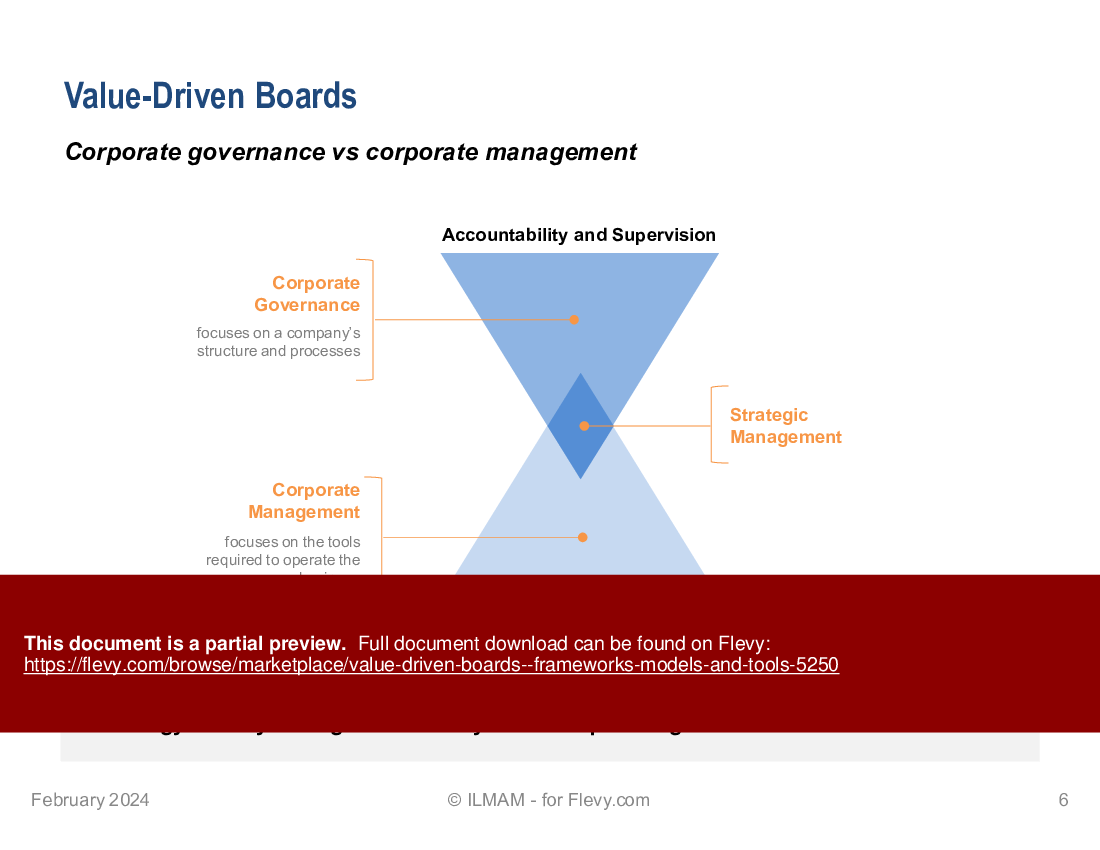
• Corporate governance vs corporate management
2. Leadership versus management
• Leadership versus management
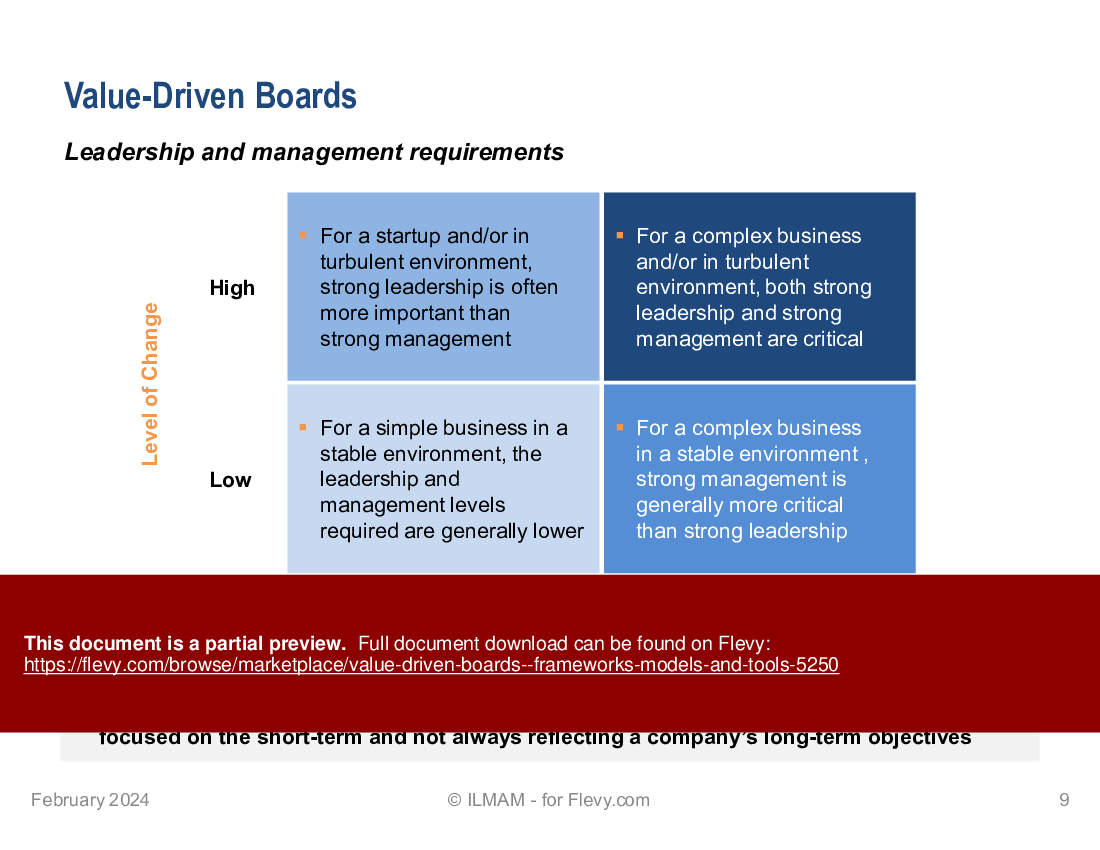
• Leadership and management requirements
• Role of chairman versus role of CEO
3. Building an effective board
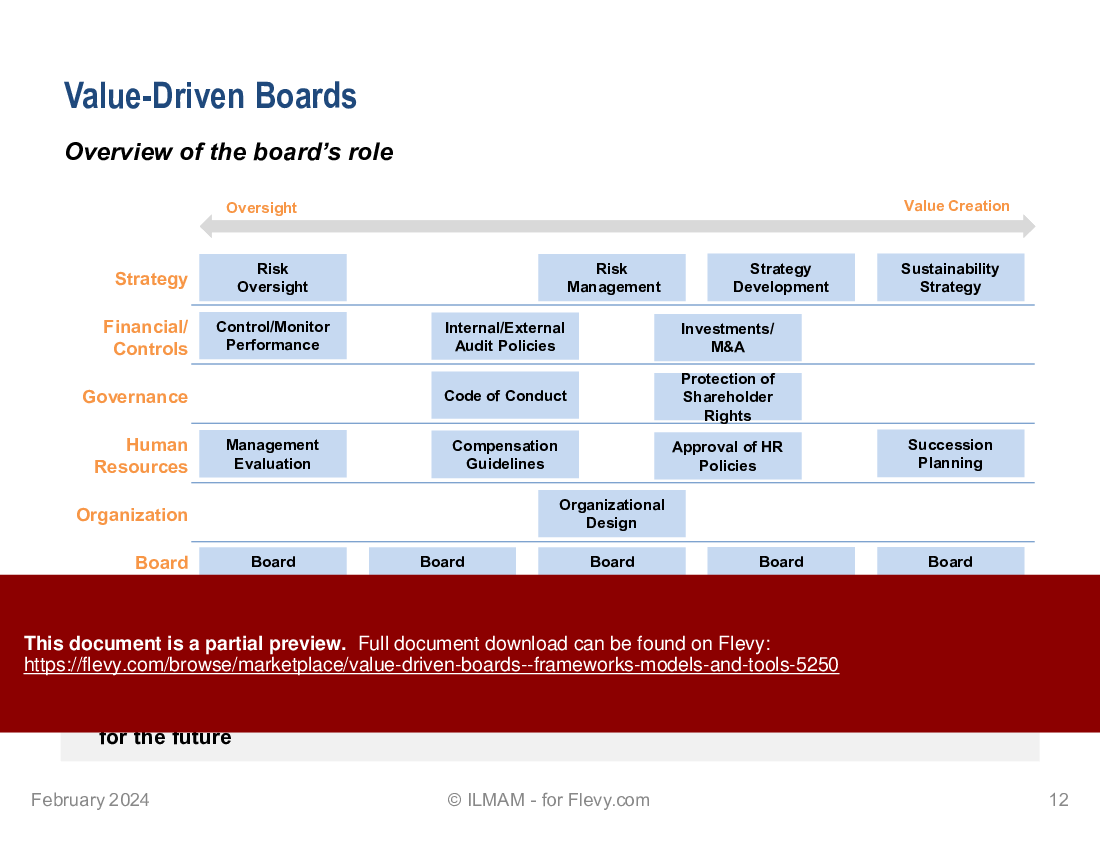
• Overview of the board's role
• Board-building framework
• The board as a source of competitive advantage
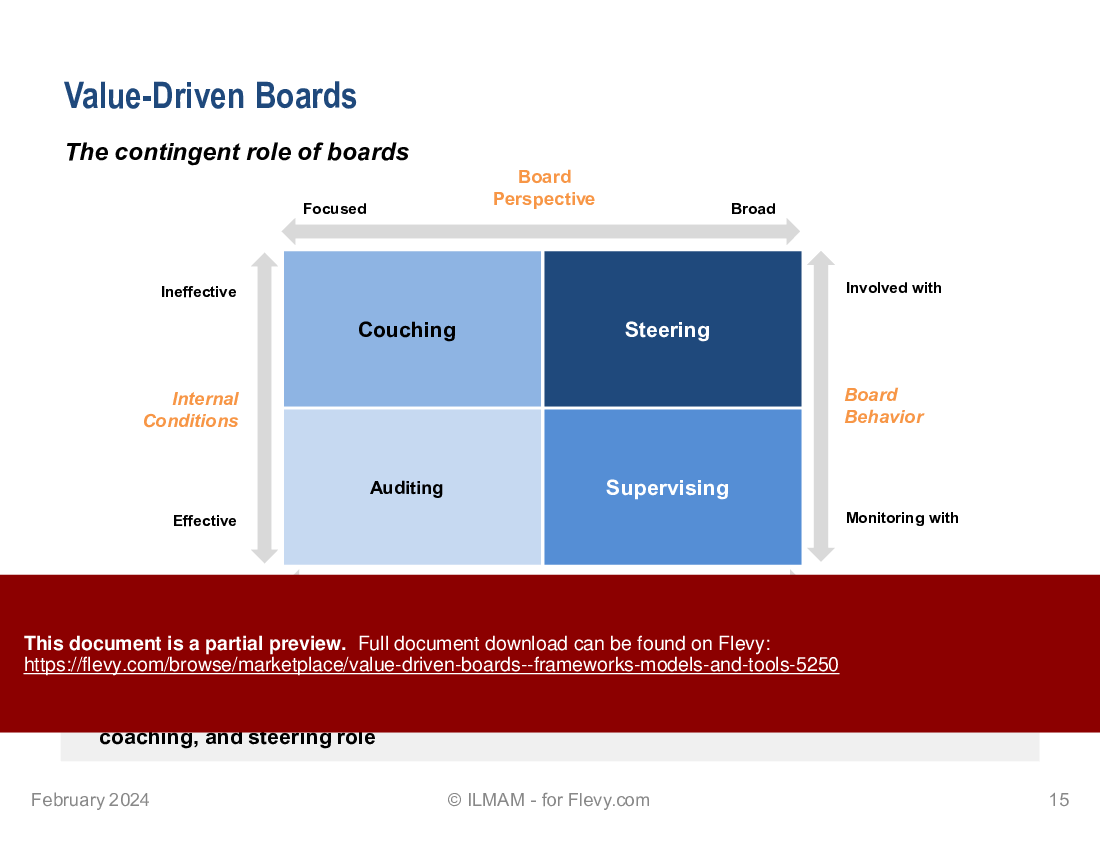
• The contingent role of boards
4. Boards and strategy
• Multiple strategy approaches
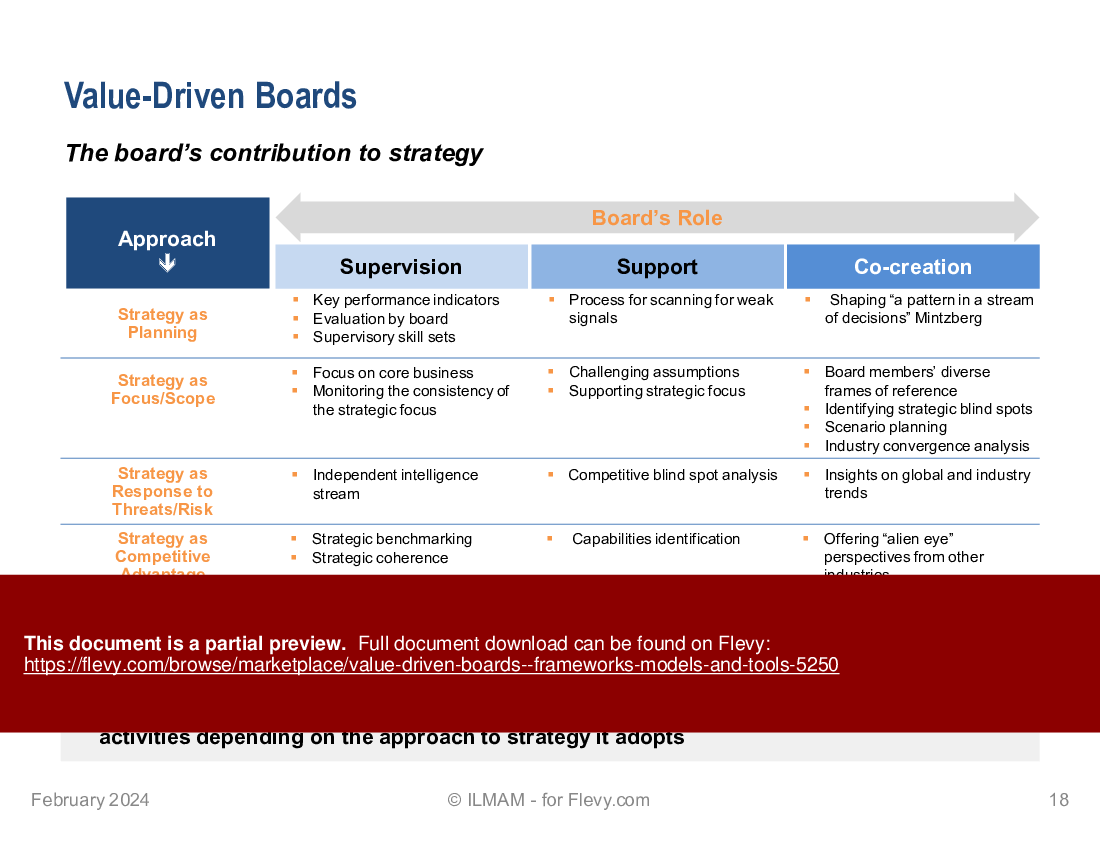
• The board's contribution to strategy
• The board's changing levels of contribution to strategy
• The impact of context on a board's role and strategic views
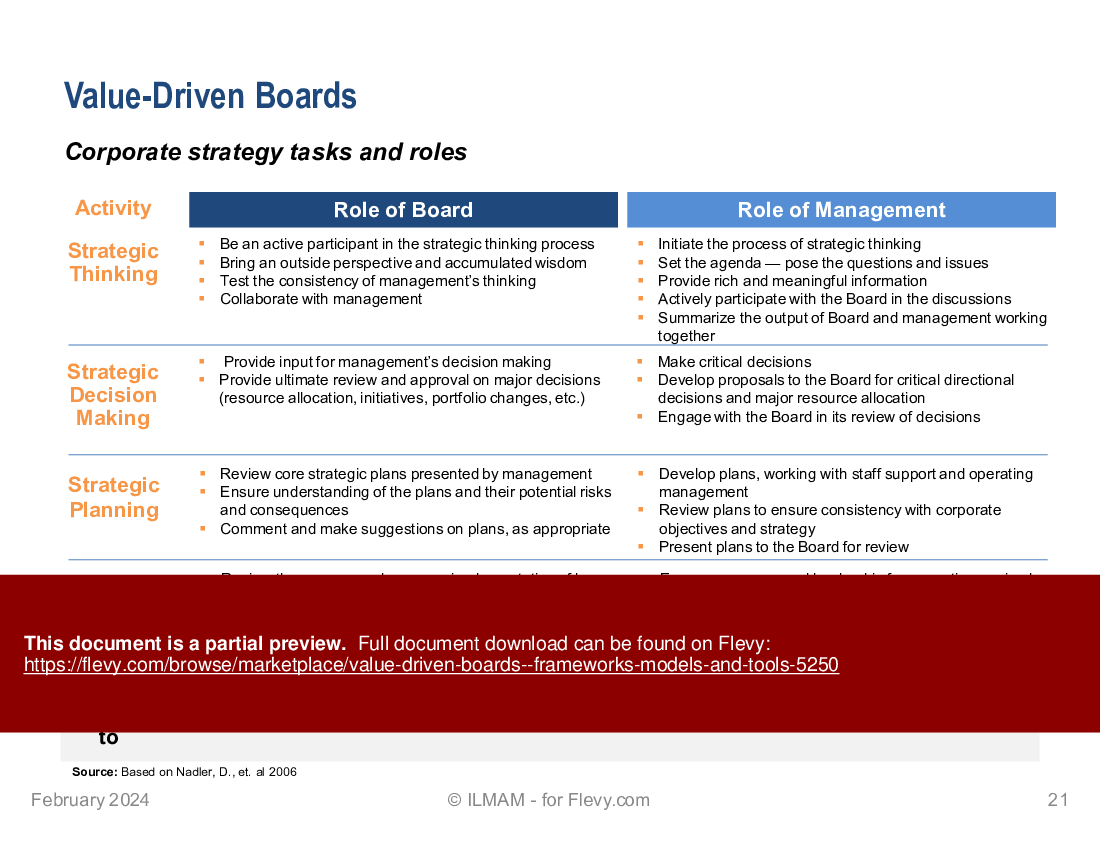
• Corporate strategy tasks and roles
• Engaging the board in strategic planning
• How forward-looking boards should spend their time
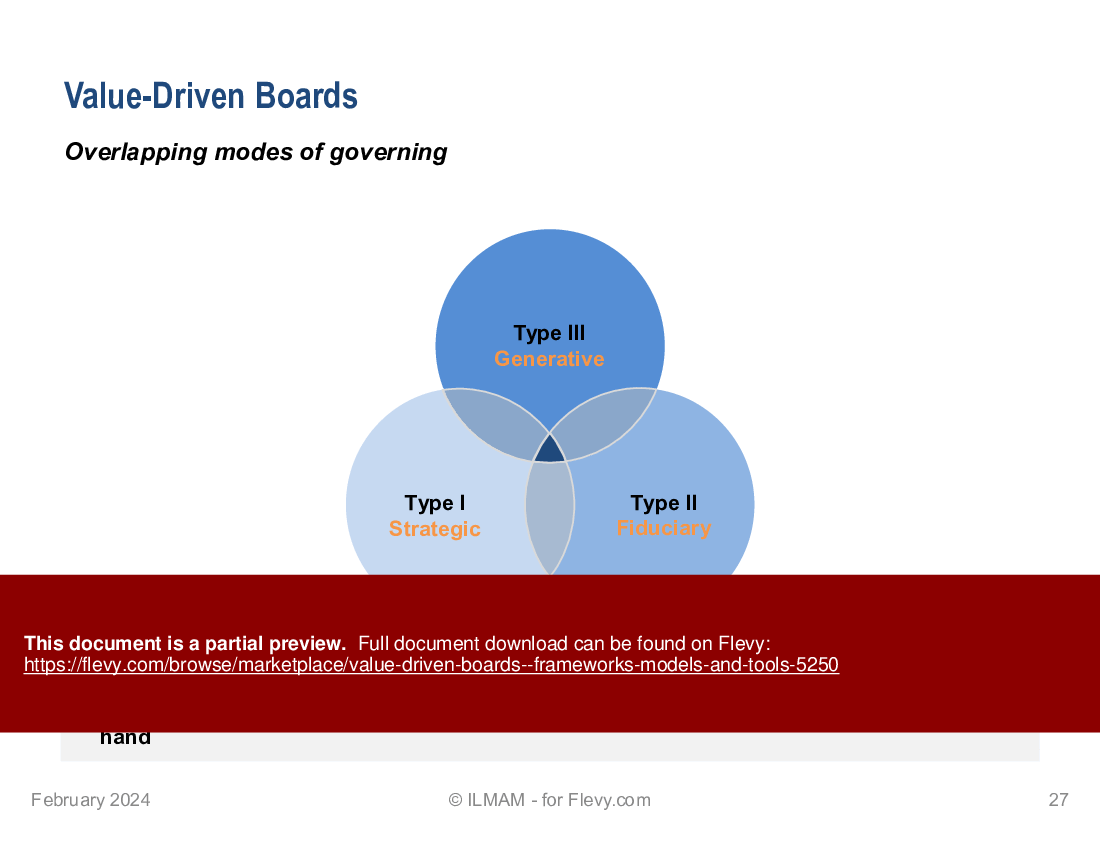
5. Governance as Leadership
• Governance as Leadership
• Three governance modes
• Overlapping modes of governing
• Four quadrants of engagement
• The generative curve
6. Value-creation
• Tricker model
• Tricker model ? detailed
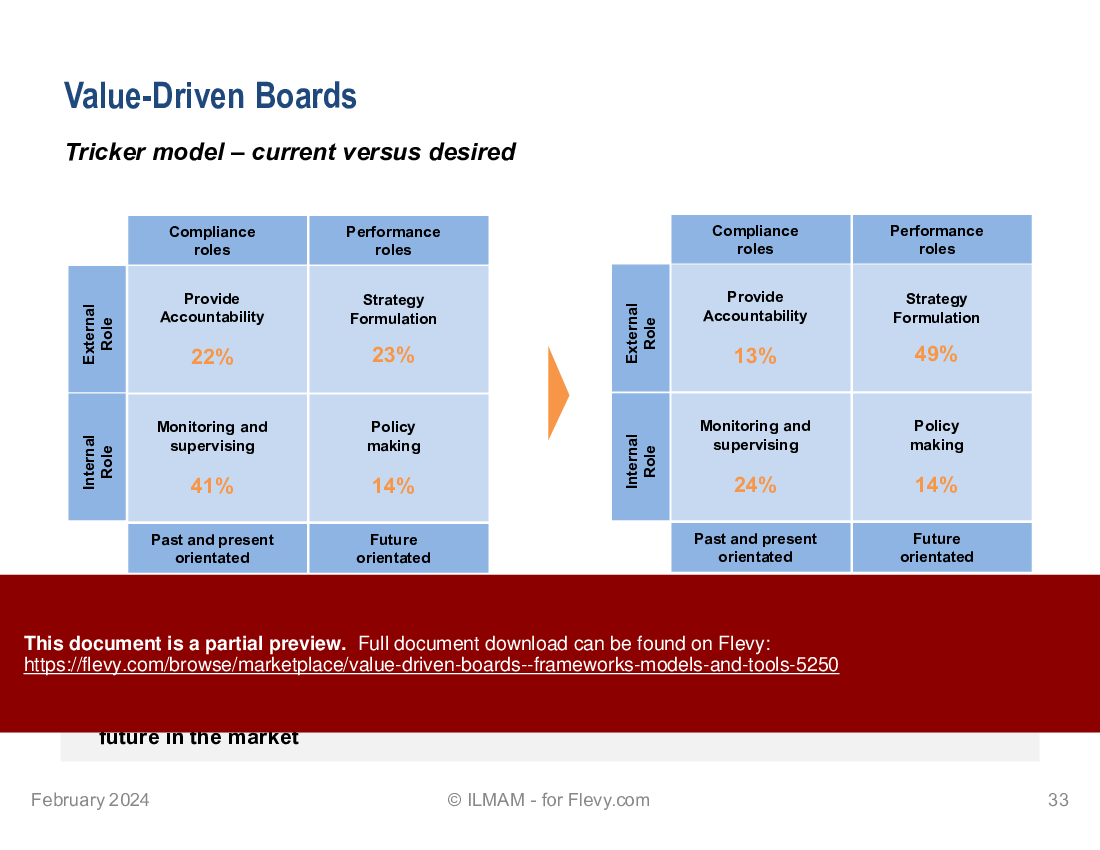
• Tricker model ? current versus desired
• Four pre-conditions to value-added board governance
• Value focused board governance
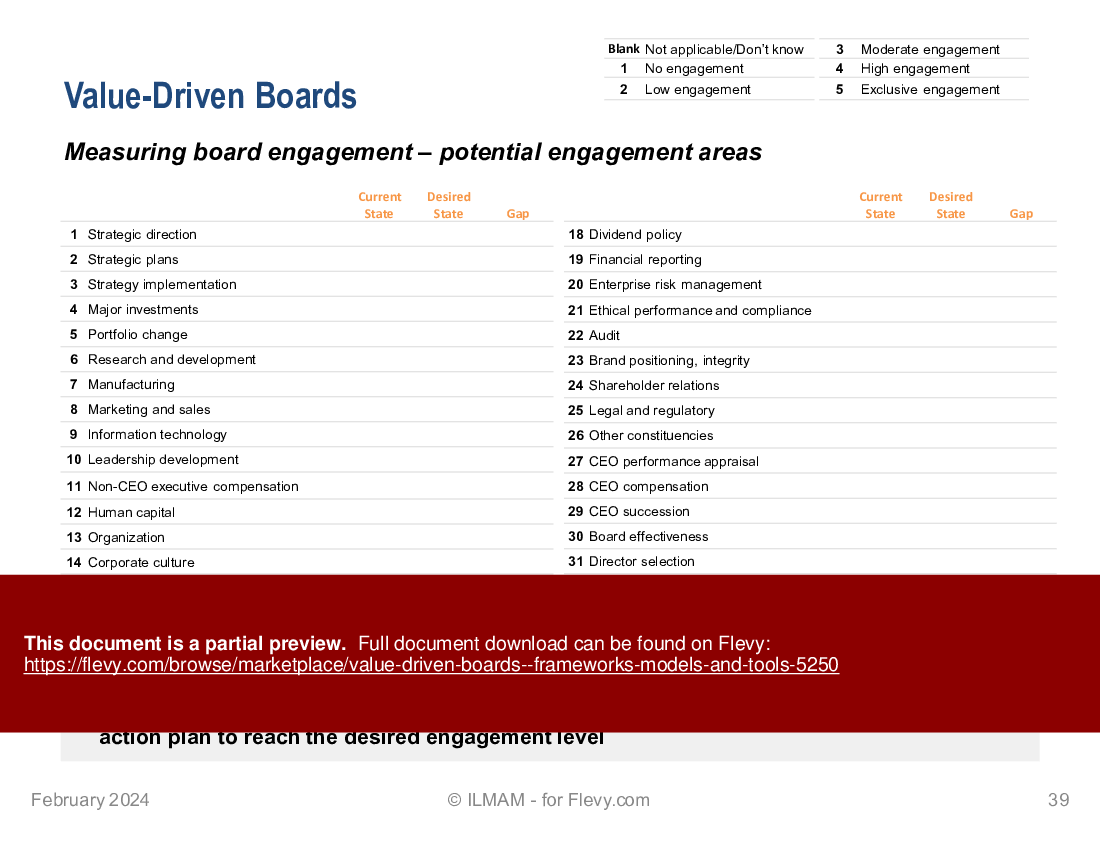
7. Board engagement
• Degree of board involvement
• The engaged board
• Measuring board engagement ? potential engagement areas
• Measuring board engagement ? illustrative outcome
8. Board evaluation
• A framework used for board evaluations
• Step 1 – What are our objectives?
• Step 2 – Who will be evaluated?
• Step 3 – What will be evaluated?
• Corporate Governance Practice Framework
• High performance board model
• Step 4 – Who will be asked?
• Step 5 – What techniques will be used?
• Board evaluation methodologies
• Step 6 – Who will do the evaluation?
• Step 7 – What will you do with the results?
The PPT emphasizes the importance of aligning corporate governance with strategic management to enhance accountability and supervision. It provides a comprehensive analysis of the roles and requirements of leadership versus management in various business environments.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Value Creation, Board of Directors PowerPoint Slides: Value-Driven Boards - Frameworks, Models and Tools PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, ILMAM - Strategy & Management Consulting
VALUE CREATION PPT SLIDES
Framework for High-Performance Board Dynamics
This PPT slide presents a framework for understanding the dynamics of high-performance boards, emphasizing the interplay between various components that contribute to effective governance. At the center is the concept of "Board Dynamics," which acts as a nexus connecting 3 key elements: Board Competencies, Board Behaviors, and Board Structures.
Board Competencies focus on the essential attributes that members should possess, including knowledge, skills, abilities, and contacts. These competencies are crucial for informed decision-making and strategic oversight. The slide suggests that a board's effectiveness is significantly influenced by the collective expertise of its members.
Board Behaviors encompass the interpersonal aspects that govern how board members interact. This includes their personality traits, values, norms, and the nature of board-management relations. The emphasis here is on the qualitative aspects of board interactions, which can greatly affect the board's overall performance and cohesion.
Board Structures refer to the formal mechanisms that guide the board's operations. This includes established policies, processes, procedures, and committees. These structures provide the necessary framework for accountability and governance, ensuring that the board functions smoothly and effectively.
To the right, the slide outlines specific Board Roles, which include strategic functions such as CEO selection and monitoring, risk management, compliance, and stakeholder communication. This section highlights the practical applications of the board's dynamics and structures in fulfilling its responsibilities.
The overarching message is clear: for a board and management team to achieve sustainable value, they must operate at a high level across these interconnected dimensions. This framework serves as a guide for organizations aiming to enhance their governance practices.