Competency Model & Matrix Development (Word DOCX)
Word (DOCX) 37 Pages
BENEFITS OF THIS WORD DOCUMENT
- Provides of Complete Sample, Guidelines and Template Competency Matrix and Model (37 pages Word Doc)
- Provides of Competency Model Framework and Core Competency Development Guideline
- Provides of Developing Competency Catalog : Step by Step
CORE COMPETENCIES WORD DESCRIPTION
Competency Model & Matrix Development
Table of Contents:
Introduction
Section 1: Brief Theoretical Background
Section 2: Concepts of Competency
Section 3: Developing Competency Catalogue : Step by Step
Appendix 1 : Competency Workshop Guideline
Appendix 2 : Core Competency Development Guideline
Appendix 3 : Focus Group Discussion Guideline
Appendix 4 : Behavioral Event Interview Guideline
Appendix 5 : Samples of Behavioral Terms – Bloom's Taxonomy
Appendix 6 : Samples of Competency Model and Matrix
This manual is aimed at providing a general guideline in developing competency model. The manual will be started by brief description about the research background upon which the concept of competence was originally invented and developed.
Then, section two will provide a general understanding of competency concepts. Several issues that will be addressed are: definition and elements of competency; types of competency and competency model framework.
Section three will explore detailed activity for each step in developing competency catalogue and competency profile. Specifically, there are four elements addressed in each step:
• Description of activity
• Key inputs to the process
• Key activities performed (including tools and template used)
• Key deliverables
In the appendix section, we will provide interview guideline for focus group discussion and behavioral event interview technique.
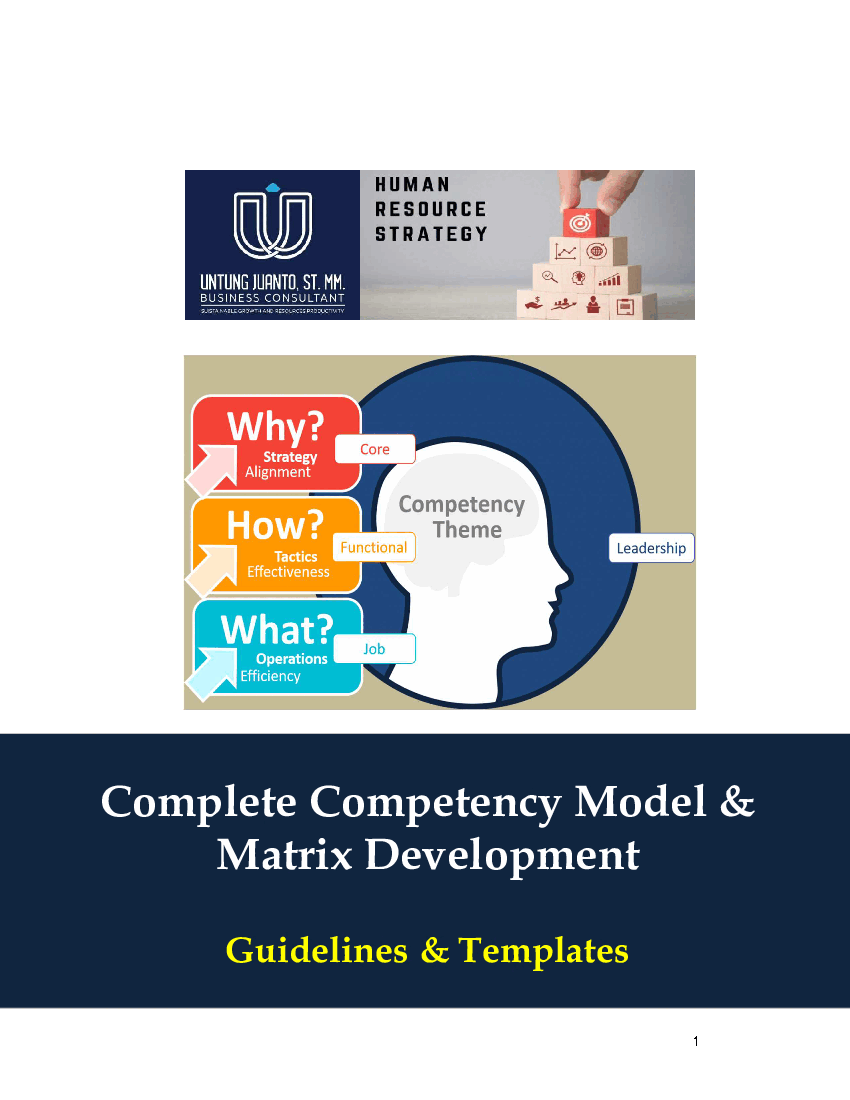
What is Competency?
Competency is the vital behavioral skills, knowledge and personal attributes that are translations of organizational capabilities and are deemed essential for success. They distinguish exemplary performers from adequate performers.
In that regard, competencies offer a highly descriptive means of discussing job performance. They go beyond traditional job descriptions because they focus on how employees perform their jobs, not simply on what they do. While job descriptions detail specific tasks, competencies encompass the tangible and intangible abilities employees possess. For instance, a necessary competency for a marketing professional might be the ability to perform detailed market analysis while another competency might be leadership qualities, as evidenced through the ability
Competency Modeling Matures: The Work of Richard Boyatzis. Boyatzis wrote the first empirically-based and fully-researched book on competency model developments. It was with Boyatzis that job competency came to widely understood to mean an underlying characteristic of a person that leads or causes superior or effective performance. Boyatzis was explicit in describing the importance of clearly-defined competency as reflected in specific behavior and clearly defined performance outcomes when he wrote that "the important points is that specific actions cause, or lead to, the specified results. Certain characteristics or abilities of the person enable him or her to demonstrate the appropriate specific actions"(Boyatzis, 1982, p. 12).
As founding developer of competency modeling in the United States, Boyatzis grounded competency interventions on documented behavioral indicators that caused or influenced effective job performance. Boyatzis, like Flanagan, stressed the importance of systematic analysis in collecting and analyzing examples of the actual performance of individuals doing the work. The method for documenting the actual performance was collected through the behavioral event interview (BEI), an intensive face-to-face interview that involves soliciting critical incidents from performers and documenting what the performers thinking and doing during the incidents (BEI technique will be explained further in Appendix section).
Components of Competency
There are four major components of competency:
1. Skill: capabilities acquired through practice. It can be a financial skill such as budgeting, or a verbal skill such as making a presentation.
2. Knowledge: understanding acquired through learning. This refers to a body of information relevant to job performance. It is what people have to know to be able to perform a job, such as knowledge of policies and procedures for a recruitment process.
3. Personal attributes: inherent characteristics which are brought to the job, representing the essential foundation upon which knowledge and skill can be developed.
4. Behavior: The observable demonstration of some competency, skill, knowledge and personal attributes. It is an essentially definitive expression of a competency in that it is a set of action that, presumably, can be observed, taught, learned, and measured.
Regards,
UJ Consulting
This Word document includes practical guidelines for conducting competency workshops and focus group discussions. It also provides a comprehensive table of proficiency levels to help assess and develop managerial competencies effectively.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Core Competencies Word: Competency Model & Matrix Development Word (DOCX) Document, UJ Consulting