We can divide the strategic planning process into 6 steps:
1. Define Your Vision and Mission
It is important for management to first define its vision and mission. A clear and compelling vision and mission, together, act as a guiding star, reflecting the organization's aspirations and the impact it aims to make.
The mission captures the essence of the organization–who it serves, what it does, its objectives, and its approach to reaching those strategic objectives.
Although everyone feels they grasp the concept of a "vision," oftentimes, organizations describe their vision in vague, unstructured, and descriptive terms. This leads to confusion and ambiguity. Instead, a company’s vision should be well-conceived, structured, and descriptive. More explicitly, a vision consists of 2 core components:
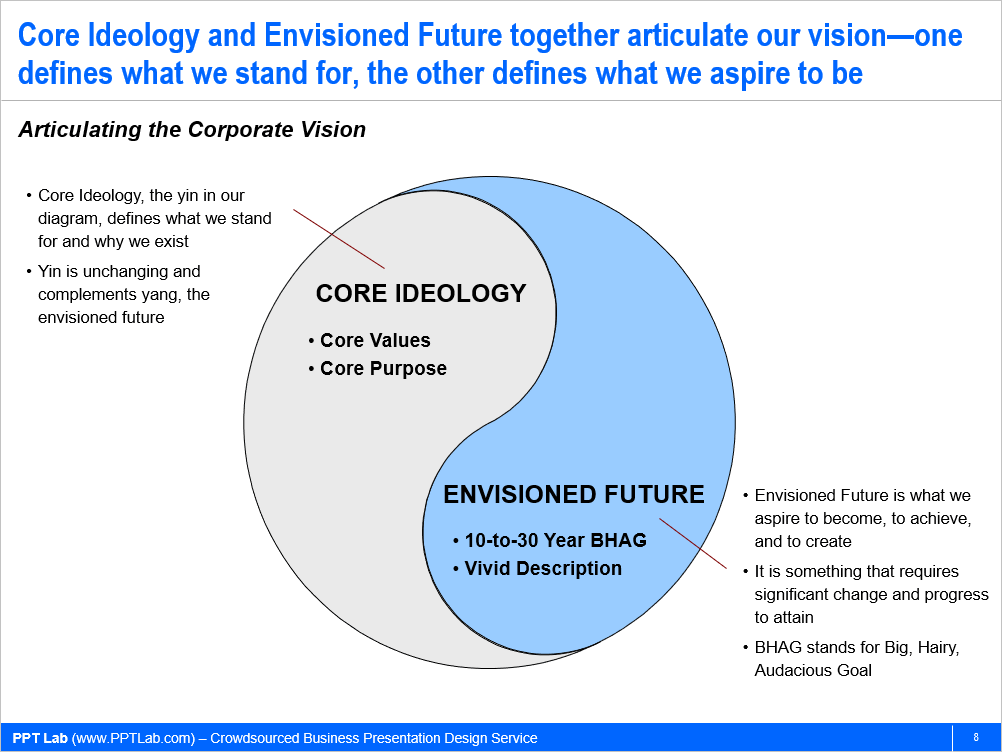
- Core Ideology: This defines what we stand for and why we exist (our core values and purpose). It is unchanging, even as markets and competitive dynamics change. Our core ideology contains the organization’s core values and core purpose.
- Envisioned Future: This is what we aspire to become, achieve, and create, often encompassing a 10+ year, long-term goal.
Let's examine a real world example with Tesla, currently the world’s largest EV manufacturer.

Tesla's mission statement is: "to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy." This statement is concise and captures the essence of Tesla:
- Who it serves: The world, indicating a global scope.
- What it does: Accelerates the transition to sustainable energy.
- Its objectives: To make sustainable energy solutions more accessible and dominant.
- Its approach: Through innovation in electric vehicles, energy storage, and solar technology.
This mission statement clearly outlines Tesla's strategic objectives and its approach to achieving them. It speaks to the organization's commitment to sustainability and innovation, targeting a global audience and aiming to lead a significant shift in energy consumption patterns.
Tesla's vision statement aims to "create the most compelling car company of the 21st century by driving the world's transition to electric vehicles." This vision integrates both core components of an effective vision:
- Core Ideology: The commitment to sustainability and innovation, underpinned by the drive to lead the transition to electric vehicles. It reflects Tesla's core values of sustainability, innovation, and excellence.
- Envisioned Future: Tesla aspires to be the most compelling (not necessarily the biggest) car company of the 21st century, which implies leadership in innovation, design, and sustainability within the automotive industry. It suggests a long-term goal of changing the automotive and energy industries, envisioning a future where electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions are prevalent.
Tesla's vision and mission are well-aligned, with the mission focusing on the immediate strategic objectives of accelerating the transition to sustainable energy and the vision laying out a long-term aspiration to revolutionize the automotive industry. Together, they provide a clear, compelling guide for the company's direction, strategies, and actions, reflecting both the impact Tesla aims to make and its aspirations for the future.
Once the management team agrees upon a shared vision and mission, we can move forward to setting our strategic goals.
2. Set Short-, Medium-, and Long-term Goals
When setting our strategic goals, there are 2 important frameworks we can use.
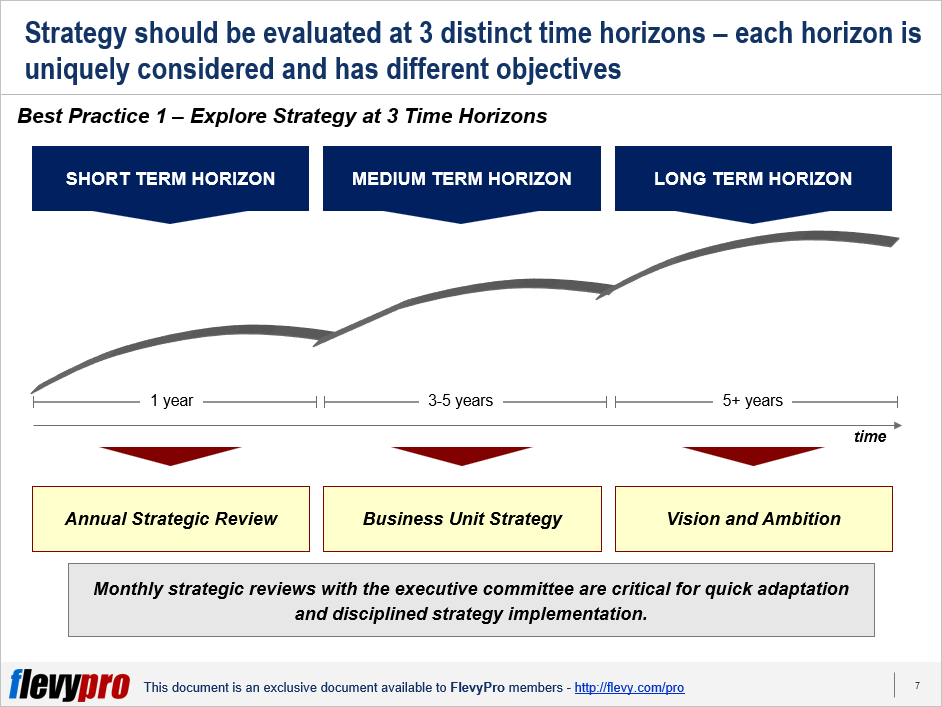
The first is around time frames, where we can leverage McKinsey's 3 Horizons of Growth. As the name suggests, there are 3 time horizons to explore:
- Short-term horizon (1-year timeframe): The objective here is to challenge the current strategy, evaluate progress, and explore options to accelerate execution. The scope is around products, regions, and functions. As we explore the short-term strategy, it’s important to encourage a culture of creativity and real dialogue. We should seek to avoid a budget-focused process and discussion.
- Medium-term horizon (3-5 year timeframe): The purpose of the medium-term horizon discussion is to identify the steps necessary to realize the vision. The scope is around the business unit. Our focus in this horizon is to develop clear, actionable business plans that describe the multi-year strategic initiatives to transform vision into value.
- Long-term horizon (5+ year timeframe): Lastly, the objective over the long-term horizon is to define, validate, or redefine the vision, mission, and direction of the organization.
Each horizon is uniquely considered and has different strategic objectives.
The second framework is around goal-setting. Here, we can use Peter Drucker’s SMART goals framework. SMART is an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound, the 5 criteria for effective goals. These criteria help translate the broad vision into tangible targets that provide direction and motivation.
Here is an example of a "smart" short-term goal: Increase the company's market share in the mid-range smartphone segment by 5% over the next 12 months.
This goal meets the SMART criteria in that it is:
- Specific: We are specifying the metric and market.
- Measurable: An increase in market share is easily measured.
- Achievable: A 5% market share increase seems feasible and not unrealistically ambitious.
- Relevant: Relevancy is self-evident, as this goal ties directly to company profitability.
- Time-bound: We specify a timeframe of the next 12 months.
3. Encourage Productive Strategic Dialogue
Most organizations repeat the same strategic planning process year in and year out. This leads to a situation where the effectiveness of the strategic planning process diminishes, as most analyses become adjustments of last year’s analyses. The same inputs lead to similar conclusions, and creativity is sapped from the sessions.
So, how do we break this cycle? The answer is to encourage productive and stimulating "strategic dialogue" by asking different questions.
Great strategists need to learn the "art of questioning." Here are a few guiding principles around this:
- Questions shouldn't be too broad (e.g. "How do we disrupt the industry?"). They should be focused enough to provide actionable insights.
- Questions also shouldn’t be too narrow (e.g. "What should the pricing be?"). Narrow questions may overlook broader strategic considerations and limit the scope of analysis, missing out on opportunities for more comprehensive insights.
- The leadership team should engage in a strategic workshop to articulate and prioritize key questions we need to answer in the next 3-5 years.
Examples of solid questions that drive strategic dialogue include:
- How can we differentiate our products/services in a crowded market?
- What adjacencies should we explore to drive future growth?
- How can we leverage emerging technologies to create new value propositions?
Once the right questions are selected, we can have teams address these questions. These teams will design new, relevant analyses, develop strategic recommendations, and repeat the process next year.
4. Engage a Broad Group of Stakeholders
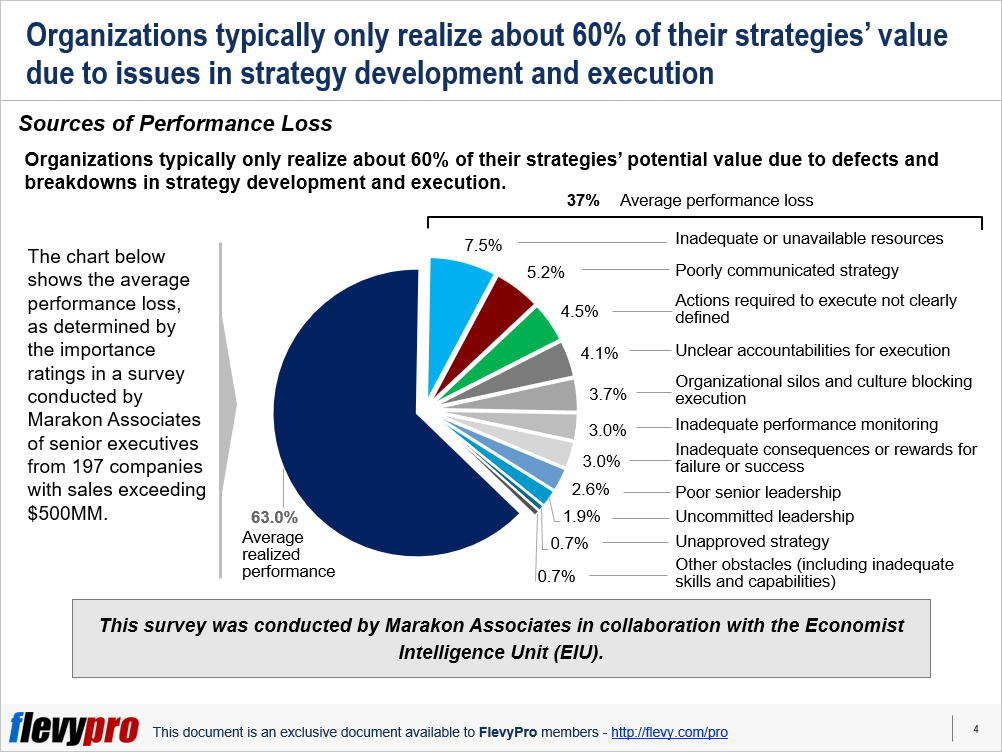
Organizations that engage a broad, decentralized group of both internal and external stakeholders in their strategic planning efforts yield stronger results than organizations that leave strategy in the hands of a small, centralized team. This is the key to effective stakeholder management.
Involving a broad group from different backgrounds, generations, and geographies prevents groupthink and is more likely to surface alternative ideas and perspectives. It is common to also engage participants external to the organization—e.g., customers, suppliers, consultants.
This approach improves our strategic "peripheral vision." In other words, it makes us more adept at spotting both opportunities and risks early. Engaging diverse stakeholders helps uncover blind spots and potential issues that a centralized team might miss.
To effectively engage stakeholders, organizations can:
- Identify key stakeholder groups and representatives from each group.
- Conduct interviews, focus groups, or surveys to gather input and perspectives.
- Invite stakeholders to participate in strategic planning workshops or sessions.
- Leverage online collaboration tools and platforms to facilitate engagement.
- Provide clear communication on the strategic planning process and the role of stakeholders.
It is also important to engage stakeholders early on, as this increases buy-in, which helps with the strategy implementation process later on, thus bridging the strategy-execution gap. Early involvement fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among stakeholders, making them more likely to support and champion the chosen strategy.
5. Identify Frameworks That Help You Execute Your Plan
Frameworks are structured approaches to analyzing and solving common business problems. There are hundreds of strategic management frameworks available for all types of business challenges and situations, particularly in the realm of strategy development and strategic thinking.
Frameworks are useful because they allow you to not only comprehensively think about a business situation, but to do so efficiently. Strategic management frameworks are typically developed by strategy consulting firms—part of their trade secret. Commonly recognized frameworks include SWOT analysis, Porter's 5 Forces, and the BCG Growth-Share Matrix.
Let's take a look at the Strategy Framework Canvas (SFC), which is a unifying framework that can guide us in selecting the appropriate corporate strategy for our circumstances and executing it effectively. This model is particularly useful for large organizations facing changes.
SFC identifies 5 distinct archetypal approaches to strategy:
- Classic Strategy
- Adaptive Strategy
- Visionary Strategy
- Leader Strategy
- Renewal Strategy
Got to our
Strategy Development topic page for a more in-depth discussion on the 5 strategy archetypes.
You can also explore the top 100 business frameworks utilized by management consultants here.
6. Continuously Monitor Performance
Now we move from planning to execution. High-performing organizations use real-time performance tracking. They continuously monitor resource deployment patterns and their results against plans, leveraging continuous feedback to reset planning assumptions and reallocate resources accordingly.
This real-time approach allows management to identify and find flaws in the plan, as well as shortfalls and deviations in execution—and to avoid confusing one with the other. By identifying and rectifying issues in strategy implementation expediently, we can further improve our chances of bridging the strategy-execution gap.
To effectively monitor performance, organizations should define and track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that are aligned with their strategic objectives. KPIs provide a quantitative way to measure progress, identify areas of concern, and course-correct as needed. They also help ensure accountability and transparency across the organization.
In other words, with KPIs, organizations can ensure that their performance aligns with strategic objectives, making it easier to reset planning assumptions and reallocate resources as necessary. The exact selection of KPIs varies depending on the organization and industry. You can leverage the KPI Depot, a vast database of 20,000+ KPIs, to identify the most appropriate KPIs for your organization.
Continual performance monitoring is particularly important in highly volatile industries. In such environments, events outside the organization’s control can render a plan useless. Regular tracking of KPIs allows for agile adjustments to the strategy in response to changing market conditions or unforeseen circumstances.
High-performing organizations exhibit certain attributes that enable successful strategy execution, including:
- Clear communication of the strategy and its rationale to all stakeholders.
- Alignment of organizational structure, processes, and resource allocation with strategic priorities.
- Empowerment of employees and a culture that supports innovation and continuous improvement.
- Effective use of data and analytics to inform decision-making and monitor progress.
- Agility and adaptability to pivot the strategy as needed in response to changing conditions.
By continuously monitoring performance through well-defined KPIs, high-performing organizations can identify and address gaps between strategy and execution, ultimately increasing their chances of achieving their desired outcomes.

 Tesla's mission statement is: "to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy." This statement is concise and captures the essence of Tesla:
Tesla's mission statement is: "to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy." This statement is concise and captures the essence of Tesla:





