Land Development Real Estate Model (up to 500 lots) (Excel XLSX)
Excel (XLSX)
VIDEO DEMO
BENEFITS OF THIS EXCEL DOCUMENT
- A more precise framework to plan out cash flow for real estate development projects (build and sell).
REAL ESTATE EXCEL DESCRIPTION
This is a fully editable and unlocked model in Excel. The model was built based on the following unit economics:
Introduction
Lot development in real estate involves acquiring raw land, developing it into buildable lots, and selling those lots to builders or end-users. The economics of such projects are complex, requiring careful planning and financial modeling to ensure profitability. Utilizing a comprehensive financial model, like the one described, allows developers to simulate various scenarios (plan cash flow), forecast revenues, and assess project feasibility. This breakdown will delve into the key economic factors of lot development, using the provided model as a contextual framework.
1. Land Acquisition Costs
The first major economic consideration is the cost of acquiring the land. This includes the purchase price and any associated closing costs. In the model:
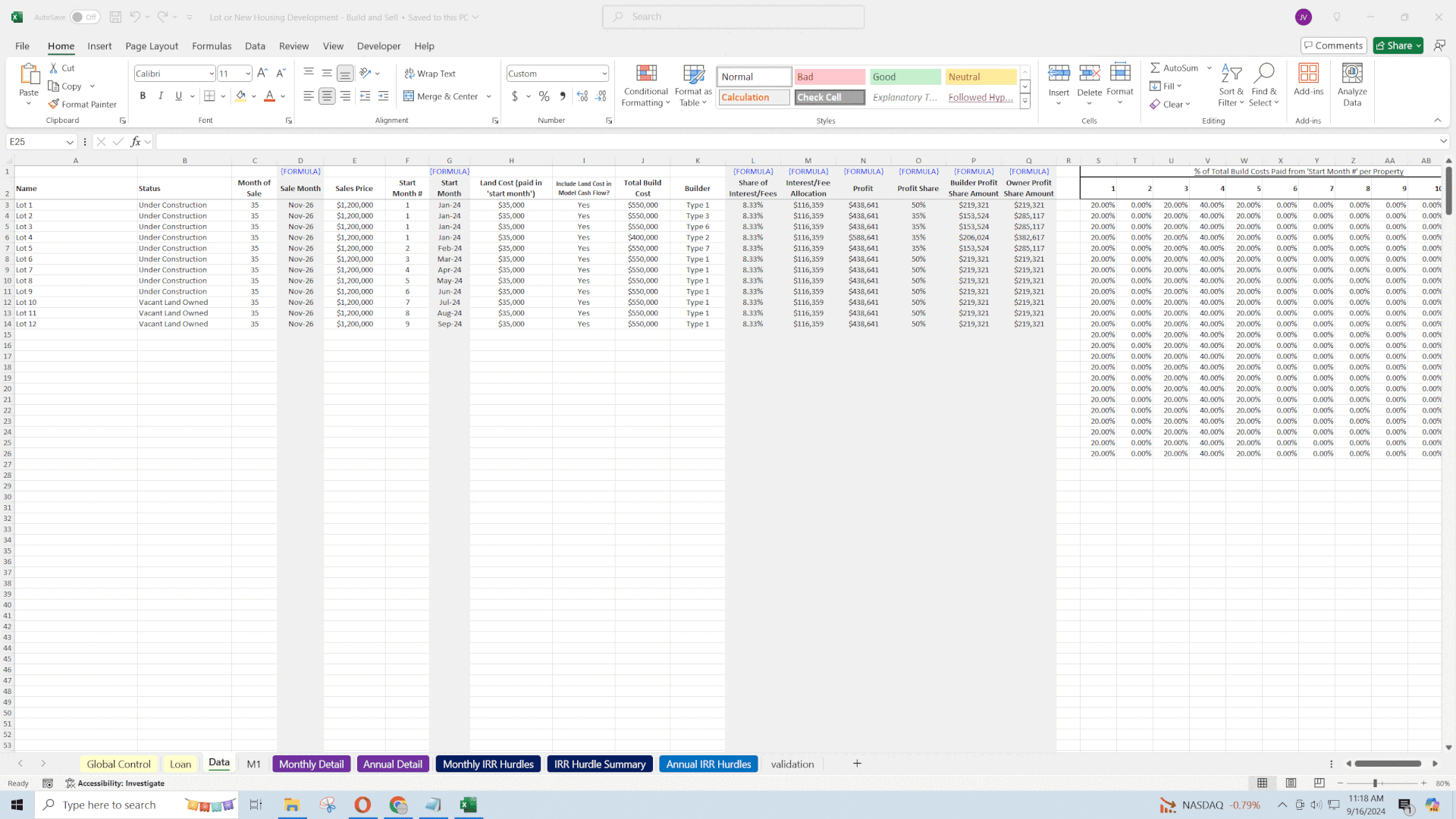
• Per-Lot Land Cost: Each lot has an individually defined land cost, allowing for precise allocation of expenses.
• Timing: The land cost is associated with the start month of each lot, impacting cash flow projections.
• Economic Impact: Accurate estimation and timing of land acquisition costs are crucial as they represent significant upfront capital outlay and influence financing needs.
2. Development Costs
Development costs encompass all expenses required to prepare the land for sale, including infrastructure, utilities, and construction.
• Total Build/Construction Costs: Defined per lot, providing granular control over expenses.
• Payment Schedule: The model allows specifying the percentage of total build costs paid in specific months relative to the lot's start month.
• Economic Impact: Staggering development costs according to project phases improves cash flow management and reduces the need for excessive upfront capital.
3. Timing of Costs and Cash Flows
Timing is a critical economic factor affecting cash flow and profitability.
• Dynamic Start and Sale Months: Each lot can have unique start and sale months, reflecting realistic project timelines.
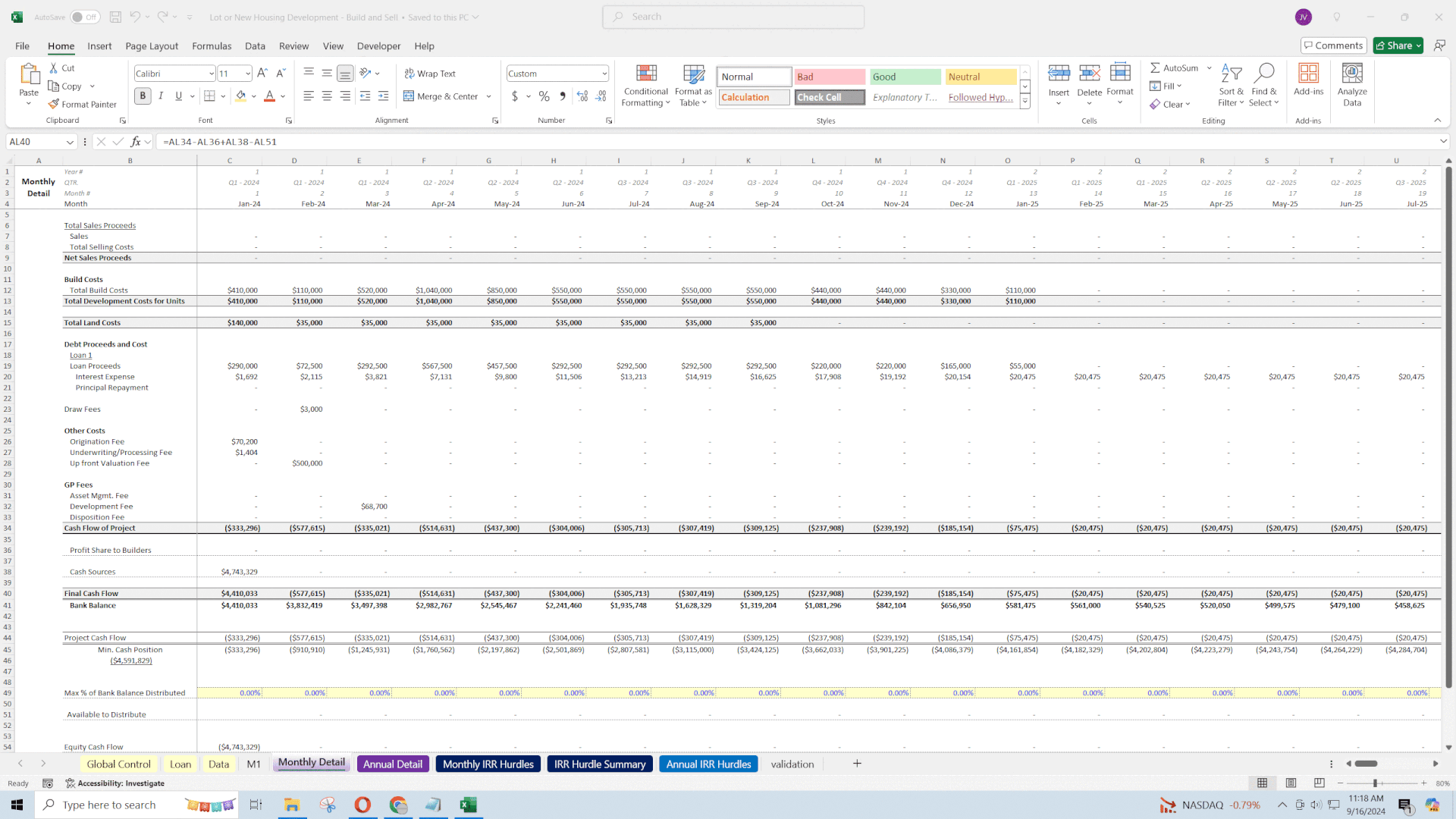
• Monthly Cash Flow Projections: Costs and revenues are mapped on a monthly basis over a 60-month horizon.
• Economic Impact: Precise timing of costs and revenues allows developers to identify funding gaps, plan for financing, and optimize the schedule to enhance returns.
4. Sales Revenue
Revenue projections are based on the sale of developed lots.
• Sale Amount per Lot: Individually defined, accommodating variations in lot value.
• Selling Costs: Calculated as a percentage of the sales price, representing commissions, marketing, and closing costs.
• Economic Impact: Estimating realistic sale prices and associated costs is vital for forecasting profitability and ensuring the project's financial viability.
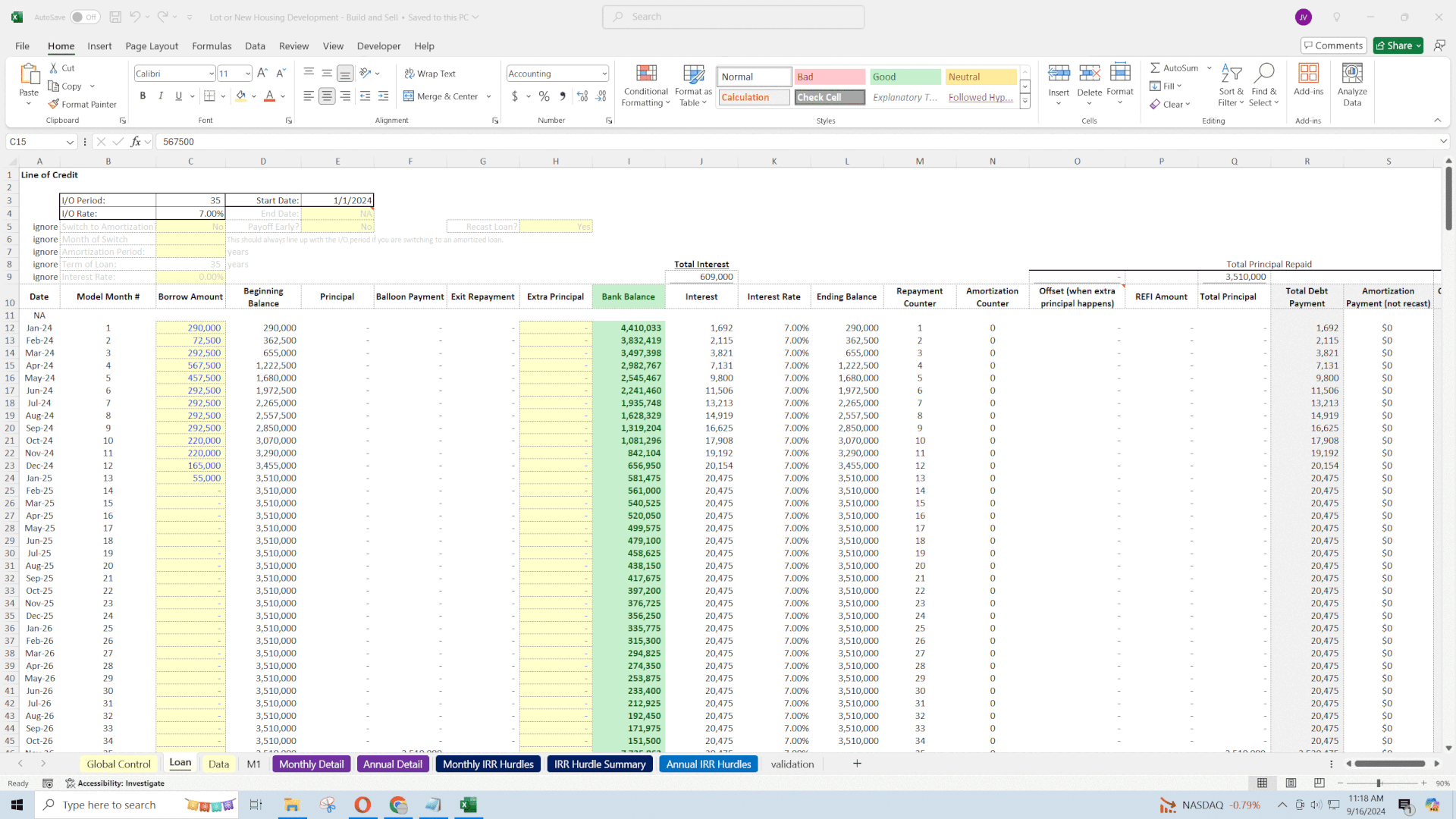
5. Financing Considerations
Access to financing can significantly affect the economics of lot development.
• Interest-Only Loan Option: The model includes an interest-only loan with:
• Manual Draw Amounts: Specify loan draws per month to match funding needs.
• Dynamic Interest Calculation: Interest expenses adjust based on outstanding loan balances.
• Manual Repayment: Control over when and how much to repay.
• Loan Fees: Options to include origination fees, valuation fees, draw fees, and underwriting/processing fees, with timing of when these fees affect cash flow.
• Economic Impact: Efficient use of debt can enhance returns but also introduces interest expenses and repayment obligations. Modeling these accurately is essential for assessing net profitability.
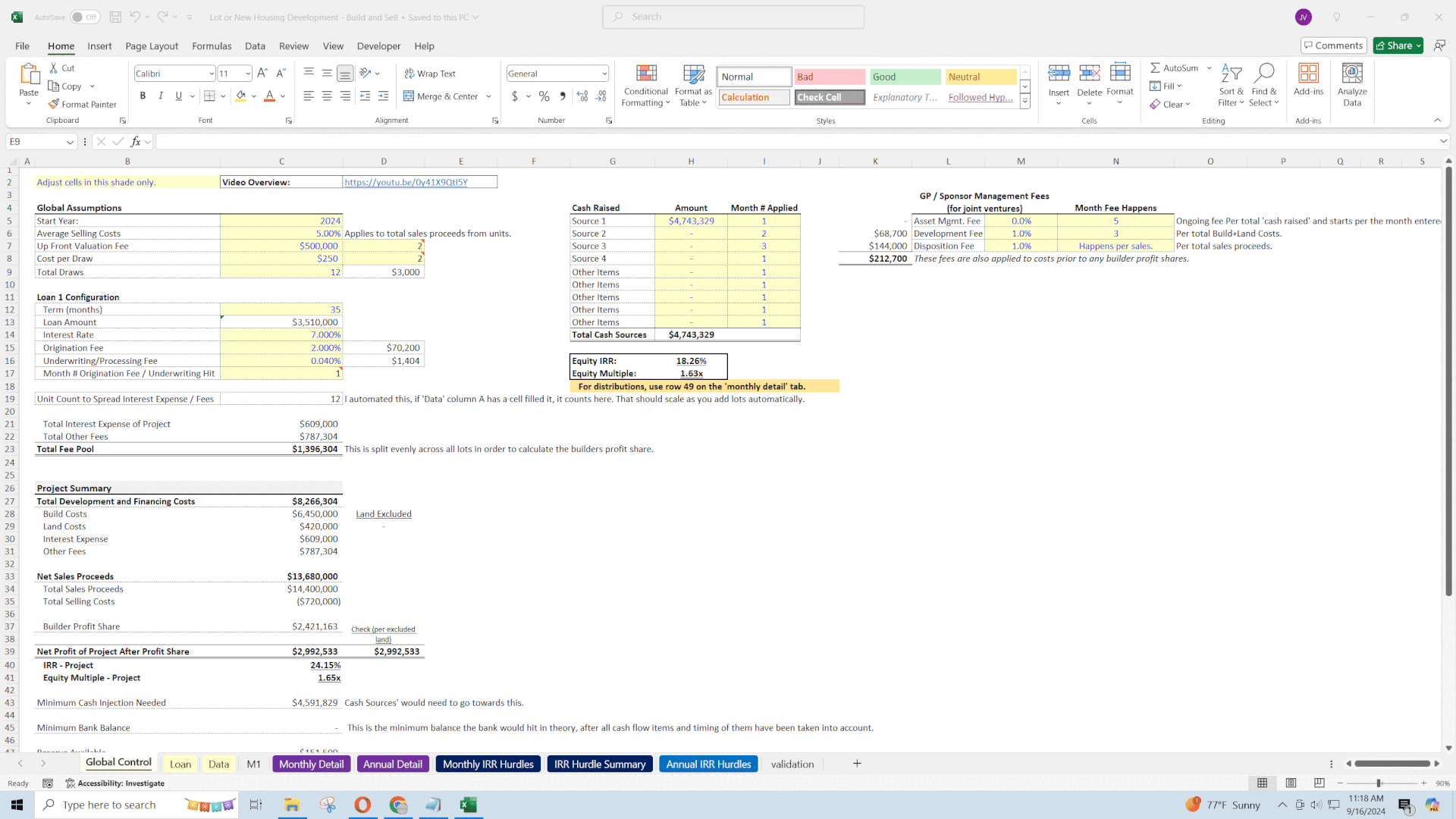
6. Profitability Metrics
Assessing the project's profitability involves analyzing various return metrics.
• Profit per Lot: The model distributes total fees and interest across all lots, providing a net profit figure per lot.
Return Metrics:
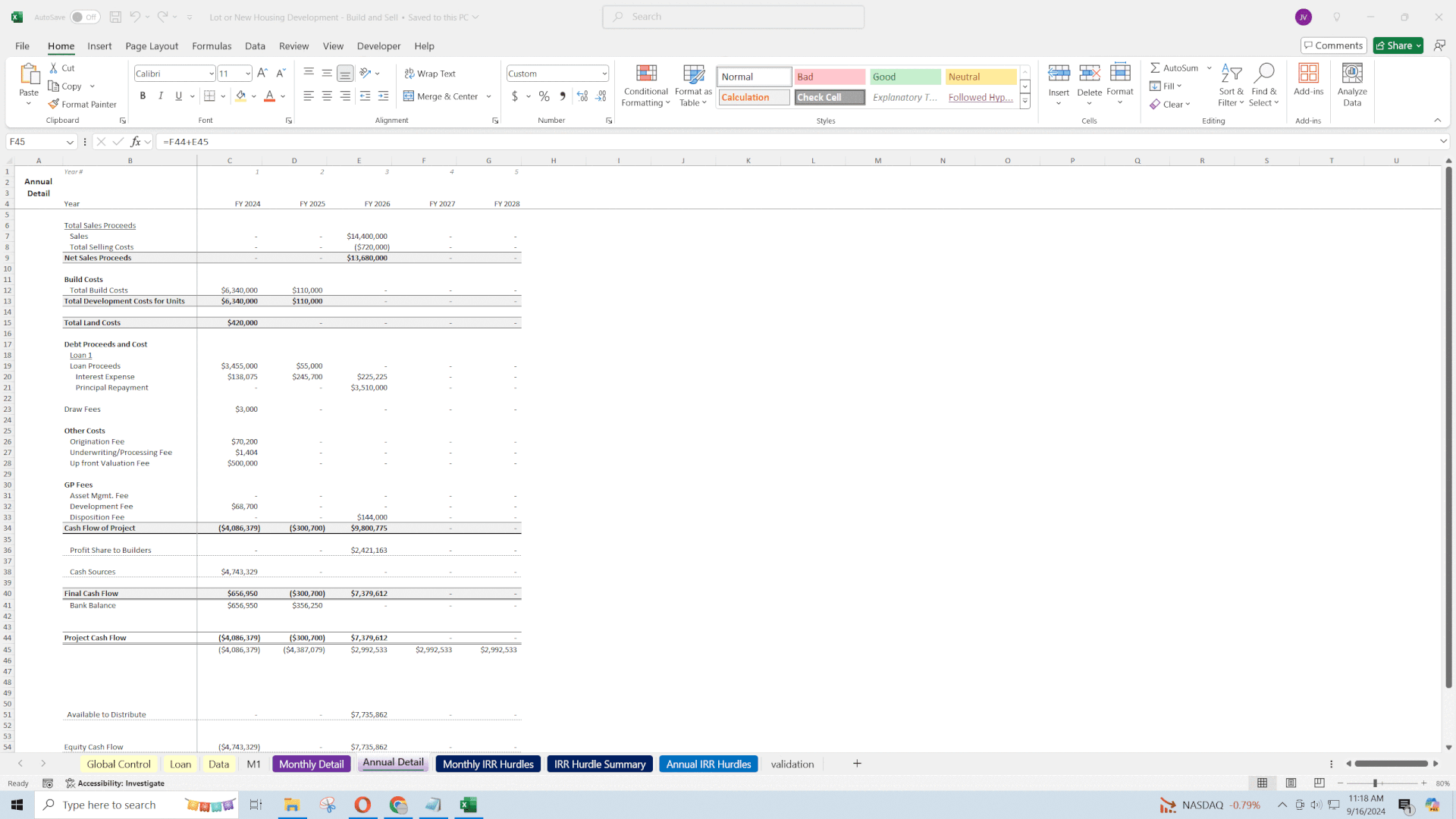
• Internal Rate of Return (IRR): Both levered (including financing effects) and unlevered (excluding financing).
• Equity Multiple: Ratio of total cash inflows to outflows.
• Project Summary: High-level overview of total costs, proceeds, and net profit.
• Economic Impact: These metrics help determine whether the project meets the developer's investment thresholds and are crucial for attracting investors or securing financing.
7. Joint Venture Considerations
In projects involving partnerships or investors, profit-sharing arrangements affect the economics.
• General Partner (GP) Fees:
• Construction Fee: Compensation for managing the development process.
• Disposition Fee: Fee upon the sale of the lots.
• Asset Management Fee: Ongoing fee for managing the investment.
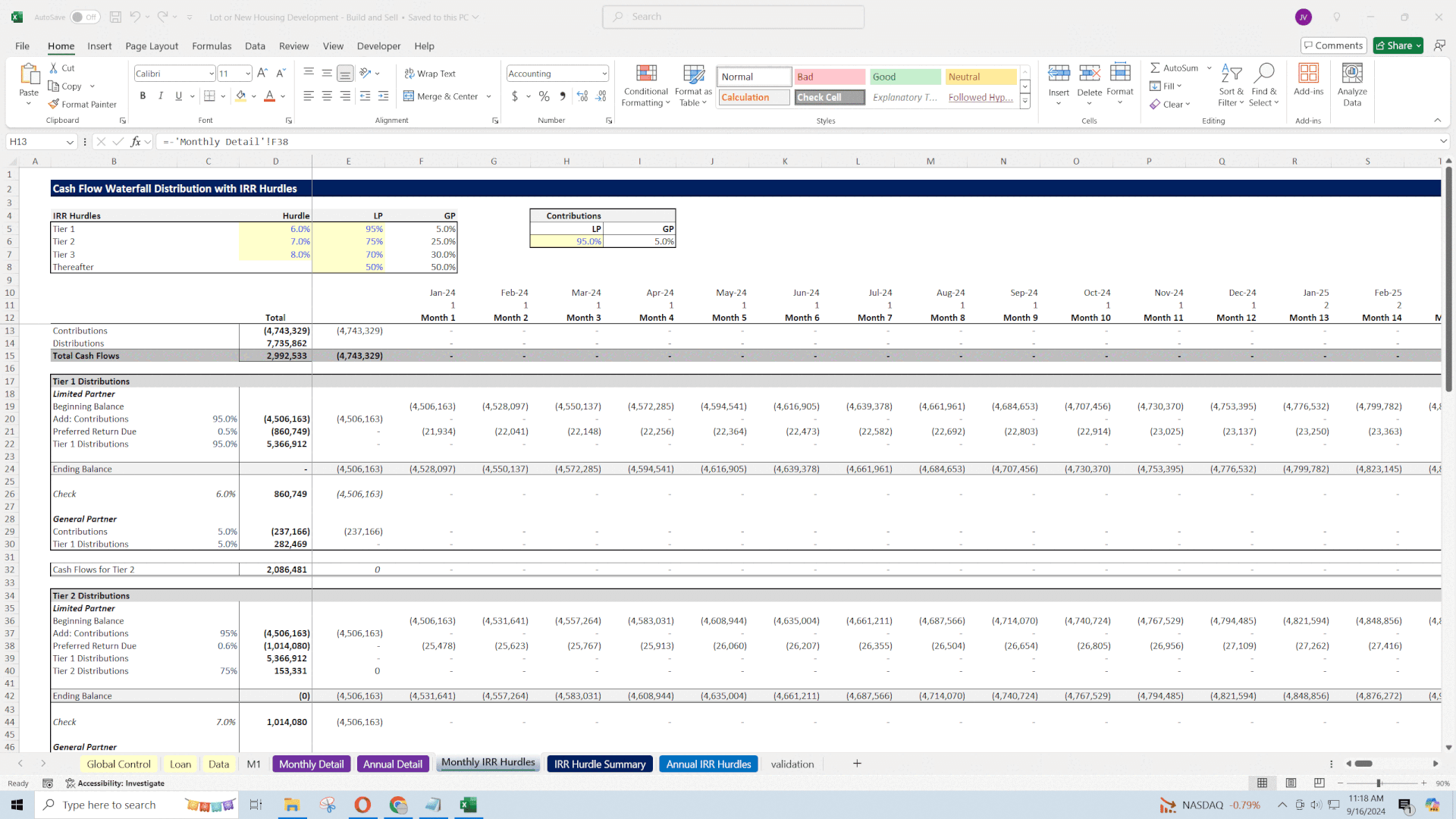
IRR Hurdle Waterfall:
• Up to 3 Hurdles: Define tiers where the profit-sharing ratio changes once certain IRR thresholds are met.
• Monthly and Annual Conventions: Flexibility in calculating returns based on different timeframes.
• Economic Impact: Structuring the profit-sharing correctly aligns incentives between partners and can make the project more attractive to potential investors by offering competitive returns.
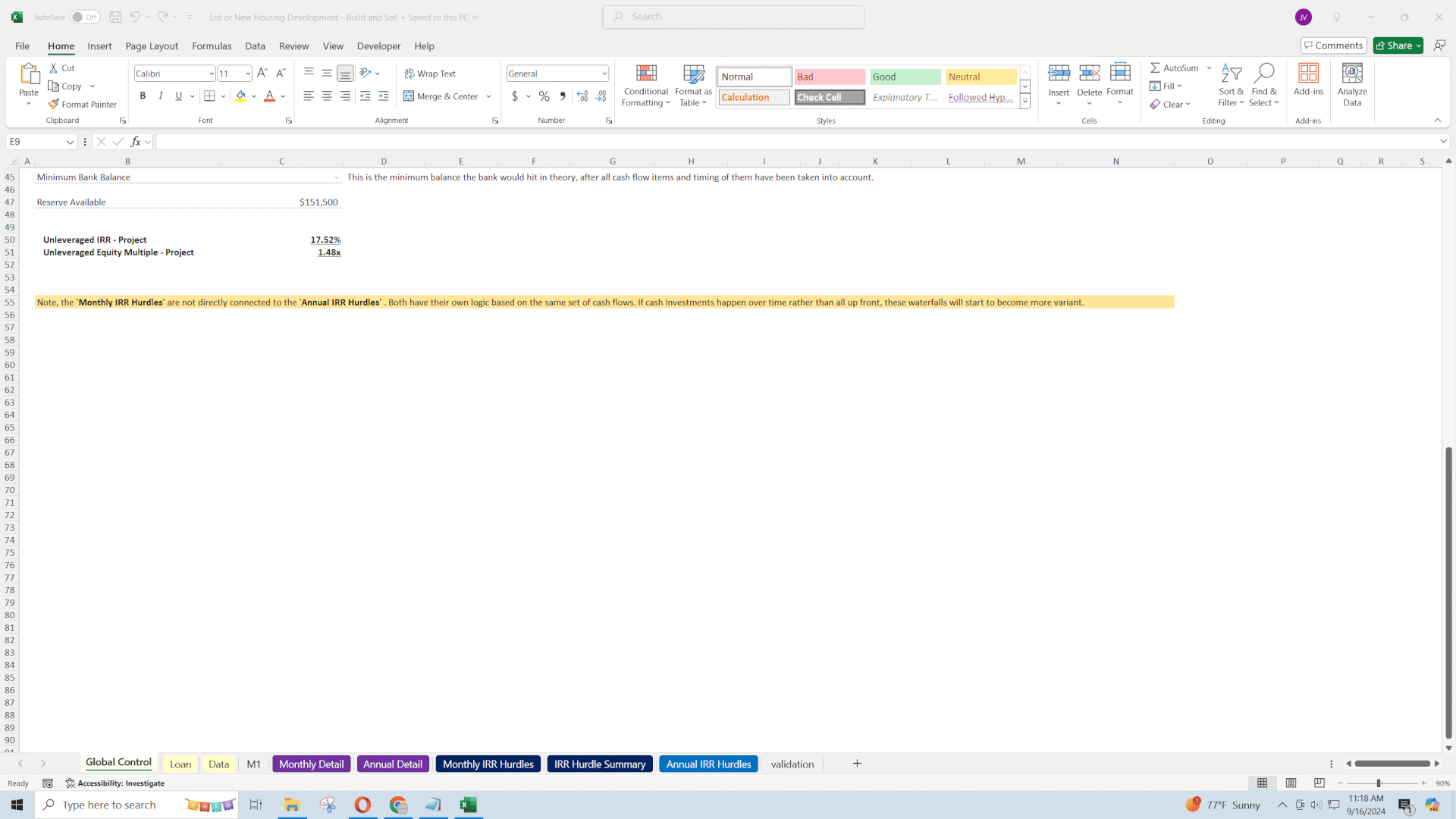
8. Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management ensures the project remains solvent throughout its lifecycle.
• Bank Balance Tracking: The model's "bank balance" row shows how changes in timing and assumptions affect the required investment amount.
• Distributions to Investors:
• Manual Distribution Inputs: Specify the percentage of the bank balance to distribute to investors each month.
• Impact on Cash Flow: Distributions reduce available cash, affecting funding needs and timing.
• Economic Impact: Maintaining a positive cash flow is essential to cover ongoing expenses and avoid financing shortfalls. Strategic distributions can keep investors satisfied while ensuring the project's financial health.
9. Detailed Lot Configuration
The ability to configure each lot individually adds precision to the economic analysis.
• Up to 500 Lots: While the default is set for up to 500 lots, the model is scalable.
• Individual Metrics: Each lot can have unique assumptions for costs, timing, and sales.
• Dummy Data: The model includes sample data for 20-40 lots, which can be customized.
• Economic Impact: Granular control allows for more accurate forecasting, especially in projects where lots may vary significantly in size, cost, or sale price.
Conclusion
Breaking down the economics of lot development requires a comprehensive understanding of all cost components, revenue streams, timing factors, and financing arrangements. The described financial model provides a robust framework for analyzing these elements in detail. By allowing for individual lot configuration, dynamic timing, and detailed cost inputs, the model enables developers to forecast cash flows accurately, assess profitability, and make informed decisions.
Understanding these economic factors is crucial for:
• Evaluating Project Feasibility: Determining if the projected returns meet investment criteria.
• Securing Financing: Presenting detailed financial projections to lenders or investors.
• Optimizing Returns: Identifying areas to reduce costs, adjust timing, or enhance revenues.
• Risk Management: Anticipating potential shortfalls and planning contingencies.
• By leveraging such a comprehensive model, developers can navigate the complexities of lot development with greater confidence, ultimately transforming their real estate vision into a profitable reality.
Instructional video included in file.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Real Estate, Integrated Financial Model Excel: Land Development Real Estate Model (up to 500 lots) Excel (XLSX) Spreadsheet, Jason Varner | SmartHelping