PPT DESCRIPTION
Variance analysis is used to understand and assess the drivers of change in measured variables. Variance analysis helps explain and understand what drives the difference between two measures of the same variable. Variance analysis explains differences between measures by breaking those measures into their base components. This deck has 37 slides and contents include:
• What is variance analysis?
• Linear variance
• Two component variance analysis
• Variance analysis with more than two components
• Key takeaways
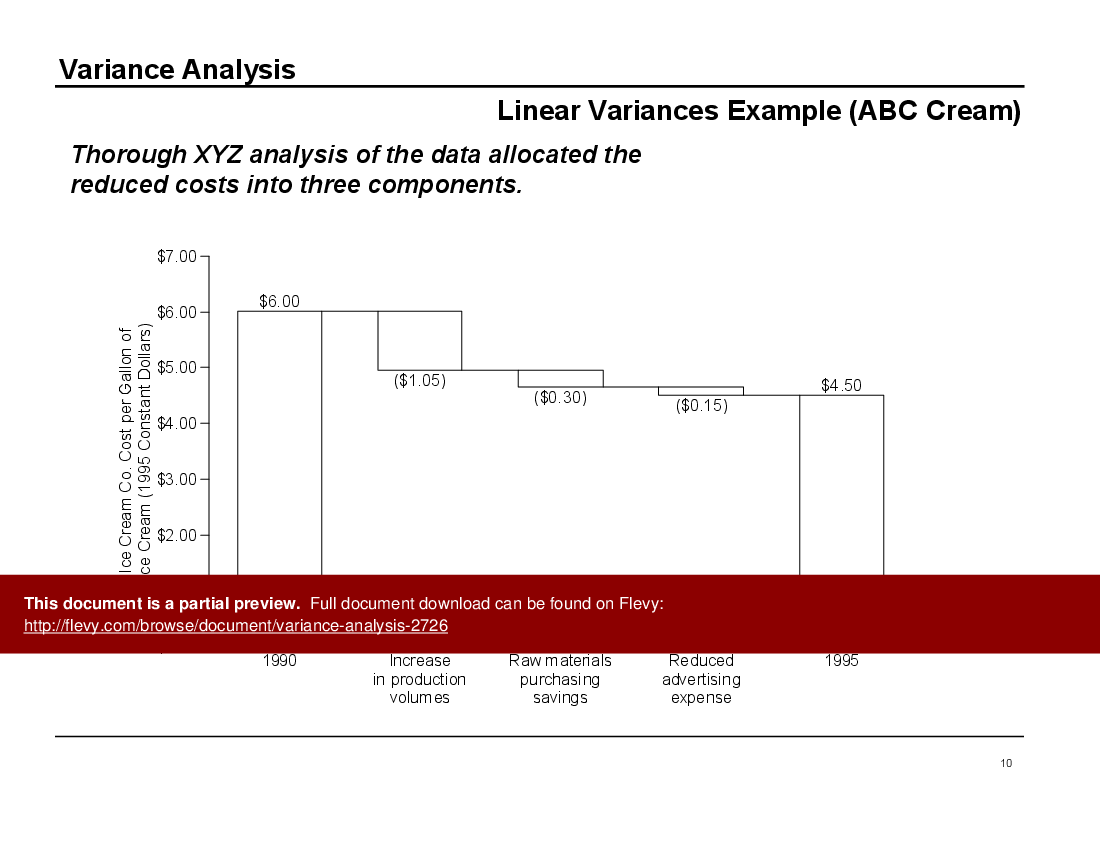
This comprehensive presentation on variance analysis not only explains the fundamental concepts, but also dives deep into practical applications. The document includes real-world examples, such as the case of ABC Ice Cream, where cost reductions over five years are analyzed. This example illustrates how variance analysis can pinpoint specific areas of cost savings, providing actionable insights for cost management.
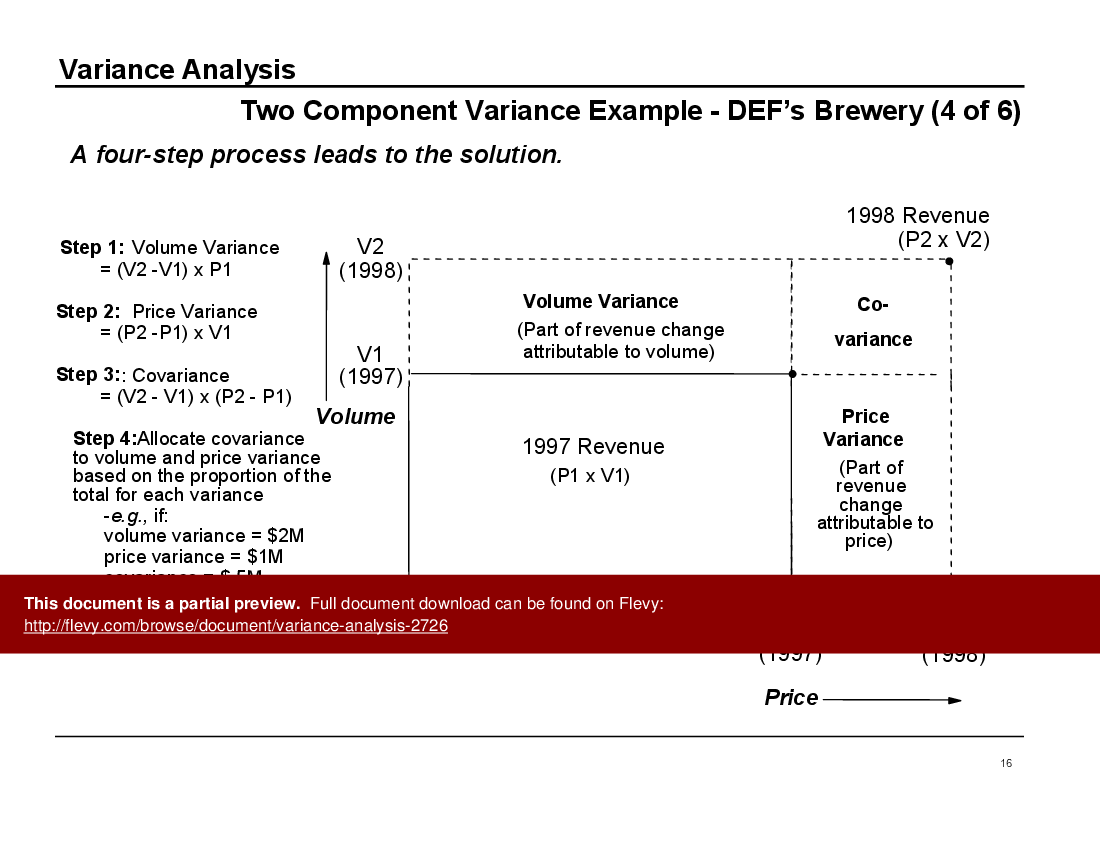
The deck also covers a detailed two-component variance analysis using DEF’s Brewery as a case study. This section breaks down revenue growth into volume and price variances, offering a step-by-step guide to understanding the drivers behind financial performance. This methodical approach ensures that executives can clearly see the impact of different factors on their bottom line.
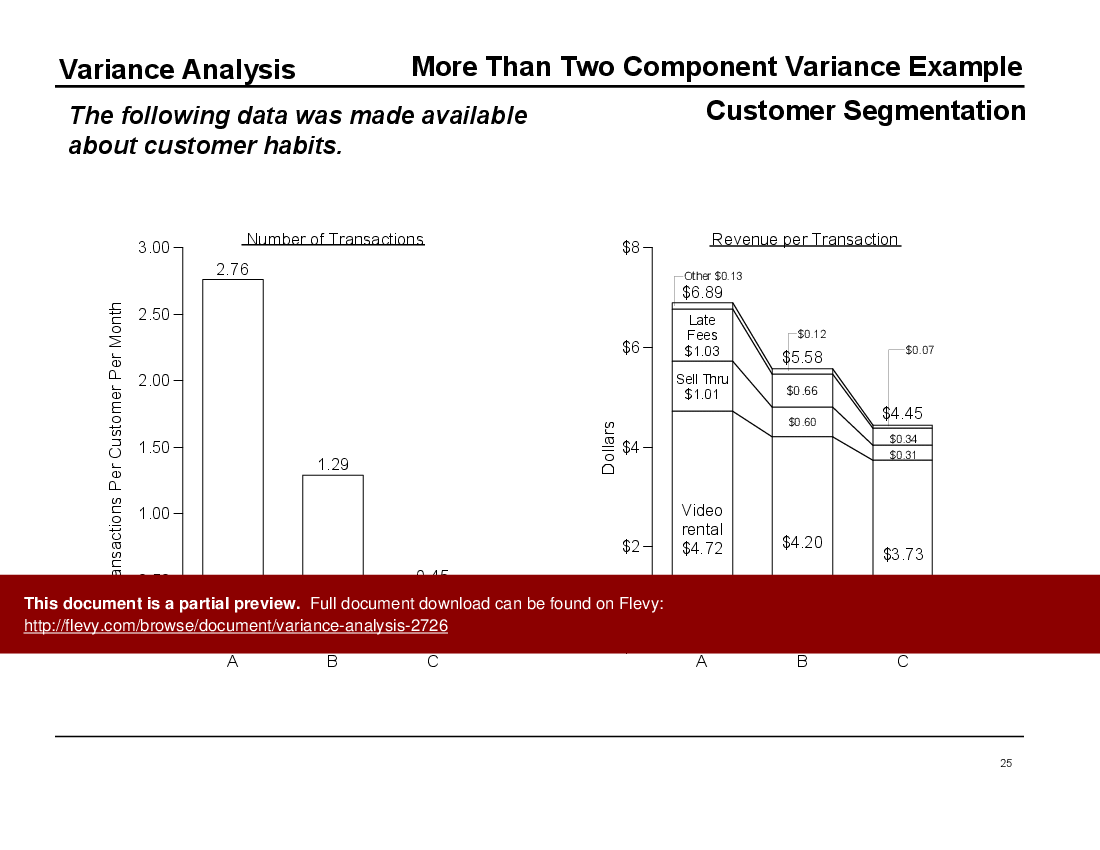
For more complex scenarios, the document explores multi-component variance analysis with examples from GHK Video. This part of the presentation highlights how variance analysis can be used to segment customers and understand spending patterns. By breaking down revenue per customer type, businesses can tailor their strategies to different market segments, optimizing their marketing and sales efforts.
The presentation is rounded out with sample spreadsheets that provide a hands-on approach to calculating variances and covariances. These tools are invaluable for executives looking to implement variance analysis in their own organizations. The spreadsheets demonstrate how to allocate variances to different factors, making it easier to identify key areas for improvement and drive strategic decision-making.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 37-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Variance Analysis PPT provides a structured approach to understanding the factors influencing changes in key business metrics. This consulting-grade presentation, akin to McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality, equips corporate executives and consultants with the tools to dissect revenue, cost, and profit variances effectively. Users will learn to identify true profit drivers, assess the impact of various components on financial outcomes, and make informed decisions based on actionable insights derived from variance analysis.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Financial analysts seeking to deepen their understanding of revenue and cost drivers
• Business consultants advising clients on performance improvement strategies
• Corporate executives responsible for strategic decision-making and financial oversight
• Operations managers looking to optimize cost structures and profitability
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During financial reviews to assess performance against targets
• When analyzing product line profitability to identify areas for improvement
• In strategy sessions focused on cost reduction and revenue enhancement initiatives
Learning Objectives
• Define variance analysis and its significance in financial performance assessment
• Build a framework for linear variance analysis to evaluate single-component impacts
• Establish a two-component variance analysis to dissect revenue changes by volume and price
• Analyze scenarios involving more than 2 components to understand complex revenue drivers
• Identify actionable insights from variance analysis to inform strategic decisions
• Develop proficiency in using spreadsheets for variance calculations and reporting
Table of Contents
• What Is Variance Analysis? (page 3)
• Linear Variance Analysis (page 7)
• Two Component Variance Analysis (page 13)
• Variance Analysis with More Than Two Components (page 22)
• Key Takeaways (page 36)
Primary Topics Covered
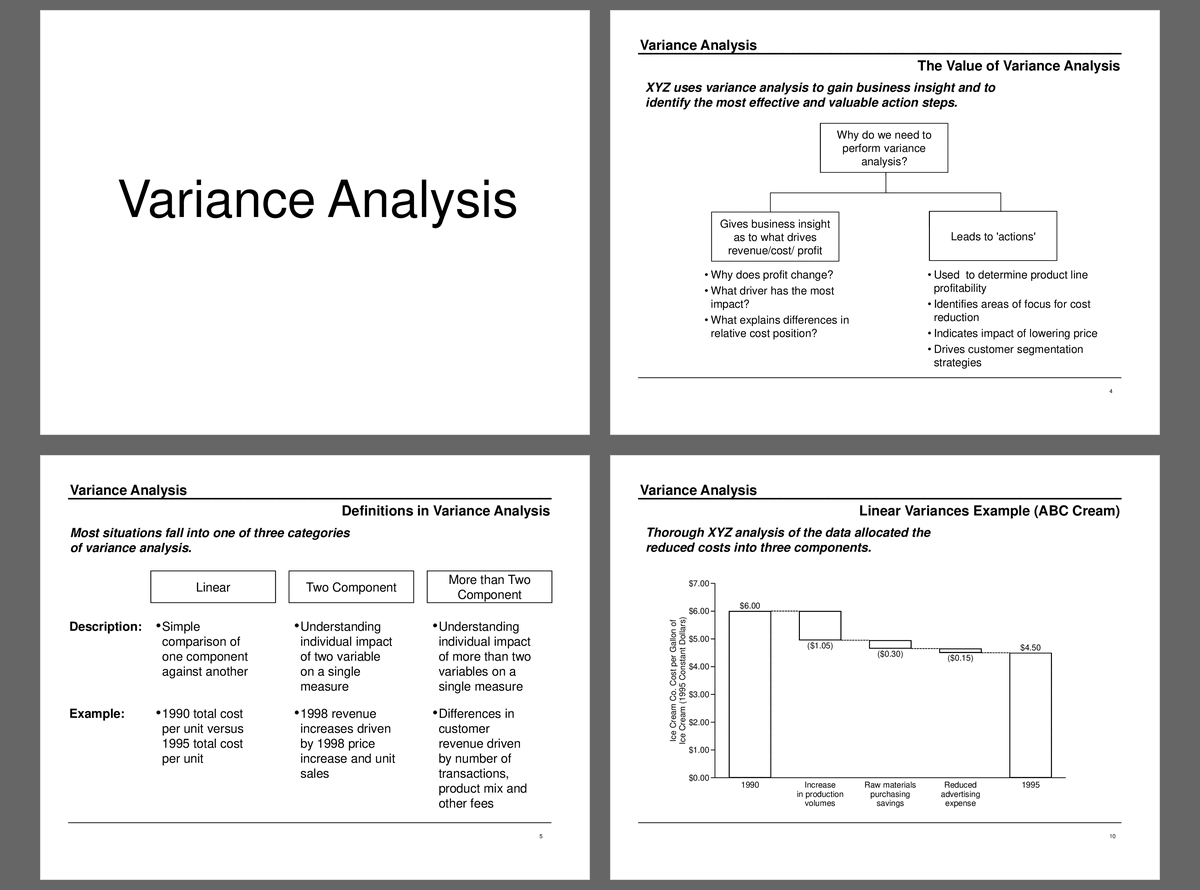
• Variance Analysis Definition - Variance analysis helps assess the drivers of change in measured variables, explaining differences between 2 measures of the same variable.
• Linear Variance - A straightforward comparison of one component against another, exemplified by the cost analysis of ABC Ice Cream.
• Two Component Variance - Analyzing revenue growth at DEF’s Brewery by separating the impacts of price and volume changes.
• More Than Two Component Analysis - Understanding customer spending patterns at GHK Video by segmenting revenue drivers across multiple variables.
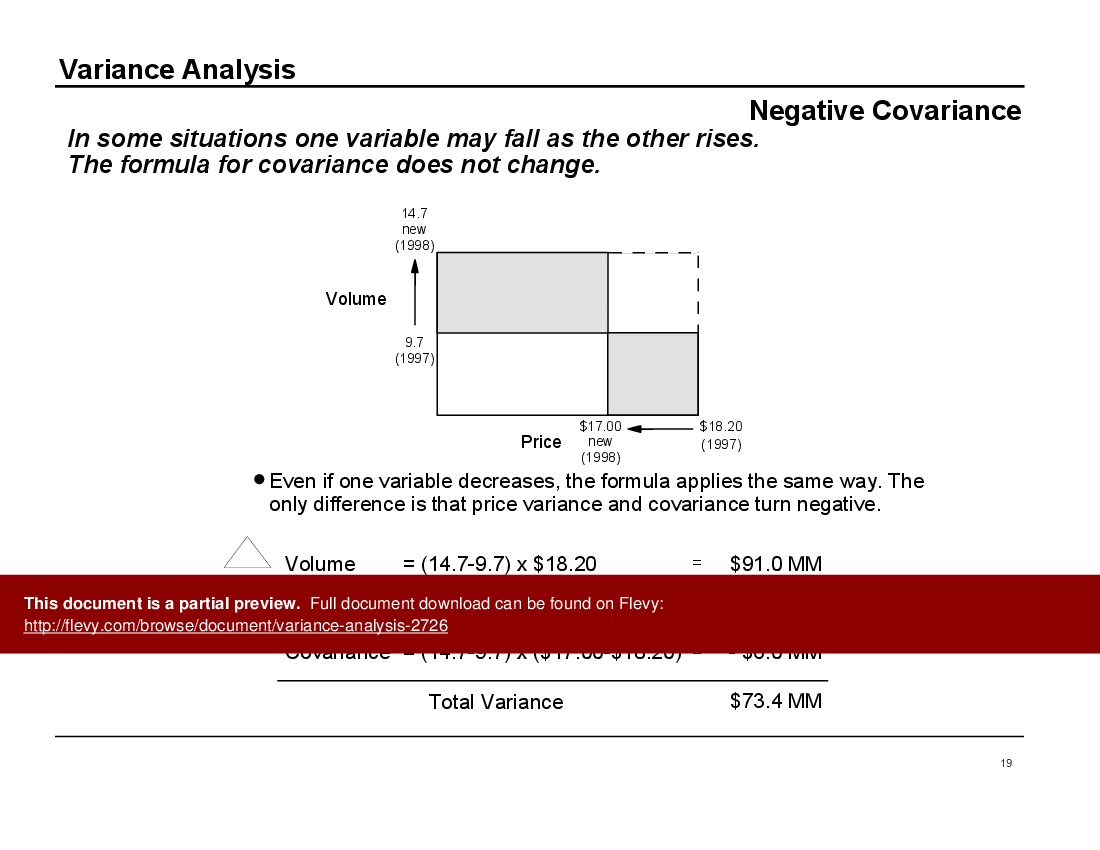
• Covariance - The concept of covariance explains the variance attributable to simultaneous changes in multiple variables.
• Actionable Insights - Utilizing variance analysis to identify key areas for cost reduction and revenue enhancement strategies.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Linear variance analysis template for single-component assessments
• Two-component variance analysis model for revenue breakdowns by volume and price
• Spreadsheet examples for calculating variances and covariances
• Framework for segmenting customer data to analyze spending patterns
• Guidelines for interpreting variance results to inform strategic initiatives
• Action plan template for implementing insights derived from variance analysis
Slide Highlights
• Overview of variance analysis and its importance in business decision-making
• Detailed examples of linear variance analysis with ABC Ice Cream
• Step-by-step breakdown of two-component variance analysis at DEF’s Brewery
• Visual aids illustrating covariance and its impact on revenue analysis
• Customer segmentation analysis at GHK Video demonstrating multiple variance drivers
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Variance Analysis (30 minutes)
• Overview of variance analysis and its applications
• Discussion on the importance of understanding financial metrics
Linear Variance Analysis Session (60 minutes)
• Case study review of ABC Ice Cream
• Hands-on exercise calculating linear variances
Two Component Variance Analysis Workshop (90 minutes)
• Deep dive into DEF’s Brewery case
• Group activity on calculating and interpreting two-component variances
More Than Two Component Analysis Discussion (60 minutes)
• Exploration of GHK Video’s customer segmentation
• Interactive session on identifying revenue drivers across multiple components
Customization Guidance
• Adjust the case studies to reflect your organization’s specific industry and metrics
• Tailor the variance analysis templates to align with your internal reporting standards
• Incorporate your company’s terminology and metrics into the provided frameworks
• Modify the examples to include relevant data from your organization for practical application
Secondary Topics Covered
• Understanding the implications of variance analysis on strategic planning
• Techniques for effectively communicating variance findings to stakeholders
• Best practices for integrating variance analysis into regular financial reviews
• The role of variance analysis in performance management and operational efficiency
Topic FAQ
What are the common steps in performing variance analysis for business metrics?
Variance analysis typically begins with defining the measure and the comparison, then performs linear variance for single components, two-component decomposition (e.g., price vs. volume), and multi-component analysis for more complex drivers, followed by interpretation and action planning. See pages 3, 7, 13, and 22 for these sections.How does two-component variance analysis separate the effects of price and volume?
Two-component variance analysis isolates the revenue change into the portion attributable to price changes and the portion due to volume changes by calculating each component’s contribution to total variance. Flevy's Variance Analysis includes a step-by-step two-component case study using DEF’s Brewery as an example.What is covariance and why is it important in variance analysis?
Covariance measures how 2 variables change together and captures variance that arises from their interaction, explaining effects not attributable to single variables alone. The deck explains covariance conceptually and includes visual aids illustrating its impact on revenue analysis and interpretation of variance.I need to analyze product-line profitability—which variance approaches should I consider?
For a single dominant cost driver, use linear variance to compare one component over time; for revenue changes, apply two-component price/volume decomposition; for multiple contributing factors or segments, use multi-component analysis. Flevy's Variance Analysis supplies a linear template and a two-component model for these scenarios.How can variance analysis be applied to customer segmentation and spending patterns?
Apply multi-component variance analysis to segment revenue by customer type, breaking down revenue-per-customer and transaction frequency to identify which segments drive change. The presentation demonstrates this with the GHK Video customer-segmentation example and provides a framework for segmenting customer data.What should I look for when choosing a variance analysis template for my finance team?
Choose templates that match your use cases: single-component (linear) templates, two-component revenue models, multi-component frameworks, spreadsheet examples for calculations, and guidance for interpreting results and creating an action plan—look specifically for included spreadsheet examples and an action plan template.How much time should I plan for training the team to use variance analysis tools effectively?
The deck’s suggested workshop agenda sequences learning and hands-on exercises across 4 sessions totaling about 240 minutes: 30-minute introduction, 60-minute linear session, 90-minute two-component workshop, and 60-minute multi-component discussion, which can guide training time estimates.Are there ready-made spreadsheet models for calculating variances and covariances I can use immediately?
Yes—sample spreadsheets for calculating variances and covariances are included, demonstrating how to allocate variances to different factors and supporting hands-on calculation and reporting using the provided spreadsheet examples.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is variance analysis?
Variance analysis is a financial tool used to assess the differences between expected and actual performance, helping to identify the drivers of change in revenue, costs, and profits.
How can variance analysis improve decision-making?
By breaking down financial metrics into their components, variance analysis provides insights that inform strategic decisions, enabling organizations to focus on areas that drive profitability.
What are the key components of linear variance analysis?
Linear variance analysis typically involves comparing one variable against another to understand the impact of changes, such as production costs over time.
How do I conduct a two-component variance analysis?
To conduct a two-component variance analysis, separate the impacts of 2 variables, such as price and volume, on overall revenue, and calculate their respective contributions to changes.
What is covariance in variance analysis?
Covariance measures the degree to which 2 variables change together, helping to explain the variance that cannot be attributed to a single variable alone.
How can I apply variance analysis to customer segments?
Variance analysis can be applied to customer segments by analyzing spending patterns and transaction frequencies to identify which segments drive the most revenue.
What tools can assist in performing variance analysis?
Spreadsheets are commonly used for variance analysis, allowing users to calculate variances and visualize data effectively.
How often should variance analysis be conducted?
Variance analysis should be conducted regularly, ideally during financial reviews or when significant changes in business operations occur, to ensure timely insights.
Glossary
• Variance Analysis - A method for evaluating the differences between expected and actual financial performance.
• Linear Variance - A comparison of one variable against another to assess changes.
• Two Component Variance - An analysis that separates the impacts of 2 variables on a single measure.
• Covariance - A statistical measure that indicates the extent to which 2 variables change together.
• Revenue Drivers - Factors that significantly influence revenue generation within a business.
• Customer Segmentation - The process of dividing a customer base into distinct groups based on shared characteristics.
• Actionable Insights - Practical recommendations derived from data analysis that can guide decision-making.
• Spreadsheet Model - A structured format for organizing and analyzing financial data using spreadsheet software.
• Revenue per Transaction - The average revenue generated from each customer transaction.
• Cost Structure - The various costs incurred by a business in its operations.
• Profitability Analysis - An evaluation of a company's ability to generate profit relative to its revenue.
• Performance Metrics - Quantitative measures used to assess the effectiveness of a business or individual.
• Financial Oversight - The process of monitoring and managing financial activities within an organization.
• Strategic Decision-Making - The process of making choices that will shape the direction of an organization.
• Operational Efficiency - The ability to deliver products or services in the most cost-effective manner without sacrificing quality.
• Cost Reduction Strategies - Initiatives aimed at decreasing expenses while maintaining or improving output.
• Revenue Enhancement Initiatives - Efforts to increase revenue through various means, such as marketing or product development.
• Profit Drivers - Elements that significantly contribute to a company's profitability.
• Financial Review - A systematic examination of a company's financial performance and position.
• Business Insight - Understanding gained from analyzing data that informs strategic decisions.
• Performance Improvement - Efforts aimed at enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations.
PPT SLIDES
Source: Variance Analysis PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Documents & Files
This document is available as part of the following discounted bundle(s):
Save %!
Essential Consulting Knowledge Builder
This bundle contains 21 total documents. See all the documents to the right.