Relative Cost Position Analysis (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 48 Slides
COST OPTIMIZATION PPT DESCRIPTION
Relative cost position (RCP) is a key analytical tool used for cost analysis.
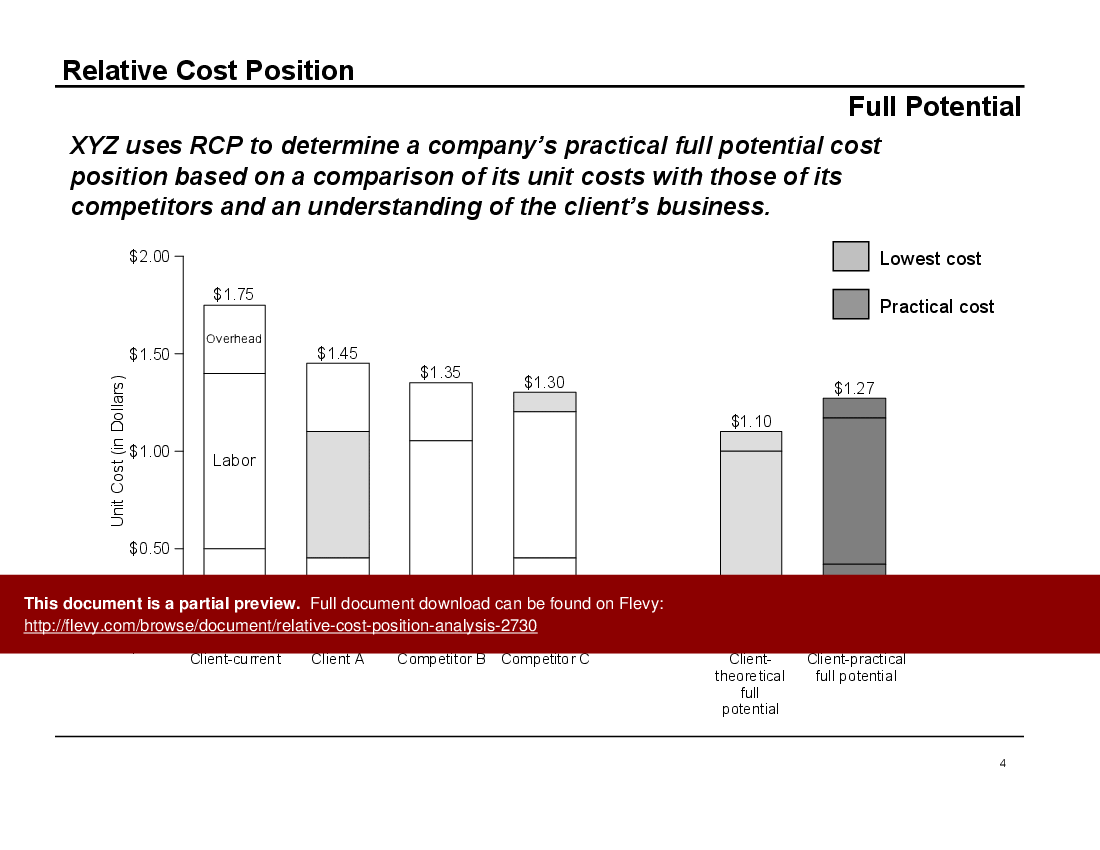
We can use RCP to determine a company's practical full potential cost position based on a comparison of its unit costs with those of its competitors and an understanding of the client's business. RCP analysis helps answer both strategic and tactical questions.
This deck has 48 slides and contents include:
• The relative cost position (RCP) concept
• Applications
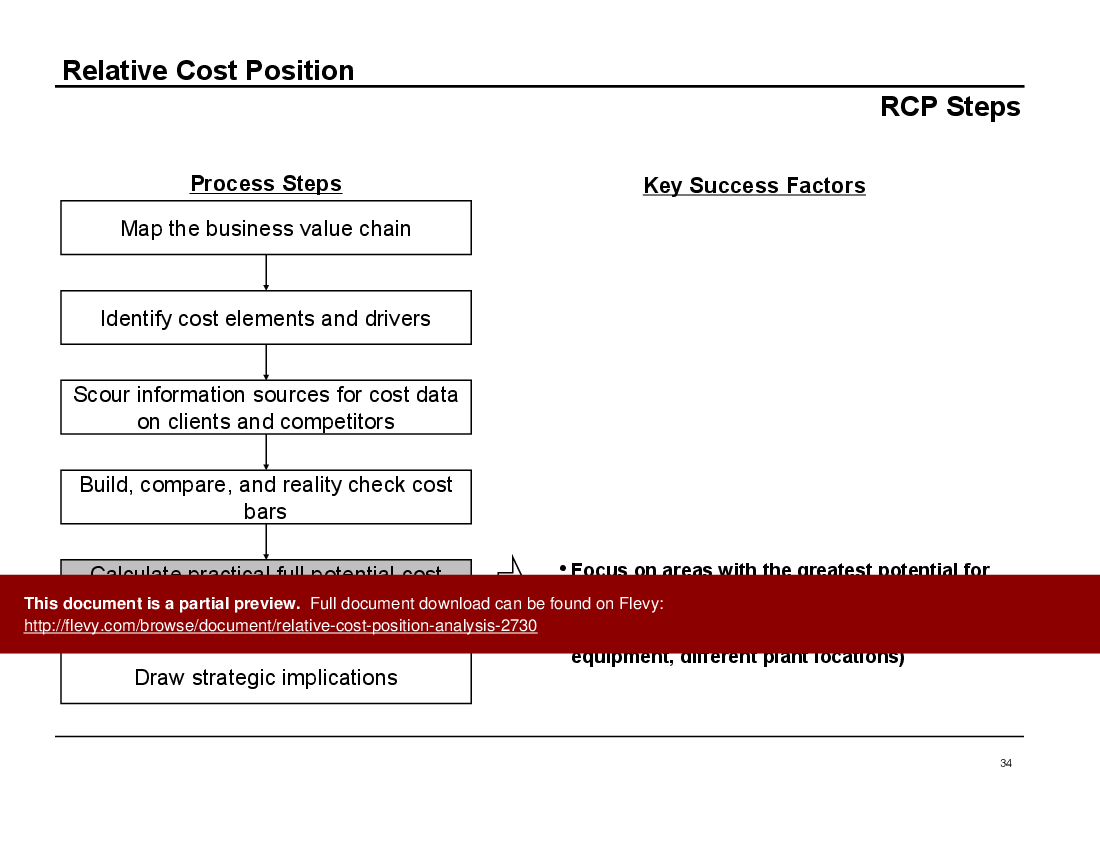
• RCP Steps
• Client example
• Challenges
• Key takeaways
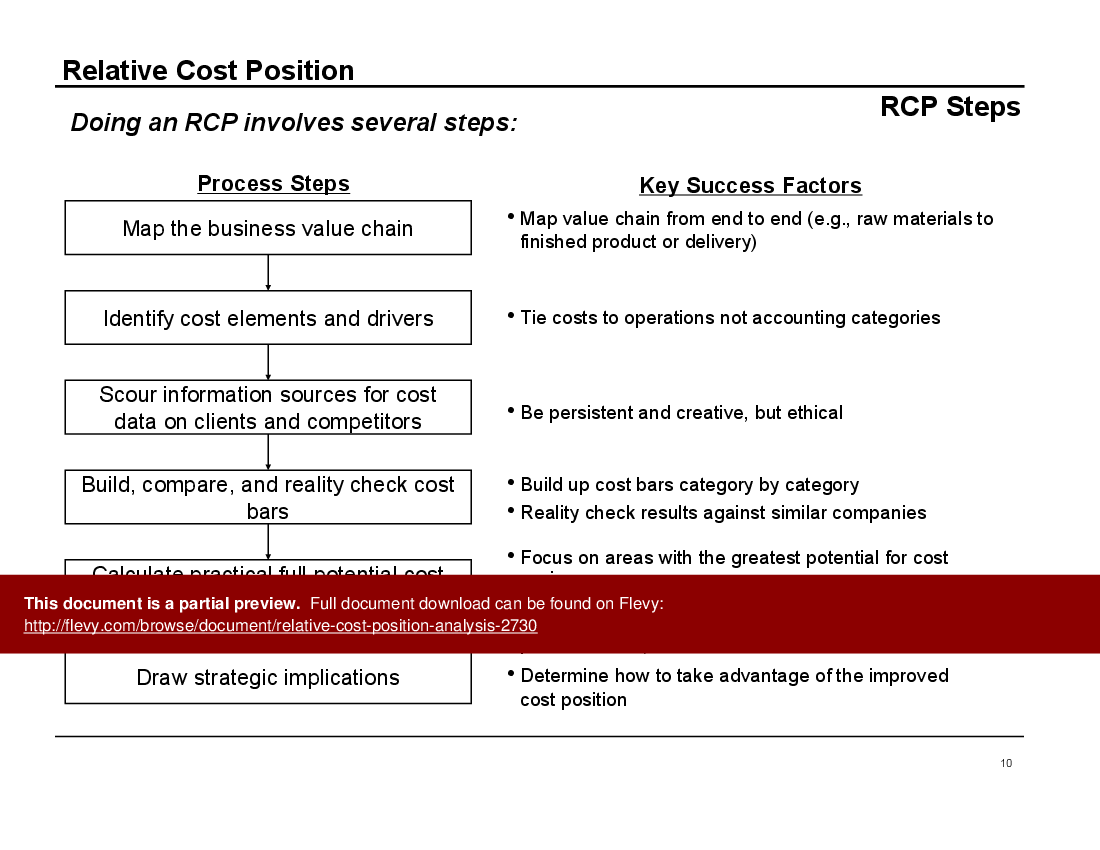
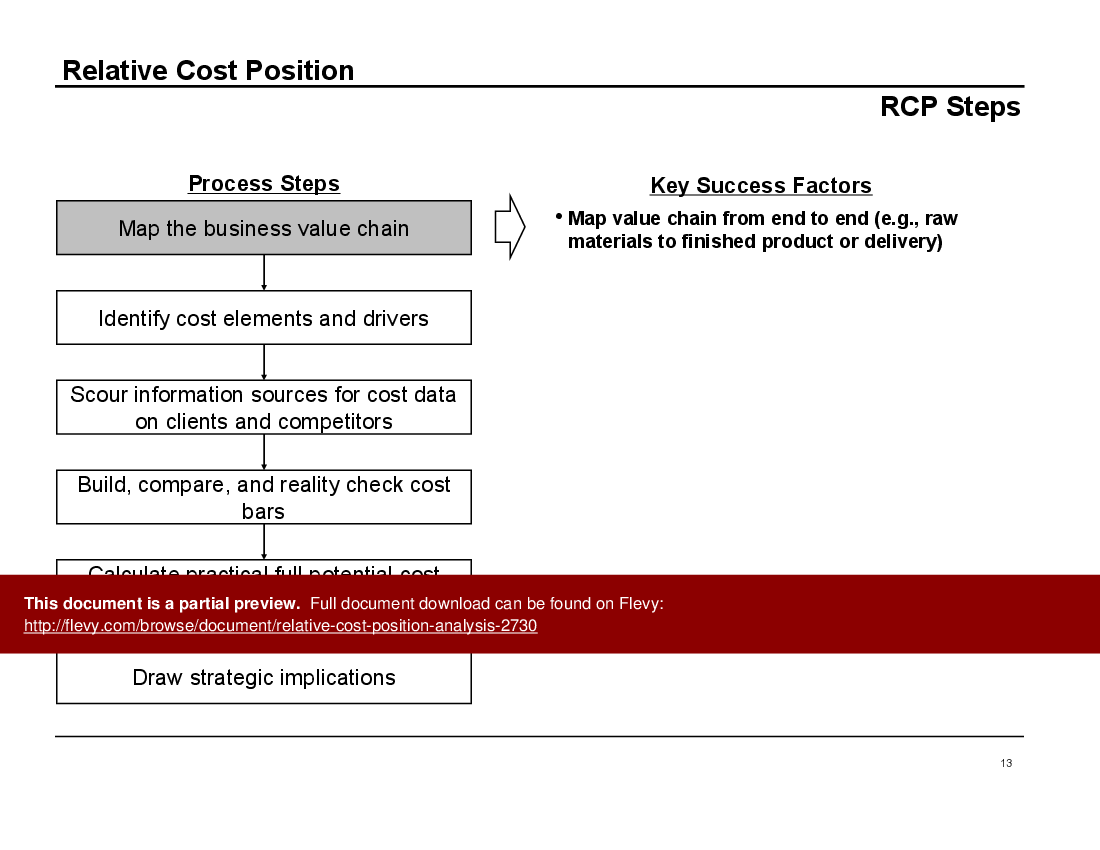
The Relative Cost Position Analysis document is a comprehensive guide for executives looking to gain a competitive edge through cost management. It includes detailed steps for mapping the business value chain, identifying cost elements and drivers, and scouring information sources for cost data on clients and competitors. The process is thorough and involves building, comparing, and reality-checking cost bars to ensure accuracy and relevance.
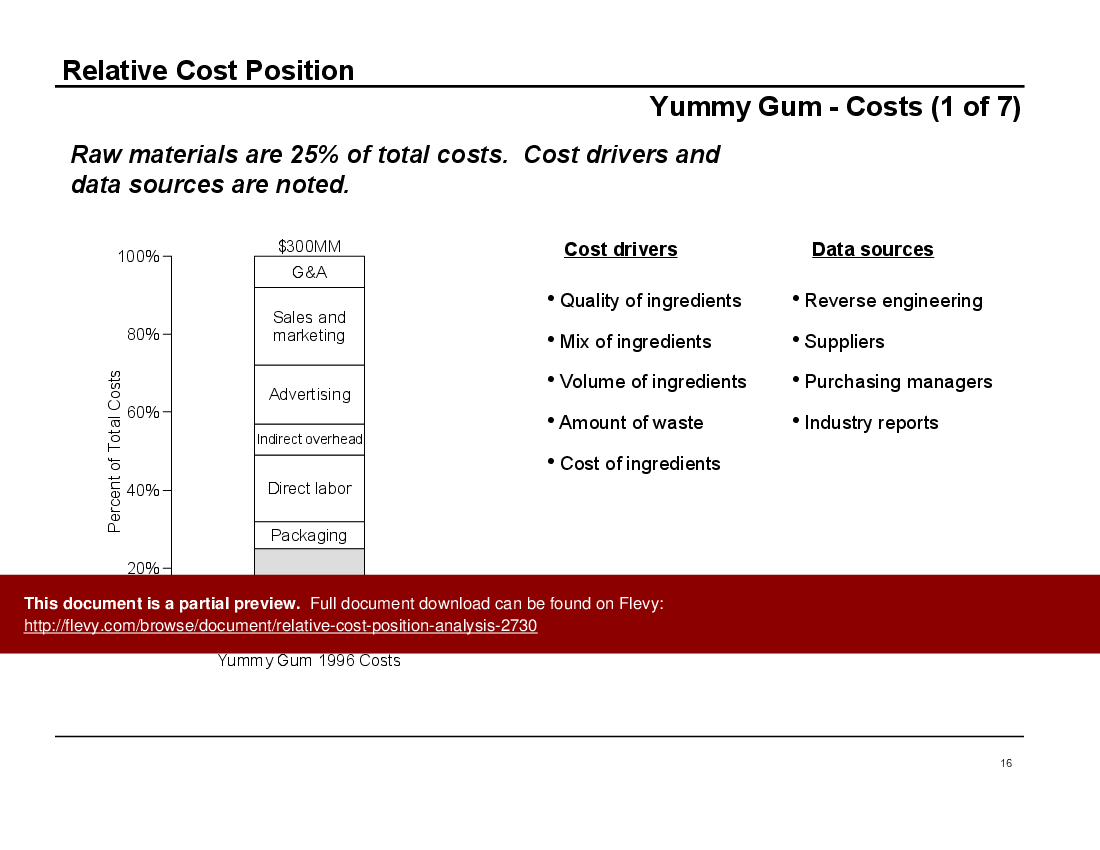
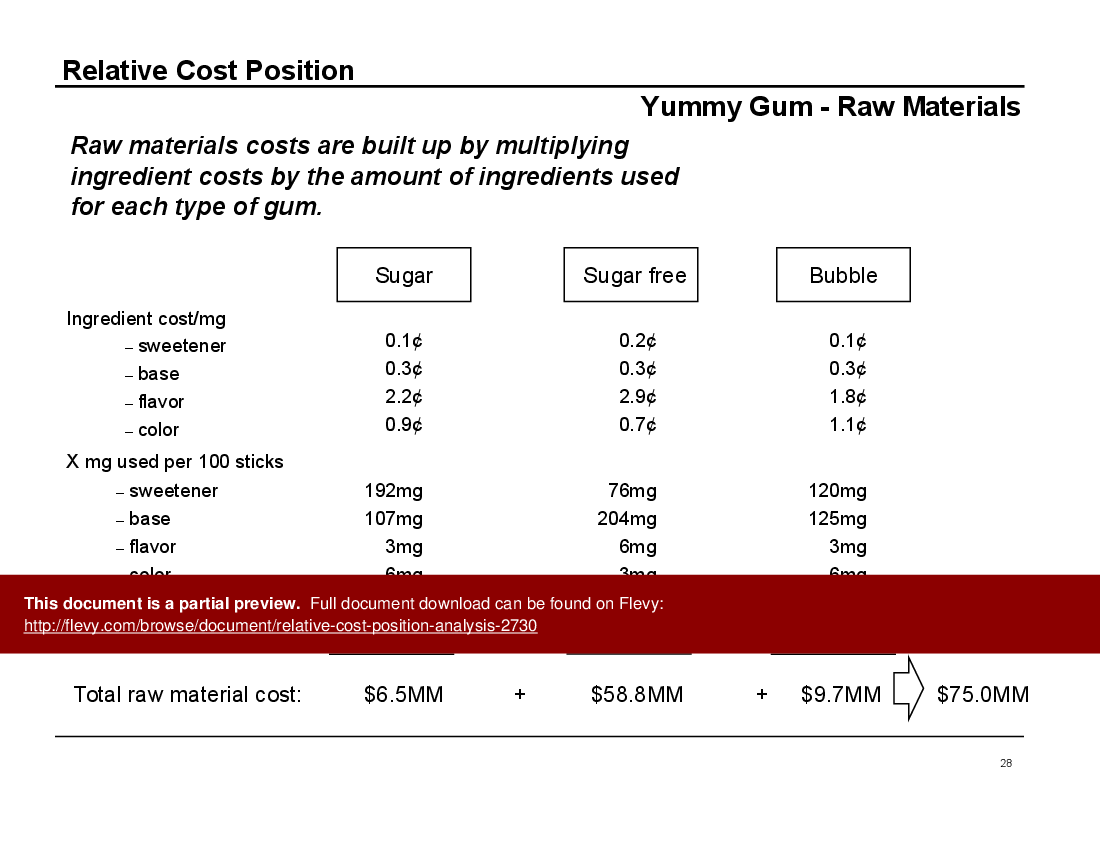
The document also provides real-world examples of how RCP has been used effectively by companies. One case study highlights a chewing gum manufacturer that identified $29MM in annual savings through RCP analysis. Another example shows how a client in the diaper business regained 10% market share by leveraging RCP to identify optimal pricing strategies. These examples underscore the practical applications and tangible benefits of RCP.
Key success factors are emphasized throughout the document. For instance, mapping the value chain from end to end and tying costs to operations rather than accounting categories are crucial steps. The document also stresses the importance of being persistent and creative in gathering cost data while maintaining ethical standards. These insights are invaluable for executives aiming to optimize their cost structures.
The document also addresses common challenges in conducting RCP. Understanding competitors' cost structures and determining the client's practical full potential cost position are highlighted as critical areas. The document provides strategies for overcoming these challenges, such as focusing on areas with the greatest potential for cost savings and adjusting for the client's specific situation. This makes the document not just a theoretical guide, but a practical toolkit for cost management.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 48-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Relative Cost Position Analysis (RCP) presentation is a consulting-grade tool designed to help businesses assess their cost structures in comparison to competitors. This deck, reflecting the quality of McKinsey, Bain, or BCG, provides a structured approach to identifying cost advantages and optimizing cost efficiency. Users will learn to analyze their relative cost position, enabling strategic decision-making that enhances profitability and competitive standing.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to understand cost dynamics in their industry
• Financial analysts focused on cost optimization and competitive analysis
• Operations managers aiming to improve efficiency and reduce costs
• Strategy consultants assisting clients in cost structure evaluations
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to identify cost reduction opportunities
• When assessing competitive positioning in pricing strategies
• In preparation for mergers or acquisitions to evaluate potential synergies
Learning Objectives
• Define the Relative Cost Position concept and its relevance in cost analysis
• Identify key cost elements and drivers within a business value chain
• Analyze competitor cost structures and benchmark against industry standards
• Calculate practical full potential cost positions and identify savings opportunities
• Draw strategic implications from RCP analysis to inform decision-making
• Develop actionable steps for cost reduction based on RCP findings
Table of Contents
• Relative Cost Position Concept (page 2)
• Applications of RCP (page 7)
• RCP Steps (page 10)
• Client Example: Yummy Gum (page 12)
• Challenges in RCP Analysis (page 43)
• Key Takeaways (page 45)
Primary Topics Covered
• Relative Cost Position (RCP) - A framework for analyzing a company's cost structure in relation to competitors, focusing on identifying cost advantages and optimizing efficiency.
• Applications of RCP - Real-world examples illustrating how RCP has led to significant cost savings and improved market positions for various clients.
• RCP Steps - A systematic approach detailing the steps involved in conducting an RCP analysis, from mapping the value chain to drawing strategic implications.
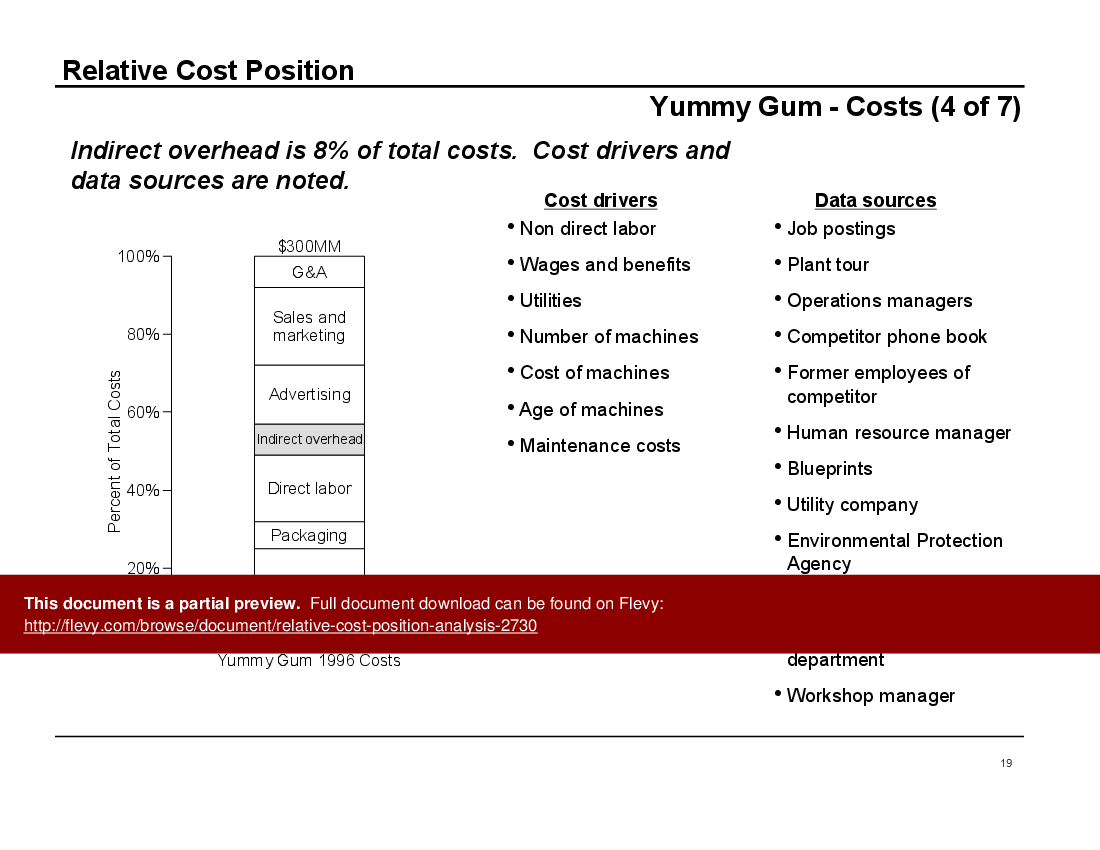
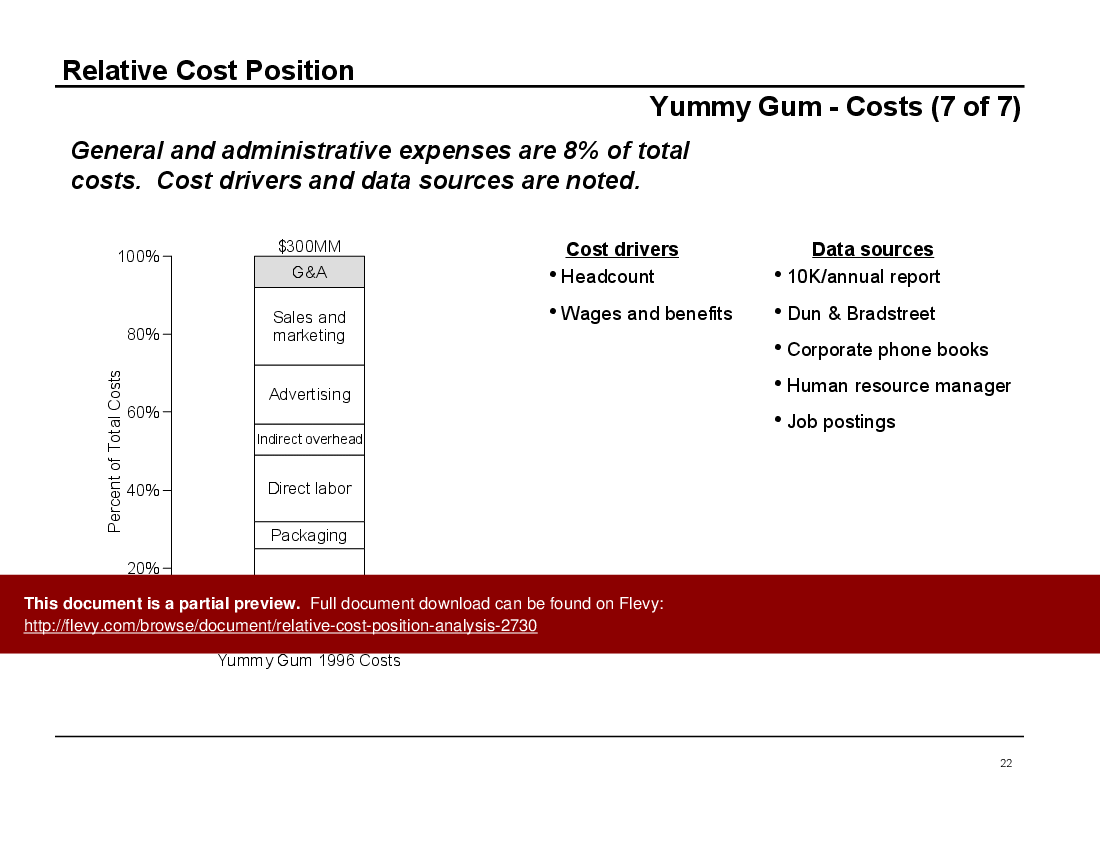
• Client Case Study: Yummy Gum - An in-depth look at how RCP analysis was applied to improve profitability in a competitive market.
• Challenges in RCP Analysis - Common obstacles faced when gathering competitor data and determining practical cost positions.
• Key Takeaways - Essential insights and best practices for effectively utilizing RCP in cost analysis.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• RCP analysis framework template for mapping cost structures
• Value chain mapping tool to identify cost drivers
• Cost comparison charts for benchmarking against competitors
• Strategic implication worksheets for decision-making
• Data collection guides for sourcing competitor cost information
• Savings potential calculators to quantify cost reduction opportunities
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the Relative Cost Position concept and its significance in cost analysis
• Detailed applications showcasing successful RCP implementations
• Step-by-step guide on conducting an RCP analysis with key success factors
• Case study of Yummy Gum illustrating practical applications of RCP
• Challenges section addressing common data-gathering issues in RCP analysis
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Relative Cost Position (30 minutes)
• Overview of RCP and its importance in cost analysis
• Discussion on strategic and tactical questions RCP can answer
RCP Analysis Steps (60 minutes)
• Detailed walkthrough of the RCP steps
• Group exercise on mapping a value chain
Case Study Discussion: Yummy Gum (45 minutes)
• Review of the Yummy Gum case study
• Identifying key takeaways and implications for participants' organizations
Customization Guidance
• Adjust the value chain mapping to reflect specific industry contexts
• Tailor cost elements and drivers based on the unique business environment
• Incorporate company-specific data sources for competitor analysis
• Modify strategic implications based on organizational goals and market conditions
Secondary Topics Covered
• Cost-sharing analysis and its role in competitive positioning
• Activity-based costing as a method for detailed cost analysis
• Profitability analysis across product lines and its impact on cost strategies
• Overhead and fixed/variable cost analysis for comprehensive cost understanding
• Best demonstrated practices in cost management and optimization
Topic FAQ
What are the key steps involved in a Relative Cost Position (RCP) analysis?
An RCP analysis follows a systematic sequence: map the business value chain end-to-end, identify cost elements and drivers, gather competitor cost data, build and compare cost structures (cost bars), and draw strategic implications to prioritize savings opportunities. These are the RCP Steps outlined in the deck.How should I map a value chain for cost analysis so it supports RCP?
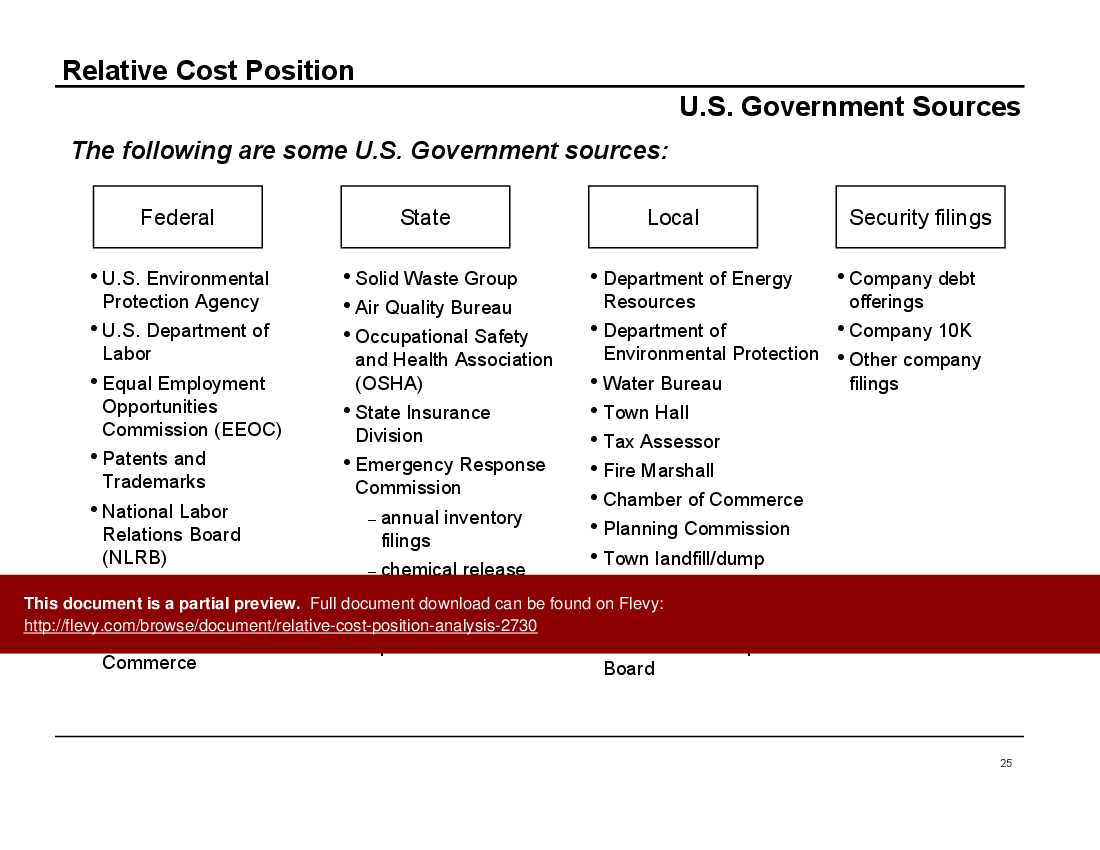
Map processes end-to-end and link cost items to operational activities rather than accounting buckets, ensuring each step’s cost drivers are explicit. The deck provides a value chain mapping tool and recommends tying costs to operations to support accurate benchmarking with competitors.What sources can I use to estimate competitors’ unit costs for RCP benchmarking?
Use a mix of public and primary sources: financial reports, industry benchmarks, supplier interviews, market research, and government filings. The document’s data collection guides describe these sources and how to use them for competitor cost estimation.How do I determine the practical full potential cost position for my company?
Determine it by comparing your unit costs with competitor benchmarks, building comparable cost bars, and reality-checking assumptions against operational constraints. The approach combines unit-cost comparisons with iterative reality checks to estimate a practical full potential cost position.What should I look for when choosing an RCP toolkit or template?
Look for templates and tools that support each RCP step: an RCP analysis framework, value chain mapping tool, cost comparison charts, data collection guides, and savings calculators. The Relative Cost Position Analysis deck explicitly includes these deliverables, including an RCP analysis framework template.How long does an initial RCP assessment or workshop typically take?
The deck includes a suggested workshop agenda totaling about 135 minutes: 30 minutes for RCP introduction, 60 minutes for RCP analysis steps and a value-chain exercise, and 45 minutes for a case study discussion, supported by the 48-slide PowerPoint.I’m evaluating potential M&A synergies—how can RCP help quantify them?
Use RCP to map both firms’ value chains, identify overlapping cost drivers, benchmark unit costs, and quantify achievable savings via savings potential calculators. The method helps translate operational overlaps and supplier leverage into quantified savings estimates using savings potential calculators.What kind of ROI or outcomes have companies seen from RCP work?
The author examples show quantifiable outcomes: a chewing gum manufacturer identified $29MM in annual savings and a diaper client regained 10% market share after applying RCP-based pricing and cost changes, illustrating tangible outcomes such as $29MM in annual savings.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the Relative Cost Position (RCP)?
RCP is an analytical tool used to evaluate a company's cost structure in relation to its competitors, identifying areas for potential cost savings and efficiency improvements.
How can RCP analysis benefit my organization?
RCP analysis helps organizations understand their competitive cost position, enabling informed decisions on pricing strategies, cost reduction efforts, and overall market positioning.
What are the key steps in conducting an RCP analysis?
The key steps include mapping the business value chain, identifying cost elements and drivers, gathering competitor cost data, building and comparing cost structures, and drawing strategic implications.
What challenges might I face during RCP analysis?
Challenges include obtaining accurate competitor cost data, understanding different manufacturing processes, and determining the practical full potential cost position of your organization.
How can I customize the RCP analysis for my specific industry?
Customization can be achieved by adjusting the value chain mapping, tailoring cost elements to reflect industry standards, and incorporating relevant data sources for competitor analysis.
What types of data sources should I consider for RCP analysis?
Data sources include financial reports, industry benchmarks, supplier interviews, market research, and government filings, among others.
Can RCP analysis be applied to any industry?
Yes, RCP analysis is versatile and can be adapted to various industries, including manufacturing, retail, and services, to assess cost structures and competitive positioning.
What are some examples of successful RCP applications?
Successful applications include identifying significant cost savings for a chewing gum manufacturer and helping a diaper business regain market share through strategic pricing adjustments.
Glossary
• Relative Cost Position (RCP) - A framework for comparing a company's cost structure against competitors.
• Value Chain - A series of steps that a company takes to deliver a product or service to the market.
• Cost Drivers - Factors that cause changes in the cost of an activity or process.
• Activity-Based Costing - A costing method that assigns overhead and indirect costs to specific activities.
• Cost Sharing Analysis - Evaluating how costs are distributed among different products or services.
• Fixed Costs - Costs that do not change with the level of production or sales.
• Variable Costs - Costs that vary directly with the level of production.
• Overhead Costs - Ongoing business expenses not directly attributed to creating a product or service.
• Benchmarking - Comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests or best practices.
• Market Position - The rank of a brand or product in relation to competitors in the market.
• Strategic Implications - The potential outcomes or effects that a decision may have on an organization’s strategy.
• Cost Structure - The types and proportions of costs incurred by a business.
• Savings Potential - The estimated amount of cost reduction achievable through optimization efforts.
• Supplier Base - The collection of suppliers that a company uses to source materials or services.
• Negotiation Leverage - The advantage gained in negotiations, often through understanding costs and market conditions.
• Operational Efficiency - The ability to deliver products or services in the most cost-effective manner without sacrificing quality.
• Market Share - The portion of a market controlled by a particular company or product.
• Competitor Analysis - The process of evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of competitors within the market.
• Cost Advantage - A condition where a company can produce goods or services at a lower cost than its competitors.
• Profitability Analysis - An assessment of a company's ability to generate profit relative to its revenue, assets, or equity.
• Financial Analysis - The evaluation of a company's financial performance through metrics and ratios.
COST OPTIMIZATION PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Cost Optimization PowerPoint Slides: Relative Cost Position Analysis PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Documents & Files