Total Quality Management - Statistical Concepts (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 70 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Understand variation and Explain mean, range, standard deviation and normal distribution
- Explain measurement system analysis (MSA) and Describe process capability
- Discuss sampling and Understand quality assurance, quality policy and quality manual
SPC PPT DESCRIPTION
Introduction:
The recent global economic challenges have compelled organizations to deliver top-quality products while maintaining affordability. To thrive in this demanding environment, organizations must adopt Total Quality Management (TQM) principles. This comprehensive document delves into the core principles of TQM, with a special focus on statistical concepts that drive continuous improvement.
1. Total Quality Management (TQM):
• *Responding to Economic Pressures*: Explore how the global recession has intensified the need for organizations to produce high-quality, cost-effective products.
• *TQM's Crucial Role*: Understand why TQM is essential for achieving organizational success, customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.
2. The Strategic Embrace of Quality:
• *Evolving Quality Control*: Trace the transformation from traditional quality control to Total Quality Management, emphasizing quality's strategic significance.
• *TQM's Never-Ending Quest for Perfection*: Learn about TQM's commitment to continuous improvement with the ultimate goal of achieving perfection.
3. Approaches to Quality Control:
• *Acceptance Sampling*: Explore the acceptance sampling method for quality control.
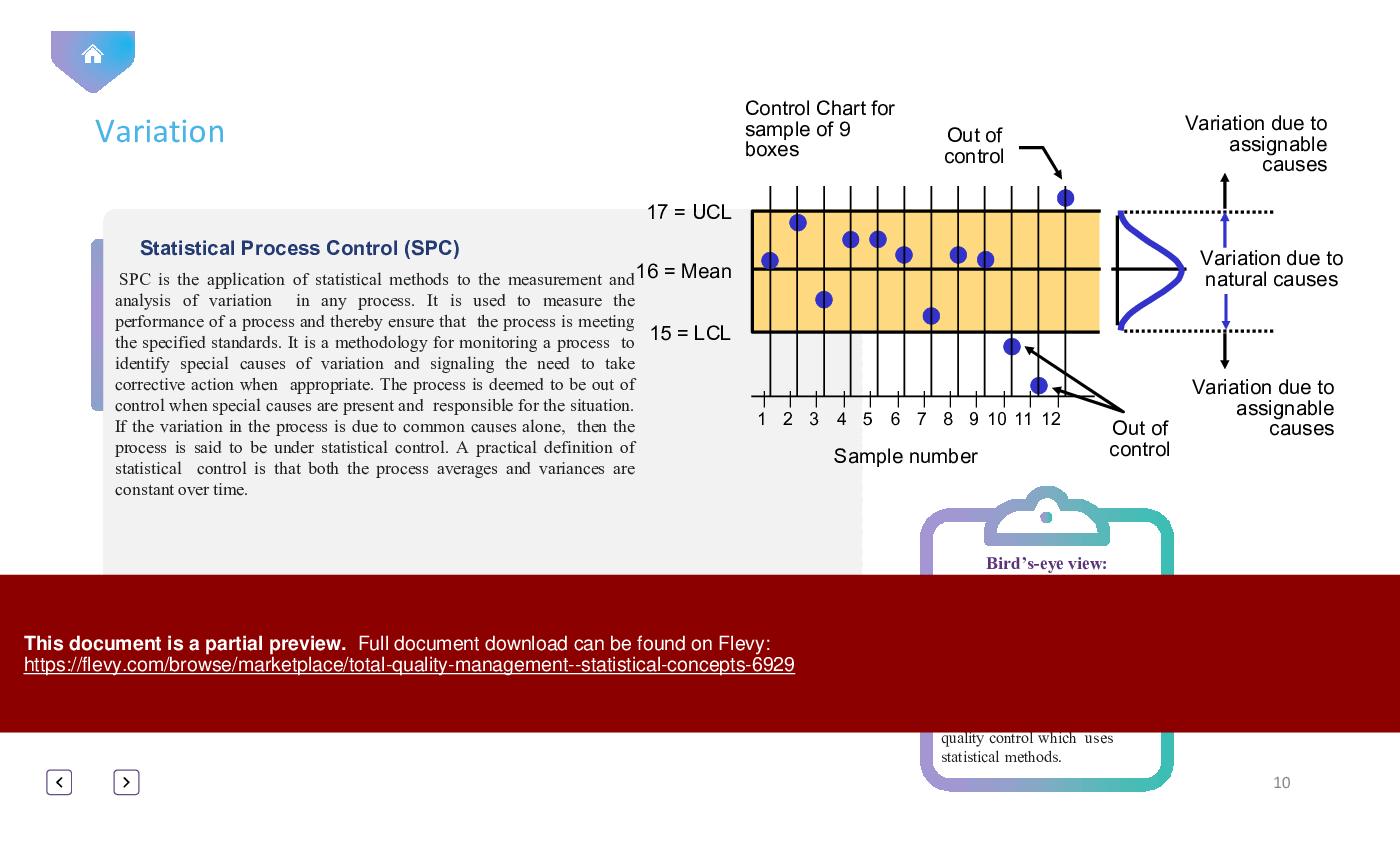
• *Statistical Process Control*: Delve into the principles of statistical process control for maintaining consistent quality.
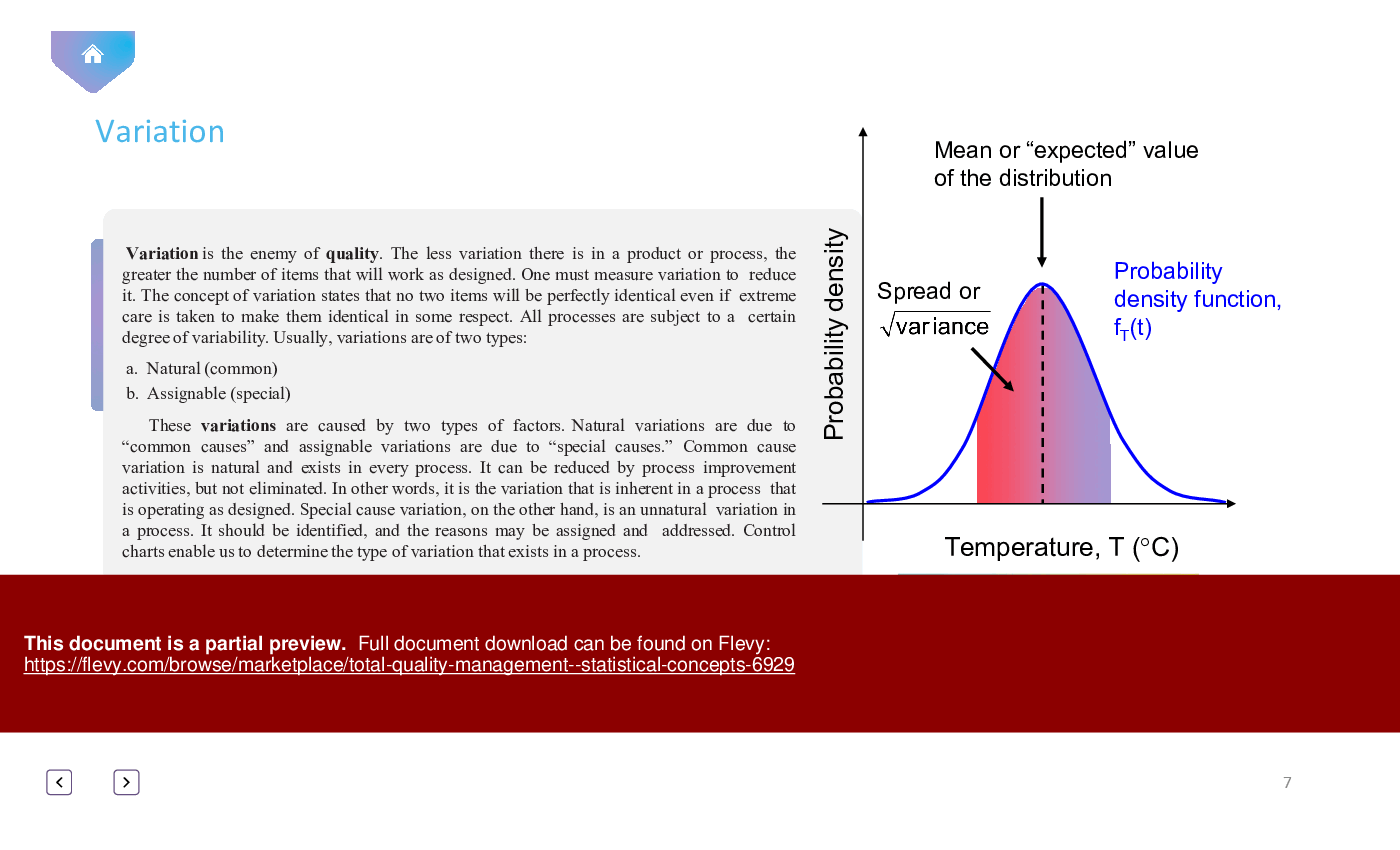
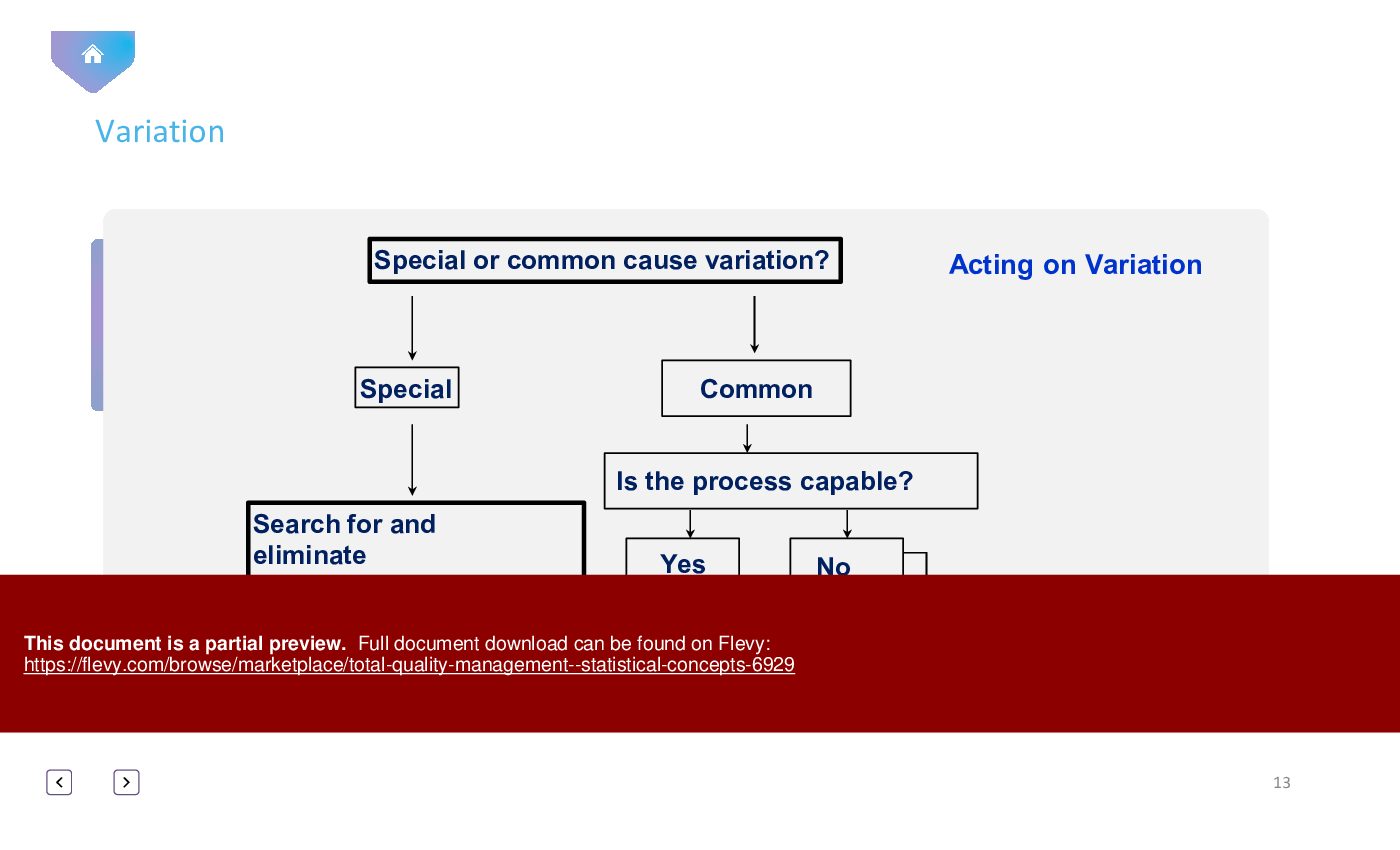
4. Understanding Variation:
• *Variation as the Foe of Quality*: Recognize how variation in a product or process can hinder quality.
• *The Imperfection of Identical Items*: Understand the concept that no two items can be perfectly identical, even with meticulous care.
5. Statistical Concepts in TQM:
• *Introduction to Statistical Concepts*: Gain an overview of statistical concepts and their role in Total Quality Management.
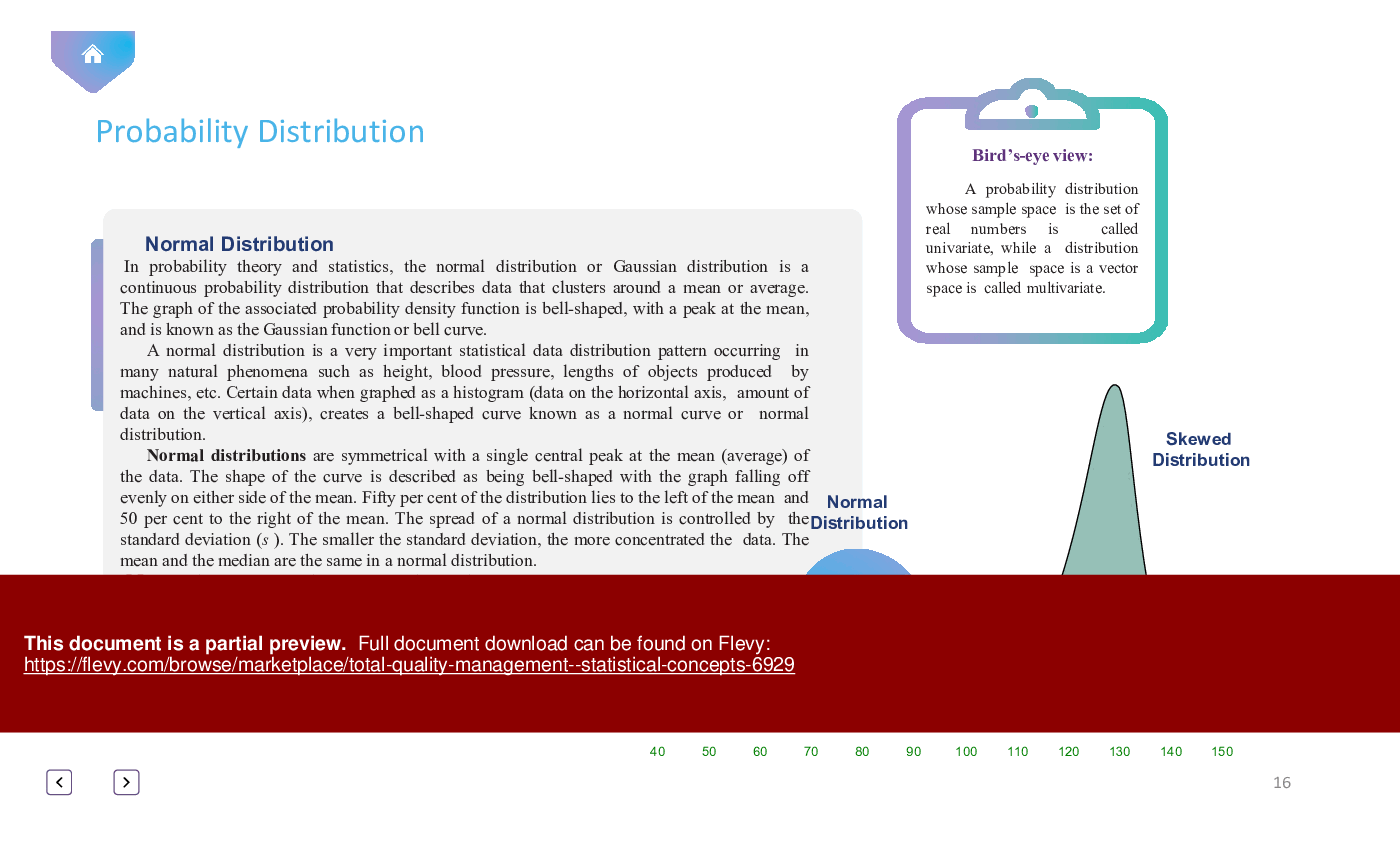
• *Key Statistical Measures*: Explore statistical measures such as mean, range, standard deviation, and normal distribution.
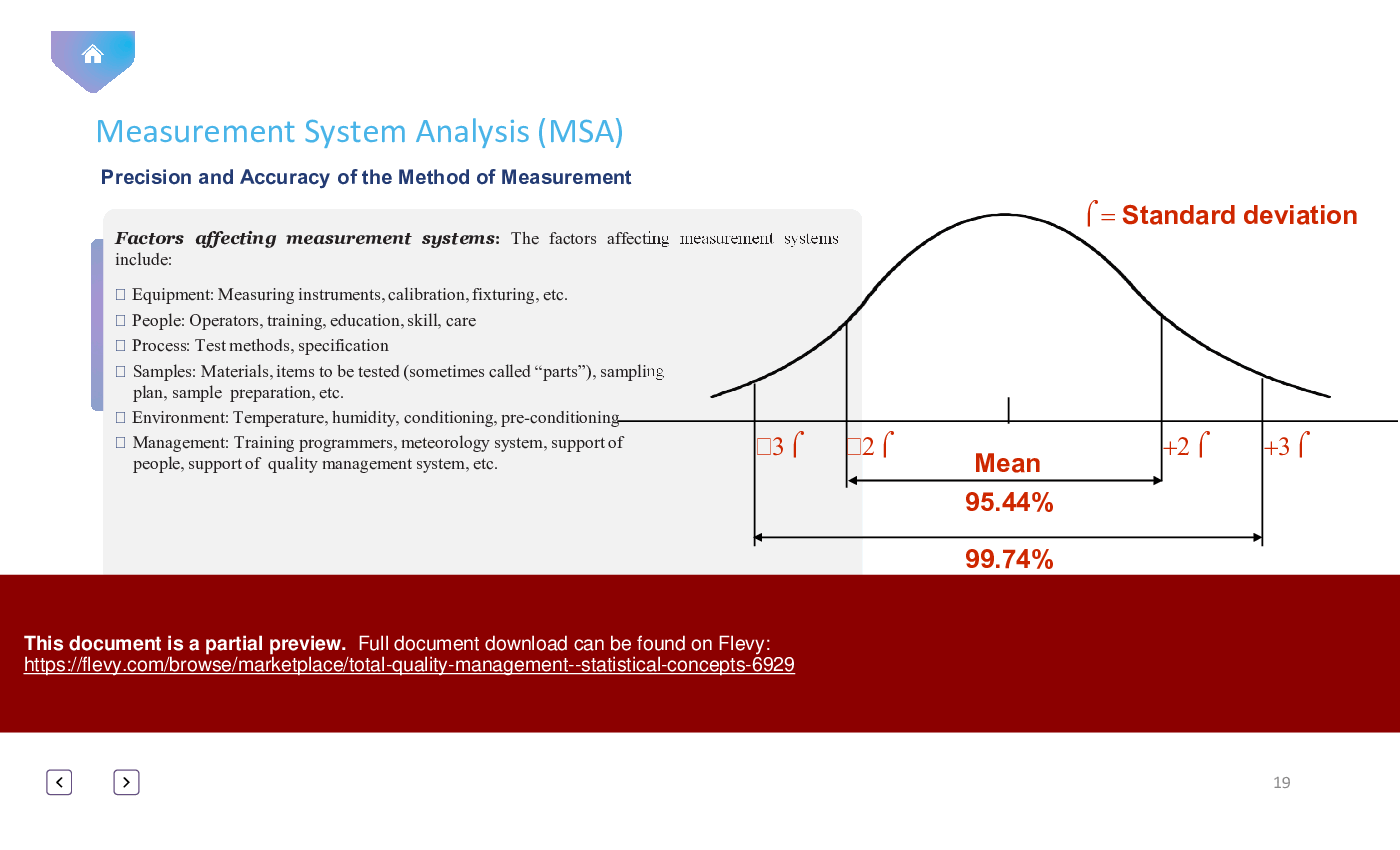
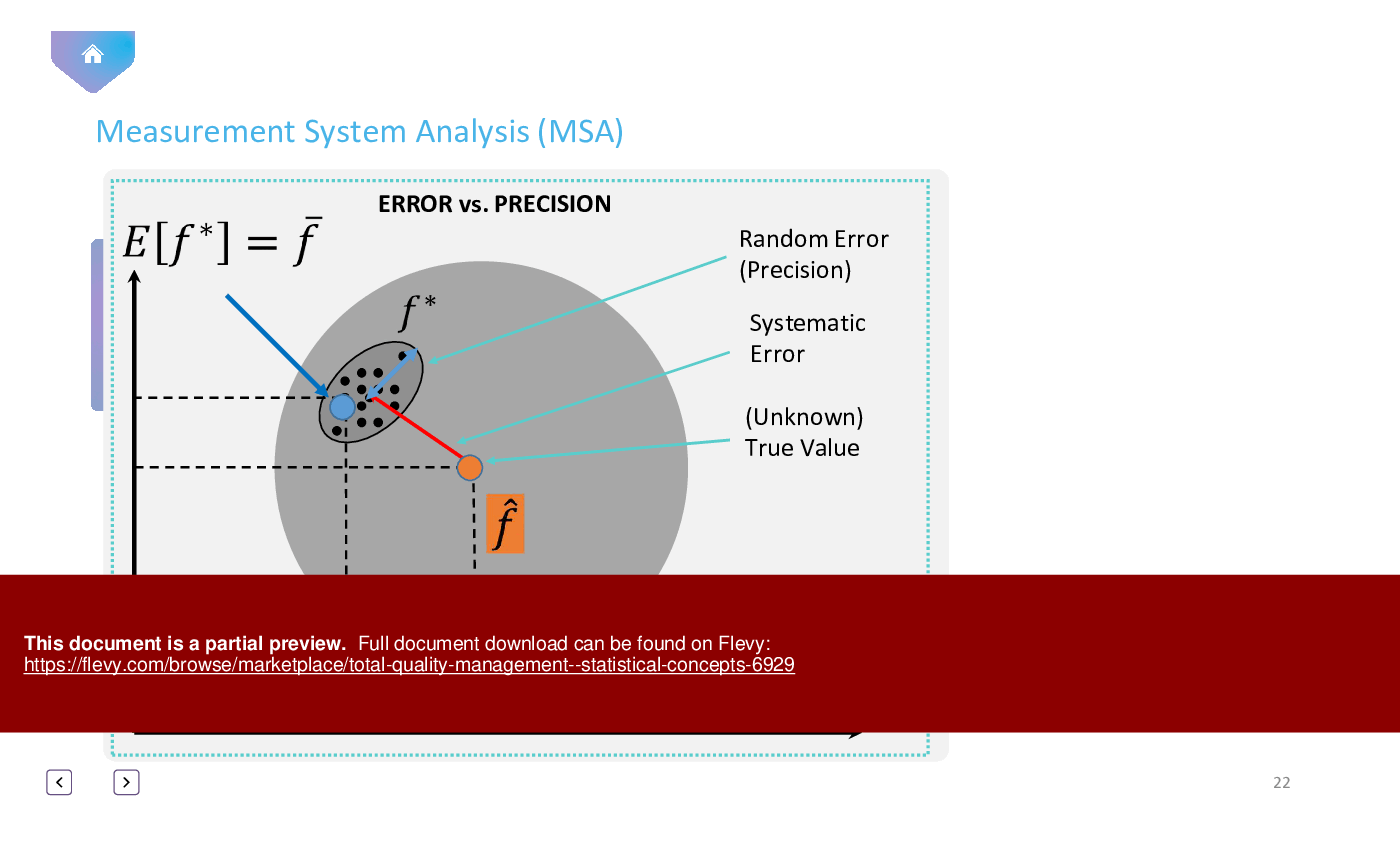
• *Measurement System Analysis (MSA)*: Understand the importance of Measurement System Analysis in ensuring accurate data.
• *Process Capability*: Learn about process capability and its significance in maintaining quality.
• *Sampling Techniques*: Explore various sampling techniques for quality control.
• *Quality Assurance, Quality Policy, and Quality Manual*: Examine the importance of quality assurance and associated documentation.
This 70-slide PowerPoint presentation delves deep into statistical concepts related to Total Quality Management. It offers valuable insights and practical guidance for organizations looking to harness the power of statistics to achieve quality excellence.
The document is fully customizable and includes compelling visuals, diagrams, and engaging content to facilitate a comprehensive understanding of Quality Systems concepts.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 70-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Total Quality Management - Statistical Concepts" presentation provides a comprehensive overview of essential statistical tools and methodologies used in quality management. Developed by experts with extensive consulting backgrounds, this PPTX equips corporate executives and quality managers with the knowledge to implement Statistical Process Control (SPC), understand process capability, and utilize quality assurance frameworks effectively. By leveraging these statistical concepts, organizations can enhance their quality management systems, reduce variability, and achieve higher standards of excellence.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Quality Assurance Managers overseeing quality control processes
• Operations Managers focused on process improvement and efficiency
• Corporate Executives aiming to integrate quality management into strategic planning
• Consultants providing guidance on quality management systems
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During quality management training sessions to enhance team capabilities
• In strategy meetings focused on improving operational excellence
• When implementing new quality assurance protocols or frameworks
Learning Objectives
• Define key statistical concepts relevant to Total Quality Management
• Build a framework for implementing Statistical Process Control (SPC)
• Establish methods for measuring process capability and quality assurance
• Identify and analyze variations in processes to enhance quality
• Develop a comprehensive understanding of Measurement System Analysis (MSA)
• Apply sampling techniques to improve quality inspection processes
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Total Quality Management (page 2)
• Variation in Quality Management (page 6)
• Measurement System Analysis (MSA) (page 17)
• Process Capability (page 25)
• Sampling Techniques (page 43)
• Quality Assurance Frameworks (page 61)
• Summary of Key Concepts (page 68)
Primary Topics Covered
• Variation - Understanding the types of variation (natural and assignable) and their impact on quality.
• Statistical Process Control (SPC) - Application of statistical methods to monitor and control processes to ensure quality standards are met.
• Measurement System Analysis (MSA) - Evaluating the measurement process to identify sources of variation and improve accuracy.
• Process Capability - Assessing a process's ability to produce output within specified limits and understanding capability indices.
• Sampling - Techniques for selecting samples to determine the quality of a lot without inspecting every item.
• Quality Assurance - Frameworks and principles for ensuring that products and services meet quality requirements.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• SPC control chart templates for monitoring process performance
• MSA checklists for evaluating measurement systems
• Process capability assessment templates for evaluating production processes
• Sampling plans for effective quality inspection
• Quality assurance program outlines for organizational implementation
• Training materials for quality management best practices
Slide Highlights
• Overview of Statistical Process Control (SPC) and its significance in quality management
• Detailed explanation of Measurement System Analysis (MSA) parameters
• Graphical representations of process capability indices (Cp and Cpk)
• Sampling methods and their applications in quality assurance
• Case studies illustrating successful quality management implementations
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Quality Management Concepts (60 minutes)
• Overview of Total Quality Management principles
• Discussion on the importance of statistical methods in quality
Statistical Process Control Workshop (90 minutes)
• Hands-on session on creating and interpreting control charts
• Group activity on identifying variations in processes
Measurement System Analysis Session (60 minutes)
• Review of MSA techniques and their application
• Case study analysis on measurement accuracy
Process Capability and Sampling Techniques (90 minutes)
• Interactive discussion on process capability assessments
• Practical exercises on sampling methods and plans
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the SPC control charts to reflect specific process metrics and standards
• Adjust the MSA templates to align with organizational measurement systems
• Modify sampling plans based on product characteristics and inspection requirements
• Incorporate company-specific quality assurance policies into the framework
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of leadership in fostering a quality culture
• Techniques for continuous improvement in quality management
• The impact of technology on quality assurance processes
• Best practices for training staff in quality management principles
Topic FAQ
What are the core statistical tools used in Total Quality Management?
Core tools include Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor processes, Measurement System Analysis (MSA) to evaluate measurement accuracy, process capability assessment using indices like Cp and Cpk, and sampling techniques for inspection. These tools are typically implemented via control charts, capability calculations, and sampling plans.How does Statistical Process Control (SPC) help reduce variation in manufacturing processes?
SPC applies statistical methods to monitor process data over time, enabling detection of assignable causes versus common-cause variation and determining when a process is operating within specification limits. Practitioners use control charts to identify out-of-control signals and guide corrective actions through SPC control charts.What is Measurement System Analysis (MSA) and when should I run one?
MSA evaluates the measurement process to ensure accuracy and reliability, identifying sources of variation from instruments, operators, or methods. Typical triggers include new measurement systems, recurring data anomalies, or before capability studies; MSA is supported by checklists and procedures such as MSA checklists.What should I look for when buying a quality management slide toolkit for my team?
Buyers should seek coverage of SPC, MSA, process capability, and sampling plus ready-to-use templates (control charts, capability templates), customization guidance, and training materials. Also confirm inclusion of program outlines for organizational rollout; examples include SPC control chart templates and MSA checklists.My company just merged—how can statistical quality tools help integrate production lines?
Use standardized SPC to monitor merged-line performance, run process capability assessments to compare capability across lines, and implement common sampling plans to align inspection. These steps help identify variation sources and harmonize quality controls using process capability assessments and sampling plans.Are templates and tools in quality management slide decks worth the cost?
Templates reduce setup time and ensure consistent analysis by providing prebuilt control charts, MSA checklists, capability assessment sheets, and sampling plans. For teams needing repeatable training and rollout materials, a slide deck with those assets and training materials—such as a 70-slide deck—can shorten deployment time.How do I interpret Cp and Cpk when assessing process capability?
Cp and Cpk compare process spread and centering against specification limits to indicate whether outputs fit customer requirements; Cp measures spread versus spec width, while Cpk accounts for process mean location. Visualizing these with histograms and control charts helps interpret capability via indices Cp and Cpk.Which sampling techniques are commonly used for quality inspection and when should I use acceptance sampling?
Acceptance sampling is used to decide whether to accept or reject lots without full inspection, appropriate when inspecting every item is impractical. Sampling plans let organizations estimate lot quality efficiently; acceptance sampling is the primary technique highlighted for lot-level inspection decisions.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is Total Quality Management (TQM)?
TQM is a management approach focused on long-term success through customer satisfaction, involving all members of an organization in improving processes, products, services, and the culture in which they work.
How does Statistical Process Control (SPC) work?
SPC uses statistical methods to monitor and control a process, allowing for the identification of variations and ensuring that the process operates within specified limits.
What is Measurement System Analysis (MSA)?
MSA is a method used to evaluate the measurement process to ensure its accuracy and reliability, identifying sources of variation that can affect quality.
What are process capability indices?
Process capability indices, such as Cp and Cpk, measure a process's ability to produce output within specified limits, indicating how well the process meets customer specifications.
Why is sampling important in quality management?
Sampling allows organizations to assess the quality of a lot without inspecting every item, saving time and resources while still providing a reliable estimate of quality.
How can organizations implement quality assurance effectively?
Organizations can implement quality assurance by developing a structured quality management system, defining roles and responsibilities, and ensuring continuous monitoring and improvement.
What are the benefits of using statistical methods in quality management?
Statistical methods provide objective data for decision-making, help identify areas for improvement, and enhance the overall quality of products and services.
How can I ensure my measurement system is accurate?
Regular calibration, training of personnel, and conducting MSA can help ensure that measurement systems provide accurate and reliable data.
What is the significance of the Six Sigma methodology?
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach aimed at reducing defects and improving quality by identifying and eliminating causes of variation in processes.
Glossary
• Total Quality Management (TQM) - An organization-wide approach to continuous improvement in quality.
• Statistical Process Control (SPC) - A method of quality control using statistical methods to monitor and control processes.
• Measurement System Analysis (MSA) - A technique to evaluate the accuracy and reliability of measurement systems.
• Process Capability - The ability of a process to produce output within specified limits.
• Sampling - The process of selecting a subset of items from a larger population for inspection.
• Quality Assurance - A systematic approach to ensuring that products and services meet quality requirements.
• Control Chart - A graphical tool used in SPC to monitor process variability over time.
• Capability Index (Cp, Cpk) - Metrics used to assess process capability relative to specification limits.
• Defect Rate - The frequency of defects in a production process, often expressed per million opportunities.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to enhance products, services, or processes.
• Quality Policy - A formal statement from management outlining the organization's commitment to quality.
• Calibration - The process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy of measurement instruments.
• Acceptance Sampling - A statistical method used to determine whether to accept or reject a lot based on a sample.
• Attribute Data - Data that can be counted and classified into categories (e.g., defective or non-defective).
• Variable Data - Data that can be measured on a continuous scale (e.g., weight, length).
• Common Cause Variation - Natural variation inherent in a process.
• Assignable Cause Variation - Variation that can be traced to specific causes.
• Quality Control - The operational techniques and activities used to fulfill quality requirements.
• ISO 9000 - A set of international standards for quality management systems.
• Six Sigma - A data-driven methodology for eliminating defects and improving quality.
Source: Best Practices in SPC, TQM PowerPoint Slides: Total Quality Management - Statistical Concepts PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting