Platform Business Models (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 31 Slides FlevyPro Document
PLATFORM STRATEGY PPT DESCRIPTION
Enabled by new capabilities in the Digital Age, many organizations are trying to shift from a Products to Platform business model. The drive behind such a shift can also be attributed to the huge success of platform companies—e.g., Amazon, Google, and Apple. These organizations started out as a retailer, search engine, and computer manufacturer, respectively, but later transformed into Platform models.
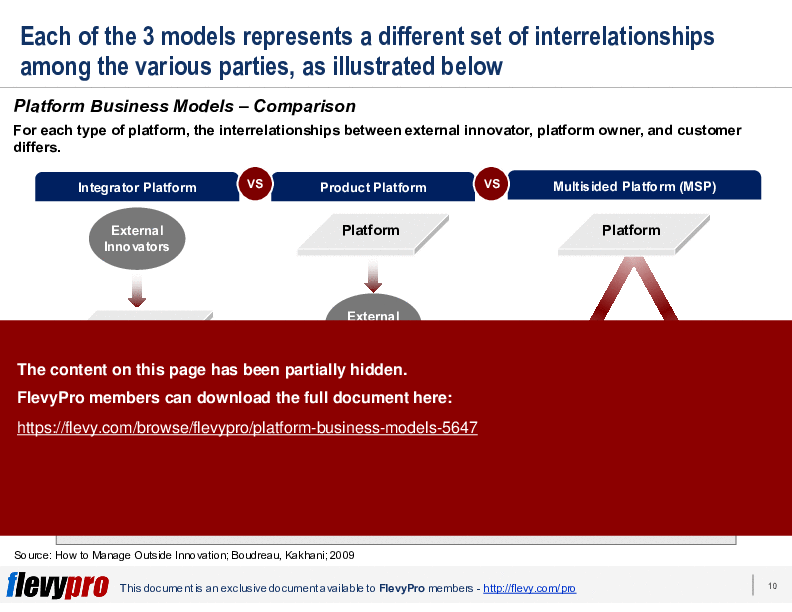
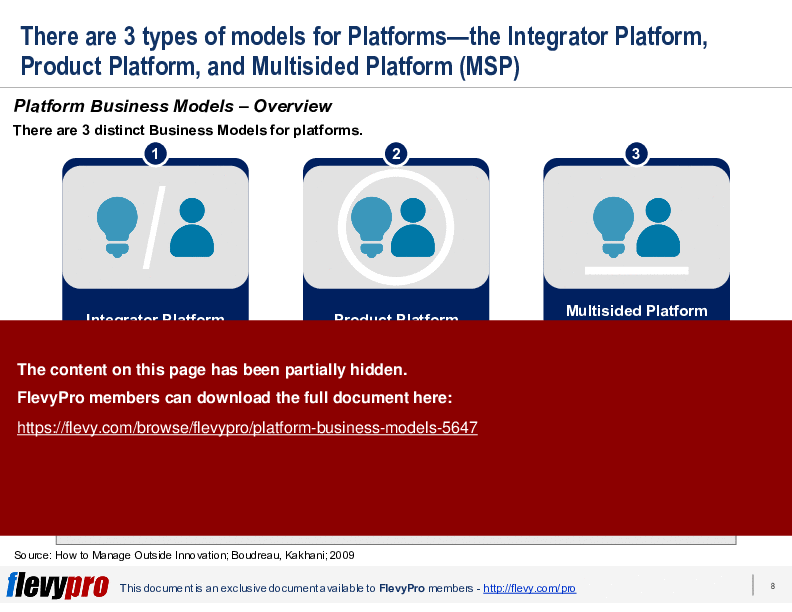
In creating a Platform, there are 3 distinct Business Models that exist:
1. Integrator Platform
2. Product Platform
3. Multisided Platform (MSP)
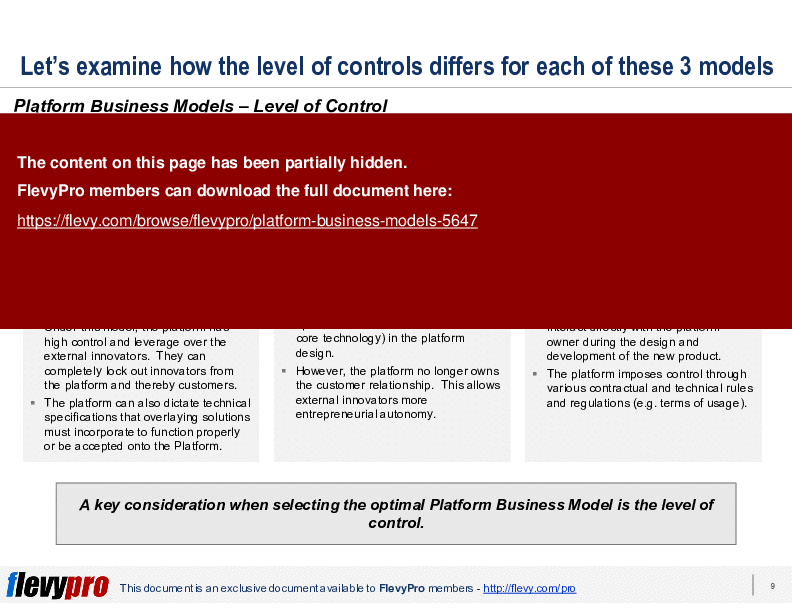
Each type of Platform Business Model has a different degree of control for the platform—and likewise, different level of autonomy for the participants. Building and managing a successful platform is difficult—it requires carefully balancing strategic tradeoffs among various participant groups. We examine each model in depth and provide numerous examples.
Additional topics discussed include Open Innovation, Markets vs. Communities, Type of Product Platforms, Platform Design, among others.
This deck also includes slide templates for you to utilize in your own business presentations.
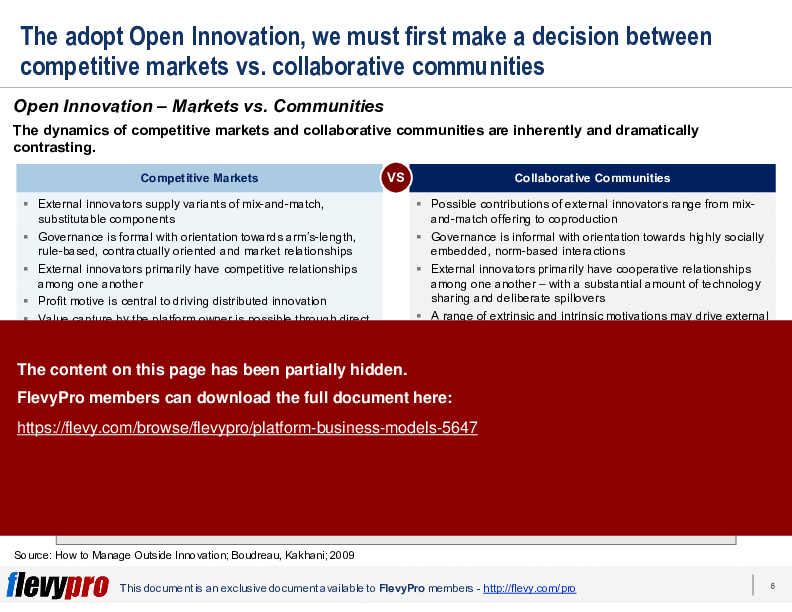
This presentation delves into the intricacies of Open Innovation, emphasizing the pivotal decision between competitive markets and collaborative communities. It outlines the contrasting dynamics and governance structures of these two approaches, providing a comprehensive analysis to help you navigate the complexities of Open Innovation Management. The framework also explores the critical role of external innovators and how their contributions can be harnessed effectively within different market structures.
The PPT further breaks down the three primary platform business models—Integrator, Product, and Multisided Platforms (MSP)—highlighting their unique control mechanisms and participant autonomy. Detailed examples and case studies illustrate the practical applications and strategic considerations for each model. This resource is essential for executives aiming to leverage platform strategies to drive innovation and growth in their organizations.
Got a question about this document? Email us at flevypro@flevy.com.
PLATFORM STRATEGY PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Business Model, Platform Strategy PowerPoint Slides: Platform Business Models PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting
Did you need more documents?
Consider a FlevyPro subscription from $39/month. View plans here.
For $10.00 more, you can download this document plus 2 more FlevyPro documents. That's just $13 each.