Six Sigma - Sampling Plans & Sample Sizes (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + (XLS) 120 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Determine Sample Sizes for Estimating One Parameter
- Hypothesis Testing & Sample Sizes for One Parameter
- Hypothesis Testing & Sample Sizes for Comparing Two Parameters
SIX SIGMA PROJECT PPT DESCRIPTION
The Six Sigma Sampling & Sample SizesTraining Module v1.0 includes:
1. MS PowerPoint Presentation including 120 slides covering
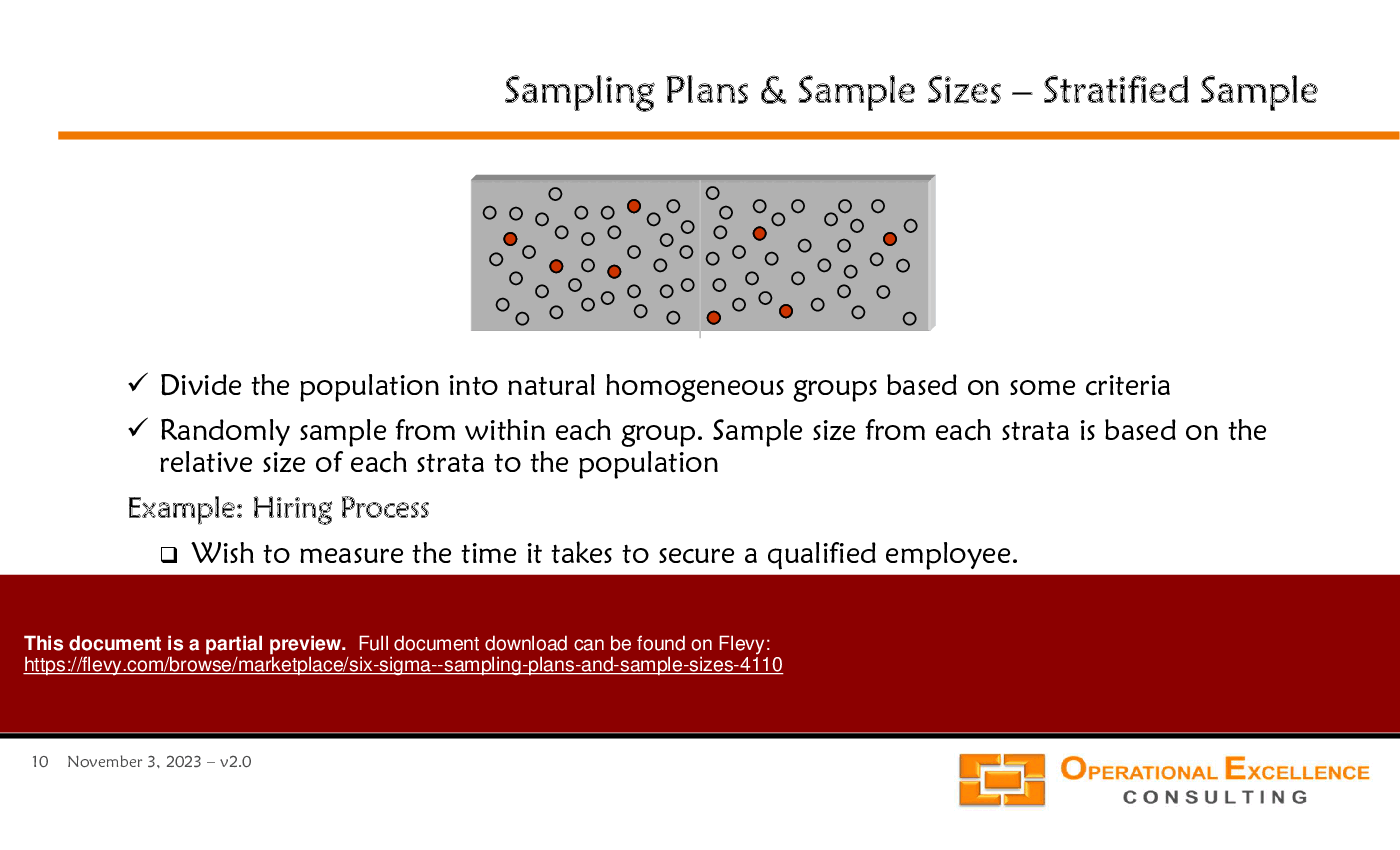
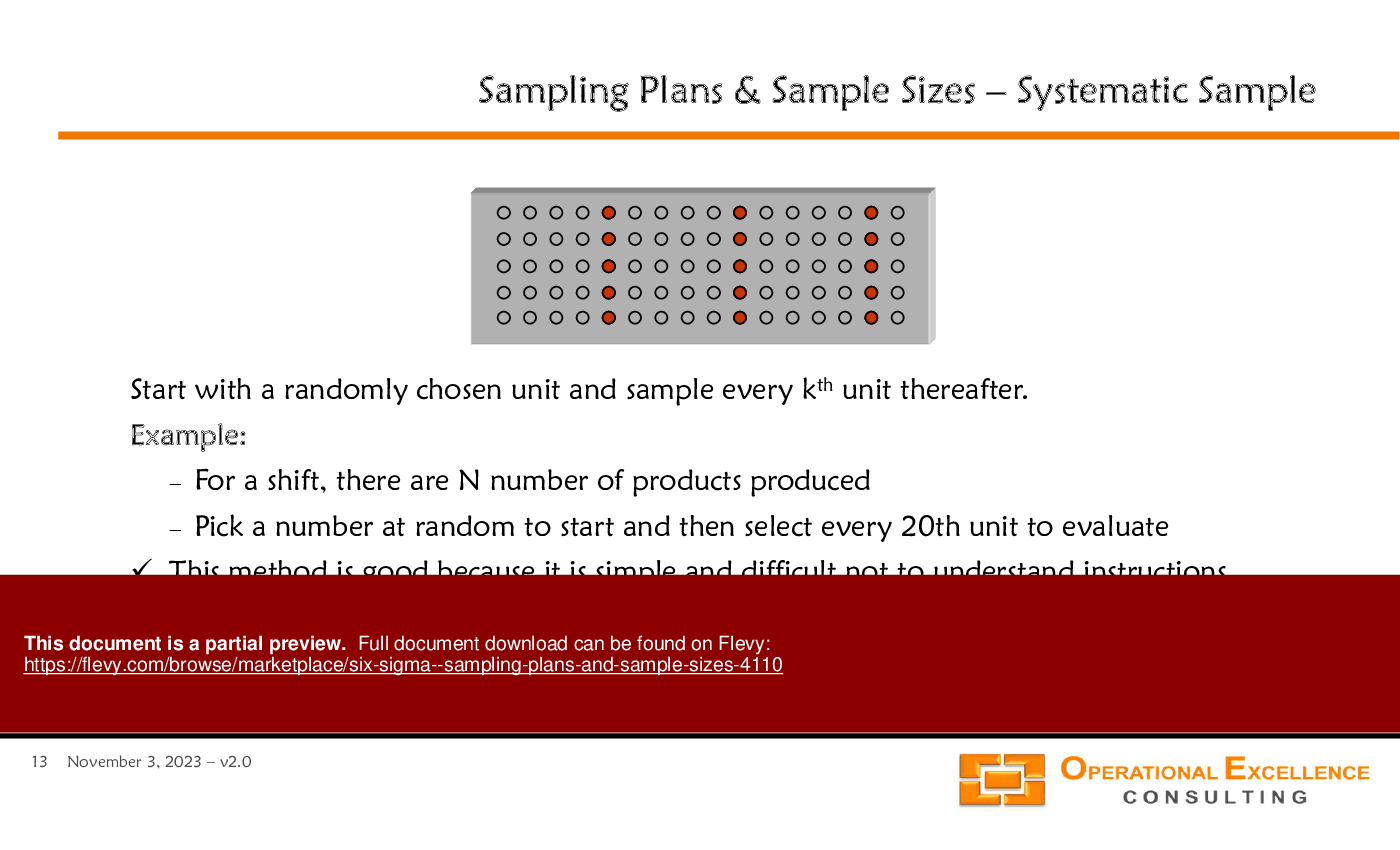
• Sampling Plans (Simple Random Sampling, Stratified Sampling, Cluster Sampling, Systematic Sampling, Subgroup Sampling),
• Sample Sizes for Estimating One Parameter,
• Introduction to Hypothesis Testing,
• Hypothesis Testing & Sample Sizes for One Parameter,
• Hypothesis Testing & Sample Sizes for Comparing Two Parameters, and
• Hypothesis Testing & Sample Sizes for Design of Experiments (DOE).
2. MS Excel Six Sigma Confidence Interval Analysis Calculator making it really easy to calculate Confidence Intervals (mean value, standard deviation, capability indices, proportions, count) and perform a Comparison of two Statistics (mean values, standard deviations, proportions, counts).
Note: The material is based on Minitab 19. Please visit their website to download a 30-day free trial license.
"After you have downloaded the training material, you can change any part of the training material and remove all logos and references to Operational Excellence Consulting. You can share the material with your colleagues and clients, and re-use it as you need. The only restriction is that you cannot publicly re-distribute, sell, rent or license the material as though it is your own. Thank you."
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 120-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Six Sigma - Sampling Plans & Sample Sizes" presentation is a comprehensive guide designed for professionals seeking to enhance their understanding of statistical sampling methods and sample size determination. Developed by an experienced Operational Excellence Coach, this material provides practical insights into various sampling techniques, hypothesis testing, and the application of Minitab for data analysis. Users will learn how to implement effective sampling strategies to ensure data-driven decision-making in quality control, market research, and operational processes.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Quality Assurance Managers overseeing product and process quality
• Data Analysts conducting statistical analysis for operational improvements
• Project Managers implementing Six Sigma methodologies in their projects
• Operational Excellence teams focused on process optimization and efficiency
• Market Researchers gathering and analyzing customer data
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During training sessions for new team members on statistical sampling techniques
• When developing quality control processes in manufacturing or service delivery
• In workshops focused on data-driven decision-making and hypothesis testing
• For project kick-offs involving Six Sigma methodologies and statistical analysis
Learning Objectives
• Define various sampling methods including simple random, stratified, and cluster sampling
• Build sample size calculations for estimating parameters with desired confidence levels
• Establish hypothesis testing frameworks, including Type I and Type II errors
• Apply statistical software like Minitab for sample size determination and analysis
• Interpret confidence intervals and margins of error in the context of sampling
• Utilize subgroup sampling techniques to monitor process variations effectively
Table of Contents
• Sampling Plans (page 1)
• Sample Sizes for Estimating One Parameter (page 17)
• Hypothesis Testing (Type I and Type II Error) (page 50)
• Hypothesis Testing for One Parameter (page 62)
• Hypothesis Testing for Comparing Two Parameters (page 78)
• Hypothesis Testing for Design of Experiments (page 109)
Primary Topics Covered
• Sampling Plans - Overview of various sampling methods including simple random, stratified, cluster, systematic, and subgroup sampling to ensure unbiased representation of populations.
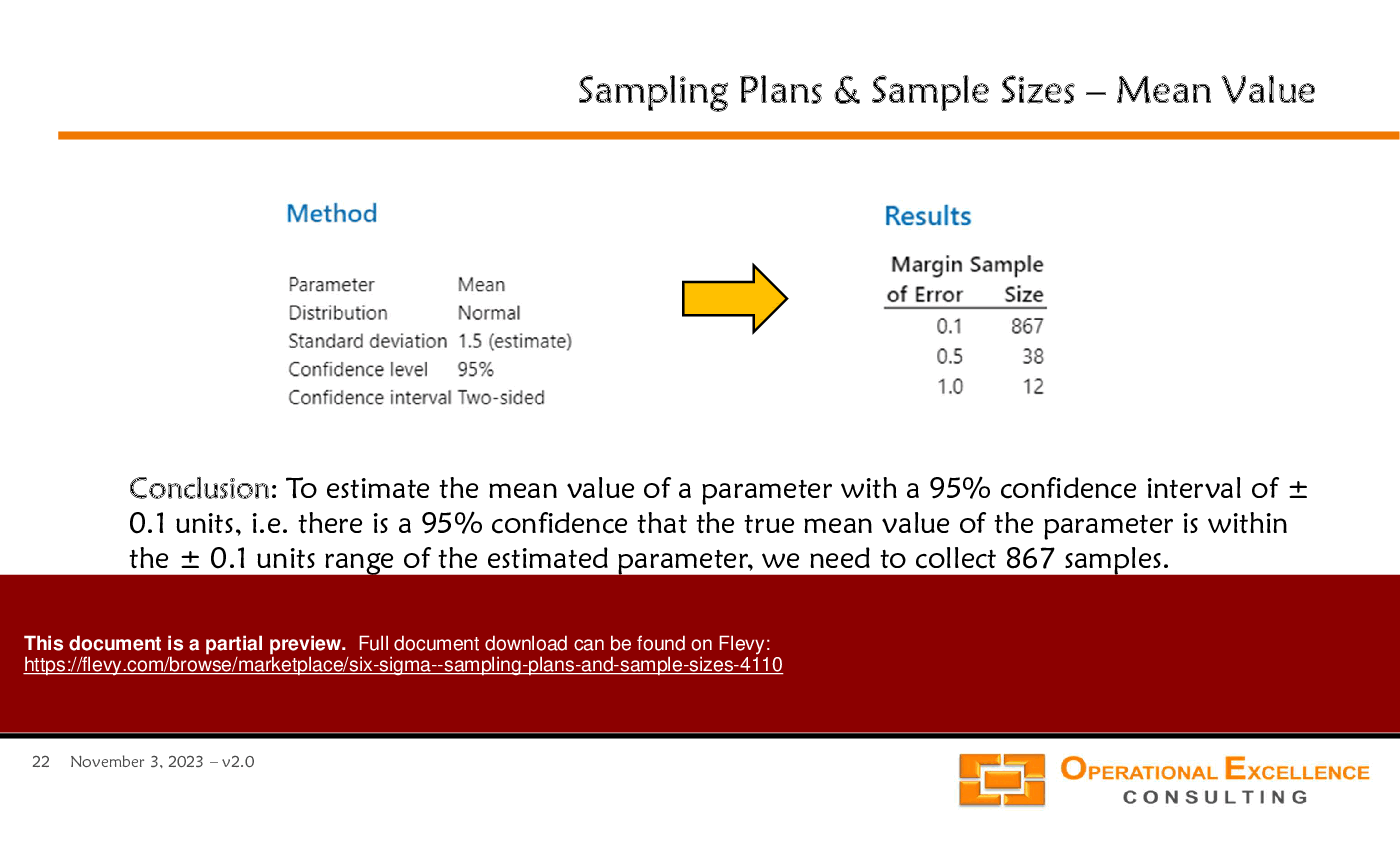
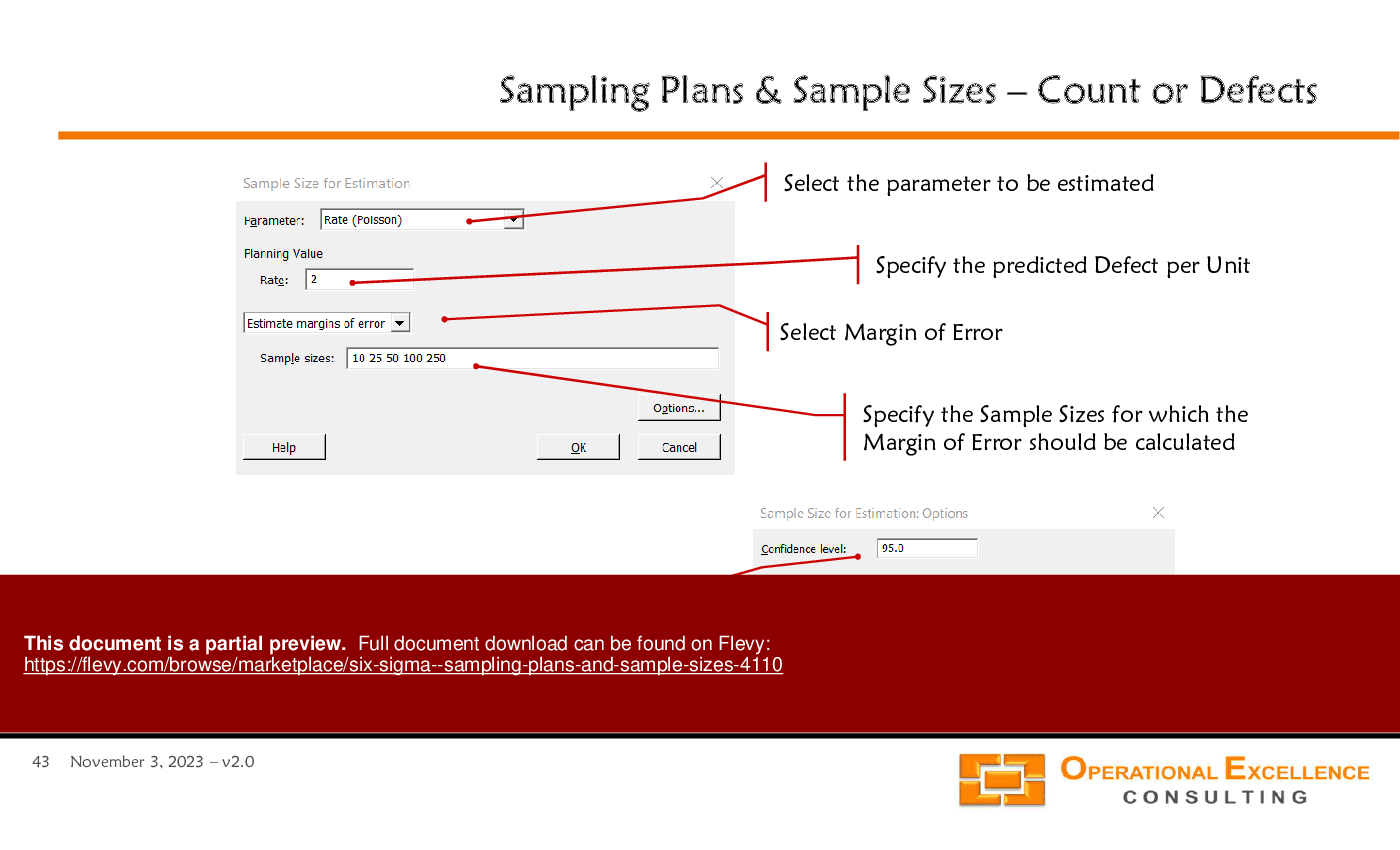
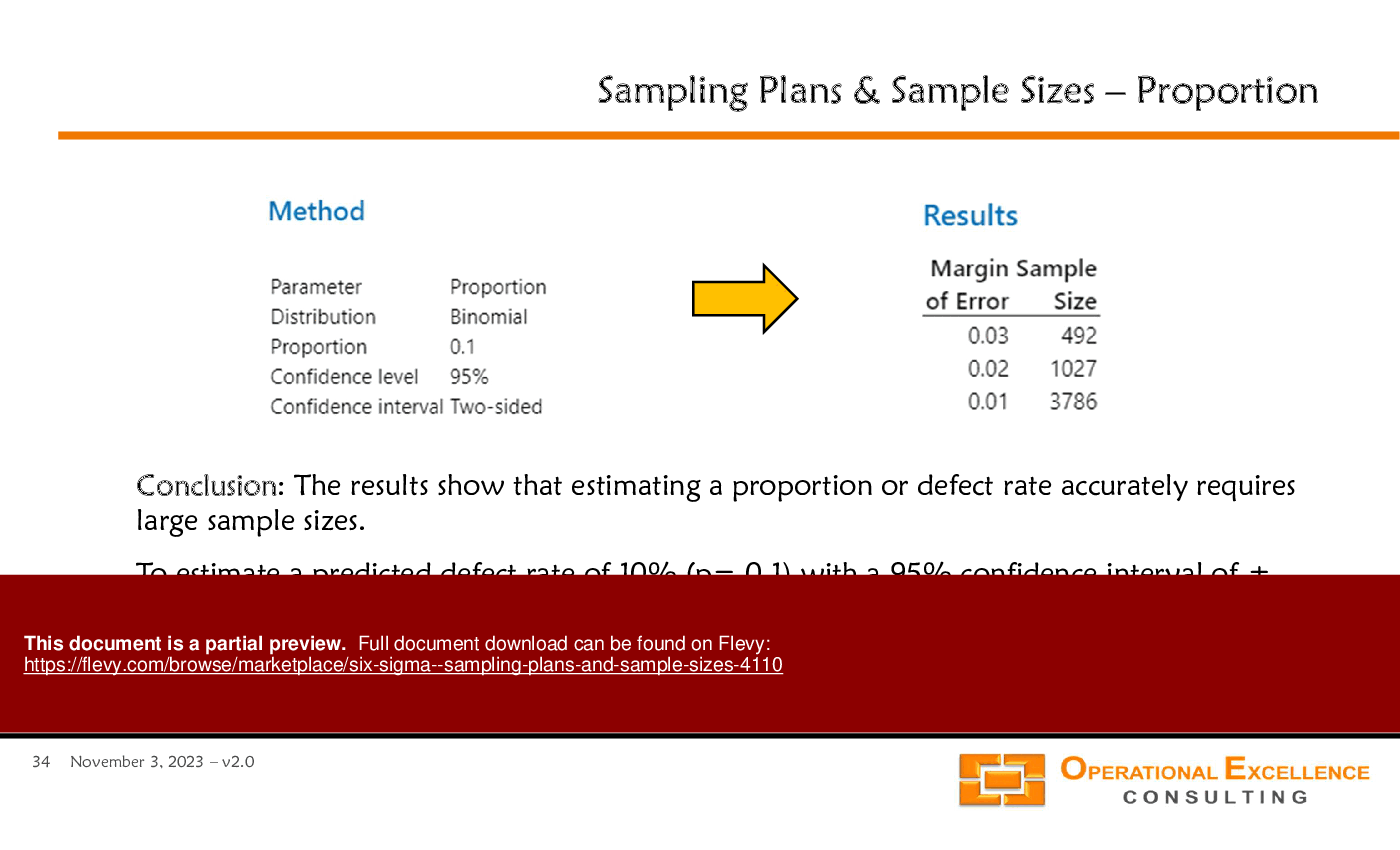
• Sample Size Determination - Guidelines for calculating sample sizes necessary for estimating population parameters with specified confidence levels and margins of error.
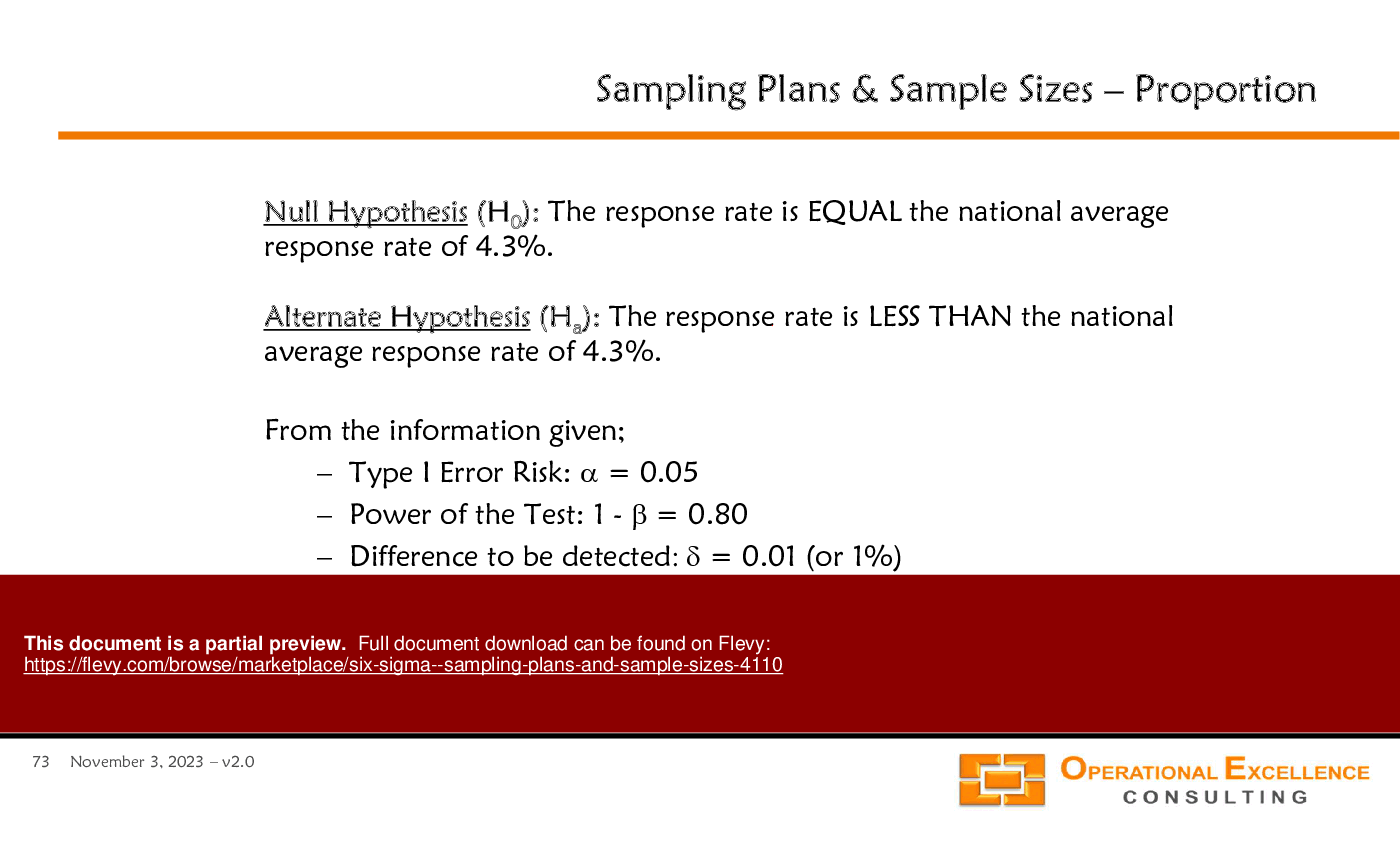
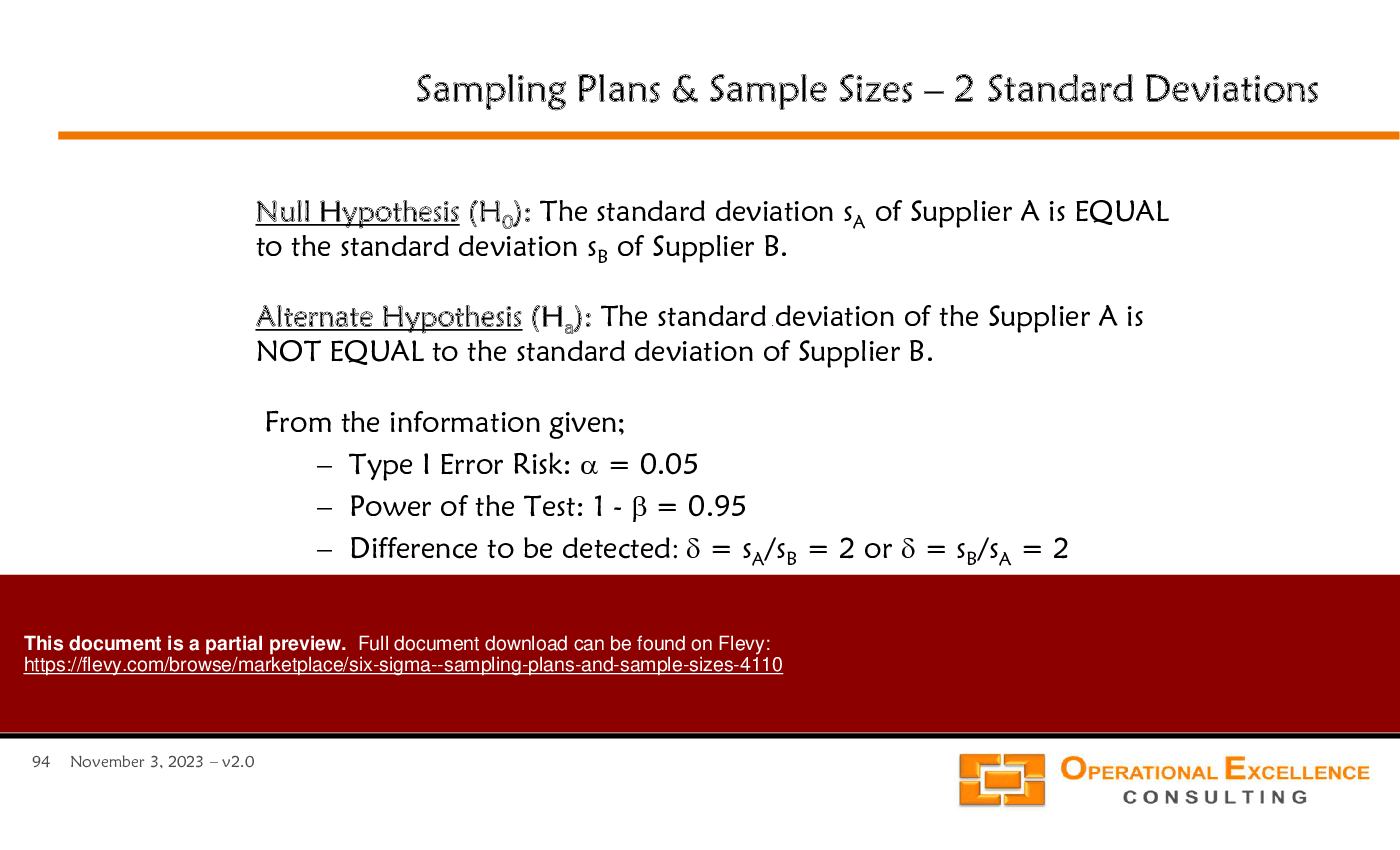
• Hypothesis Testing Fundamentals - Introduction to null and alternate hypotheses, including the significance of Type I and Type II errors in statistical decision-making.
• Statistical Analysis with Minitab - Practical application of Minitab software for conducting hypothesis tests and determining sample sizes based on user-defined parameters.
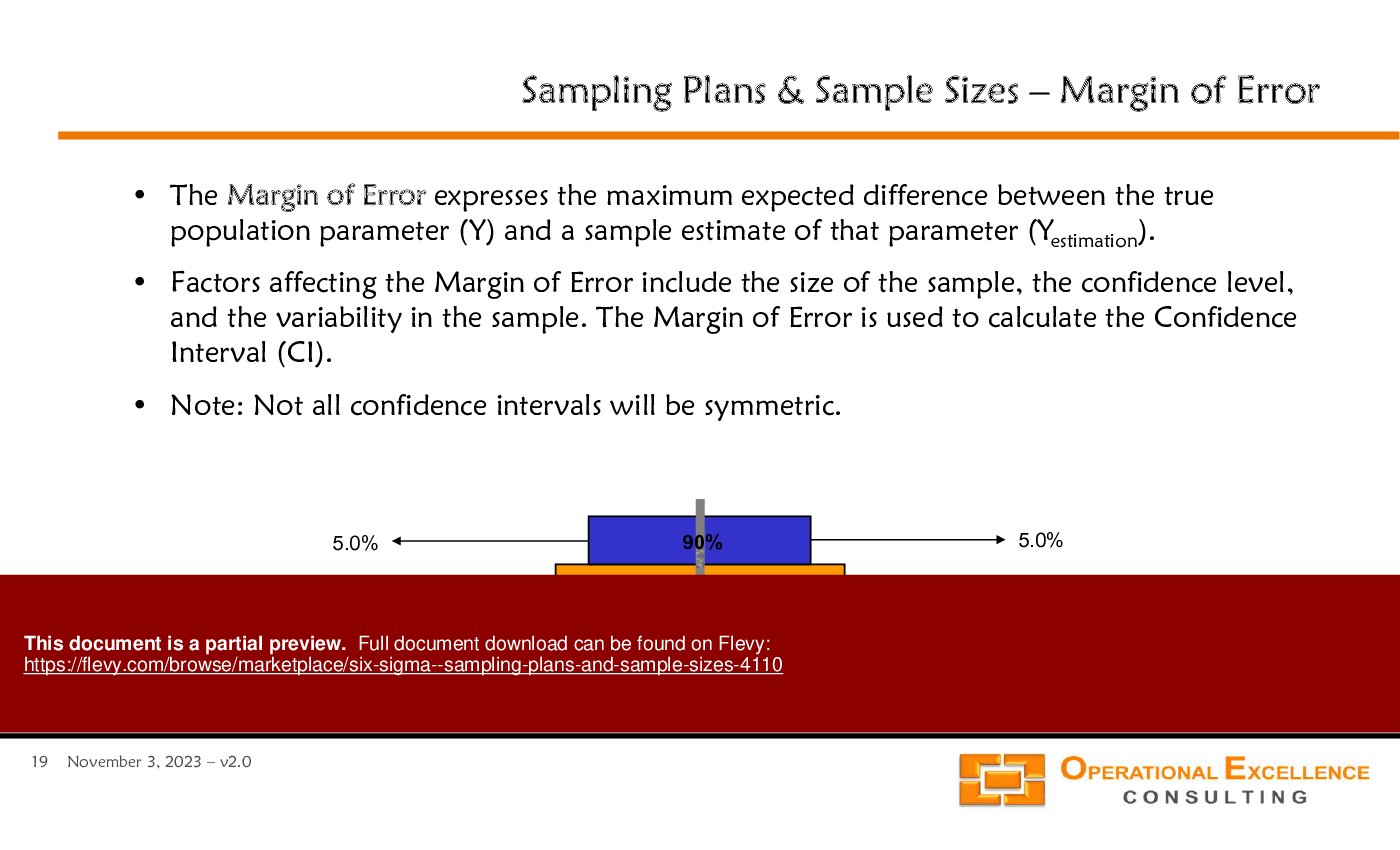
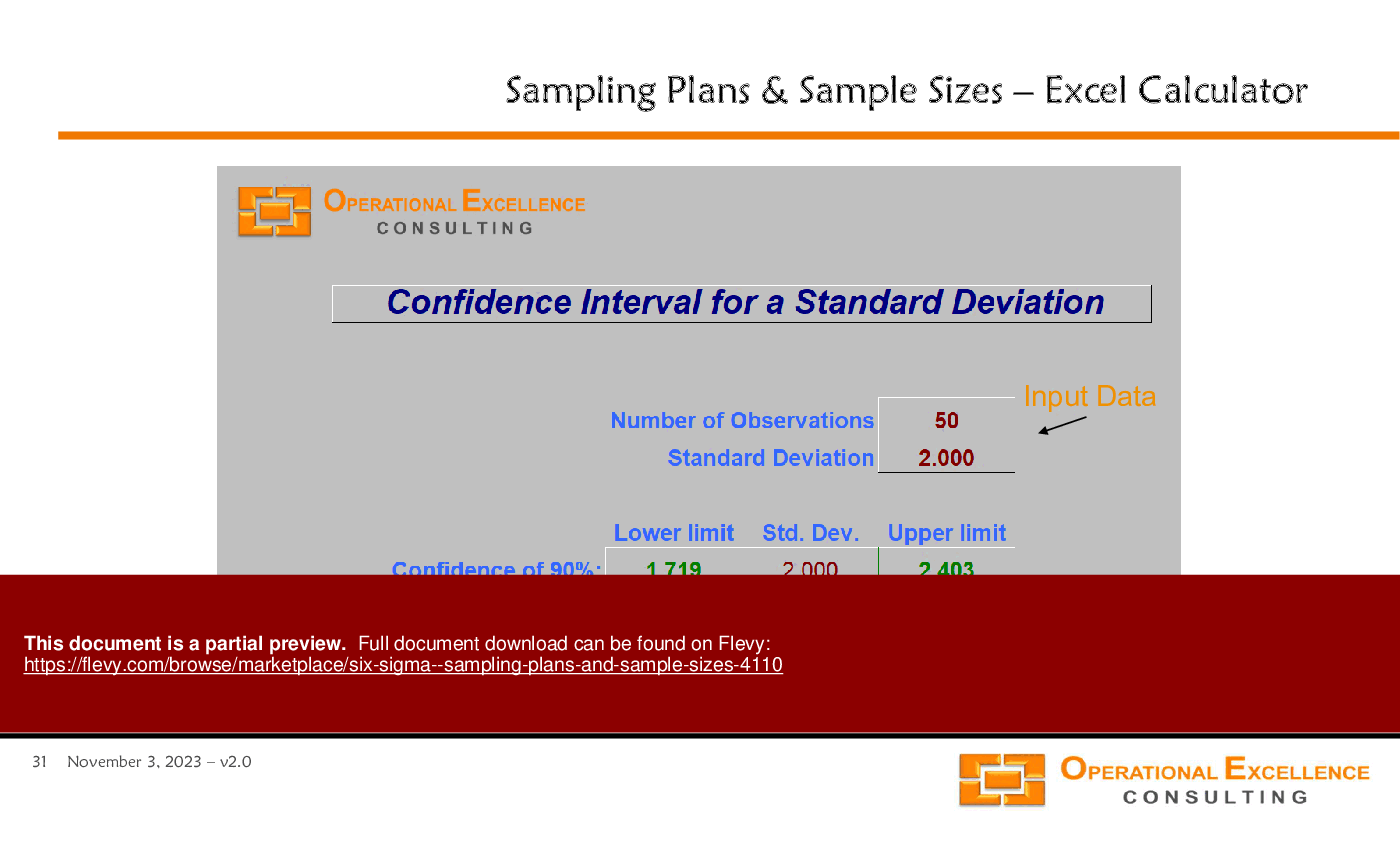
• Confidence Intervals - Explanation of confidence intervals and their relationship to sample size, variability, and confidence levels in estimating population parameters.
• Design of Experiments - Insights into planning and executing experiments to test hypotheses regarding multiple factors and their effects on outcomes.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Sample size calculation templates for estimating means, proportions, and standard deviations
• Minitab usage guides for conducting hypothesis tests and analyzing data
• Excel calculators for quick reference on confidence intervals and margins of error
• Frameworks for developing sampling plans tailored to specific operational needs
• Visual aids illustrating the power of tests and sampling distributions
Slide Highlights
• Detailed explanations of sampling methods with practical examples
• Visual representations of confidence intervals and their implications
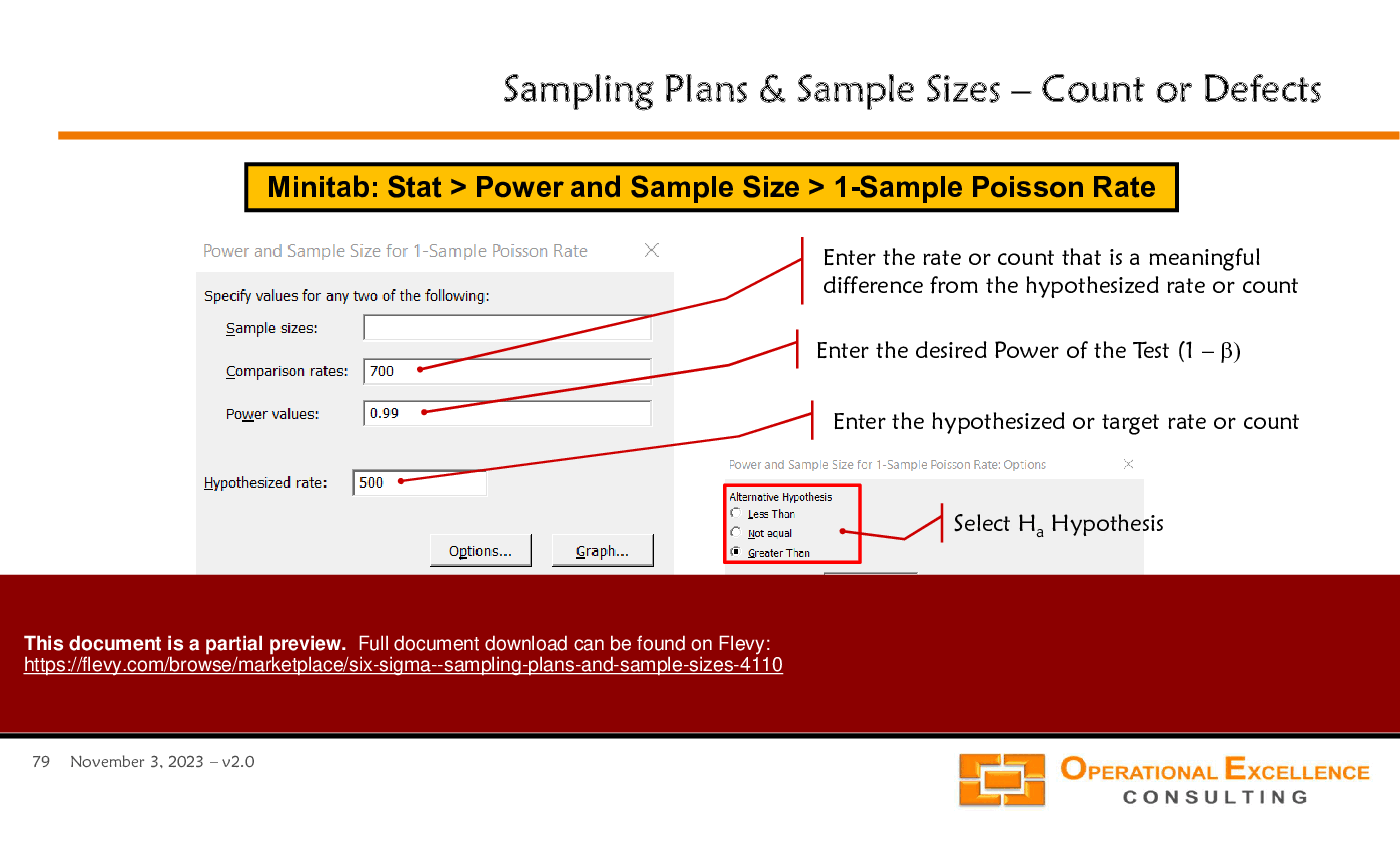
• Step-by-step guides for using Minitab in sample size determination
• Case studies demonstrating the application of hypothesis testing in real-world scenarios
• Power curves illustrating the relationship between sample size and detection probability
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Sampling Techniques (60 minutes)
• Overview of sampling methods and their applications
• Group discussion on challenges in data collection and analysis
Sample Size Calculations (90 minutes)
• Hands-on session using Minitab for sample size determination
• Exercises on calculating confidence intervals and margins of error
Hypothesis Testing Fundamentals (60 minutes)
• Explanation of Type I and Type II errors with examples
• Interactive case studies to reinforce learning
Design of Experiments (90 minutes)
• Planning and executing experiments using fractional factorial designs
• Group activity to develop a sampling plan for a specific project
Customization Guidance
• Adapt the presentation to include specific industry examples relevant to your organization
• Modify statistical examples to reflect actual data from your projects
• Integrate company-specific terminology and metrics into the sampling plans and templates
• Customize Minitab examples to align with the software version used in your organization
Secondary Topics Covered
• Sources of variation in sampling and their impact on data quality
• Common issues in sampling plans and how to mitigate them
• Advanced techniques for subgroup sampling and systematic sampling
• Statistical process control methods and their relationship to sampling
Topic FAQ
What are the common sampling methods and when should I use each?
Common methods covered include simple random, stratified, cluster, systematic, and subgroup sampling. Use simple random for unbiased general estimates, stratified to ensure representation across subgroups, cluster when sampling natural groups, systematic for every-kth selection, and subgroup sampling to monitor process variation — 5 methods.How do I determine the right sample size for estimating a mean or proportion?
Sample size relies on the desired confidence level, margin of error, and population variability; statistical formulas translate these inputs into a required n. Practical tools and templates support these calculations; Flevy's Six Sigma - Sampling Plans & Sample Sizes includes sample size calculation templates and an Excel calculator.What is the difference between Type I and Type II errors in hypothesis testing?
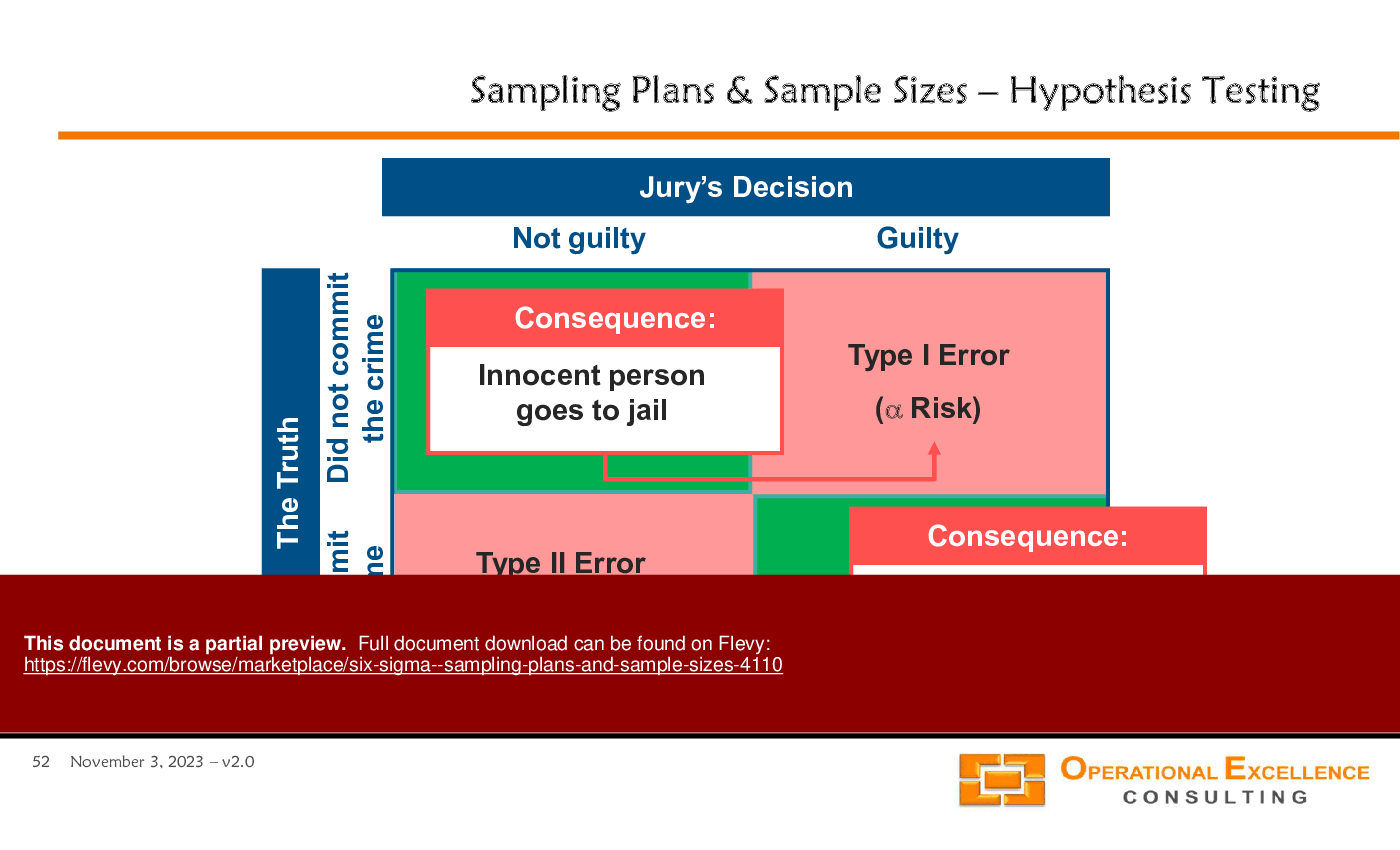
A Type I error rejects a true null hypothesis, while a Type II error fails to reject a false null hypothesis. Managing these errors requires selecting appropriate significance levels and power when planning tests; the presentation covers Type I and Type II error concepts on page 50.How can I use Minitab to calculate sample sizes and run hypothesis tests?
Minitab provides built-in routines for power analysis, sample-size calculation, and hypothesis testing for means, proportions, and variance comparisons. The training material includes step-by-step Minitab usage guides based on Minitab 19 to demonstrate these procedures, with worked examples.What should I look for when buying a sampling-plans and sample-size toolkit?
Look for coverage of sampling methods, clear sample-size calculation guidance, hypothesis-testing content, software examples (e.g., Minitab), and reusable templates or calculators. Also check for customization guidance and training-ready slides; this product provides 120 slides and an Excel calculator.How much time should I allocate for a workshop teaching sampling and sample-size topics?
A suggested agenda in the material schedules 4 blocks: 60 minutes for sampling techniques, 90 minutes for sample-size calculations, 60 minutes for hypothesis testing, and 90 minutes for design of experiments, totaling 300 minutes (5 hours).I need to design a QC sampling plan after a production line change—what steps should I follow?
Start by selecting an appropriate sampling method (e.g., subgroup or stratified), estimate variability and acceptable margin of error, compute sample sizes for required confidence and power, and validate with capability indices and subgroup monitoring. Use sample size templates and subgroup sampling techniques.Are templates and calculators worth purchasing for sampling and sample-size work?
Templates and calculators standardize calculations, reduce manual errors, and speed training and deployment. They are particularly useful for repeated analyses and workshops; this product includes an Excel Six Sigma Confidence Interval Analysis Calculator and sample size templates.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the purpose of sampling in quality control?
Sampling allows organizations to make inferences about a larger population based on a smaller subset, ensuring quality without inspecting every item.
How do I determine the appropriate sample size?
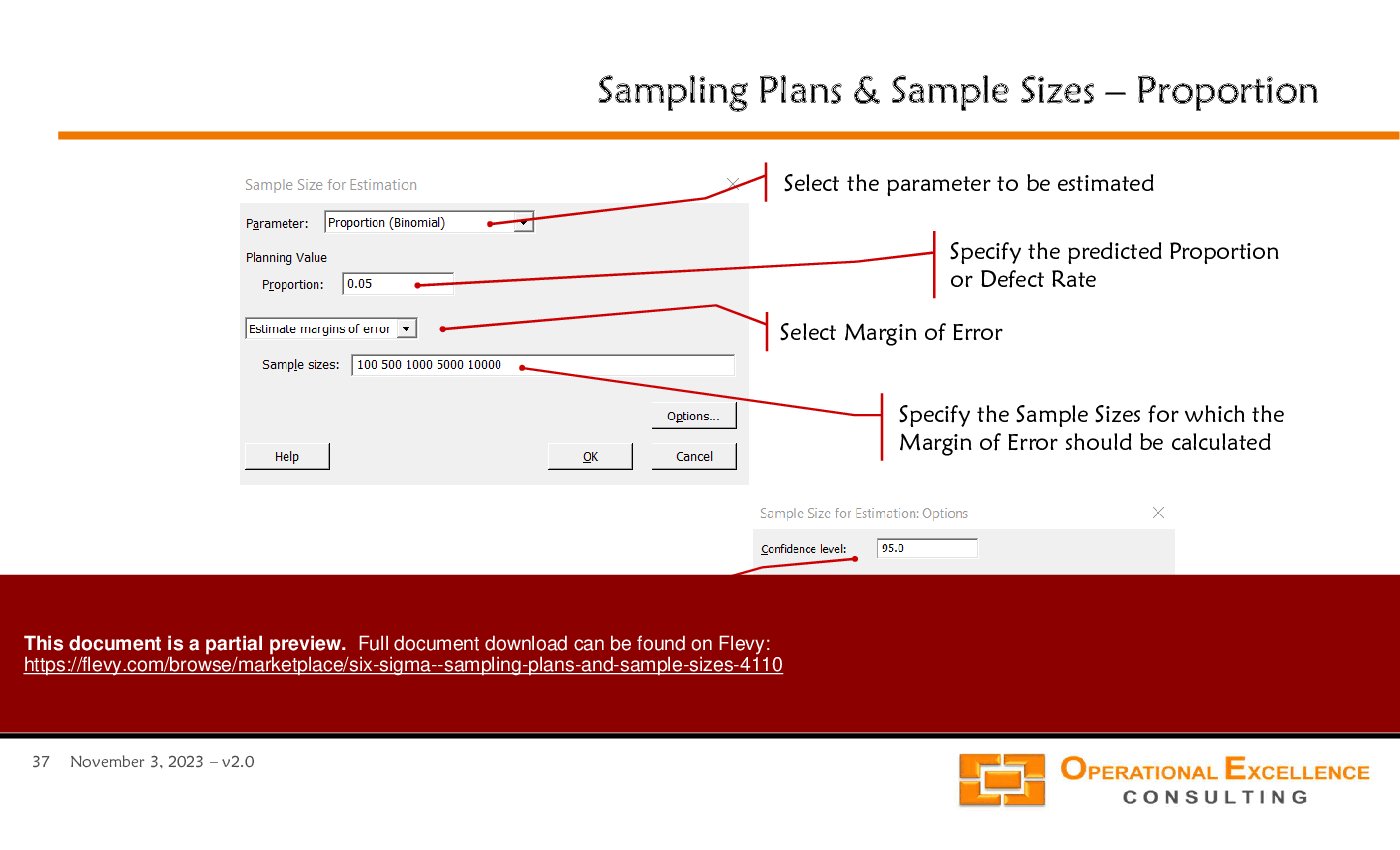
Sample size can be determined using statistical formulas that consider the desired confidence level, margin of error, and population variability.
What is the difference between Type I and Type II errors?
Type I error occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, while Type II error occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected.
How can Minitab assist in hypothesis testing?
Minitab provides tools for conducting various hypothesis tests, calculating sample sizes, and analyzing data efficiently.
What factors affect the width of a confidence interval?
The width of a confidence interval is influenced by the sample size, confidence level, and variability within the sample.
Can this material be customized for specific training needs?
Yes, the presentation can be tailored to include industry-specific examples and terminology relevant to your organization.
What are the common pitfalls in sampling plans?
Common pitfalls include selection bias, non-response bias, and improper execution of sampling methods, which can lead to inaccurate conclusions.
How do I apply these concepts in a real-world scenario?
The concepts can be applied by developing a structured sampling plan for quality control, market research, or operational improvements within your organization.
Glossary
• Sampling - The process of selecting a subset of individuals from a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population.
• Confidence Interval - A range of values derived from sample data that is likely to contain the population parameter with a specified level of confidence.
• Margin of Error - The maximum expected difference between the true population parameter and a sample estimate.
• Type I Error - The error made when rejecting a true null hypothesis.
• Type II Error - The error made when failing to reject a false null hypothesis.
• Hypothesis Testing - A statistical method used to make decisions about population parameters based on sample data.
• Minitab - A statistical software package used for data analysis, including hypothesis testing and sample size determination.
• Stratified Sampling - A sampling method that involves dividing the population into subgroups and randomly sampling from each subgroup.
• Cluster Sampling - A sampling technique where the population is divided into clusters, and entire clusters are randomly selected for analysis.
• Systematic Sampling - A method of sampling where every kth unit is selected from a list of the population.
• Subgroup Sampling - Sampling that involves taking measurements from several outputs of a process step at defined intervals.
• Power of a Test - The probability that the test will correctly reject a false null hypothesis.
• Standard Deviation - A measure of the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values.
• Fractional Factorial Design - An experimental design that uses a fraction of the full factorial design to study the effects of multiple factors.
• ANOVA - Analysis of variance, a statistical method used to compare means among 3 or more groups.
• Proportion - A statistical measure that represents a part of a whole, often expressed as a percentage.
• Defect Rate - The frequency of defects in a production process, typically expressed as a ratio or percentage.
• Count or Defects - A method of measuring the number of defects or errors in a given sample or population.
• Capability Index - A measure of how well a process meets specified limits or tolerances.
• Excel Calculator - A tool used to perform statistical calculations in Microsoft Excel, often for confidence intervals and sample sizes.
SIX SIGMA PROJECT PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Six Sigma Project PowerPoint Slides: Six Sigma - Sampling Plans & Sample Sizes PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Operational Excellence Consulting LLC