Hybrid Financing: Preferred Stock, Warrants & Convertible (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 49 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Provides of Types of hybrid securities : Preferred stock. Warrants. Convertibles
- Provides of WACC Effects
- Provides of What conversion price (Pc) is built into the bond?
FINANCING PPT DESCRIPTION
Hybrid Financing: Preferred Stock, Warrants, and Convertibles
Lecture Outline
1. Types of hybrid securities : Preferred stock. Warrants. Convertibles
2. How does preferred stock differ from common stock and debt?
3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of preferred stock
4. What is floating rate preferred?
5. How can a knowledge of call options help one understand warrants and convertibles?
6. Will the warrants bring in additional capital when exercised?
7. Should all debt be issued with warrants?
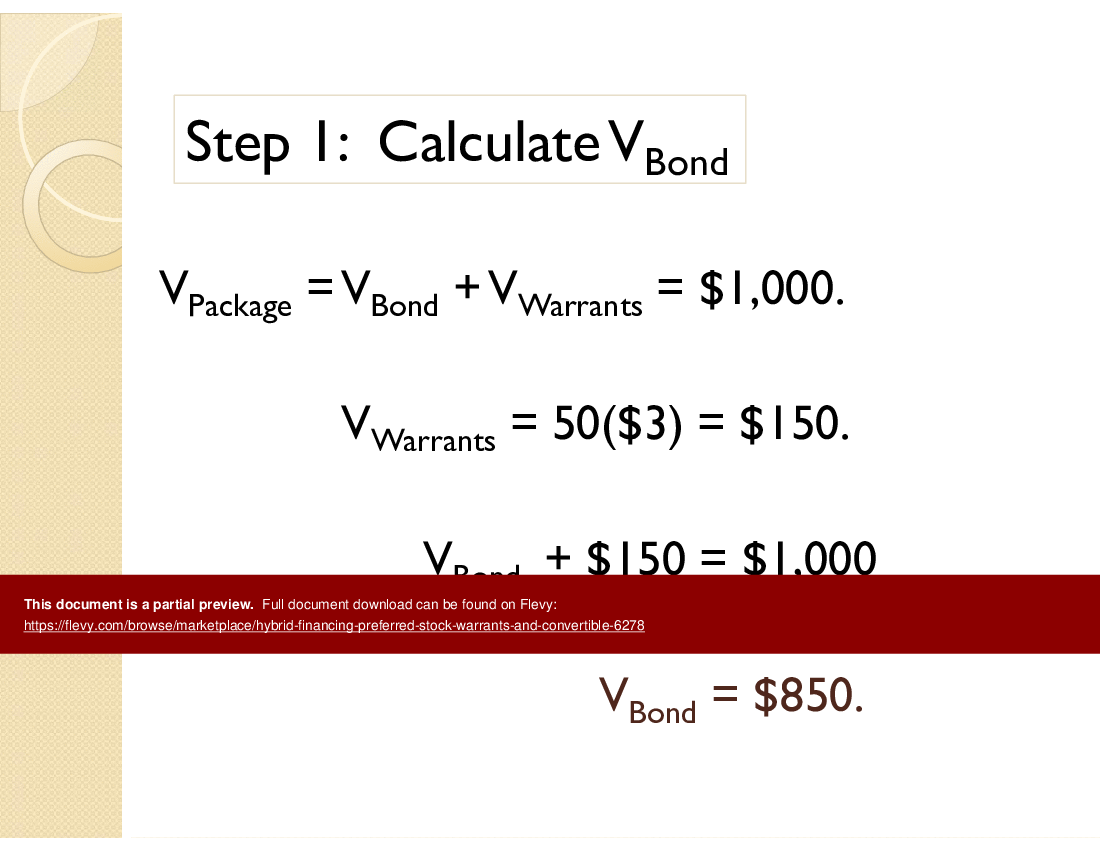
8. What conversion price (Pc) is built into the bond?
9. What is the convertible's straight debt value?
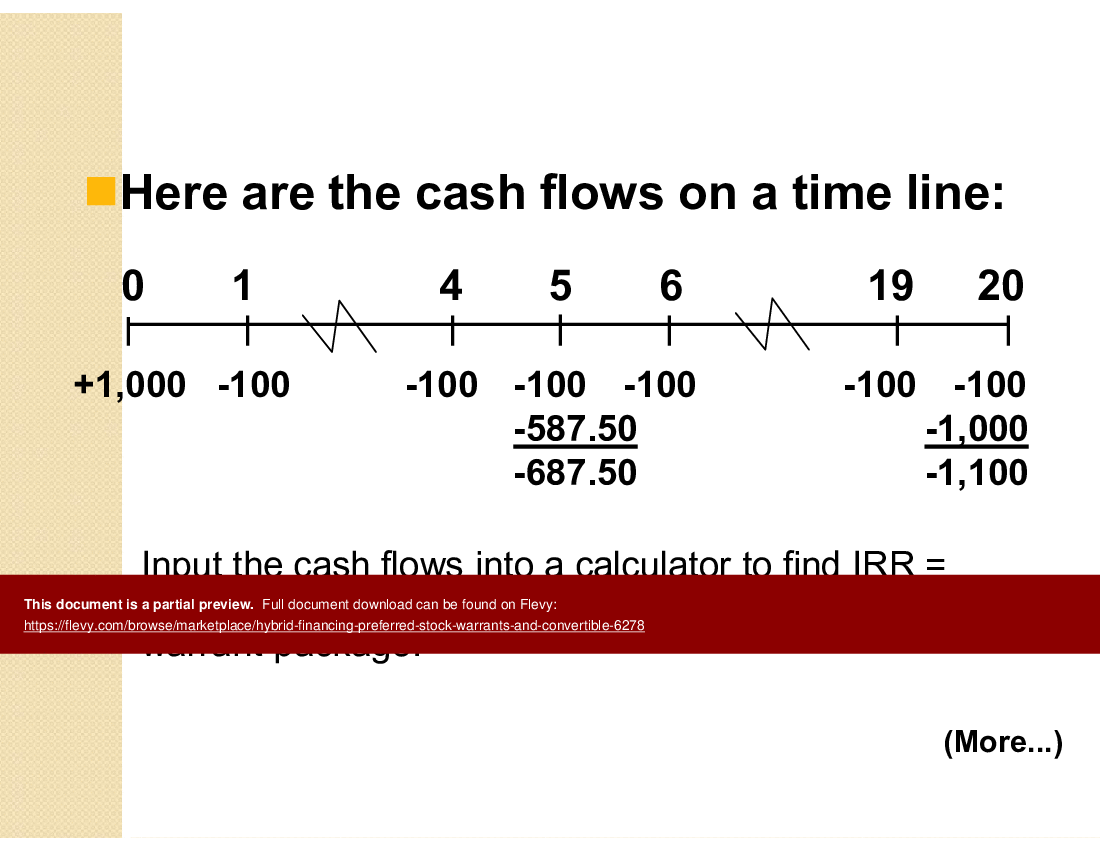
10. What is the formula for the bond's expected conversion value in any year?
11. What is the convertible's expected cost of capital to the firm?
12. Does the cost of the convertible appear to be consistent with the costs of debt and equity?
13. WACC Effects
14. The differences between warrants and convertibles.
15. How do convertibles help minimize agency costs?
16. Agency Costs Between Current Shareholders and New Shareholders
The use of convertible securities—generally bonds or preferred stocks that can be exchanged for common stock of the issuing corporation—has soared during the last decade. In recent years there have been instances where the capital raised through convertible securities has exceeded the amount of capital raised through common stock. Why do companies use convertibles so heavily?
To answer this question, recognize that convertibles virtually always have coupon rates that are lower than would be required on straight, nonconvertible bonds or preferred stocks. There-fore, if a company raises $100 million by issuing convertible bonds, its interest expense is lower than if it financed with nonconvertible debt. But why would investors be willing to buy convertibles, given their lower cash payments?
The answer lies in the conversion feature—if the price of the issuer's stock rises, the holder of the convertible can exchange it for stock and realize a capital gain. So, convertibles hold down the cash costs of financing by giving investors an opportunity for capital gains. A convertible bond's value is tied to the price of the stock into which it is convertible, whereas a nonconvertible bond's price is based on its fixed-income payments. Therefore, convertibles' prices rise and fall much more than regular bonds' prices; hence, convertibles are relatively risky.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Financing PowerPoint Slides: Hybrid Financing: Preferred Stock, Warrants & Convertible PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, UJ Consulting