INVESTMENT VEHICLES PDF DESCRIPTION
The objective of this document is to provide basic information regarding the various types of investment instruments that can be used to structure transactions. The goal is to create awareness of the standard securities, alternative investment structures, and the associated legal terms that can be used to better position XYZ to maximize returns as equity owners of a venture.
1 Equity (Stock)
Equity is ownership. Equity is what companies sell to investors to fund the company and what entrepreneurs retain to realize the value of what they have created. Equity represents the value of a company as a goingconcern. It is the most permanent form of investment in a company. Equity does not require repayment and sodoes not deplete company cash, as debt repayments do. Usually, equity takes the form of stock ownership (of which there are many variations) and carries with it certainrights the owner can exercise that are distinctive from rights secured by a note, debenture, or other debt instrument.
2 Derivatives
A derivative is a financial product that is based upon (or "derived" from) another product. Derivatives modifyrisk exposure by directly offset or hedging a position or by indirectly offsetting a position (i.e using a cross-hedge). They are also used for investment or speculative purposes.
3 Debt (?Bonds?)
Debt is defined as a sum owed by one party to another. The three largest issuers of debt are domestic corporations, municipal governments and the federal government. Each class features additional and significant differences. Each firm may sell different kinds of bonds: Some debt may be publicly placed, whereas other bonds might be privately placed ("private placement"). Some may be collateralized or secured by specific assets of a company, whereas other bonds might be unsecured. Depending on their objectives, borrowers differ in their preferences for raising debt capital. As a result, the distinctions among various types of issuers correspond closely to differences among bonds in yield, denomination, safety of principal, maturity, tax status, and other provisions such as call and put provisions and sinking fund.
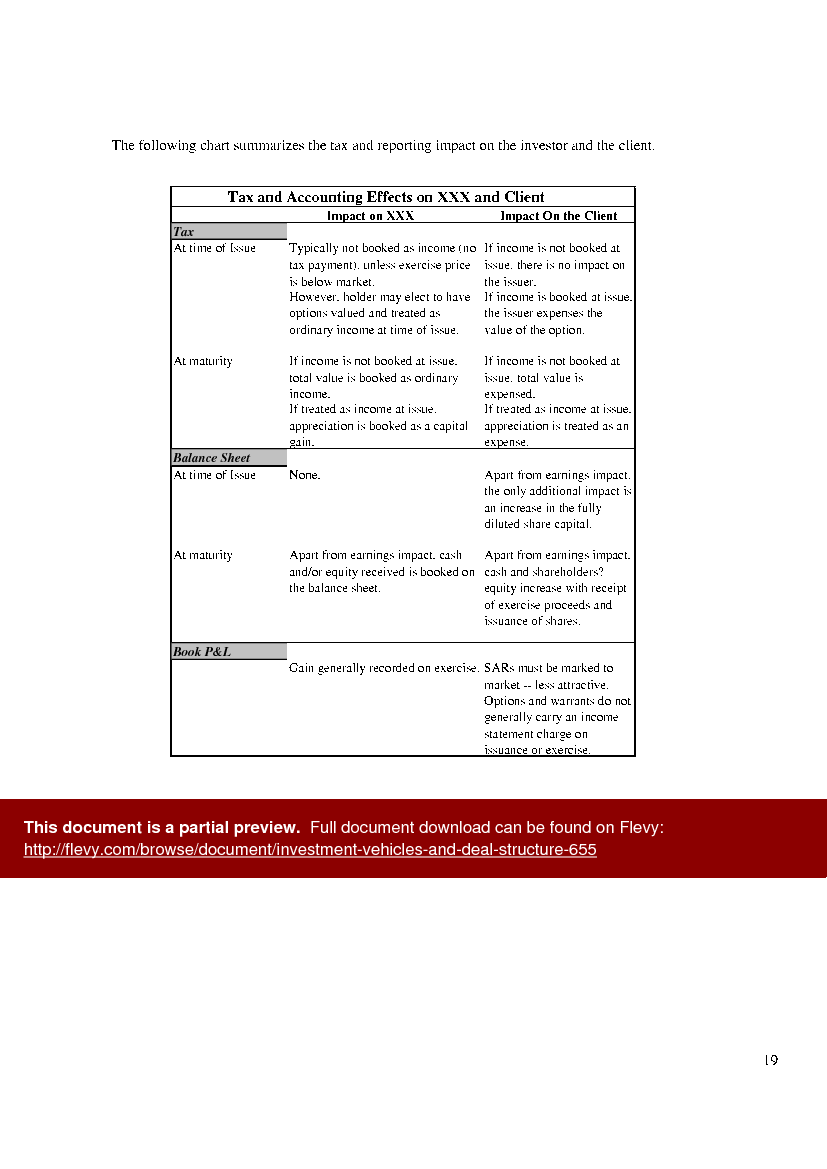
This document also covers the tax implications and balance sheet effects of different investment vehicles. It provides insights into how these instruments impact the book profit and loss of a company.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Investment Vehicles, Entrepreneurship PDF: Investment Vehicles & Deal Structure PDF (PDF) Document, Documents & Files