Agile Product Development Playbook for Executive Leadership (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 53 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Align Your Teams to Deliver Outstanding Products with Agile and Design
- Build Your Agile Muscles to Create Next-Generation Digital Offerings
- Speak the Language: Decode the Buzzwords Around Modern Product Development
AGILE PPT DESCRIPTION
*Why Agile & Design*
Overview of agile principles such as delivering customer value, embracing change, cross-functional collaboration, fast feedback cycles
Summary of design thinking principles – focus on user needs, rapid iterative prototyping, tolerance for failure.
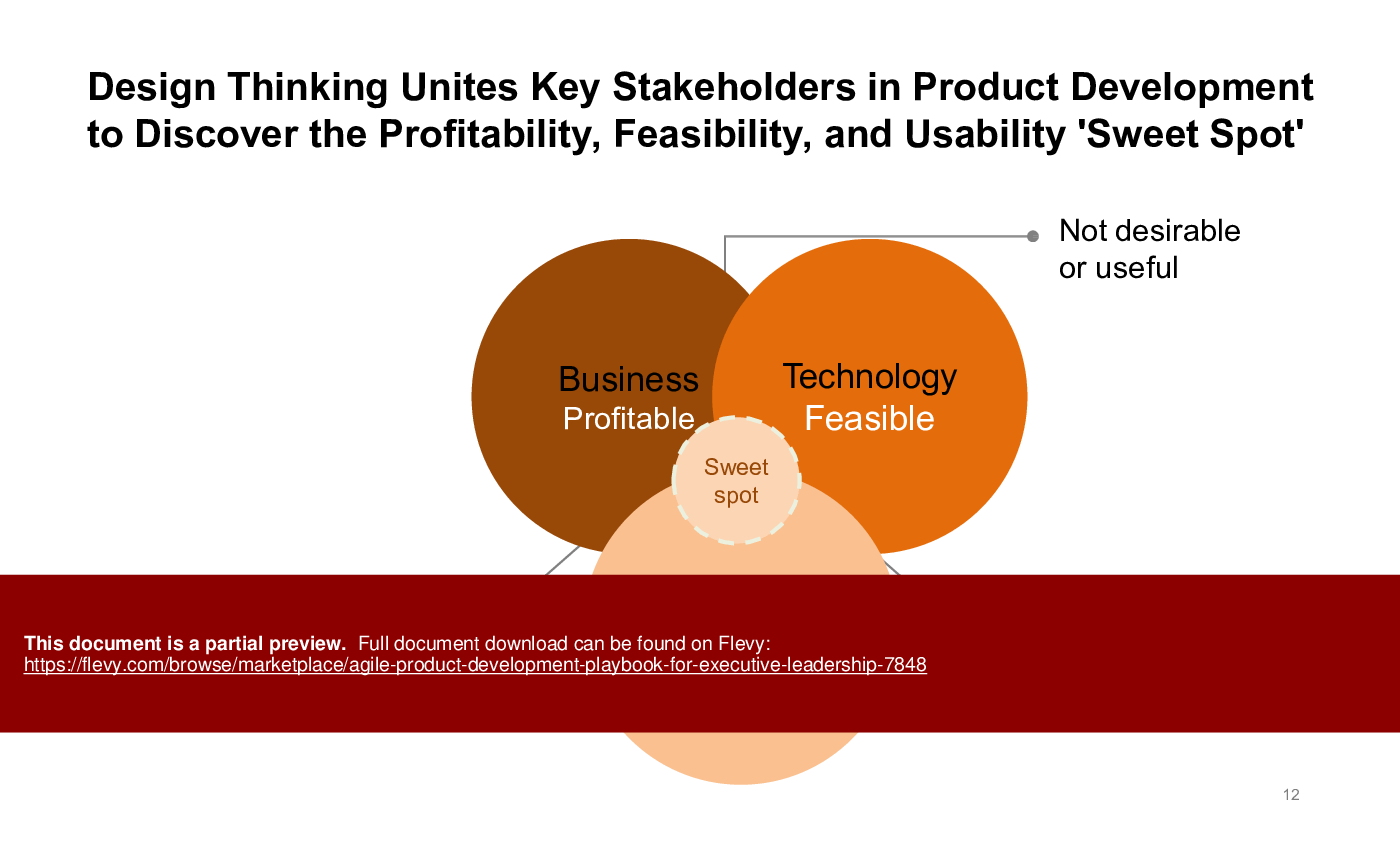
Explanation of why agile and design thinking are complementary approaches for building great products
*How to bring Agile & Design to life*
Forming cross-functional squads with clear roles and responsibilities
Implementing agile ceremonies like sprint planning, standups, reviews, retrospectives,
Integrating design sprints and rapid prototyping into the development lifecycle
Gathering user feedback early and often
Promoting a culture of experimentation and learning
*Agile Capability Development*
Overview of core competencies needed for agile-design excellence at the team and individual level
Maturity model and assessment framework to evaluate current agile-design capabilities
Training guides and resources to level up skills in areas like user research, rapid prototyping, agile engineering practices
*Terms & Definitions*
Glossary of key terminology related to agile, design thinking, and modern product development
Clarification of language used by various roles across product teams, design teams, and engineering teams
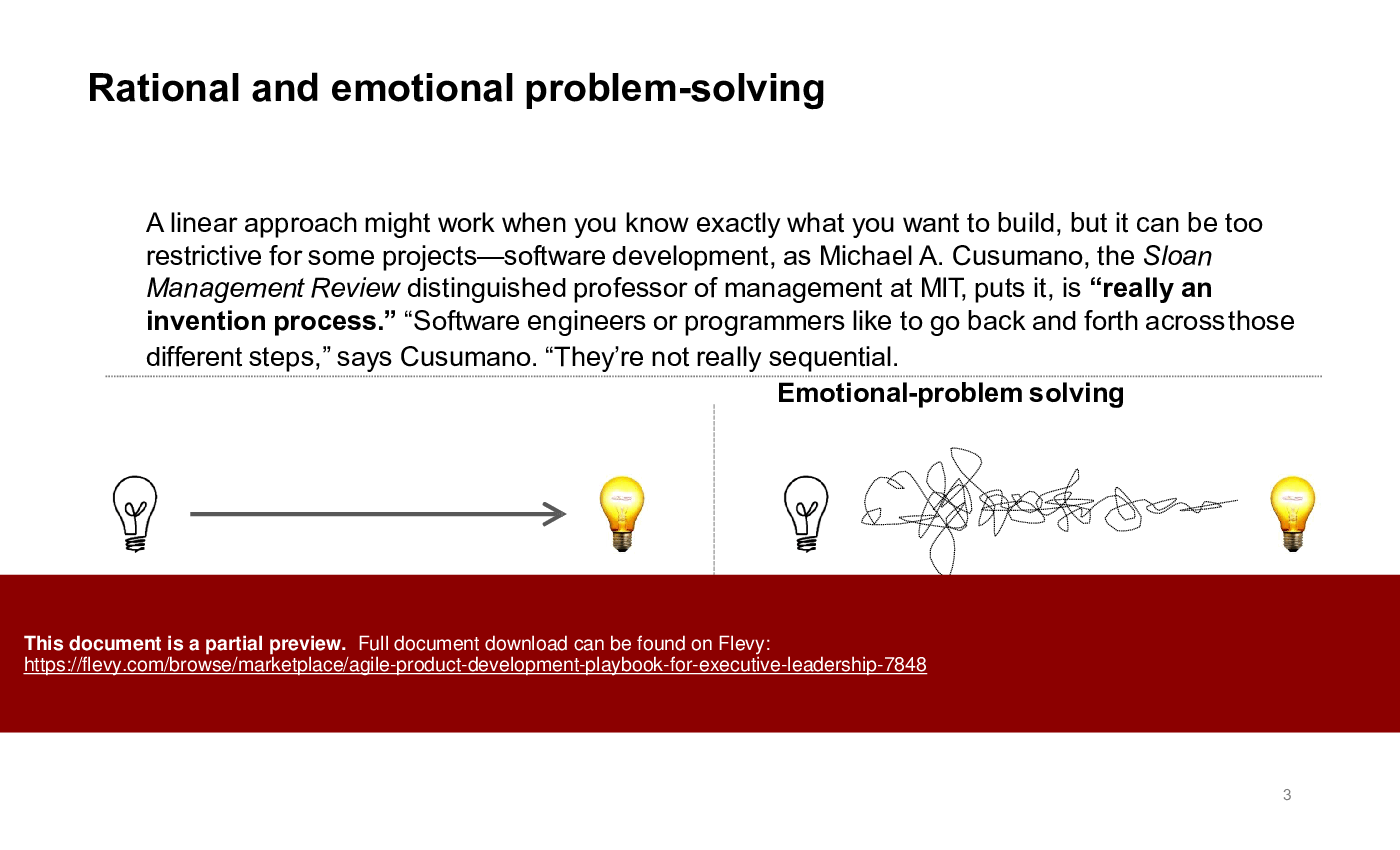
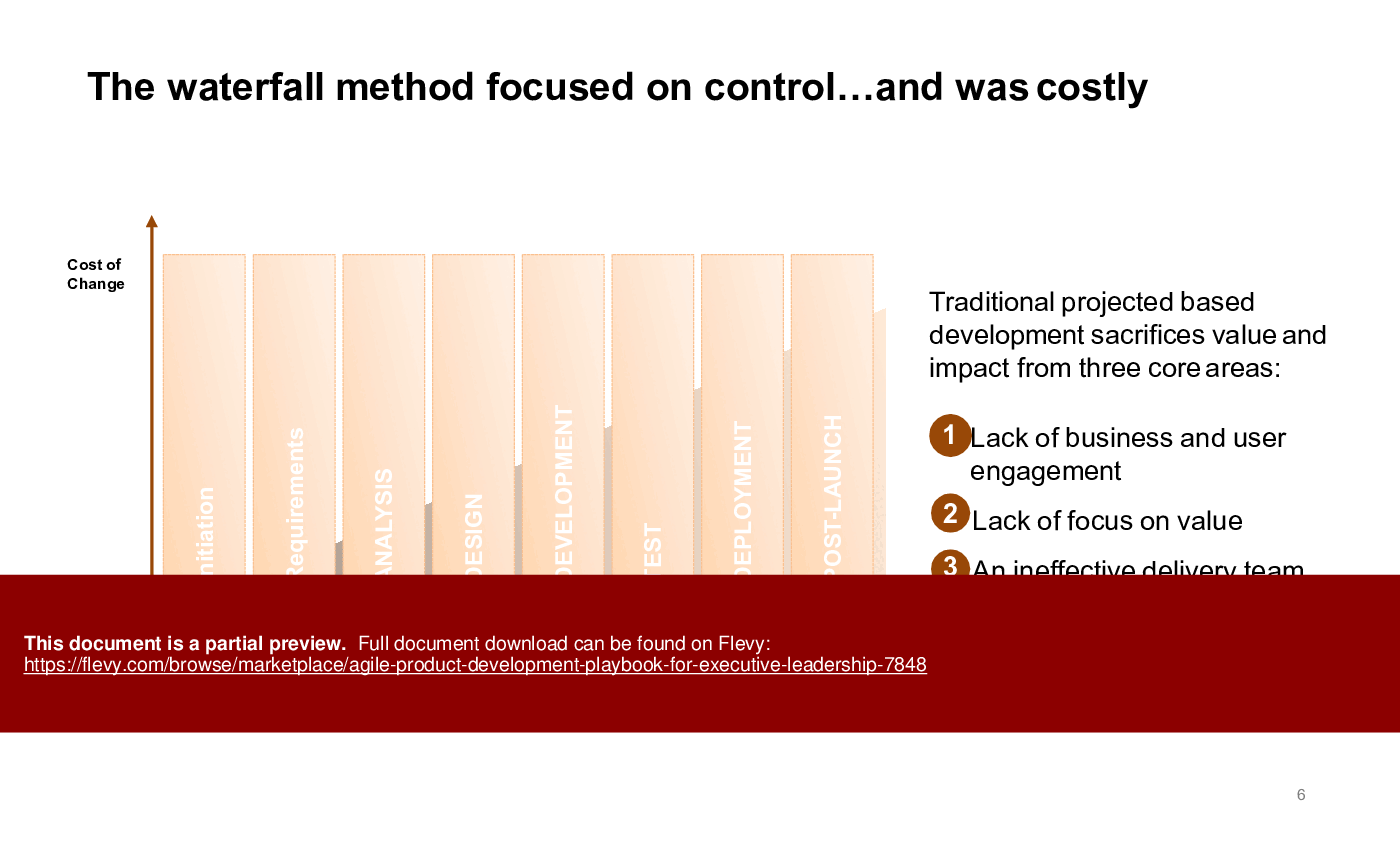
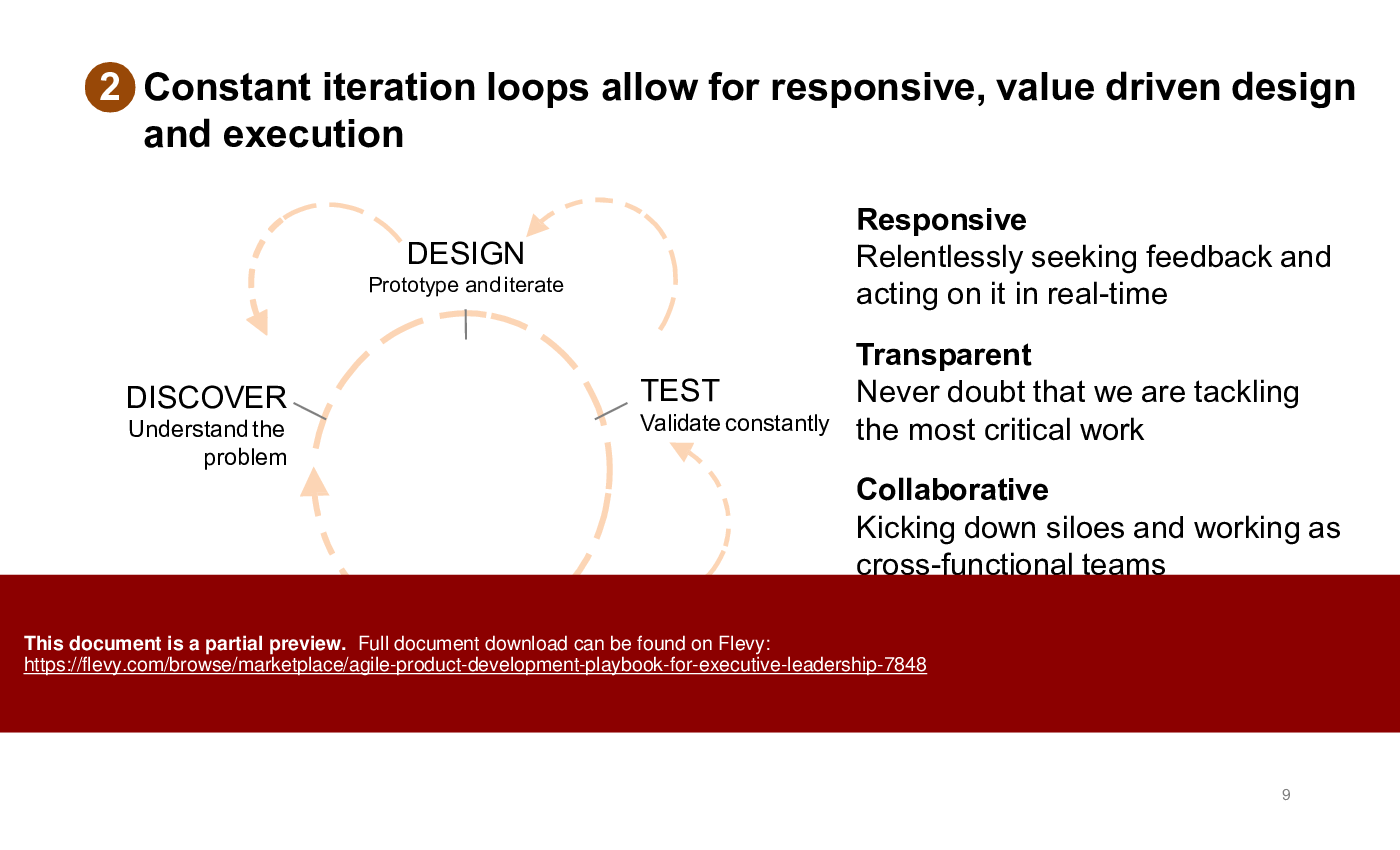
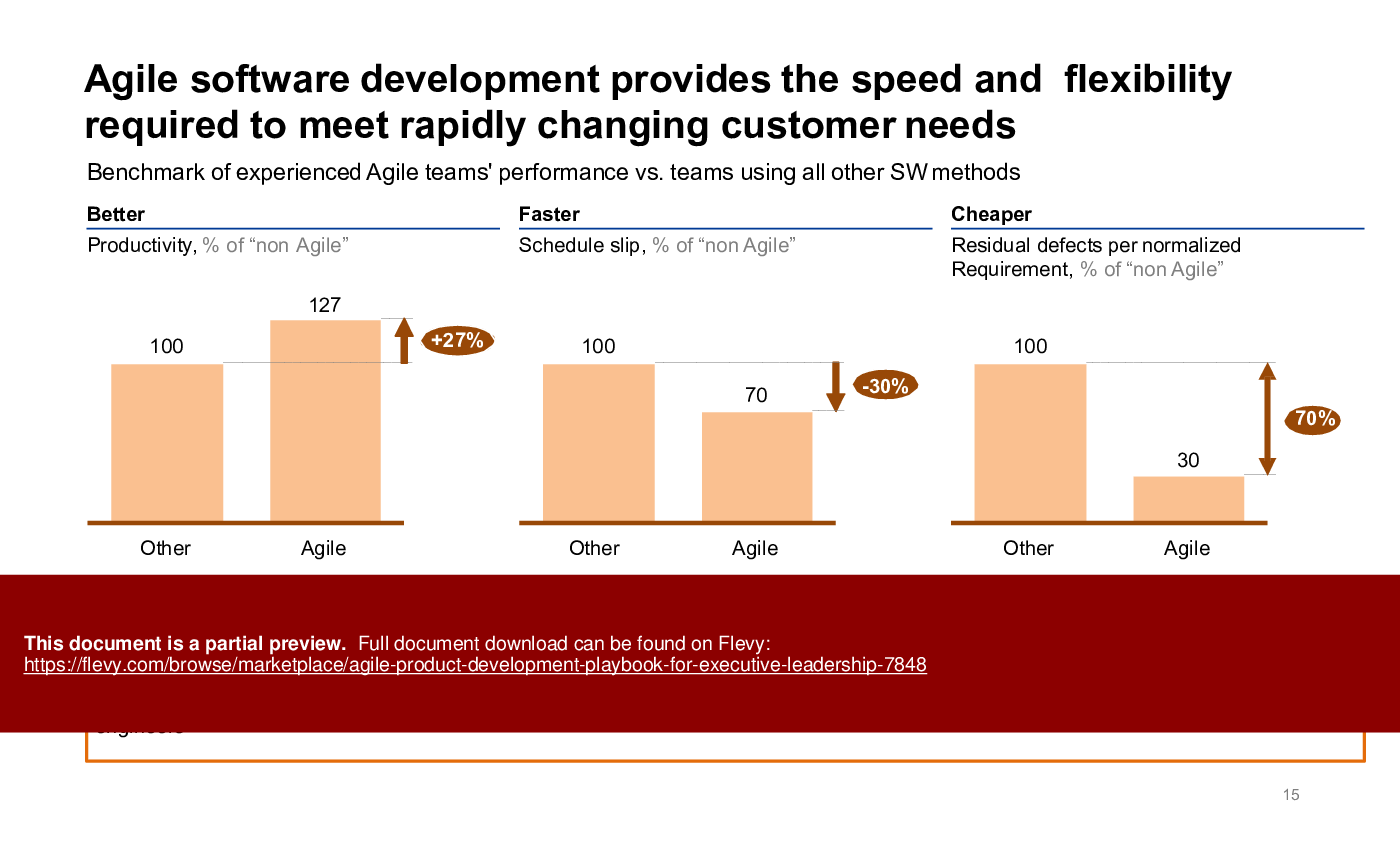
This playbook also delves into the nuanced balance between rational and emotional problem-solving, highlighting the non-linear nature of software development. It emphasizes the importance of iterative loops in design and testing, ensuring responsiveness and value-driven outcomes. The content underscores the pitfalls of traditional waterfall methods, advocating for agile's flexibility to meet rapidly changing customer needs.
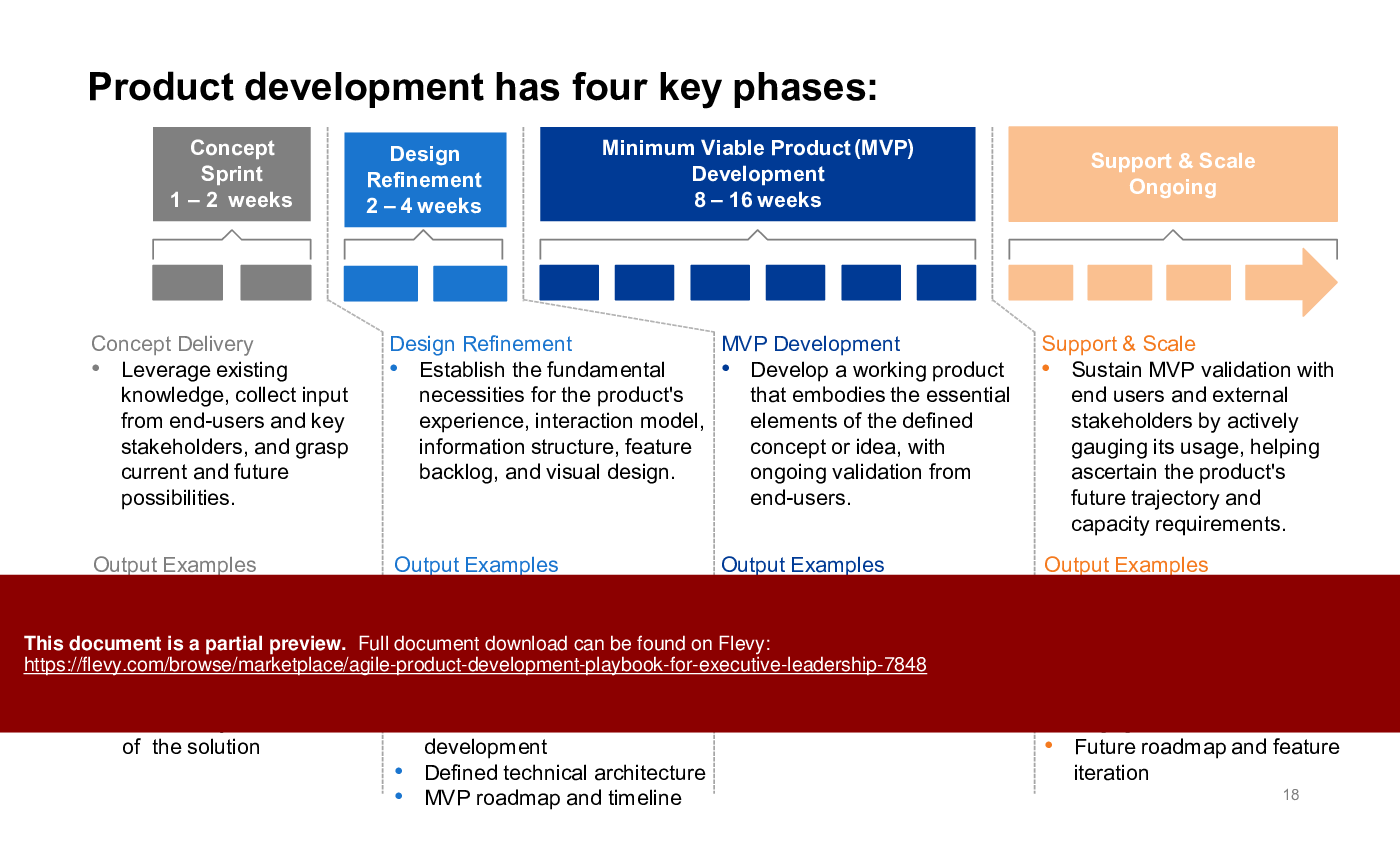
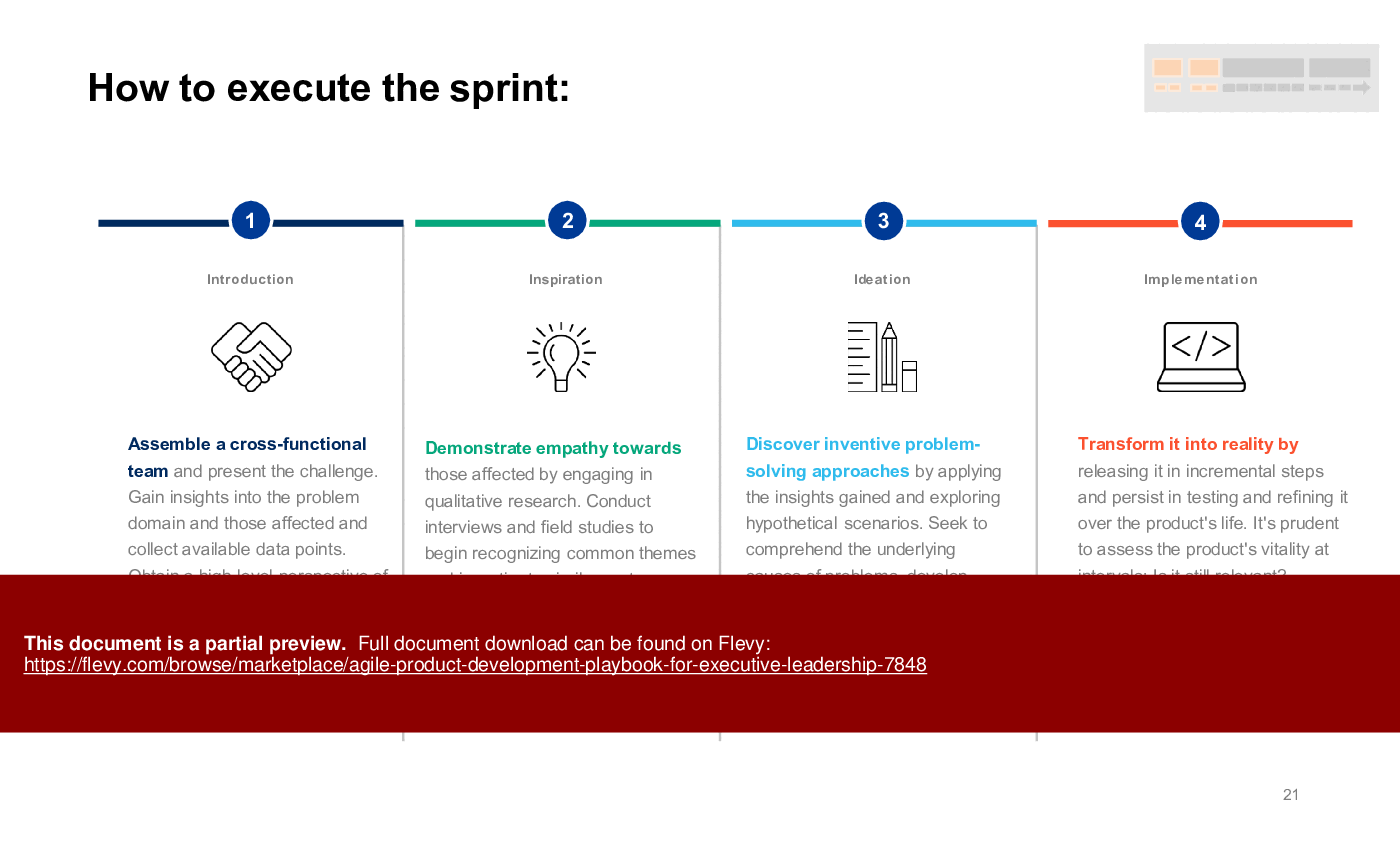
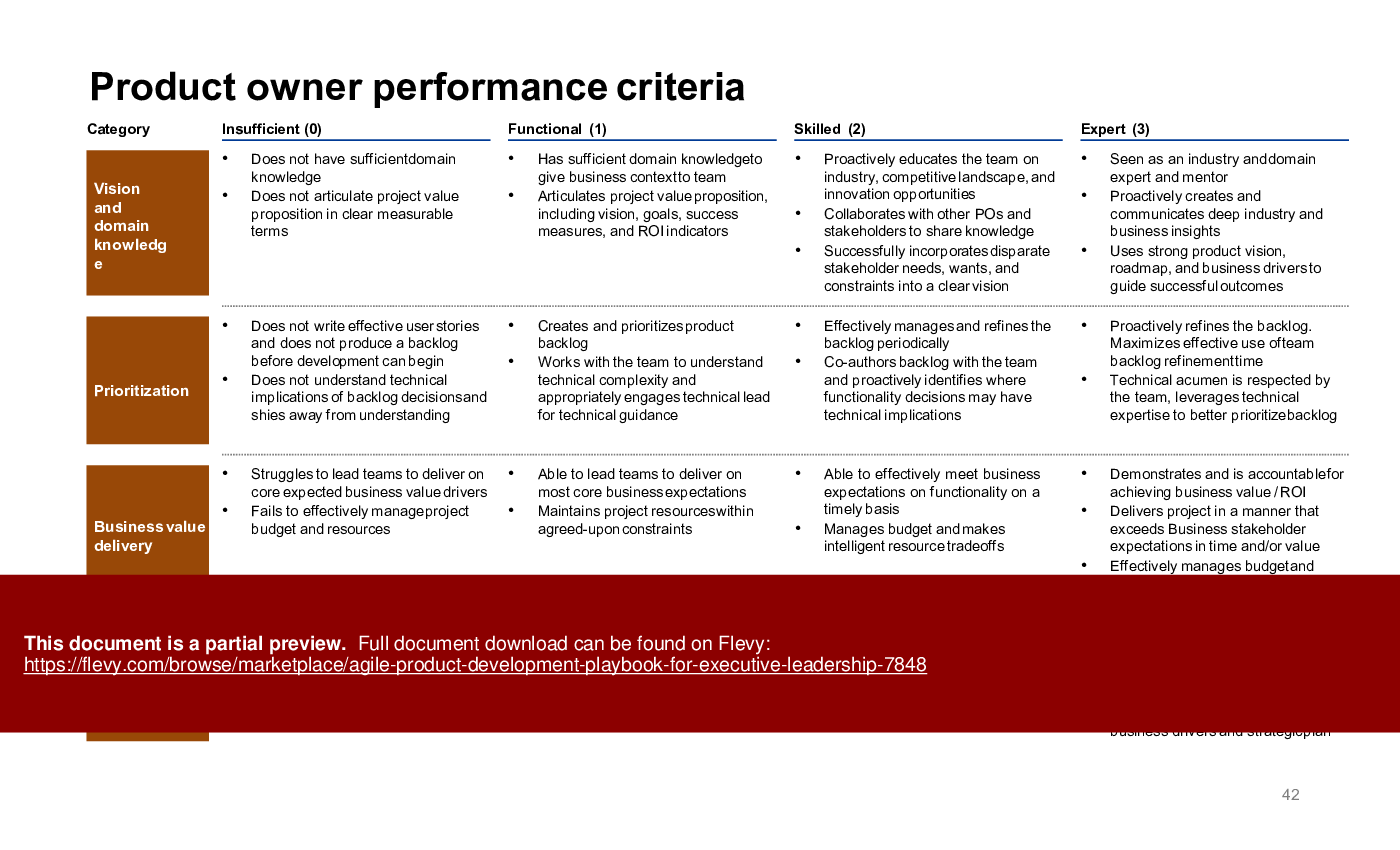
The PPT outlines the four key phases of product development, from concept sprints to support and scaling. It provides actionable insights on executing sprints, assembling cross-functional teams, and leveraging user feedback. The playbook also includes performance criteria for product owners and UX designers, ensuring roles are clearly defined and aligned with agile principles.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 53-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Agile Product Development Playbook for Executive Leadership is a consulting-grade resource designed to empower leaders in driving agile initiatives within their organizations. This playbook equips executives with the necessary frameworks and methodologies to enhance product development processes, ensuring alignment between business objectives and user needs. By leveraging agile principles and design thinking, leaders can foster a culture of innovation, collaboration, and responsiveness to market demands. This playbook serves as a comprehensive guide to navigating the complexities of agile product development, enabling teams to deliver value efficiently and effectively.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Executive leaders overseeing product development initiatives
• Product managers responsible for aligning business and user needs
• Agile coaches facilitating team transitions to agile methodologies
• Cross-functional team members involved in product design and delivery
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During the initiation of agile product development projects
• When assessing team capabilities and readiness for agile transformation
• For workshops aimed at integrating design thinking into agile processes
Learning Objectives
• Define the principles of agile and design thinking and their interrelationship
• Build a toolkit for assessing agile capabilities within teams
• Establish a framework for iterative product development and user feedback
• Create a roadmap for implementing agile methodologies in product teams
• Identify key roles and responsibilities in agile product development
• Develop strategies for fostering collaboration and transparency across teams
Table of Contents
• Why Agile & Design (page 1)
• How to Bring Agile & Design to Life (page 2)
• Agile Capability Development (page 3)
• Case Example: Directed Diagnostics for Merchandising (page 4)
• Terms & Definitions (page 5)
Primary Topics Covered
• Agile Principles - Agile focuses on iterative development, allowing teams to adapt to changing requirements and deliver value quickly.
• Design Thinking - A human-centered approach that emphasizes empathy and creativity in solving user problems and enhancing product usability.
• Agile Capability Assessment - Tools and frameworks for evaluating the agile maturity of teams and identifying areas for improvement.
• Iterative Development - The process of developing products in short cycles, enabling rapid feedback and continuous improvement.
• Cross-Functional Collaboration - The importance of diverse team roles in achieving successful product outcomes and fostering innovation.
• User-Centric Focus - Prioritizing user needs and feedback throughout the product development lifecycle to ensure relevance and satisfaction.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Agile capability assessment toolkit for evaluating team readiness
• Framework for conducting effective sprint retrospectives and planning sessions
• User journey mapping templates to visualize customer interactions
• Prototyping tools for rapid iteration and user feedback
• Backlog management templates for prioritizing features and user stories
• Metrics dashboard for tracking agile performance and product health
Slide Highlights
• Overview of agile principles and their benefits in product development
• Visual representation of the iterative development process and its phases
• Case study of successful agile implementation in merchandising
• Framework for assessing team capabilities and identifying growth areas
• Key roles and responsibilities in agile product teams
Potential Workshop Agenda
Agile Principles Overview (60 minutes)
• Introduce agile principles and design thinking concepts
• Discuss the benefits of integrating agile and design methodologies
• Engage participants in a group discussion on current challenges
Capability Assessment Workshop (90 minutes)
• Guide teams through the agile capability assessment toolkit
• Identify strengths and areas for improvement within teams
• Develop action plans for enhancing agile practices
User-Centric Design Session (60 minutes)
• Explore user journey mapping and its importance in product development
• Conduct hands-on activities to create user personas and scenarios
• Review best practices for gathering user feedback
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the agile capability assessment toolkit to reflect specific team dynamics and organizational goals
• Adjust user journey mapping templates to align with unique customer interactions and touchpoints
• Modify sprint planning and retrospective frameworks to fit the team’s workflow and cadence
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of servant leadership in agile environments
• Strategies for fostering a culture of continuous improvement
• Techniques for effective backlog management and prioritization
• The impact of cross-functional teams on product success
• Best practices for conducting user research and usability testing
Topic FAQ
What are the typical phases of an agile product development lifecycle?
Many agile playbooks break product development into iterative phases; this playbook outlines 4 key phases spanning concept sprints, iterative development, testing/validation, and support & scaling. The approach emphasizes short cycles, rapid feedback, and staged scaling across 4 key phases.How does design thinking fit into an agile product process?
Design thinking brings human-centered research, empathy mapping, rapid prototyping, and tolerance for failure into agile cycles to ensure solutions meet user needs. The combination encourages early user feedback and iterative prototyping to validate assumptions through rapid iterative prototyping.What is an agile capability assessment and how is it used?
An agile capability assessment evaluates team maturity, core competencies, and growth areas using a maturity model and assessment framework. Organizations run facilitated workshops to identify gaps and build action plans; the playbook includes an agile capability assessment toolkit.What should I look for when choosing an executive-focused agile playbook?
Look for content that covers core principles, capability assessment tools, practical templates for sprint planning and retrospectives, user-journey mapping, prototyping aids, backlog management, and metrics tracking. A useful playbook includes workshop agendas and templates such as retrospective and backlog templates.How much time do the recommended workshops usually take and how should I schedule them?
The playbook provides example agendas with durations: a 60-minute Agile Principles Overview, a 90-minute Capability Assessment Workshop, and a 60-minute User-Centric Design Session. These modular sessions can be scheduled across one or multiple days, including a 90-minute capability assessment workshop.I need to assess my team’s readiness for agile—what practical first step should I take?
Begin with an agile capability assessment workshop using a maturity model to evaluate current skills and behaviors, then identify targeted training and pilot sprints. The playbook provides a guided capability assessment toolkit and training resources to structure that first assessment.How can executives use an agile playbook to align business objectives and user needs?
Executives can use the playbook’s user-journey mapping, MVP definitions, backlog prioritization templates, and roadmap framework to translate business goals into prioritized, testable product increments and measurable outcomes, culminating in a roadmap for implementing agile methodologies.Are purchased playbooks and templates worth it versus building internal materials?
Purchased playbooks offer ready-made templates, workshop agendas, assessment frameworks, and role definitions that reduce design time and standardize runbooks. For teams wanting a packaged approach, the playbook delivers those artifacts in a 53-slide PPTX format.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the Agile methodology?
Agile is a flexible approach to product development that emphasizes iterative progress, customer collaboration, and responsiveness to change.
How does design thinking complement agile practices?
Design thinking enhances agile by ensuring that user needs are prioritized, fostering creativity, and encouraging collaboration across teams.
What tools are included in the agile capability assessment?
The toolkit includes templates for evaluating team maturity, frameworks for identifying growth areas, and metrics for tracking progress.
How can I implement agile in my organization?
Start by assessing current capabilities, providing training for teams, and gradually integrating agile practices into existing workflows.
What are the key roles in an agile product team?
Key roles include the Product Owner, Scrum Master, Agile Coach, and cross-functional team members such as developers and designers.
What is a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)?
An MVP is the simplest version of a product that delivers core functionality to users, allowing for early feedback and iterative improvement.
How do I measure the success of agile initiatives?
Success can be measured through metrics such as team velocity, user satisfaction, and the quality of deliverables produced during sprints.
What challenges might I face when transitioning to agile?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of understanding of agile principles, and difficulties in team collaboration.
Glossary
• Agile - A methodology focused on iterative development and customer collaboration.
• Design Thinking - A problem-solving approach centered on user needs and empathy.
• MVP (Minimum Viable Product) - The simplest product version that delivers value to users.
• Backlog - A prioritized list of work items needed to complete a product.
• Sprint - A fixed time period during which specific work is completed.
• Scrum Master - The facilitator of the Scrum process, responsible for coaching the team.
• Product Owner - The individual responsible for defining the product vision and managing the backlog.
• User Journey - A visual representation of the steps a user takes when interacting with a product.
• Retrospective - A meeting to reflect on the team's performance and identify areas for improvement.
• Cross-Functional Team - A team composed of members from different functional areas working together on a project.
• Capacity - The amount of work a team can complete in a given time frame.
• Burn-Down Chart - A visual tool for tracking progress against work remaining in a sprint.
• Kanban Board - A tool for visualizing work and optimizing workflow.
• User Story - A short description of a feature from the perspective of the end user.
• Velocity - A measure of how much work a team can complete in a sprint.
• Stakeholders - Individuals with a vested interest in the outcome of a project.
• Servant Leadership - A leadership style that focuses on serving the team and removing obstacles to their success.
• Continuous Integration - An engineering practice that involves frequently integrating code changes into a shared repository.
• Empathy Mapping - A tool used to understand user needs and experiences.
• Feedback Loop - A process for continuously gathering and integrating user feedback into product development.
AGILE PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Agile, Product Management PowerPoint Slides: Agile Product Development Playbook for Executive Leadership PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, WallStBizStrategist