Product Management KPIs (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 32 Slides FlevyPro Document
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS PPT DESCRIPTION
Product Managers are responsible for defining the features or functions of a Product and for overseeing the development of the Product. The role of Produce Managers spans many activities from strategic to tactical and can vary based on the organizational structure of the organization.
Typically, Product Leaders are involved with the entire Product Lifecycle. However, the Product Management's primary focus is on driving New Product Development.
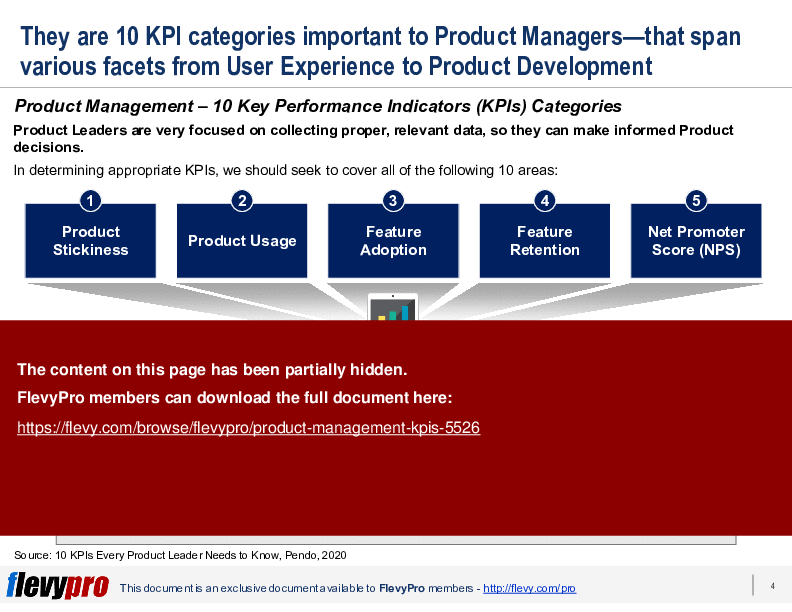
To successfully execute these roles, it's important for Product Management to collect and synthesize proper, relevant data to make informed Product decisions.
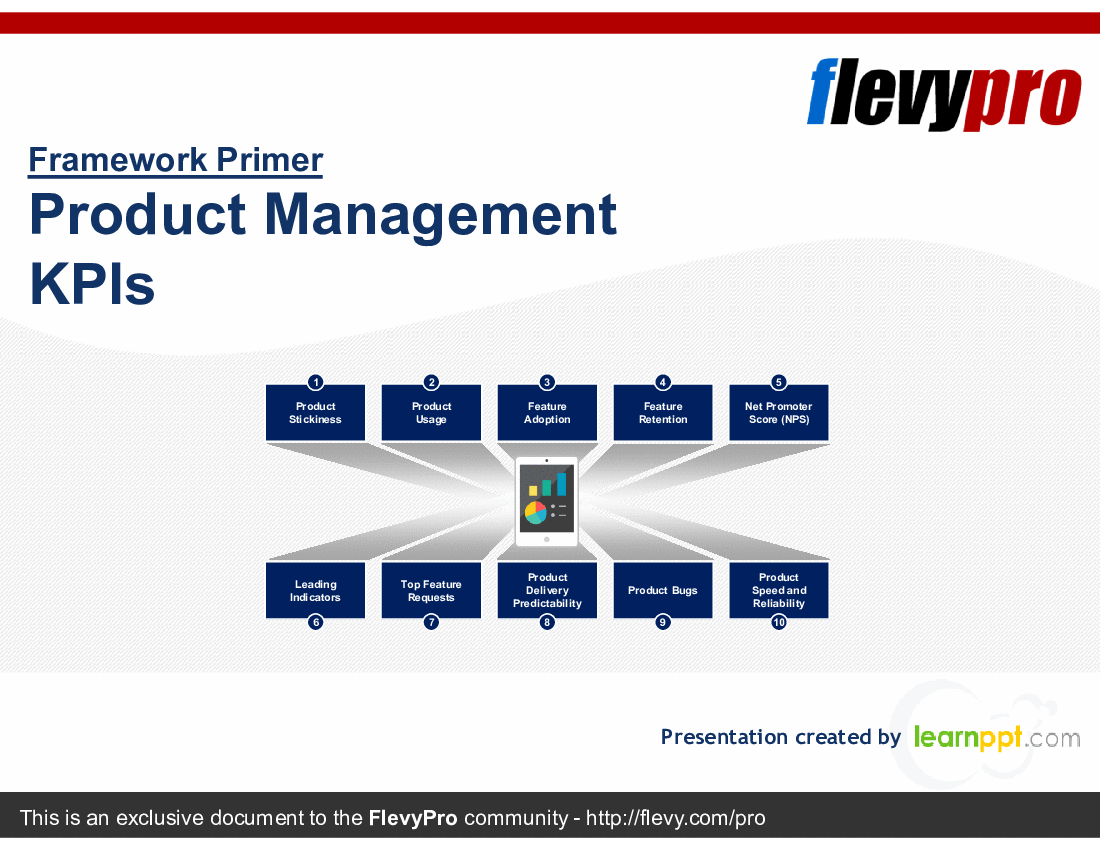
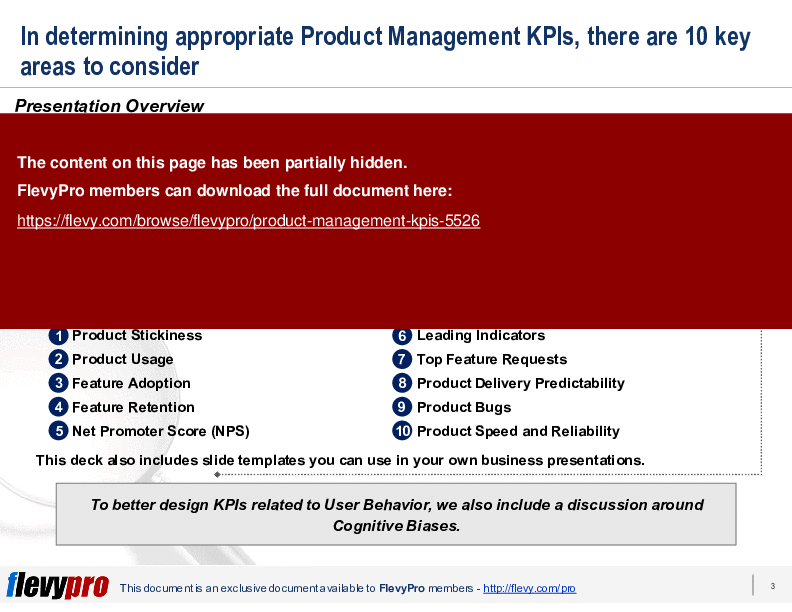
In this presentation, we discuss 10 categories of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that Product Management should be evaluating. These areas range from Product Stickiness to Net Promoter Score (NPS) to Leading Indicators.
To better design KPIs related to User Behavior, we also include a discussion around Cognitive Biases.
This deck also includes slide templates you can use in your own business presentations.
This presentation provides a comprehensive guide to the essential KPIs that Product Managers need to monitor for optimal product performance. It covers critical areas such as Product Stickiness, Feature Adoption, and Net Promoter Score, ensuring that you have a robust framework for evaluating product success. The inclusion of Cognitive Biases offers a nuanced understanding of user behavior, which is crucial for designing effective KPIs.
The deck is designed to be practical and actionable, with slide templates that can be directly applied to your business presentations. It emphasizes the importance of data-driven decision-making and provides detailed explanations on how to measure and interpret each KPI. This resource is invaluable for Product Leaders aiming to enhance their product management strategies and drive better business outcomes.
Got a question about this document? Email us at flevypro@flevy.com.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 32-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Product Management KPIs" presentation provides a comprehensive overview of key performance indicators essential for effective product management. Developed by experienced consultants, this deck focuses on ten critical KPI categories, including Product Stickiness, Product Usage, and Net Promoter Score (NPS). It equips product managers with actionable insights and templates to enhance decision-making, track user engagement, and optimize product features. By leveraging these KPIs, organizations can better understand user behavior, drive product improvements, and ultimately achieve greater market success.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Product Managers seeking to enhance product performance and user engagement
• Product Development Teams focused on tracking and optimizing feature usage
• Marketing Teams aiming to align product offerings with customer needs
• Executives interested in measuring product success and customer satisfaction
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During product strategy sessions to define and measure success metrics
• When launching new features to track adoption and engagement
• In quarterly reviews to assess product performance and user feedback
• For training sessions aimed at developing a data-driven product culture
Learning Objectives
• Define key performance indicators relevant to product management
• Build a framework for measuring product stickiness and user engagement
• Establish metrics for tracking feature adoption and retention
• Analyze Net Promoter Score (NPS) to gauge customer loyalty
• Identify leading indicators that predict product success
• Create actionable templates for ongoing KPI tracking and reporting
Table of Contents
• Overview (page 3)
• Product KPI Categories (page 4)
• Behavioral Psychology (page 21)
• Templates (page 25)
Primary Topics Covered
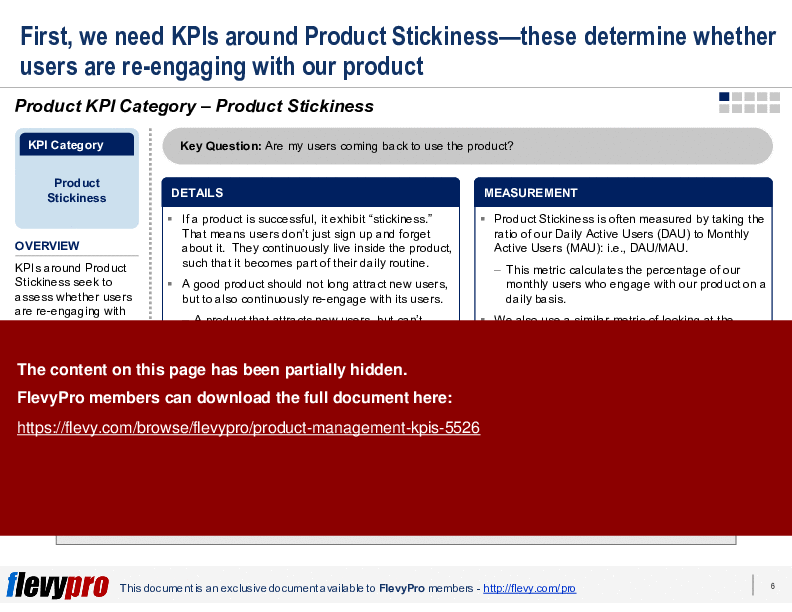
• Product Stickiness - Measures user re-engagement with the product, indicating its value in daily routines.
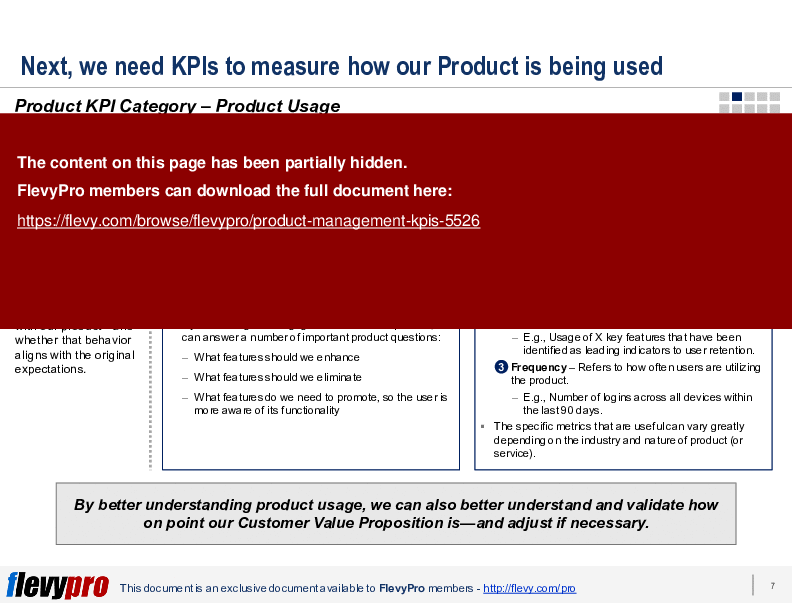
• Product Usage - Evaluates how users interact with the product, identifying which features are most utilized.
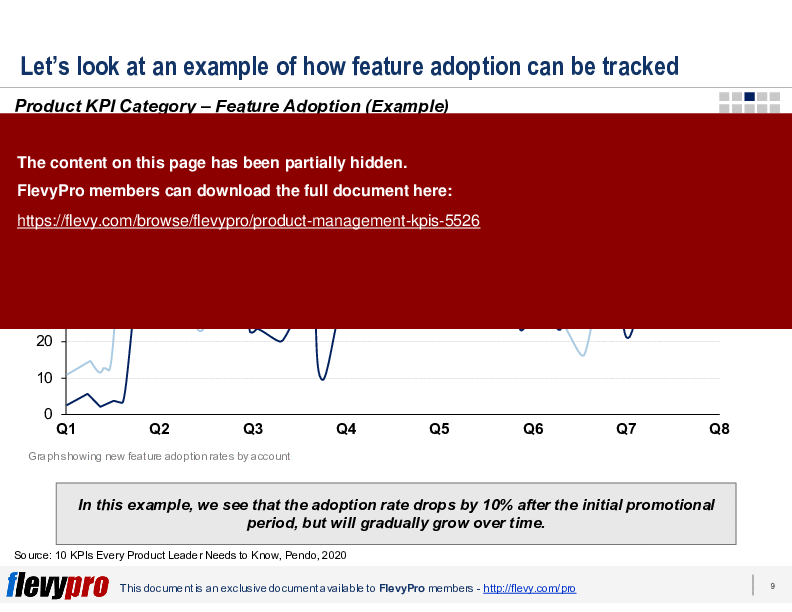
• Feature Adoption - Tracks the rate at which new features are embraced by users post-launch.
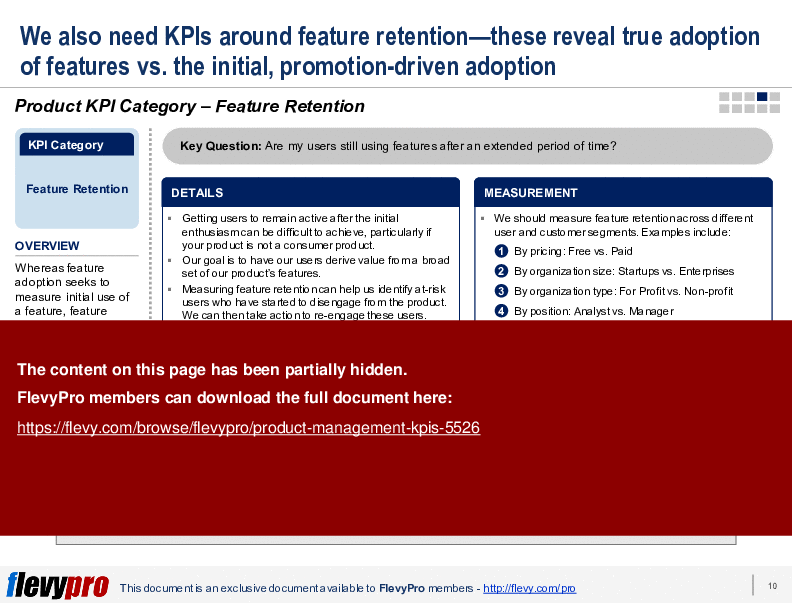
• Feature Retention - Assesses ongoing use of features over time, highlighting user engagement beyond initial adoption.
• Net Promoter Score (NPS) - Gauges customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend the product to others.
• Leading Indicators - Identifies metrics that predict future product performance and user behavior.
• Top Feature Requests - Collects and prioritizes user feedback on desired product enhancements.
• Product Delivery Predictability - Measures the reliability of the product development timeline and milestones.
• Product Bugs - Tracks software issues to maintain product quality and user satisfaction.
• Product Speed and Reliability - Evaluates performance metrics critical for user experience in SaaS and online products.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• KPI tracking templates for measuring product stickiness and usage
• Feature adoption metrics to assess new feature performance
• NPS survey templates for gauging customer loyalty
• Reporting frameworks for leading indicators and feature requests
• Bug tracking templates to monitor product quality
• Delivery predictability metrics for project management
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the ten KPI categories essential for product management
• Visual representation of product stickiness metrics and their importance
• Case studies illustrating feature adoption trends over time
• NPS reporting examples at both account and user levels
• Frameworks for identifying and prioritizing top feature requests
Potential Workshop Agenda
KPI Definition and Framework Session (60 minutes)
• Discuss key performance indicators relevant to product management
• Define metrics for measuring product stickiness and usage
• Develop a shared understanding of NPS and its implications
Feature Adoption and Retention Workshop (90 minutes)
• Analyze recent feature launches and adoption rates
• Identify strategies for improving feature retention
• Create action plans for enhancing user engagement
NPS and Customer Feedback Analysis (60 minutes)
• Review NPS results and implications for product strategy
• Discuss methods for collecting and analyzing user feedback
• Develop a roadmap for addressing customer concerns
Customization Guidance
• Tailor KPI definitions to align with specific product goals and user segments
• Adjust templates to reflect unique organizational metrics and reporting needs
• Incorporate industry-specific benchmarks for NPS and feature adoption rates
• Modify tracking frameworks to include additional relevant metrics
Secondary Topics Covered
• Cognitive biases affecting user behavior and decision-making
• Strategies for enhancing user engagement through product design
• Best practices for conducting effective user feedback surveys
• Methods for analyzing and interpreting KPI data for actionable insights
Topic FAQ
What are the main KPI categories product managers should track first?
Core KPI categories include Product Stickiness, Product Usage, Feature Adoption, Feature Retention, Net Promoter Score (NPS), Leading Indicators, Top Feature Requests, Product Delivery Predictability, Product Bugs, and Product Speed/Reliability. A practical KPI program typically begins by mapping these ten KPI categories to business objectives and user segments, covering ten categories.How can I measure product stickiness in practice?
Product stickiness is commonly measured by the ratio of Daily Active Users (DAU) to Monthly Active Users (MAU), which indicates re-engagement frequency. Tracking DAU/MAU over time and by cohort helps reveal whether the product becomes part of users’ routines; the deck references DAU/MAU as the stickiness metric.What are leading indicators and how do they help predict product performance?
Leading indicators are behavioral or usage metrics that precede outcomes like conversions or account growth; they act as early signals of future performance. Examples include engagement patterns, early feature activation, or initial retention rates that correlate with downstream metrics, described in the deck as predictors of future product performance.How should teams use NPS as part of a KPI dashboard?
NPS measures customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend; teams should collect NPS at account and user levels, analyze verbatim feedback, and link NPS trends to product changes. The presentation includes NPS survey templates and reporting examples at both account and user levels for practical use with NPS surveys.What features should I expect in a KPI slide deck I might purchase?
Useful KPI decks provide defined KPI categories, measurement definitions, templates for tracking stickiness and usage, NPS survey templates, bug-tracking formats, and reporting frameworks for leading indicators and feature requests. The Product Management KPIs deck explicitly includes slide templates and reporting frameworks as deliverables.How do I track feature adoption and what timeframe matters after launch?
Track feature adoption by measuring the percentage of users engaging with a new feature over time, ideally monitoring adoption for at least 30 days post-launch to observe initial uptake and short-term retention; the deck recommends measuring feature adoption over that period.My team struggles with product quality issues—what KPI areas should we focus on first?
For product quality, focus on Product Bugs and Product Speed and Reliability metrics: bug counts by feature, ratio of reported-to-fixed bugs over time, page load times, action response times, and uptime. Monitoring these metrics helps prioritize fixes and preserves user experience through bug-tracking templates.Are slide templates and KPI tools worth buying for a small product team?
Slide templates and prebuilt KPI tools can accelerate report creation, standardize definitions, and enable repeatable tracking across releases; practical decks include KPI tracking templates, NPS survey templates, and bug tracking formats that are directly usable as slide templates.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What are the key performance indicators for product management?
Key performance indicators include Product Stickiness, Product Usage, Feature Adoption, Feature Retention, Net Promoter Score (NPS), and others that help assess product success.
How can I measure product stickiness?
Product stickiness can be measured by calculating the ratio of Daily Active Users (DAU) to Monthly Active Users (MAU). Higher ratios indicate greater user engagement.
What is the significance of Net Promoter Score (NPS)?
NPS measures customer loyalty and satisfaction, predicting future growth by assessing how likely customers are to recommend the product.
How do I track feature adoption effectively?
Track feature adoption by measuring the percentage of users who engage with new features over time, ideally for at least 30 days post-launch.
What are leading indicators in product management?
Leading indicators are metrics that predict future performance, such as user engagement patterns that correlate with conversions and account growth.
How can I prioritize feature requests?
Establish a centralized system for collecting feature requests, allowing you to analyze user feedback and prioritize based on demand and potential impact.
What metrics should I use for product delivery predictability?
Metrics include completion of key milestones, deliverables, workstreams, unit tests, and overall adherence to the product roadmap.
How can I ensure product quality?
Track product bugs by measuring the breakdown of bugs by feature and comparing the number of bugs reported to those fixed over time.
What metrics indicate product reliability and speed?
Metrics include page load time, action response time, website uptime, and service availability, all critical for maintaining a positive user experience.
Glossary
• Product Stickiness - Measure of user re-engagement with a product.
• Product Usage - Assessment of how users interact with product features.
• Feature Adoption - Rate at which new features are utilized by users.
• Feature Retention - Long-term usage of features beyond initial engagement.
• Net Promoter Score (NPS) - Metric for gauging customer loyalty.
• Leading Indicators - Metrics predicting future product performance.
• Top Feature Requests - User feedback on desired product enhancements.
• Product Delivery Predictability - Reliability of the product development timeline.
• Product Bugs - Software errors impacting product functionality.
• Product Speed and Reliability - Performance metrics critical for user satisfaction.
• Cognitive Biases - Psychological factors affecting user decision-making.
• User Engagement - Measure of how actively users interact with a product.
• Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) - Prediction of the net profit attributed to the entire future relationship with a customer.
• Behavioral Psychology - Study of how cognitive biases influence decision-making.
• Survey Methodology - Techniques for collecting user feedback effectively.
• Data-Driven Decisions - Making choices based on data analysis rather than intuition.
• User Feedback - Insights gathered from users regarding their experience with a product.
• Feature Enhancement - Improvements made to existing product features based on user input.
• Product Lifecycle - Stages a product goes through from development to decline.
• Market Fit - The degree to which a product satisfies market demand.
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATORS PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Key Performance Indicators, Product Strategy, Product Management, Net Promoter Score PowerPoint Slides: Product Management KPIs PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting
Did you need more documents?
Consider a FlevyPro subscription from $39/month. View plans here.
For $10.00 more, you can download this document plus 2 more FlevyPro documents. That's just $13 each.