Psychology of Market Entry Analysis (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 27 Slides FlevyPro Document
MARKET RESEARCH PPT DESCRIPTION
For every successful market entry, about market entry attempts end in failure. This failure is attributed to many factors—timing, scale, competition, capabilities, and particularly irrational decision making. The decision to successfully enter a market necessitates detailed analysis. These critical decisions, however, often get tainted by Cognitive Biases—the systematic errors in the way people process information. Cognitive Biases distort executives’ perception regarding their firm’s capabilities, potential market, and competition.
The presentation starts by highlighting a 2-pronged approach to Market Entry Analysis:
1. Develop a Reference Class
2. Remove Bias from Decisions
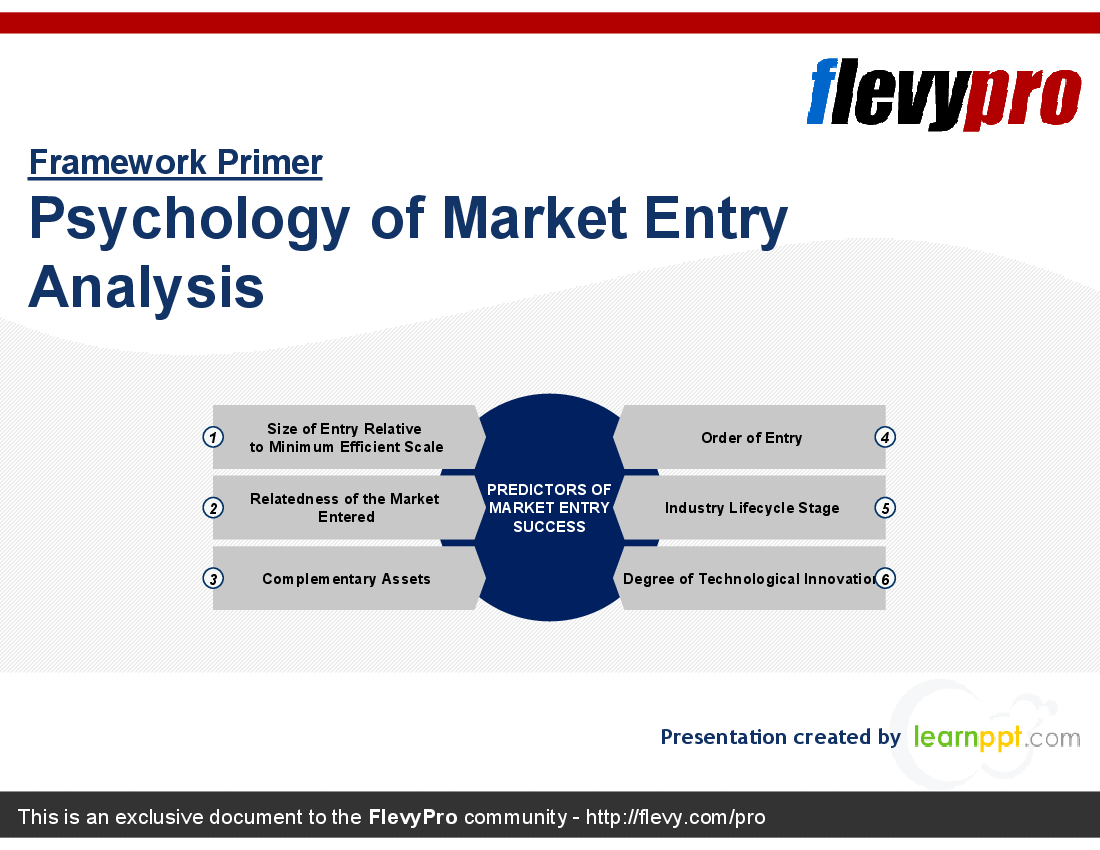
The deck then discusses the 6 key factors of market entry success:
1. Size of entry relative to minimum efficient scale
2. Relatedness of the market entered
3. Complementary assets
4. Order of entry
5. Industry lifecycle stage
6. Degree of technological innovation
The details of the 5 core issues in removing biases from decisions are then highlighted:
1. Value Proposition and Capabilities
2. Market Size
3. Competition
4. Market Share and Revenue
5. Costs
The slide deck also includes some slide templates for you to use in your own business presentations.
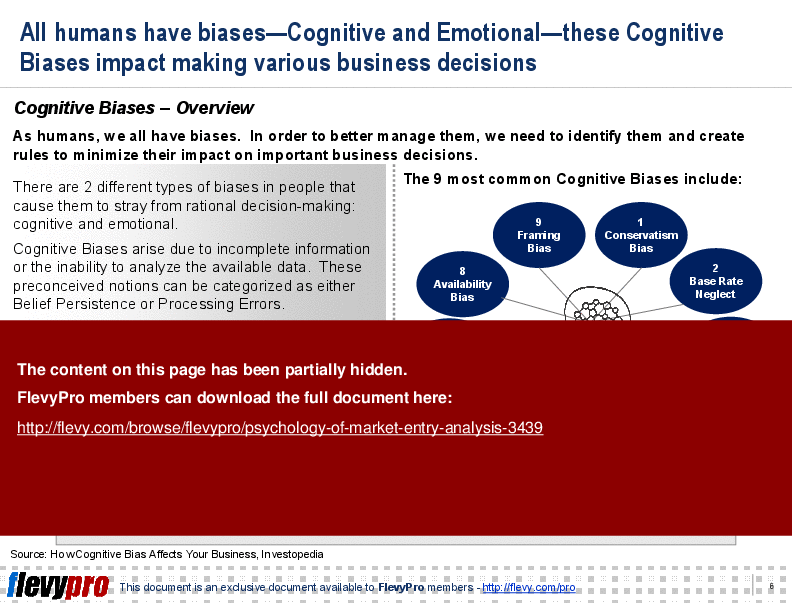
This PPT delves into the intricacies of cognitive biases and their impact on market entry decisions. It emphasizes the importance of developing a reference class to mitigate these biases and make informed decisions. The presentation also covers the nine most common cognitive biases that can distort decision-making, such as framing bias, conservatism bias, and availability bias.
Executives will find actionable insights on how to identify and counteract these biases, ensuring a more rational approach to market entry. The document also includes practical templates to facilitate the application of these concepts in real-world scenarios. This resource is essential for any executive looking to enhance their market entry strategy and avoid costly mistakes.
Got a question about this document? Email us at flevypro@flevy.com.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 27-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Psychology of Market Entry Analysis" presentation provides a structured framework for executives to enhance their decision-making processes regarding market entry. Crafted by former consultants from McKinsey and the Big 4, this presentation emphasizes the significant financial implications of flawed market entry decisions. It introduces a two-pronged approach to mitigate cognitive biases that often cloud judgment, enabling leaders to make informed choices based on empirical data and historical precedents. By understanding the predictors of market entry success and implementing strategic frameworks, executives can significantly improve their chances of successful market penetration.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives responsible for strategic planning and market entry decisions
• Business development teams evaluating new market opportunities
• Consultants advising clients on market entry strategies
• Market analysts conducting competitive assessments and feasibility studies
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions for new market entries
• When conducting risk assessments for potential market opportunities
• In workshops aimed at training teams on cognitive biases in decision-making
• For presentations to stakeholders on market entry strategies and frameworks
Learning Objectives
• Define the critical factors influencing successful market entry decisions
• Identify and mitigate cognitive biases affecting decision-making processes
• Develop a reference class to inform market entry strategies
• Analyze the predictors of market entry success and their implications
• Establish a framework for evaluating market size, competition, and costs
• Create actionable templates for market entry analysis
Table of Contents
• Overview (page 3)
• Cognitive Biases (page 6)
• Approach – Develop a Reference Class (page 9)
• Approach – Remove Bias from Decisions (page 13)
• Templates (page 20)
Primary Topics Covered
• Cognitive Biases - Systematic errors that affect decision-making, leading to flawed judgments in market entry.
• Develop a Reference Class - Utilizing historical data from similar market entries to inform current decisions and mitigate biases.
• Predictors of Market Entry Success - Six key factors that influence the likelihood of successful market entry, including size of entry and industry lifecycle stage.
• Remove Bias from Decisions - Strategies to identify and eliminate biases impacting market entry analysis, focusing on value proposition and competition.
• Market Size and Revenue - Techniques for accurately estimating market potential and anticipating competitor responses.
• Costs - Importance of realistic cost forecasting to avoid the planning fallacy in market entry decisions.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Market entry analysis template for assessing potential opportunities
• Reference class framework for evaluating past market entry decisions
• Checklist for identifying cognitive biases in decision-making
• Cost estimation model based on historical data
• Market size estimation template for segmenting potential customers
• Competitor analysis framework to identify existing and potential rivals
Slide Highlights
• Overview of cognitive biases and their impact on decision-making
• Framework for developing a reference class to inform market entry strategies
• Detailed analysis of the 6 predictors of market entry success
• Strategies for removing biases from decisions, including practical recommendations
• Templates for market entry analysis and cost estimation
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Market Entry Analysis (30 minutes)
• Overview of cognitive biases and their implications
• Discussion on the importance of a structured approach
Developing a Reference Class (60 minutes)
• Identifying historical market entries relevant to current decisions
• Group activity to analyze past successes and failures
Removing Bias from Decisions (60 minutes)
• Interactive session on recognizing and mitigating biases
• Case studies to illustrate the impact of biases on market entry
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the reference class examples to align with your industry and market context
• Adjust the cognitive bias identification framework to reflect your organization's specific challenges
• Modify the templates to include metrics and terminology relevant to your business
Secondary Topics Covered
• Behavioral economics and its relevance to market entry decisions
• The role of emotional biases in executive decision-making
• Case studies of successful and failed market entries
• Techniques for conducting effective market research
Topic FAQ
What is a reference class and how is it used in market entry analysis?
A reference class groups historical, similar market-entry cases to inform expectations about outcomes and timelines. Using a reference class helps counteract over-optimism by benchmarking market size, costs, and competitor behavior against precedent; the deck includes a reference class framework to structure this analysis.What are the main cognitive biases that affect market entry decisions?
Market entry decisions are commonly distorted by biases such as framing bias, conservatism bias, availability bias, optimism bias, anchoring and adjustment, planning fallacy, and competitive blind spots. The presentation highlights nine common biases and shows how they skew perceptions of market size, costs, and capabilities.What factors most strongly predict whether a market entry will succeed?
The presentation identifies 6 predictors of market entry success: size of entry relative to minimum efficient scale, relatedness of the market entered, complementary assets, order of entry, industry lifecycle stage, and degree of technological innovation — a 6-factor checklist.How should I estimate market size for a potential new market?
Accurate market-size estimates require customer segmentation, pricing and elasticity assumptions, benchmarking against historical entries, and scenario testing for competitor responses. The deck supplies a market size estimation template to structure segmentation and benchmark inputs.What should I look for when choosing a market-entry toolkit for a corporate project?
Look for tools that combine empirical benchmarking (reference-class analysis), bias identification checklists, market-size and cost-estimation templates, and competitor frameworks. A suitable toolkit provides practical templates and a structured approach; this presentation bundles those elements, including 6 specific templates and models.I need to present entry risks to the board—what framework helps structure the narrative?
Structure the board presentation around the two-pronged approach: present reference-class benchmarks first, then demonstrate how bias-removal and structured checks alter forecasts for value proposition, market size, competition, revenue, and costs. The deck supports this narrative with templates and a bias checklist.Are ready-made market-entry templates and checklists valuable for small teams on tight timelines?
Pre-built templates can shorten analysis time by standardizing segmentation, cost estimation, competitor assessment, and bias checks. For teams needing repeatable outputs, the presentation supplies ready-made deliverables such as a market entry analysis template and a cost estimation model to accelerate work.How can I anticipate competitor responses when entering a new market?
Anticipate competitor moves by conducting gaming exercises or role-play scenarios to simulate likely strategies and reactions, then map those outcomes into market-share and revenue scenarios. The presentation recommends gaming exercises as a practical technique to surface competitor responses.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What are cognitive biases, and how do they affect market entry decisions?
Cognitive biases are systematic errors in thinking that can lead to flawed decision-making. They affect market entry by distorting perceptions of market size, competition, and the firm's capabilities.
How can I develop a reference class for my market entry analysis?
A reference class can be developed by analyzing historical market entries of similar companies, focusing on both successes and failures to gain insights into potential outcomes.
What are the 6 predictors of market entry success?
The 6 predictors include size of entry relative to minimum efficient scale, relatedness of the market entered, complementary assets, order of entry, industry lifecycle stage, and degree of technological innovation.
How can I effectively remove biases from my decision-making process?
Implement structured decision-making processes, educate decision-makers on recognizing biases, and utilize frameworks that encourage objective analysis of data.
What templates are included in this presentation?
The presentation includes templates for market entry analysis, cost estimation, competitor analysis, and cognitive bias identification.
How can I estimate market size accurately?
Accurate market size estimation involves segmenting customers, using pricing and elasticity assumptions, and benchmarking against historical data from similar market entries.
What common biases should I be aware of when making market entry decisions?
Common biases include optimism bias, anchoring and adjustment, competitive blind spots, and the planning fallacy.
How do I anticipate competitor responses in a new market?
Conduct gaming exercises where executives role-play competitors to gain insights into potential strategies and responses.
Glossary
• Cognitive Bias - Systematic errors in thinking that affect decision-making.
• Reference Class - A group of similar past decisions used to inform current choices.
• Market Entry Success - The likelihood of successfully entering a new market based on various predictors.
• Planning Fallacy - The tendency to underestimate the duration and cost of a project.
• Market Size Estimation - The process of estimating the potential demand for a product in a market.
• Competitive Blind Spots - The failure to recognize potential competitors in the market.
• Value Proposition - The unique value a product or service offers to customers.
• Complementary Assets - Resources that enhance the effectiveness of a firm's core capabilities.
• Industry Lifecycle Stage - The phase of development of an industry, impacting market entry opportunities.
• Technological Innovation - The degree of new technology required to compete in a market.
• Cost Estimation - The process of predicting the costs associated with market entry.
• Market Share - The percentage of a market controlled by a particular company.
• Revenue Forecasting - Predicting future revenue based on market analysis and historical data.
• Game Theory - A mathematical framework for strategizing in competitive situations.
• Behavioral Economics - The study of psychological factors influencing economic decision-making.
• Decision-Making Process - The steps taken to arrive at a conclusion or choice.
• Templates - Pre-designed documents or frameworks used to streamline analysis and reporting.
• Market Analysis - The assessment of market conditions to inform business strategies.
• Strategic Planning - The process of defining an organization's direction and making decisions on allocating resources.
• Executive Decision-Making - The process by which executives make strategic choices for their organizations.
MARKET RESEARCH PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Market Analysis, Cognitive Bias, Market Entry PowerPoint Slides: Psychology of Market Entry Analysis PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting
Did you need more documents?
Consider a FlevyPro subscription from $39/month. View plans here.
For $10.00 more, you can download this document plus 2 more FlevyPro documents. That's just $13 each.