Rogers' Five Factors (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 29 Slides
PRODUCT STRATEGY PPT DESCRIPTION
This document discusses Rogers' Five Factors, framework for analyzing and understanding the diffusion and adoption of product innovations.
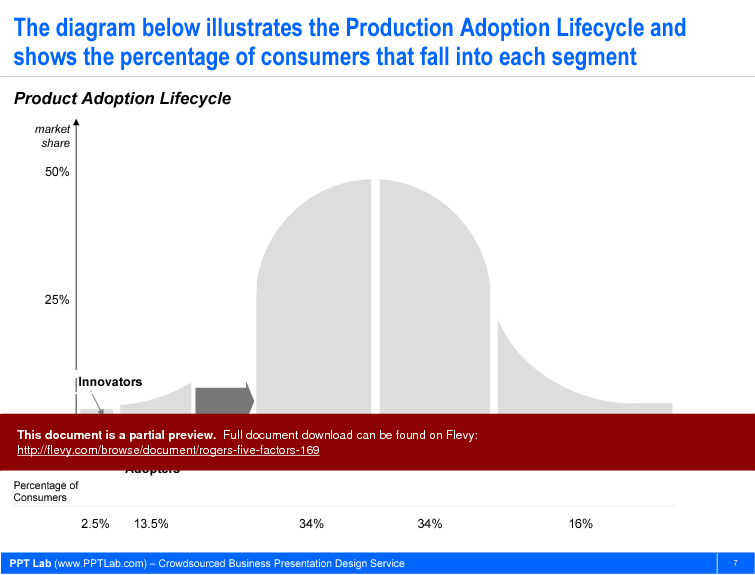
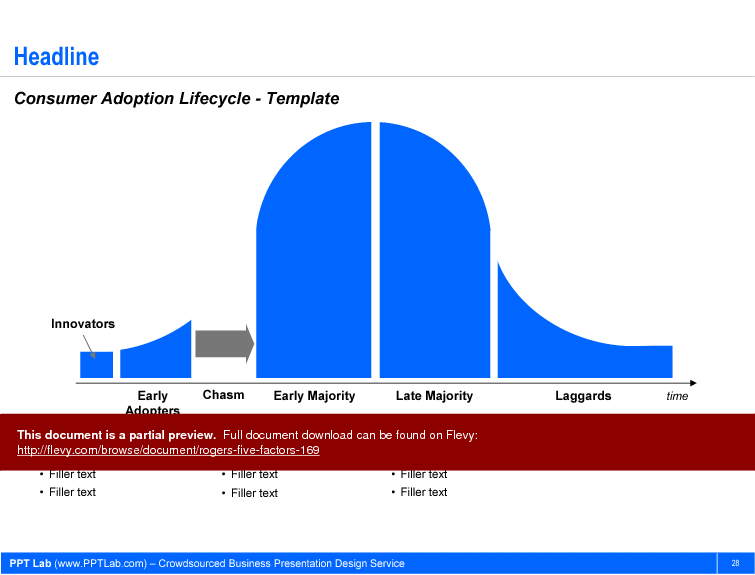
Businesses are interested in understanding how innovations diffuse, so that they can better predict and manage this consumer adoption. A popular framework for this is the Consumer Adoption Lifecycle (or Product Lifecycle), which traces the adoption of a product as it passes through 5 categories of consumers. This is a viewpoint that focuses on people.
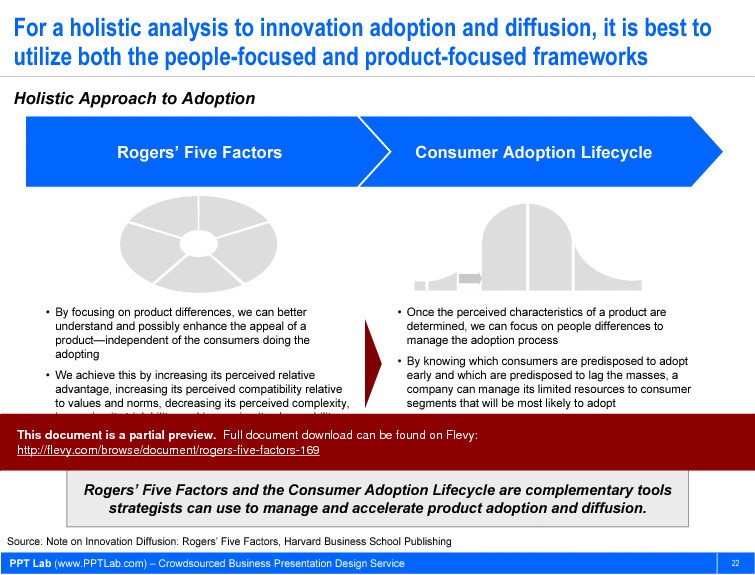
Rogers' Five Factors is a product-focused framework that should be used in conjunction with the Consumer Adoption Lifecycle. Developed by Everett Rogers, this framework proposes that the rate of innovation diffusion is largely driven by 5 product-based factors:
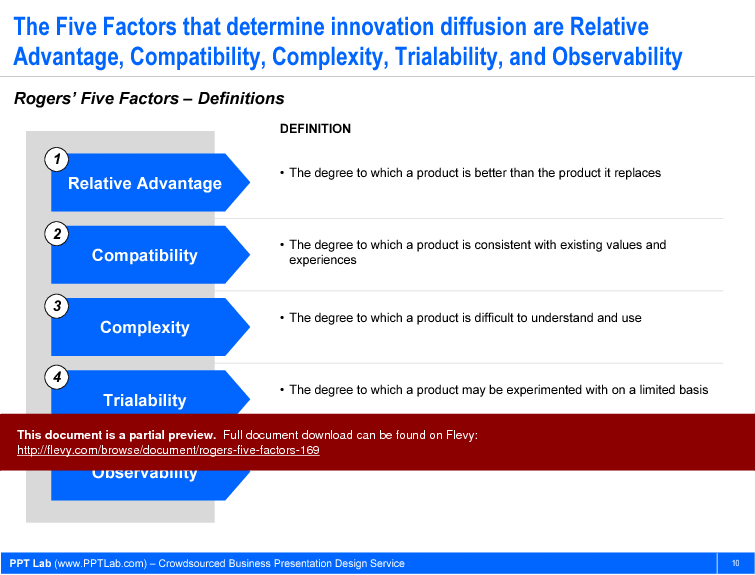
1. Relative advantage
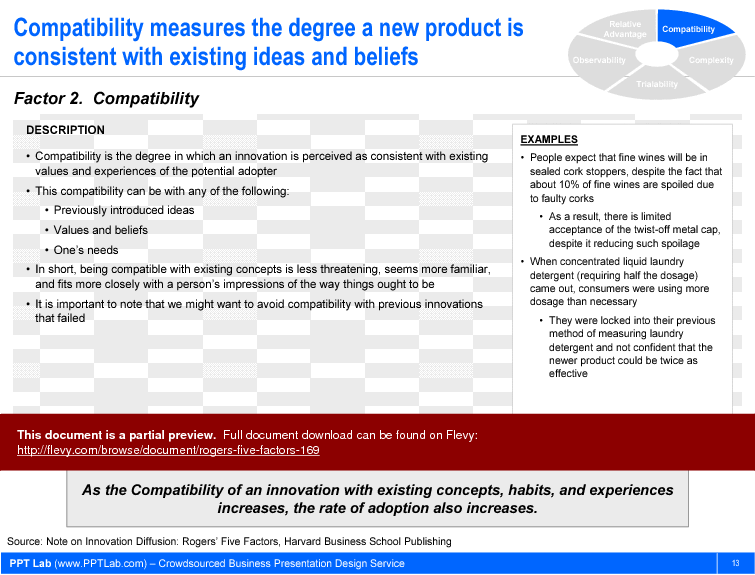
2. Compatibility
3. Complexity
4. Trialability
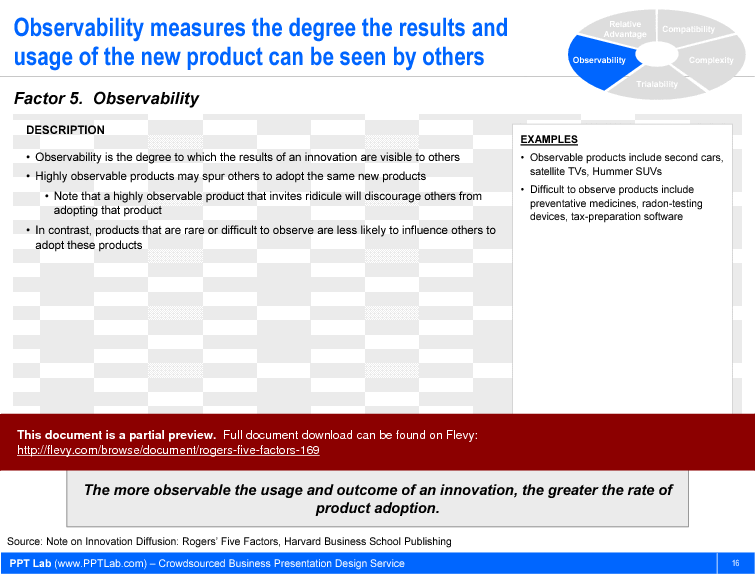
5. Observability
This document explains the framework, provides examples, shows how to use this framework with the Production Adoption Lifecycle, and includes PowerPoint templates that can be leveraged in your own analysis.
Gain a comprehensive understanding of how each of Rogers' Five Factors influences the adoption process through detailed definitions and real-world examples. This document delves into the nuances of each factor, providing insights into how relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, trialability, and observability can be leveraged to accelerate product adoption. The inclusion of case studies, such as the telephone adoption, illustrates the practical application of these factors in historical contexts, offering valuable lessons for modern innovations.
The document also features a holistic approach to adoption, integrating both the Rogers' Five Factors and the Consumer Adoption Lifecycle frameworks. This dual approach ensures that you can address both product-specific and consumer-specific variables, optimizing your strategy for maximum market penetration. With customizable PowerPoint templates, this resource equips you with the tools needed to analyze and present your findings effectively, making it an indispensable asset for any business strategist.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 29-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
Rogers' Five Factors is a product-focused framework for analyzing the diffusion and adoption of innovations. Developed by Everett Rogers, this framework identifies 5 key product attributes that significantly influence the rate of innovation adoption: Relative Advantage, Compatibility, Complexity, Trialability, and Observability. This document provides a comprehensive overview of Rogers' Five Factors, including detailed explanations, case examples, and customizable PowerPoint templates. It is designed for professionals seeking to enhance their understanding of innovation diffusion and improve their strategic approach to product adoption, all presented in a McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality format (consulting-grade; not affiliated).
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Product Managers seeking to understand the dynamics of innovation adoption
• Marketing Teams aiming to enhance product launch strategies
• Business Analysts focused on consumer behavior and market trends
• Consultants advising clients on innovation strategies
• Executives looking to drive product adoption within their organizations
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During product development phases to assess potential adoption barriers
• In marketing strategy sessions to refine messaging based on consumer perceptions
• When conducting workshops on innovation management and diffusion strategies
• For presentations aimed at stakeholders to illustrate the importance of product attributes in adoption
Learning Objectives
• Define Rogers' Five Factors and their relevance to innovation adoption
• Analyze the impact of Relative Advantage on consumer decision-making
• Evaluate the role of Compatibility in aligning new products with existing consumer values
• Assess the Complexity of innovations and strategies to mitigate perceived difficulties
• Develop Trialability strategies to encourage consumer experimentation
• Enhance Observability to improve product visibility and encourage adoption
Table of Contents
• Overview (page 4)
• Rogers' Five Factors (page 9)
• Case Example (page 17)
• Summary (page 21)
• Templates (page 24)
Primary Topics Covered
• Relative Advantage - The degree to which a product is perceived as better than the one it replaces, influencing adoption rates.
• Compatibility - The extent to which a product aligns with existing values and experiences, facilitating acceptance.
• Complexity - The perceived difficulty of understanding and using a product, which can hinder adoption.
• Trialability - The ability to experiment with a product on a limited basis, reducing uncertainty for potential adopters.
• Observability - The visibility of a product's usage and benefits, which can encourage others to adopt it.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• PowerPoint templates for analyzing each of Rogers' Five Factors
• Case study examples illustrating the application of the framework
• Worksheets for assessing product attributes and their impact on adoption
• Presentation slides summarizing key insights and findings
• Customizable frameworks for strategic planning sessions
Slide Highlights
• Diagram illustrating the relationship between Rogers' Five Factors and innovation adoption
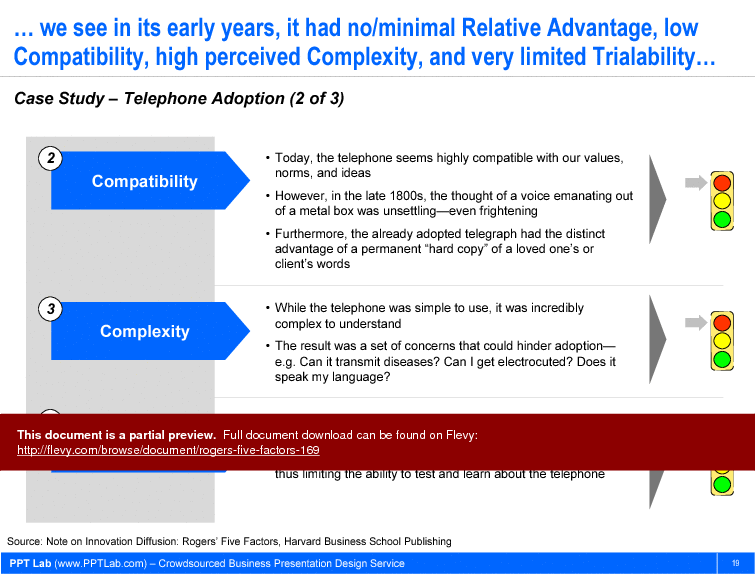
• Case study slide detailing the slow adoption of the telephone and the factors influencing it
• Visual representation of the Product Adoption Lifecycle compared to Rogers' Five Factors
• Summary slide encapsulating the importance of each factor in driving adoption
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Rogers' Five Factors (30 minutes)
• Overview of the framework and its significance
• Discussion of each factor and its implications for product adoption
Group Analysis Session (60 minutes)
• Breakout groups to evaluate a product using Rogers' Five Factors
• Presentation of findings and group discussion
Case Study Review (30 minutes)
• Examination of the telephone adoption case
• Insights on how the Five Factors influenced its market penetration
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the templates to reflect specific product attributes relevant to your analysis
• Adjust case study examples to align with your industry or market context
• Incorporate company-specific data to enhance the relevance of the findings
Secondary Topics Covered
• Consumer Adoption Lifecycle and its relationship with Rogers' Five Factors
• Strategies for enhancing product visibility and consumer engagement
• The role of marketing in shaping perceptions of Relative Advantage
• Techniques for reducing Complexity through user education
FAQ
What are Rogers' Five Factors?
Rogers' Five Factors are Relative Advantage, Compatibility, Complexity, Trialability, and Observability, which influence the rate of innovation adoption.
How can I apply this framework to my product?
Use the framework to assess each factor's impact on your product, identifying strengths and areas for improvement to enhance adoption.
What is the significance of Relative Advantage?
Relative Advantage measures how much better a product is perceived compared to existing alternatives, directly affecting its adoption rate.
Why is Compatibility important?
Compatibility ensures that a new product aligns with existing consumer values and experiences, making it easier for potential adopters to accept.
How does Complexity affect adoption?
Higher perceived Complexity can deter consumers from adopting a product, emphasizing the need for effective education and support.
What role does Trialability play?
Trialability allows consumers to test a product before full commitment, reducing uncertainty and increasing the likelihood of adoption.
How can Observability influence adoption rates?
Products that are easily observable can encourage others to adopt them, as visible benefits can create social proof.
Can I customize the templates provided?
Yes, the templates are designed to be customizable to fit your specific product analysis and presentation needs.
What is the Consumer Adoption Lifecycle?
The Consumer Adoption Lifecycle describes the stages consumers go through when adopting a new product, complementing the insights from Rogers' Five Factors.
Glossary
• Relative Advantage - The perceived benefit of a new product over its predecessor.
• Compatibility - The alignment of a new product with existing values and experiences.
• Complexity - The perceived difficulty of understanding and using a new product.
• Trialability - The ability to test a product on a limited basis before full adoption.
• Observability - The visibility of a product's use and benefits to potential adopters.
• Consumer Adoption Lifecycle - A model describing the stages of consumer adoption of new products.
• Innovation Diffusion - The process by which new ideas and products spread within a market.
• Market Penetration - The extent to which a product is recognized and used within a market.
• Perceived Characteristics - Attributes of a product as viewed by potential consumers.
• Social Proof - The tendency of individuals to conform to the actions of others in their social group.
• Product Attributes - Features or characteristics of a product that influence consumer decisions.
• Market Trends - Patterns and tendencies in consumer behavior and preferences over time.
• Stakeholder Engagement - The involvement of various parties in the decision-making process regarding a product.
• Strategic Planning - The process of defining a strategy or direction for a business or product.
• Consumer Behavior - The study of how individuals make decisions to spend their resources on consumption-related items.
• Innovation Management - The discipline of managing processes in innovation.
• Product Design - The process of creating a new product to be sold by a business to its customers.
• Marketing Strategy - A plan for reaching potential consumers and turning them into customers of the product or service.
• User Education - Providing information and training to consumers to help them understand and use a product effectively.
• Market Research - The action or activity of gathering information about consumers' needs and preferences.
PRODUCT STRATEGY PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Product Strategy, Product Launch Strategy, Product Adoption PowerPoint Slides: Rogers' Five Factors PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, PPT Lab