TPM: Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + Zip archive file (ZIP) 175 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Provides a framework for sustaining equipment performance through the practice of Autonomous Maintenance.
- Provides step-by-step guidance on the implementation of Autonomous Maintenance.
- Provides guidance on how to apply TPM tools such activity boards and one-point lessons.
TPM PPT DESCRIPTION
Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) is one of the most important building blocks in any Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) program. Autonomous Maintenance refers to TPM activities that involve operators in maintaining their own equipment, independent of the maintenance department.
One of the basic principles of TPM is that operators are the first line of defense against unplanned equipment downtime. Operators and others in daily contact with equipment can use their knowledge and familiarity with operating conditions to predict and prevent breakdowns and other equipment-related losses. They do this through regular cleaning and inspection of equipment, and through team-based autonomous. maintenance activities that tackle equipment-related problems.
Activities in an Autonomous Maintenance program include: daily inspections, lubrication, parts replacement, simple repairs, abnormality detection and precision checks.
The goals of the Autonomous Maintenance program are to prevent equipment deterioration, restore equipment to its ideal state, and establish basic conditions needed to keep equipment well maintained.
Developed by our JIPM-certified TPM instructor, this Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) PPT presentation is packed with diagrams, examples and practical tips and can be used to train shopfloor staff participating in autonomous maintenance activities.
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This training package includes:
1. Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) PPT training presentation (PowerPoint format)
2. The Seven Steps of Autonomous Maintenance poster (PDF format, in color and monochrome, printable in A3 size)
3. Autonomous Maintenance Framework poster (PDF format, in color and monochrome, printable in A3 size)
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Understand the key concepts of TPM and Autonomous Maintenance activities.
2. Learn how to implement the Autonomous Maintenance activities, step by step.
3. Learn how to use activity boards, meetings and one-point lessons to promote TPM goals.
4. Understand the critical success factors in sustaining Autonomous Maintenance activities on the shopfloor.
CONTENTS
1. Overview of TPM
• Common Features of Workplaces with Poor TPM Implementation
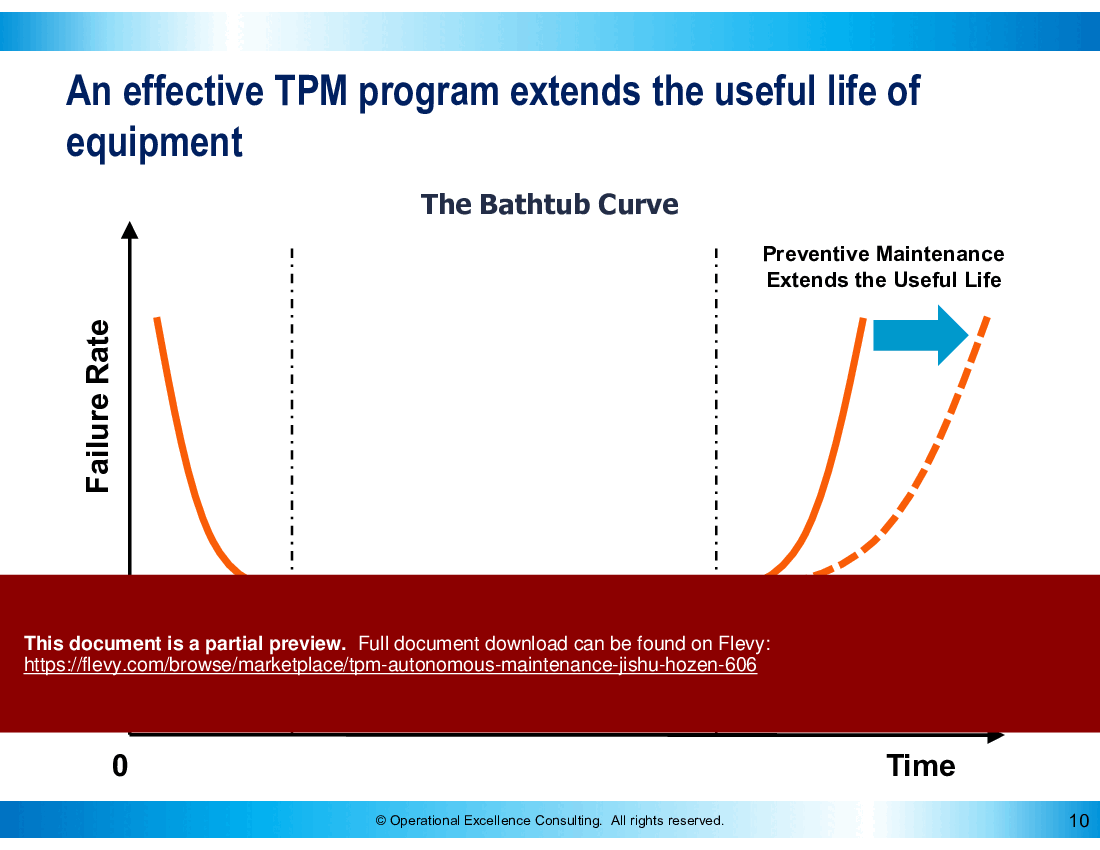
• Machine Failures Have Many Hidden Causes
• What is TPM?
• TPM Principles
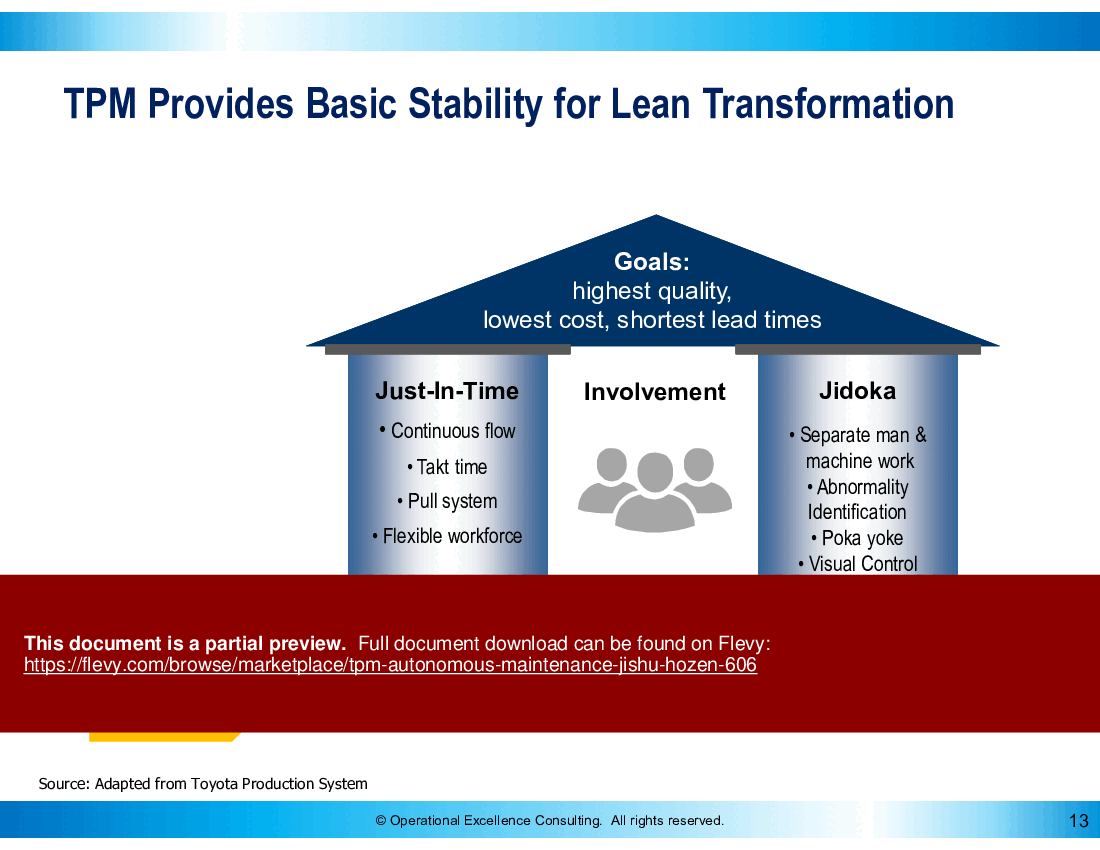
• TPM Provides a Basic Foundation for Lean Transformation
• TPM Eliminates/Reduces Waste
• Why Is TPM Important?
• TPM Goals
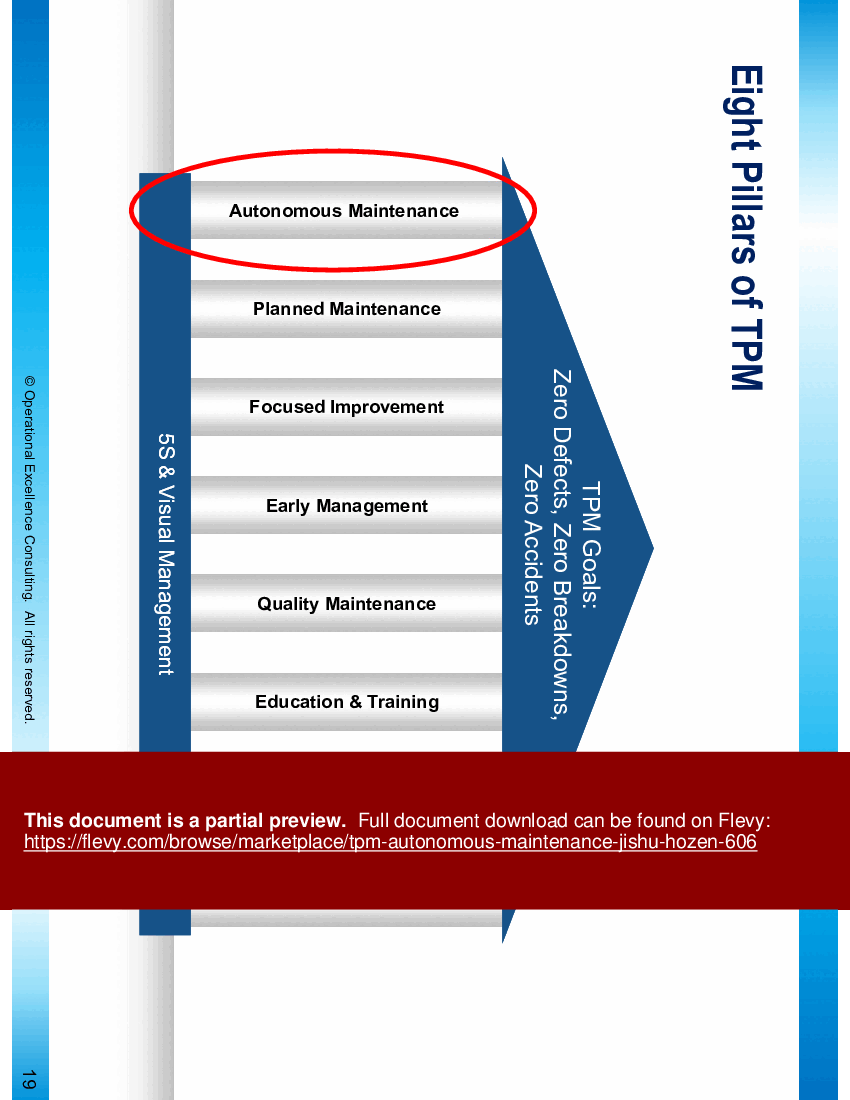
• Eight Pillars of TPM
• TPM Benefits
2. Introduction to AM
• What is AM?
• What AM is Not
• AM is a Paradigm Shift
• AM Facilitates a Culture Change
• Characteristics of AM Programs
• Goals of AM
• Natural & Forced Deterioration
• AM Approach
3. Tools of AM
• 3 Key Tools for AM
• Activity Board
• Examples of Activity Board
• What is One-Point Lesson?
• 3 Purposes of One-Point Lesson
• Philosophy of One-Point Lesson
• One-Point Lessons as a Cascading Tool
• Types of One-Point Lessons
• Examples of One-Point Lessons
• Four Equipment-related Skills for Operators
4. How to Implement the Seven Steps of AM: The Step by Step Approach
• 7 Steps of AM
• Step 1: Clean & Inspect
• Step 2: Eliminate problem sources and inaccessible areas
• Step 3: Draw up cleaning and lubricating standards
• Step 4: Conduct general inspections
• Step 5: Conduct autonomous inspections
• Step 6: Standardize through visual workplace management
• Step 7: Implement autonomous equipment management
5. Sustaining AM
• How to Sustain AM?
*Note: The Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance (JIPM) is a nonprofit research, consulting, and educational organization that helps companies increase organizational efficiency and profitability through improved maintenance of manufacturing equipment, processes, and facilities. The JIPM is the sponsoring organization for the TPM Excellence Award, awarded annually to recognize excellence in company-wide maintenance systems. Based in Japan, JIPM is the innovator of methodologies that have been implemented around the world.
The presentation highlights the importance of activity boards and regular team meetings in driving continuous improvement. It also includes practical tips for inspections and lubrication to ensure optimal equipment performance.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 175-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation on Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) is designed to empower operators with the skills and knowledge necessary for effective equipment care. Developed by a JIPM-certified TPM instructor, it outlines a structured approach to implementing Autonomous Maintenance through 7 key steps. By leveraging this presentation, organizations can enhance equipment reliability, reduce downtime, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. The content includes practical tools, templates, and best practices that facilitate the transition to a proactive maintenance environment.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Operations Managers overseeing maintenance teams
• Production Supervisors responsible for equipment performance
• Continuous Improvement Leaders focused on TPM initiatives
• Training Coordinators developing skill-building programs
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During TPM training sessions for operators
• When launching or revitalizing Autonomous Maintenance programs
• For workshops aimed at improving equipment reliability and operator engagement
Learning Objectives
• Understand the fundamental principles and concepts of TPM and AM activities
• Gain proficiency in measuring, auditing, and evaluating the effectiveness of AM activities
• Learn the step-by-step process for implementing AM activities, including the use of activity boards and one-point lessons
• Identify critical success factors for sustaining AM activities on the shop floor
Table of Contents
• Key Concepts & Principles of TPM and AM Activities (page 3)
• Core Practices of AM: Cleaning, Inspection, Containment & Lubrication (page 41)
• Key Tools of AM Activities (page 57)
• The 7 Steps of AM (page 80)
• Measuring & Auditing AM Activities (page 157)
• JIPM TPM Excellence Criteria for AM (page 163)
• Sustaining AM (page 167)
Primary Topics Covered
• Key Concepts of TPM and AM - Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) aims to maximize equipment effectiveness through employee involvement and proactive maintenance practices.
• Core Practices of AM - Focus on cleaning, inspection, lubrication, and containment to maintain optimal equipment conditions and prevent deterioration.
• Tools for AM Activities - Utilize activity boards, meetings, and one-point lessons to facilitate team engagement and knowledge sharing.
• The 7 Steps of AM - A structured approach including cleaning, eliminating problem sources, developing standards, training, conducting inspections, visual management, and equipment management.
• Measuring AM Effectiveness - Metrics such as OEE, defect rates, and operator skills to evaluate the success of AM initiatives.
• JIPM TPM Excellence Criteria - Standards for assessing the implementation and effectiveness of Autonomous Maintenance practices.
• Sustaining AM - Strategies for maintaining momentum in AM initiatives through leadership, training, and continuous improvement.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Activity boards for visual management of AM tasks
• One-point lesson templates for knowledge sharing among operators
• Checklists for cleaning, inspection, and lubrication standards
• Audit checklists for measuring AM implementation effectiveness
• Training materials for general inspection skills
• Documentation templates for tracking maintenance activities
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the 7 Steps of Autonomous Maintenance
• Visual examples of activity boards and one-point lessons
• Key metrics for evaluating AM success
• JIPM TPM Excellence criteria for AM implementation
• Strategies for sustaining AM initiatives
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Autonomous Maintenance (30 minutes)
• Overview of TPM and AM principles
• Discussion on the importance of operator involvement
Step-by-Step Implementation (90 minutes)
• Break down the 7 steps of AM
• Group activities to develop cleaning and lubrication standards
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement (60 minutes)
• Review key metrics for AM effectiveness
• Brainstorm strategies for sustaining AM initiatives
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the presentation to reflect specific equipment and operational contexts
• Adjust training materials to align with the skill levels of operators
• Incorporate company-specific examples and case studies to enhance relevance
• Modify checklists and templates to fit organizational standards and practices
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of leadership in driving TPM initiatives
• Techniques for effective visual management in the workplace
• Strategies for fostering a culture of continuous improvement
• The importance of safety in maintenance activities
• Integration of AM practices with other TPM pillars
Topic FAQ
What are the core steps of Autonomous Maintenance and how do they progress?
Autonomous Maintenance follows a structured seven-step progression starting with cleaning and inspection, eliminating problem sources, creating cleaning and lubrication standards, conducting general inspections, implementing autonomous inspections, standardizing via visual workplace management, and implementing autonomous equipment management. These are presented as the 7 Steps of AM.What tools support operator-led AM activities on the shop floor?
Core tools include activity boards for visual management, one-point lesson templates for short practical training, checklists for cleaning/inspection/lubrication, audit checklists to measure implementation, and documentation templates to track maintenance activities. These tools are described in the AM tools section and deliverables.How can I measure the effectiveness of my Autonomous Maintenance program?
Effectiveness is measured using metrics such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), defect rates, counts of tags raised and resolved, and operator skill assessments. The presentation includes guidance on measuring and auditing AM activities and references OEE and operator skills as key metrics.What role does visual management play in sustaining AM activities?
Visual management standardizes work, communicates status, and makes deviations visible, supporting autonomous inspections and daily task tracking. Practical examples include activity boards and visual workplace management used to standardize AM tasks and sustain operator engagement on the shop floor.What should I look for when buying an AM training package for my plant?
Look for step-by-step implementation guidance covering the 7 Steps, practical shop-floor tools (activity boards, one-point lessons), measurable audit criteria, customization guidance for equipment contexts, and supporting printables. Flevy's TPM: Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) lists these elements and is delivered as a 175-slide PPT with supplemental posters.How long should a typical AM workshop be and what agenda items are practical?
A practical workshop can run about 180 minutes (3 hours) using a suggested agenda: a 30-minute TPM/AM introduction, 90 minutes breaking down the 7 Steps with group development of standards, and 60 minutes on measuring AM success and sustaining initiatives, as outlined in the workshop agenda.If I need to start AM after a merger, what should operators focus on first?
Begin with Step 1: Clean & Inspect to restore equipment to ideal condition and reveal hidden issues, then develop cleaning and lubricating standards and introduce simple documentation and one-point lessons to embed practices. The approach starts explicitly with cleaning and inspection.How can training coordinators tailor AM training for operators with different skill levels?
Tailor content by aligning examples to specific equipment, adjusting the complexity of one-point lessons, using activity boards for clear visual tasks, and printing the provided AM posters in A3 for shop-floor reference. The package includes one-point lesson templates and A3-printable posters.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is Autonomous Maintenance?
Autonomous Maintenance is a proactive maintenance strategy where operators take ownership of routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubrication, and inspection to enhance equipment reliability.
How does AM benefit operators?
AM empowers operators by increasing their knowledge of equipment, fostering a sense of ownership, and enabling them to identify and address issues before they escalate into failures.
What are the key steps in implementing AM?
The key steps include cleaning and inspecting equipment, eliminating problem sources, developing cleaning and lubrication standards, conducting training, performing autonomous inspections, standardizing through visual management, and implementing autonomous equipment management.
How can we measure the effectiveness of AM?
Effectiveness can be measured through various metrics such as Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), defect rates, the number of tags raised and resolved, and operator skill assessments.
What tools can support AM activities?
Activity boards, one-point lessons, checklists, and audit templates are essential tools that facilitate the implementation and monitoring of AM activities.
How do we sustain AM initiatives?
Sustaining AM requires active leadership, continuous training, regular audits, sharing success stories, and incorporating AM practices into daily operations.
What is the role of visual management in AM?
Visual management helps standardize processes, track progress, and communicate important information effectively, making it easier for operators to perform their tasks.
How can we ensure operator engagement in AM?
Engagement can be fostered through training, recognition of contributions, and involving operators in decision-making processes related to maintenance activities.
Glossary
• Autonomous Maintenance (AM) - Maintenance performed by operators to ensure equipment reliability.
• Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) - A holistic approach to equipment maintenance that involves all employees.
• Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) - A measure of how well a manufacturing operation is utilized compared to its full potential.
• One-Point Lesson - A short, focused training tool that addresses a specific topic related to equipment maintenance.
• Activity Board - A visual management tool used to track tasks and progress in AM activities.
• Cleaning Standards - Established guidelines for maintaining cleanliness and lubrication of equipment.
• Inspection Skills Training - Training programs designed to enhance operators' ability to identify equipment issues.
• JIPM - Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance, an organization that promotes TPM practices.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to improve products, services, or processes.
• Visual Management - Techniques used to make the status of work processes visible and understandable.
• Maintenance Tags - Labels used to identify equipment issues that require attention.
• Skill Matrix - A tool used to assess and track the skills of operators in relation to maintenance tasks.
• 5S - A methodology for organizing and managing the workspace to improve efficiency and safety.
Source: Best Practices in TPM, Jishu Hozen PowerPoint Slides: TPM: Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen) PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Operational Excellence Consulting