Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) - 2 Day Presentation (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) + Zip archive file (ZIP) 208 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Improve reliability of plant & equipment
- Measure the machine performance losses and understand better
- Introduce autonomous maintenance
TPM PPT DESCRIPTION
Reliability Centered Maintenance and Total Productive Maintenance presentation is intended to help as a 2-day workshop material for Operations and Maintenance personnel.
This presentation consists of over 200 slides and comprises of the following:
Group Activity – Define Maintenance Excellence
Maintenance Excellence – Activity
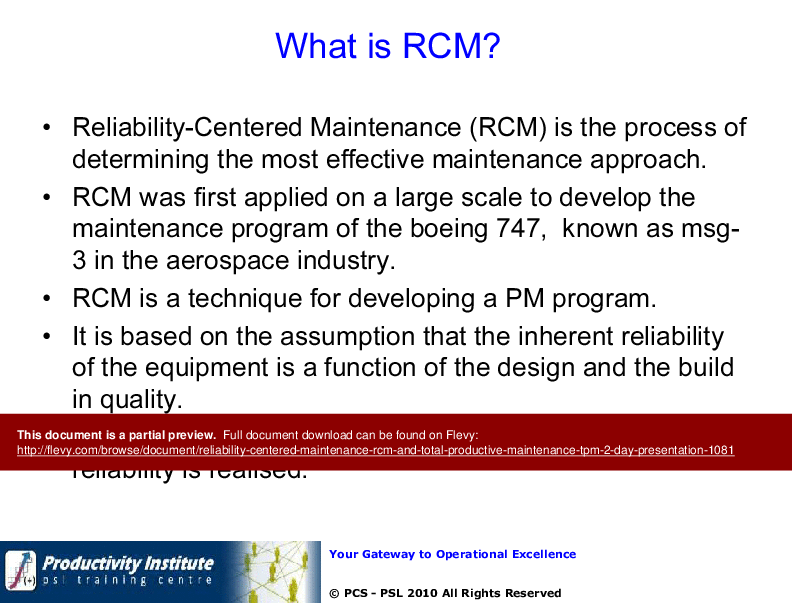
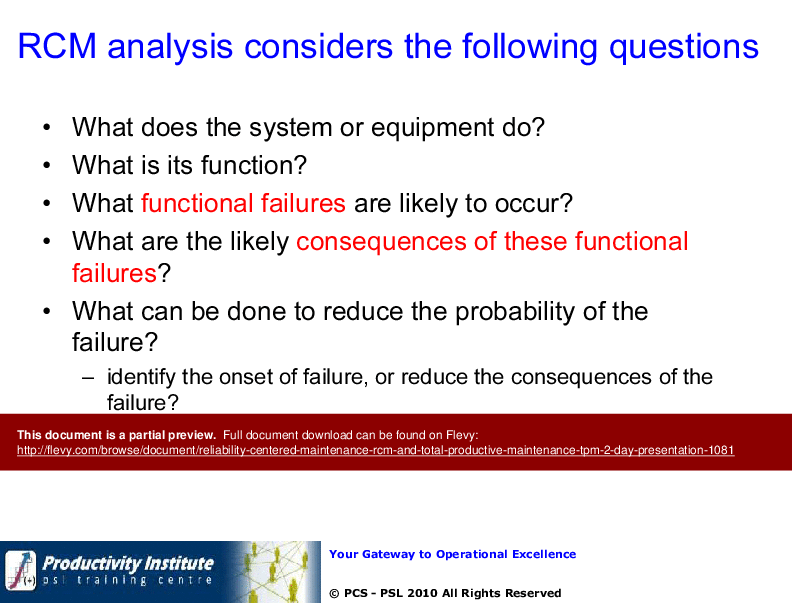
What is RCM?
Objective & goal of RCM
Techniques employed by RCM
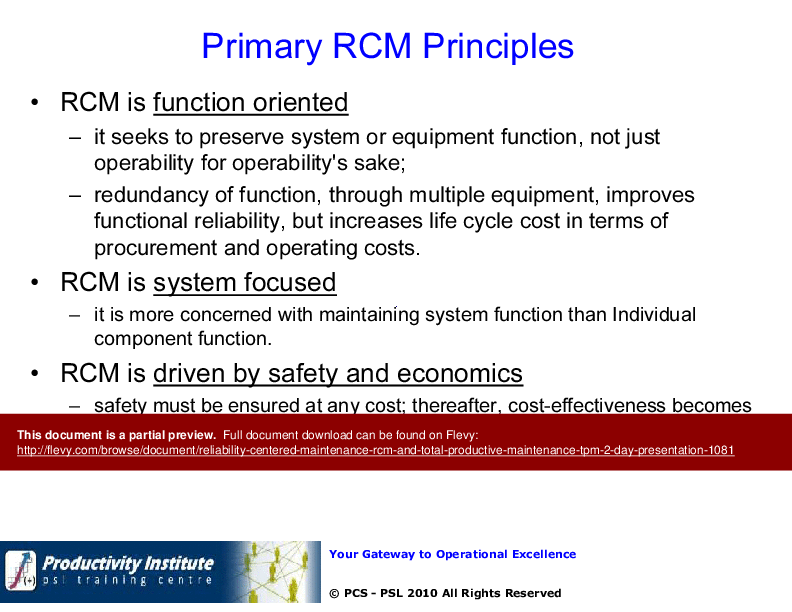
Primary RCM Principles
Types of Maintenance Tasks
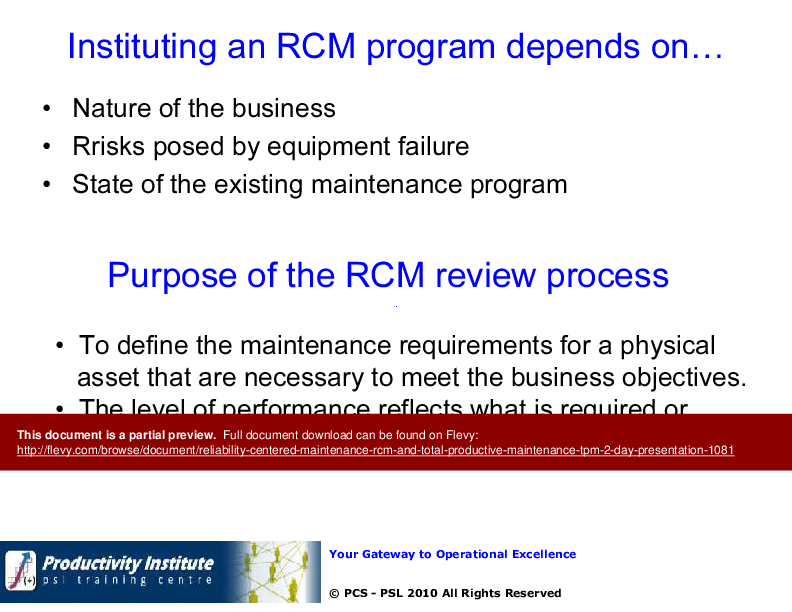
RCM Considerations, Applicability + Benefits
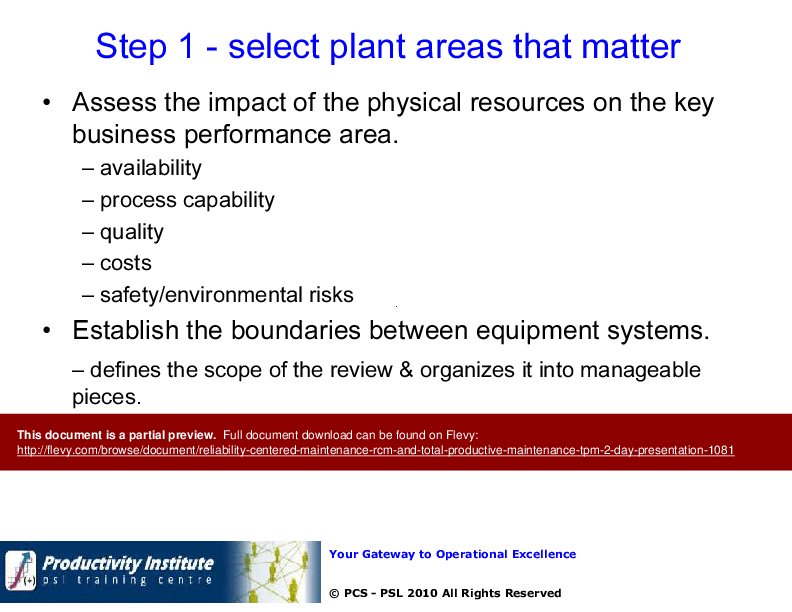
Steps in RCM Implementation
TPM vision, definition, origins, principles
8 Pillars of TPM
TPM Self-Assessment
Autonomous maintenance
Equipment & Process Improvement
Equipment Losses, Manpower & Material Losses
OEE – what it is & Calculations
Activity OEE Calculation
Other pillars of TPM
TPM Implementation – 12 steps
Benefits & OEE Tracker
Proactive Maintenance Analysis
Liaison with Ops, Communicating OEE,
Group Activity – OEE Communication/Importance
Ops. Skills, Cleanliness,
Monitoring – Gauges, Lubrication, Contamination, Vibration, One point Lesson
Activity – Maintenance / Operations
Analysis of Maintenance History, MTBF and its calculation
Activity – MTBF Calculation
Improving Equipment performance
FMEA, Types, Calculating RPN
Activity
HAZOP Hazard and Operability Analysis
Condition Monitoring Analysis / Predictive Maintenance / Condition Based Monitoring
Vibration Monitoring, Oil sampling & testing, Thermography, Types, Ultrasonics, Human Senses and Condition Monitoring Strategy
Activity -
Maintenance Excellence
Activity – Why equipment fails?
3 Contributors, Lubrication, Vibration and contamination
Proactive Maintenance – 6 big losses, OEE
Prioritization of equipment problems
Focused equipment & process Improvement
Cleaning, Inspection, Equipment tagging, CI
Maintenance Strategies – TPM or RCM? Or Other?
Activity: TPM vs RCM
Maintenance Excellence – making the difference
Activity: Using our senses
Eliminating lubrication issues, frequency, type, Mistake proofing, Standards, Visual management, Automation, daily Checks
Activity – Improving Lubrication Practices
Vibration Practices and improvement
Activity – Reducing Vibration
Contamination
Activity – Reducing Contamination
Operator Involvement – Check lists, visual controls
Also included with this document is a bonus zip of 41 Lean documents (includes templates, case studies, articles, posters, charts, and more).
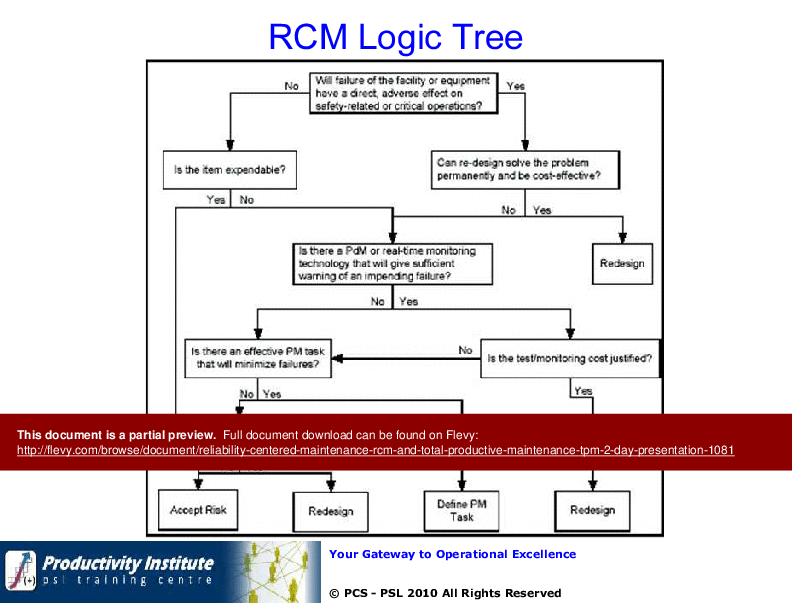
The presentation delves into the intricacies of RCM logic trees and the critical questions to consider during RCM analysis. It also emphasizes the importance of optimizing tactics and programs to adapt to industry changes and economic conditions.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 208-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This two-day presentation on Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is designed to equip participants with essential strategies for enhancing maintenance operations. Developed by a certified LSS Master Black Belt with extensive global training experience, this workshop focuses on practical applications of RCM and TPM principles to improve equipment reliability, reduce downtime, and optimize maintenance costs. Attendees will learn to implement systematic maintenance strategies that align with organizational goals, ensuring operational excellence.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Maintenance Managers and Supervisors seeking to enhance their team's effectiveness
• Operations Managers focused on improving equipment reliability and performance
• Quality Assurance Professionals aiming to reduce defects and downtime
• Continuous Improvement Leaders interested in integrating RCM and TPM methodologies
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During organizational transitions to establish robust maintenance frameworks
• When implementing new equipment or processes that require maintenance strategies
• For teams aiming to improve Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) metrics
Learning Objectives
• Define Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) principles
• Identify and implement effective maintenance strategies tailored to organizational needs
• Analyze maintenance history using metrics such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
• Develop proactive maintenance plans that incorporate predictive and preventive techniques
• Establish communication protocols for liaising between maintenance and operations teams
• Conduct assessments to measure and improve maintenance excellence within the organization
Table of Contents
• Introduction to RCM and TPM (page 3)
• Objectives and Goals of RCM (page 5)
• Techniques Employed by RCM (page 7)
• Primary Principles of RCM (page 9)
• Types of Maintenance Tasks (page 11)
• Steps in RCM Implementation (page 13)
• Overview of TPM (page 15)
• Eight Pillars of TPM (page 17)
• OEE Calculation and Importance (page 19)
• Maintenance Excellence Assessment (page 21)
• Group Activities and Workshops (page 23)
Primary Topics Covered
• Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) - A systematic approach to identifying maintenance needs based on equipment functions and failure modes, prioritizing safety and economic considerations.
• Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) - A holistic approach that engages all employees in maintaining equipment to achieve zero defects, accidents, and downtime.
• Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) - A key performance metric that combines availability, performance, and quality to assess equipment efficiency.
• Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) - A critical reliability metric that helps in planning maintenance activities and improving equipment uptime.
• Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) - A structured approach to identifying potential equipment failures and their impacts, guiding proactive maintenance strategies.
• Condition Monitoring Techniques - Methods such as vibration analysis, oil sampling, and thermography to assess equipment health and predict failures.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• RCM Implementation Plan Template for systematic maintenance strategy development
• TPM Self-Assessment Tool to evaluate current maintenance practices
• OEE Calculation Worksheet to track and analyze equipment performance
• FMEA Chart Template for identifying and mitigating potential failure modes
• Condition Monitoring Checklist to ensure regular assessment of equipment health
• Maintenance Excellence Assessment Framework to measure organizational performance
Slide Highlights
• Overview of RCM principles emphasizing function-oriented and safety-driven approaches
• Detailed explanation of TPM's eight pillars and their impact on operational efficiency
• Visual representation of OEE metrics and their calculation methods
• Group activity slides designed to foster collaboration and practical application of concepts
• Case studies illustrating successful RCM and TPM implementations in various industries
Potential Workshop Agenda
Day 1:
Introduction to RCM and TPM (90 minutes)
• Define RCM and TPM principles
• Discuss objectives and goals of RCM
• Group activity: Define Maintenance Excellence
Steps in RCM Implementation (90 minutes)
• Identify key functions and productivity goals
• Analyze plausible functional failures
• Develop maintenance tactics
Day 2:
Condition Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance (90 minutes)
• Discuss condition monitoring techniques
• Group activity: Develop improvement strategies
TPM Implementation Steps (90 minutes)
• Review the 12 steps for effective TPM implementation
• Conduct a self-assessment for TPM readiness
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the RCM and TPM frameworks to align with specific organizational needs and goals
• Modify assessment tools to reflect industry-specific metrics and performance indicators
• Adjust group activities to focus on relevant equipment and operational challenges
Secondary Topics Covered
• Proactive Maintenance Analysis and its significance
• Importance of operator involvement in maintenance practices
• Techniques for effective communication between maintenance and operations teams
• Strategies for continuous improvement in maintenance processes
• Safety and environmental management in maintenance operations
Topic FAQ
What are the main differences between Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)?
RCM is a function-oriented, safety- and failure-mode-driven approach that prioritizes maintenance tactics based on equipment functions and failure consequences. TPM is a holistic, workforce-engaging approach that aims to eliminate defects, accidents, and downtime through the involvement of all employees and the implementation of TPM’s eight pillars, as covered in the presentation.What are the typical steps in an RCM implementation process?
Typical RCM steps include assessing current maintenance practices, identifying key equipment functions, analyzing plausible functional failures, and developing tailored maintenance tactics. The presentation outlines these steps in a structured sequence under "Steps in RCM Implementation," with guidance beginning on page 13.How is Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) calculated and used to prioritize maintenance?
OEE combines availability, performance, and quality metrics to quantify equipment efficiency. Organizations use OEE to identify major loss categories and prioritize improvement actions that boost uptime and throughput; the deck includes an OEE Calculation Worksheet and OEE explanation on page 19.Which condition monitoring techniques are commonly applied for predictive maintenance?
Common condition monitoring techniques include vibration analysis, oil sampling and testing, thermography, ultrasonics, and structured use of human senses. These methods support condition-based monitoring strategies and are summarized in the presentation’s Condition Monitoring section and associated Condition Monitoring Checklist.How should I choose a commercial RCM/TPM training pack for my team?
Match the pack to your audience (shop floor to directors), workshop length, and required tools; look for content covering RCM logic, TPM pillars, OEE, MTBF, FMEA, and condition monitoring. Consider packs that include facilitator materials and templates; this presentation is a two-day deck with 208 slides and a bonus ZIP of 41 Lean documents.What deliverables and templates are typical in a maintenance workshop package?
A practical package includes implementation plan templates, self-assessment tools, calculation worksheets, FMEA charts, checklists, and assessment frameworks. For example, Flevy’s Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) - 2 Day Presentation lists an RCM Implementation Plan Template, TPM Self-Assessment, OEE Calculation Worksheet, and FMEA Chart Template.I need to reduce downtime after a merger—what framework combination should I use?
Use RCM to identify critical equipment functions and failure modes, apply FMEA to prioritize risks, and deploy TPM practices to engage operators in autonomous maintenance. Combine MTBF analysis and OEE tracking to target biggest losses; the presentation includes MTBF calculation activities and TPM self-assessment tools for these steps.Are prebuilt maintenance templates and checklists worth buying for in-house improvement work?
Prebuilt templates can standardize assessments, speed workshop preparation, and provide calculation-ready tools for MTBF and OEE analysis. The referenced presentation bundles such assets, including an RCM Implementation Plan Template and a bonus ZIP of 41 Lean documents, which can reduce setup time for training and audits.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)?
RCM is a systematic approach to determining the most effective maintenance strategies based on equipment functions, failure modes, and safety considerations.
How does Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) differ from traditional maintenance?
TPM involves all employees in maintenance activities, focusing on proactive measures to eliminate defects, accidents, and downtime, rather than reactive fixes.
What is Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)?
OEE is a performance metric that measures the efficiency of equipment by combining availability, performance, and quality metrics.
How can I implement RCM in my organization?
Start by assessing current maintenance practices, identifying critical equipment, and developing a tailored RCM strategy that aligns with organizational goals.
What are the benefits of using FMEA?
FMEA helps identify potential failure modes, assess their impact, and develop strategies to mitigate risks, ultimately improving equipment reliability.
How often should condition monitoring be performed?
Condition monitoring frequency should be determined based on equipment usage, operational conditions, and historical performance data.
What role do operators play in TPM?
Operators are crucial in TPM as they are trained to perform basic maintenance tasks, monitor equipment conditions, and contribute to continuous improvement efforts.
What is the significance of MTBF?
MTBF is a key reliability metric that helps organizations plan maintenance activities, reduce downtime, and improve overall equipment performance.
How can I assess my organization's maintenance excellence?
Use the Maintenance Excellence Assessment tool provided in the workshop to evaluate current practices and identify areas for improvement.
Glossary
• Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) - A systematic approach to maintenance focused on equipment reliability and function.
• Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) - A maintenance philosophy that involves all employees in maintaining equipment to achieve operational excellence.
• Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) - A metric that combines availability, performance, and quality to assess equipment efficiency.
• Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) - A reliability metric that measures the average time between equipment failures.
• Failure Mode Effect Analysis (FMEA) - A structured approach to identifying potential failures and their impacts.
• Condition Monitoring - Techniques used to assess equipment health and predict failures.
• Proactive Maintenance - Maintenance strategies focused on preventing failures before they occur.
• Autonomous Maintenance - A TPM practice where operators take responsibility for basic maintenance tasks.
• Equipment Performance - A measure of how well equipment operates compared to its designed capabilities.
• Maintenance Excellence - The pursuit of optimal maintenance practices that enhance operational performance.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to enhance products, services, or processes.
• Safety Management - Practices aimed at ensuring safe operations and minimizing risks.
• Environmental Management - Strategies to minimize environmental impact during maintenance activities.
Source: Best Practices in TPM, Jishu Hozen, Reliability Centered Maintenance PowerPoint Slides: Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) - 2 Day Presentation PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, OpEx Academy NZ