Integrating Enterprise Performance and Risk Management (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + supplemental PDF 68 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Learn how to view enterprise and corporate performance management (EPM/CPM) as the seamless integration of managerial methods rather than as a process.
- Understand how to identify and differentiate strategic KPIs in a balanced scorecard and operational performance indicators in dashboards.
- Recognize the differences of the three categories of risks.
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
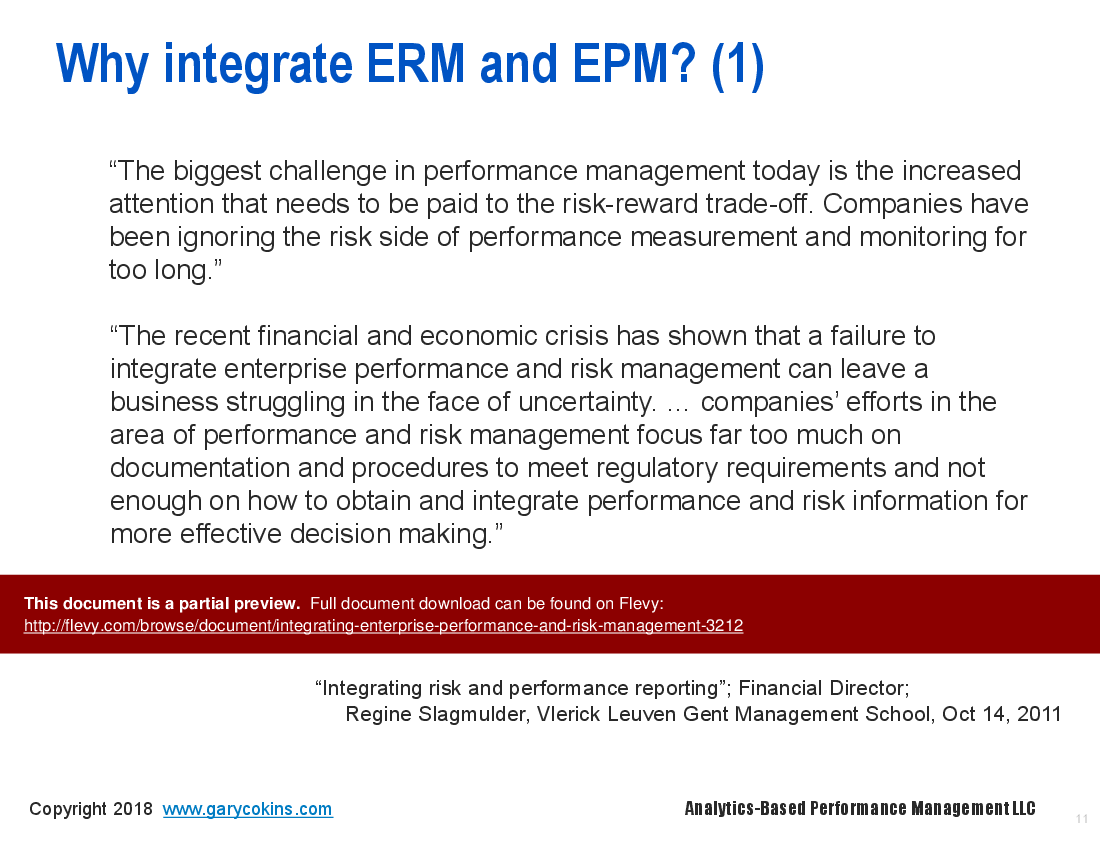
There is increasing attention regarding the "overlap" of enterprise risk management (ERM) and enterprise performance management (EPM). The former refers to key risk and control indicators (KRIs and KCIs) and the latter to key performance indicators (KPIs). How do they fit together and produce synergy?
The past decade has demonstrated that the initial ERM focus on identifying, monitoring, and avoiding potential threats was too narrow, and ERM programs ended up disconnected from the value creation cycle. More recently, executives are realizing that to actually improve organizational results, ERM must integrate risk, strategic planning, and enterprise performance management.
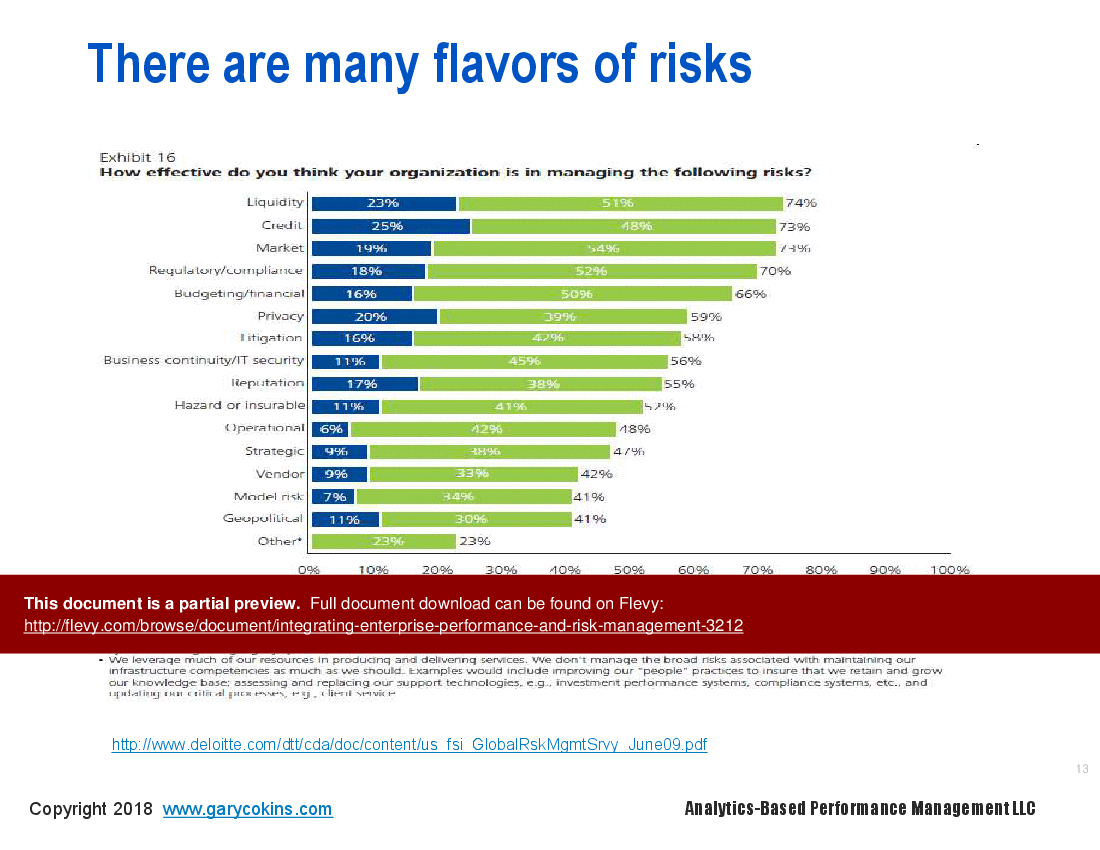
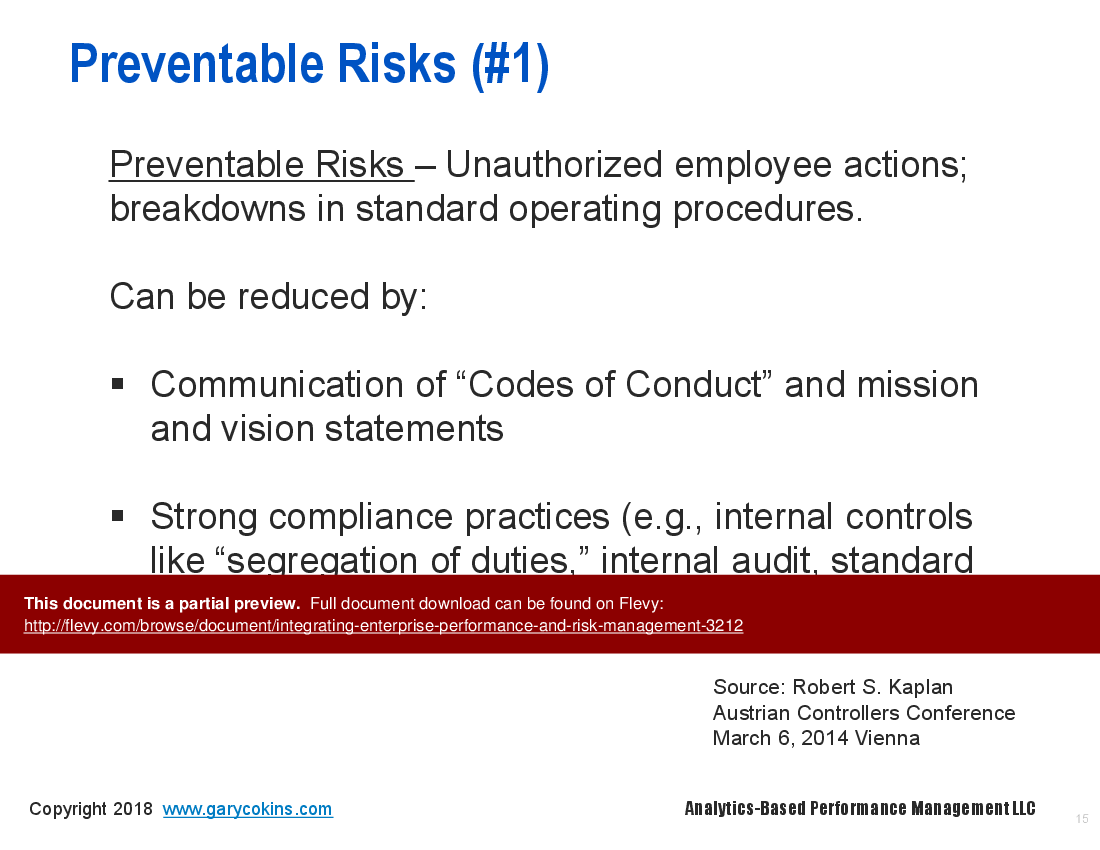
There is a need to manage three categories of risk: (1) preventable risks, (2) strategy execution risks, and (3) external risks.
How should an organization apply an enterprise risk-based performance management framework to match risk exposure with risk appetite? The framework is designed to help answer strategic questions such as "where do we want to go, how will we get there, and how's our progress?" Organizations struggle with how to integrate a risk perspective into key business decision-making processes, and how to overcome the common pitfalls of integrating risk and enterprise performance management.
Failure to integrate enterprise risk management (ERM) and enterprise performance management (EPM) has hidden costs that prevent organizations from fully delivering on their value creation potential. What are the warning signs and root causes of common obstacles to integrating ERM and performance management? These may include:
• lack of a common understanding among managers as to what enterprise performance management (EPM) is and what it accomplishes
• lack of tools that enable managers to effectively link strategy to operations
• lack of analysis capabilities to support risk-adjusted performance management
• inability of cross-functional teams to align their risk-taking behavior to corporate strategy and better collaborate
This presentation is ideal for managers who have struggled to integrate ERM and EPM into their decision support systems. It provides a compelling call to action for those looking to champion EPM initiatives.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 68-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation on Integrating Enterprise Performance and Risk Management is crafted by Gary Cokins, a recognized expert in the field with nearly 50 years of experience. It aims to equip corporate executives and managers with the knowledge to effectively integrate Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) and Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) frameworks. By leveraging analytics-based performance management, attendees will learn how to enhance decision-making processes, align strategic objectives with risk assessments, and ultimately drive shareholder value through informed risk-reward trade-offs.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives overseeing strategic planning and performance management
• Risk management professionals seeking to align ERM with EPM
• Financial analysts focused on integrating risk assessments into performance metrics
• Managers responsible for implementing performance improvement initiatives
• Consultants advising organizations on performance and risk integration
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to align risk and performance objectives
• In workshops aimed at improving decision-making frameworks
• When developing or revising corporate governance policies related to risk management
Learning Objectives
• Define Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) and its significance in organizational strategy
• Identify the benefits of integrating ERM and EPM for enhanced decision-making
• Analyze various types of risks and their impact on performance management
• Develop strategies for balancing risk exposure with organizational risk appetite
• Create actionable plans for integrating risk assessments into performance metrics
• Utilize scenario planning and budgeting as tools for effective risk management
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Enterprise Performance Management (page 4)
• Importance of Integrating ERM and EPM (page 11)
• Types of Risks in Performance Management (page 14)
• Strategies for Risk Mitigation (page 20)
• Balancing Risk Exposure with Risk Appetite (page 19)
• Case Studies of ERM and EPM Integration (page 24)
• Action Steps for Implementation (page 67)
Primary Topics Covered
• Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) - EPM encompasses the methodologies and tools used to manage and improve organizational performance, integrating analytics to support strategic objectives.
• Integration of ERM and EPM - The combination of ERM and EPM enhances decision-making by ensuring that risk considerations are embedded in performance assessments.
• Types of Risks - Understanding preventable, strategy execution, and external risks is crucial for effective performance management and risk mitigation.
• Risk Appetite - Organizations must align their risk exposure with their risk appetite to optimize financial returns while managing potential threats.
• Scenario Planning - Utilizing scenario planning allows organizations to stress-test strategies against potential risks and uncertainties.
• Actionable Implementation Steps - The presentation outlines specific actions for integrating ERM and EPM, including stakeholder education and rapid prototyping.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Framework for integrating ERM and EPM into decision-making processes
• Risk assessment grid for budgeting and resource allocation
• Scenario planning templates for strategic stress-testing
• Guidelines for developing a balanced scorecard that incorporates risk metrics
• Action plan templates for implementing integrated performance management strategies
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the integration framework for ERM and EPM
• Visual representation of the risk assessment grid
• Case studies illustrating successful ERM and EPM integration
• Key metrics for measuring performance and risk alignment
• Action steps for immediate implementation of strategies
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to EPM and ERM Integration (60 minutes)
• Overview of EPM and ERM concepts
• Discussion on the importance of integration
• Identification of key stakeholders
Risk Assessment and Scenario Planning (90 minutes)
• Introduction to risk types and their implications
• Hands-on session on creating a risk assessment grid
• Group exercise on scenario planning
Action Planning for Implementation (60 minutes)
• Development of actionable steps for integrating ERM and EPM
• Assigning roles and responsibilities for execution
• Establishing timelines and milestones for follow-up
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the risk assessment grid to reflect specific organizational risks and appetite
• Adjust scenario planning exercises to align with current strategic initiatives
• Incorporate company-specific metrics into the balanced scorecard framework
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of analytics in performance management
• Governance structures for effective risk management
• Communication strategies for stakeholder engagement
• Techniques for fostering a risk-aware organizational culture
Topic FAQ
What are the main components of integrating ERM and EPM in practice?
Integrating ERM and EPM embeds risk considerations into performance measurement by linking KRIs and KPIs, classifying risks (preventable, strategy execution, external), applying analytics to decision-making, and using tools such as scenario planning and a risk assessment grid to align performance with risk appetite and strategy, and by using a balanced scorecard framework.How does an organization apply risk appetite to performance management?
Risk appetite sets the acceptable level of risk when making strategic choices and allocating resources; it should be translated into operational thresholds and performance metrics so decision-makers can balance returns and risk exposure using tools such as a risk assessment grid to guide budgeting and resource decisions.What role does scenario planning play in risk-adjusted performance management?
Scenario planning is used to stress-test strategic options and budgets against potential external and execution risks, enabling organizations to evaluate alternative outcomes, quantify impacts on performance measures, and prepare contingency actions using scenario planning templates for strategic stress-testing.What should I look for when buying an ERM–EPM integration toolkit?
Buyers should seek an integration framework, explicit tools for linking KRIs to KPIs, a risk assessment grid for budgeting, scenario planning templates, balanced scorecard guidance, and implementation action-plan templates; Flevy's Integrating Enterprise Performance and Risk Management includes those specific deliverables.How long does a practical workshop to introduce ERM–EPM integration typically take?
A standard workshop agenda provided in the deck outlines a 60-minute introduction to concepts, a 90-minute risk assessment and scenario planning session, and a 60-minute action planning segment, totaling about a 3.5-hour facilitated session using the presentation’s materials.I need to include risk into my annual budgeting process—what steps should I take?
Start by identifying key risks affecting budget lines, map those risks to KPIs and KRIs, use a risk assessment grid to prioritize allocations, and run scenario-based budget stress tests to evaluate impacts; the presentation supplies a risk assessment grid and scenario planning templates to support these steps.How can organizations measure whether ERM and EPM integration is working?
Measure integration success by tracking improvements in decision-making quality, the degree to which performance metrics reflect risk exposures, and movement toward strategic targets and shareholder value; concretely, assess alignment between KPIs and KRIs and the use of integrated metrics in governance reviews.Are ready-made templates for ERM–EPM integration valuable for implementation?
Templates reduce design time and provide a repeatable structure for aligning risk and performance, helping with stakeholder education, rapid prototyping, and rollout; useful items include a framework for integration, risk assessment grids, scenario planning templates, and action plan templates.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the primary focus of this presentation?
The presentation focuses on integrating Enterprise Risk Management and Enterprise Performance Management to enhance decision-making and drive shareholder value.
Who will benefit most from this presentation?
Corporate executives, risk management professionals, and financial analysts will find the content particularly beneficial for aligning performance metrics with risk assessments.
How can organizations implement the strategies discussed?
Organizations can start by educating stakeholders, developing action plans, and utilizing scenario planning to integrate ERM and EPM effectively.
What types of risks are discussed?
The presentation covers preventable risks, strategy execution risks, and external risks, emphasizing their impact on organizational performance.
What tools are provided for integration?
Tools include risk assessment grids, scenario planning templates, and action plan frameworks to facilitate the integration of ERM and EPM.
How does risk appetite influence performance management?
Risk appetite determines the level of risk an organization is willing to accept, guiding decision-making and resource allocation in performance management.
What is scenario planning?
Scenario planning is a strategic tool used to anticipate potential risks and uncertainties, allowing organizations to stress-test their strategies.
How can organizations measure the success of integration?
Success can be measured through the effectiveness of decision-making processes, alignment of performance metrics with risk assessments, and overall shareholder value.
Glossary
• Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) - A framework for managing and improving organizational performance through analytics and strategic alignment.
• Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) - A systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that may affect an organization's objectives.
• Risk Appetite - The amount of risk an organization is willing to accept in pursuit of its objectives.
• Scenario Planning - A strategic planning method used to create flexible long-term plans based on varying future scenarios.
• Risk Assessment Grid - A tool used to evaluate risks based on their likelihood and impact on organizational objectives.
• Balanced Scorecard - A performance management tool that translates an organization’s strategic objectives into a set of performance measures.
• Preventable Risks - Risks that can be eliminated through effective management and compliance practices.
• Strategy Execution Risks - Risks associated with the execution of strategic initiatives aimed at achieving superior returns.
• External Risks - Risks arising from uncontrollable external factors that can impact organizational performance.
• Stakeholder Engagement - The process of involving individuals or groups who may be affected by or have an effect on an organization’s objectives.
• Action Plan - A detailed plan outlining actions needed to achieve specific goals or objectives.
• Governance Structure - The framework of rules, relationships, and processes that guide decision-making and accountability in an organization.
Source: Best Practices in Performance Management, Risk Management, Analytics PowerPoint Slides: Integrating Enterprise Performance and Risk Management PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Gary Cokins