Activity-Based Cost Management (ABC/M) (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) + supplemental PDF 101 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Learn what has caused interest in ABC/M and how an ABC/M model is designed.
- Learn how to calculate profit and loss statements for customers, Use ABC data for process improvement, and to perform "predictive accounting" for capacity-sensitive driver-based budgets / rolling financial forecasts, what-if analysis, and outsou
- Understand how to overcome implementation barriers to ABC/M such as behavioral resistance to change and fear of being measured and held accountable.
COST OPTIMIZATION PPT DESCRIPTION
Critics have claimed that traditional managerial accounting is at best useless and at worst dysfunctional and misleading. Today's general ledger and budgeted spending systems support departmental and "stovepipe" managerial philosophies. In contrast, activity-based costing (ABC) information supports process-based thinking. ABC is a key component of the increasingly popular enterprise and corporate performance management (EPM/CPM) systems.
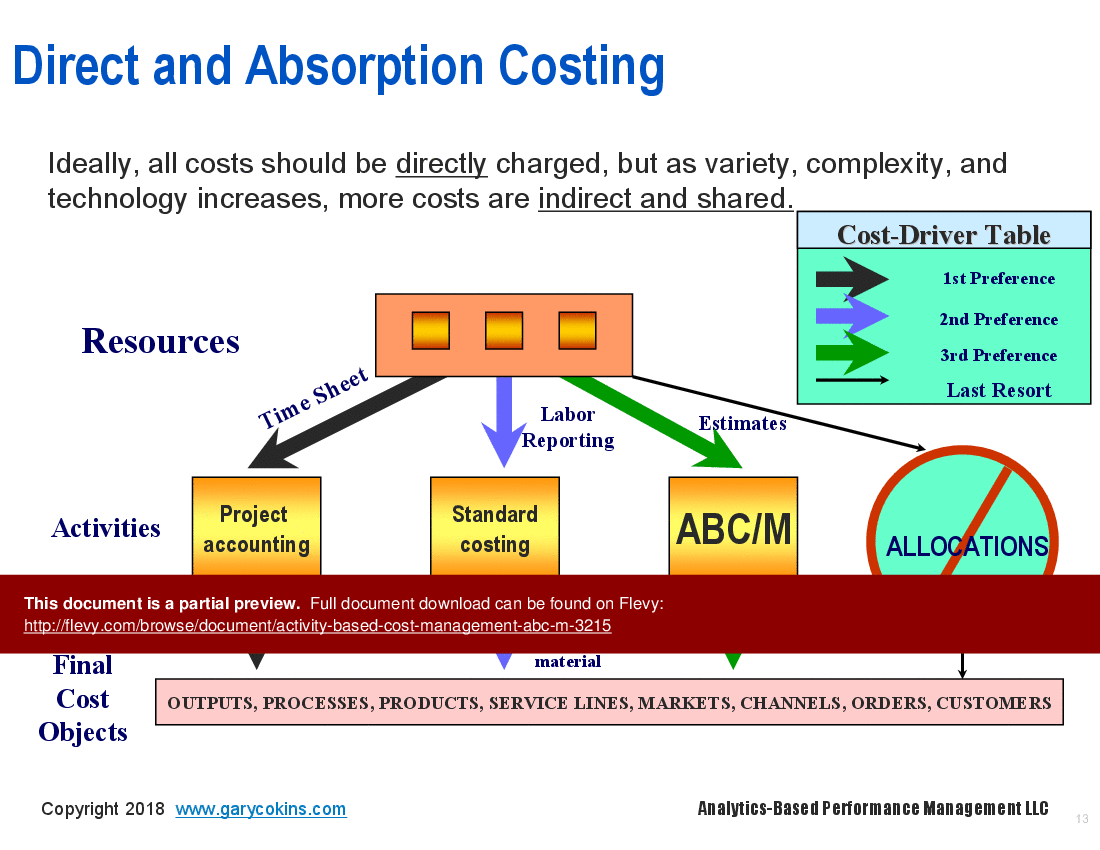
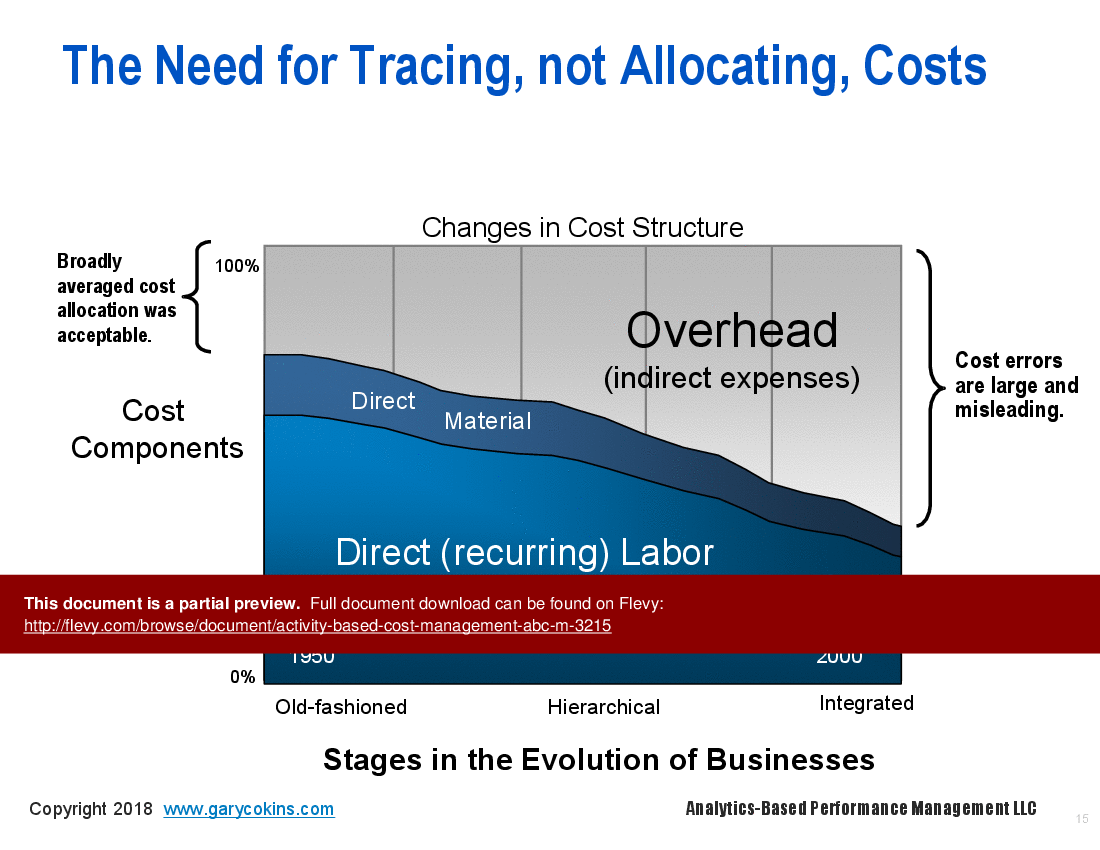
Cross-functional processes are now recognized as the integrating theme for how work gets done, how outputs are produced, and how customers get served. Only ABC can bring truly accurate fact-based measures and visibility to costs. ABC does not use broadly averaged cost allocations, but rather traces cost using cause-and-effect activity cost drivers. The resulting cost visibility informs manager about what things costs and more importantly why things have costs. ABC goes beyond product costing to also measure channel and customer profitability.
ABC also helps reduce costs and improve productivity by reporting per-unit costs that can be used as benchmarks and to monitors cost trends. ABC can also associate costs with value, quality, and waste, with their strategic importance, with their level of performance, and other "attributes" of work. All of this cost and trait data are further translated into which products, channels, customers or internal company-sustaining workforce staff cause and consume all of the in exactly what proportions.
Ultimately cost data is simply a means-to-ends where the ends are the decision-making of the organization. Today an emerging focus is to become a "learning organization." Unlike traditional accounting reports to which managers react by being happy or sad, ABC data makes them smarter!
This presentation is ideal for managers who have faced challenges in implementing strategic cost management using ABC principles. It also serves as a valuable resource for those looking to champion ABC initiatives within their organizations.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 101-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This Activity-Based Cost Management (ABC/M) presentation, developed by Gary Cokins, a recognized expert in enterprise performance management, provides a comprehensive overview of activity-based costing principles. It is designed for managers who seek to enhance strategic cost management through effective decision support systems. The presentation covers essential topics such as calculating product and service-line profitability, implementing ABC with rapid prototyping, and understanding customer profitability. By utilizing this management accounting framework, executives will be equipped to drive operational efficiency and optimize financial performance.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Finance and Accounting Managers seeking to improve cost management practices
• Operations Managers focused on enhancing process productivity
• Business Analysts aiming to integrate business analytics into decision-making
• Senior Executives looking to champion strategic cost management initiatives
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to align cost management with business objectives
• When introducing activity-based costing methodologies to finance teams
• In workshops aimed at improving profitability analysis and reporting
Learning Objectives
• Define activity-based costing (ABC) and its relevance in modern managerial accounting
• Calculate product and service-line profitability using ABC principles
• Implement ABC through rapid prototyping to enhance decision-making
• Analyze channel and customer profitability to identify cost drivers
• Differentiate between driver rate-based ABC and time-driven ABC (TDABC)
• Utilize operational ABC for process productivity improvement
• Develop predictive accounting practices, including driver-based budgeting and rolling forecasts
• Identify barriers to ABC adoption and strategies to overcome them
Table of Contents
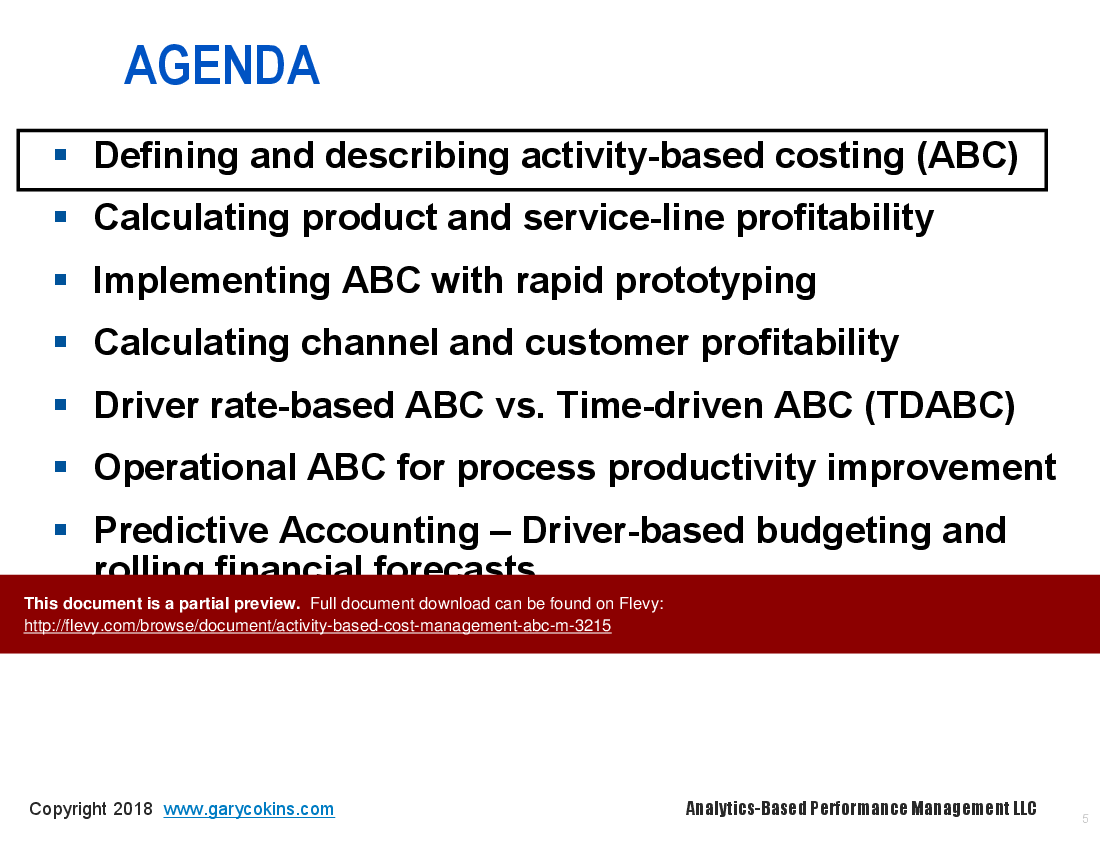
• Defining and Describing Activity-Based Costing (ABC) (page 5)
• Calculating Product and Service-Line Profitability (page 12)
• Implementing ABC with Rapid Prototyping (page 26)
• Calculating Channel and Customer Profitability (page 34)
• Driver Rate-Based ABC vs. Time-Driven ABC (TDABC) (page 54)
• Operational ABC for Process Productivity Improvement (page 56)
• Predictive Accounting – Driver-Based Budgeting and Rolling Financial Forecasts (page 76)
• Barriers Slowing the Adoption Rate of ABC (page 92)
Primary Topics Covered
• Activity-Based Costing (ABC) - A costing methodology that assigns costs to activities based on their use of resources, providing a more accurate reflection of costs associated with products and services.
• Profitability Analysis - Techniques for calculating profitability at the product, service, channel, and customer levels, enabling better decision-making.
• Rapid Prototyping - An iterative approach to implementing ABC that allows for quick adjustments and refinements, ensuring the system meets organizational needs.
• Predictive Accounting - A forward-looking approach that incorporates driver-based budgeting and rolling forecasts to enhance financial planning.
• Barriers to Adoption - Common challenges organizations face when implementing ABC, including technical, perception, and organizational behavior barriers.
• Cost Drivers - Factors that influence the cost of activities, essential for understanding and managing profitability.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• ABC implementation roadmap template for structured deployment
• Profitability analysis framework for product and service lines
• Rapid prototyping guide for iterative ABC system development
• Cost driver identification worksheet to enhance cost visibility
• Predictive accounting model for budgeting and forecasting
• Barriers assessment checklist to identify and address adoption challenges
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the ABC framework and its benefits for strategic cost management
• Comparison of driver rate-based ABC and time-driven ABC methodologies
• Case studies illustrating successful ABC implementation and its impact on profitability
• Visual representations of cost assignment networks and cost drivers
• Insights into the evolution of managerial accounting practices and their relevance today
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to ABC (30 minutes)
• Overview of activity-based costing principles
• Discussion on the importance of accurate cost management
Profitability Analysis Techniques (60 minutes)
• Hands-on exercises calculating product and service-line profitability
• Group discussions on channel and customer profitability
Implementing ABC with Rapid Prototyping (90 minutes)
• Interactive session on developing a rapid prototyping approach
• Case studies on successful ABC implementations
Overcoming Barriers to ABC Adoption (30 minutes)
• Identifying common challenges and strategies to address them
• Group brainstorming on fostering a culture of cost management
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the ABC implementation roadmap to align with specific organizational goals and timelines
• Adjust profitability analysis frameworks to reflect unique product and service offerings
• Incorporate company-specific cost drivers into the cost driver identification worksheet
• Modify the workshop agenda based on participant expertise and organizational needs
Secondary Topics Covered
• Historical evolution of managerial accounting practices
• The role of predictive analytics in financial management
• Integration of ABC with other costing methods
• The impact of customer-centric strategies on profitability
• The importance of aligning budgeting processes with strategic objectives
Topic FAQ
What are the core steps or phases in implementing activity-based costing in an organization?
Implementation steps outlined focus on defining activities, identifying cost drivers, building cost assignment networks, iterative or rapid prototyping of the ABC system, allocating costs for product/service/channel/customer profitability, and integrating operational ABC into productivity improvement. The presentation supplies an ABC implementation roadmap template and a rapid prototyping guide.How does time-driven ABC (TDABC) differ from driver rate-based ABC?
The material differentiates driver rate-based ABC from time-driven ABC (TDABC) and provides a side-by-side comparison of the 2 approaches. For method details and comparative discussion, see the section titled "Driver Rate-Based ABC vs. Time-Driven ABC (TDABC)" located on page 54.How can ABC be used to analyze customer and channel profitability?
ABC assigns costs to activities via identified cost drivers, then traces those activity costs to products, channels, or customers to reveal true profitability. The deck includes techniques and tools for channel and customer profitability analysis and provides a cost driver identification worksheet and a profitability analysis framework.What are common barriers to adopting ABC and how are they addressed?
Common barriers cited include technical challenges, perceptions of complexity, and organizational resistance to change. Suggested responses include creating a compelling need for change, education, and demonstrating ABC benefits; the presentation includes a barriers assessment checklist to diagnose and address adoption issues.What should I look for when buying an ABC toolkit or slide deck for my finance team?
Key factors include practitioner-authored content, practical templates (implementation roadmap, profitability framework), coverage of TDABC and predictive accounting, workshop agendas, and sufficient slide detail for training. Flevy's Activity-Based Cost Management (ABC/M) matches these needs and is provided as a 101-slide PPT with a supplemental PDF.Are templates and worksheets in ABC toolkits worth the investment for a small finance team?
Templates and worksheets aim to reduce setup effort by providing structured steps—an implementation roadmap, rapid prototyping guide, cost driver identification worksheet, and predictive accounting model—to speed deployment and standardize analysis; examples include the cost driver worksheet and predictive accounting model.How do I integrate ABC into driver-based budgeting and rolling forecasts?
Use predictive accounting techniques that link driver volumes to financial outcomes: driver-based budgeting, rolling financial forecasts, and updating driver assumptions. The presentation covers predictive accounting and provides a predictive accounting model and guidance on driver-based budgeting, with material beginning around page 76.How can I run a one-day workshop to introduce ABC to stakeholders?
The sample agenda lays out timed sessions: a 30-minute ABC introduction, a 60-minute profitability analysis workshop with hands-on exercises, a 90-minute rapid prototyping implementation session, and a 30-minute discussion on overcoming adoption barriers—these timed modules are included in the workshop agenda.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is activity-based costing (ABC)?
ABC is a costing methodology that assigns costs to activities based on their actual use of resources, providing a more accurate picture of product and service costs.
How can ABC improve profitability analysis?
ABC allows organizations to identify and analyze the true costs associated with products, services, channels, and customers, leading to more informed decision-making.
What are the main barriers to adopting ABC?
Barriers include technical challenges, perception of complexity, and organizational resistance to change.
How does rapid prototyping work in ABC implementation?
Rapid prototyping involves iterative development of the ABC system, allowing organizations to make adjustments based on feedback and ensure the system meets their needs.
What is predictive accounting?
Predictive accounting is a forward-looking approach that uses driver-based budgeting and rolling forecasts to enhance financial planning and decision-making.
How can organizations overcome resistance to ABC adoption?
Creating a compelling need for change, providing education, and demonstrating the benefits of ABC can help overcome resistance.
What tools can assist in implementing ABC?
Tools include implementation roadmaps, profitability analysis frameworks, and cost driver identification worksheets.
How does ABC differ from traditional costing methods?
Unlike traditional costing methods that allocate costs broadly, ABC provides a more precise allocation based on actual resource usage, leading to better insights into profitability.
What role do cost drivers play in ABC?
Cost drivers are the factors that influence the cost of activities, and identifying them is crucial for accurate cost management and profitability analysis.
How can predictive accounting enhance budgeting processes?
Predictive accounting aligns budgeting with future driver volumes, ensuring that financial plans are more responsive to changing business conditions.
Glossary
• Activity-Based Costing (ABC) - A method of assigning costs to products and services based on the resources they consume.
• Cost Driver - A factor that causes a change in the cost of an activity.
• Profitability Analysis - The process of determining the profitability of products, services, channels, or customers.
• Predictive Accounting - A budgeting approach that forecasts future financial performance based on driver analysis.
• Rapid Prototyping - An iterative approach to developing systems that allows for quick adjustments and refinements.
• Barriers to Adoption - Challenges that organizations face when implementing new practices or systems.
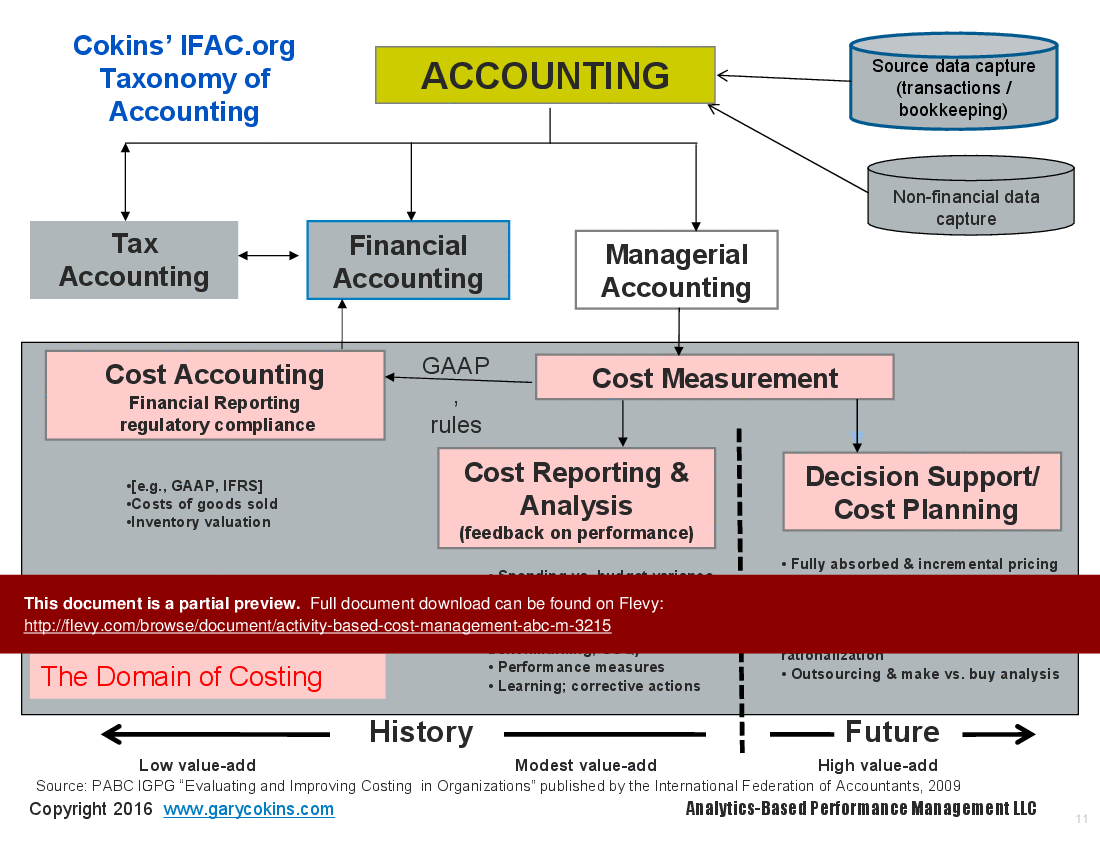
• Cost Assignment Network - A framework that illustrates how costs are assigned to activities and ultimately to cost objects.
• Rolling Financial Forecasts - A budgeting method that continuously updates forecasts based on actual performance and changing conditions.
• Operational ABC - The use of ABC principles to improve operational efficiency and productivity.
• Driver-Based Budgeting - A budgeting approach that links financial outcomes to specific business drivers.
• Customer Profitability - The analysis of profitability at the customer level, considering all associated costs.
• Strategic Cost Management - The practice of managing costs in a way that supports an organization's strategic objectives.
• Value-Added Activities - Activities that contribute to the value of a product or service from the customer's perspective.
• Non-Value-Added Activities - Activities that do not add value to the product or service and can be eliminated or reduced.
• Cost of Quality (COQ) - The total costs associated with ensuring that a product or service is of good quality, including prevention, appraisal, and failure costs.
• Benchmarking - The process of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests or best practices from other companies.
• Lean Accounting - An approach to accounting that supports lean manufacturing principles by focusing on value creation and waste reduction.
• Financial Modeling - The process of creating a numerical representation of a company's financial performance.
• KPI (Key Performance Indicator) - A measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives.
• SWOT Analysis - A strategic planning tool used to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to business competition or project planning.
• Activity-Based Management (ABM) - The use of activity-based costing information to improve business processes and decision-making.
• Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) - The total cost of acquiring, operating, and maintaining a product or service over its lifecycle.
• Value Stream Mapping - A lean-management method for analyzing the flow of materials and information currently required to bring a product or service to a consumer.
Source: Best Practices in Cost Optimization, Management Accounting, Activity Based Costing PowerPoint Slides: Activity-Based Cost Management (ABC/M) PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Gary Cokins