Business Analytics for the CFO Function (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) + supplemental PDF 72 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Learn why business analytics and leveraging Big Data provide a competitive advantage.
- Understand the difference between business intelligence (BI) and business analytics.
- Learn how to imbed statistics and analytics into enterprise and corporate performance management (EPM/CPM) methods including differentiating forecasting from predictive modeling.
ANALYTICS PPT DESCRIPTION
The CFO's finance and accounting function can leverage analytics, especially predictive ones, embedded in their financial reporting, planning, and decision making.
Finance and accounting professional are typically considered to be very quantitative. They are by nature number-crunchers. But collecting, validating, and reporting data is not the same thing as analyzing the information that can be gleaned from data. Most organizations are drowning in data, but starving for information.
The CFO function is experiencing a shift from beyond financial reporting to dealing with and reporting non-financial information. Finance people are increasingly involved with creating and monitoring performance measurements. But do they know how to identify the appropriate measures? Their task should not be about what can be measured but what should be measured. And don't stop there. This is not about just monitoring the dials of a scorecard or dashboard, but moving the dials. The decisions involved to improve performance require analytics of all flavors.
Most companies are far from where they want and need to be when it comes to implementing analytics and are still relying on gut feeling, rather than hard data, when making decisions. Volatility and complexity are the new normal.
When you step back to see a perspective of importance, financial accounting simply deals with valuation ? for example, what is an organization worth if you were to sell it? But managerial accounting is about creating value ? its information contributes to management decisions that financial accounting ultimately deals with afterwards. Arguably managerial accounting is more important than financial accounting. But the issue does not stop there. Analysis must be added to reporting. How else can the sales and marketing functions determine which types of customers are more attractive to retain, to grow, to win-back, and to acquire? And for the attractive types, what is the optimal level of spending for each customer micro-segment to retain, grow, or acquire them?
What is needed today is the seamless integration of managerial methods such as balanced scorecards, strategy maps, capacity-sensitive driver-based budgets and rolling financial forecasts, and measuring and managing channel and customer profitability (using activity-based costing principles). Each one can be amplified by embedding business analytics with them. The methods are collectively intended to align manager and employee behavior and limited resources to focus on the organization's strategic priorities and objectives and better decision making.
This presentation provides a comprehensive overview of the maturity stages of analytics and its application within the CFO function. It covers essential topics such as Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) and Business Intelligence (BI) and their integration with Business Analytics (BA).
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 72-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation titled "Business Analytics for the CFO Function" is crafted by Gary Cokins, a recognized expert in enterprise performance management (EPM) and business analytics (BA). It aims to equip CFOs and finance leaders with essential insights into integrating analytics into decision-making processes. The presentation covers the significance of business analytics in enhancing financial performance, improving decision-making, and fostering a data-driven culture. By leveraging the concepts outlined, executives will be able to transform data into actionable insights, ultimately driving better financial outcomes.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• CFOs and finance executives seeking to enhance decision-making through analytics
• Financial planners and analysts involved in enterprise performance management
• Managers aiming to integrate business analytics into their financial strategies
• Executives looking for a compelling call to action regarding EPM and BA improvements
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to align analytics with financial goals
• In workshops focused on improving financial decision-making processes
• When addressing challenges in integrating analytics into existing systems
Learning Objectives
• Define the role of business analytics in enhancing financial performance
• Build a framework for integrating analytics into decision-making processes
• Establish a clear understanding of enterprise performance management principles
• Identify key metrics and analytics that drive financial insights
• Develop actionable strategies for leveraging data in financial planning
• Recognize the importance of predictive analytics in forecasting financial outcomes
Table of Contents
• Overview – Maturity Stages of Analytics (page 5)
• What is Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) (page 10)
• What is Business Analytics … and Why? (page 12)
• Examples of Applying Business Analytics (page 31)
• BI and BA for the CFO Function and EPM (page 34)
• Benefits and Summary (page 66)
Primary Topics Covered
• Maturity Stages of Analytics - Discusses the progression of analytics capabilities from descriptive to prescriptive analytics, emphasizing the need for advanced analytical techniques.
• Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) - Defines EPM as the integration of various methods, including business analytics, to enhance strategic decision-making.
• Business Analytics - Explores the necessity of business analytics in gaining competitive advantages and making informed decisions.
• Applications of Business Analytics - Provides real-world examples of how analytics can be applied across different sectors, including finance and marketing.
• Benefits of Business Analytics - Highlights the advantages of adopting analytics, such as improved decision-making and reduced uncertainty.
• Challenges in EPM Adoption - Identifies barriers to implementing EPM and analytics, including technical and organizational hurdles.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Framework for integrating business analytics into financial planning
• Templates for KPI correlation analysis and customer profitability analysis
• Guidelines for developing a balanced scorecard and strategy map
• Models for predictive analytics in financial forecasting
• Action plans for overcoming barriers to EPM adoption
• Resources for continuous education on analytics and performance management
Slide Highlights
• Overview of analytics maturity stages illustrating the evolution from basic reporting to advanced predictive modeling
• Visual representation of the relationship between business analytics and enterprise performance management
• Case studies showcasing successful applications of analytics in various industries
• Charts illustrating the impact of analytics on decision-making and financial outcomes
• Summary slide encapsulating the benefits of integrating analytics into the CFO function
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Business Analytics (60 minutes)
• Define business analytics and its importance in finance
• Discuss the role of the CFO in leveraging analytics
Integrating Analytics into EPM (90 minutes)
• Explore frameworks for EPM and business analytics integration
• Identify key metrics and analytics for financial insights
Case Studies and Applications (60 minutes)
• Review real-world examples of successful analytics implementation
• Discuss lessons learned and best practices
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the presentation to reflect specific organizational goals and metrics
• Adjust case studies to align with industry-specific challenges and solutions
• Incorporate company-specific data and examples to enhance relevance
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of data governance in business analytics
• Techniques for effective data visualization and reporting
• Strategies for fostering a data-driven culture within finance teams
• The impact of emerging technologies on business analytics
• Ethical considerations in data usage and analytics
Topic FAQ
What are the maturity stages of analytics and how do they apply to finance teams?
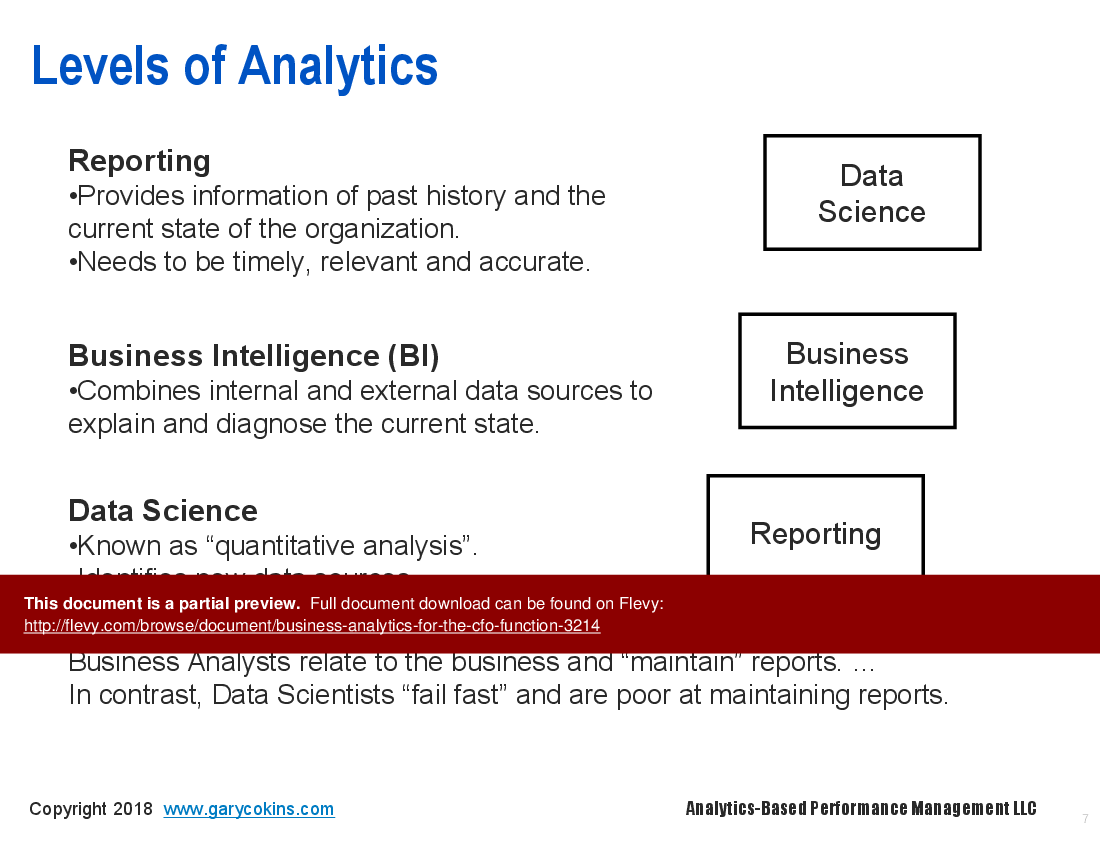
Analytics maturity typically progresses from descriptive (historical reporting) to diagnostic (why things happened), then predictive (forecasting likely outcomes) and prescriptive (optimization and recommendations). Finance teams move from reporting to insight-driven forecasting and decision support as they advance through these stages, ending with prescriptive analytics and optimization.How does enterprise performance management (EPM) incorporate business analytics for better decisions?
EPM incorporates analytics by linking strategic objectives, performance measures, and planning processes so analytics inform decisions. Typical components include balanced scorecards, strategy maps, driver-based budgets and rolling forecasts; analytics provide forecasts, KPI correlation and scenario analysis to guide strategy execution and resource allocation in balanced scorecards and rolling financial forecasts.What is the practical difference between business intelligence and business analytics for finance functions?
Business intelligence (BI) focuses on collecting, validating and reporting historical data and trends, while business analytics (BA) emphasizes statistical, predictive and prescriptive techniques to forecast outcomes and recommend actions. Finance uses BI for historical dashboards and BA for forecasting and optimization, distinguishing BI’s reporting from BA’s predictive and prescriptive analytics.How can CFOs apply predictive analytics to improve financial forecasting?
CFOs can use predictive analytics to identify trends, estimate future revenue or cost drivers, and test scenarios that feed rolling forecasts and driver-based budgets. Embedding predictive models into planning helps reduce uncertainty and supports proactive decisions in areas such as cash flow forecasting and scenario planning with predictive analytics models in rolling financial forecasts.What should I look for when buying a business analytics deck for the CFO function?
Prioritize decks that explain analytics maturity, define EPM, show how BA differs from BI, include KPI and customer profitability templates, and provide predictive forecasting models plus customization guidance. For example, Flevy's Business Analytics for the CFO Function includes a maturity framework, KPI correlation and customer profitability templates useful for finance teams.How much practical value do prebuilt templates and models provide versus building analytics tools in-house?
Prebuilt templates accelerate adoption, provide standardized measures and teaching artifacts for education and buy-in, and enable small pilots before full rollout. They are especially useful for framing balanced scorecards, strategy maps, KPI correlation exercises and customer profitability analysis to jump-start EPM integration and governance.I need to align analytics with strategic planning — which framework should I follow?
Start with an analytics maturity assessment, then map analytics capabilities to EPM components: define strategy with a strategy map, select KPIs for a balanced scorecard, and link drivers into capacity-sensitive budgets and rolling forecasts. Flevy's Business Analytics for the CFO Function presents this integration approach using balanced scorecard and strategy map guidance.What are common organizational barriers to EPM and analytics adoption and how can they be addressed?
Common barriers include technical gaps, behavioral resistance, and lack of education or leadership buy-in. Mitigation involves focused education, executive sponsorship, starting with manageable pilot projects, and establishing data governance and implementation action plans; practical resources include action plans and data governance guidance.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the primary focus of this presentation?
The presentation focuses on integrating business analytics into the CFO function to enhance decision-making and improve financial performance.
Who can benefit from this presentation?
CFOs, finance executives, and managers involved in enterprise performance management will find this presentation particularly beneficial.
What are the key learning outcomes?
Participants will learn to define business analytics, build frameworks for integration, and identify key metrics that drive financial insights.
How can organizations overcome barriers to EPM adoption?
Organizations can address technical, perception, and behavioral barriers by fostering a culture of analytics and providing education on its benefits.
What tools are provided in this presentation?
The presentation includes frameworks, templates, and action plans for integrating analytics into financial planning and decision-making.
How does business analytics differ from business intelligence?
Business analytics focuses on predictive and prescriptive insights, while business intelligence primarily deals with historical data reporting and analysis.
What are the benefits of adopting business analytics?
Benefits include deeper insights, reduced uncertainty, improved decision-making, and higher ROI from leveraging automation.
How can this presentation be customized?
The content can be tailored to reflect specific organizational goals, industry challenges, and company-specific data.
What is the importance of predictive analytics in finance?
Predictive analytics helps forecast financial outcomes and identify trends, enabling proactive decision-making.
How can organizations ensure successful implementation of analytics?
Organizations should focus on education, buy-in from leadership, and starting with small, manageable projects to build momentum.
Glossary
• Business Analytics - The use of statistical analysis and data to drive business decisions.
• Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) - A framework for managing an organization's performance through analytics and strategic planning.
• Predictive Analytics - Techniques that use statistical algorithms and machine learning to identify the likelihood of future outcomes based on historical data.
• Key Performance Indicator (KPI) - A measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives.
• Data Governance - The management of data availability, usability, integrity, and security in an organization.
• Balanced Scorecard - A strategic planning and management system used to align business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization.
• Strategy Map - A visual representation of an organization's objectives and the relationships between them.
• Descriptive Analytics - The interpretation of historical data to identify trends and patterns.
• Prescriptive Analytics - The use of optimization and simulation algorithms to advise on possible outcomes.
• Data Visualization - The graphical representation of information and data to communicate insights clearly.
• Customer Profitability Analysis - An assessment of the profitability of individual customers or customer segments.
• Activity-Based Costing (ABC) - A costing method that assigns overhead and indirect costs to specific activities related to producing a product or service.
• Rolling Financial Forecasts - A method of forecasting that continuously updates financial projections based on new data and trends.
• Risk Assessment Grid - A tool used to evaluate the probability and impact of risks on business objectives.
• Ad Hoc Reporting - Reports created on the fly to answer specific business questions.
• Operational Resource Capacity Planning - The process of determining the production capacity needed by an organization to meet changing demands for its products.
• Statistical Analysis - The collection and interpretation of data to identify trends and patterns.
• Data Mining - The practice of examining large datasets to uncover hidden patterns and correlations.
• Insight - An accurate and deep understanding of a complex situation or problem.
• ROI (Return on Investment) - A performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment.
Source: Best Practices in Analytics, CFO PowerPoint Slides: Business Analytics for the CFO Function PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Gary Cokins