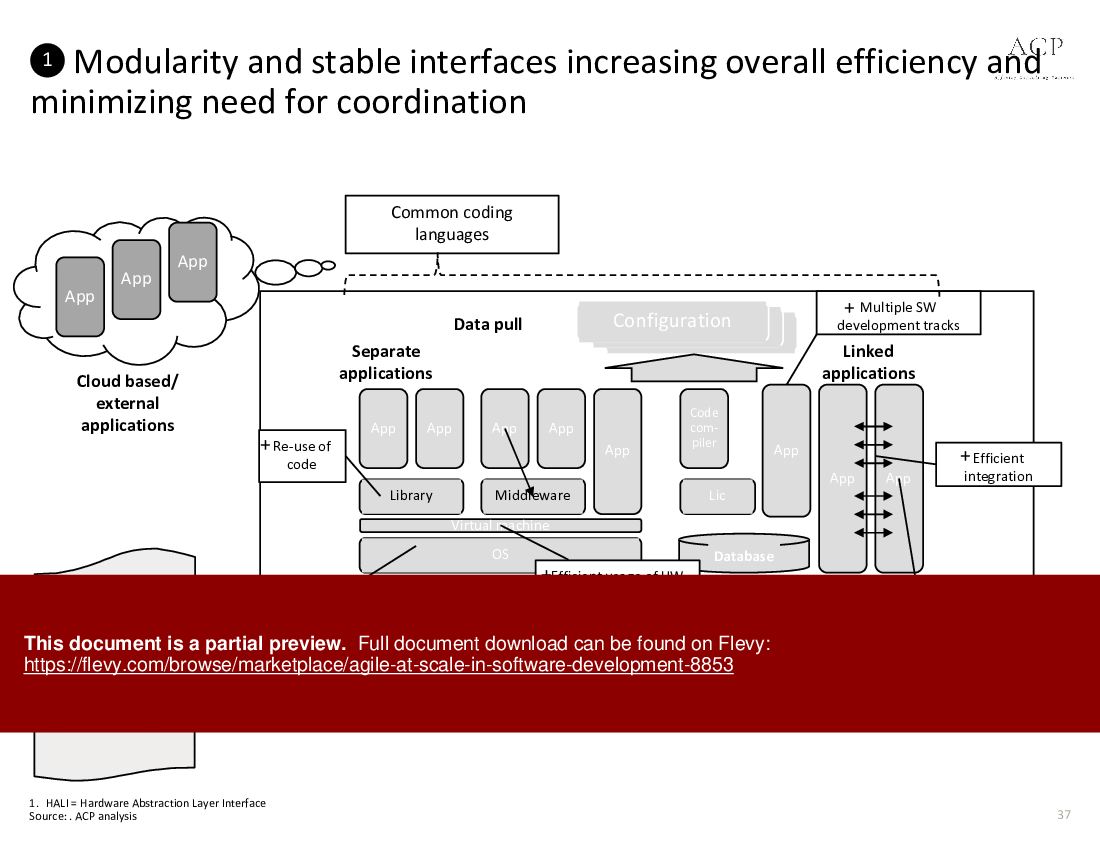
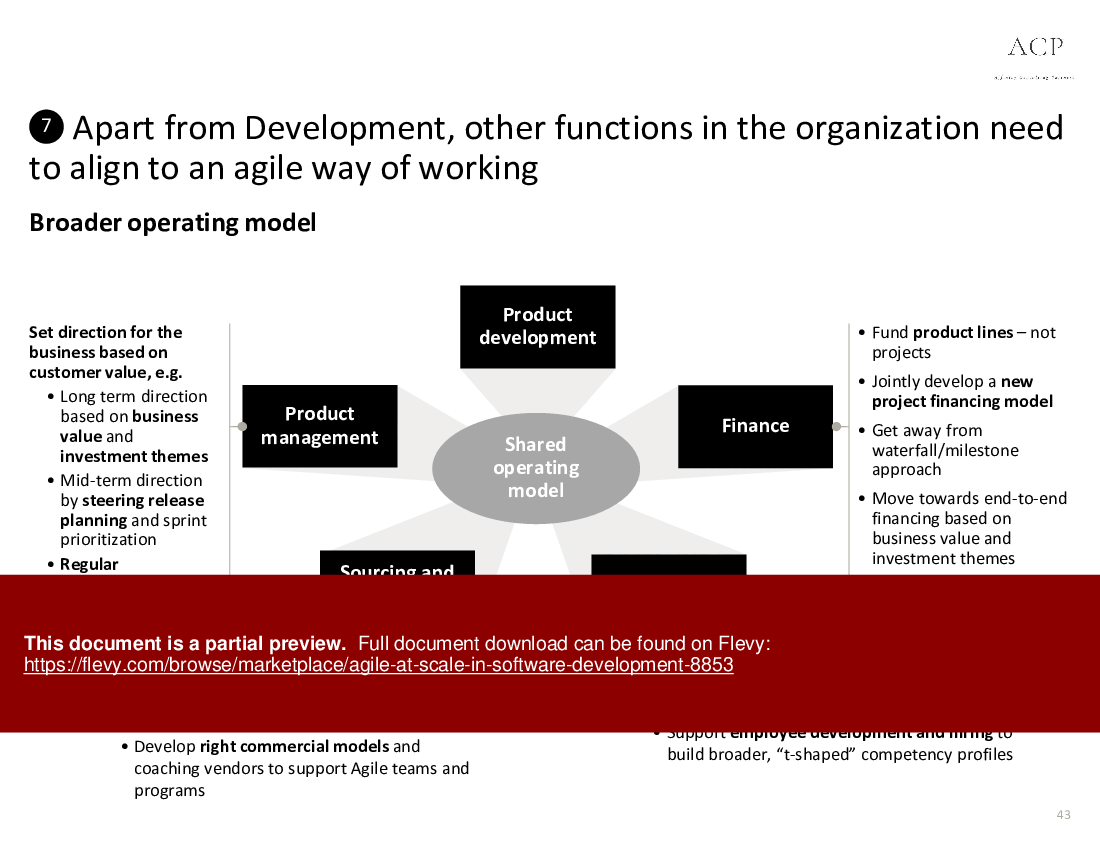
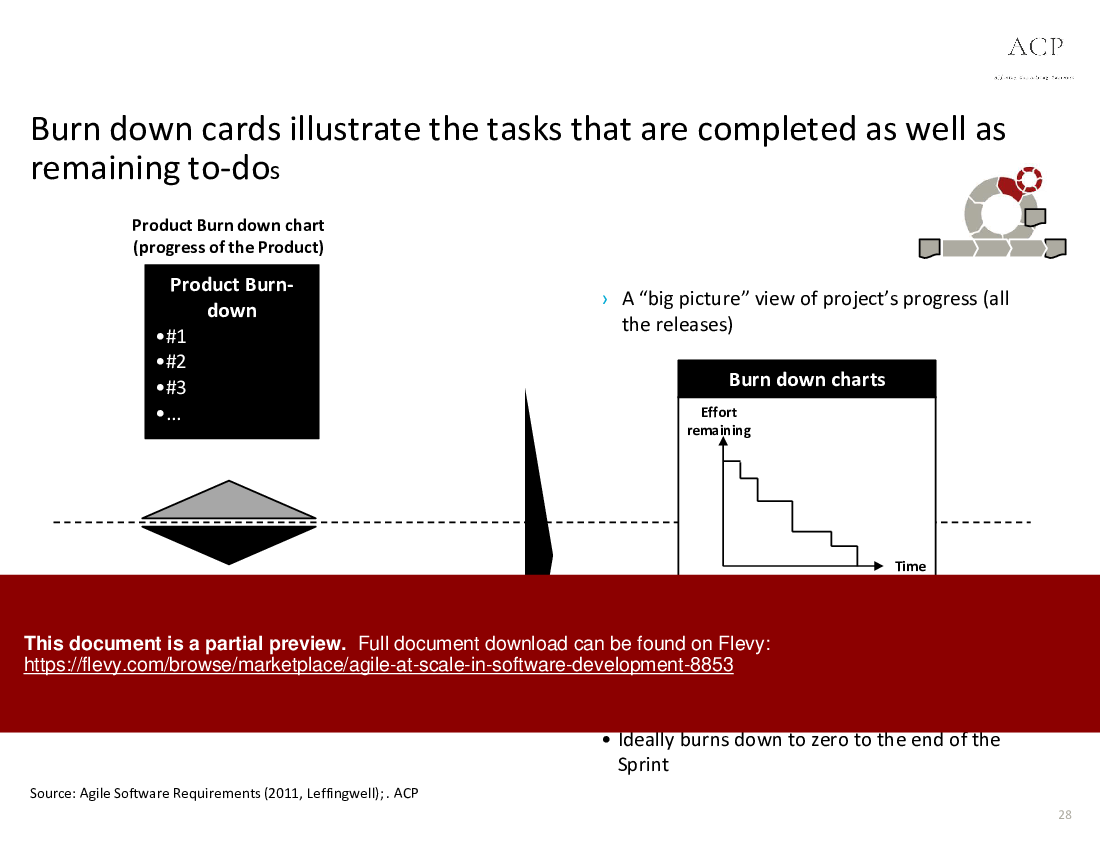
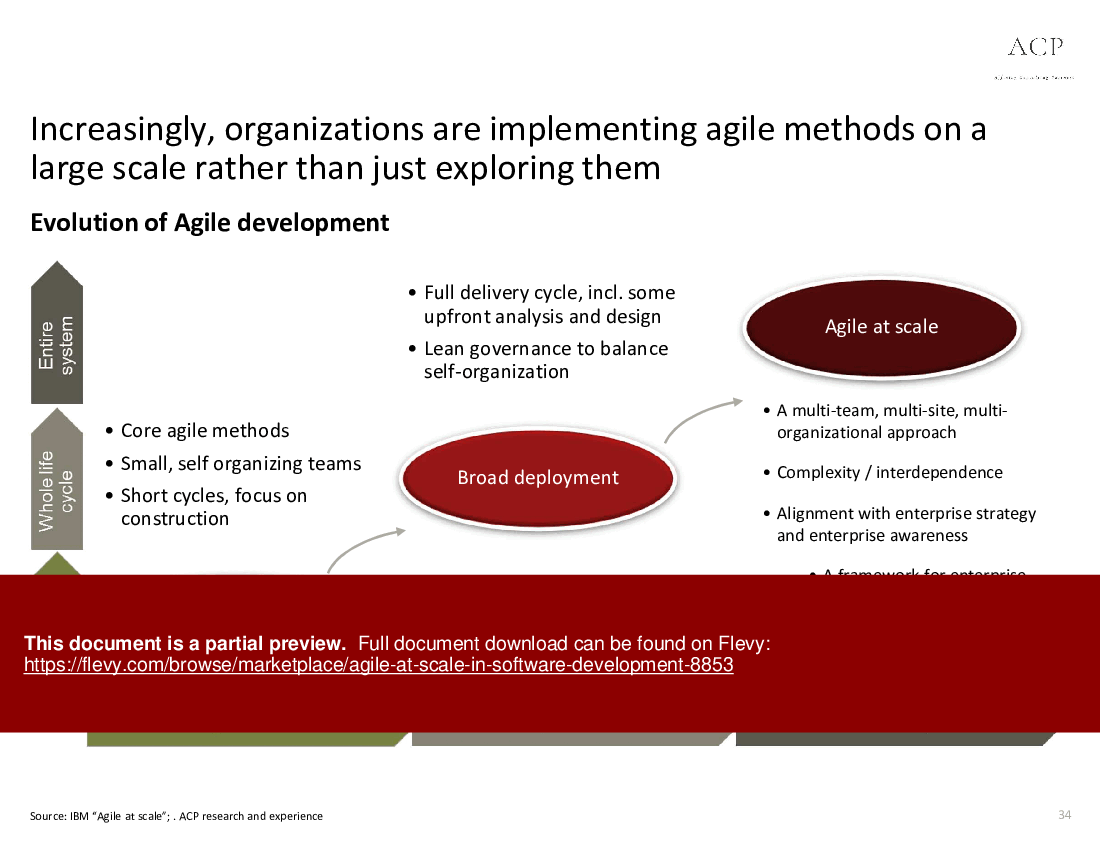
Agile at Scale in Software Development (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 48 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Agile software development
- Change management
- Agile Project Management
AGILE PPT DESCRIPTION
This PPT deck and Word document consider Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming, that have transformed software development by emphasizing iterative progress, collaboration, and adaptability. However, scaling Agile for large projects and enterprise-level development presents unique challenges and requires specific strategies.
Challenges of Scaling Agile:
• Complex Coordination: Large projects require extensive synchronization among teams working on interdependent components.
• Consistent Practices: Different interpretations of Agile principles across teams can lead to process inconsistencies.
• Cultural Shift: Transitioning to Agile involves significant changes in organizational culture, moving from hierarchical structures to self-organizing teams.
• Tool Integration: Seamlessly integrating various tools for project management, continuous integration, and communication is essential.
Strategies for Scaling Agile:
-Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe): SAFe provides structured guidelines for roles, responsibilities, and processes at the enterprise level, aligning teams around value streams.
• Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS): LeSS extends Scrum principles to larger projects, emphasizing simplicity, clear vision, and strong team collaboration.
• Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD): DAD offers a hybrid approach incorporating elements from Scrum, Lean, and Kanban, tailored to the organization's needs.
• Agile Program Management: Establishing an Agile Program Management Office (APMO) ensures alignment with strategic goals, monitors progress, and facilitates communication.
Case Studies:
• Spotify: Spotify's model organizes teams into "squads," "tribes," "chapters," and "guilds," promoting autonomy and alignment.
• ING Bank: ING Bank reorganized into small, cross-functional teams called "squads," improving responsiveness to market changes and customer needs.
Benefits of Scaling Agile:
• Improved Responsiveness: Organizations can swiftly adapt to market changes and customer feedback.
• Enhanced Collaboration: Agile fosters a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
• Increased Transparency: Enhanced visibility into project progress aids in informed decision-making.
• Higher Quality: Iterative development and continuous testing lead to higher-quality software.
The deck explores how Agile in software creation involves navigating significant challenges but offers substantial benefits. By adopting suitable frameworks and learning from successful implementations, organizations can achieve a more responsive, collaborative, and transparent development process, leading to high-quality software and business success.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 48-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation, titled "Agile at Scale in Software Development," offers a consulting-grade toolkit designed to guide organizations in implementing Agile methodologies across large-scale software projects. Drawing from extensive experience with leading high-tech companies, this deck provides actionable insights into overcoming challenges associated with Agile transformation. It equips corporate executives and integration leaders with the strategies necessary to enhance operational efficiency, foster innovation, and accelerate time-to-market for new products and services. By leveraging Agile practices, organizations can optimize workflows, improve collaboration, and ultimately deliver higher-quality software solutions.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives overseeing software development initiatives
• Integration leaders managing Agile transformation projects
• Project managers responsible for cross-functional team collaboration
• Consultants advising organizations on Agile methodologies
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During the planning phase of an Agile transformation initiative
• When assessing current software development processes and identifying bottlenecks
• To train teams on Agile practices and methodologies
• For workshops aimed at refining Agile implementation strategies
Learning Objectives
• Define the key differences between Agile and traditional software development methodologies
• Identify the core principles of Agile that enhance flexibility and responsiveness
• Establish best practices for implementing Agile at scale across multiple teams
• Develop a comprehensive Agile transformation roadmap tailored to organizational needs
• Create an environment that fosters continuous improvement and team empowerment
• Measure the effectiveness of Agile practices through relevant KPIs
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Agile vs. Traditional Development (page 4)
• Incorporating Agile Methodologies into Practice (page 17)
• Key Success Factors for Applying Agile at Scale (page 34)
• Considerations for Large Scale Implementation (page 44)
Primary Topics Covered
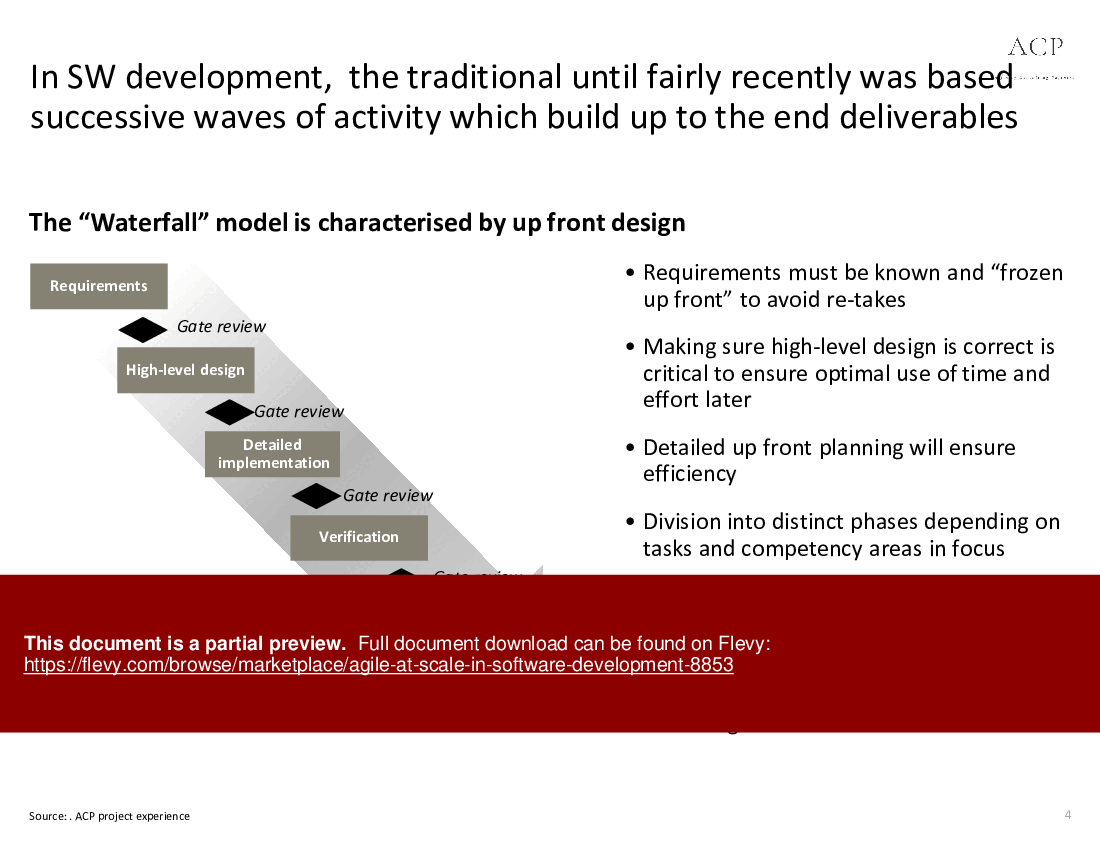
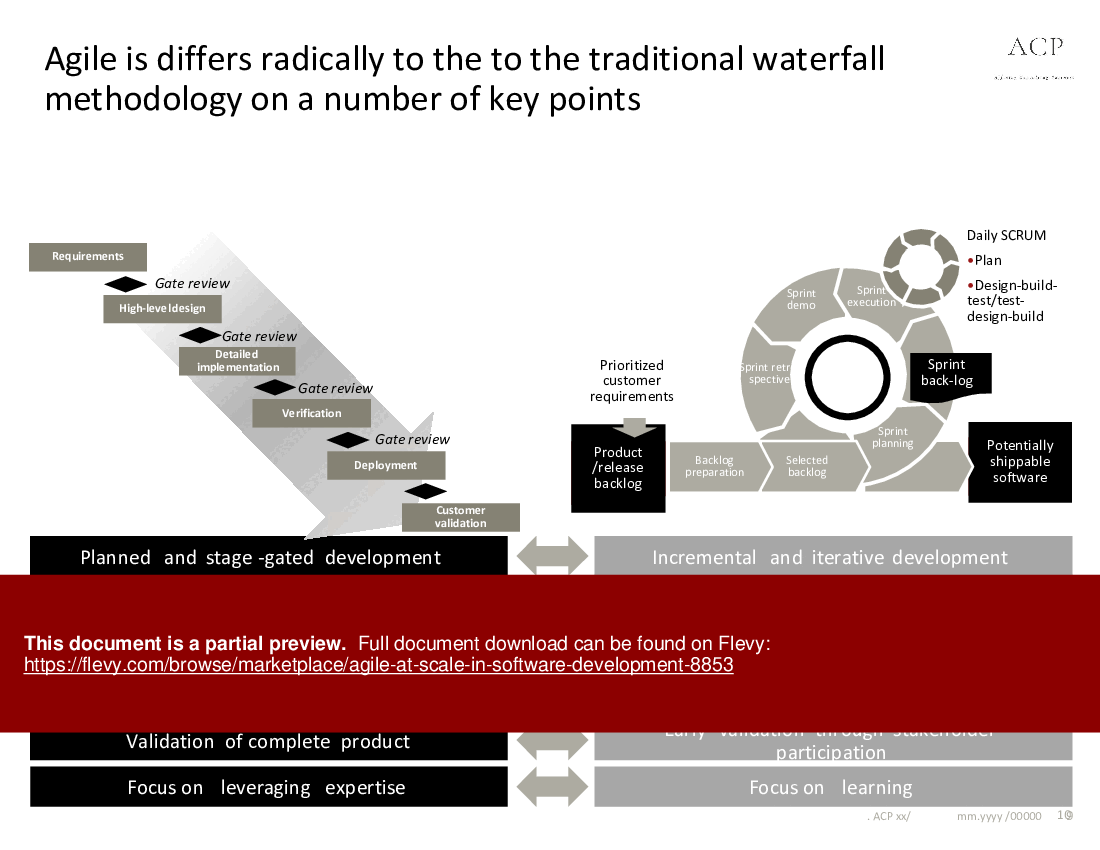
• Agile vs. Waterfall - Agile methodologies prioritize customer satisfaction through iterative development, contrasting with the linear, phase-gated Waterfall model.
• Agile Principles - Emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and responsiveness to change, allowing teams to adapt to evolving requirements.
• Implementation Strategies - Provides a structured approach for integrating Agile practices across multiple teams and projects.
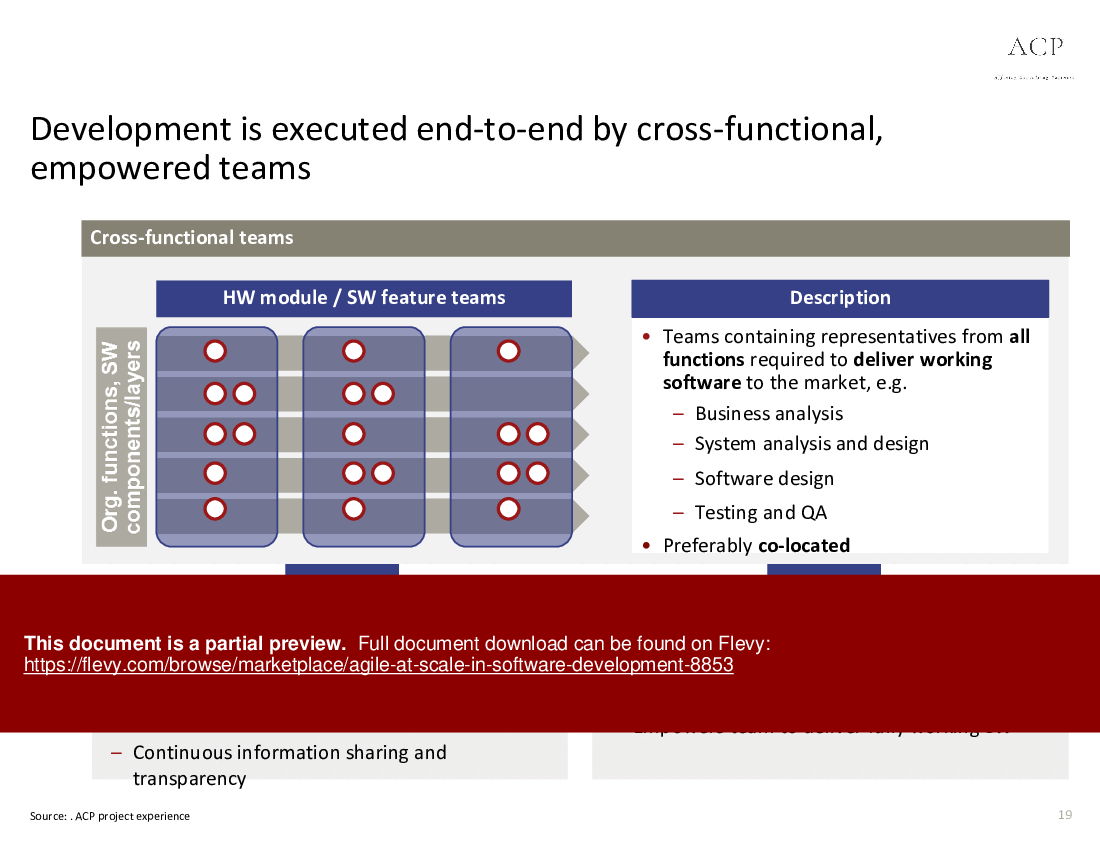
• Team Empowerment - Focuses on creating self-organizing teams that take ownership of their work and are accountable for deliverables.
• Continuous Improvement - Encourages regular retrospectives and feedback loops to enhance team performance and product quality.
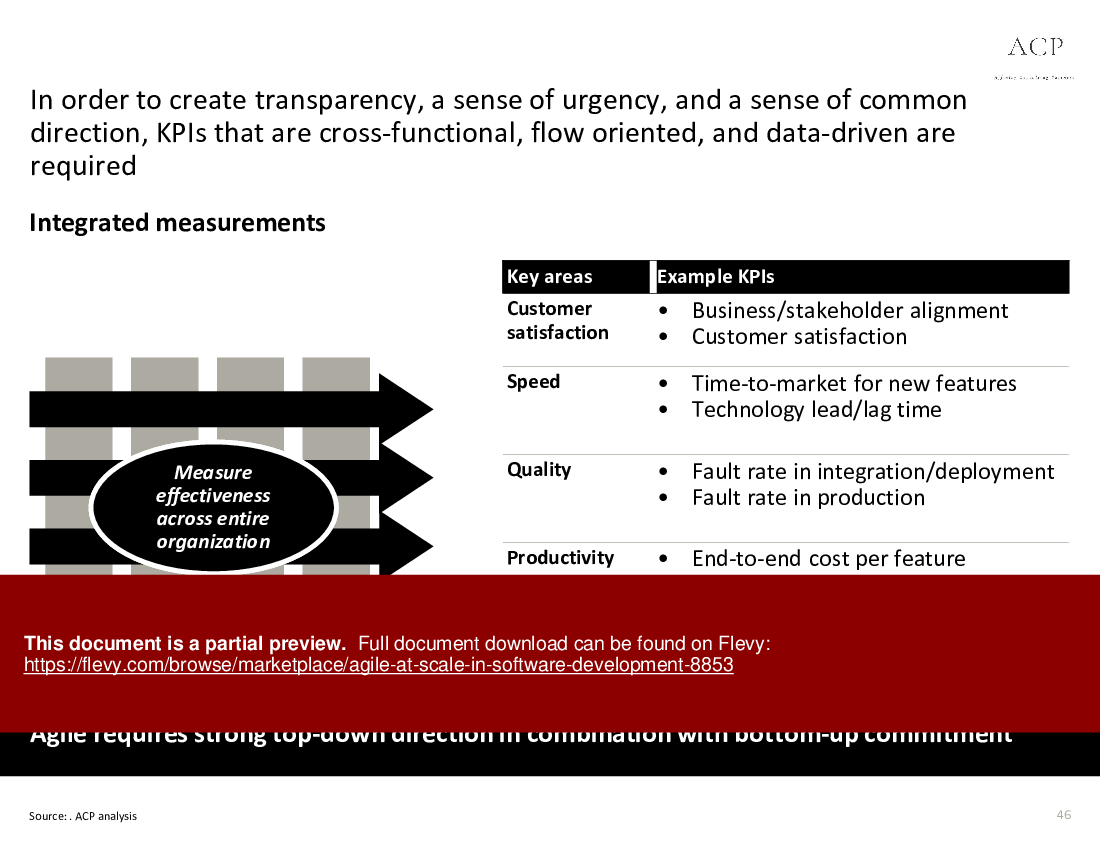
• Performance Metrics - Identifies key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of Agile implementations and drive organizational alignment.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Agile transformation roadmap template for planning and execution
• Sprint planning and backlog management templates
• Retrospective meeting framework for continuous improvement
• Performance measurement dashboard for tracking Agile KPIs
• User story mapping tool to prioritize customer requirements
• Visual project board template for managing workflow and progress
Slide Highlights
• Overview of Agile vs. Waterfall methodologies, highlighting key differences in approach and outcomes
• Case studies demonstrating successful Agile transformations in high-tech companies
• Visual representations of Agile processes, including sprint cycles and daily stand-ups
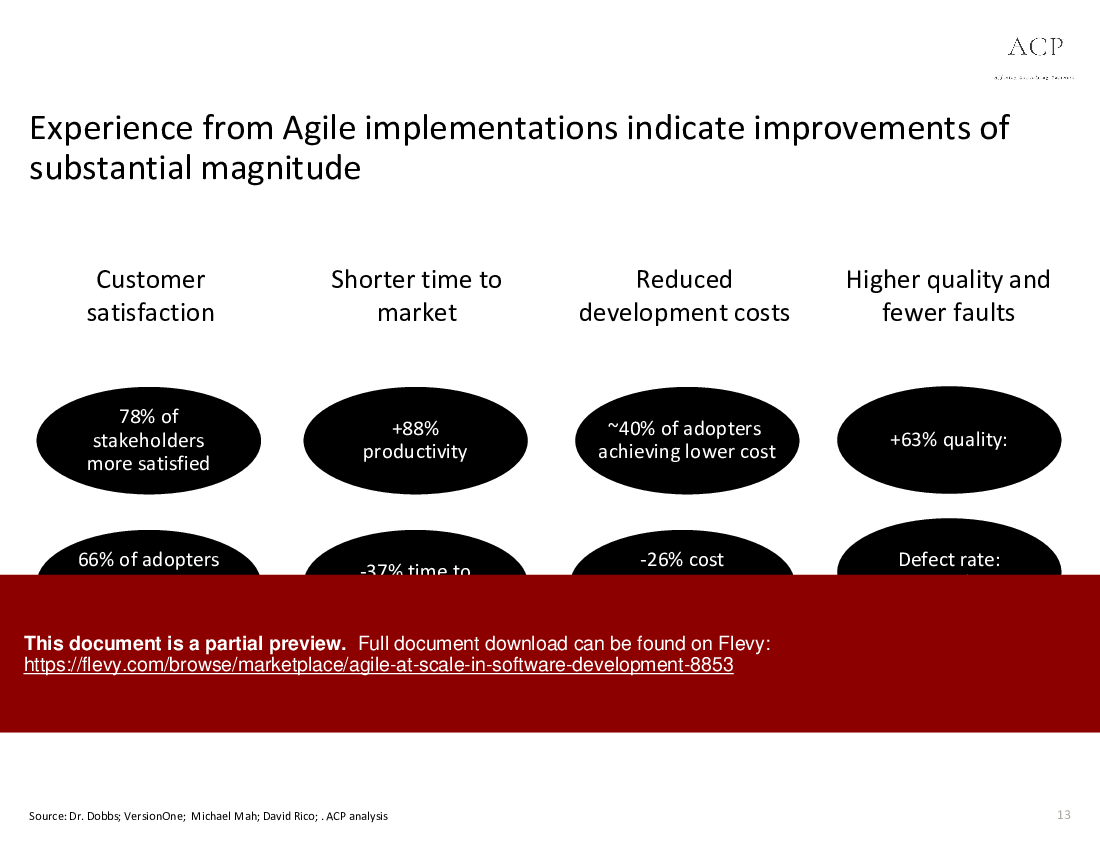
• Metrics illustrating the impact of Agile on project delivery times and customer satisfaction
• Best practices for building cross-functional, empowered teams
Potential Workshop Agenda
Agile Transformation Kickoff (90 minutes)
• Introduce Agile principles and methodologies
• Discuss current challenges in software development
• Identify goals for Agile transformation
Sprint Planning Workshop (120 minutes)
• Define user stories and prioritize the backlog
• Create a sprint plan with actionable tasks
• Establish team roles and responsibilities
Retrospective and Continuous Improvement Session (60 minutes)
• Review sprint outcomes and team performance
• Identify areas for improvement and action items
• Foster a culture of feedback and adaptation
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the Agile transformation roadmap to align with specific organizational goals and challenges
• Adjust sprint planning templates to reflect team capacity and project timelines
• Incorporate industry-specific compliance and security requirements into Agile practices
• Modify performance metrics to align with organizational objectives and stakeholder expectations
Secondary Topics Covered
• Challenges of scaling Agile in complex organizations
• Strategies for maintaining alignment between Agile teams and business objectives
• The role of leadership in fostering an Agile culture
• Tools and technologies that support Agile development practices
• Case studies of successful Agile implementations in various industries
Topic FAQ
What are the main differences between Agile and Waterfall in software development?
Agile emphasizes iterative development, frequent customer feedback, and adaptability to changing requirements, while Waterfall is a linear, phase-gated approach that requires complete requirements upfront. Agile organizes work into time-boxed iterations such as sprints, whereas Waterfall progresses through distinct sequential phases.How should an organization measure success when implementing Agile at scale?
Common metrics include time-to-market, customer satisfaction, defect rates, and team productivity. Measuring these often requires a consolidated view through dashboards that track delivery cadence, quality, and stakeholder outcomes; Flevy's Agile at Scale in Software Development includes a performance measurement dashboard to support this.Which enterprise frameworks are available for scaling Agile across large organizations?
The author guidance names several scaling approaches: Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), Large-Scale Scrum (LeSS), and Disciplined Agile Delivery (DAD). It also recommends establishing an Agile Program Management Office (APMO) to coordinate alignment and governance across value streams.How can teams ensure continuous improvement in Agile practices?
Teams should run regular retrospectives and feedback loops to surface improvements, capture action items, and adapt processes. The product includes a retrospective meeting framework and workshop agendas designed to institutionalize continuous improvement through recurring reflection and action.What should I look for when choosing an Agile-at-scale toolkit for my company?
Buyers should prioritize usable templates for roadmap planning, sprint planning, backlog management, retrospective facilitation, and KPI tracking, plus customization guidance and case studies to adapt practices to context; for example, look for an Agile transformation roadmap template and a performance measurement dashboard.How much time and internal resources are typically needed to run the kickoff and sprint planning workshops in this kind of toolkit?
The sample workshop agendas in the deck specify realistic durations: an Agile Transformation Kickoff at 90 minutes, a Sprint Planning Workshop at 120 minutes, and a Retrospective and Continuous Improvement Session at 60 minutes, which can be staffed by product owners, Scrum Masters, and team leads.I just merged 2 development organizations—what practical first steps should I take to implement Agile across teams?
Start by assessing current processes to identify bottlenecks, run a planning-phase kickoff to set goals, and build a tailored Agile transformation roadmap; use training and targeted workshops to align practices and use tools like a user story mapping tool and the Agile transformation roadmap template.How can leadership reduce resistance and support an enterprise Agile transformation?
Leadership should engage stakeholders early, provide resources and training, and demonstrate early wins to build momentum. Establishing program-level governance and an Agile Program Management Office (APMO) helps maintain alignment, monitoring, and communication across teams.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What are the key differences between Agile and Waterfall methodologies?
Agile focuses on iterative development and flexibility, allowing for changes throughout the project lifecycle, while Waterfall is a linear approach that requires complete requirements upfront.
How can organizations effectively implement Agile at scale?
Successful implementation requires a structured approach, including training, clear communication, and alignment with organizational goals.
What metrics should be used to measure Agile success?
Key performance indicators include time-to-market, customer satisfaction, defect rates, and team productivity.
How can teams ensure continuous improvement in Agile practices?
Regular retrospectives and feedback loops help teams identify areas for improvement and adapt their processes accordingly.
What role do leadership and management play in Agile transformation?
Leadership is crucial for fostering a supportive culture, providing resources, and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
How can Agile methodologies be adapted for different industries?
Customization of Agile practices to meet industry-specific requirements and compliance standards is essential for successful implementation.
What are common pitfalls in Agile implementation?
Common pitfalls include treating Agile as merely a development practice, neglecting stakeholder involvement, and failing to conduct retrospectives.
How can organizations overcome resistance to Agile transformation?
Engaging stakeholders early, providing training, and demonstrating quick wins can help alleviate resistance and build support for Agile practices.
Glossary
• Agile - A methodology emphasizing iterative development and flexibility in response to change.
• Waterfall - A linear project management approach requiring complete requirements upfront.
• Sprint - A time-boxed period during which specific work is completed and made ready for review.
• Backlog - A prioritized list of work items or features to be completed in a project.
• User Story - A brief description of a feature from the perspective of the end user.
• Retrospective - A meeting held at the end of a sprint to reflect on the team's performance and identify improvements.
• KPI - Key Performance Indicator, a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively an organization is achieving key business objectives.
• Cross-Functional Team - A group of individuals with different expertise working together towards a common goal.
• Continuous Integration - A practice where code changes are automatically tested and merged into a shared repository frequently.
• Scrum - An Agile framework for managing complex projects, emphasizing teamwork, accountability, and iterative progress.
• Lean - A methodology focused on minimizing waste and maximizing value in processes.
• Empowered Team - A team that has the authority and autonomy to make decisions regarding their work.
• Stakeholder - An individual or group with an interest in the outcome of a project.
• Increment - A portion of the product that is delivered at the end of a sprint, representing a step towards the final product.
• Product Owner - The individual responsible for defining and prioritizing the product backlog.
• Scrum Master - The facilitator for the Scrum team, ensuring that Agile practices are followed.
• Test-Driven Development (TDD) - A software development approach where tests are written before the code itself.
• Burn Down Chart - A visual representation of work completed versus work remaining in a sprint.
• Visual Project Board - A tool used to manage and visualize project progress and tasks.
• Feature - A distinct aspect of a product that delivers value to the user.
AGILE PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Agile, Software PowerPoint Slides: Agile at Scale in Software Development PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Affinity Consulting Partners