Management by Objectives (MBO) (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 17 Slides FlevyPro Document
Sorry, this document is currently only available to FlevyPro subscribers.
You can join FlevyPro for only $39/month.
Or, you can subscribe to the Performance Management Stream, our curated collection of Performance Management frameworks.
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
Management by Objectives (MBO), developed by Peter Drucker, relies on the defining of objectives for each employee and then comparing and directing their performance against the objectives which have been set. The goal to increase the performance of the organization by matching organizational goals with the objectives of employees throughout the organization.
MBO is based on the thinking that various hierarchies within companies need to be integrated. There was a need for commitment, responsibility, and maturity. MBO becomes a process by which the objectives of an organization are agreed to and decided between the management and the employees. Through this approach, the employees understand what is expected of them and help set their own individual goals. As a result, they attain both their personal goals and the organization's targets. MBO also includes continuous tracking of the processes and providing feedback to reach the objectives.
A key underlying concept of MBO is that all objectives must be S.M.A.R.T.—i.e., Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-related.
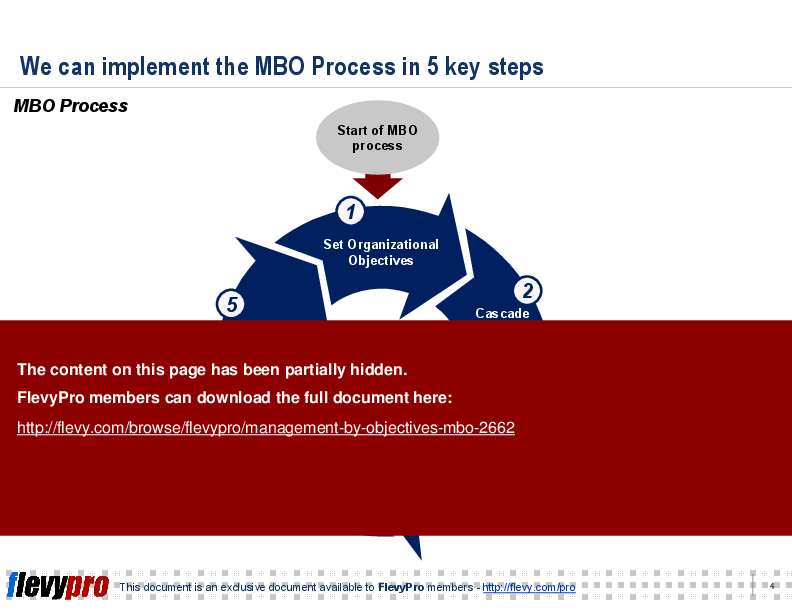
The MBO framework is meticulously designed to align individual performance with organizational goals through a structured five-step process. Starting with setting organizational objectives, cascading these objectives to employees, and then monitoring progress ensures that each step is strategically aligned. This method encourages active participation and fosters a culture of accountability and transparency within the organization.
The PPT also delves into the advantages and disadvantages of MBO, providing a balanced view. While it highlights increased motivation and improved communication, it also addresses potential pitfalls such as the time-consuming nature of the process and the challenges in setting realistic objectives. This comprehensive analysis equips executives with the insights needed to implement MBO effectively, ensuring alignment and driving performance.
Got a question about this document? Email us at flevypro@flevy.com.
PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Performance Management, SMART, Management by Objectives, Peter Drucker PowerPoint Slides: Management by Objectives (MBO) PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, PPT Lab
Sorry, this document is currently only available to FlevyPro subscribers.
You can join FlevyPro for only $39/month.
Or, you can subscribe to the Performance Management Stream, our curated collection of Performance Management frameworks.
Did you need more documents?
Consider a FlevyPro subscription from $39/month. View plans here.