Introduction to Balanced Scorecard (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 60 Slides
BALANCED SCORECARD PPT DESCRIPTION
This presentation is an introduction of the balanced scorecard concepts and its application in corporate performance measurement. It has been used by a major consulting firm in conducting education sessions for its clients in a balanced scorecard project.
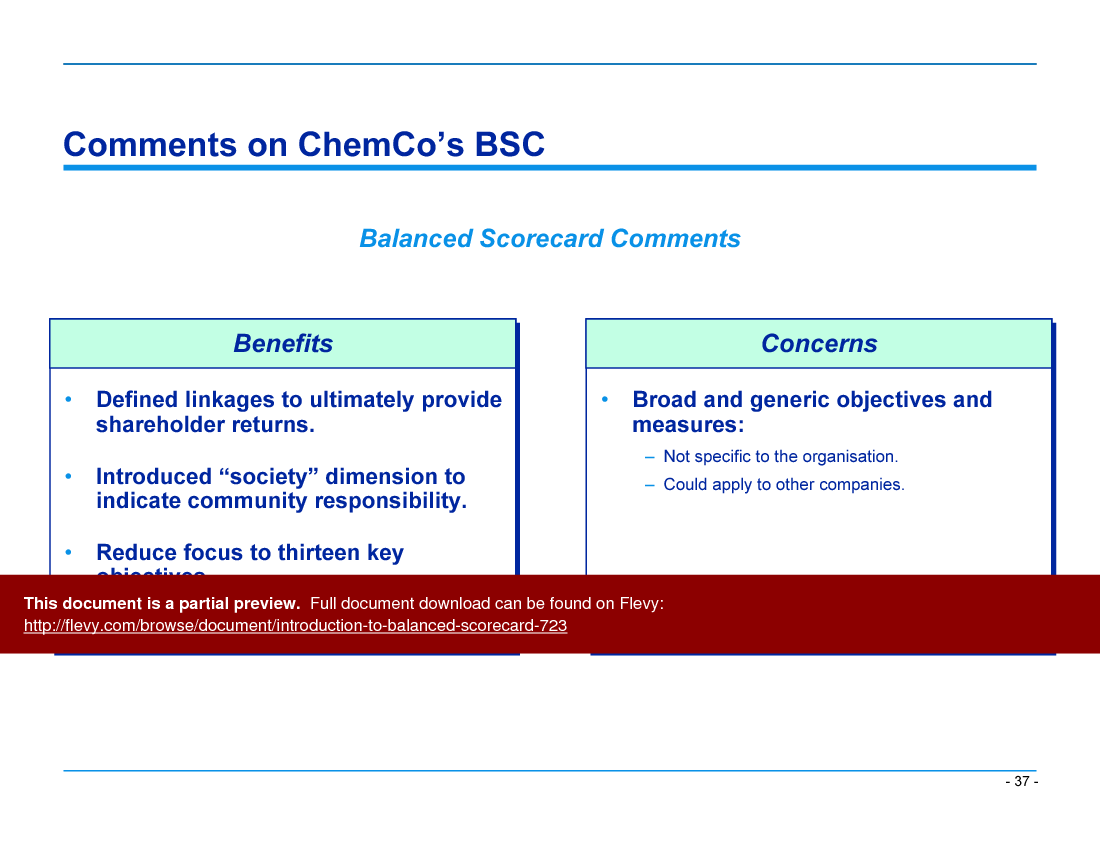
The contents include: BSC concept, BSC process, what makes a good objective and measure, example objectives and measures, example BSCs (Telco, Chemco, Manufco, OilCo, AluminumCo), lessons learned.
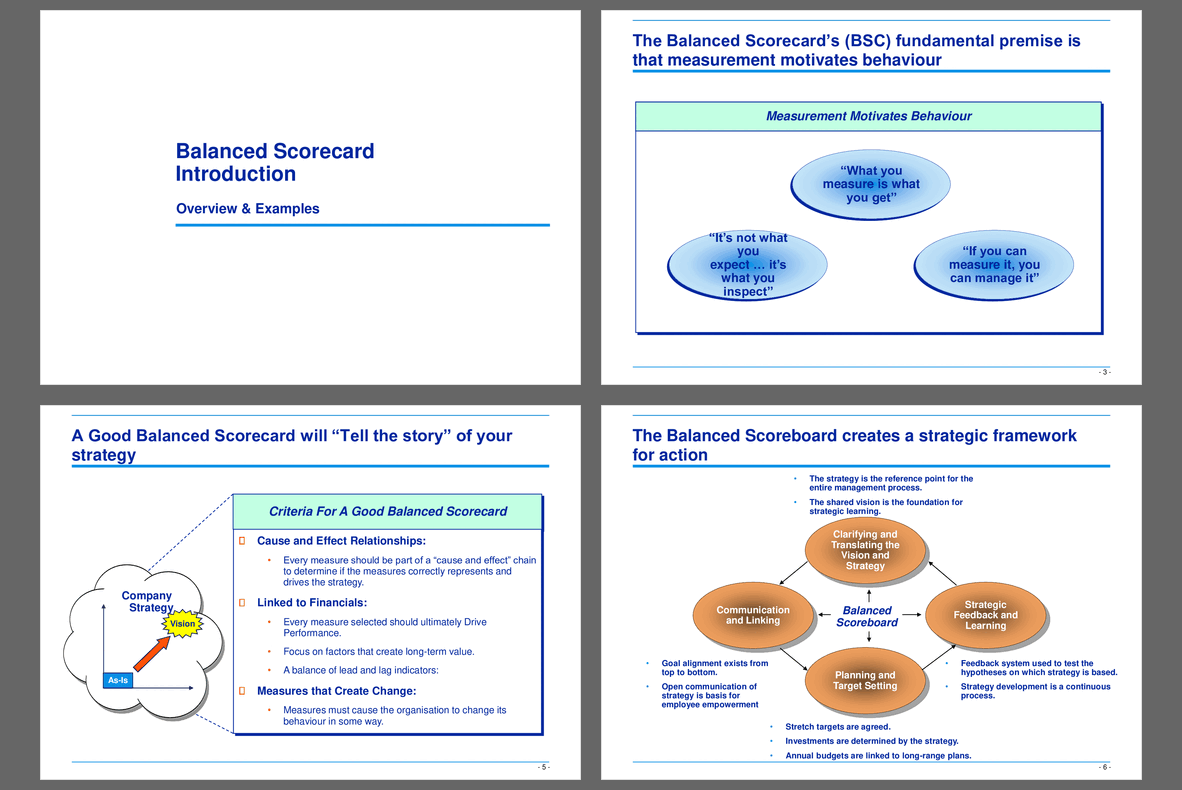
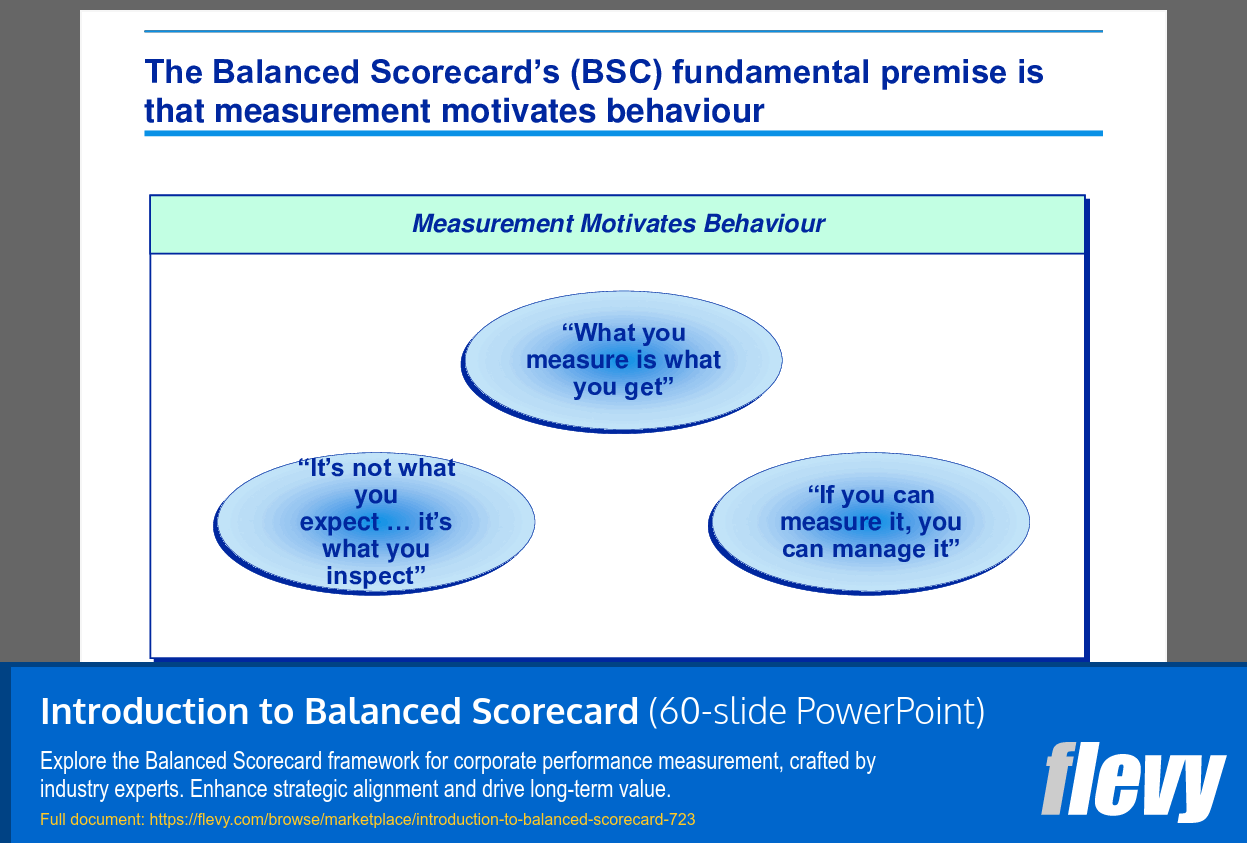
The BSC's focus is on factors which create long-term economic value in an organisation, for example:
+ Customer focus.
+ Organisational learning.
+ Business processes.
Traditional accounting measures are by definition backward looking:
+ Financial measures only reflect the results of actions already taken.
+ Do not provide an indication of future financial performance.
+ Do not indicate desired performance.
+ Do not provide a basis for planning and target setting.
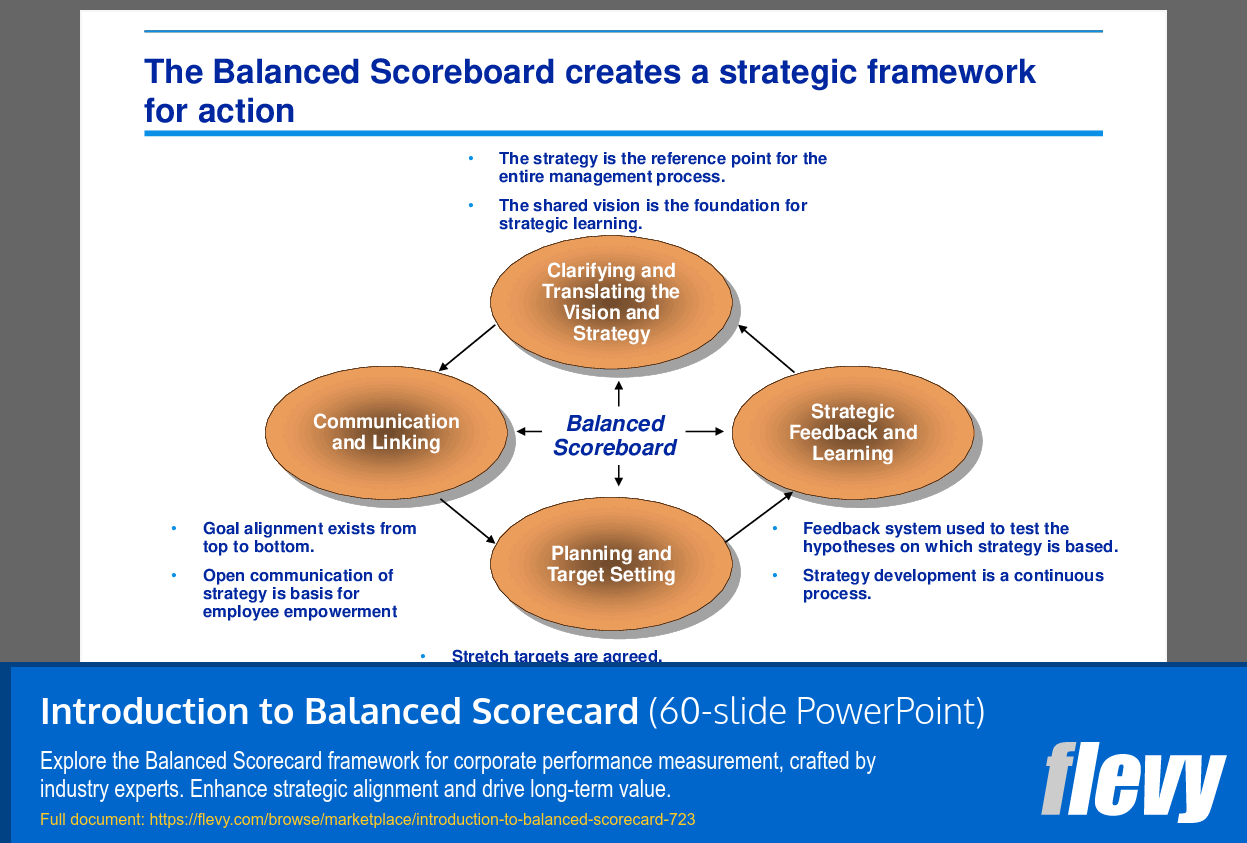
The Balanced Scorecard (BSC) translates an organization's vision and strategy into a comprehensive set of performance measures across four dimensions: Financial/Shareholder, Customers and Partners, Internal Processes, and Learning and Innovation. This multi-faceted approach ensures that all aspects of the business are aligned with the strategic objectives. It’s not just about financial metrics; it’s about creating a balanced view that includes customer satisfaction, internal processes, and the capacity for learning and growth.
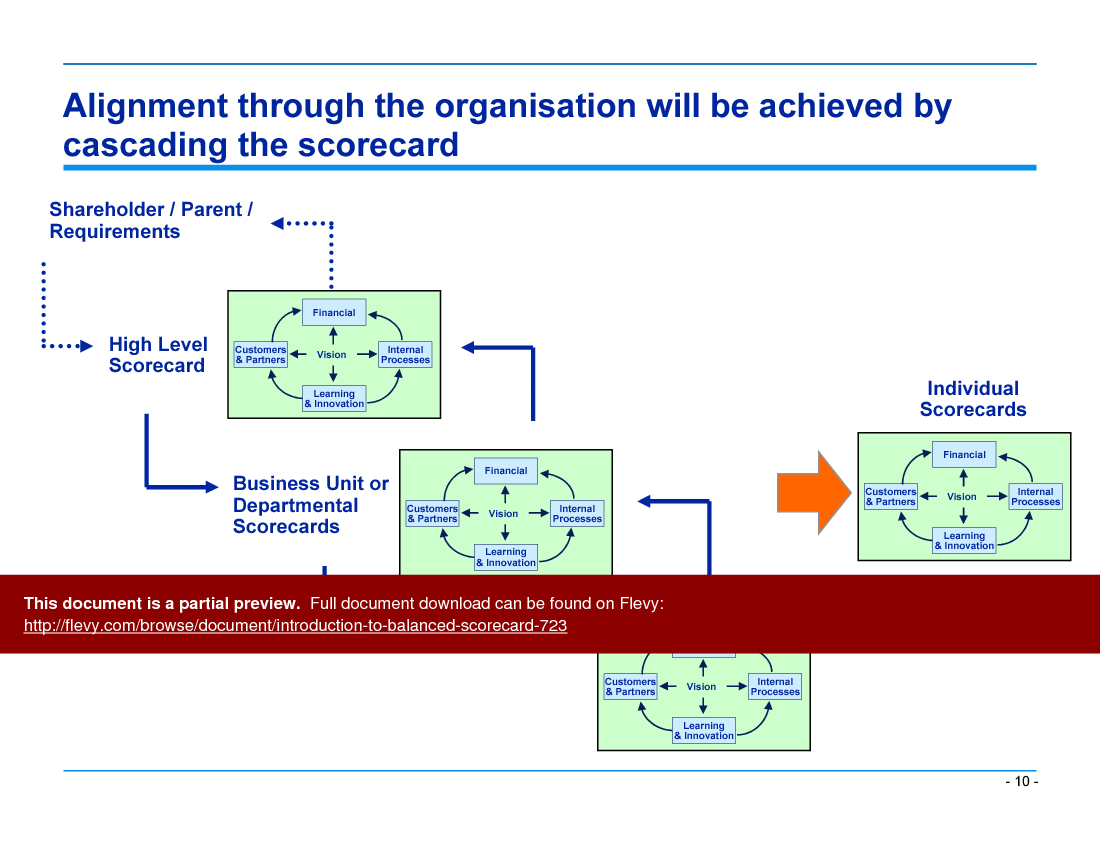
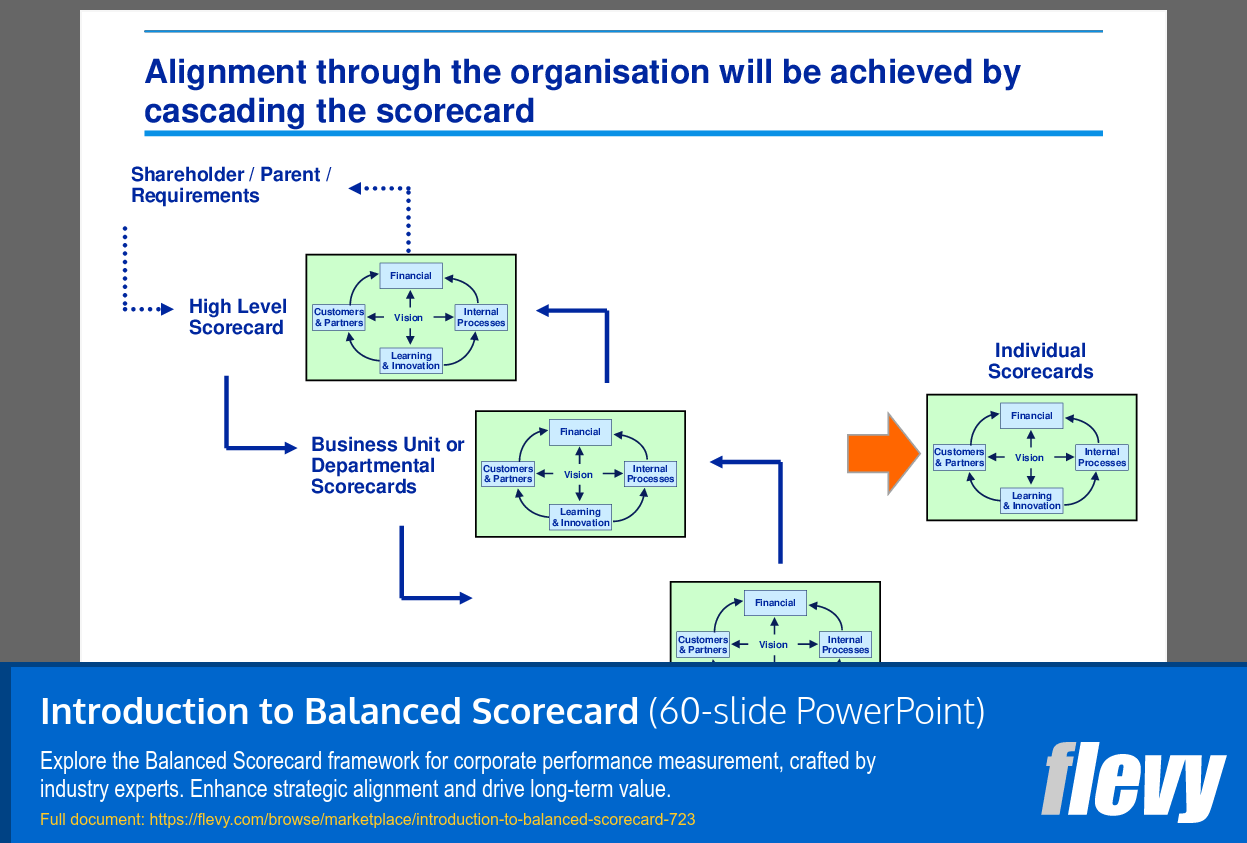
Alignment is key. The BSC framework cascades from high-level corporate goals down to individual scorecards, ensuring that every department and employee is focused on the strategic objectives. This cascading process helps in maintaining consistency and coherence across the organization. It also facilitates communication and understanding of the strategy at all levels, making it easier to manage and measure performance.
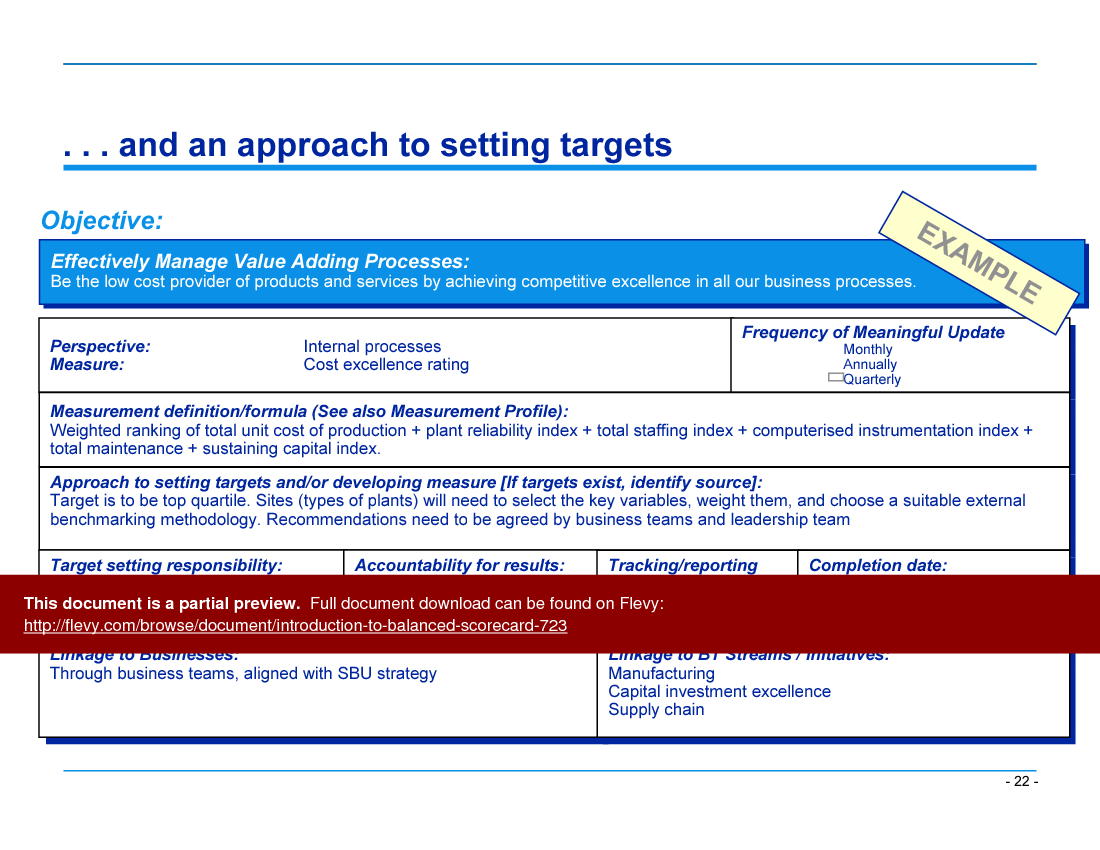
The document also emphasizes the importance of clear definitions for objectives, measures, and targets. Objectives define what needs to be achieved, measures indicate how success will be quantified, and targets specify the desired level of performance. By adhering to these definitions, organizations can ensure that their BSC is not only comprehensive, but also actionable. This clarity helps in setting realistic and achievable goals, ultimately driving the organization towards its strategic vision.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 60-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Introduction to Balanced Scorecard (BSC) presentation is a consulting-grade resource designed to equip corporate executives, integration leaders, and consultants with a comprehensive understanding of the Balanced Scorecard framework. This presentation, reflecting McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality rigor (not affiliated), outlines how the BSC can transform organizational strategy into actionable performance metrics. Buyers will learn to measure and manage key performance indicators that drive long-term economic value, aligning organizational objectives with financial outcomes. The BSC framework emphasizes a holistic approach to performance management, ensuring that all levels of the organization are aligned toward common goals.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to implement strategic performance measurement systems
• Integration leaders managing organizational change and performance tracking
• Consultants advising clients on strategic planning and performance management
• Business unit leaders responsible for aligning departmental objectives with corporate strategy
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to define and align organizational objectives
• When implementing performance management systems across departments
• For training sessions on the Balanced Scorecard methodology and its application
Learning Objectives
• Define the Balanced Scorecard framework and its importance in strategic management
• Build a comprehensive set of objectives, measures, and targets across the 4 BSC dimensions
• Establish cause-and-effect relationships to drive organizational performance
• Implement a cascading scorecard system to align objectives from the corporate level down to individual contributors
• Develop a feedback and learning system to continuously refine strategy and performance metrics
• Identify key performance indicators that promote organizational change and accountability
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Balanced Scorecard (page 3)
• The BSC Concept (page 4)
• Criteria for a Good Balanced Scorecard (page 5)
• Clarifying and Translating Vision and Strategy (page 6)
• Four Dimensions of Performance (page 7)
• Objectives, Measures, and Targets (page 8)
• Cascading the Scorecard (page 10)
• BSC Design and Implementation (page 13)
• Business Management Process (page 14)
• Examples of Balanced Scorecards (page 24)
• Lessons Learned (page 54)
Primary Topics Covered
• Balanced Scorecard Framework - The BSC framework translates organizational vision and strategy into measurable objectives across 4 key dimensions: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and innovation.
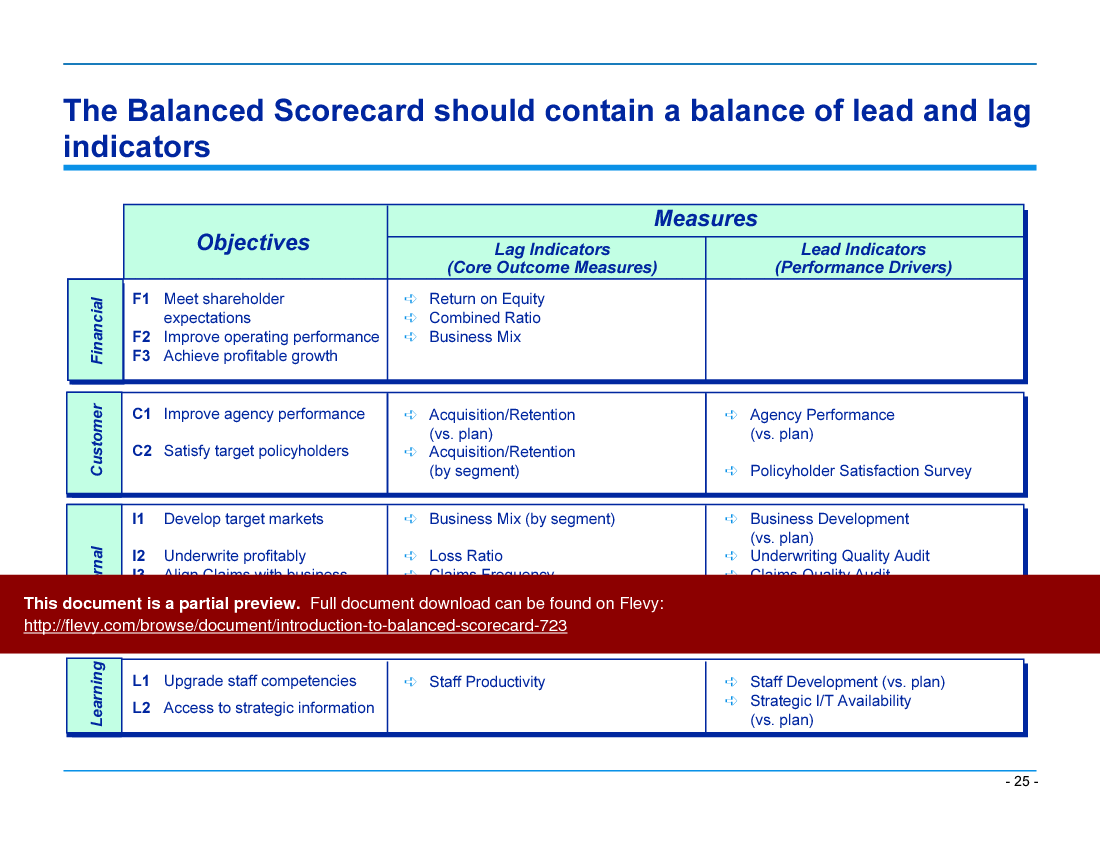
• Performance Measurement - Emphasizes the importance of measuring what drives behavior, focusing on both lead and lag indicators to ensure comprehensive performance tracking.
• Strategic Alignment - Discusses how to align objectives across various organizational levels through a cascading scorecard approach, ensuring that all employees are working toward shared goals.
• Continuous Improvement - Introduces the concept of a feedback loop that allows organizations to learn from performance data and adapt strategies accordingly.
• Implementation Challenges - Identifies common pitfalls in BSC implementation and provides guidance on how to avoid them for successful adoption.
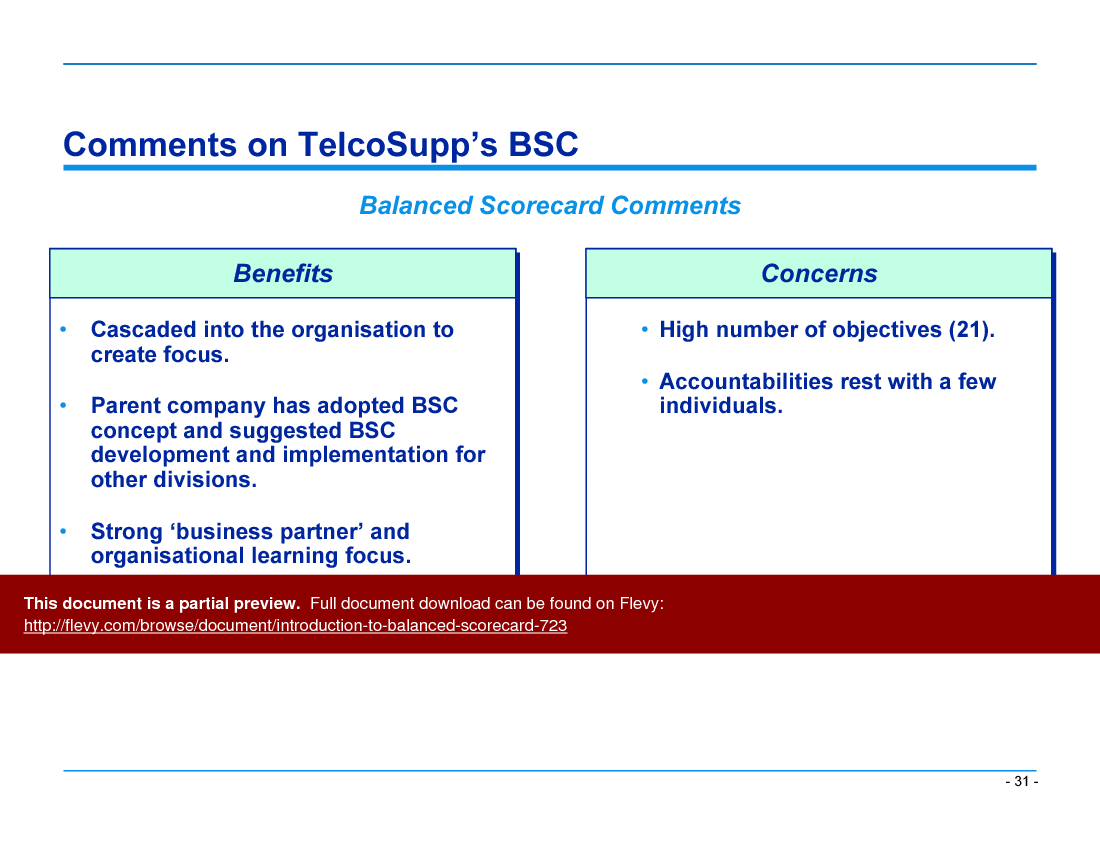
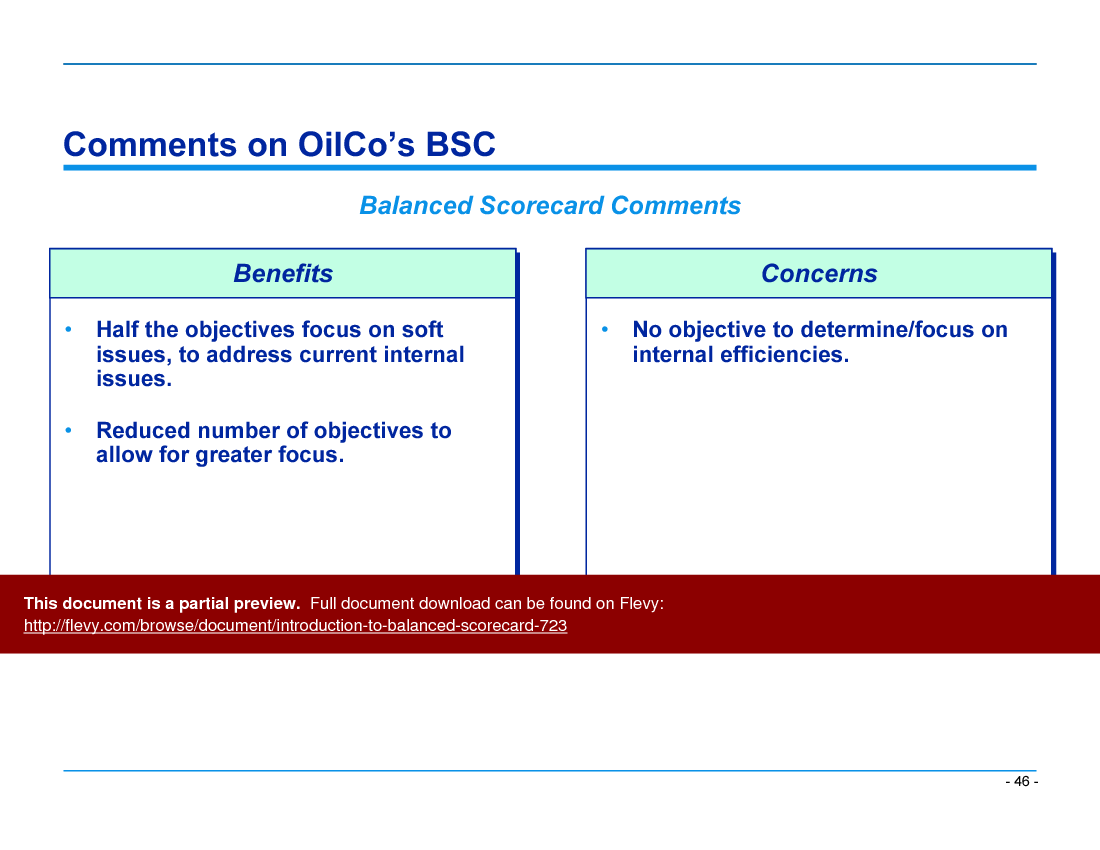
• Case Studies - Presents real-world examples of BSC applications in various industries, showcasing how organizations have successfully implemented the framework to drive performance.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Balanced Scorecard template for defining objectives, measures, and targets
• Example scorecards for various organizational levels (corporate, departmental, individual)
• Guidelines for establishing cause-and-effect relationships within the scorecard
• Framework for cascading scorecards throughout the organization
• Checklist for common pitfalls in BSC implementation and strategies to mitigate them
• Performance tracking dashboard template to visualize key metrics
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the Balanced Scorecard framework and its 4 dimensions
• Visual representation of the cascading scorecard approach
• Example objectives and measures for each BSC perspective
• Key criteria for developing effective performance measures
• Case study slides illustrating successful BSC implementations in various organizations
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Balanced Scorecard (60 minutes)
• Overview of BSC principles and framework
• Discussion on the importance of performance measurement
Developing Objectives and Measures (90 minutes)
• Workshop on defining objectives for each BSC dimension
• Interactive session to create measurable targets
Cascading the Scorecard (60 minutes)
• Strategies for aligning departmental and individual scorecards with corporate objectives
• Best practices for communication and engagement
Continuous Improvement and Feedback (60 minutes)
• Establishing a feedback loop for performance monitoring
• Techniques for refining objectives and measures based on performance data
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the BSC template to reflect specific organizational goals and strategies
• Adjust performance measures to align with industry benchmarks and standards
• Incorporate organizational terminology and metrics relevant to your business context
• Develop case studies or examples specific to your organization’s challenges and successes
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of leadership in BSC implementation
• Strategies for engaging employees in the performance management process
• The importance of aligning BSC with corporate culture and values
• Techniques for integrating BSC with other management frameworks
• The impact of technology on performance measurement and reporting
Topic FAQ
What are the 4 perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard and why include them?
The Balanced Scorecard organizes performance into 4 perspectives—Financial/Shareholder, Customers and Partners, Internal Processes, and Learning and Innovation—to ensure measurement beyond financial outcomes and to connect drivers of future value with results, covering both lead and lag indicators across the 4 dimensions.How do lead and lag indicators work in a Balanced Scorecard?
Lead indicators predict future performance and guide behavior, while lag indicators reflect past outcomes. The BSC emphasizes including both so organizations can plan and track progress; Flevy's Introduction to Balanced Scorecard provides guidance on selecting and balancing lead and lag indicators within scorecards and measures.What does cascading a scorecard mean and how is it applied?
Cascading a scorecard is the process of translating corporate objectives into aligned objectives, measures, and targets at departmental and individual levels so everyone contributes to strategy execution; the presentation includes a cascading scorecard framework and example scorecards to illustrate this process.I need to align a business unit's goals with corporate strategy—what steps should I follow?
Define the unit’s role in corporate strategy, map cause-and-effect links to corporate objectives, set measurable objectives and targets across the 4 BSC dimensions, and cascade agreed measures down to team and individual scorecards; templates and example scorecards in Flevy's Introduction to Balanced Scorecard support these steps.What should I look for when choosing a Balanced Scorecard toolkit or training deck?
Look for clear templates for objectives, measures, and targets; tools for mapping cause-and-effect; guidance on cascading scorecards; example scorecards for different levels; and materials addressing common implementation pitfalls, such as a checklist for common pitfalls in BSC implementation.Are paid Balanced Scorecard templates useful for a mid-sized company considering limited internal resources?
Paid templates provide pre-built structure for defining objectives, measures, targets, cascading, and performance visualization, which can reduce design time and provide examples; Flevy's Introduction to Balanced Scorecard bundles these deliverables in a 60-slide PowerPoint.How often should an organization review and update its Balanced Scorecard?
The BSC should be reviewed regularly to remain relevant and aligned with strategy; the guidance recommends reviewing the scorecard in conjunction with strategic planning sessions to update objectives, measures, and targets as needed.Can the Balanced Scorecard be adapted across industries, and are there industry examples to copy?
Yes—the BSC is customizable to different industry contexts. The presentation includes example scorecards and measures used for multiple industries, specifically example BSCs for Telco, Chemco, Manufco, OilCo, and AluminumCo.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the Balanced Scorecard?
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management framework that translates an organization’s vision and strategy into measurable objectives across 4 dimensions: financial, customer, internal processes, and learning and innovation.
How does the BSC differ from traditional measurement approaches?
Unlike traditional measurement methods that focus solely on financial outcomes, the BSC incorporates a broader range of performance indicators that drive long-term value creation, including customer satisfaction and internal process efficiency.
What are the key components of a successful BSC?
A successful BSC includes clearly defined objectives, measurable indicators, achievable targets, and a cascading structure that aligns goals across all levels of the organization.
How can organizations ensure alignment through the BSC?
Organizations can achieve alignment by cascading the scorecard from the corporate level down to individual contributors, ensuring that all employees understand their role in achieving strategic objectives.
What are common pitfalls in BSC implementation?
Common pitfalls include lack of leadership buy-in, unclear objectives, excessive measures, and failure to communicate the scorecard effectively throughout the organization.
How often should the BSC be reviewed?
The BSC should be reviewed regularly, ideally in conjunction with strategic planning sessions, to ensure that it remains relevant and aligned with organizational goals.
Can the BSC be adapted for different industries?
Yes, the BSC framework is flexible and can be customized to fit the specific needs and challenges of various industries, making it a versatile tool for performance management.
What role does technology play in the BSC?
Technology can enhance the BSC by providing tools for data collection, analysis, and reporting, enabling organizations to track performance metrics more efficiently.
How can organizations measure the success of their BSC implementation?
Success can be measured through improvements in key performance indicators, employee engagement levels, and alignment of departmental objectives with corporate strategy.
What is the importance of feedback in the BSC process?
Feedback is crucial for continuous improvement, allowing organizations to adapt their strategies and performance measures based on real-time data and changing circumstances.
Glossary
• Balanced Scorecard - A strategic management tool that translates vision and strategy into measurable objectives across 4 dimensions.
• Lead Indicator - A performance measure that predicts future success.
• Lag Indicator - A performance measure that reflects past performance outcomes.
• Cascading Scorecard - The process of aligning scorecards at various organizational levels to ensure strategic alignment.
• Performance Metric - A quantifiable measure used to evaluate success in achieving objectives.
• Strategic Alignment - The process of ensuring that all organizational activities are aligned with the overall strategy.
• Continuous Improvement - An ongoing effort to enhance products, services, or processes.
• Feedback Loop - A system for monitoring performance and making adjustments based on results.
• Objectives - Specific goals that an organization aims to achieve.
• Targets - Specific performance levels that an organization seeks to achieve within a defined timeframe.
• Accountability - The responsibility assigned to individuals for achieving specific objectives.
• Vision - The desired future state of an organization that guides its strategy and objectives.
• Strategy - A plan of action designed to achieve long-term goals.
• Performance Management - The process of ensuring that organizational goals are met efficiently and effectively.
• Key Performance Indicator (KPI) - A measurable value that demonstrates how effectively an organization is achieving key business objectives.
• Stakeholder - An individual or group that has an interest in the success of an organization.
• Organizational Learning - The process of creating, retaining, and transferring knowledge within an organization.
• Financial Performance - A measure of how well an organization uses its assets to generate revenue.
• Customer Satisfaction - A measure of how products or services meet or exceed customer expectations.
• Internal Processes - The operations and procedures that an organization uses to deliver value to customers.
BALANCED SCORECARD PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Balanced Scorecard PowerPoint Slides: Introduction to Balanced Scorecard PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Documents & Files