Balanced Scorecard - Comprehensive Guide (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 54 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Provide an understanding of Balanced Score Cards
- Provide ways of overcoming the short-falls of Balanced Score Cards
- Provide examples of Balanced Score Cards for reference
BALANCED SCORECARD PPT DESCRIPTION
The objectives of this document are:
• Provide an understanding of Balanced Score Cards (BSC):
• Definition – What they are?
• Context – When the are used?
• Benefits – Why they are used?
• Development and implementation – How they are used?
• Provide ways of overcoming the short-falls of Balanced Score Cards
• Provide examples of Balanced Score Cards for reference
This guide delves into the core principles of the Balanced Scorecard, emphasizing its balanced approach, focus on key measures, and the importance of cause-and-effect relationships. It highlights how the Balanced Scorecard links financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth measures to strategic objectives. The PPT provides a detailed methodology for defining, measuring, capturing, and reporting performance, ensuring that all performance metrics are aligned with business goals.
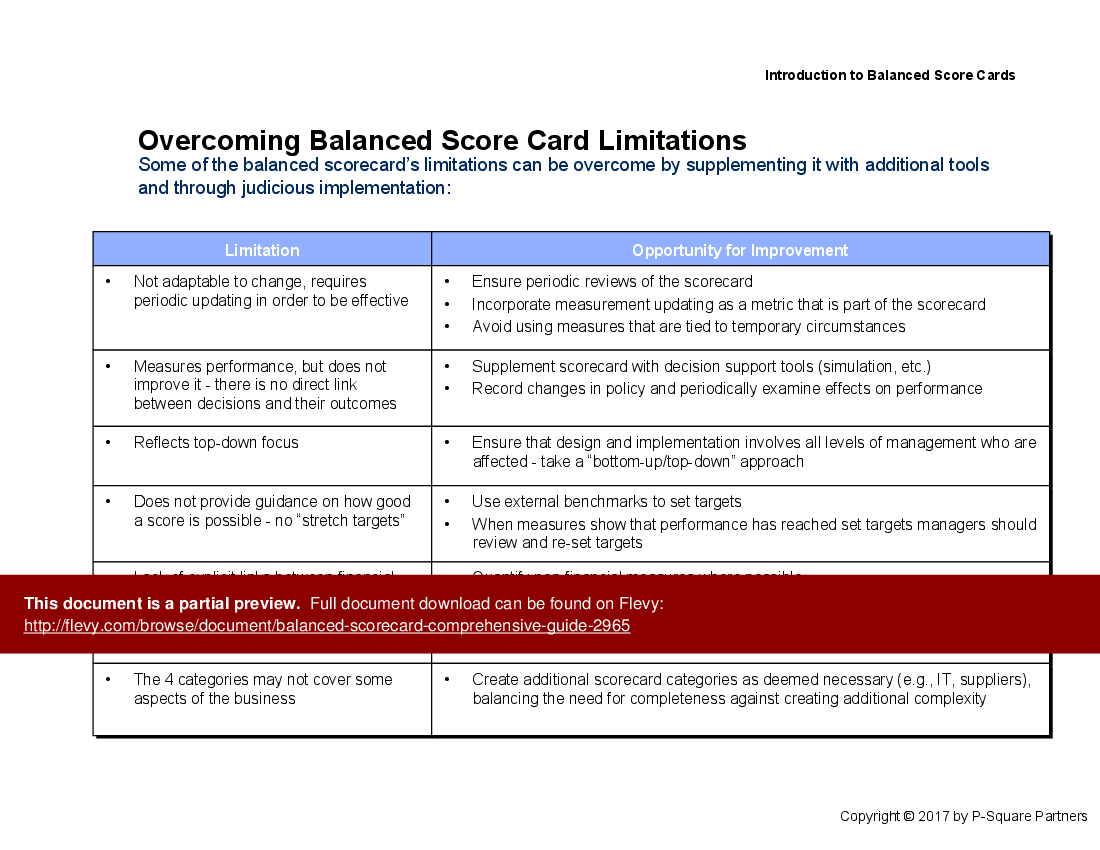
The document also addresses common limitations of the Balanced Scorecard and offers practical solutions to overcome these challenges. It suggests periodic reviews, incorporating external benchmarks, and using decision support tools to enhance the effectiveness of the scorecard. The guide emphasizes the importance of involving all levels of management in the design and implementation process to ensure comprehensive and accurate performance measurement.
Additionally, the guide includes real-world examples of Balanced Scorecard measures, providing a clear illustration of how to apply these principles in various business contexts. It outlines a structured approach to developing, implementing, and managing Balanced Scorecards, ensuring that businesses can effectively track and improve their performance across multiple dimensions. This comprehensive guide is an essential resource for executives looking to leverage the Balanced Scorecard to drive strategic performance management.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 54-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This Balanced Scorecard guide, crafted by seasoned consultants, offers a McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality framework for understanding and implementing Balanced Scorecards (BSC). It provides a thorough exploration of BSC principles, development processes, and practical applications for both business and project performance management. Buyers will gain insights into aligning strategic objectives with measurable performance indicators, overcoming common limitations, and utilizing real-world examples to enhance organizational effectiveness.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to implement strategic performance management frameworks
• Project managers aiming to track and enhance project outcomes
• Business analysts focused on aligning departmental goals with overarching strategies
• Performance improvement teams looking to make intangible assets visible
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to align business objectives with performance metrics
• When initiating project management frameworks to ensure accountability and track benefits
• In performance reviews to assess progress against strategic goals and adjust as necessary
Learning Objectives
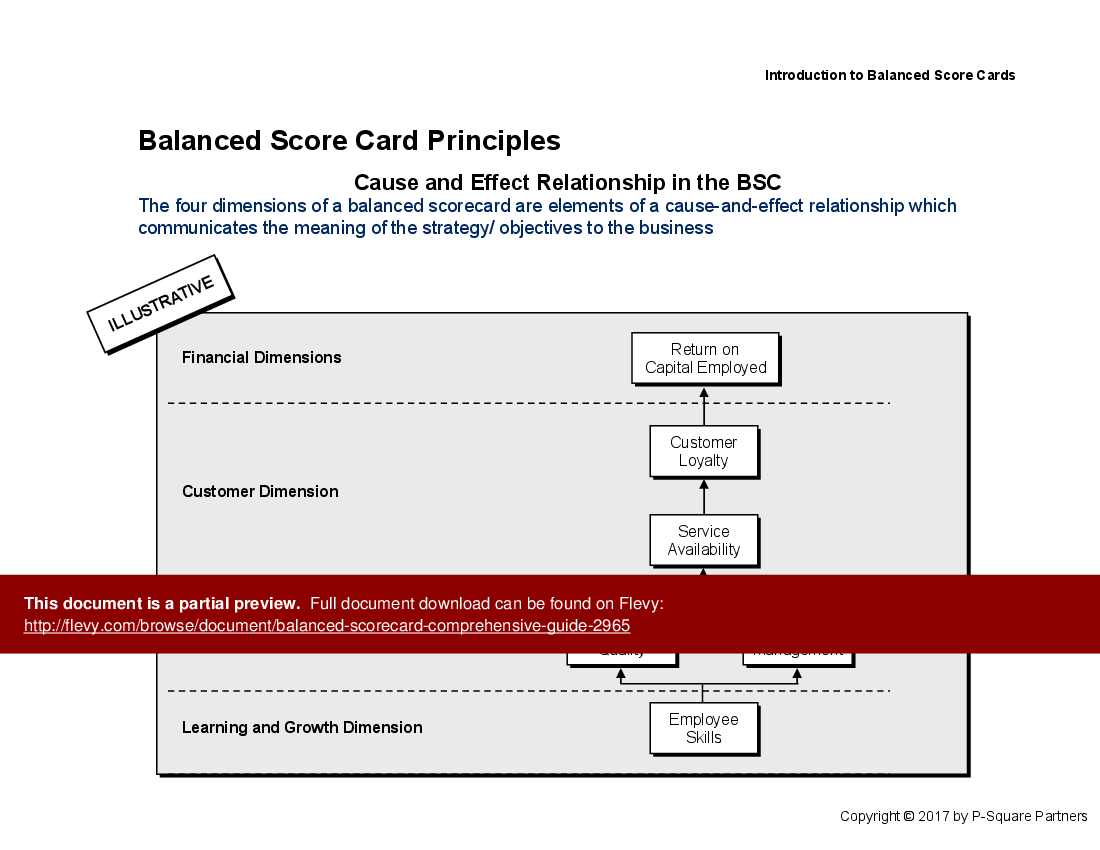
• Define the Balanced Scorecard and its 4 dimensions: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth
• Develop and implement a Balanced Scorecard tailored to specific organizational needs
• Identify and overcome common limitations associated with traditional Balanced Scorecards
• Utilize real-world examples to illustrate effective Balanced Scorecard applications
• Establish a systematic approach for ongoing performance management and iterative improvement
• Create actionable performance measures that reflect both short-term and long-term strategic goals
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Balanced Scorecards (page 3)
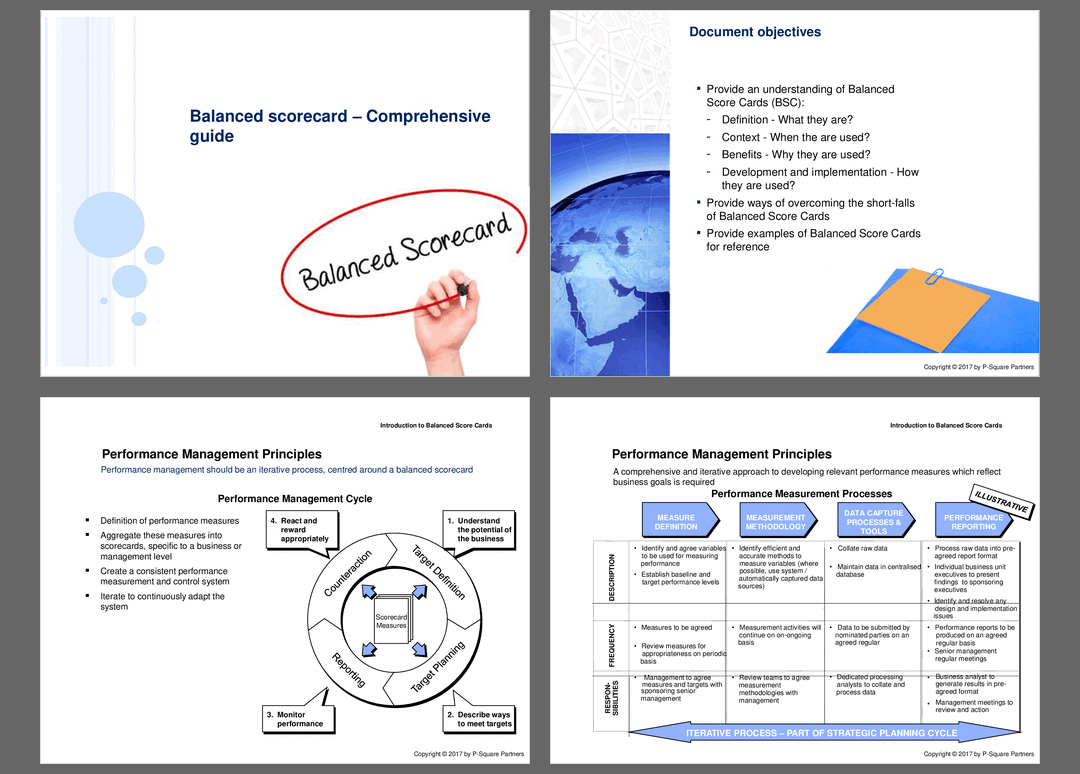
• Performance Management Principles (page 5)
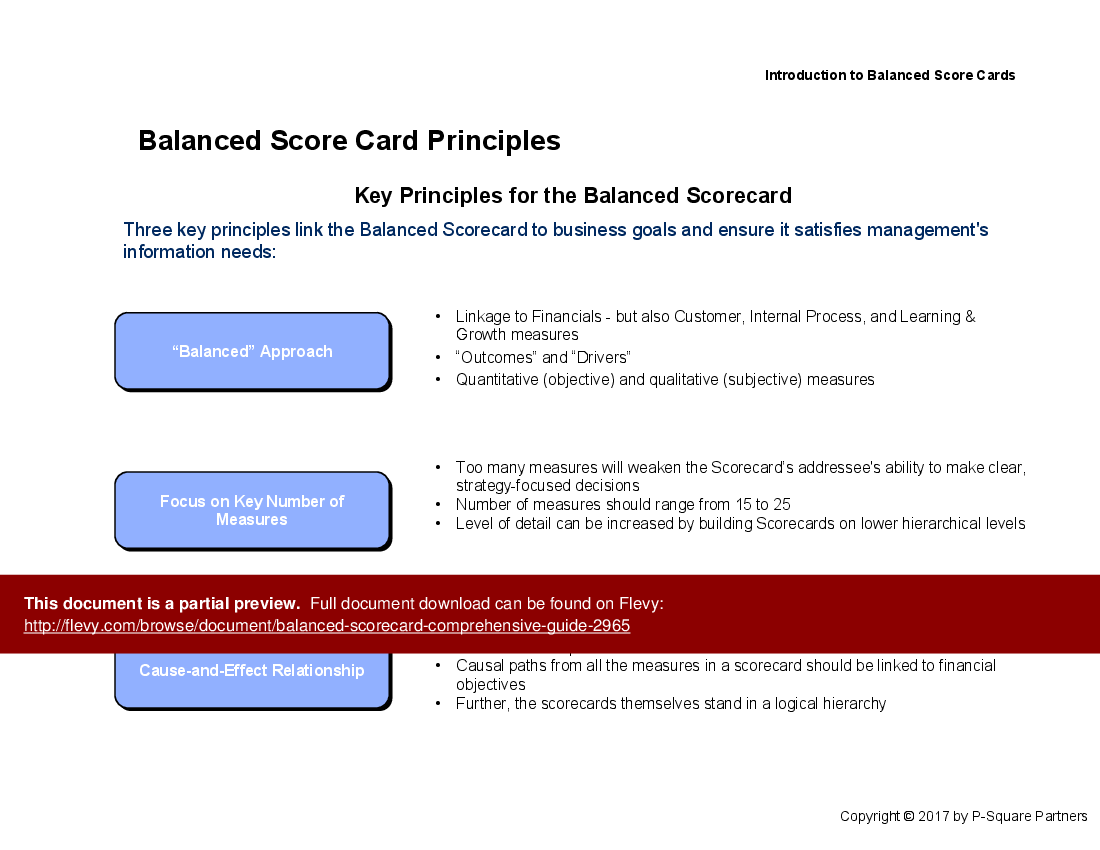
• Balanced Scorecard Principles (page 10)
• Overcoming Balanced Scorecard Limitations (page 15)
• Balanced Scorecards for Business Performance Management (page 20)
• Balanced Scorecards for Project Performance Management (page 25)
Primary Topics Covered
• Balanced Scorecard Overview - A foundational understanding of Balanced Scorecards as tools for measuring and managing business performance through a balanced view of financial and non-financial indicators.
• Performance Management Principles - Key principles that guide effective performance management, including iterative processes and accountability measures.
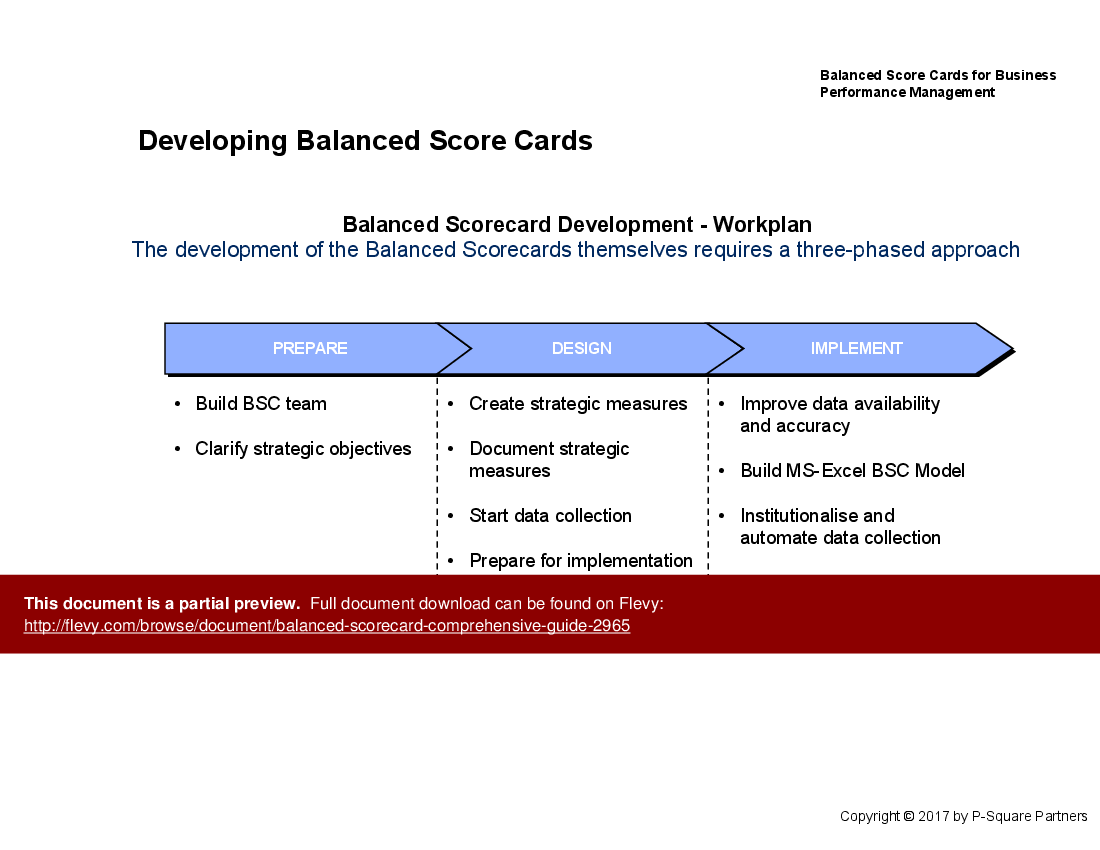
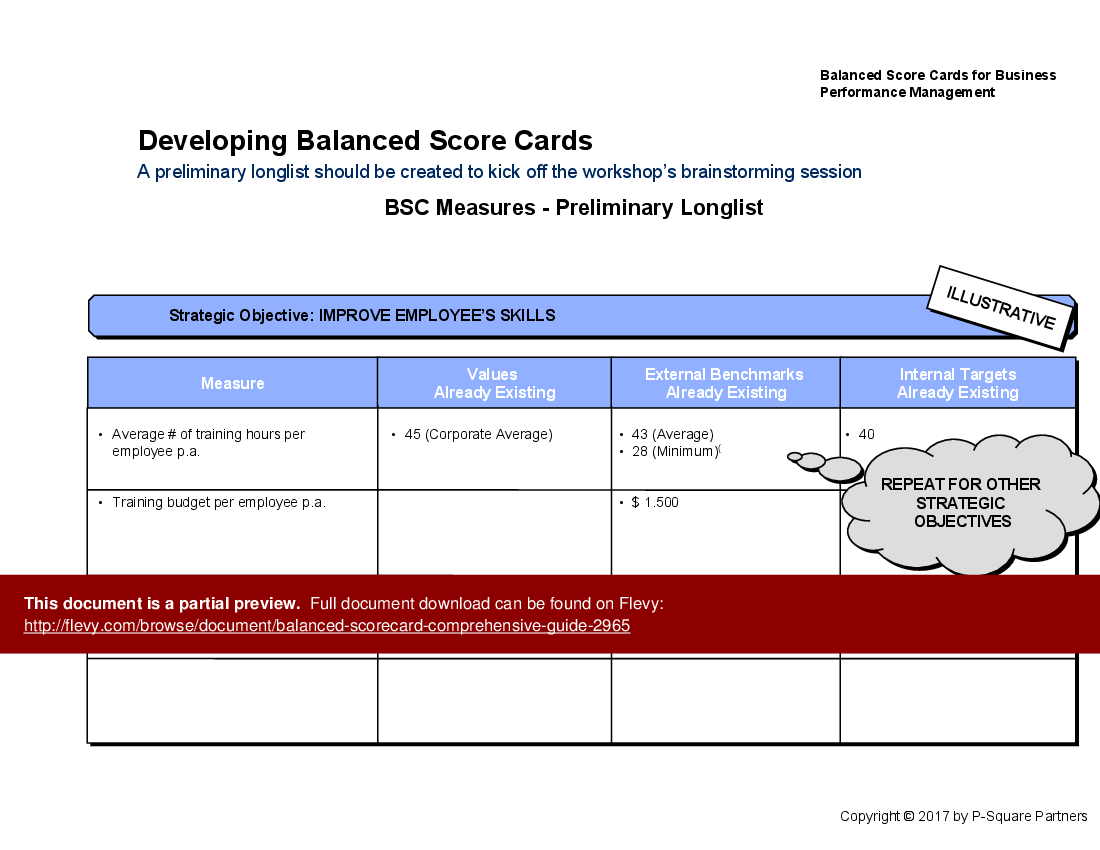
• Balanced Scorecard Development - A structured approach to creating and implementing Balanced Scorecards, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives.
• Limitations of Balanced Scorecards - Common challenges faced when using Balanced Scorecards and strategies for overcoming these obstacles.
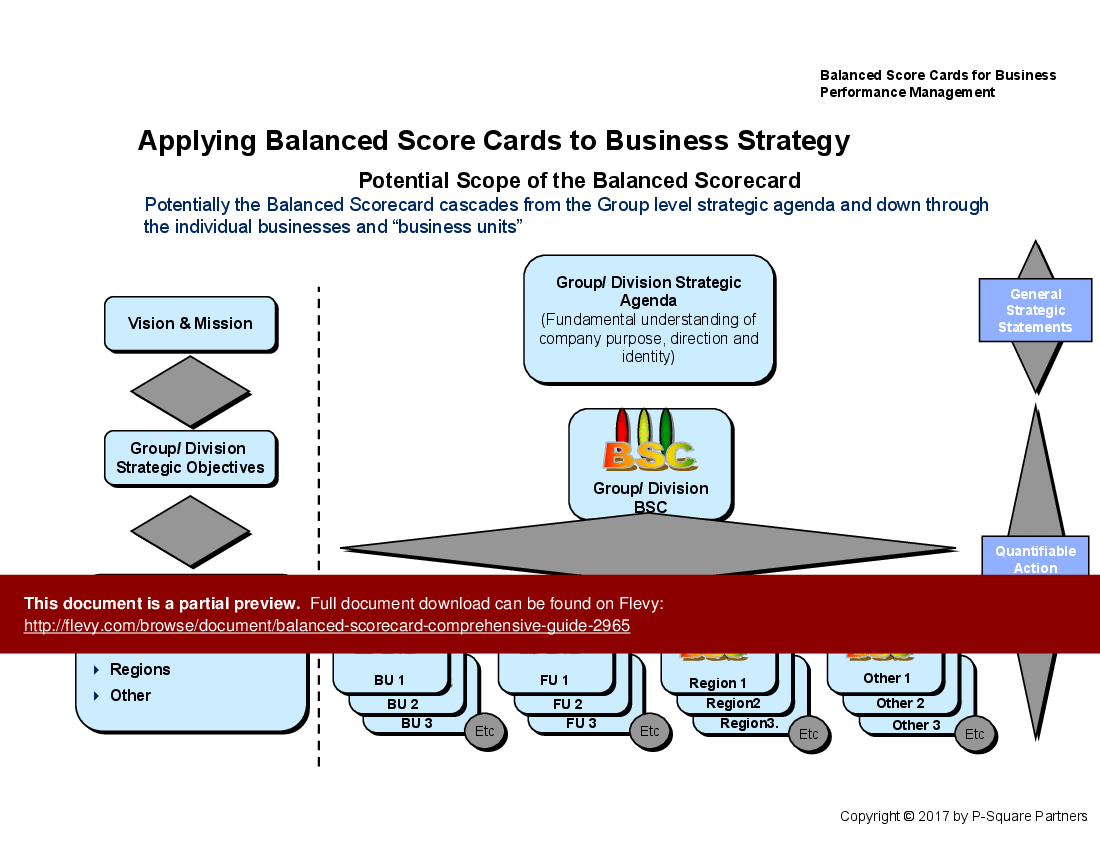
• Business Performance Management - Application of Balanced Scorecards in managing overall business performance and aligning departmental goals.
• Project Performance Management - Utilizing Balanced Scorecards to track project outcomes and ensure successful implementation of project objectives.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Balanced Scorecard templates for business and project performance management
• Performance measurement frameworks that integrate financial and non-financial metrics
• Iterative performance management cycle documentation
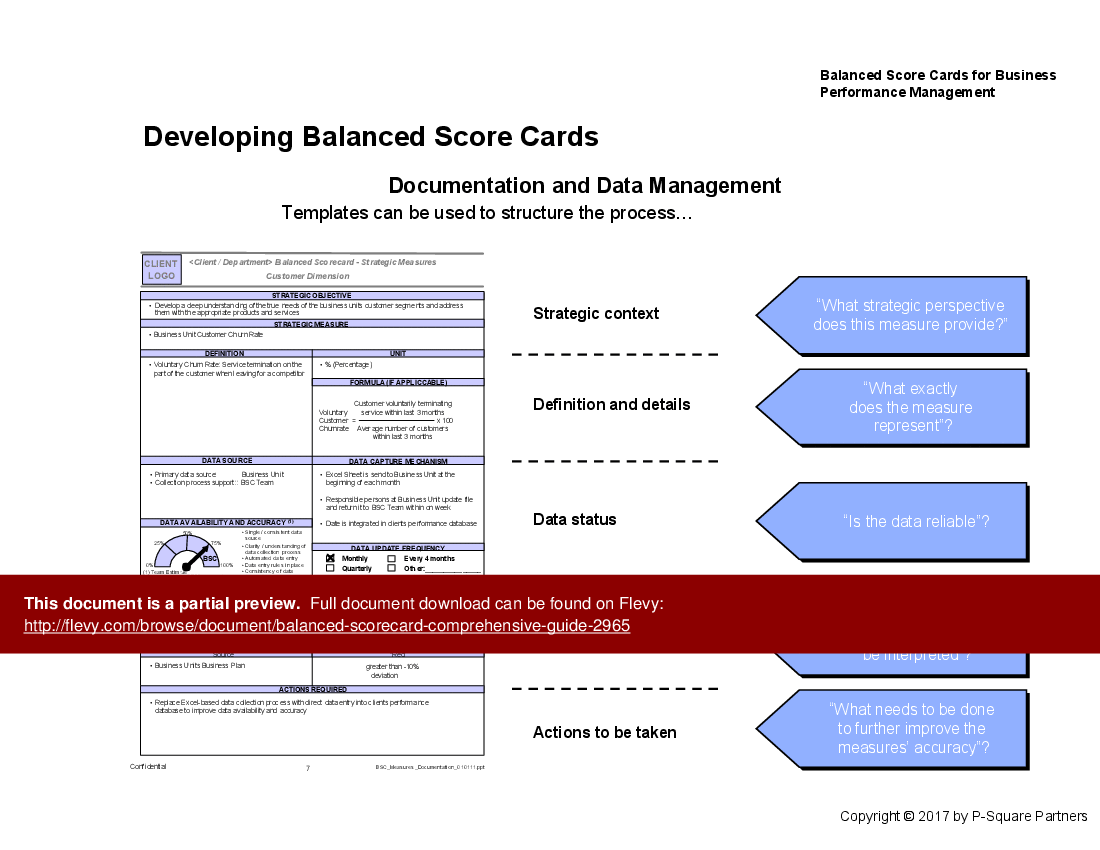
• Data capture and reporting tools to facilitate ongoing performance tracking
• Examples of Balanced Scorecards tailored to various business contexts
• Guidelines for conducting post-implementation reviews and lessons learned sessions
Slide Highlights
• Overview slide detailing the 4 dimensions of the Balanced Scorecard
• Performance Management Cycle slide illustrating the iterative nature of performance management
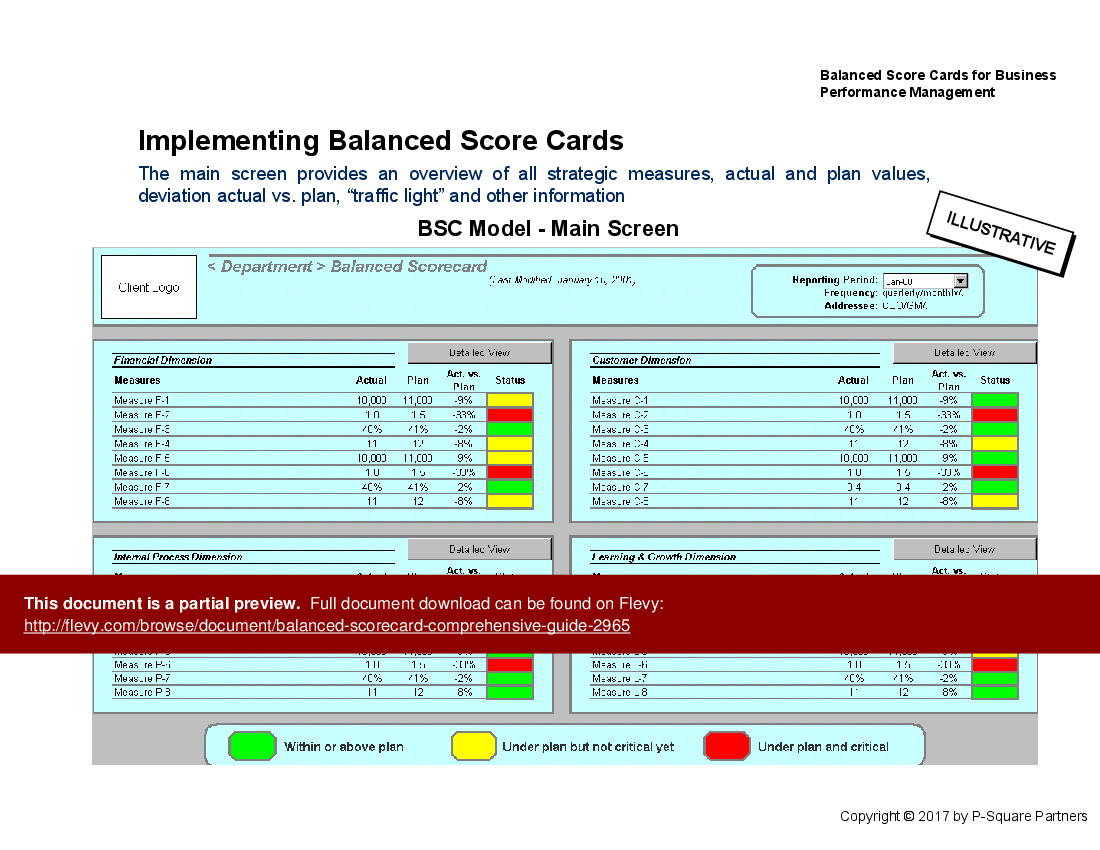
• Sample Balanced Scorecard showcasing key performance indicators across various business functions
• Limitations and opportunities for improvement slide outlining common challenges and solutions
• Project Management Meeting and Reporting Timeline slide for effective project tracking
Potential Workshop Agenda
Balanced Scorecard Introduction Session (90 minutes)
• Overview of Balanced Scorecard principles and applications
• Discussion on aligning departmental goals with strategic objectives
• Interactive session on identifying key performance indicators
Performance Management Implementation Workshop (120 minutes)
• Hands-on development of a tailored Balanced Scorecard
• Group work on overcoming common limitations in performance management
• Presentation of group findings and feedback session
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the Balanced Scorecard metrics to reflect specific organizational goals and industry standards
• Adjust performance measures based on the unique needs of different business units
• Incorporate feedback mechanisms to ensure continuous improvement of the Balanced Scorecard
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of executive sponsorship in successful Balanced Scorecard implementation
• Integration of qualitative and quantitative measures in performance tracking
• Best practices for data collection and reporting in performance management
• Strategies for fostering buy-in from all levels of management
Topic FAQ
What are the 4 perspectives of a Balanced Scorecard and why include both financial and non-financial measures?
The Balanced Scorecard organizes performance into 4 perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning & Growth. Including financial and non-financial measures provides a balanced view of past performance and future capability, helping translate strategy into measurable objectives across the 4 dimensions.How do I develop effective KPIs for each Balanced Scorecard perspective?
Develop KPIs by defining strategic objectives, mapping cause-and-effect links between objectives and measures, and selecting a mix of financial and non-financial indicators that align with strategy. Engage stakeholders for relevance and ensure KPIs map to the 4 perspectives and performance measurement frameworks.What common limitations do organizations face with Balanced Scorecards and how can they be mitigated?
Common limitations include rigidity to change, complexity, and limited guidance on target setting. Mitigation approaches in the guidance include periodic reviews, incorporating external benchmarks, and using decision support and reporting tools to adjust measures and maintain relevance, as described in the documentation.How can a Balanced Scorecard be applied to project performance management?
For projects, a Balanced Scorecard tracks outcomes against predefined project objectives, establishes accountability, and integrates reporting timelines into governance. The guide includes project-focused templates and a Project Management Meeting and Reporting Timeline slide to support project performance management.Our team is small and needs to implement a Balanced Scorecard quickly—what practical steps should we follow?
Tailor metrics to core objectives, adjust measures for specific units, and build feedback loops for continuous improvement. The guide offers customization guidance plus suggested workshop formats—a 90-minute introduction or a 120-minute implementation workshop—to accelerate adoption and design.What should I look for when purchasing a Balanced Scorecard template or toolkit?
Look for templates for both business and project performance, performance measurement frameworks, iterative performance cycle documentation, data capture and reporting tools, and example scorecards that can be tailored. The Balanced Scorecard - Comprehensive Guide lists these deliverables and templates for customization.Are paid Balanced Scorecard templates more time-efficient than building one from scratch?
Paid templates typically provide pre-built Balanced Scorecard templates, sample scorecards, data capture/reporting tools, and workshop agendas that support faster implementation. The Balanced Scorecard - Comprehensive Guide specifically includes templates, examples, and iterative cycle documentation to reduce design time.How often should a Balanced Scorecard be reviewed to remain effective?
A Balanced Scorecard should be reviewed periodically to reflect changing business conditions and strategy. The guidance recommends regular updates, stakeholder feedback, and use of iterative performance management cycle documentation and post-implementation review guidelines to maintain relevance.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is a Balanced Scorecard?
A Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management tool that helps organizations align business activities to the vision and strategy of the organization, improve internal and external communications, and monitor organizational performance against strategic goals.
How do I implement a Balanced Scorecard?
Implementation involves defining strategic objectives, developing relevant performance measures, and ensuring alignment across all levels of the organization. It is crucial to engage stakeholders throughout the process for effective adoption.
What are the limitations of a Balanced Scorecard?
Common limitations include inflexibility to change, potential complexity, and a lack of clear guidance on target setting. These can be mitigated through regular reviews and adjustments to the scorecard.
How can I ensure my Balanced Scorecard remains relevant?
Regularly update the scorecard to reflect changing business conditions, incorporate feedback from users, and ensure that performance measures align with current strategic objectives.
What types of performance measures should I include?
Include a mix of financial and non-financial measures that reflect both past performance and future potential, ensuring a balanced view of organizational health.
How often should I review the Balanced Scorecard?
Performance measures should be reviewed periodically to ensure they remain relevant and effective in tracking progress against strategic goals.
Can the Balanced Scorecard be used for project management?
Yes, the Balanced Scorecard can effectively track project performance by measuring outcomes against predefined objectives and ensuring accountability for results.
What is the role of data in a Balanced Scorecard?
Data is essential for measuring performance against targets, informing decision-making, and facilitating continuous improvement in organizational processes.
Glossary
• Balanced Scorecard - A strategic management tool that translates an organization's vision and strategy into a set of performance measures.
• Performance Management - The process of ensuring that organizational goals are consistently being met in an effective and efficient manner.
• Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) - Specific metrics used to evaluate the success of an organization in achieving its objectives.
• Strategic Objectives - Specific goals that an organization aims to achieve in alignment with its mission and vision.
• Iterative Process - A cyclical approach to performance management that involves continuous assessment and adjustment.
• Financial Measures - Metrics that assess the financial performance of an organization, such as profit margins and return on investment.
• Non-Financial Measures - Metrics that evaluate other aspects of performance, such as customer satisfaction and employee engagement.
• Data Capture - The process of collecting and managing data for analysis and reporting purposes.
• Executive Sponsorship - The support and commitment from senior management to drive the implementation of strategic initiatives.
• Post-Implementation Review - A process to evaluate the outcomes of a project after its completion to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement.
• Stakeholder Engagement - The involvement of individuals or groups who have an interest in the outcomes of a project or initiative.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to enhance products, services, or processes to achieve incremental gains in efficiency or quality.
BALANCED SCORECARD PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Balanced Scorecard PowerPoint Slides: Balanced Scorecard - Comprehensive Guide PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, P-Square Partners