Digital Transformation: Blockchain Technology (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 87 Slides
DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION PPT DESCRIPTION
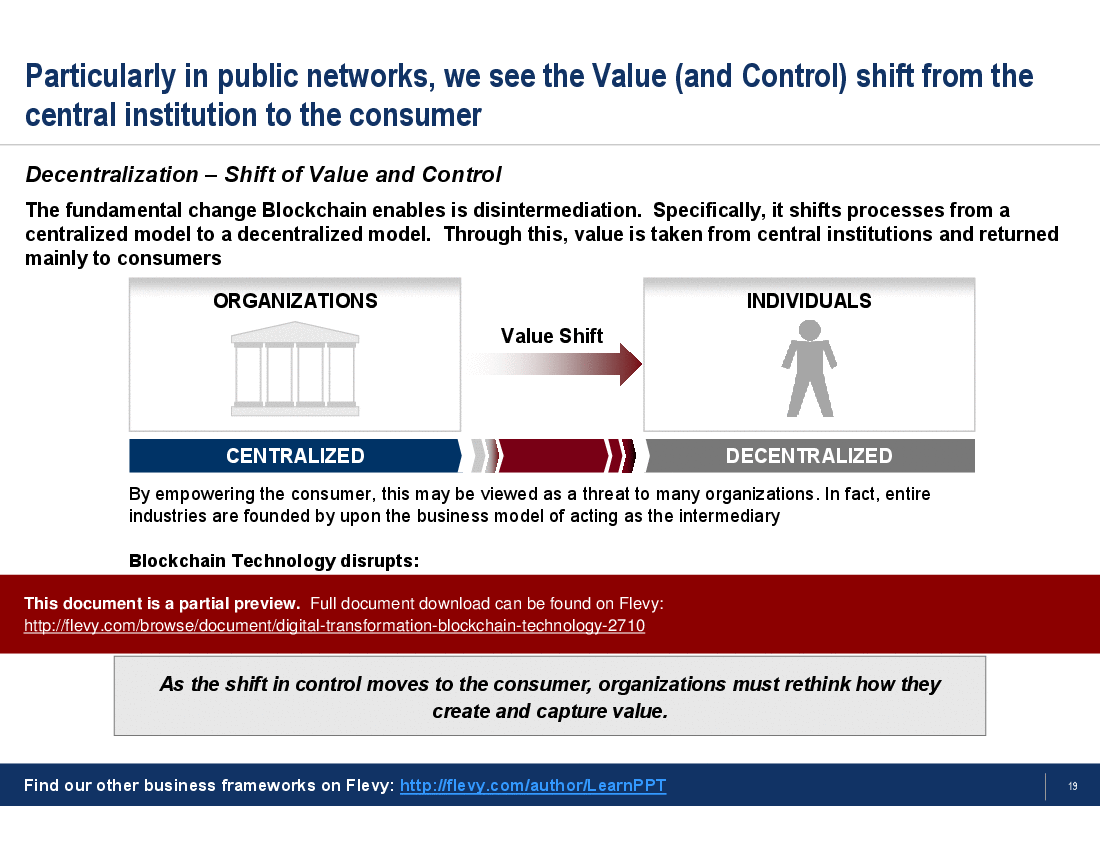
Blockchain Technology is an emerging database technology that has gained widespread appeal across many industries, mostly driven by the rise of cryptocurrencies—most notably Bitcoin. It provides numerous process benefits, including efficiency, security, transparency/openness, low cost, data integrity, among others. Perhaps its greatest benefit is disintermediation—which has the very real potential to disrupt industries and completely alter how global trade is conducted. Disintermediation and decentralization shifts Control and Value from the organization to the consumer.
This presentation explains what Blockchain Technology actually is. Specific topics covered include:
• Blockchain Myths
• Types of Blockchain Networks
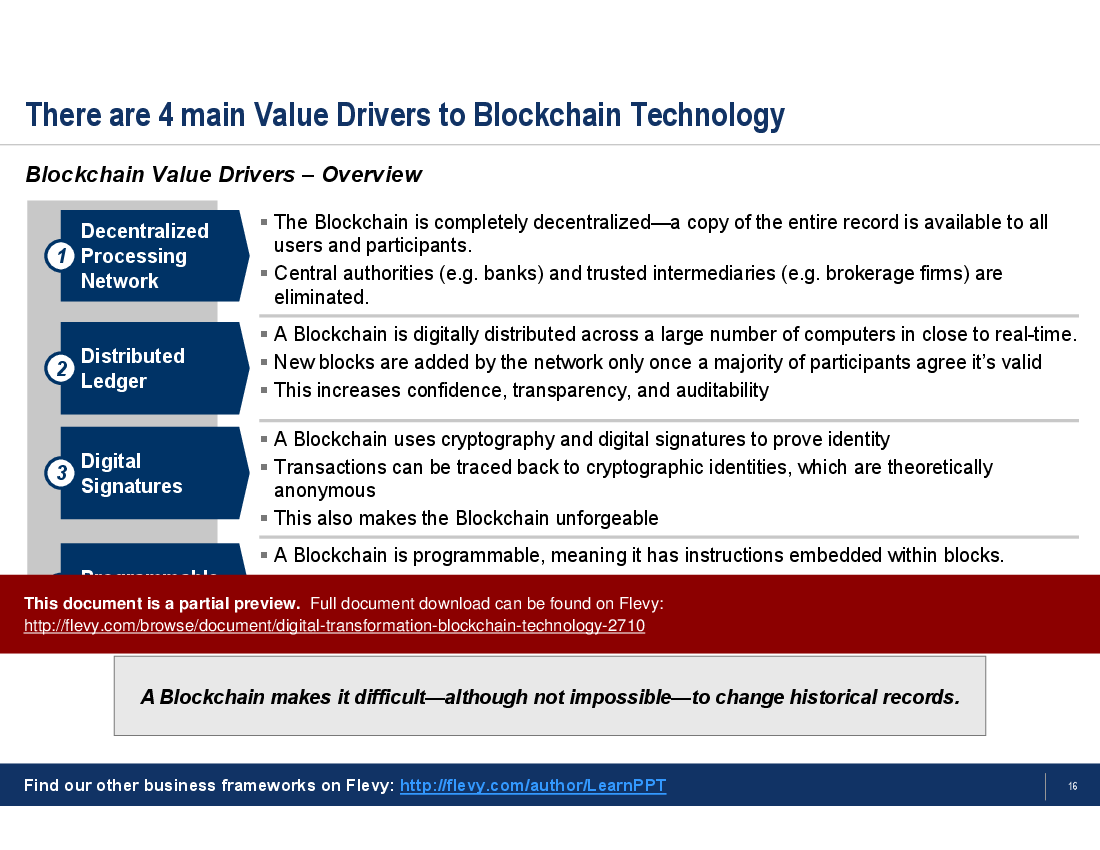
• Value Drivers and Shift
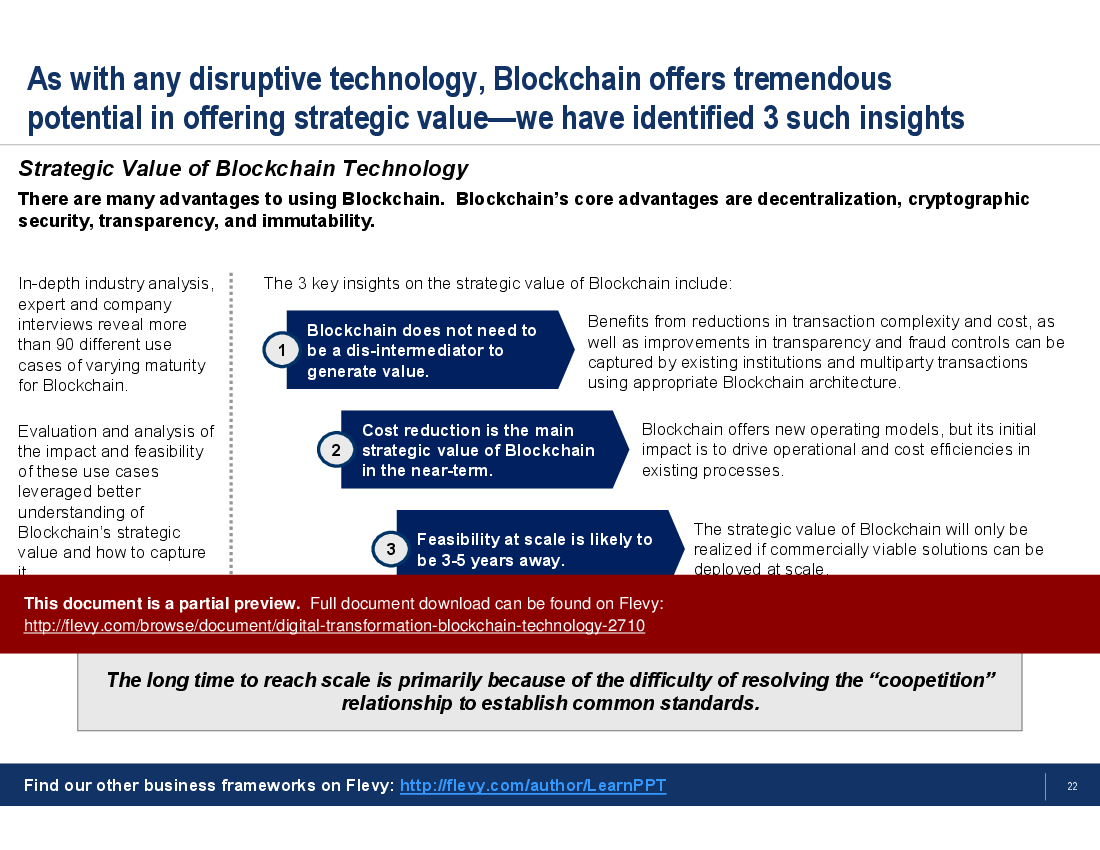
• Strategic Value of Blockchain
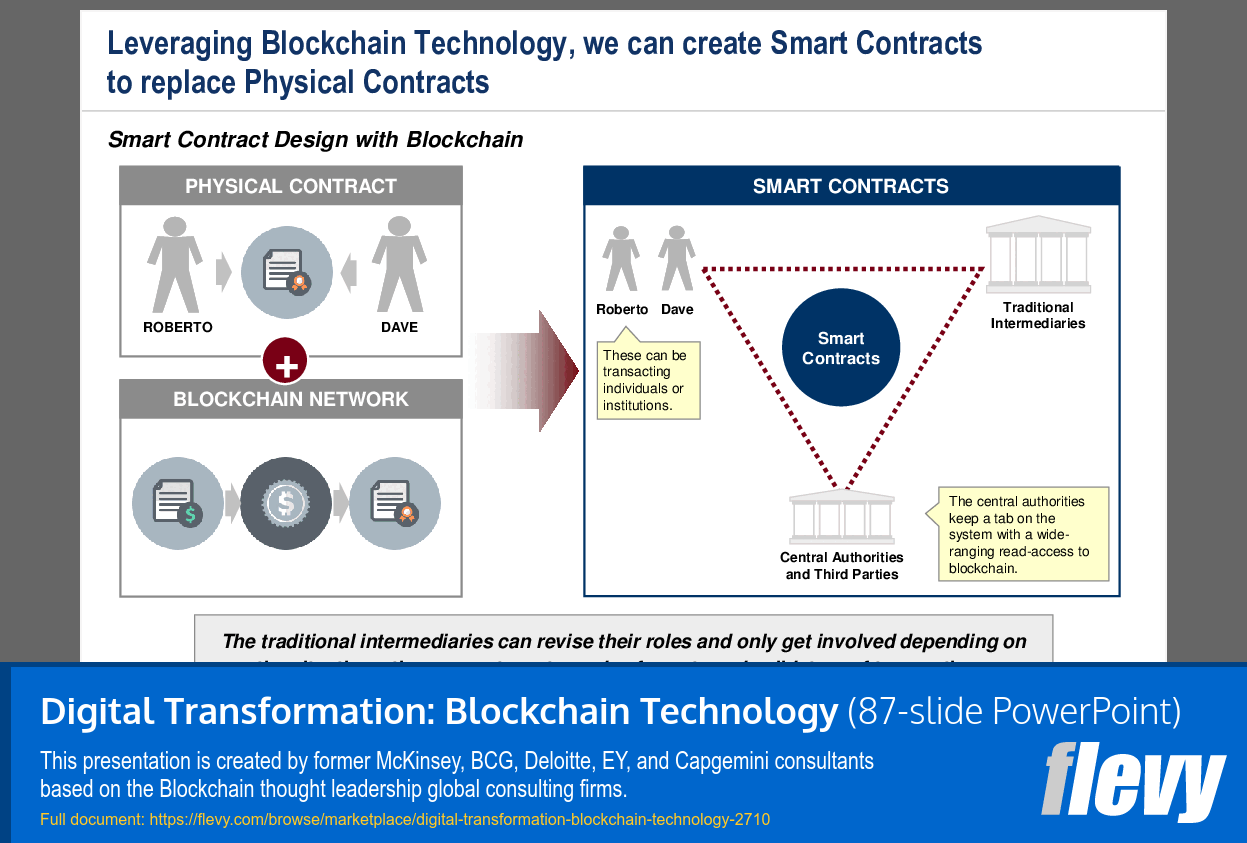
• Smart Contracts
• Blockchain Strategy
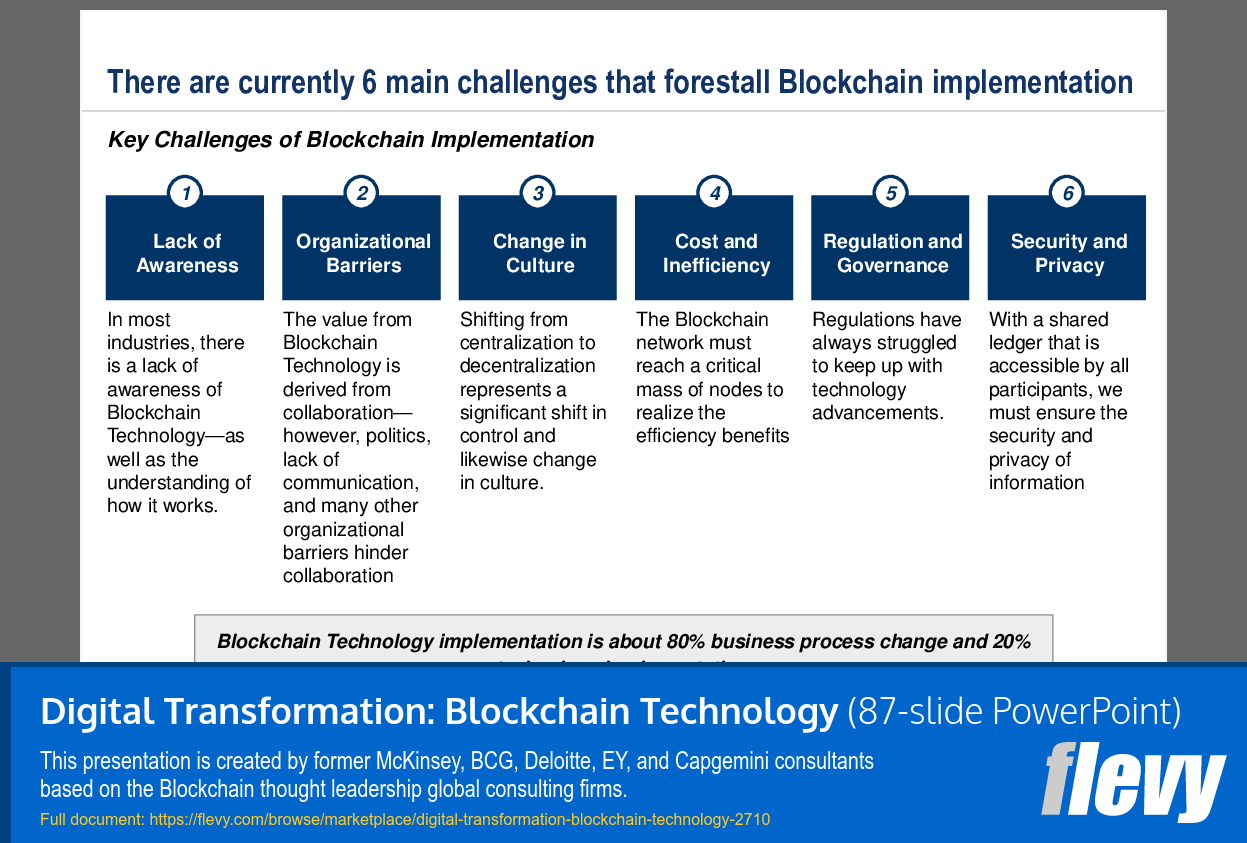
• Implementation Challenges
• Application Evaluation Dimensions
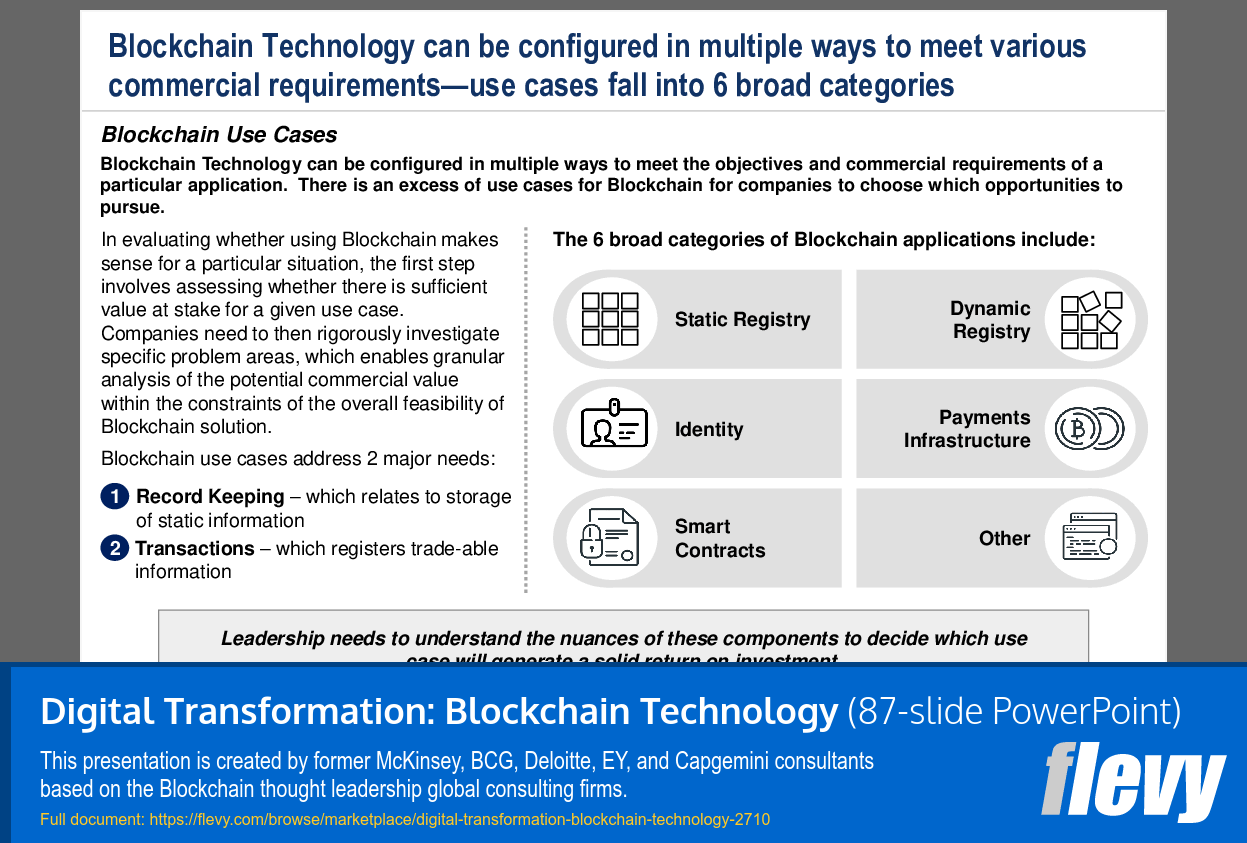
• Use Cases and Industry Applications
• Solution Platforms
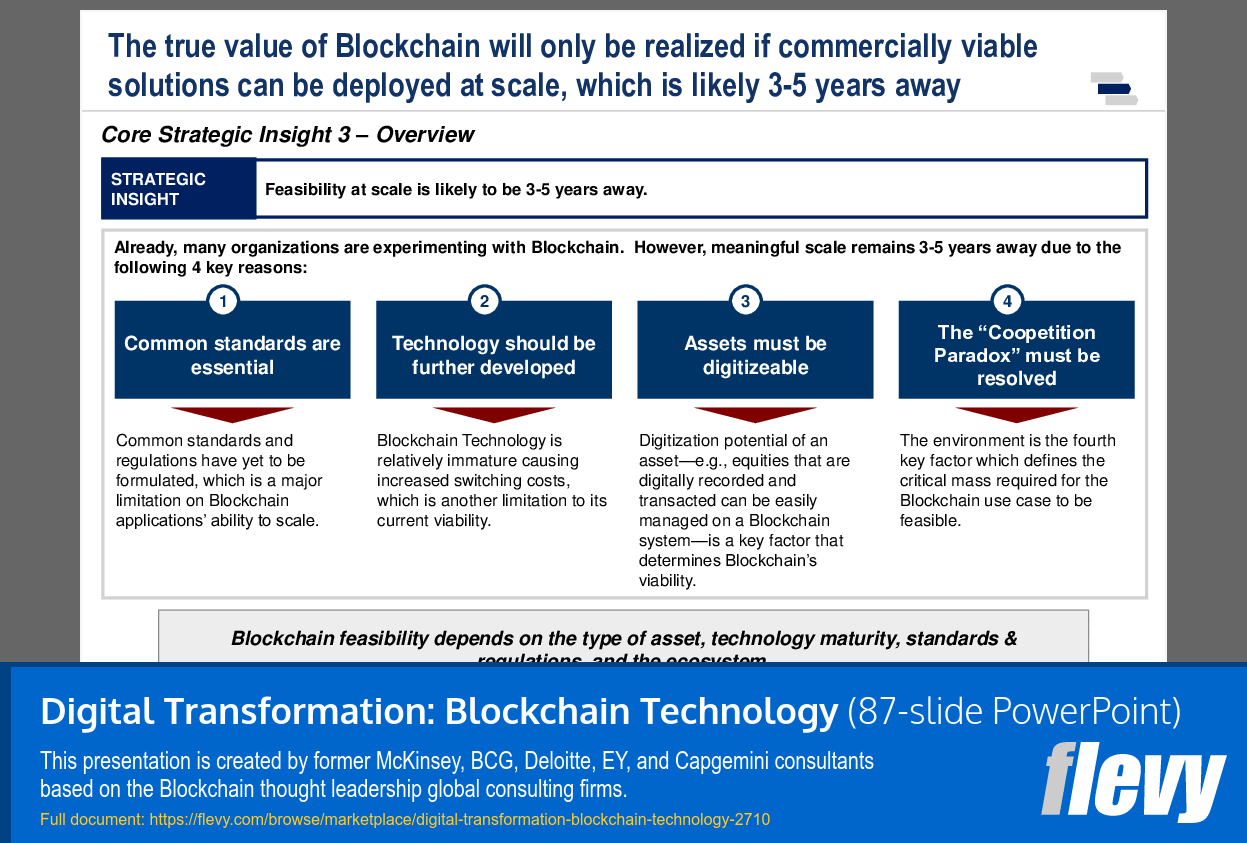
Blockchains can be used for record management (e.g. events, customer records, medical records), identity management, transaction processing, and proving provenance. The World Economic Forum (WEF) predicts at least 10% of the global GDP will be stored in Blockchain Networks by 2025.
This document also includes slide templates for to you use in your own business presentations.
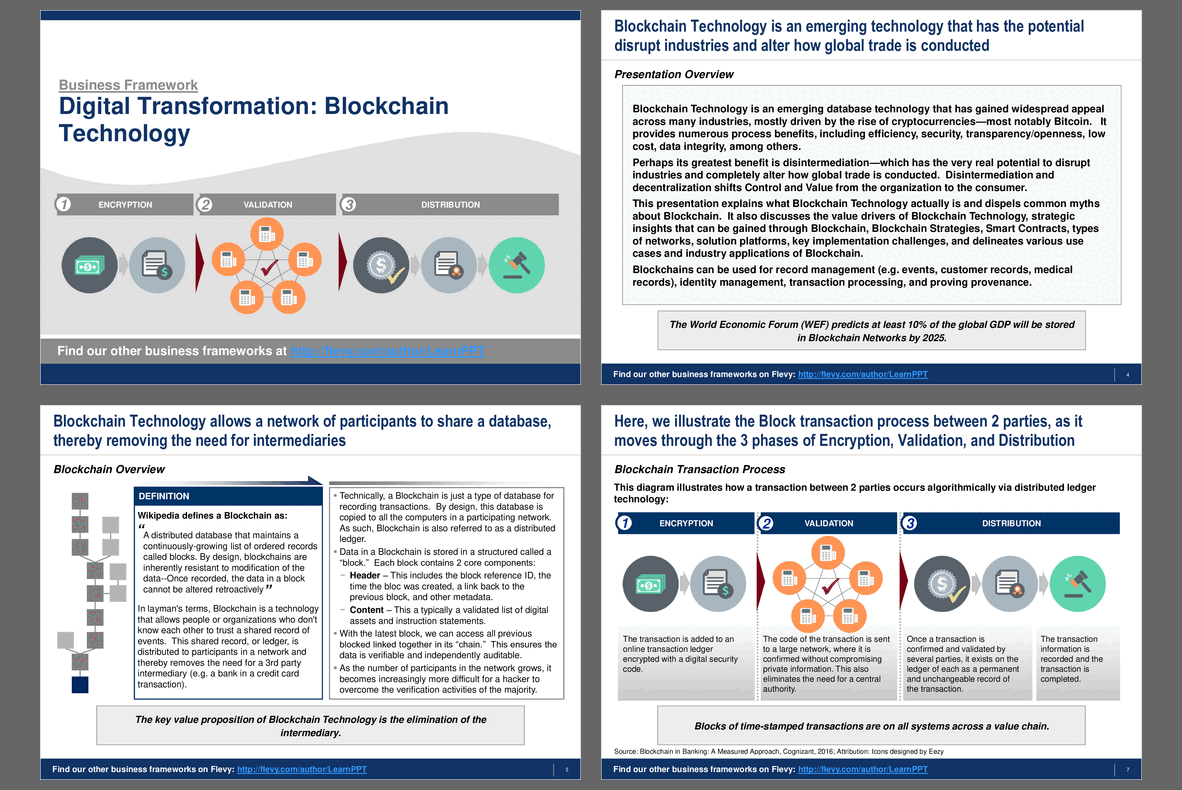
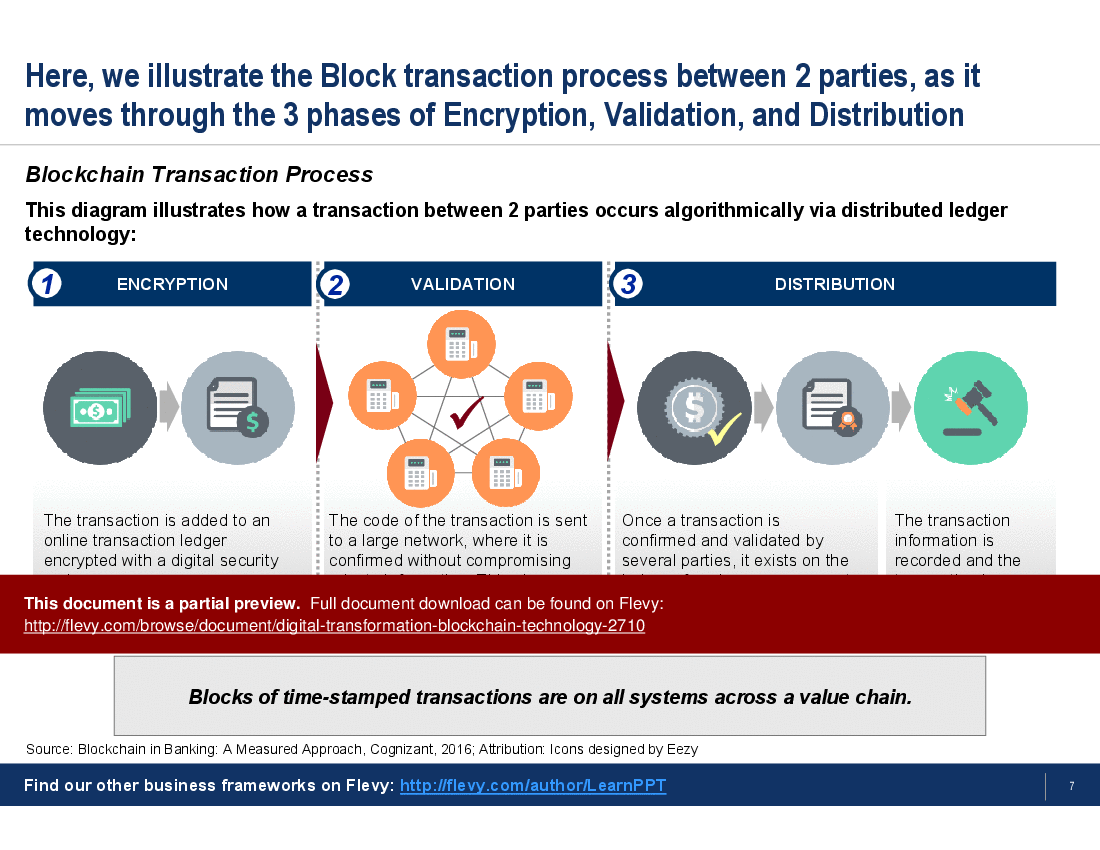
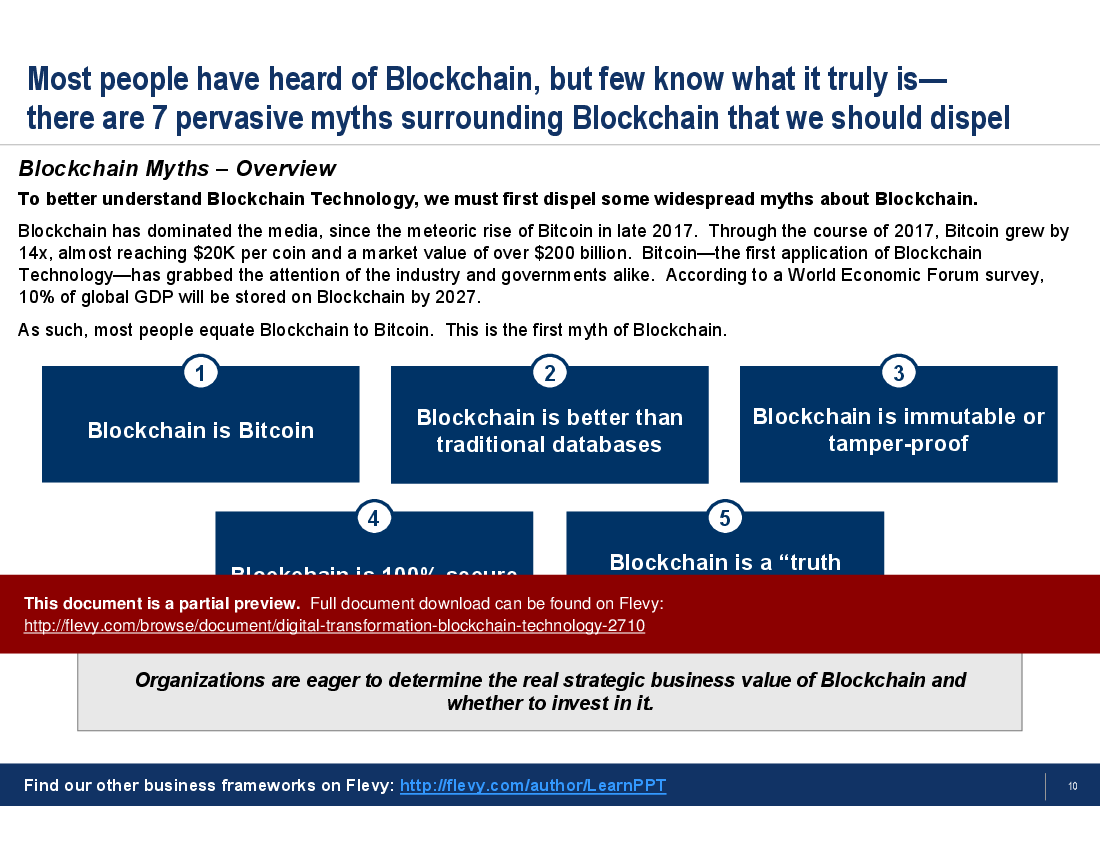
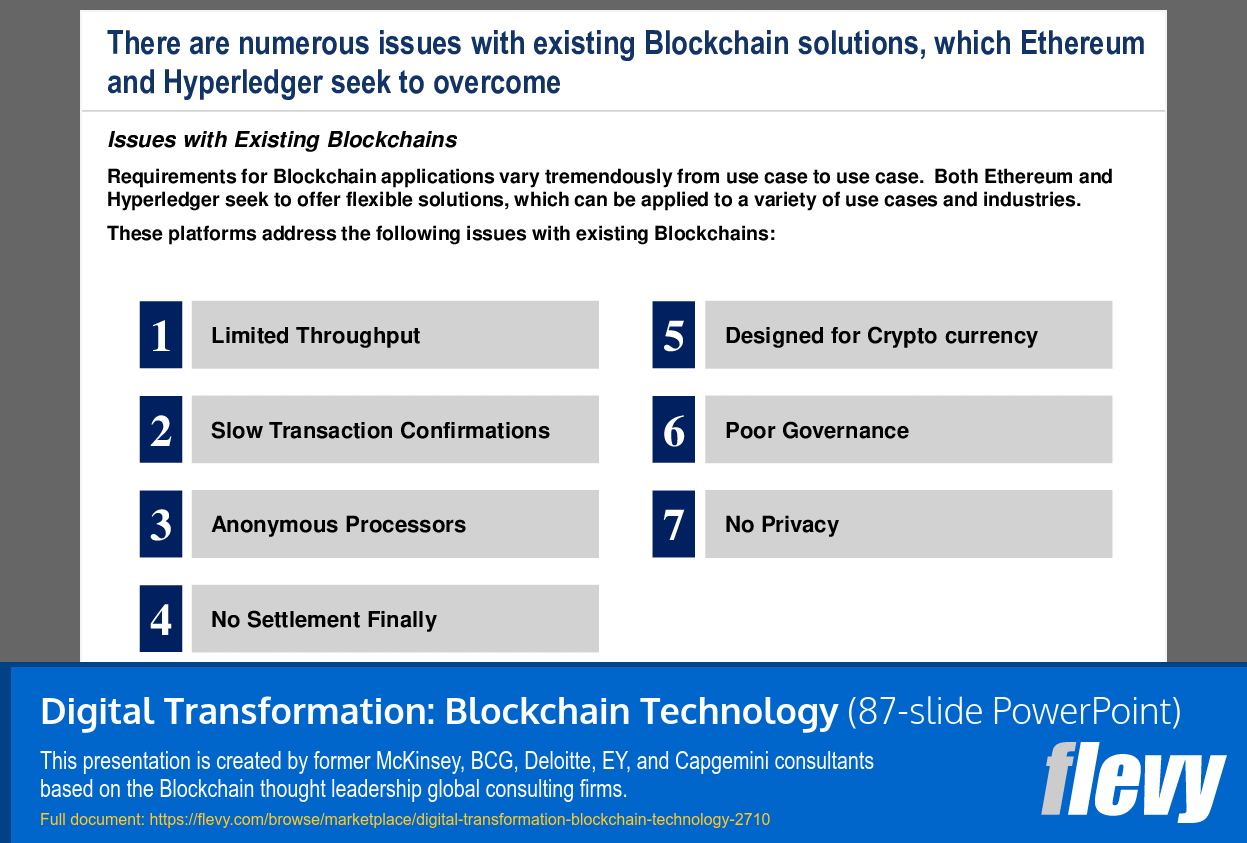
The PPT delves into the intricacies of Blockchain transaction processes, breaking them down into three fundamental phases: Encryption, Validation, and Distribution. This step-by-step breakdown provides a clear understanding of how transactions are securely processed and validated across a distributed ledger. The presentation also tackles common myths about Blockchain, offering a reality check on misconceptions such as the belief that Blockchain is synonymous with Bitcoin or that it is entirely tamper-proof.
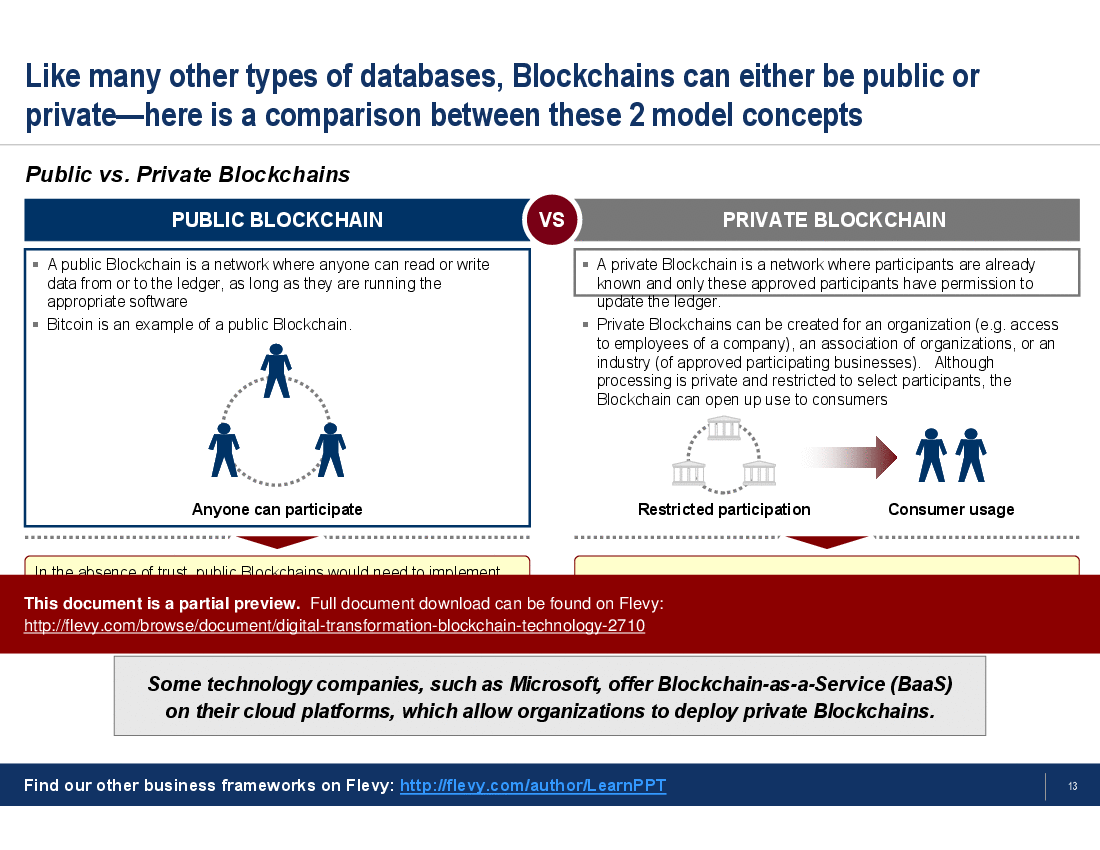
The comparison between public and private Blockchains highlights the flexibility of Blockchain technology in different organizational contexts. Public Blockchains, accessible to anyone, contrast with private Blockchains that restrict participation to known entities, offering a tailored approach for various business needs. The document also identifies four main value drivers of Blockchain, emphasizing its decentralized nature, distributed ledger technology, digital signatures, and programmability. These elements collectively enhance transparency, security, and efficiency in business operations.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 87-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation on Digital Transformation: Blockchain Technology is crafted by former consultants from McKinsey, BCG, Deloitte, EY, and Capgemini, embodying a McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality standard (consulting-grade; not affiliated). It serves as a comprehensive guide for corporate executives and integration leaders to understand the disruptive potential of blockchain technology across various industries. The presentation covers essential concepts, strategic insights, implementation challenges, and practical applications, enabling organizations to harness blockchain for operational efficiency, enhanced security, and improved transparency.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to understand blockchain's strategic implications for their business.
• Integration leaders responsible for implementing digital transformation initiatives.
• Consultants advising clients on blockchain technology adoption and strategy.
• IT and operations teams evaluating blockchain solutions for process improvement.
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions focused on digital transformation initiatives.
• When assessing the feasibility of blockchain applications within specific business units.
• For workshops aimed at educating teams on blockchain technology and its potential impact.
Learning Objectives
• Define blockchain technology and its core components.
• Identify common myths and misconceptions surrounding blockchain.
• Evaluate the strategic value and potential applications of blockchain across industries.
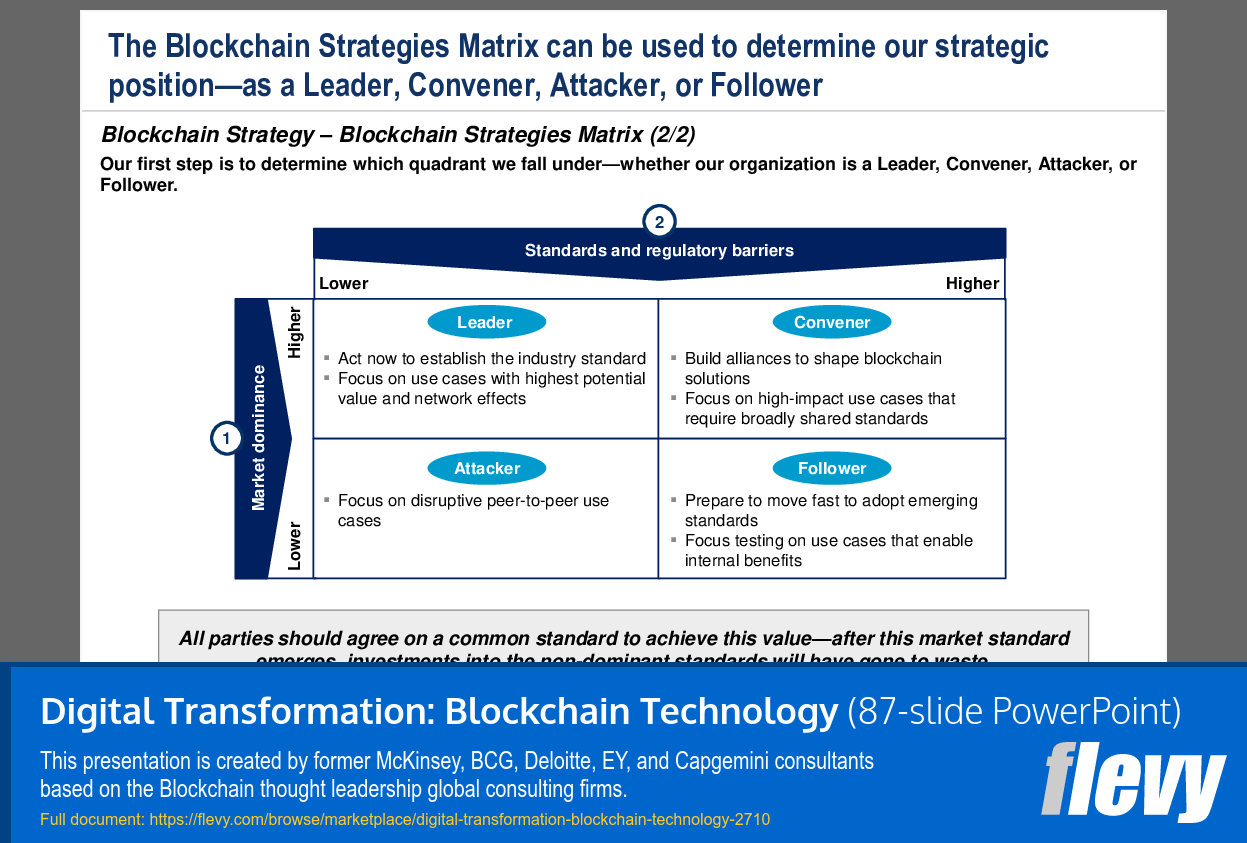
• Develop a blockchain strategy tailored to organizational needs and market conditions.
• Analyze implementation challenges and identify solutions for successful adoption.
• Assess various blockchain networks and their suitability for specific use cases.
Table of Contents
• Overview (page 3)
• Blockchain Myths (page 9)
• Types of Blockchain Networks (page 12)
• Value Drivers and Shift (page 15)
• Strategic Value of Blockchain (page 21)
• Smart Contracts (page 28)
• Blockchain Strategy (page 33)
• Implementation Challenges (page 37)
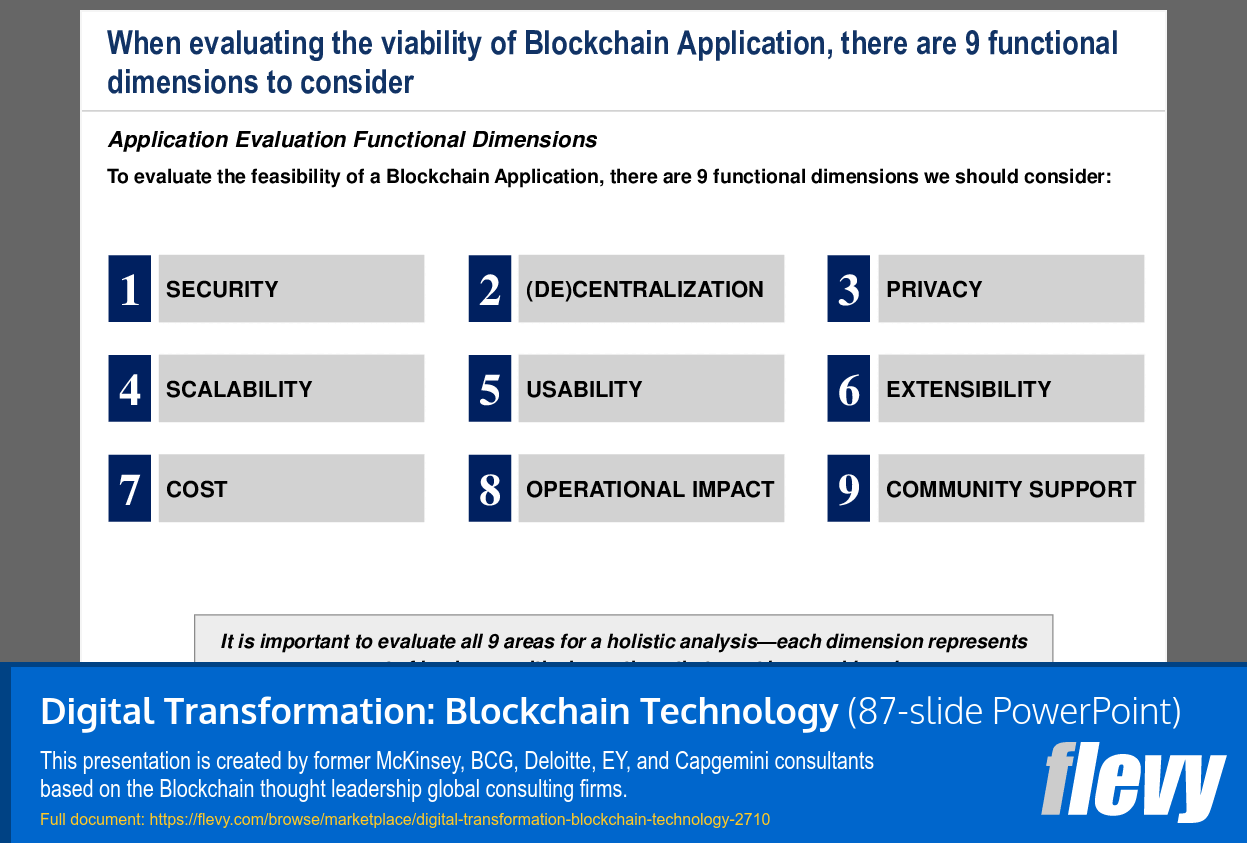
• Application Evaluation Dimensions (page 45)
• Use Cases and Industry Applications (page 50)
• Solution Platforms (page 63)
• Templates (page 72)
Primary Topics Covered
• Blockchain Overview - An introduction to blockchain technology, its definition, and key characteristics, emphasizing its potential to disrupt traditional business models.
• Blockchain Myths - A critical examination of common misconceptions about blockchain, clarifying its capabilities and limitations.
• Types of Blockchain Networks - An exploration of public, private, and consortium blockchains, detailing their unique features and use cases.
• Value Drivers - Identification of the main value drivers of blockchain technology, including decentralization, security, and programmability.
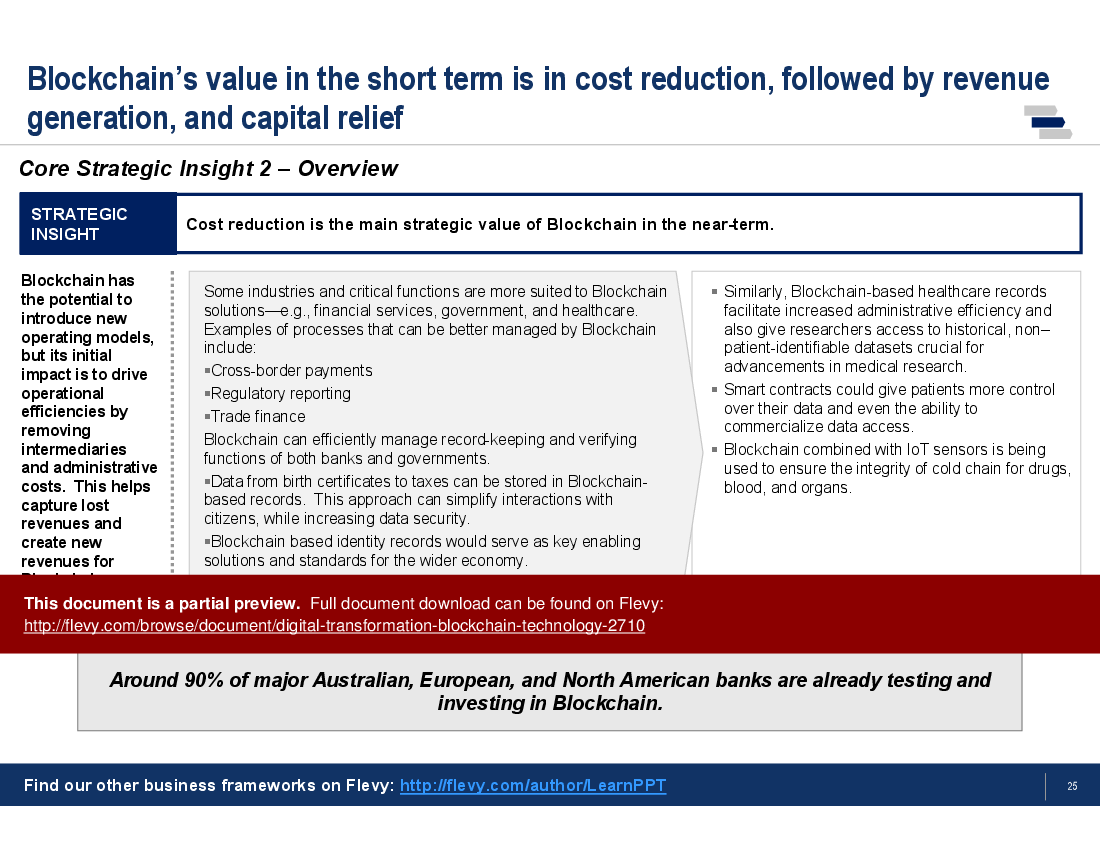
• Strategic Value - Insights into how blockchain can create strategic advantages for organizations, focusing on cost reduction and operational efficiencies.
• Smart Contracts - An overview of smart contracts, their functionality, and their implications for automating business processes.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Blockchain implementation strategy template to guide organizations in adopting blockchain technology.
• Smart contract design framework for developing automated agreements using blockchain.
• Evaluation criteria checklist for assessing potential blockchain applications.
• Use case assessment template to identify and prioritize blockchain opportunities.
• Risk management framework for addressing challenges associated with blockchain implementation.
• Communication plan template for educating stakeholders about blockchain initiatives.
Slide Highlights
• Overview of blockchain technology and its potential to disrupt industries.
• Key myths surrounding blockchain technology debunked with factual insights.
• Comparison of public, private, and consortium blockchain networks.
• Value drivers that highlight the benefits of adopting blockchain solutions.
• Strategic insights on how organizations can leverage blockchain for competitive advantage.
• Lifecycle of smart contracts and their role in automating business transactions.
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Blockchain (30 minutes)
• Overview of blockchain technology and its significance.
• Discussion of common myths and misconceptions.
Evaluating Blockchain Opportunities (60 minutes)
• Identifying potential use cases within the organization.
• Assessing the feasibility and value of blockchain applications.
Developing a Blockchain Strategy (90 minutes)
• Framework for creating a tailored blockchain strategy.
• Group exercises to outline implementation plans and address challenges.
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the blockchain strategy template to align with specific organizational goals and market conditions.
• Modify use case assessment criteria based on industry-specific needs and regulatory requirements.
• Adjust communication plans to fit the organizational culture and stakeholder preferences.
Secondary Topics Covered
• Implementation challenges specific to blockchain technology adoption.
• Evaluation dimensions for assessing blockchain applications.
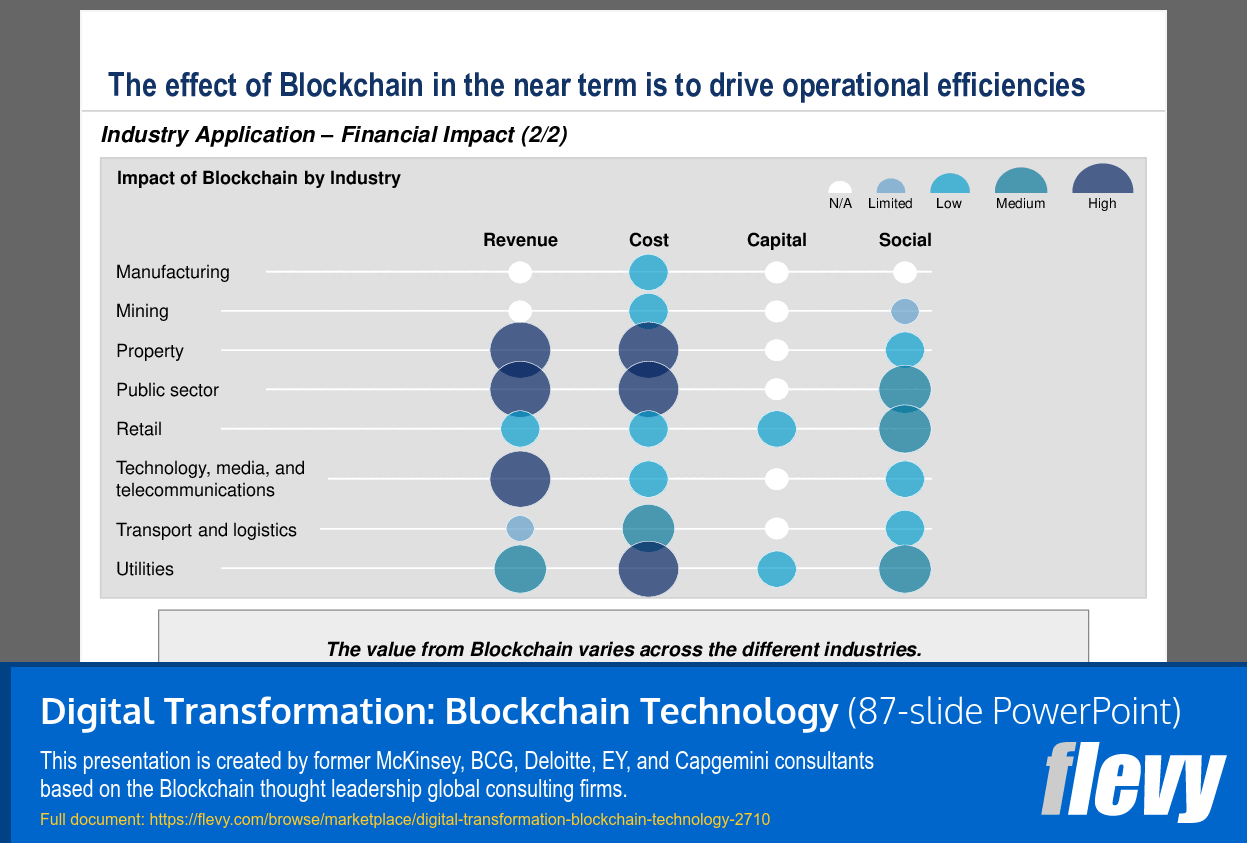
• Industry-specific use cases demonstrating blockchain's versatility.
• Overview of leading blockchain solution platforms and their capabilities.
Topic FAQ
What are the core phases of a blockchain transaction process I should understand?
A blockchain transaction is typically described in 3 fundamental phases: Encryption (securing data and creating digital signatures), Validation (consensus and transaction verification), and Distribution (propagating the validated transaction across the ledger). The presentation breaks the process into these 3 phases: Encryption, Validation, and Distribution.What types of blockchain networks exist and how do they differ for enterprise use?
The main types are public blockchains (open to anyone), private blockchains (restricted to authorized participants), and consortium blockchains (shared among a group of organizations). Each type balances openness, privacy, and governance differently; the deck compares public, private, and consortium blockchains as distinct options.How do smart contracts function and when should my organization consider them?
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with terms written in code that automate business transactions without intermediaries. They are appropriate when process rules can be codified and automated; the presentation includes an overview of smart contracts and a lifecycle discussion covering their design and automation role.What are the typical implementation challenges organizations face with blockchain?
Common challenges include lack of awareness, organizational barriers, regulatory compliance issues, and the need for cultural change around decentralization. The deck explicitly lists these implementation challenges and provides frameworks and templates to address them, such as a risk management framework.How should I evaluate whether a specific business process is a good fit for blockchain?
Evaluate potential applications based on security, scalability, privacy, usability, and community support; prioritize processes where decentralization or tamper-evidence adds value. The presentation provides an evaluation criteria checklist and a use case assessment template to guide this analysis with those dimensions.Our team has limited budget and time—what should we look for when buying a blockchain strategy toolkit?
Look for resources that cover strategy, implementation challenges, technical evaluation, and ready-to-use templates for planning and stakeholder communication. The Flevy product Digital Transformation: Blockchain Technology includes slide templates, an implementation strategy template, and a communication plan template to accelerate work.What outputs should a one-day blockchain workshop produce for executive stakeholders?
A practical workshop should produce an agreed list of candidate use cases, preliminary feasibility assessments, a draft blockchain strategy or roadmap, identified risks, and stakeholder communication points. The presentation’s suggested workshop agenda maps to outputs like a use case list, feasibility assessment, and a draft implementation plan using the provided templates.How can I compare blockchain solution platforms to pick the right one for my use case?
Compare platforms by capabilities, governance model, scalability, privacy features, and suitability for targeted use cases. The deck includes a section on solution platforms and provides evaluation dimensions to compare platform capabilities against organizational requirements.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring data integrity and security without the need for intermediaries.
What are common misconceptions about blockchain?
Common misconceptions include the belief that blockchain is synonymous with Bitcoin, that it is entirely secure, and that it is inherently better than traditional databases.
How can organizations benefit from blockchain?
Organizations can benefit from blockchain through improved operational efficiencies, enhanced security, reduced costs, and increased transparency in transactions.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, enabling automated and trustless transactions.
What are the main types of blockchain networks?
The main types of blockchain networks are public, private, and consortium blockchains, each serving different purposes and use cases.
What challenges do organizations face when implementing blockchain?
Organizations may face challenges such as lack of awareness, organizational barriers, regulatory compliance issues, and the need for cultural change.
How do I evaluate potential blockchain applications?
Evaluate potential blockchain applications by assessing their security, scalability, privacy, usability, and community support.
What industries are most likely to benefit from blockchain?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, and public sector are poised to benefit significantly from blockchain technology.
Glossary
• Blockchain - A decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers.
• Smart Contract - A self-executing contract with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
• Public Blockchain - A blockchain network accessible to anyone, allowing anyone to participate in the network.
• Private Blockchain - A blockchain network restricted to authorized participants, enhancing privacy and control.
• Consensus Mechanism - A protocol used to achieve agreement on a single data value among distributed processes or systems.
• Cryptography - The practice of securing information by transforming it into an unreadable format for unauthorized users.
• Decentralization - The distribution of authority and control away from a central entity, promoting transparency and trust.
• Token - A digital asset created on a blockchain, representing a unit of value or utility.
• Distributed Ledger - A database that is consensually shared and synchronized across multiple sites, institutions, or geographies.
• Mining - The process of validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain, often rewarded with cryptocurrency.
• KYC (Know Your Customer) - A process used by businesses to verify the identity of their clients to prevent fraud.
• Interoperability - The ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and work together seamlessly.
• Use Case - A specific application of blockchain technology that addresses a particular business problem or need.
• Tokenization - The process of converting rights to an asset into a digital token on a blockchain.
• Regulatory Compliance - Adhering to laws and regulations governing the use of blockchain technology and data management.
• Digital Identity - An online representation of an individual or organization, often secured through blockchain technology.
• Data Integrity - The accuracy and consistency of data stored in a blockchain, ensuring it remains unaltered.
• Auditability - The ability to verify and trace transactions on a blockchain for compliance and transparency purposes.
• Decentralized Application (DApp) - An application that runs on a blockchain network, utilizing smart contracts for functionality.
• Consensus Algorithm - A mechanism used to achieve agreement on the validity of transactions in a blockchain network.
• Tokenomics - The study of the economic model behind a cryptocurrency or token, including its supply, demand, and utility.
DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Digital Transformation, Bitcoin, Blockchain PowerPoint Slides: Digital Transformation: Blockchain Technology PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting