Structured Communication, Presentation Development, and Storyboarding (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 40 Slides
PRESENTATION DEVELOPMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
This presentation talks to the topics of structure communication, presentation development, and storyboarding. These topics related to formulating a cohesive, powerful business presentation.
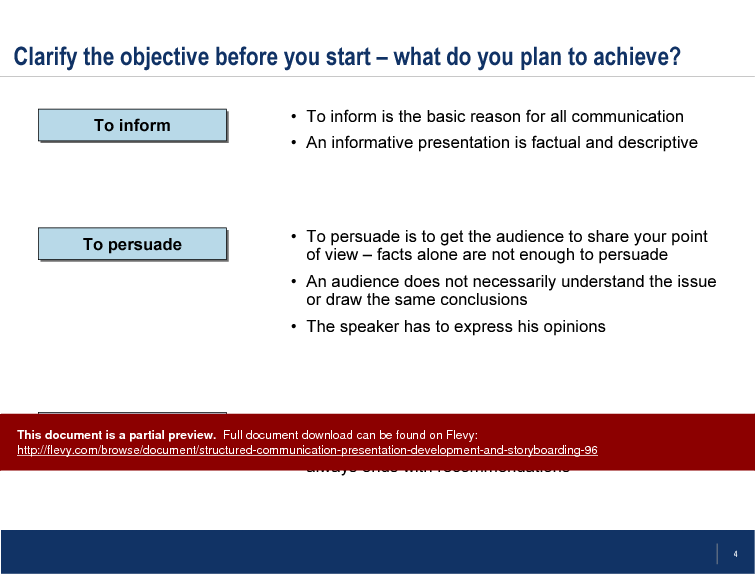
This document dives deep into the essential elements of structured communication, ensuring your message is clear and impactful. It emphasizes the importance of defining your objective, whether to inform or persuade, and tailors your approach accordingly. The presentation guides you in crafting a narrative that your audience can easily follow, using storyboarding techniques to map out your key messages and supporting data.
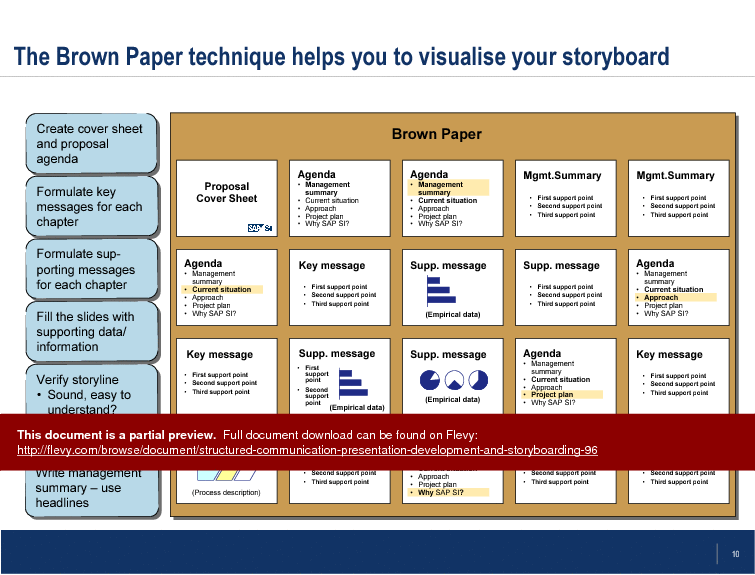
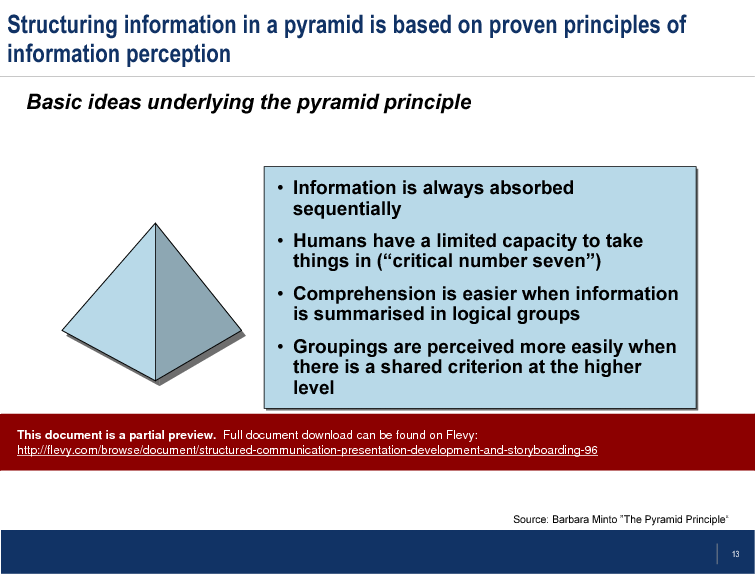
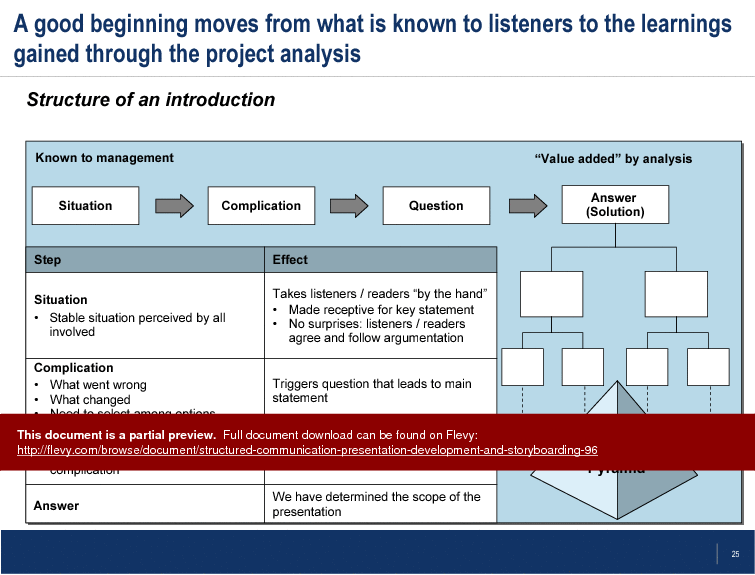
The Brown Paper technique is highlighted as a powerful tool for visualizing your storyboard, helping you organize your content logically and coherently. This method ensures that each section of your presentation is aligned with your overall objective, making it easier for your audience to grasp complex information. The document also covers the Pyramid Principle, a proven approach to structuring information that enhances comprehension and retention.
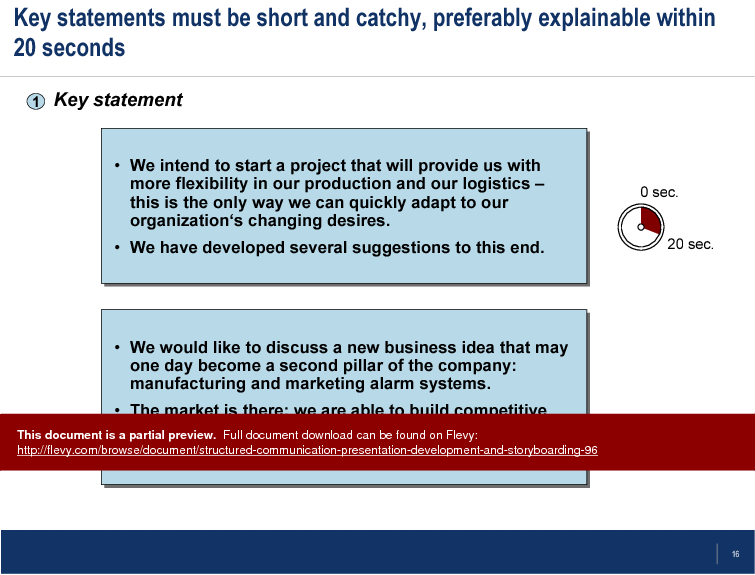
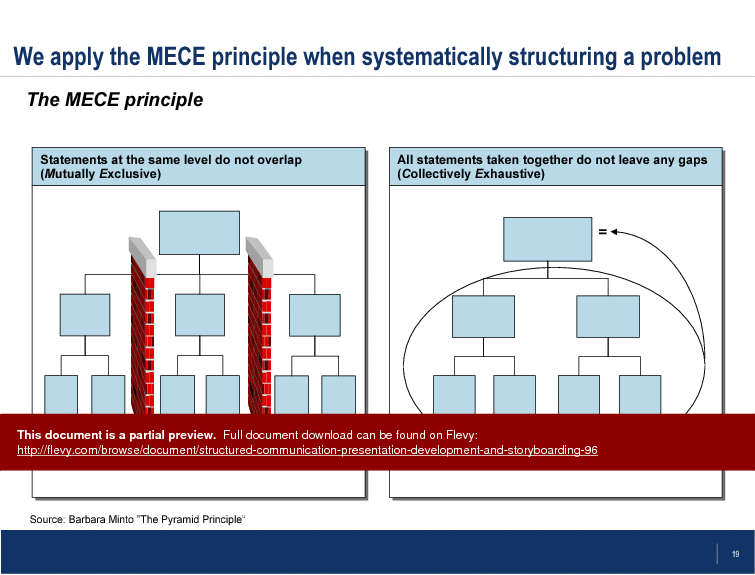
Key statements are another focus, with guidelines on making them short, catchy, and easily explainable within 20 seconds. This ensures your audience quickly understands the main points, keeping their attention and interest. The MECE principle is applied to systematically structure problems, ensuring that all statements are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive, leaving no gaps in your argument.
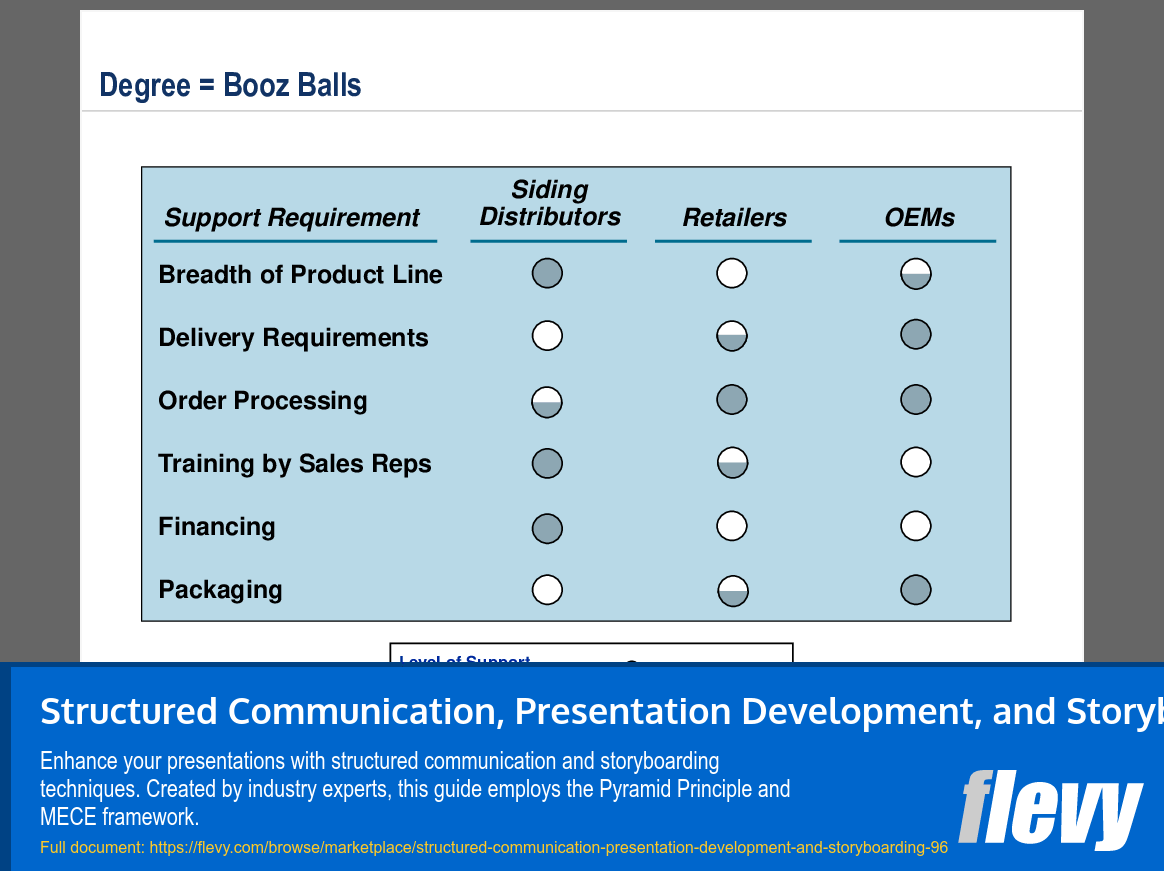
Standard formats are recommended for their practical advantages, providing a ready-made framework that promotes writing and production efficiencies. This consistency helps your audience know where to look for specific types of information, enhancing their overall experience. The document also emphasizes the power of graphics in presentations, advocating for simpler visuals that convey both numerical and visual messages effectively.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 40-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation on Structured Communication, Presentation Development, and Storyboarding is crafted to elevate your presentation skills to a McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality standard (consulting-grade; not affiliated). It provides a systematic approach to distilling complex information into clear conclusions and actionable recommendations. By employing the Pyramid Principle and MECE framework, this guide enables users to effectively communicate their messages, ensuring that presentations are not only informative, but also persuasive and engaging.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives tasked with delivering strategic presentations
• Integration leaders responsible for stakeholder communication
• Consultants aiming to enhance client presentations
• Project managers needing to convey complex project details clearly
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During the development of high-stakes presentations for board meetings
• When preparing for client engagements that require clarity and persuasion
• In workshops focused on improving team communication strategies
Learning Objectives
• Define the core principles of effective communication in presentations
• Build a structured storyboard to guide presentation development
• Establish a clear communication strategy tailored to audience needs
• Apply the Pyramid Principle to organize information logically
• Create compelling visuals that enhance data presentation
• Utilize the MECE framework to ensure clarity and completeness in arguments
Table of Contents
• Communication Strategy (page 2)
• Storyboarding (page 5)
• Five Principles of Document Writing (page 6)
• The Pyramid Principle (page 12)
• Structuring Your Presentation (page 22)
• Presenting Data (page 31)
Primary Topics Covered
• Communication Strategy - Focuses on the importance of clarity in conveying conclusions and recommendations derived from various analyses.
• Storyboarding - Emphasizes the need for early planning to visualize and organize presentation content effectively.
• Five Principles of Document Writing - Outlines essential principles such as writing for the audience and maintaining simplicity.
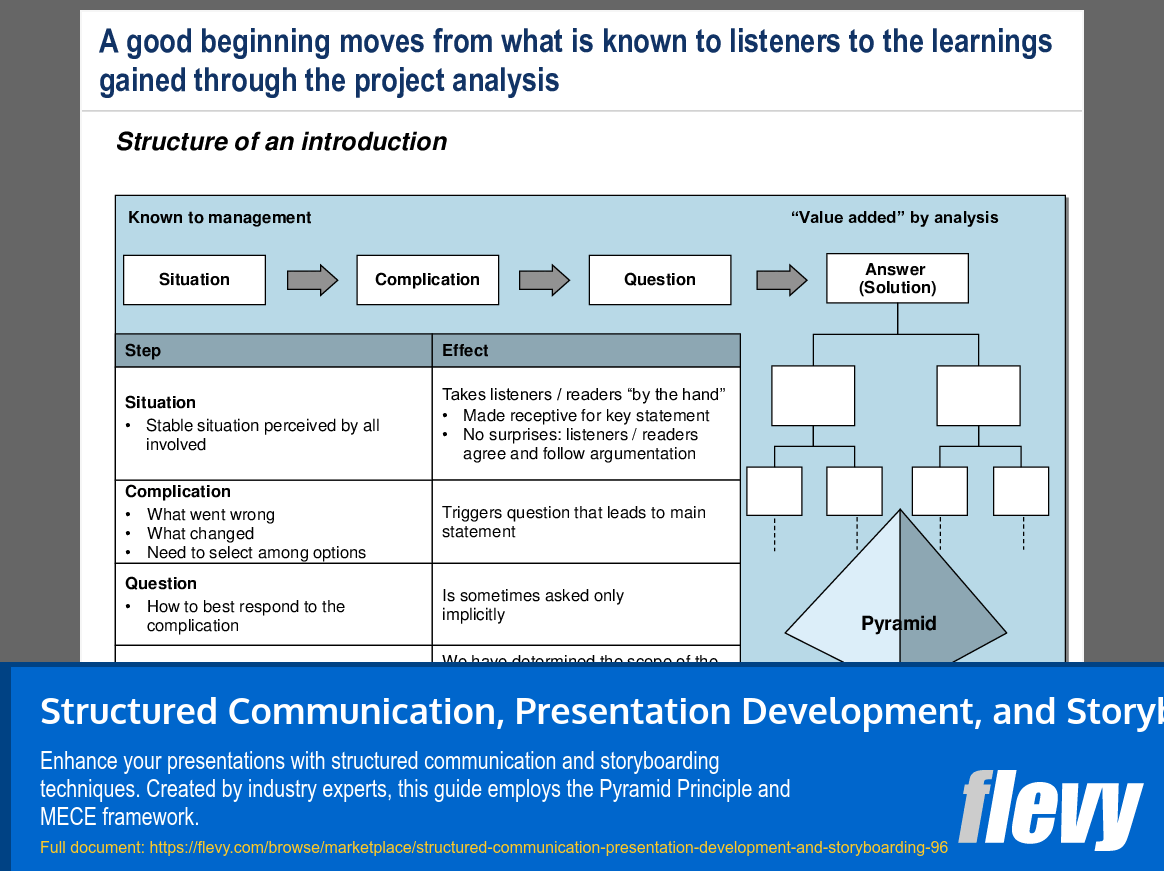
• The Pyramid Principle - Introduces a structured approach to presenting information hierarchically for better comprehension.
• Structuring Your Presentation - Details the horizontal and vertical logic required to create coherent presentations.
• Presenting Data - Discusses best practices for presenting data visually to enhance understanding and retention.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Storyboard template for organizing presentation content
• Message template to clarify communication objectives and key messages
• Pyramid structure outline for logically arranging arguments
• Visual guidelines for effective data presentation
• Brown Paper technique for visualizing story flow
• Standard formats for consistency across presentations
Slide Highlights
• Introduction slide emphasizing the importance of clarity in communication
• Storyboarding slide illustrating the process of organizing ideas
• Pyramid Principle slide demonstrating the hierarchical structure of arguments
• Data presentation slide showcasing effective use of visuals
• Five principles slide summarizing key document writing strategies
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Structured Communication (60 minutes)
• Overview of communication strategy and its importance
• Discuss the role of storyboarding in presentation development
Pyramid Principle Application (90 minutes)
• Explore the Pyramid Principle and its practical applications
• Hands-on activity to create a pyramid structure for a sample presentation
Data Presentation Techniques (60 minutes)
• Review best practices for presenting data visually
• Group exercise to redesign a data-heavy slide for clarity
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the storyboard template to fit specific project needs and audience preferences
• Adjust the message template to align with organizational terminology and objectives
• Incorporate company branding into presentation formats for consistency
Secondary Topics Covered
• Importance of audience analysis in communication
• Techniques for engaging the audience during presentations
• Strategies for handling questions and feedback effectively
• Best practices for follow-up communication post-presentation
Topic FAQ
What is the Pyramid Principle and how does it structure a presentation?
The Pyramid Principle is a hierarchical method for organizing information so conclusions and supporting arguments are presented logically, improving comprehension and retention. It helps users lead with the key message and group supporting points beneath it, as shown in the product's Pyramid Principle slide and pyramid structure outline.How does the MECE framework prevent gaps or overlaps in an argument?
MECE stands for mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive; it guides users to split issues so items do not overlap and all relevant areas are covered. Applying MECE helps ensure completeness and clarity when structuring problems, a concept reinforced in the presentation's explanation of the MECE principle.What is storyboarding and why should teams use it before slide production?
Storyboarding is the visual planning of a presentation’s flow to ensure ideas are organized before formal slide development. It helps teams check coherence and narrative sequencing early, often using the Brown Paper technique and the provided storyboard template to map story flow and alignment.What should I look for in a structured communication template for high-stakes presentations?
Seek templates that combine a clear message template, a storyboard template, a pyramid structure outline, and visual guidelines so you can define objectives, sequence arguments, and present data consistently. The Flevy product Structured Communication, Presentation Development, and Storyboarding includes each of those templates.How can I judge the cost versus value of buying presentation templates and frameworks?
Evaluate templates by estimated time savings, consistency benefits, and production efficiency; templates that provide standard formats and reusable message/storyboard structures tend to reduce drafting time and rework. The presentation explicitly cites standard formats and templates as means to achieve writing and production efficiencies.I need to present complex project findings to a board — which framework will make recommendations clear?
Start by clarifying the communication objective, then apply the Pyramid Principle to lead with conclusions and group supporting arguments, use MECE to structure issues, and employ simple visuals for key numbers. The product’s guidance centers on the Pyramid Principle and message template to support that workflow.What techniques make data-heavy slides easier to understand for executives?
Use simple, clean tables, highlight key numbers, and select appropriate graphics that convey the message visually rather than cluttering slides. The presentation’s Presenting Data section and visual guidelines recommend these practices and include example slides demonstrating effective visuals.Can a workshop help my team adopt structured communication methods, and what might it include?
Yes; the presentation contains a sample workshop agenda with timed modules to teach and practice structured communication, including a 60-minute introduction, a 90-minute Pyramid Principle application with hands-on activities, and a 60-minute data presentation exercise.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the Pyramid Principle?
The Pyramid Principle is a structured approach to presenting information hierarchically, allowing for better comprehension and retention of key messages.
How can storyboarding improve my presentations?
Storyboarding helps visualize the flow of information, ensuring that ideas are organized logically and communicated effectively.
What are the 5 principles of document writing?
The 5 principles include writing for your audience, keeping it simple, supporting assertions with facts, using active voice, and telling a good story.
Why is it important to clarify the communication objective?
Clarifying the objective ensures that the presentation is focused, whether the goal is to inform, persuade, or provoke action.
How can I effectively present data?
Use simple and clean tables, highlight key numbers, and choose appropriate graphics to convey your message clearly.
What role does audience analysis play in communication?
Understanding your audience allows you to tailor your message and presentation style to meet their needs and expectations.
How can I ensure my presentation is persuasive?
Incorporate compelling arguments, support them with data, and engage the audience through storytelling techniques.
What is the Brown Paper technique?
The Brown Paper technique is a visual method for sketching out story flow and verifying the coherence of your presentation.
Glossary
• Communication Strategy - A plan for effectively conveying messages to an audience.
• Storyboarding - The process of organizing ideas visually before developing a presentation.
• Pyramid Principle - A method for structuring information hierarchically for clarity.
• MECE Principle - A framework ensuring that statements are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive.
• Visual Guidelines - Best practices for presenting data and information visually.
• Message Template - A structured format for clarifying communication objectives.
• Brown Paper Technique - A visual approach to planning and verifying presentation flow.
• Active Voice - A writing style that emphasizes directness and clarity by using active verbs.
• Document Writing Principles - Key strategies for effective written communication.
• Data Presentation - Techniques for displaying data in a clear and impactful manner.
• Engagement Techniques - Strategies for maintaining audience interest during presentations.
• Follow-up Communication - The process of engaging with the audience after the presentation to reinforce messages.
PRESENTATION DEVELOPMENT PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Presentation Development, Pyramid Principle, MECE PowerPoint Slides: Structured Communication, Presentation Development, and Storyboarding PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Process Consulting