Quality Assurance for Projects (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 42 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Provides a basis upon which to roll-out a Quality Assurance Framework
- Introduces the concept of 'what does good look like?'
- Acts as support for other frameworks and policies aimed at improving the success rate of projects.
QUALITY MANAGEMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
A 42-slide pack that looks into the process of defining and applying a Quality Assurance Frame for Projects.
The document covers creating the framework (the scope, the required standards, the scoring mechanism, tailoring the approach, etc.).
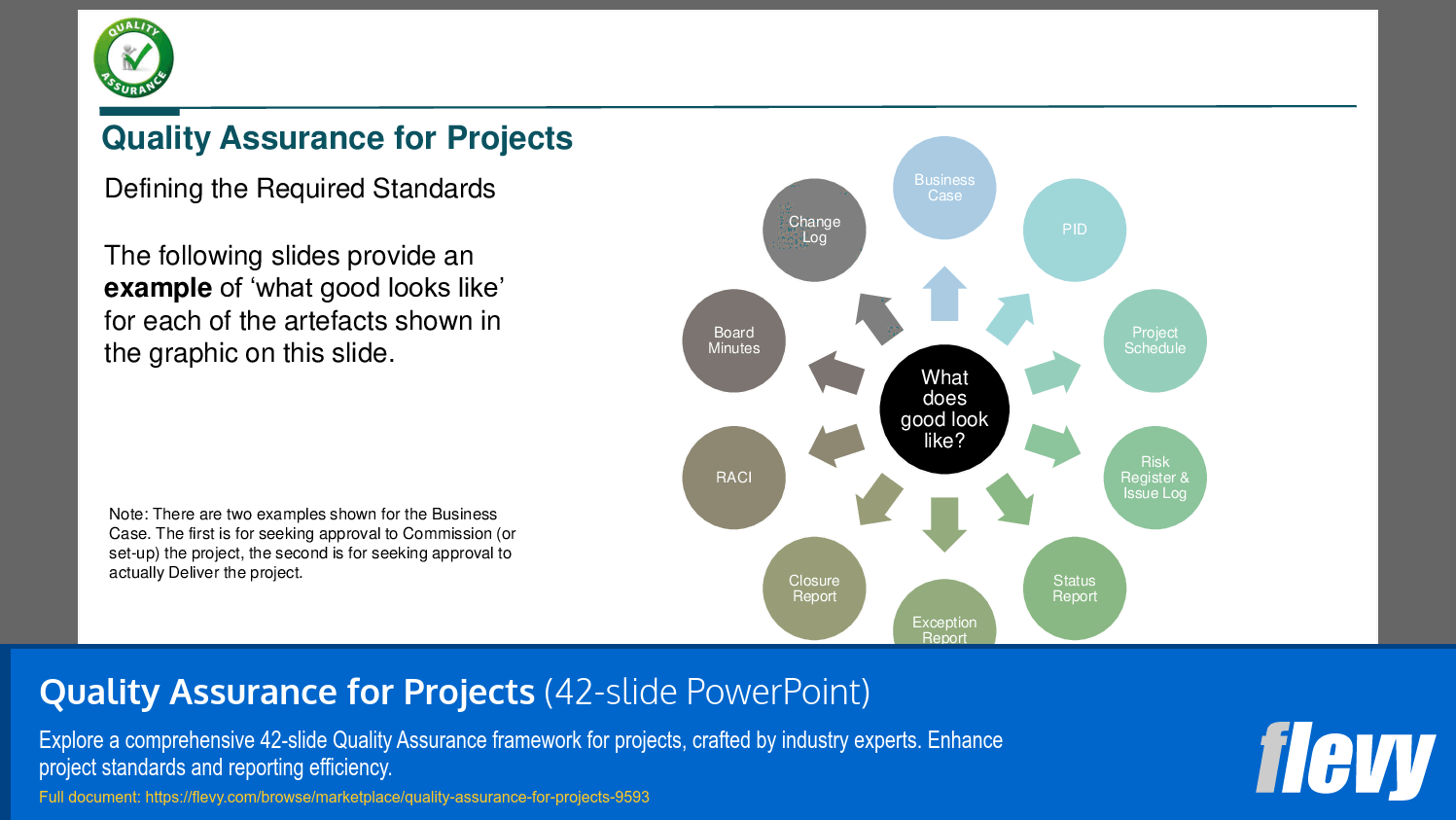
Contains both illustrations and examples of how to created quality standards for each of the typical artefacts that a project produces (e.g. the Business Case, the Risk Register, the Issue Log, the Project Schedule, the Change Log, the Project Status Report, the Project Exception Report, the Project Closure Report, the RACI Chart, the PID, and the Project Board Minutes).
Sections include: Roles & Responsibilities (who are the key players in the process and how to they contribute), Reporting (the important of reporting not just within individual projects, but also at the organizational level where other projects and programmes could be impacted), Education (this document emphasizes the huge importance of this, specifically the need to avoid an 'Us versus Them' situation between those being assessed (the Project Management Group) and those conducting the assessments (the Assessment Team)).
Completely configurable to the needs of any organisation.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 42-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Quality Assurance for Projects" presentation provides a structured framework designed to ensure that project deliverables meet established quality standards and stakeholder expectations. This framework emphasizes the importance of quality management throughout the project lifecycle, focusing on the creation and maintenance of key project artifacts. By implementing this quality assurance framework, organizations can enhance project outcomes, foster a culture of continuous improvement, and ensure alignment with business objectives.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Project Managers overseeing project execution and quality assurance
• Quality Assurance teams responsible for implementing and monitoring quality frameworks
• Project Sponsors advocating for quality standards and supporting project teams
• Portfolio Managers tracking the overall health of multiple projects
• Stakeholders interested in ensuring project deliverables meet expectations
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During project initiation to establish quality standards and frameworks
• At project milestones to assess quality and compliance with standards
• In project review meetings to discuss quality assurance findings and improvements
Learning Objectives
• Define the concept of Quality Assurance and its significance in project management
• Establish a Quality Assurance Framework that aligns with organizational goals
• Identify and define the scope of project artifacts subject to quality assessment
• Develop measurable quality standards for project deliverables
• Implement a scoring mechanism to evaluate the quality of project artifacts
• Clarify roles and responsibilities related to quality assurance within project teams
• Create effective reporting mechanisms to communicate quality assessment results
• Foster a culture of education and continuous improvement regarding quality practices
• Apply practical approaches to tailor quality assurance processes to specific project needs
• Differentiate between Quality Assurance and Stage Gate Review processes
Table of Contents
• What is Quality Assurance? (page 3)
• How Does a Quality Framework Add Value? (page 4)
• Defining the Scope (page 6)
• Defining the Required Standards (page 7)
• Defining the Scoring Mechanism (page 20)
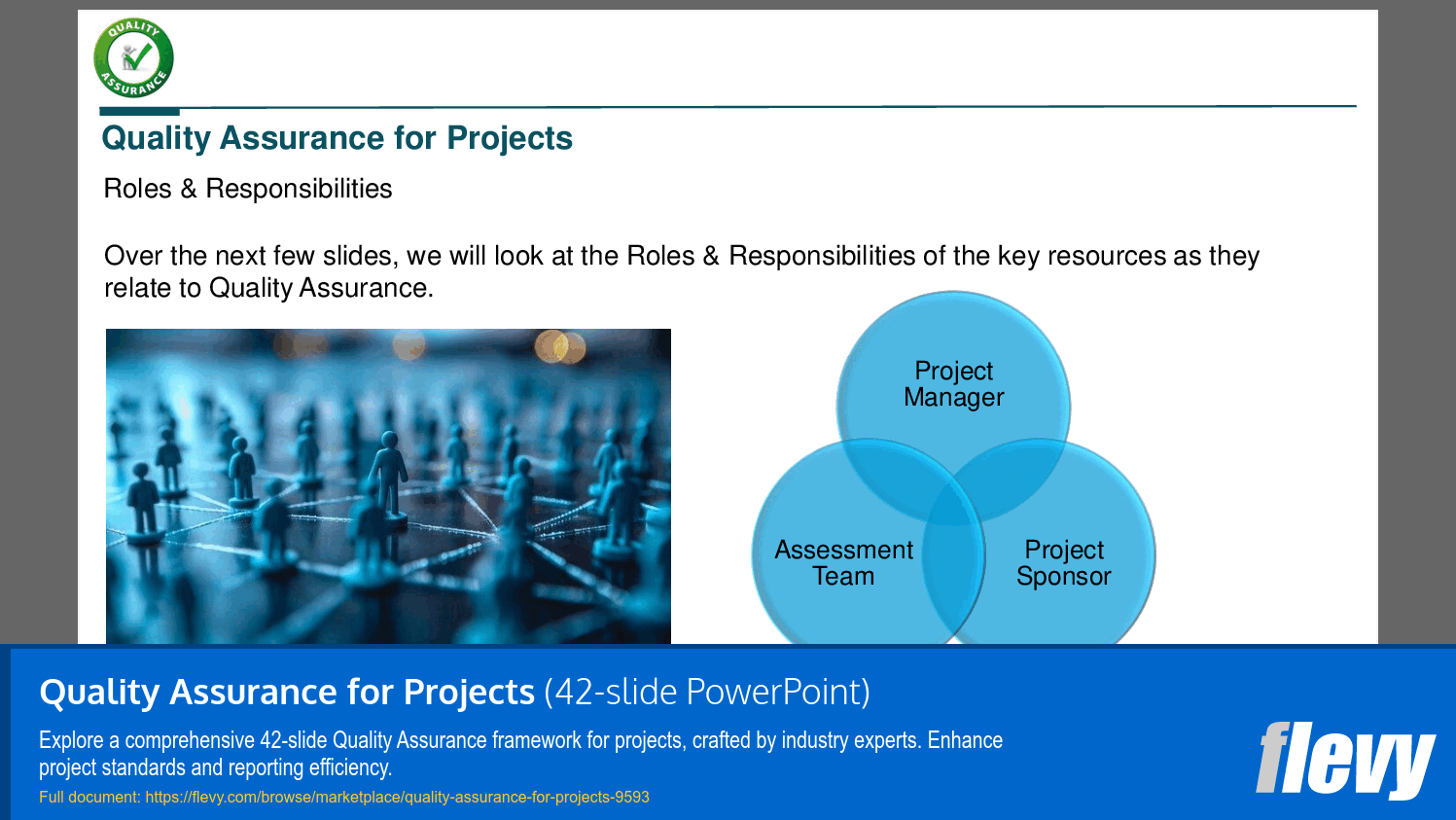
• Roles & Responsibilities (page 24)
• Reporting (page 28)
• Education (page 35)
• Applying Practicality (page 39)
• Quality Assurance vs Stage Gate Review (page 42)
Primary Topics Covered
• Quality Assurance Definition - Quality Assurance encompasses practices and processes ensuring project deliverables meet required standards and stakeholder expectations.
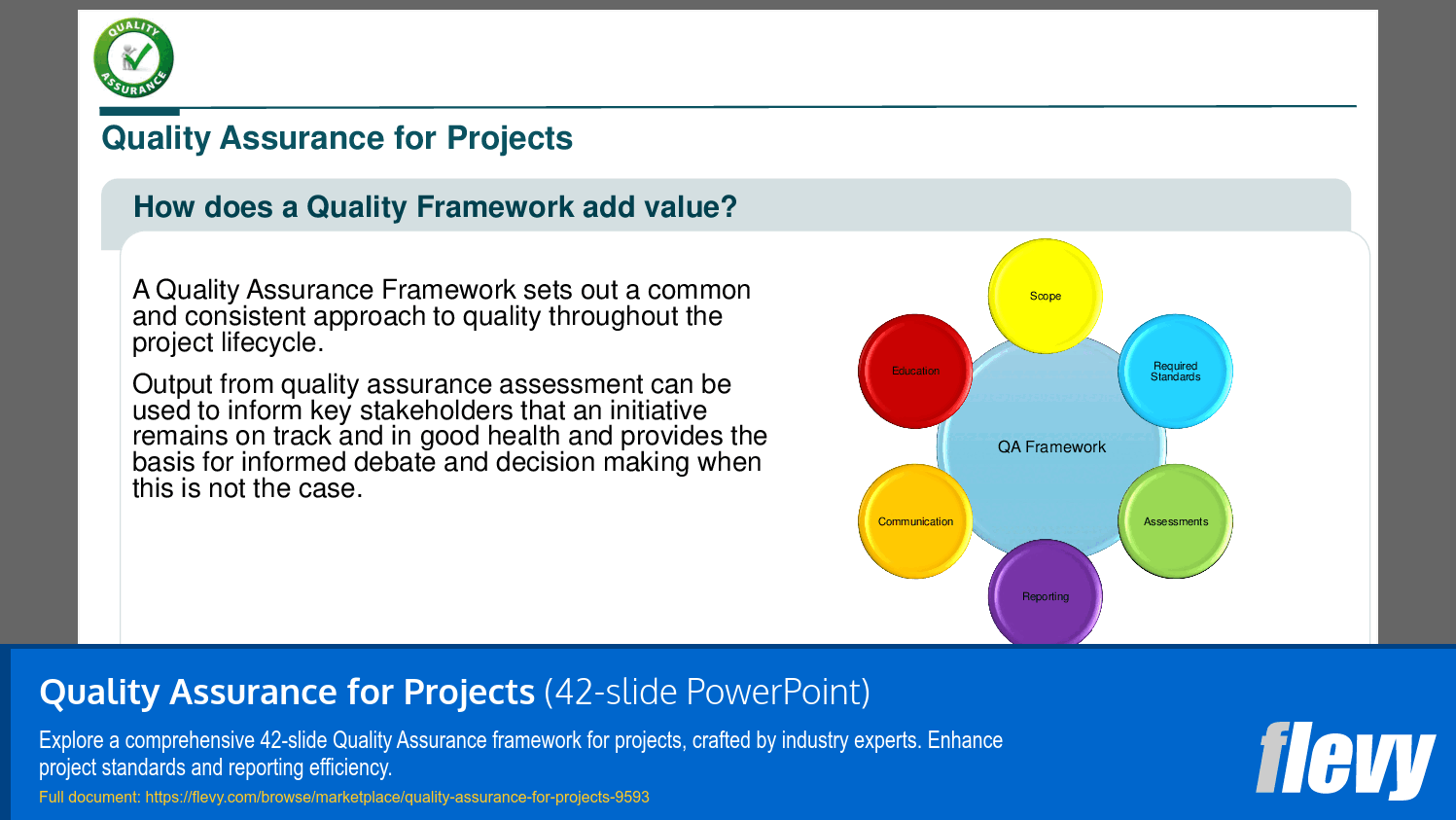
• Quality Framework Value - A Quality Assurance Framework provides a consistent approach to quality, enabling informed decision-making and proactive risk management.
• Scope Definition - Establishing which project artifacts will undergo quality assessment through collaborative discussions among project teams.
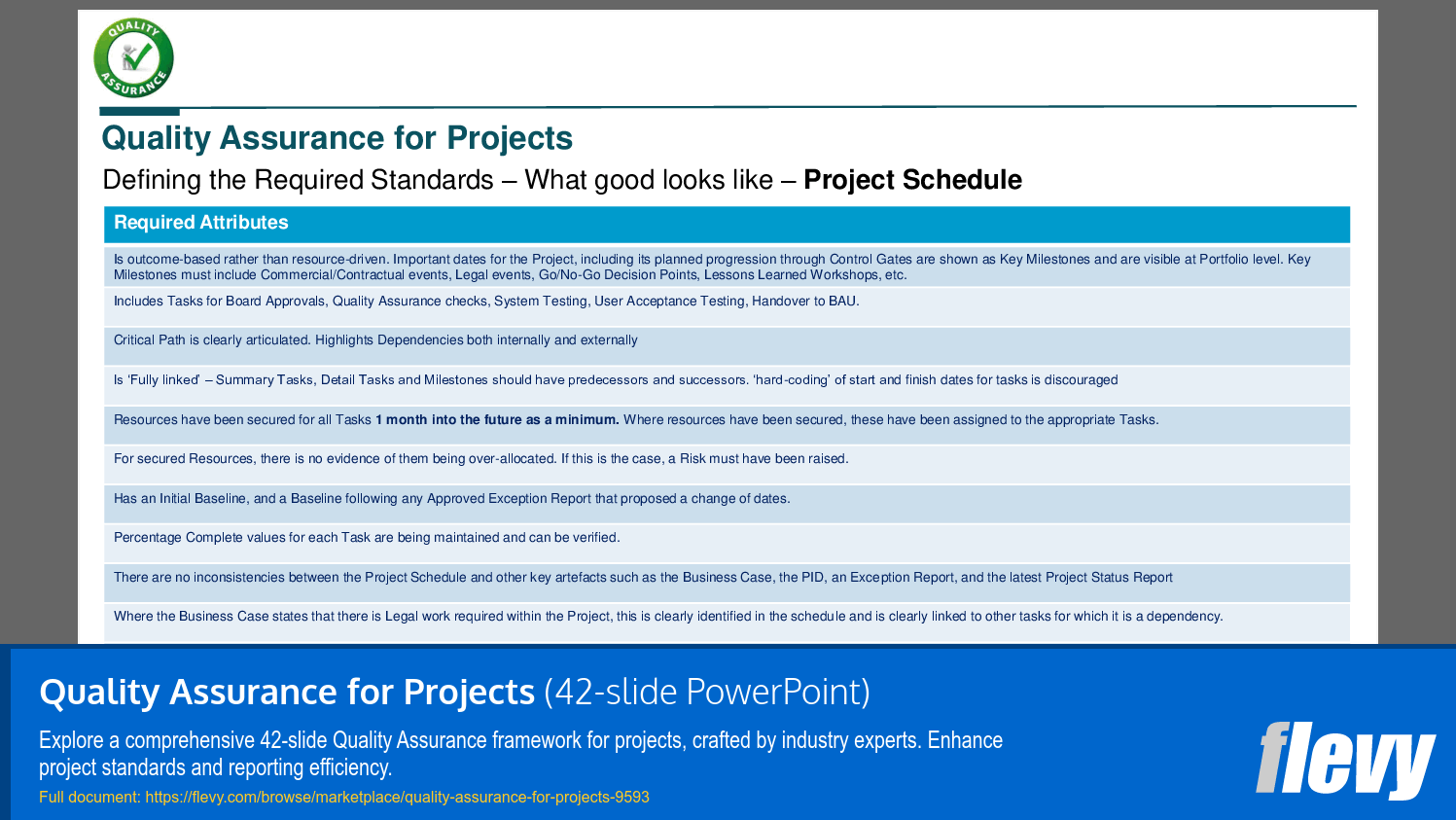
• Required Standards - Setting realistic and measurable quality standards for project artifacts to ensure they meet organizational expectations.
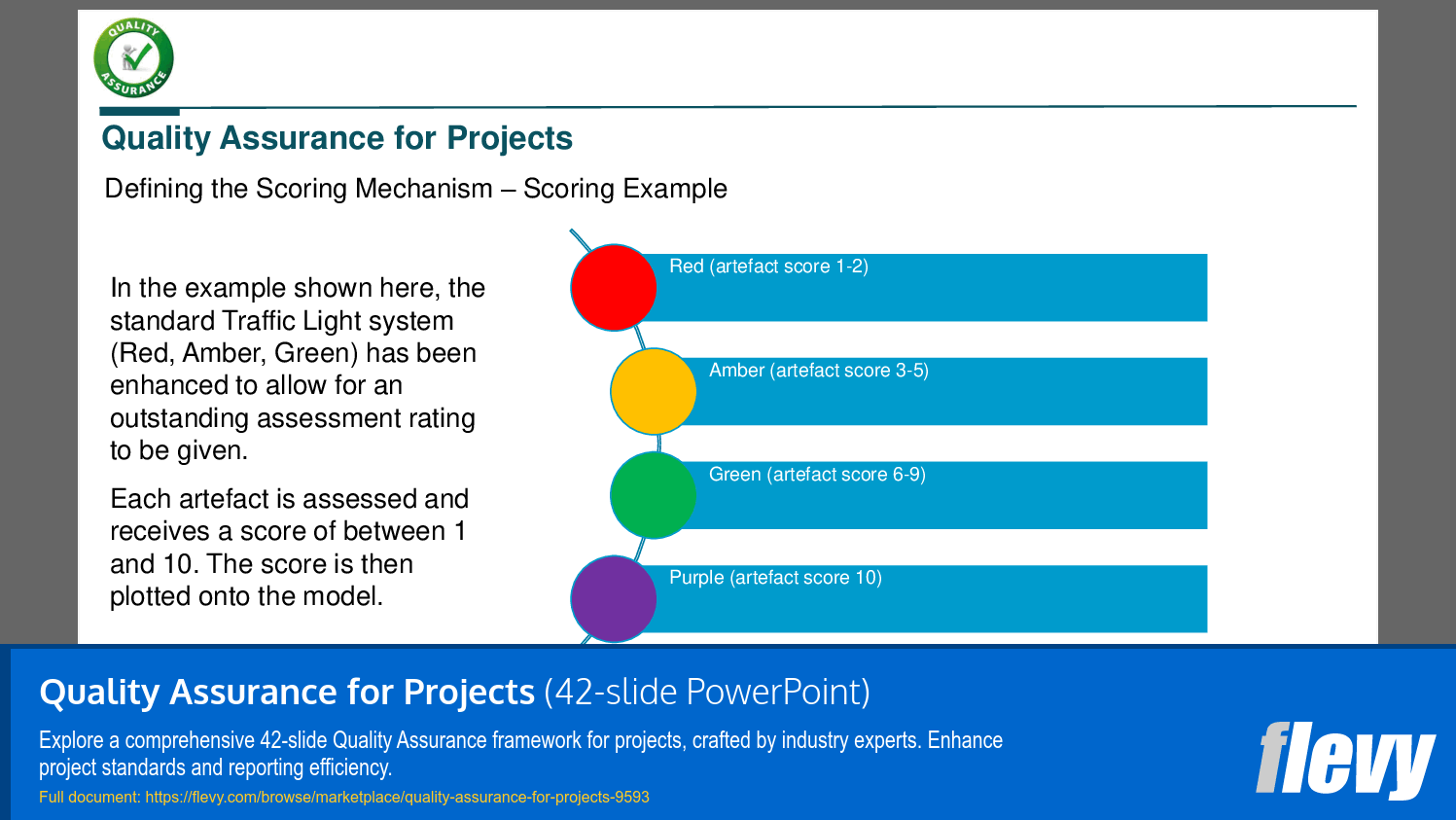
• Scoring Mechanism - Implementing a scoring system, such as a Traffic Light model, to evaluate the quality of project artifacts effectively.
• Roles and Responsibilities - Clarifying the roles of Project Managers, Sponsors, and Assessment Teams in maintaining quality assurance throughout project execution.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Quality Assurance Framework template for establishing quality standards
• Artifact assessment templates for evaluating project deliverables
• Scoring mechanism model for assessing quality (Traffic Light system)
• Reporting dashboard templates for communicating quality assessment results
• Education materials for training project teams on quality assurance practices
• Lessons Learned Log template for documenting insights and improvements
Slide Highlights
• Overview of Quality Assurance and its importance in project management
• Visual representation of the Quality Assurance Framework components
• Examples of required standards for key project artifacts, such as Business Cases and Risk Registers
• Scoring mechanism examples illustrating the Traffic Light assessment system
• Reporting trends and patterns that indicate the effectiveness of the Quality Assurance Framework
Potential Workshop Agenda
Quality Assurance Framework Overview (60 minutes)
• Introduce the concept of Quality Assurance and its significance
• Discuss the components of a Quality Assurance Framework
• Review the roles and responsibilities of project team members
Artifact Assessment Workshop (90 minutes)
• Define the scope of project artifacts for assessment
• Collaboratively establish required quality standards
• Develop templates for assessing project deliverables
Scoring Mechanism and Reporting (60 minutes)
• Introduce the scoring mechanism for quality assessment
• Discuss reporting requirements and dashboard creation
• Review case studies of successful quality assurance implementations
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the Quality Assurance Framework to fit specific project needs and organizational culture
• Adjust the scope of quality assessments based on available resources and project priorities
• Modify the scoring mechanism to align with organizational standards and expectations
• Customize reporting formats to meet the needs of different stakeholders
Secondary Topics Covered
• The importance of stakeholder engagement in quality assurance
• Best practices for documenting lessons learned during project execution
• Strategies for fostering a culture of quality and continuous improvement
• The relationship between quality assurance and project governance
Topic FAQ
What are the main components of a project quality assurance framework?
A project quality assurance framework defines which artifacts will be assessed, sets measurable standards, implements a scoring mechanism, assigns roles and responsibilities, establishes reporting, provides education, and captures lessons learned. These components include scope definition, required standards, a scoring mechanism, roles & responsibilities, reporting, education, and a Lessons Learned Log.How do I set measurable quality standards for project artifacts?
Measurable standards are set through consultative sessions with project teams and stakeholders, then tailored to organizational expectations and project priorities. Standards should be realistic and specific to each artifact type so teams can objectively assess compliance for items like the Business Case and Risk Register.What scoring mechanisms are commonly used to assess artifact quality?
A commonly used approach is a Traffic Light (RAG) scoring model that assigns Red, Amber, or Green ratings to artifact quality levels, providing clear assessment outcomes and escalation triggers; this Traffic Light model is one example of a scoring mechanism referenced in the Quality Assurance for Projects pack.How should roles and responsibilities be defined for quality assurance activities?
Roles should specify who creates artifacts, who conducts assessments, and who governs quality standards—typically the Project Manager produces deliverables, the Project Sponsor provides oversight, and an Assessment Team executes reviews and recommendations, with each role’s responsibilities documented and agreed up front.What should I look for when buying a project quality assurance toolkit?
Buyers should look for templates to define a QA framework, artifact assessment templates, a clear scoring mechanism, reporting/dashboard templates, education materials, and guidance for tailoring the approach. Quality Assurance for Projects includes artifact assessment templates and a Traffic Light scoring model as specific components.How much workshop time is typical to implement a QA framework from a template?
An initial implementation can be structured as workshops: a 60-minute framework overview, a 90-minute artifact assessment workshop, and a 60-minute scoring and reporting session—totaling 210 minutes as a suggested starting agenda in the Quality Assurance for Projects materials.I need to improve deliverable quality after repeated post-go-live issues—where should I start?
Begin by defining scope and measurable standards at project initiation, run collaborative artifact assessments, implement a consistent scoring mechanism, and create reporting to surface trends and lessons learned. The Quality Assurance for Projects pack suggests starting with scope and standards and using a Traffic Light scoring mechanism.After a merger, how can I ensure consistent deliverables across multiple projects?
Standardize artifact expectations and templates across projects, apply a consistent scoring mechanism, and consolidate results into organizational reporting dashboards to identify systemic gaps and cross-project risks. Use common artifact templates (e.g., Business Case, Risk Register) and reporting dashboards to track cross-project trends.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the purpose of a Quality Assurance Framework?
A Quality Assurance Framework ensures that project deliverables meet established quality standards, facilitating informed decision-making and proactive risk management.
How do I define the scope of quality assessments?
The scope should be defined through consultative sessions involving project management teams and stakeholders to agree on which artifacts will be assessed.
What are the required standards for project artifacts?
Required standards should be realistic, measurable, and tailored to the organization’s expectations, ensuring that each artifact meets quality requirements.
How is the scoring mechanism implemented?
A scoring mechanism, such as a Traffic Light system, can be used to evaluate artifacts, assigning scores based on quality levels and providing clear assessment outcomes.
What roles are involved in quality assurance?
Key roles include the Project Manager, Project Sponsor, and Assessment Team, each with specific responsibilities related to quality assurance practices.
How is quality assurance reported?
Quality assurance findings should be communicated through dashboards and reports that present trends, patterns, and overall quality assessment results to stakeholders.
What educational support is provided for quality assurance?
Educational support includes workshops, drop-in sessions, and a Knowledge Hub to ensure project teams understand the Quality Assurance Framework.
How can I apply practicality in quality assurance?
Practicality can be applied by tailoring the framework to specific project needs, adjusting the scope of assessments, and implementing incremental rollouts.
What is the difference between Quality Assurance and Stage Gate Review?
Quality Assurance focuses on ensuring project artifacts meet quality standards, while Stage Gate Review assesses whether the project is on track to meet its deliverables and business case viability.
Glossary
• Quality Assurance - Practices and processes ensuring project deliverables meet required standards.
• Quality Framework - A structured approach to managing quality throughout the project lifecycle.
• Artifact - Any document or deliverable produced during the project lifecycle.
• Scoring Mechanism - A system for evaluating the quality of project artifacts.
• RAG - Red, Amber, Green; a color-coded system for reporting project status.
• Lessons Learned Log - A document for capturing insights and improvements from project experiences.
• Stakeholder - An individual or group with an interest in the project's outcome.
• Project Manager - The individual responsible for planning, executing, and closing a project.
• Project Sponsor - The individual who champions the project and provides resources.
• Assessment Team - The group responsible for conducting quality assessments and ensuring adherence to standards.
• Dashboard - A visual representation of key performance indicators and project status.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to enhance products, services, or processes.
• Governance - The framework of rules and practices that guide project management.
Source: Best Practices in Quality Management PowerPoint Slides: Quality Assurance for Projects PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Dartview Consulting