Lean Six Sigma - Process Risk Analysis (FMEA) (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + Excel (XLSX) 131 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- the systematic analysis of a manufacturing, service or administrative process,
- the identification of critical and/or significant process characteristics, and
- the identification of process deficiencies and development of an effective corrective action plan.
LEAN PPT DESCRIPTION
The Lean Six Sigma – Process Risk Analysis & Mistake-Proofing Training Module provides you with a step-by-step approach, as well as examples, exercises, and templates, to analyze and eliminate risks in your manufacturing, service or business processes. This training module includes:
1. 132 PowerPoint slides covering
• Introduction to Process Risk Analysis & Mistake-Proofing,
• Process Variables Map,
• Cause & Effect Matrix,
• Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis,
• Sixteen Human Error Modes,
• Six Mistake-Proofing Principles,
• Seven Types of Poka-Yoke Devices and Examples,
• Process Control Plan,
• and 6 Workshop Exercises.
2. MS Excel Process Variables Map Template & Example
3. MS Excel Cause & Effect Matrix Template & Example
4. MS Excel Process FMEA Template & Example
5. MS Excel Process Control Plan Template & Example
"After you have downloaded the training material, you can change any part of the training material and remove all logos and references to Operational Excellence Consulting. You can share the material with your colleagues and clients, and re-use it as you need. The only restriction is that you cannot publicly re-distribute, sell, rent or license the material as though it is your own. Thank you."
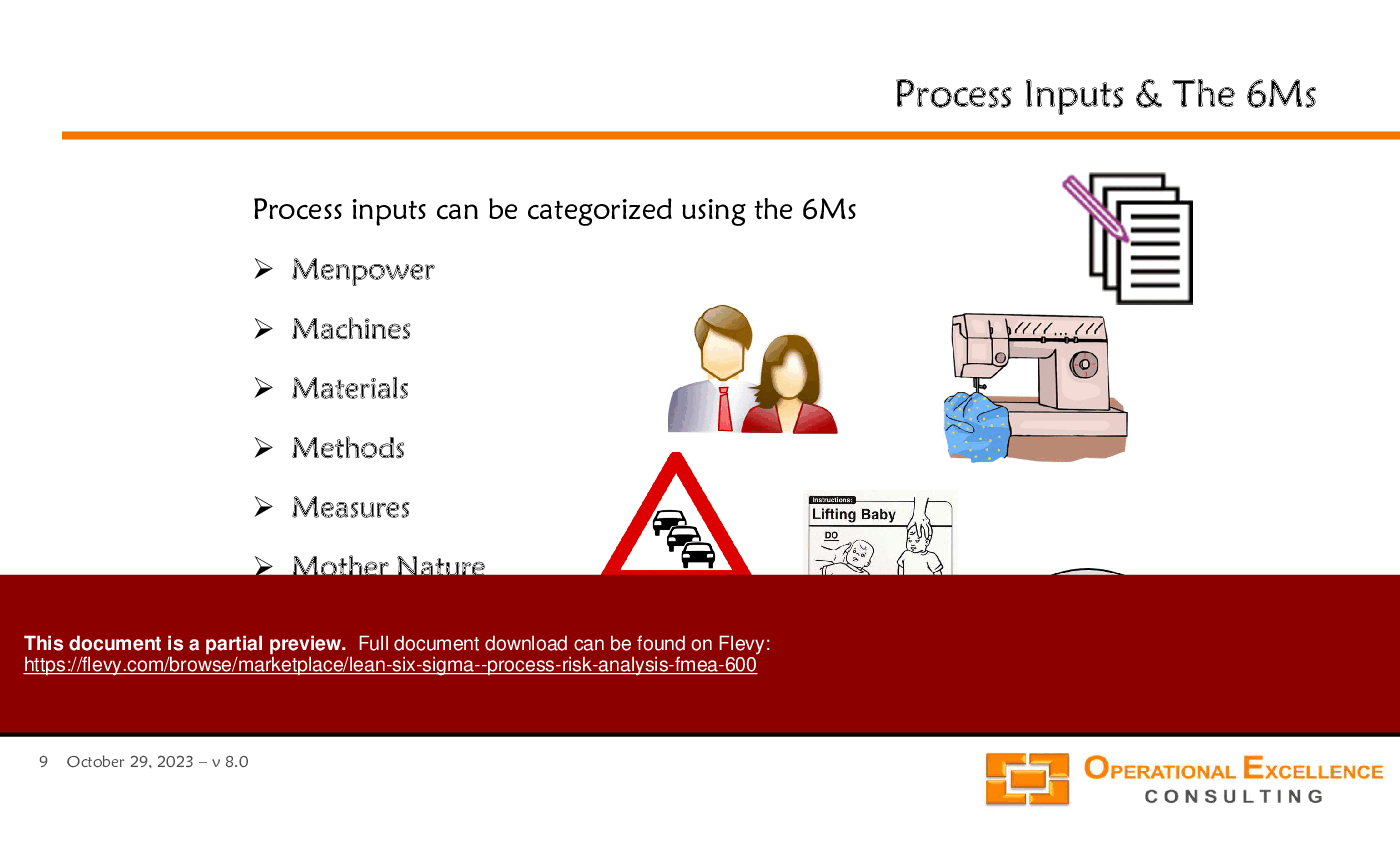
This comprehensive module delves into the intricacies of process inputs using the 6Ms framework: Manpower, Machines, Materials, Methods, Measures, and Mother Nature. It guides you through the essentials of Process Variables Mapping, ensuring you capture all value-added and non-value-added steps, major activities, and data collection points. The module emphasizes the importance of documenting the process as it is actually performed, not just as it is supposed to be performed.
The training also covers the Cause & Effect Matrix, which helps in funneling the complete list of inputs and process variables for further evaluation using FMEA. It includes detailed steps for identifying process steps, adding specifications, and prioritizing variables. This structured approach ensures a thorough review and assessment of your Process Control Plan, enabling you to identify and implement low-hanging fruit and quick wins efficiently.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 131-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Process Risk Analysis (FMEA) & Mistake Proofing" presentation provides a structured approach to identifying and preventing defects in manufacturing and business processes. Developed by Operational Excellence Consulting LLC, this training module emphasizes the importance of systematic risk analysis and mistake-proofing techniques to enhance operational efficiency. By integrating methodologies such as Process Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Root Cause Analysis, and Poka-Yoke principles, this presentation equips teams with the tools necessary to minimize errors and improve process reliability.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Quality Assurance Managers focused on reducing defects and improving process quality
• Operational Excellence Leaders implementing Lean Six Sigma methodologies
• Process Improvement Teams conducting risk assessments and control planning
• Cross-functional teams involved in product development and manufacturing processes
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During process improvement initiatives to identify potential failure modes
• When implementing new processes or products to ensure reliability
• In training sessions aimed at fostering a culture of quality and accountability
Learning Objectives
• Define the principles of Process Risk Analysis and Mistake Proofing
• Develop a comprehensive Process Variables Map for current processes
• Create and analyze a Cause & Effect Matrix to identify critical inputs
• Conduct a Process FMEA to prioritize potential failure modes
• Implement effective mistake-proofing solutions using Poka-Yoke principles
• Establish a Process Control Plan to ensure ongoing process reliability
Table of Contents
• Overview of Process Risk Analysis & Mistake Proofing (page 2)
• Agenda for Training Session (page 4)
• Process Variables Mapping (page 13)
• Cause & Effect Matrix Basics (page 24)
• Process FMEA Overview (page 42)
• Risk Analysis Methodology (page 66)
• Developing a Process Control Plan (page 121)
Primary Topics Covered
• Process Risk Analysis - A systematic approach to identifying potential defects and their impacts on customer satisfaction.
• Mistake Proofing - Techniques designed to prevent errors from becoming defects, enhancing overall process reliability.
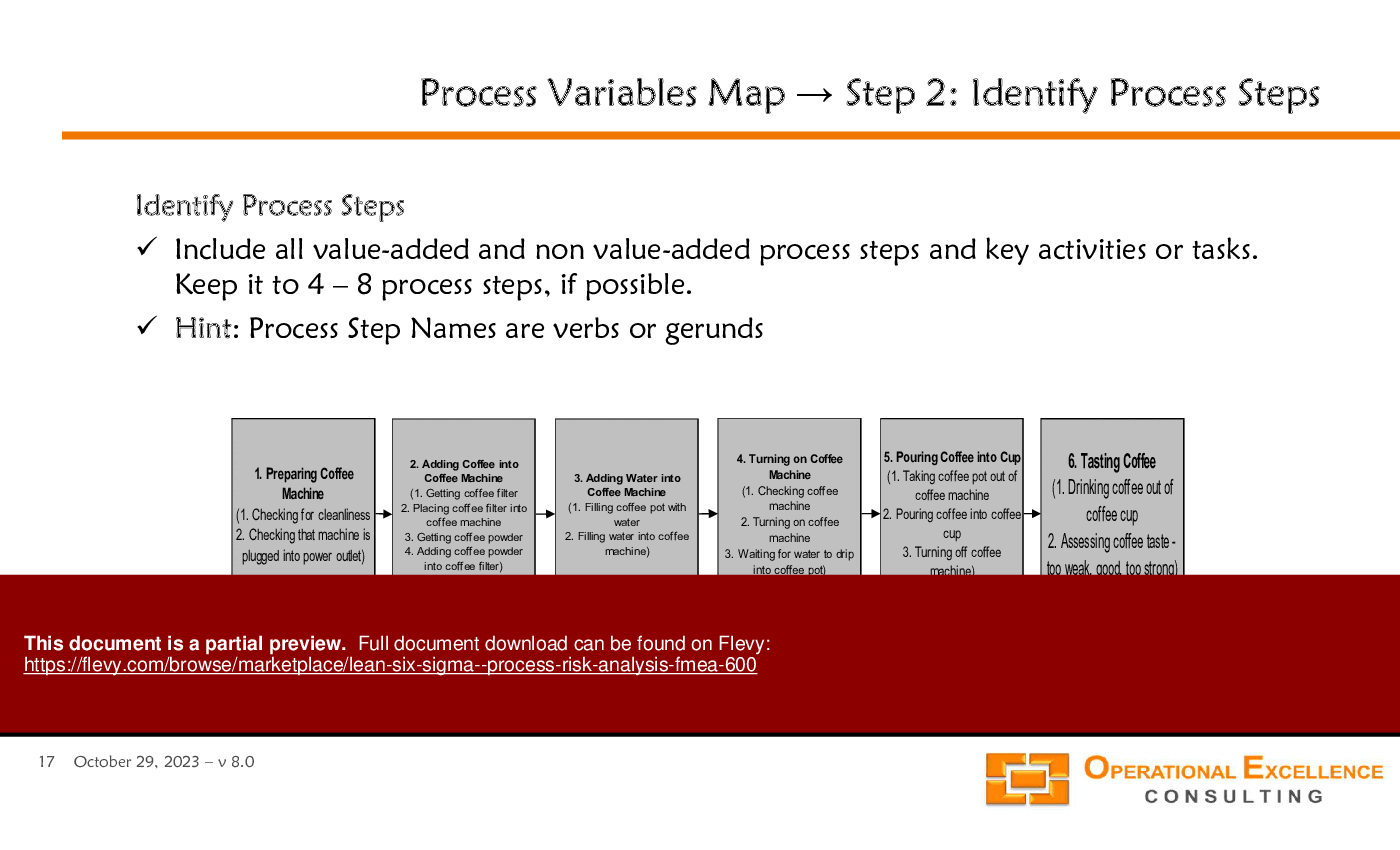
• Process Variables Mapping - A visual representation of process steps, inputs, and outputs to identify critical control points.
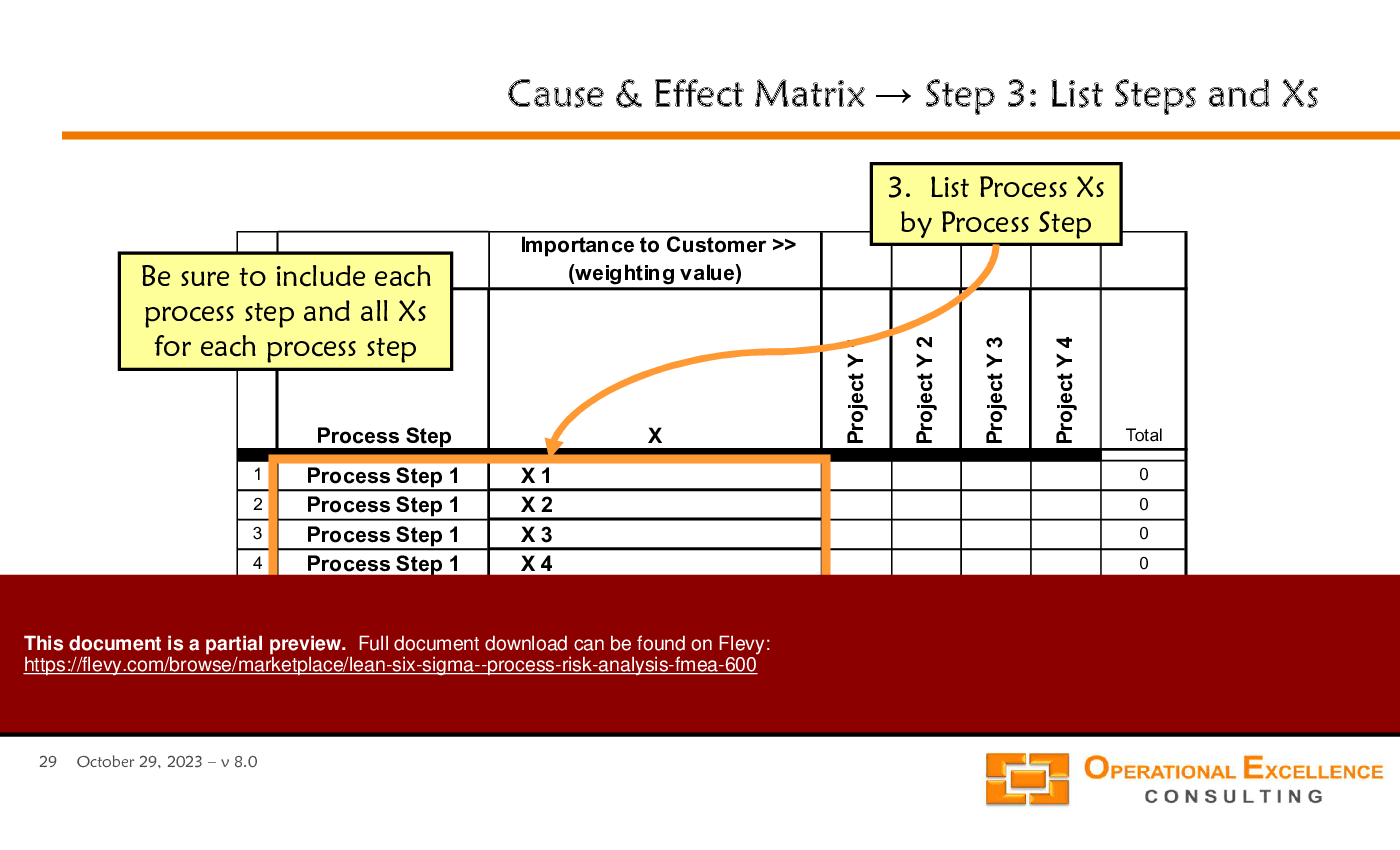
• Cause & Effect Matrix - A tool for quantifying customer requirements and correlating them with process inputs.
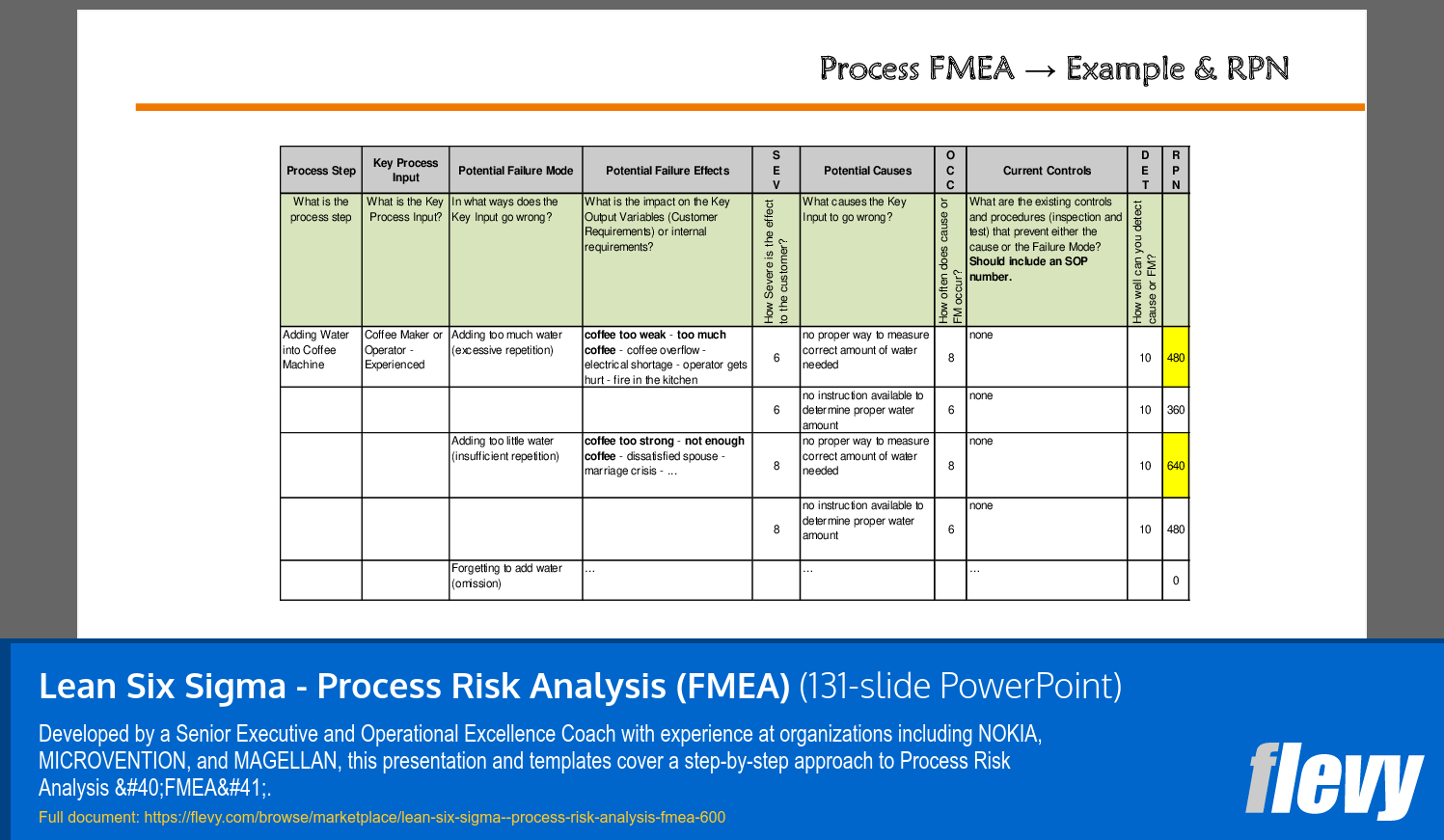
• Process FMEA - A structured method for evaluating potential failure modes and prioritizing corrective actions.
• Risk Analysis - Assessment of severity, occurrence, and detection to calculate Risk Priority Numbers (RPN).
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Process Variables Map template for documenting process steps and inputs
• Cause & Effect Matrix template for analyzing customer requirements
• FMEA template for identifying and prioritizing potential failure modes
• Process Control Plan template for ensuring ongoing process reliability
• Poka-Yoke implementation guidelines for mistake-proofing processes
Slide Highlights
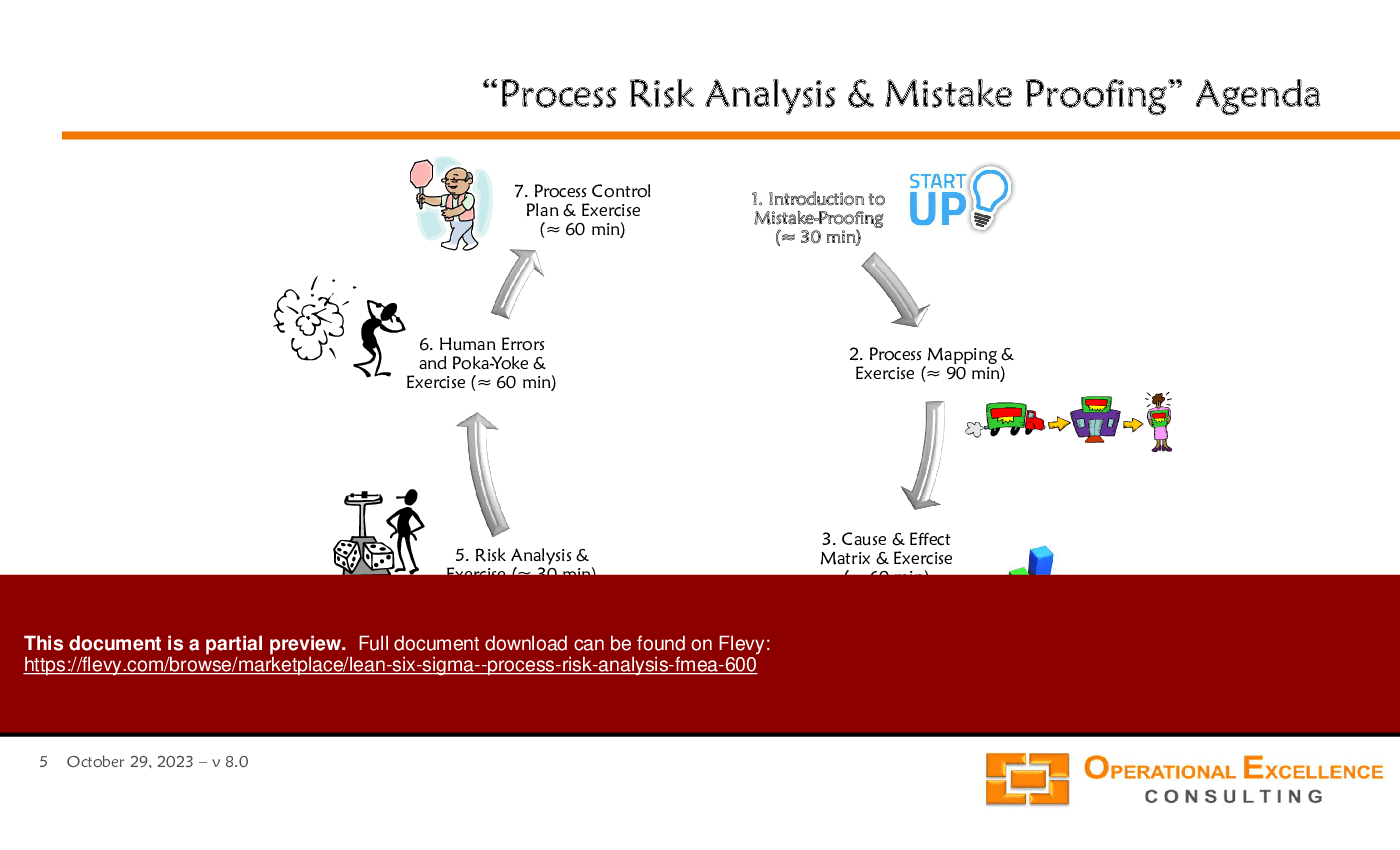
• Overview of the 10-step Process Risk Analysis approach
• Visual representation of the Cause & Effect Matrix
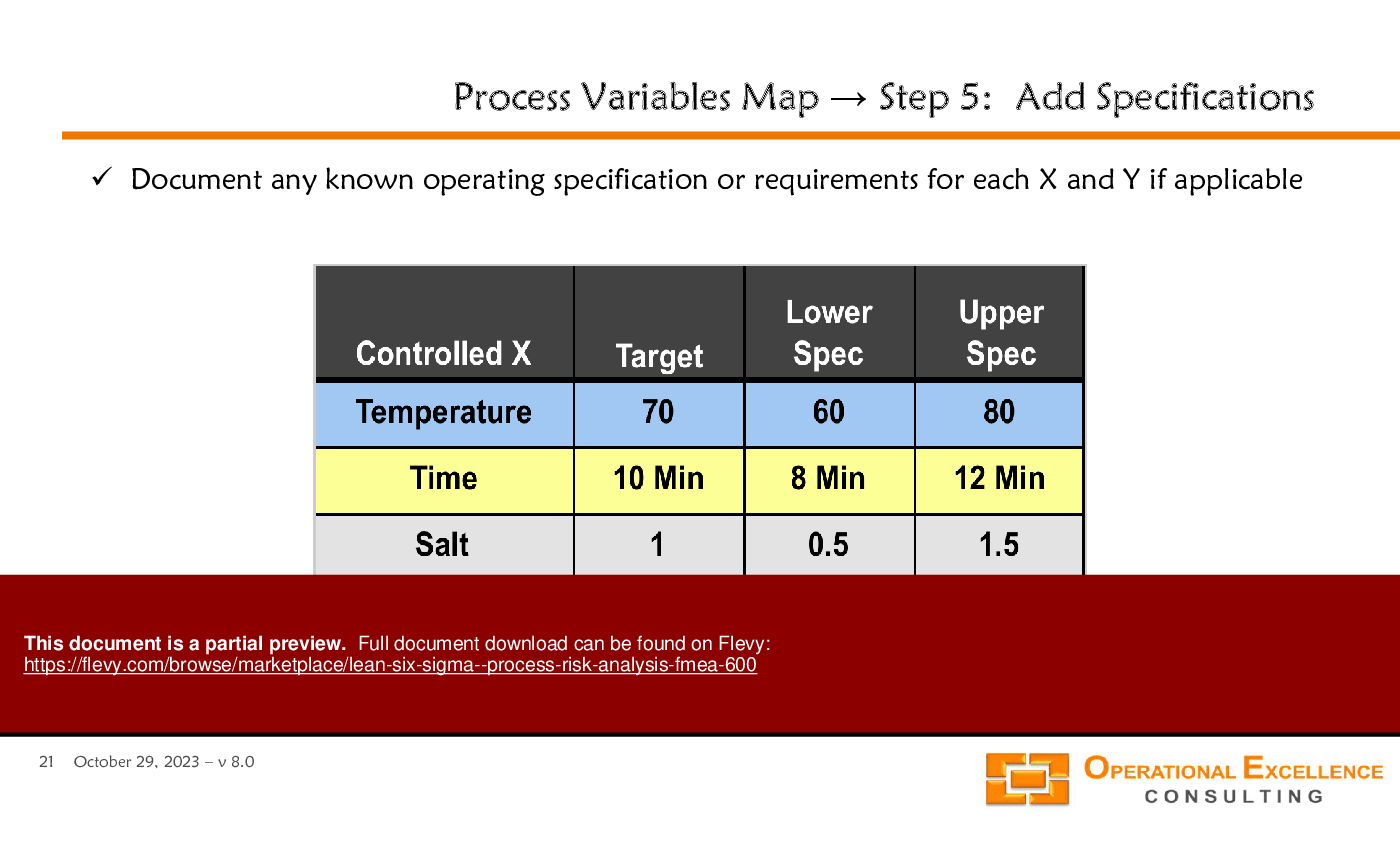
• Example of a Process Variables Map using the coffee-making process
• Detailed explanation of the FMEA process and its benefits
• Real-world examples of mistake-proofing techniques and their applications
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Mistake-Proofing (30 minutes)
• Overview of key concepts and importance
• Discussion on common human errors in processes
Process Mapping & Exercise (90 minutes)
• Hands-on activity to create a Process Variables Map
• Identification of critical inputs and outputs
Cause & Effect Matrix & Exercise (60 minutes)
• Development of a Cause & Effect Matrix
• Group analysis of customer requirements
Process FMEA & Exercise (60 minutes)
• Conducting a Process FMEA on selected processes
• Prioritization of potential failure modes
Risk Analysis & Exercise (30 minutes)
• Assessment of severity, occurrence, and detection for identified risks
Human Errors and Poka-Yoke & Exercise (60 minutes)
• Exploration of human error modes and mistake-proofing principles
• Group brainstorming on Poka-Yoke solutions
Process Control Plan & Exercise (60 minutes)
• Development of a Process Control Plan for ongoing reliability
• Review of key metrics and control methods
Customization Guidance
• Modify the Process Variables Map to reflect specific organizational processes
• Tailor the Cause & Effect Matrix to align with customer requirements and priorities
• Adjust the FMEA template to include relevant failure modes specific to the organization
• Incorporate organizational terminology and metrics into the Process Control Plan
Secondary Topics Covered
• Root Cause Analysis techniques and tools
• Historical context of FMEA and its evolution across industries
• Human error modes and their impact on process reliability
• Best practices for implementing Poka-Yoke devices in various environments
FAQ
What is the purpose of Process Risk Analysis?
Process Risk Analysis aims to identify potential defects in processes and implement solutions to prevent them, thereby enhancing quality and customer satisfaction.
How does mistake-proofing work?
Mistake-proofing involves designing processes and products to prevent errors or make them easily detectable, ensuring that mistakes do not lead to defects.
What is FMEA?
FMEA, or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis, is a systematic methodology for evaluating potential failure modes within a process and prioritizing actions to mitigate risks.
How do I implement Poka-Yoke in my processes?
Poka-Yoke can be implemented by designing processes that prevent errors or by using devices that detect errors before they result in defects.
What are the key components of a Process Control Plan?
A Process Control Plan includes specifications for process characteristics, control methods, measurement systems, and reaction plans for out-of-spec conditions.
How often should the Process Control Plan be reviewed?
The Process Control Plan should be reviewed and updated regularly, typically on a quarterly basis, to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
What is the significance of the Cause & Effect Matrix?
The Cause & Effect Matrix quantifies the relationship between process inputs and customer requirements, helping teams prioritize areas for improvement.
How can I train my team on these concepts?
Utilize the provided templates and workshop exercises to facilitate hands-on learning and discussions within your team, reinforcing the concepts of risk analysis and mistake-proofing.
Glossary
• FMEA - Failure Mode and Effects Analysis, a systematic method for evaluating potential failures in processes.
• Poka-Yoke - A mistake-proofing technique designed to prevent errors from becoming defects.
• Process Variables Map - A visual tool that outlines all process steps and their associated inputs and outputs.
• Cause & Effect Matrix - A matrix that correlates customer requirements with process inputs to identify critical areas for improvement.
• Risk Priority Number (RPN) - A numerical value calculated from severity, occurrence, and detection ratings to prioritize risks.
• Control Plan - A documented plan outlining quality control actions for a specific process or product.
• Root Cause Analysis - A method for identifying the underlying causes of problems or defects in processes.
• Human Error Modes - Common types of mistakes made by individuals during processes.
• 6Ms - A framework for categorizing process inputs: Men, Machines, Materials, Methods, Measures, and Mother Nature.
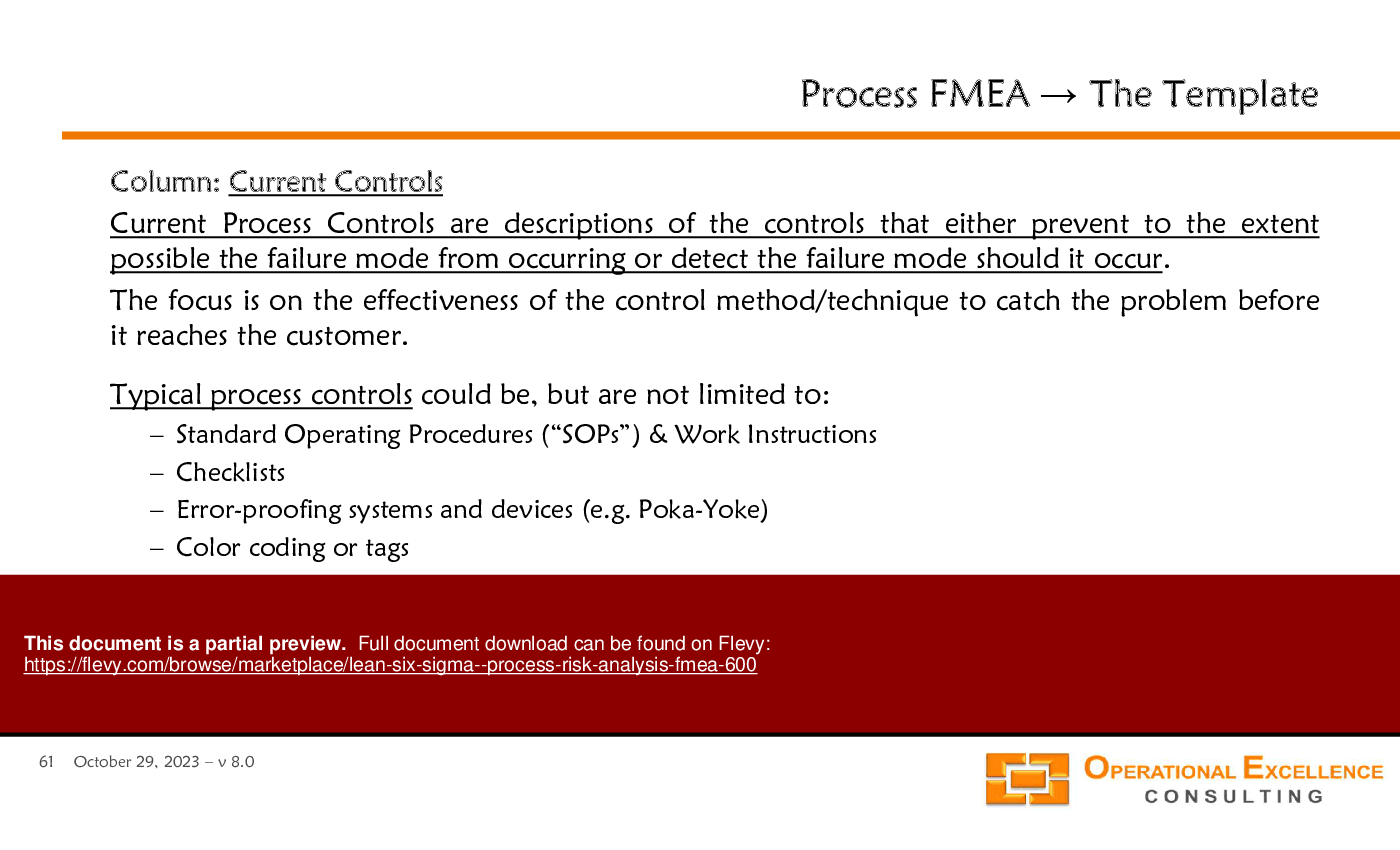
• Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) - Documented procedures that outline the steps necessary to complete a task.
• Variation Control - Techniques used to minimize variation in process outputs.
• Out-of-Control Action Plan (OCAP) - A systematic approach for addressing out-of-control situations in processes.
• Statistical Process Control (SPC) - A method of quality control that uses statistical methods to monitor and control a process.
LEAN PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Lean, Mistake-Proofing PowerPoint Slides: Lean Six Sigma - Process Risk Analysis (FMEA) PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, Operational Excellence Consulting LLC