Industry Supply Curve Analysis (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 24 Slides
SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS PPT DESCRIPTION
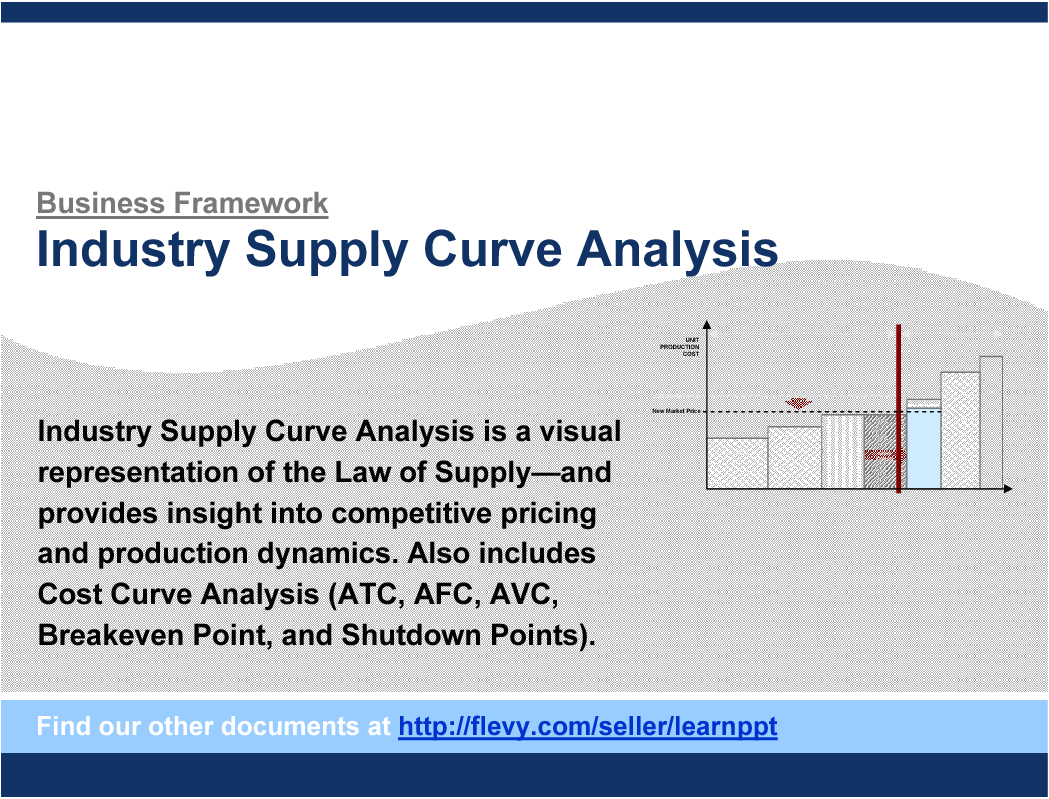
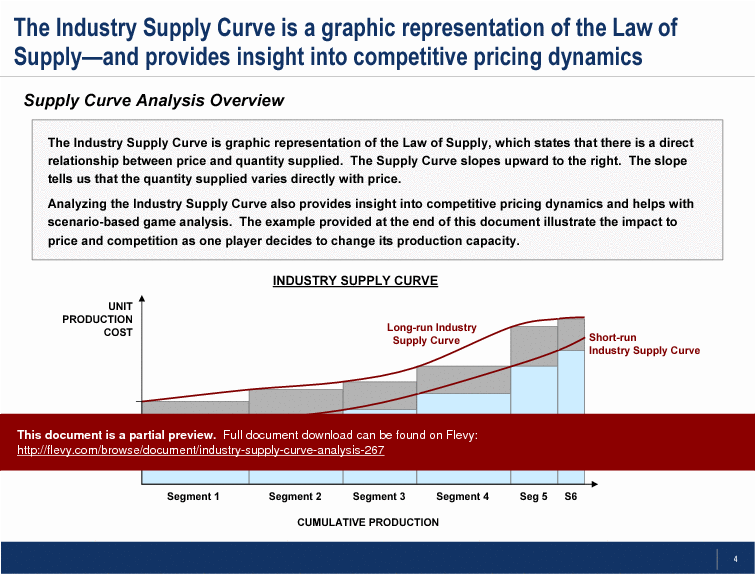
The Industry Supply Curve is graphic representation of the Law of Supply, which states that there is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied. The Supply Curve slopes upward to the right. The slope tells us that the quantity supplied varies directly with price.
Analyzing the Industry Supply Curve also provides insight into competitive pricing dynamics and helps with scenario-based game analysis. The example provided at the end of this document illustrate the impact to price and competition as one player decides to change its production capacity.
This document also covers Cost Curve Analysis (ATC, AFC, AVC, Breakeven Point, and Shutdown Points).
This comprehensive PPT provides a meticulous 10-step approach to analyzing the Industry Supply Curve, ensuring a thorough understanding of market dynamics. Each step is designed to guide you through the process, from defining industry and market boundaries to verifying the resulting supply curve. The methodology includes identifying the number of producers, grouping them into segments, and selecting representative producers to calculate production costs and capacities.
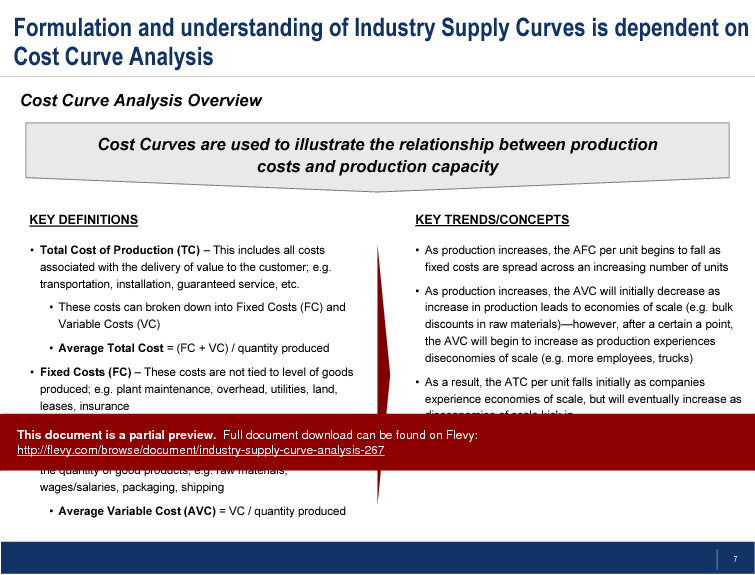
The document delves into the nuances of cost curve analysis, breaking down fixed and variable costs, and illustrating how these impact production capacity. Key trends and concepts such as economies of scale and the behavior of average total costs (ATC) and average variable costs (AVC) are explored in detail. This analysis is crucial for understanding how production increases affect cost structures and competitive positioning within the industry.
Step-by-step instructions are provided to develop a cost model using detailed cost data, perform activity-based costing (ABC), and assess production differences among competitors. The final steps involve plotting the industry supply curve and conducting a "sanity check" to ensure the accuracy and strategic relevance of the results. This document is an invaluable resource for executives looking to optimize production strategies and gain a competitive edge in their industry.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS PPT SLIDES
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 24-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Industry Supply Curve Analysis presentation is a consulting-grade resource crafted by former consultants from McKinsey, BCG, Deloitte, EY, and Capgemini. This deck provides a robust framework for understanding the Law of Supply, illustrating its implications for competitive pricing and production dynamics. Users will learn to visualize cost structures through Cost Curve Analysis, which includes critical concepts such as Average Total Cost (ATC), Average Fixed Cost (AFC), Average Variable Cost (AVC), Breakeven Points, and Shutdown Points. This presentation equips corporate executives and consultants with the tools to analyze market conditions and make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies and production capacities.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to understand market dynamics and pricing strategies
• Business analysts involved in competitive pricing and production analysis
• Consultants advising clients on market entry or pricing strategies
• Financial analysts assessing cost structures and profitability
• Strategic planners developing long-term production strategies
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions focused on market analysis
• When evaluating pricing strategies in response to market changes
• In workshops aimed at improving competitive positioning
• For training sessions on cost analysis methodologies
Learning Objectives
• Define the Industry Supply Curve and its significance in competitive analysis
• Build a comprehensive Cost Curve Analysis to assess production costs
• Establish the relationship between price and quantity supplied using the Supply Curve
• Identify key cost metrics such as Breakeven and Shutdown Points
• Analyze competitive pricing dynamics through scenario-based game analysis
• Create actionable insights for pricing and production decisions
Table of Contents
• Overview (page 3)
• Benefits & Limitations (page 5)
• Cost Curve Analysis (page 6)
• Overview (page 7)
• Cost Curves (page 8)
• Supply Curve Analysis (page 10)
• 10-Step Approach (page 11)
• Example (page 23)
Primary Topics Covered
• Overview of Supply Curve Analysis - This section introduces the Industry Supply Curve as a visual representation of the Law of Supply, emphasizing its role in understanding competitive pricing dynamics.
• Benefits of Supply Curve Analysis - Highlights the systematic approach to conducting competitive cost analysis and its utility in identifying breakeven and shutdown points.
• Limitations of Supply Curve Analysis - Discusses the challenges in accurately defining market boundaries and acquiring necessary data for analysis.
• Cost Curve Analysis - Details the relationship between production costs and capacity, including key definitions and trends.
• 10-Step Approach to Industry Supply Curve Creation - Outlines a structured methodology for constructing the Industry Supply Curve, from defining market boundaries to verifying results.
• Example of Industry Supply Curve Analysis - Provides a practical illustration of the concepts discussed, showcasing how different segments interact within the market.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Cost Curve Analysis template for visualizing production costs
• Framework for defining industry and market boundaries
• Step-by-step guide for constructing the Industry Supply Curve
• Scenario analysis tools for competitive pricing dynamics
• Breakeven and Shutdown Point analysis models
• Visual aids for illustrating Cost Curves and Supply Curves
Slide Highlights
• Overview slide introducing the Industry Supply Curve and its significance
• Benefits and Limitations slide outlining the strengths and weaknesses of Supply Curve Analysis
• Detailed Cost Curve Analysis slide explaining key cost concepts
• 10-Step Approach slide for constructing the Industry Supply Curve
• Example slide illustrating the application of the Supply Curve in a real-world context
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Supply Curve Analysis (60 minutes)
• Overview of the Law of Supply and its implications
• Discussion on competitive pricing dynamics
Cost Curve Analysis Workshop (90 minutes)
• Deep dive into Cost Curve components (ATC, AFC, AVC)
• Hands-on activity to calculate Breakeven and Shutdown Points
Industry Supply Curve Construction (120 minutes)
• Step-by-step guidance on creating the Industry Supply Curve
• Group exercise to analyze different market segments
Customization Guidance
• Adjust the industry definitions and market boundaries to reflect specific business contexts
• Tailor the Cost Curve Analysis to include company-specific cost data
• Modify the example scenarios to align with the unique competitive landscape of the organization
• Update visual aids to incorporate relevant market data and trends
Secondary Topics Covered
• Competitive market structures and their impact on Supply Curve Analysis
• The role of economies of scale in Cost Curve dynamics
• Scenario-based analysis techniques for pricing strategies
• Implications of market demand on production capacity
FAQ
What is the Industry Supply Curve?
The Industry Supply Curve is a graphical representation that shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied, illustrating how supply varies with price changes.
How do I define the market boundaries for my analysis?
Market boundaries should be defined based on customer needs and the alternative means of fulfilling those needs, including substitutes and complementary products.
What are the key components of Cost Curve Analysis?
Key components include Average Total Cost (ATC), Average Fixed Cost (AFC), Average Variable Cost (AVC), and their relationships to production levels.
How can I identify the Breakeven Point?
The Breakeven Point is identified where Marginal Cost (MC) equals the minimum Average Total Cost (ATC), indicating no profit or loss.
What are the limitations of Supply Curve Analysis?
Limitations include the necessity for accurate market definitions and the challenges in acquiring detailed data for supply curve estimation.
How does the Supply Curve impact pricing strategies?
The Supply Curve provides insights into how changes in production capacity can affect market prices and competitive dynamics.
What is the significance of the Shutdown Point?
The Shutdown Point indicates the level of production at which a company is indifferent between continuing operations or temporarily shutting down, as it incurs losses.
How can I apply the 10-Step Approach in my organization?
The 10-Step Approach can be customized to fit your organization’s specific industry and market conditions, providing a structured method for analyzing supply dynamics.
Glossary
• Industry Supply Curve - A graphical representation of the relationship between price and quantity supplied in a market.
• Cost Curve - A graphical representation illustrating the relationship between production costs and output levels.
• Average Total Cost (ATC) - The total cost of production divided by the quantity produced.
• Average Fixed Cost (AFC) - The fixed costs divided by the quantity produced.
• Average Variable Cost (AVC) - The variable costs divided by the quantity produced.
• Breakeven Point - The production level at which total revenues equal total costs, resulting in no profit or loss.
• Shutdown Point - The production level at which a firm is indifferent between continuing operations and shutting down temporarily due to losses.
• Marginal Cost (MC) - The cost of producing one additional unit of a good or service.
• Economies of Scale - The cost advantages that a business obtains due to the scale of operation, with cost per unit of output generally decreasing with increasing scale.
• Diseconomies of Scale - The phenomenon where the cost per unit increases as production scales up, often due to inefficiencies.
• Competitive Pricing Dynamics - The interactions between firms in a market that influence pricing strategies and market behavior.
• Scenario Analysis - A process of analyzing possible future events by considering alternative possible outcomes (scenarios).
• Market Demand - The total quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices.
• Production Capacity - The maximum output that a company can produce in a given period under normal conditions.
• Fixed Costs - Costs that do not change with the level of goods or services produced.
• Variable Costs - Costs that vary directly with the level of production.
• Cost Structure - The types and relative proportions of fixed and variable costs that a business incurs.
• Activity Based Costing (ABC) - A costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each.
• Market Structure - The organizational and other characteristics of a market that influence the nature of competition and pricing.
• Competitive Rivalry - The intensity of competition among existing firms in a market.
• Substitute Products - Products that can be used in place of each other.
• Complementary Products - Products that are used together, where the demand for one increases the demand for the other.
Source: Best Practices in Supply Chain Analysis, Cost Optimization PowerPoint Slides: Industry Supply Curve Analysis PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting