Business Plan Fundamentals (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 34 Slides
BUSINESS PLAN WRITING PPT DESCRIPTION
Why is a Business Plan Important?
• It forces management to think through the proposed business in detail and to consider tradeoffs
• It enables management to plan company growth and to anticipate changes in a structured way
• It allows goals to be set, against which the project's and participants' future performance can be measured
• It states what the venture will not accomplish
• It enables quick and objective decision making
• It is a persuasive argument for investment funds
• It commits the management team to a common set of goals, and contains a blueprint for achieving those goals
• It becomes a vehicle for communication
This document delves into the critical elements of a business plan, offering a comprehensive guide to crafting a robust strategy. It covers everything from market analysis to financial metrics, ensuring you leave no stone unturned. The detailed market analysis section helps you evaluate market size, demand, growth, and industry competition, providing a solid foundation for strategic decisions.
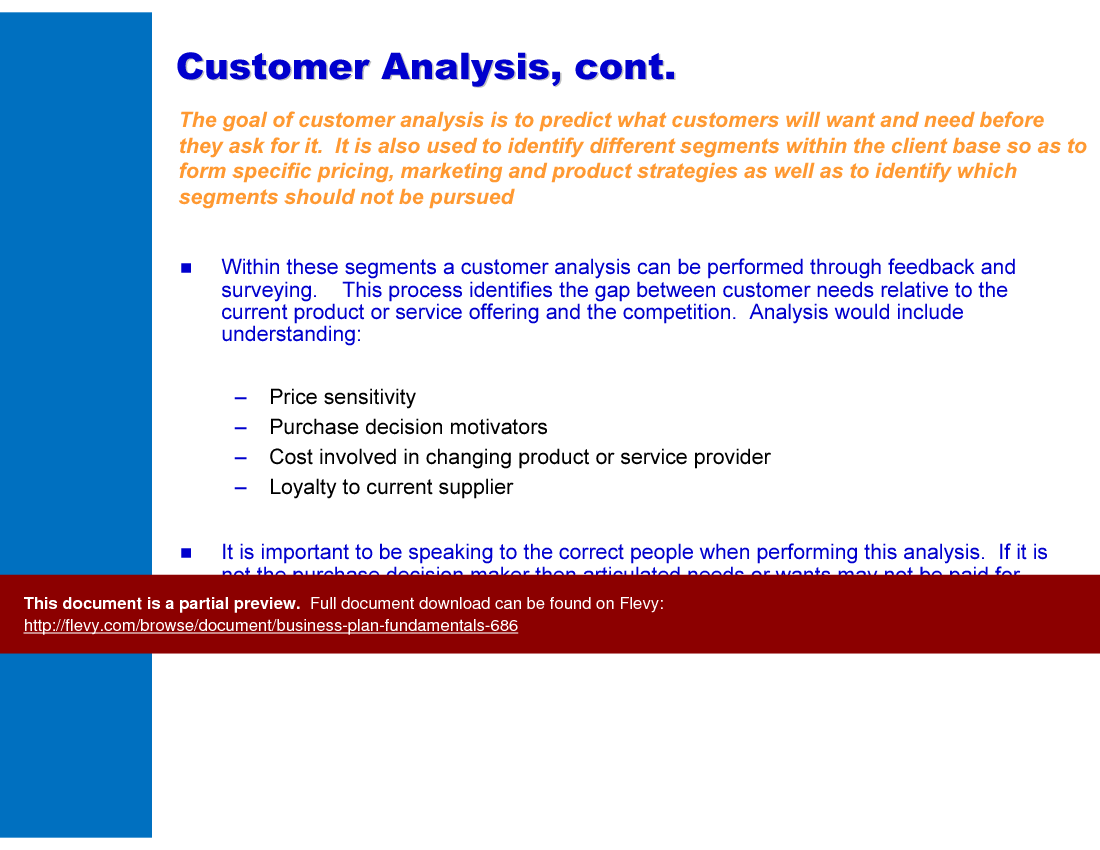
The customer analysis segment emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs and behaviors. It guides you through the process of segmenting your client base and identifying key motivators, ensuring your offerings align with market demands. This section is vital for developing targeted marketing and product strategies, setting you up for success.
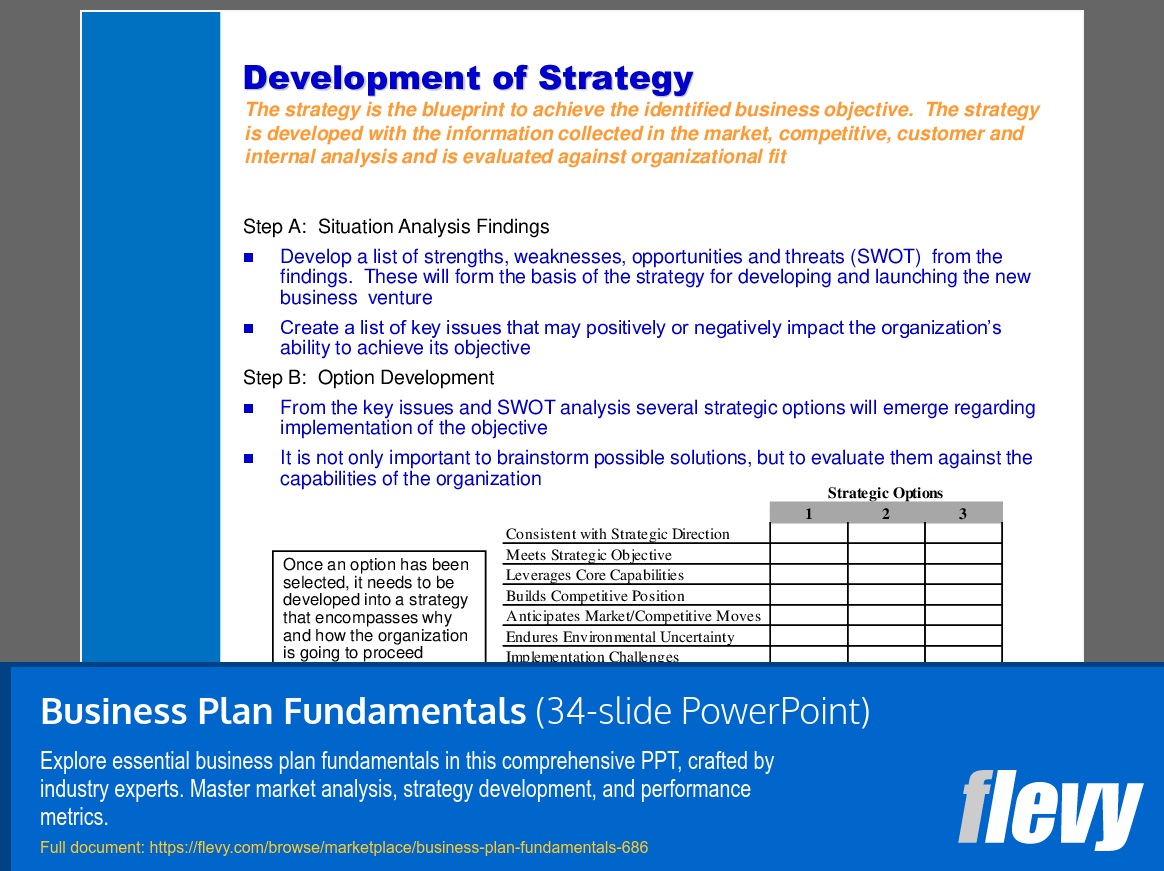
The strategy development section is a blueprint for achieving your business objectives. It includes a thorough situation analysis, SWOT analysis, and strategic option development. This part ensures that you can identify and leverage your strengths while mitigating risks. The document also covers distribution strategies, helping you choose the right channels to reach your customers effectively.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 34-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Business Plan Fundamentals presentation offers a structured approach to developing a comprehensive business plan, designed with the rigor and clarity expected from a McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality document (consulting-grade; not affiliated). This presentation guides corporate executives and managers through the critical elements of a business plan, including objective setting, situation analysis, strategy development, and financial projections. By utilizing this framework, users will be equipped to articulate their business ventures effectively, anticipate challenges, and secure necessary investments, ensuring that their plans are actionable and aligned with organizational goals.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to launch new business ventures
• Project managers responsible for strategic planning and execution
• Business analysts conducting market and competitive assessments
• Investors evaluating potential funding opportunities
• Internal teams needing a structured approach to business planning
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During the initial stages of developing a new business venture
• When preparing for investor presentations or stakeholder meetings
• In strategic planning sessions to align team objectives
• For training sessions on effective business plan development
Learning Objectives
• Define the essential components of a business plan and their significance
• Articulate the objectives and trade-offs of a proposed business venture
• Conduct a thorough situation analysis, including market, competitive, and internal assessments
• Develop actionable strategies for product, marketing, and distribution
• Create financial projections, including break-even analysis, NPV, and IRR
• Formulate a detailed action plan with milestones and resource requirements
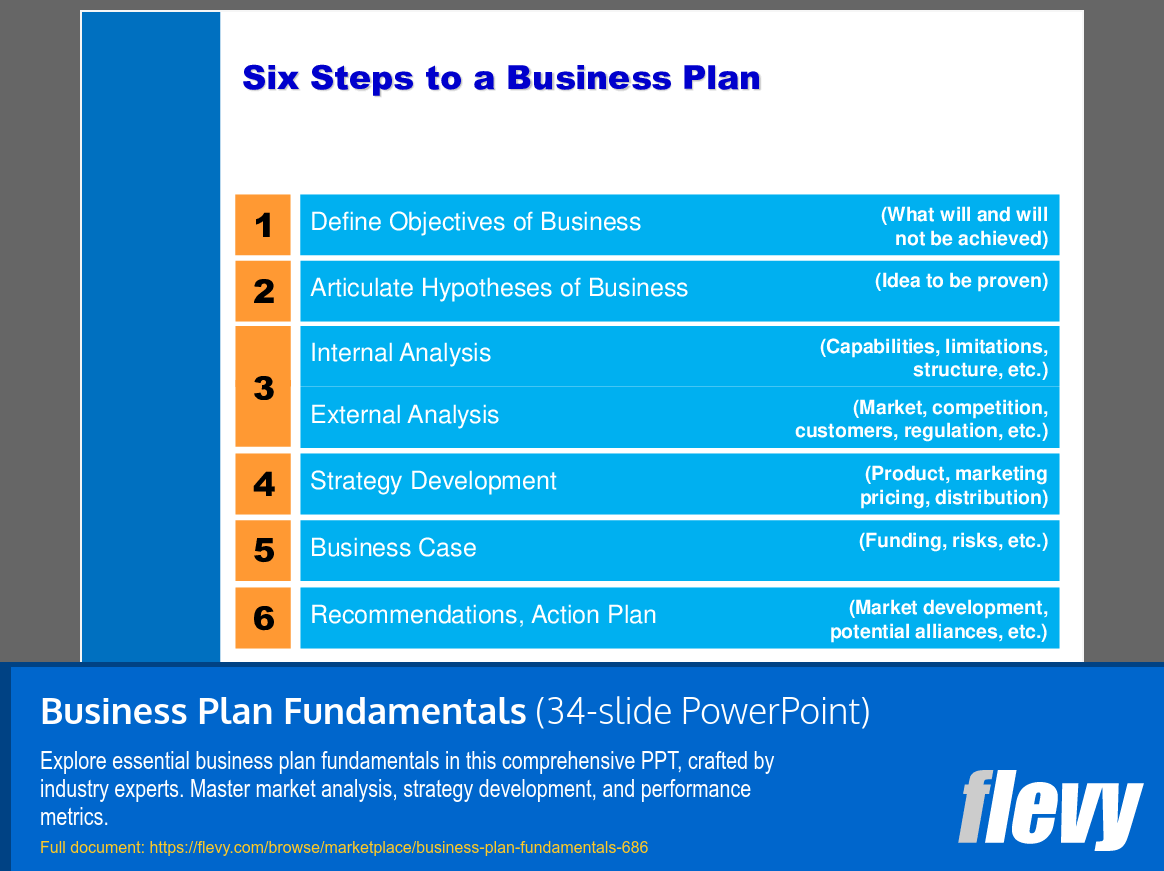
Table of Contents
• Introduction (page 3)
• Critical Elements of the Business Plan (page 5)
• Objective (page 6)
• Situation Analysis (page 7)
• Strategy Development (page 10)
• Business Case (page 12)
• Action Plan (page 15)
• Executive Summary (page 18)
Primary Topics Covered
• Business Plan Definition - A business plan is a rigorous examination of a proposed venture, detailing products, marketplace strategies, and financial impacts.
• Importance of Business Plans - Business plans facilitate detailed management planning, goal setting, and investment persuasion.
• Common Pitfalls - Identifies frequent mistakes in corporate ventures, such as underestimating costs and misjudging market demand.
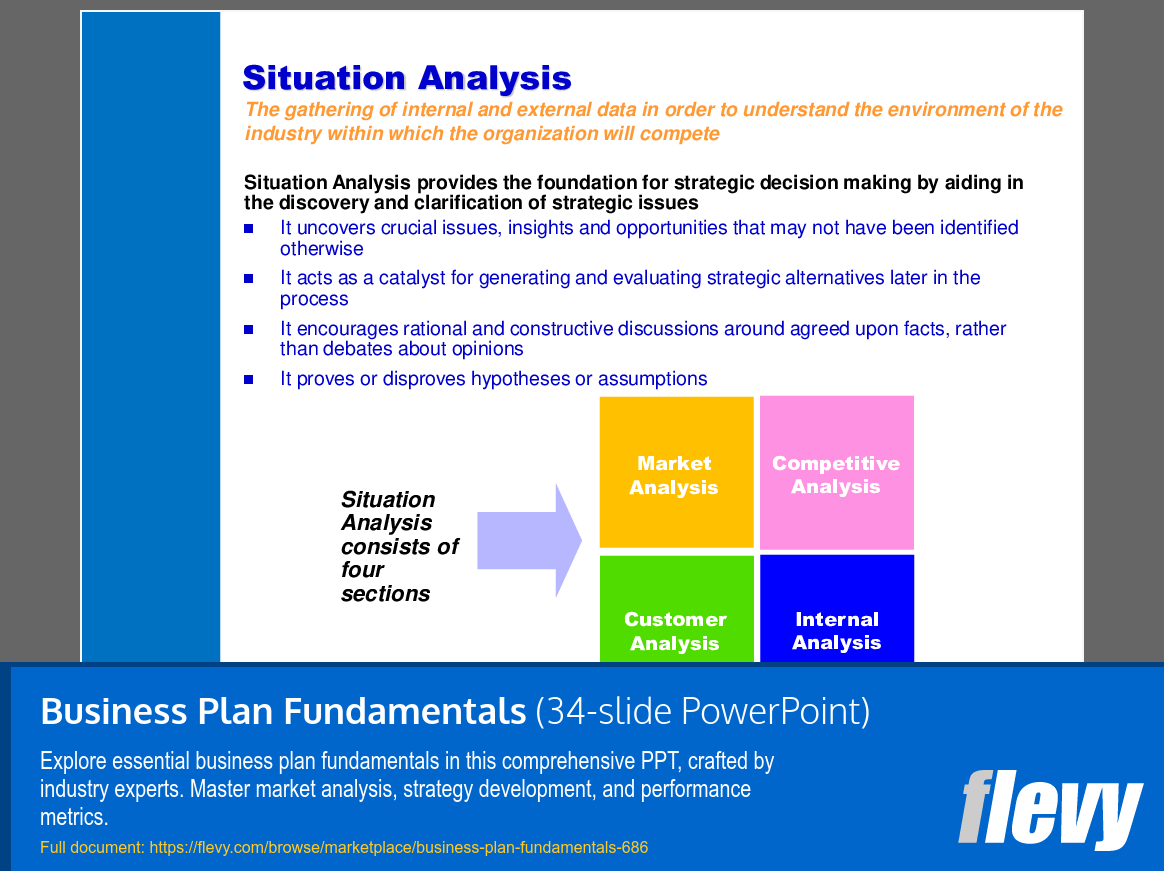
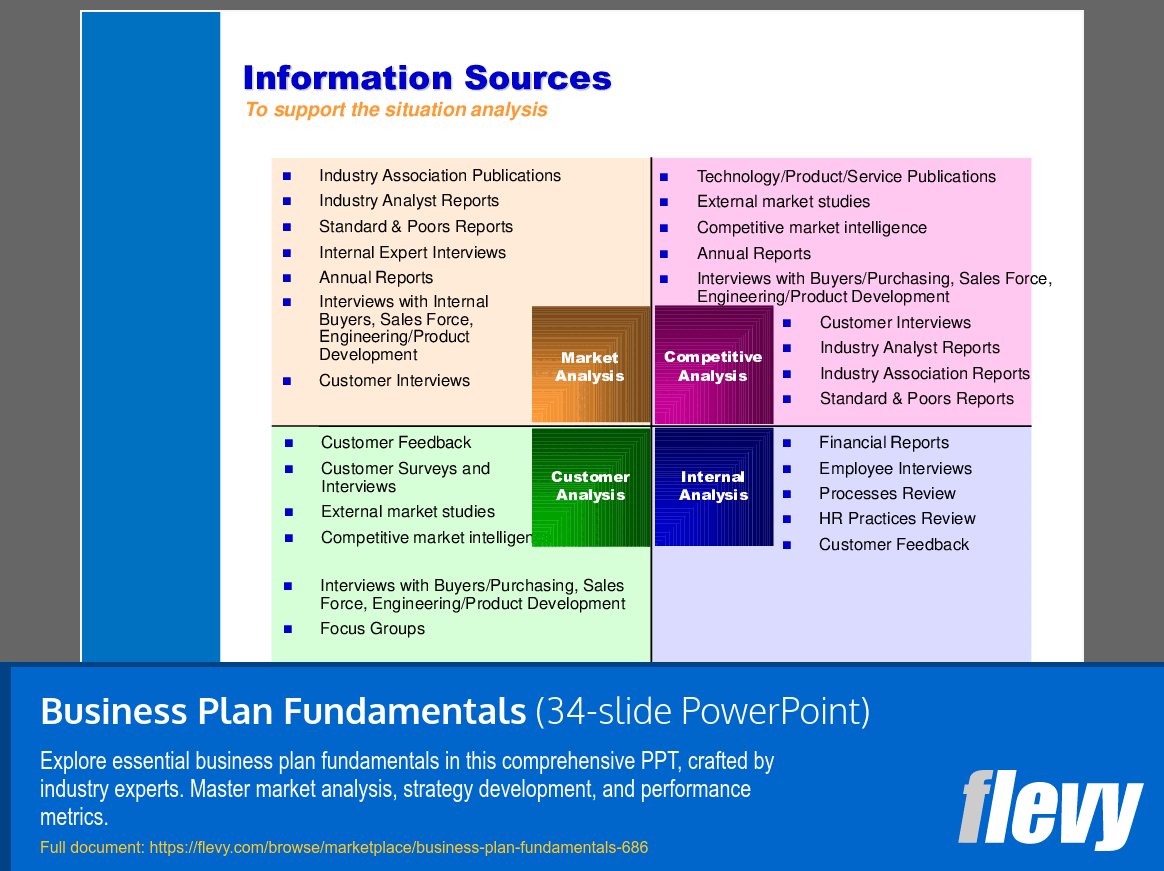
• Situation Analysis - A comprehensive assessment of internal and external factors that influence business viability.
• SWOT Analysis - A tool for evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to inform strategic decisions.
• Financial Metrics - Key financial evaluations such as break-even analysis, NPV, and IRR to assess project viability.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Business plan template for structured development
• Situation analysis framework for market and competitive assessment
• SWOT analysis tool for strategic planning
• Financial projection models including break-even and NPV calculations
• Action plan template with GANTT chart integration for task management
• Executive summary outline for concise proposal presentation
Slide Highlights
• Overview of business plan components emphasizing their interconnections
• Visual representation of the situation analysis process, including market and competitive factors
• Detailed breakdown of financial metrics and their significance in decision-making
• Examples of common pitfalls in business planning and strategies to avoid them
• Action plan framework showcasing milestones and resource allocation
Potential Workshop Agenda
Business Plan Development Workshop (2 hours)
• Introduction to business plan fundamentals and objectives
• Group activity: Conducting a situation analysis using provided templates
• Discussion on common pitfalls and strategies for success
Financial Projections Deep Dive (1 hour)
• Overview of financial metrics: break-even, NPV, and IRR
• Hands-on exercise: Creating financial projections for a sample business plan
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the business plan template to reflect specific organizational goals and market conditions
• Adjust financial assumptions based on current economic indicators and internal benchmarks
• Modify the action plan to align with resource availability and project timelines
• Incorporate company-specific terminology and strategic objectives throughout the presentation
Secondary Topics Covered
• Market demand analysis and growth forecasting
• Competitive landscape evaluation and positioning strategies
• Customer segmentation and targeted marketing approaches
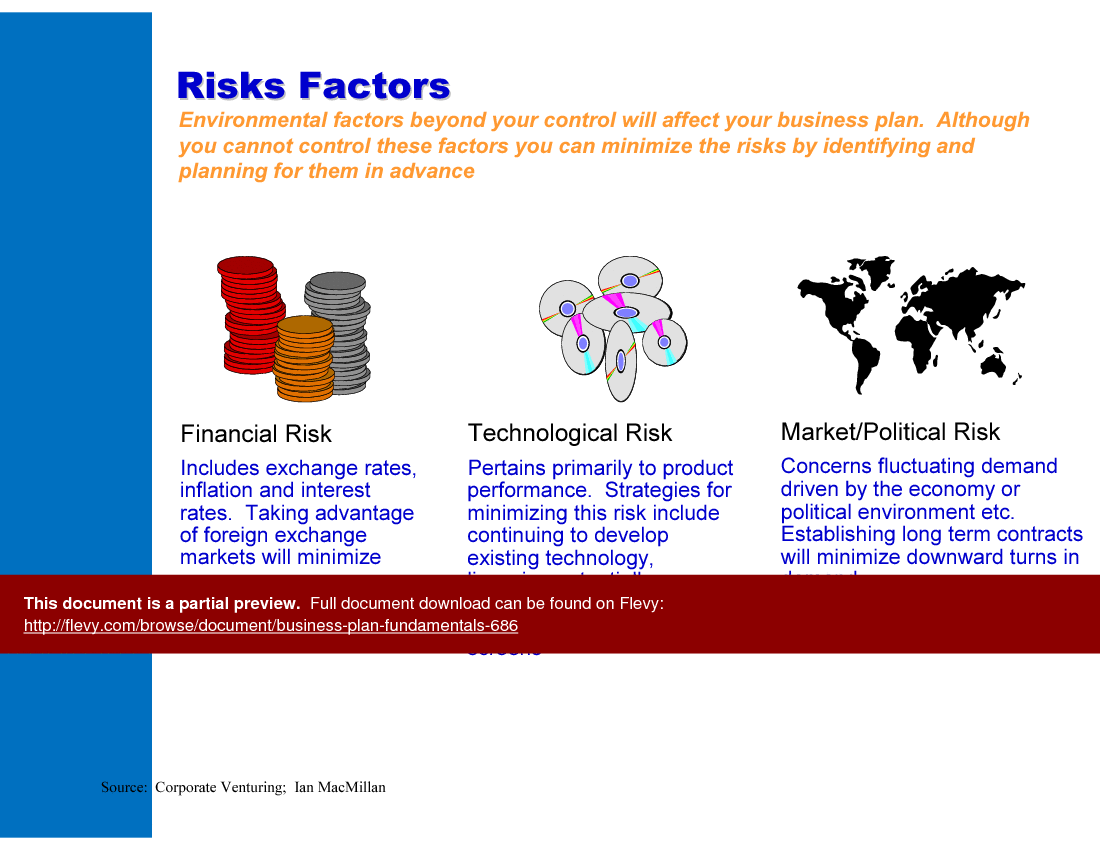
• Risk assessment and mitigation strategies
• Funding sources and financial planning
Topic FAQ
What are the typical sections to include when developing a business plan?
A well-structured business plan typically moves from introduction to defining critical elements and objectives, then through situation analysis and strategy development, into a business case and action plan, and concludes with an executive summary. The Business Plan Fundamentals organizes content across these core sections, including an Action Plan and Executive Summary.How should I structure a situation analysis for a new product or venture?
Structure a situation analysis to assess internal capabilities and external market factors: market size and demand, competitive landscape, and internal strengths/weaknesses. The Business Plan Fundamentals provides a situation analysis framework tailored for market and competitive assessment to support strategic decisions.When is a SWOT analysis most useful in business planning and how is it applied?
Use a SWOT analysis during strategy development to identify internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats, then translate findings into strategic options and risk mitigations. The presentation includes a SWOT analysis tool to inform strategic decision-making.What should I look for in a business-plan PowerPoint template if I have limited time?
Prioritize templates that include clear section headings, an executive summary outline, a situation analysis framework, ready-made financial projection models (break-even, NPV, IRR), and an action plan with GANTT chart integration. Flevy's Business Plan Fundamentals lists these specific deliverables for quick assembly.How can I assess whether buying a business-plan template is worth the cost?
Compare whether the template supplies the specific tools you need—business plan template, situation analysis framework, SWOT tool, financial projection models, and an action plan/GANTT—against your budget and expected time savings. Evaluate value by the included financial models such as break-even and NPV calculations.Which financial metrics are essential to include when preparing an investor pitch?
Investors typically expect financial viability metrics like break-even analysis, net present value (NPV), and internal rate of return (IRR), along with a clear business case and assumptions. Flevy's Business Plan Fundamentals includes templates and examples for break-even, NPV, and IRR.How can a small internal team use a business plan template to align stakeholders?
Use the template to define objectives and trade-offs, perform a situation analysis, craft a concise executive summary for stakeholders, and develop an action plan with milestones and resource requirements, using GANTT chart integration to show timelines and responsibilities.What common pitfalls should I avoid when writing a business plan for a corporate venture?
Avoid underestimating costs, misjudging market demand or customer willingness to pay, and failing to clearly define objectives and trade-offs. Address these by conducting thorough market analysis, financial projections, and a situation analysis to surface risks and assumptions.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the primary purpose of a business plan?
A business plan serves as a comprehensive document that outlines the strategy, objectives, and financial projections for a proposed business venture, facilitating informed decision-making and investment opportunities.
How can a situation analysis improve my business plan?
A situation analysis provides critical insights into market conditions, competitive dynamics, and internal capabilities, enabling more informed strategic decisions and reducing the risk of oversight.
What are common pitfalls to avoid when creating a business plan?
Common pitfalls include failing to understand customer willingness to pay, underestimating costs, and not clearly defining objectives and trade-offs, which can derail project success.
How do I conduct a SWOT analysis?
A SWOT analysis involves identifying and evaluating the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to your business venture, providing a framework for strategic planning.
What financial metrics should I include in my business plan?
Key financial metrics include break-even analysis, net present value (NPV), and internal rate of return (IRR), which help assess the viability and profitability of the venture.
How do I ensure my business plan is persuasive to investors?
Focus on clear, concise arguments that demonstrate the business’s potential for profitability, strategic fit, and the management team's capabilities, supported by solid financial projections.
What is the significance of the executive summary?
The executive summary is a concise overview of the business plan, designed to engage stakeholders and encourage them to explore the full details of the proposal.
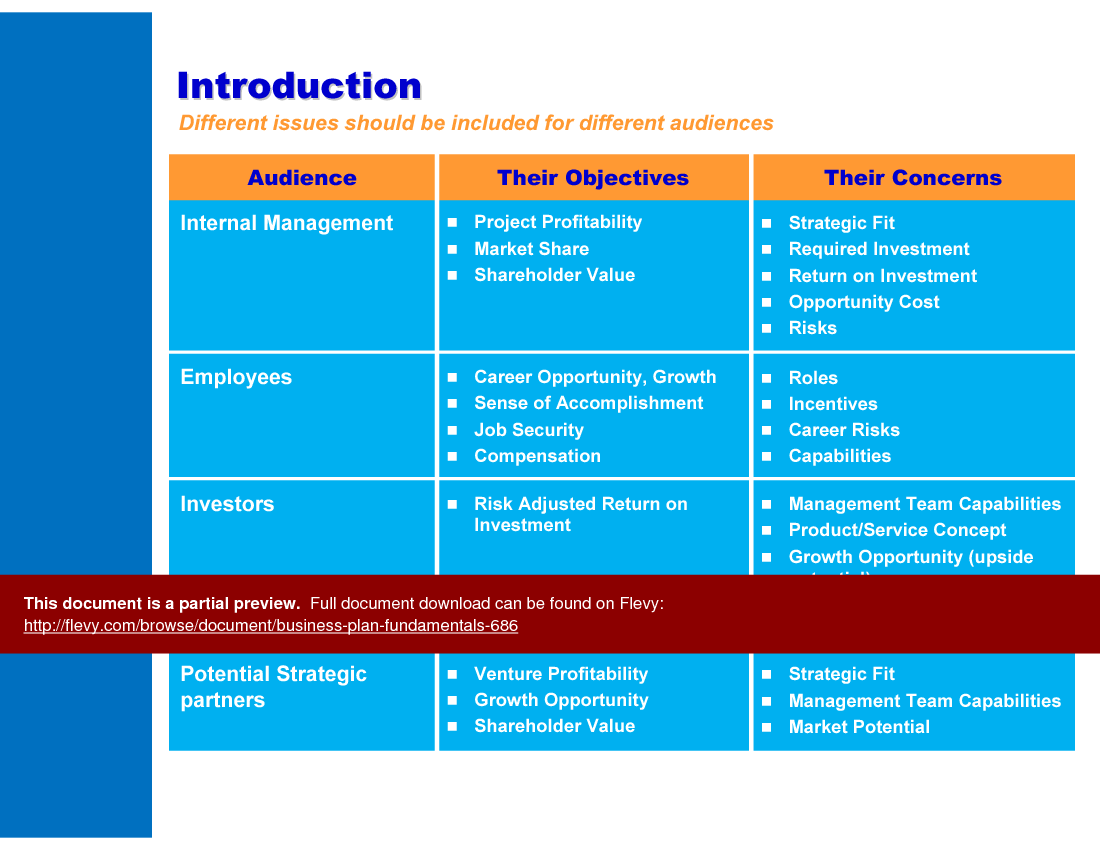
How can I tailor my business plan for different audiences?
Customize the content to address the specific objectives and concerns of each audience, such as internal management, employees, investors, and strategic partners.
What resources are needed for effective implementation of the business plan?
Identify necessary resources including personnel, technology, financial investments, and materials, and outline their acquisition timelines in the action plan.
Glossary
• Business Plan - A formal document detailing the strategy, objectives, and financial forecasts for a business venture.
• SWOT Analysis - A strategic planning tool used to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
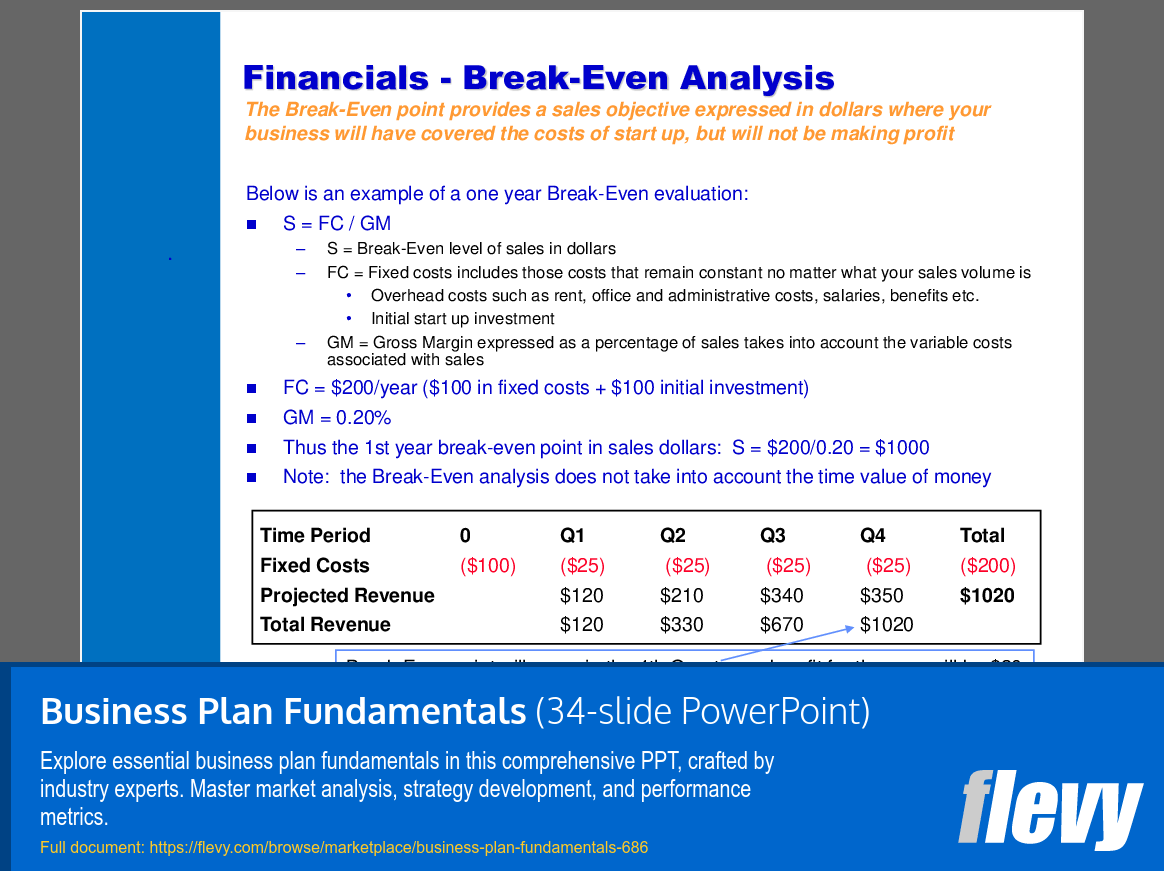
• Break-Even Analysis - A financial assessment to determine the sales volume at which total revenues equal total costs.
• Net Present Value (NPV) - A financial metric that calculates the present value of future cash flows minus the initial investment.
• Internal Rate of Return (IRR) - The discount rate at which the NPV of a project equals zero, indicating the project's profitability.
• Situation Analysis - A comprehensive evaluation of internal and external factors affecting a business venture.
• Action Plan - A detailed outline of steps, responsibilities, and timelines for implementing the business strategy.
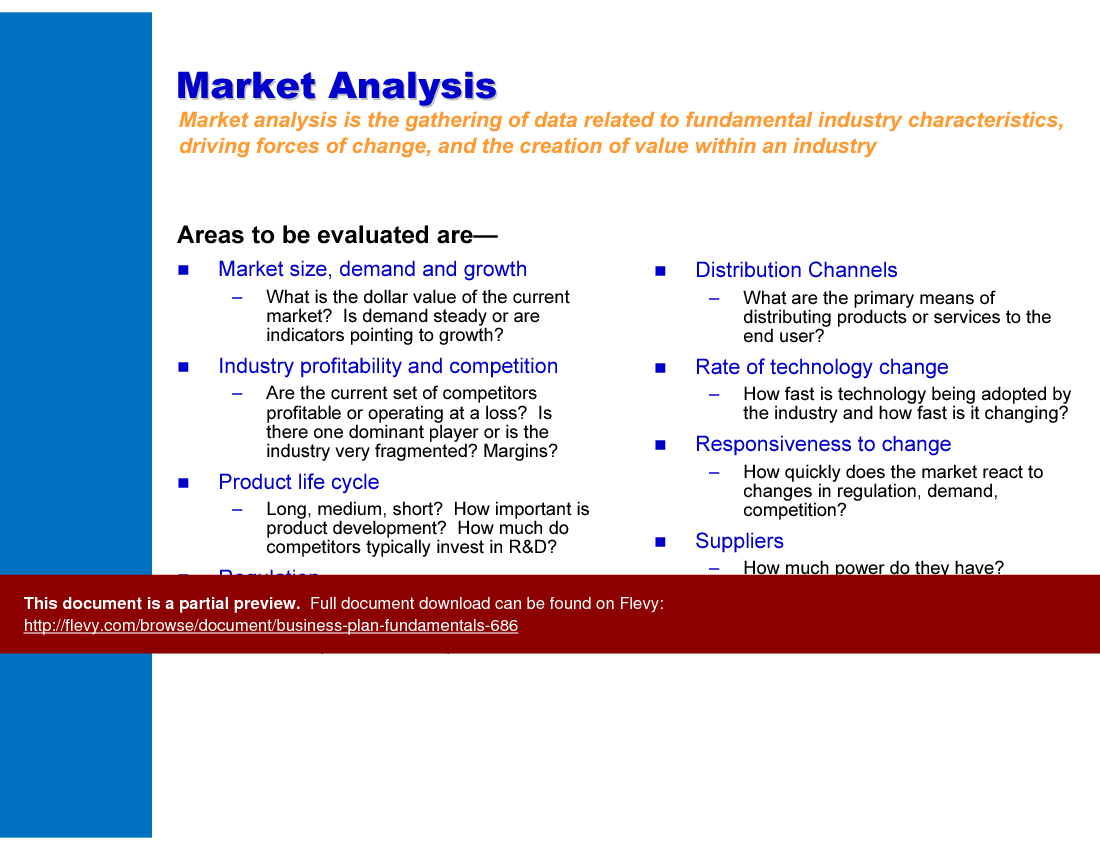
• Market Analysis - The study of market size, demand, competition, and trends to inform business decisions.
• Customer Segmentation - The process of dividing a customer base into distinct groups based on characteristics and needs.
• Financial Projections - Estimates of future revenues, expenses, and profitability based on historical data and market analysis.
• Stakeholders - Individuals or groups with an interest in the success of a business venture, including employees, investors, and partners.
• Competitive Analysis - An assessment of competitors to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and strategies.
• Funding Sources - Various means by which a business can secure financial resources for its operations and growth.
• Opportunity Cost - The potential benefits lost when choosing one alternative over another.
• Market Demand - The total quantity of a product or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various prices.
• Regulatory Factors - Legal and governmental influences that affect business operations and market entry.
• Value Proposition - The unique value a product or service offers to customers, distinguishing it from competitors.
• Trade-Offs - The compromises made when selecting one option over another in business planning.
• Milestones - Key achievements or points of progress that indicate the advancement of a project.
• GANTT Chart - A visual project management tool that outlines tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities.
• Market Share - The portion of a market controlled by a particular company or product.
• Investment Hurdle Rate - The minimum acceptable return on an investment required by an investor or company.
• Customer Feedback - Information provided by customers about their experiences and satisfaction with a product or service.
BUSINESS PLAN WRITING PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Business Plan Writing PowerPoint Slides: Business Plan Fundamentals PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Documents & Files