Analogical Strategic Reasoning (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 38 Slides
PROBLEM SOLVING PPT DESCRIPTION
Strategy is about choice. Oftentimes, executives use analogies to make strategic choices, known as Analogical Strategic Reasoning. Using this technique plays a role in strategic decision making that is large, but largely overlooked. Strategists who pay attention to their own analogical thinking will make better strategic decisions and fewer mistakes.
Analogical Strategic Reasoning is described in the HBR article "How Strategists Really Think," authored by Giovanni Gavetti and Jan Rivkin. Much of this document is based on the thinking proposed by these authors. Analogical Strategic Reasoning is often used by strategists for the following purposes:
• The amount of information available in many strategic situations is similar to the information required to draw analogies.
• The wealth of managerial experience matches the need for that experience in analogical reasoning.
• The need for creative strategies can be fulfilled through analogy's ability to spark creativity.
Successful strategy consultants and firms are known for their ability to draw lessons from one industry and apply them to another—i.e. apply Analogical Strategic Reasoning.
This document discusses the merits and methodology to Analogical Strategic Reasoning, including its strengths, common pitfalls, and other problem solving methods: Deduction and Trial and Error. This document also contains case examples and PowerPoint templates to be used in your own analyses and presentations.
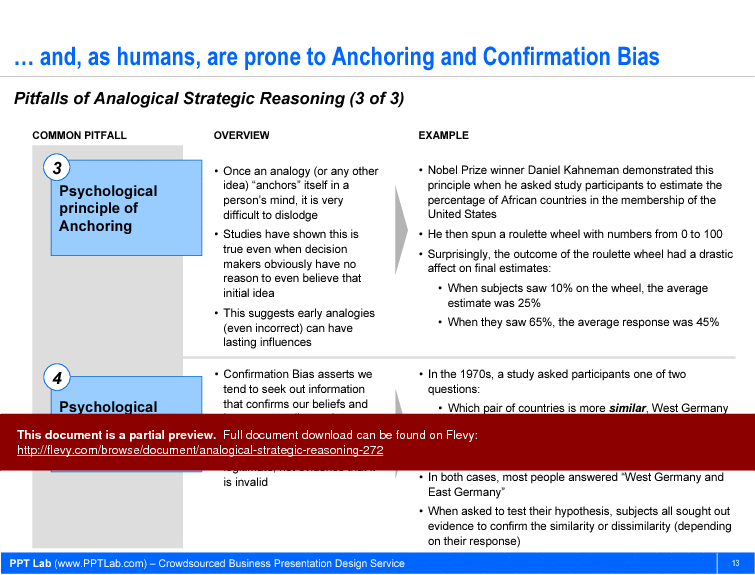
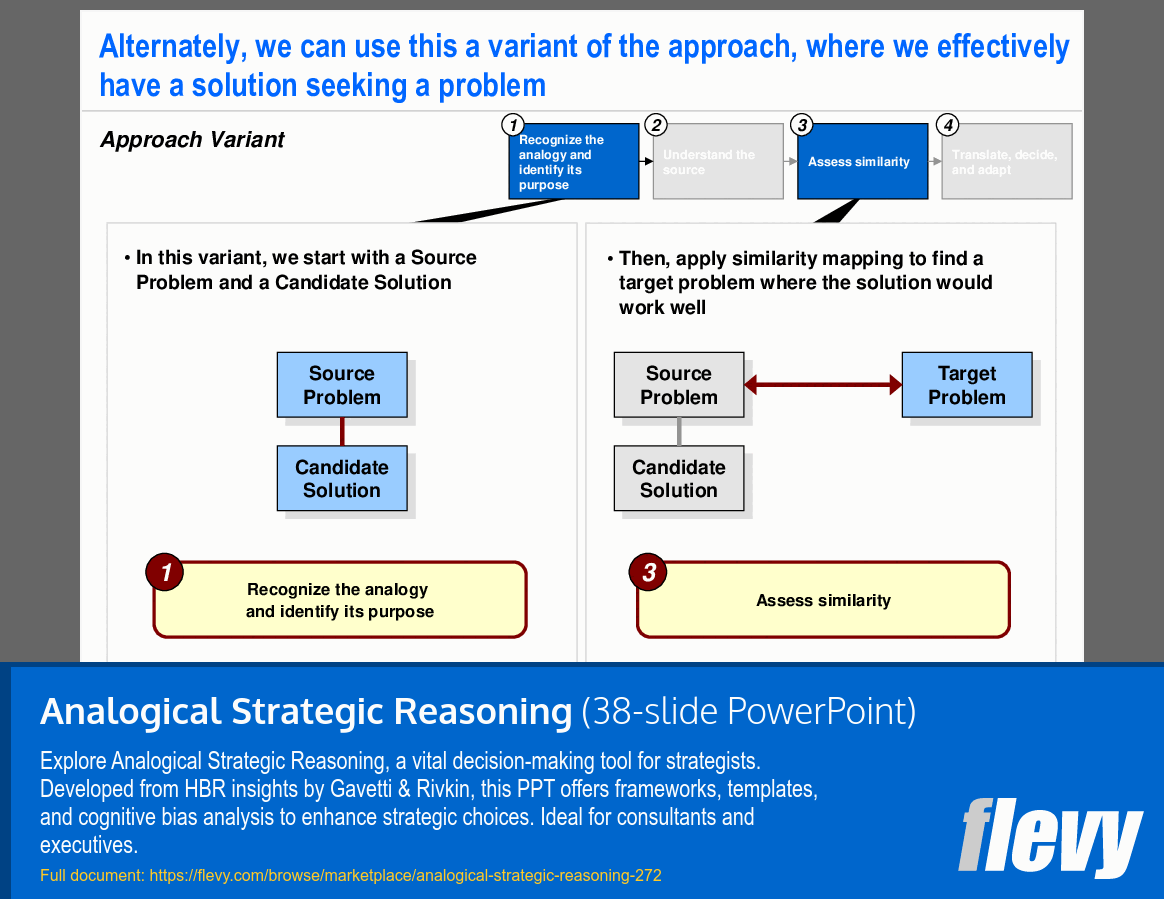
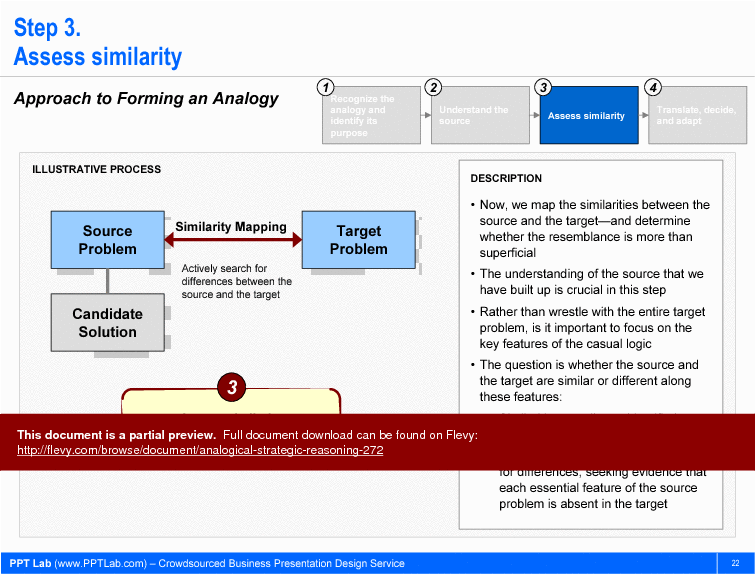
This document also delves into the psychological principles that can impact analogical reasoning, such as anchoring and confirmation bias. It highlights how these cognitive biases can skew strategic decisions if not properly managed. The four-step approach to forming an analogy—recognizing the analogy, understanding the source, assessing similarity, and translating the analogy into action—is meticulously detailed. Templates included in the document facilitate the practical application of these concepts in real-world scenarios, making it an indispensable tool for strategy consultants and executives aiming to leverage analogical reasoning effectively.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 38-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Analogical Strategic Reasoning PPT is a decision-making tool designed for strategists, rooted in insights from the Harvard Business Review article "How Strategists Really Think" by Giovanni Gavetti and Jan Rivkin. This McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality presentation (consulting-grade; not affiliated) elucidates how executives leverage analogies to enhance strategic choices. By adopting this methodology, strategists can improve decision-making processes, minimize errors, and foster creativity in strategy formulation. The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Analogical Strategic Reasoning methodology, including its strengths, pitfalls, and practical applications through case examples and PowerPoint templates.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate strategists and decision-makers seeking innovative approaches to problem-solving
• Management consultants aiming to enhance client presentations with strategic frameworks
• Business leaders tasked with navigating complex market environments
• Teams involved in strategic planning and execution across various industries
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to explore creative solutions
• When analyzing competitive landscapes and drawing lessons from other industries
• In workshops focused on enhancing decision-making frameworks and methodologies
• For presentations aimed at stakeholders to communicate strategic insights effectively
Learning Objectives
• Define Analogical Strategic Reasoning and its relevance in strategic decision-making
• Build a framework for identifying and applying analogies in business contexts
• Establish methods to assess the validity of analogies and avoid common pitfalls
• Create case examples that illustrate successful applications of Analogical Strategic Reasoning
• Develop PowerPoint presentations that effectively communicate strategic insights and frameworks
• Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of different strategic reasoning approaches
Table of Contents
• Overview (page 4)
• Strengths and Pitfalls (page 9)
• Deduction vs. Trial and Error (page 14)
• Approach to Forming an Analogy (page 18)
• Case Example (page 25)
• PowerPoint Templates (page 30)
Primary Topics Covered
• Overview of Analogical Strategic Reasoning - An introduction to the methodology and its significance in strategic decision-making.
• Strengths of Analogical Strategic Reasoning - Highlights the advantages of using analogies in strategy, including creativity and leveraging managerial experience.
• Pitfalls of Analogical Strategic Reasoning - Discusses common errors in analogical reasoning, such as superficial similarities and cognitive biases.
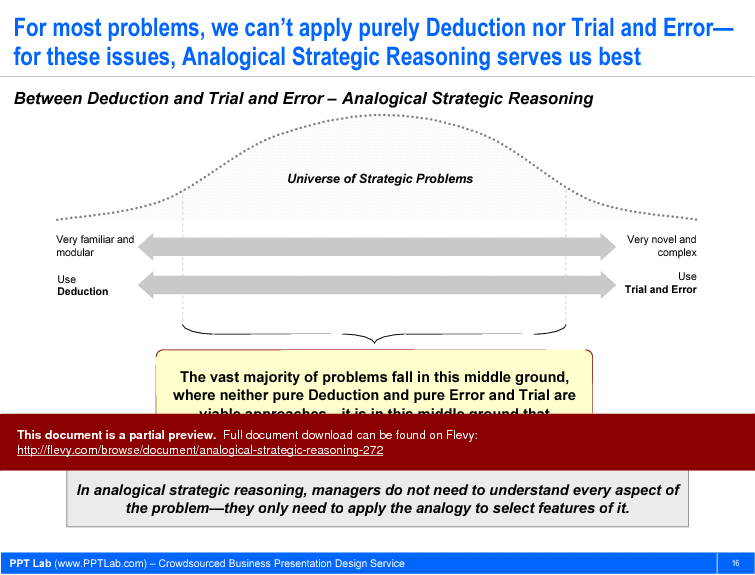
• Deduction vs. Trial and Error - Compares these traditional approaches to Analogical Strategic Reasoning, emphasizing their respective contexts of effectiveness.
• Approach to Forming an Analogy - Outlines a structured four-step process for recognizing and applying analogies in strategic contexts.
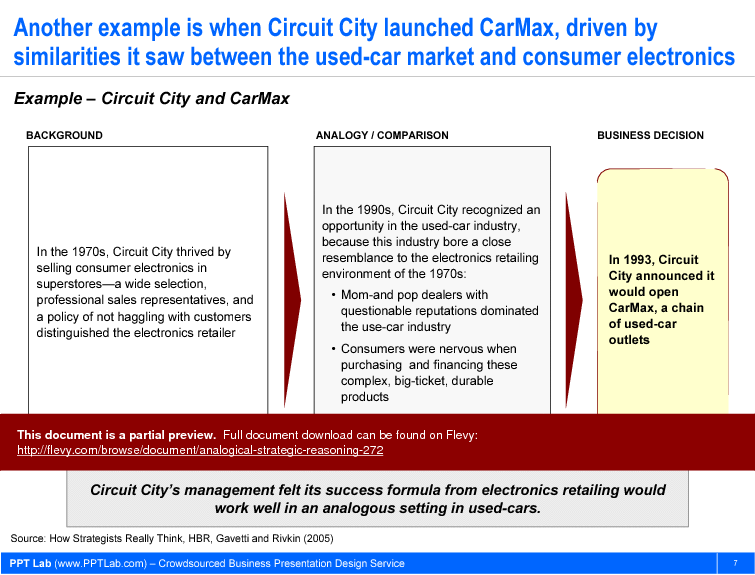
• Case Examples - Real-world applications of Analogical Strategic Reasoning, including Intel and Circuit City’s strategic decisions.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• PowerPoint templates for presenting Analogical Strategic Reasoning frameworks
• Case study examples to illustrate the application of analogies in strategy
• Structured worksheets for assessing the validity of analogies
• Frameworks for identifying and adapting analogies in various business contexts
• Guidelines for avoiding common pitfalls in analogical reasoning
• Visual aids to enhance presentations and facilitate understanding of complex concepts
Slide Highlights
• Overview slide introducing Analogical Strategic Reasoning and its importance
• Strengths and pitfalls slide detailing the advantages and common errors in analogical reasoning
• Comparison slide between deduction and trial and error approaches
• Four-step approach slide for forming analogies in strategic contexts
• Case study slides showcasing successful applications of analogical reasoning
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Analogical Strategic Reasoning (30 minutes)
• Overview of the methodology and its significance
• Discussion of strengths and pitfalls
Practical Application of Analogical Reasoning (60 minutes)
• Group exercise to identify and analyze analogies in strategic scenarios
• Presentation of findings and group discussion
Case Study Analysis (45 minutes)
• Review of case examples
• Group discussion on lessons learned and implications for strategy
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the PowerPoint templates with your company’s branding and specific case examples
• Adjust the case studies to reflect industry-specific challenges and solutions
• Modify the frameworks to align with your organization’s strategic goals and terminology
• Incorporate relevant data and metrics to enhance the presentation's impact
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of cognitive biases in strategic decision-making
• Techniques for fostering creativity in strategy formulation
• The impact of industry comparisons on strategic insights
• Methods for evaluating the effectiveness of strategic decisions
Topic FAQ
What are the main phases of Analogical Strategic Reasoning?
Analogical Strategic Reasoning follows a structured four-step process: recognizing the analogy, understanding the source context, assessing similarity (including key causal features), and translating the analogy into action. This four-step approach is detailed as the core methodology in the deck.How does analogical reasoning compare to deduction and trial-and-error approaches?
The material positions analogical reasoning as most useful when situations are neither fully novel nor fully familiar, filling a gap between deduction and trial and error. The deck includes a dedicated comparison of Deduction vs. Trial and Error on page 14.Which cognitive biases should I watch for when using analogies in strategy?
The content highlights psychological forces that can distort analogical reasoning, specifically anchoring and confirmation bias, and discusses how these biases can skew judgments if not actively managed, with guidance on mitigation techniques.What should I look for when choosing an analogical-reasoning toolkit for my team?
Evaluate whether the toolkit provides a clear methodology for forming analogies, tools to assess validity, case examples to illustrate application, and presentation-ready slides. The presence of structured worksheets and PowerPoint templates are key selection criteria.Are pre-built templates and worksheets worth purchasing for teaching analogical reasoning?
Templates and worksheets can speed workshop preparation and ensure consistent assessment of analogy validity; the product supplies PowerPoint templates, structured worksheets, and case studies to facilitate teaching and application in practice.I need to analyze a competitor from a different industry—how can analogical reasoning help?
Use the four-step process to identify a relevant source analogy, study the source’s causal drivers, assess critical similarities and differences, then translate insights into options. The deck includes case examples such as Intel and Circuit City to illustrate this approach.How can I structure a workshop to help teams avoid common pitfalls in analogical thinking?
Incorporate an overview of strengths and pitfalls, a group exercise to identify and test analogies using structured worksheets, and a case review to reinforce lessons. The product supplies a suggested workshop agenda and worksheets to support these activities.What are reasonable components to include in a 60–90 minute intro to analogical strategic reasoning?
Draw on the deck’s suggested agenda: an overview of the methodology and pitfalls, a short practical exercise to identify analogies, and a brief case discussion. The provided agenda sections include 30-minute overview, 60-minute practical application, and 45-minute case study elements.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is Analogical Strategic Reasoning?
Analogical Strategic Reasoning is a methodology where executives use analogies from one context to inform strategic decisions in another, enhancing creativity and insight.
How can this presentation be customized for my organization?
You can tailor the PowerPoint templates with your branding, adjust case studies to reflect your industry, and modify frameworks to align with your strategic goals.
What are the common pitfalls of using analogies in strategy?
Common pitfalls include relying on superficial similarities, cognitive biases, and failing to recognize important differences between the source and target contexts.
When should I use Analogical Strategic Reasoning?
Use this methodology during strategic planning sessions, competitive analysis, and when seeking innovative solutions to complex problems.
How does Analogical Strategic Reasoning compare to deduction and trial and error?
Analogical Strategic Reasoning is most effective in situations that are neither fully novel nor completely familiar, filling the gap where deduction and trial and error may fall short.
What are the strengths of Analogical Strategic Reasoning?
Strengths include leveraging managerial experience, sparking creativity, and providing a framework for making informed strategic decisions.
Can you provide an example of successful Analogical Strategic Reasoning?
Intel's "digital rebar" analogy is a prime example, where the company recognized the importance of low-end products to maintain its competitive position in the high-end market.
How can I assess the validity of an analogy?
Assess the similarities and differences between the source and target contexts, focusing on key features that influence causal logic.
What tools are included in the presentation?
The presentation includes PowerPoint templates, case study examples, and worksheets for assessing analogies in strategic contexts.
What learning outcomes can I expect from this deck?
Expect to gain a solid understanding of Analogical Strategic Reasoning, practical tools for application, and insights into avoiding common pitfalls.
Glossary
• Analogical Strategic Reasoning - A methodology for making strategic decisions by drawing parallels between different contexts.
• Cognitive Bias - Systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment.
• Deduction - A logical process where general principles are applied to specific cases.
• Trial and Error - A method of problem-solving characterized by repeated attempts until a successful solution is found.
• Case Study - An in-depth analysis of a particular instance or example used to illustrate a concept.
• Framework - A structured approach to analyzing and solving problems.
• Superficial Similarity - A resemblance that is apparent, but lacks deeper relevance.
• Causal Logic - The reasoning that connects causes to effects in a given context.
• Competitive Analysis - The assessment of competitors within a market to inform strategic decisions.
• Management Consultant - A professional who provides expert advice to organizations to improve performance.
• Strategic Decision-Making - The process of making choices that will affect the direction and success of an organization.
• Creativity in Strategy - The ability to generate innovative ideas and solutions in strategic planning.
• Market Feedback - Information gathered from customers and competitors that informs strategic adjustments.
• Industry Comparison - Analyzing similarities and differences between industries to derive insights.
• Business Model - A company's plan for how it will generate revenue and make a profit.
• Stakeholders - Individuals or groups with an interest in the success of a business or project.
• Presentation Framework - A structured outline for creating effective presentations.
• PowerPoint Template - Pre-designed slides that can be customized for presentations.
• Strategic Insight - Understanding gained from analysis that informs decision-making.
• Operational Strategy - The plan for how an organization will execute its business model effectively.
• Management Experience - Knowledge and skills gained from overseeing and directing business operations.
• Market Environment - The external factors that affect a business's operations and strategy.
PROBLEM SOLVING PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Problem Solving PowerPoint Slides: Analogical Strategic Reasoning PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, PPT Lab