Developing an effective problem statement is a critical first step in any strategic initiative. It sets the stage for a clear, focused approach to addressing challenges and leveraging opportunities within an organization. A well-crafted problem statement not only clarifies the issue at hand but also aligns team efforts and guides the decision-making process. In the realm of high-stakes corporate strategy, where ambiguity is the enemy of progress, mastering how to develop a problem statement becomes a pivotal skill for C-level executives.
The essence of a compelling problem statement lies in its ability to succinctly summarize the issue while encapsulating the impact on the organization. It should not merely describe a situation but also highlight the gap between the current state and the desired future state. This requires a deep dive into the specifics of the problem, including quantifiable metrics where possible. For instance, consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of grounding problem statements in data and evidence, arguing that a data-driven approach enhances the credibility and actionability of the strategic planning process.
However, crafting such a statement demands more than just data. It requires a nuanced understanding of the organization's strategic objectives, its operational landscape, and the broader industry context. This is where frameworks and templates come into play. They provide a structured way to dissect and present the problem, ensuring that all relevant dimensions are considered. For example, the use of a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) can help in identifying internal and external factors contributing to the problem, thereby enriching the problem statement.
Moreover, an effective problem statement should be actionable. It must inspire action and guide the direction of solution development. This means avoiding overly broad or vague statements that can lead to confusion and inefficiency. Instead, the focus should be on specificity and relevance, ensuring that the problem statement directly relates to strategic goals and can be addressed through concrete steps. This actionable focus is a hallmark of successful strategy development, as it translates complex challenges into manageable tasks.
Key Components of a Problem Statement
Developing a problem statement that meets these criteria involves several key components:
- Clarity: The statement should be clear and free from jargon, making it accessible to all stakeholders involved.
- Conciseness: Brevity is crucial. A concise statement ensures that the focus remains on the core issue.
- Specificity: The problem should be defined as specifically as possible, including who is affected, what the impact is, and where and when it occurs.
- Objectivity: The statement should be based on verifiable data and evidence rather than assumptions or speculation.
- Goal-oriented: It should imply a direction for solution development, indicating what success would look like.
These components serve as a template for executives to systematically approach problem definition. By adhering to these principles, leaders can ensure that their problem statements are not only clear and specific but also aligned with organizational goals and capable of driving effective action.
Real-World Application
In practice, the development of a problem statement often begins with a thorough analysis of the situation. This might involve gathering input from various stakeholders, conducting market research, and analyzing internal performance metrics. For instance, a decline in market share might prompt an organization to investigate underlying causes, such as changes in consumer preferences or increased competition. Through this investigative process, a specific problem statement can be formulated, such as "Over the last two years, our organization's market share has declined by 10% due to an inability to adapt to rapidly changing consumer preferences and a lack of innovation in product offerings."
This statement clearly articulates the problem, its impact on the organization, and hints at areas for potential improvement. It also sets the stage for strategic planning and solution development, focusing efforts on innovation and market adaptation. The specificity and clarity of the statement enable teams to rally around a common goal, fostering a sense of purpose and direction.
Ultimately, the ability to develop an effective problem statement is a critical competency for leaders in today's fast-paced business environment. It requires a blend of analytical rigor, strategic insight, and a keen understanding of organizational dynamics. By mastering this skill, executives can ensure that their organizations are well-positioned to tackle challenges head-on, driving performance and achieving strategic objectives.
Strategic Planning is a critical process for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today's business environment. Incorporating stakeholder feedback into this process is not just beneficial; it's essential for ensuring the plan's relevance, effectiveness, and sustainability. Stakeholders, including customers, employees, and partners, offer unique insights that can significantly enhance the Strategic Planning process. Their feedback can lead to more informed decision-making, increased buy-in, and a more agile and responsive strategy. Below, we delve into specific, detailed, and actionable insights on how to better incorporate stakeholder feedback into the Strategic Planning process.
Engaging Stakeholders Early and Often
One of the foundational steps in adapting Strategic Planning processes to incorporate stakeholder feedback is engaging these stakeholders early in the process and maintaining this engagement. Early engagement helps in understanding the expectations and perceptions of stakeholders, which can significantly influence the direction of the strategy. This can be achieved through regular surveys, focus groups, and forums. For example, Deloitte highlights the importance of "continuous engagement" where stakeholders are not only consulted at the initial stages but are involved throughout the strategy development process. This approach ensures that feedback is not a one-off event but a continuous input that shapes the strategy dynamically.
Moreover, leveraging digital platforms can facilitate broader and more efficient stakeholder engagement. Tools such as online surveys, social media, and dedicated collaboration platforms can gather extensive feedback quickly and efficiently. Accenture's research on digital platforms underscores their role in democratizing the feedback process, allowing for a wider range of voices to be heard and considered in the Strategic Planning process.
Additionally, engaging stakeholders often requires a cultural shift within the organization. It necessitates moving away from a top-down approach to a more inclusive model where feedback is not only sought but valued and acted upon. This shift can be challenging but is critical for the successful integration of stakeholder feedback into Strategic Planning. Leadership must champion this cultural change, demonstrating through actions and policies that stakeholder feedback is a cornerstone of the strategy development process.
Utilizing Advanced Analytics and Data Visualization
Another critical aspect of incorporating stakeholder feedback into Strategic Planning is the use of advanced analytics and data visualization techniques. These tools can help organizations analyze large volumes of feedback data to identify trends, patterns, and insights that might not be immediately apparent. For instance, McKinsey & Company emphasizes the role of advanced analytics in turning raw data into strategic insights. By applying machine learning and natural language processing, organizations can sift through feedback from various channels to identify key themes and sentiments.
Data visualization tools further enhance this process by making the insights accessible and understandable to decision-makers. Through interactive dashboards and visualizations, stakeholders' feedback is transformed into actionable intelligence that can guide strategic decisions. Bain & Company's research on data visualization illustrates how these tools can bridge the gap between data and decision-making, ensuring that stakeholder feedback is effectively incorporated into the Strategic Planning process.
However, the successful application of analytics and visualization requires a robust data management strategy. Organizations must ensure that feedback data is collected in a structured manner, maintaining its integrity and relevance. This involves not only the technical aspects of data collection and analysis but also establishing processes for continuously updating and refining the data as new feedback is received.
Creating Feedback Loops and Accountability Mechanisms
To truly integrate stakeholder feedback into Strategic Planning, organizations must establish clear feedback loops and accountability mechanisms. Feedback loops ensure that once feedback is collected and analyzed, it leads to actionable changes in the strategy. This involves setting up processes for regularly reviewing feedback, making strategic adjustments, and communicating these changes back to stakeholders. PwC's insights on feedback loops highlight their role in creating a dynamic Strategic Planning process that evolves in response to stakeholder input.
Accountability mechanisms are equally important. They ensure that there is clear responsibility for acting on stakeholder feedback within the organization. This can be facilitated through the establishment of dedicated roles or teams tasked with integrating feedback into the Strategic Planning process. Additionally, incorporating feedback-related metrics into performance management systems can incentivize and track the effective use of stakeholder input.
Real-world examples of these practices include companies like Starbucks and Lego, which have successfully embedded stakeholder feedback into their Strategic Planning processes. Starbucks uses a combination of digital platforms and in-store feedback mechanisms to gather customer insights, which directly influence their product development and customer experience strategies. Lego, through its Ideas platform, allows customers to submit and vote on ideas for new sets, directly involving them in the product development process.
Incorporating stakeholder feedback into Strategic Planning is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires a tailored approach that considers the unique characteristics of the organization and its stakeholders. However, by engaging stakeholders early and often, utilizing advanced analytics and data visualization, and creating feedback loops and accountability mechanisms, organizations can significantly enhance their Strategic Planning processes. This not only leads to more effective and responsive strategies but also builds stronger relationships with stakeholders, fostering a sense of ownership and commitment to the organization's success.
Leadership plays a pivotal role in the successful execution of Strategic Plans within an organization. This is not just about setting a vision and direction but also involves mobilizing resources, inspiring teams, and driving change to achieve desired outcomes. The effectiveness of leadership can significantly influence an organization's ability to implement strategies effectively and adapt to changing market dynamics. In this context, leadership is not limited to the top echelons of management but spans across all levels where strategic decisions are made and executed.
The Role of Leadership in Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning requires a clear vision, a well-defined mission, and a set of achievable goals. Leaders are responsible for crafting this vision and communicating it throughout the organization to ensure alignment. They must also be adept at making tough decisions, prioritizing initiatives, and allocating resources efficiently to support strategic objectives. Furthermore, leaders play a crucial role in fostering a culture that values strategic thinking, encouraging employees to contribute ideas and take ownership of their roles in the strategy execution process.
According to McKinsey, companies with leaders who are actively involved in the strategic planning process are 33% more likely to achieve significant success compared to those where leadership is less engaged. This statistic underscores the importance of leadership involvement not just at the planning phase but throughout the execution phase as well. Leaders must stay connected with their teams, monitor progress, and be ready to pivot strategies in response to unforeseen challenges or opportunities.
Effective leadership also involves building and nurturing a strong leadership team that can drive the execution of strategic plans at different levels of the organization. This includes developing leadership capabilities, promoting a collaborative environment, and ensuring that leaders across the organization are aligned with the strategic vision and equipped to lead their teams towards achieving strategic objectives.
Leadership and Change Management
Executing strategic plans often requires significant changes in processes, systems, and sometimes, the organizational structure itself. Leaders play a critical role in managing these changes, from planning and implementation to monitoring and controlling. They must communicate the need for change, articulate the benefits, and address any resistance from employees. Leadership is about inspiring and motivating employees to embrace change and contribute positively towards achieving strategic goals.
A study by Prosci, a leading change management research firm, found that projects with effective change management and leadership support were six times more likely to meet or exceed their objectives. This highlights the critical role of leadership in not just managing the technical aspects of change but also addressing the human side of change, which is often the most challenging part.
Leaders must also lead by example, demonstrating adaptability, resilience, and a continuous improvement mindset. This sets the tone for the entire organization and helps build a culture that is agile, innovative, and capable of navigating the complexities of change. By actively engaging with employees, listening to their concerns, and providing the necessary support and resources, leaders can ensure a smoother transition and higher success rates in executing strategic plans.
Leadership, Culture, and Performance Management
The culture of an organization plays a significant role in the execution of strategic plans. Leaders are instrumental in shaping and nurturing a culture that aligns with the organization's strategic goals. This involves promoting values such as innovation, accountability, and excellence. By embodying these values and recognizing and rewarding behaviors that contribute to strategic objectives, leaders can cultivate a culture that supports the successful execution of strategic plans.
Performance Management is another area where leadership is crucial. Leaders need to establish clear performance metrics that are aligned with strategic objectives and ensure that these metrics are communicated and understood at all levels of the organization. According to a report by Bain & Company, organizations that excel in cascading their strategic objectives down to operational metrics and aligning their performance management systems accordingly are 35% more likely to outperform their competitors.
Furthermore, leaders must continuously monitor performance, provide feedback, and make adjustments as necessary. This involves not just tracking the progress of strategic initiatives but also developing the capabilities of the team, addressing performance issues, and leveraging successes to build momentum towards achieving strategic goals. Through effective Performance Management, leaders can ensure that the organization remains focused on its strategic priorities and is equipped to navigate the challenges of execution.
In conclusion, leadership is at the heart of successful strategic plan execution. It requires a combination of strategic vision, change management, culture shaping, and performance management capabilities. Leaders who can inspire their teams, drive change, and foster a culture of excellence and innovation are more likely to lead their organizations to successfully achieve their strategic objectives.
Strategic planning is not merely a task to be checked off the annual corporate agenda. It's a critical, ongoing process that underpins long-term growth and sustainability in an ever-evolving market landscape. The question of "why do we need a plan" resonates more than ever in today's fast-paced, uncertain business environment. A well-crafted strategic plan serves as a roadmap, providing direction and a framework for decision-making, ensuring that an organization remains focused and aligned with its core objectives.
At its core, strategic planning involves setting priorities, focusing energy and resources, strengthening operations, and ensuring employees and other stakeholders are working toward common goals. It establishes a sense of direction and outlines measurable goals. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of strategic planning in navigating complex market dynamics and technological disruptions. A strategic plan, when executed effectively, enables an organization to anticipate future challenges and opportunities, making it better equipped to adapt and thrive.
Moreover, strategic planning is crucial for risk management. It allows organizations to proactively identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies, rather than reacting to unforeseen events. This proactive approach is essential for long-term sustainability, as it helps preserve resources and maintain operational stability. The framework provided by strategic planning also facilitates better performance management, enabling leaders to set clear expectations, monitor progress, and make adjustments as needed to stay on course.
Building a Robust Strategic Framework
A robust strategic framework is the backbone of effective strategic planning. This framework typically includes a clear articulation of the organization's vision, mission, and core values, along with a thorough analysis of its internal and external environments. The use of a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is a common template in this process. Consulting giants such as Deloitte and PwC advocate for a comprehensive approach that integrates market analysis, competitor analysis, and internal capability assessment to inform strategy development.
The strategic framework should also define key performance indicators (KPIs) and set realistic, achievable goals. This quantifiable approach to strategy ensures that progress can be measured and managed effectively. It's not enough to have a plan; the plan must include specific, actionable steps that drive towards the desired outcomes. This detailed roadmap is what separates successful organizations from their less successful counterparts.
Implementing a strategic framework requires disciplined execution and consistent follow-through. Change management is a critical component of this process, as it addresses the human element of strategic transformation. Leadership must be committed to guiding the organization through the necessary changes, fostering a culture of agility and continuous improvement. Real-world examples, such as IBM's strategic pivot to cloud computing and analytics, illustrate the power of a well-executed strategic plan in driving business transformation and long-term success.
Why Strategy Matters More Than Ever
In today's digital age, the pace of change is relentless. Digital transformation, globalization, and shifting consumer preferences are just a few of the factors that demand a strategic approach to management. Organizations that fail to plan are essentially planning to fail. A strategic plan not only helps an organization chart a course for growth but also builds resilience against market volatility and competitive pressures.
Strategy also plays a crucial role in innovation and differentiation. In a crowded marketplace, organizations must continually evolve to stay relevant. Strategic planning fosters an environment where innovation can thrive, by prioritizing investments in new technologies, products, and services. This focus on innovation is what enables organizations like Apple and Amazon to dominate their respective industries.
Finally, strategic planning is fundamental to organizational alignment and culture. It ensures that every department and employee is working towards a common set of goals, creating a unified, cohesive effort. This alignment is critical for achieving operational excellence and delivering superior customer value. When everyone in the organization understands the strategic direction and their role in achieving it, the potential for success is significantly amplified.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the importance of strategic planning cannot be overstated. It is the foundation upon which long-term growth and sustainability are built. By providing a clear direction, enabling risk management, and fostering innovation, a well-conceived strategic plan positions an organization to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape successfully. The question "why do we need a plan" is not just rhetorical—it's a vital consideration for any organization aiming for enduring success. In the end, strategic planning is not just about surviving; it's about thriving in an unpredictable world.
Blockchain technology, initially developed as the underlying system for cryptocurrencies, has evolved far beyond its financial roots. Its implications for industries such as Supply Chain Management and Healthcare are profound, offering opportunities for enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency. Strategic Planning within these sectors must adapt to incorporate blockchain's potential, leveraging its capabilities to drive innovation, reduce costs, and improve service delivery.
Implications for Supply Chain Management
In the realm of Supply Chain Management, blockchain technology promises to revolutionize how organizations track and manage the flow of goods and information. The decentralized nature of blockchain allows for a transparent and immutable ledger of transactions, which can significantly reduce the instances of fraud and errors. This level of transparency enables organizations to more accurately track the movement of goods, from raw materials to the final product, enhancing traceability and accountability throughout the supply chain.
Strategic Planning in Supply Chain Management must now consider how blockchain can be integrated to improve Operational Excellence. For instance, integrating blockchain can streamline operations by reducing reliance on paper-based tracking and manual verification processes, leading to significant cost savings and efficiency gains. A report by Accenture highlights that blockchain's ability to enhance transparency and trust could potentially save the logistics industry billions annually by reducing administrative costs.
Real-world examples of blockchain in Supply Chain Management include Walmart's use of blockchain to track the origin of food products. This initiative not only improves food safety by enabling faster identification and recall of contaminated products but also enhances consumer trust in the brand. Such applications underscore the need for Strategic Planning to embrace blockchain as a tool for achieving competitive advantage and Operational Excellence.
Implications for Healthcare
The Healthcare industry stands to benefit significantly from blockchain technology, particularly in the areas of patient data management and pharmaceuticals traceability. Blockchain's capability to secure and streamline the sharing of medical records can address the longstanding issues of data fragmentation and security in healthcare. By providing a single, immutable record of a patient's medical history, blockchain can facilitate better and more efficient care delivery.
Strategic Planning within Healthcare organizations must now prioritize the integration of blockchain to enhance data security and patient privacy. The ability to securely share patient data among providers can lead to improved treatment outcomes and patient experiences. Furthermore, blockchain can play a crucial role in combating counterfeit drugs, ensuring the integrity of the pharmaceutical supply chain. The use of blockchain for tracking pharmaceuticals can not only save lives by ensuring the authenticity of drugs but also protect the revenue and reputation of pharmaceutical companies.
An example of blockchain's application in healthcare is the partnership between IBM and the FDA to use blockchain technology for secure patient data exchange. This initiative aims to improve public health outcomes by facilitating more efficient and secure access to medical data. Such initiatives highlight the critical role of Strategic Planning in leveraging blockchain to address industry-specific challenges and improve overall healthcare delivery.
Strategic Planning Considerations
As organizations in Supply Chain Management and Healthcare look to incorporate blockchain technology, Strategic Planning must evolve to address several key considerations. Firstly, organizations must assess their readiness for blockchain integration, including the technological infrastructure and the skills of their workforce. This assessment will guide the development of a strategic roadmap for blockchain adoption, identifying key milestones and metrics for success.
Additionally, Strategic Planning must account for the regulatory environment surrounding blockchain. In industries like healthcare, where patient data is subject to stringent regulations, organizations must ensure that their use of blockchain complies with all legal requirements. This includes considerations around data privacy and the cross-border transfer of information.
Finally, organizations must cultivate a culture of innovation and adaptability to maximize the benefits of blockchain. This involves not only investing in the necessary technology and skills but also fostering an organizational mindset that embraces change and innovation. Strategic Planning plays a crucial role in this process, guiding the organization through the complexities of blockchain adoption and ensuring that its potential is fully realized.
In conclusion, the implications of blockchain technology for Strategic Planning in industries beyond finance are significant. By offering enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency, blockchain presents opportunities for Supply Chain Management and Healthcare to innovate and improve their operations. Strategic Planning must adapt to these technological advancements, ensuring that organizations are well-positioned to leverage blockchain's potential for competitive advantage.
Organizations across various industries are increasingly leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to identify and evaluate strategic opportunities. These technologies offer unprecedented capabilities in processing vast amounts of data, uncovering patterns, and providing insights that were previously unattainable through conventional means. By integrating AI and ML into their strategic planning processes, organizations can enhance decision-making, optimize operations, and create innovative solutions that drive competitive advantage.
Identifying Strategic Opportunities through AI and ML
AI and ML technologies can transform the way organizations identify strategic opportunities. By analyzing large datasets, AI algorithms can detect emerging trends, customer preferences, and market dynamics that are not immediately apparent. This capability enables organizations to anticipate market shifts and adapt their strategies proactively. For example, AI-powered market intelligence platforms can analyze social media, news, and other digital footprints to identify shifts in consumer behavior or emerging industry trends. This real-time market insight allows organizations to be agile, adjusting their product development, marketing strategies, and operational priorities to seize new opportunities.
Moreover, AI and ML can enhance Competitive Intelligence (CI) by automating the collection and analysis of data on competitors. This includes tracking competitors’ digital presence, product launches, and customer reviews to gain insights into their strategies and performance. By leveraging AI for CI, organizations can identify gaps in the market, uncover niches where they can differentiate themselves, and anticipate competitors' moves. For instance, AI tools can analyze patent filings and R&D activities to predict technological trends and innovations, enabling organizations to stay ahead in the innovation curve.
Additionally, AI and ML can play a crucial role in Risk Management by identifying potential threats to strategic initiatives. By analyzing historical data and current market conditions, AI models can forecast risks associated with market entry, product launches, and other strategic moves. This predictive capability allows organizations to develop contingency plans and mitigate risks before they materialize, ensuring that strategic opportunities are pursued with a clear understanding of the potential challenges.
Evaluating Strategic Opportunities with AI and ML
Once strategic opportunities are identified, the next step is to evaluate their viability and potential impact. AI and ML can significantly enhance this process by providing data-driven insights and predictive analytics. For example, AI models can simulate various scenarios to assess the potential outcomes of different strategic options. This can include financial modeling, market penetration forecasts, and competitive response simulations. By leveraging these insights, organizations can make informed decisions about which opportunities to pursue, allocate resources more effectively, and develop strategies that are aligned with their long-term objectives.
AI and ML also enable organizations to conduct a more comprehensive and nuanced analysis of customer data. This includes sentiment analysis, customer journey mapping, and personalized customer engagement strategies. By understanding customer needs and preferences at a granular level, organizations can evaluate the potential success of new products, services, or market entry strategies. For instance, AI-powered analytics platforms can identify unmet customer needs or emerging customer segments, providing a basis for developing targeted value propositions that meet these specific requirements.
Furthermore, AI and ML can facilitate Strategic Portfolio Management by optimizing the mix of initiatives an organization pursues. By analyzing the potential return on investment (ROI) and strategic fit of various opportunities, AI algorithms can recommend the optimal portfolio of projects. This helps organizations to prioritize initiatives that offer the highest strategic value, balance risk, and align with their overall strategic vision. Through this data-driven approach, organizations can ensure that their resources are focused on the opportunities that are most likely to drive sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Real-World Examples of AI and ML in Strategic Opportunity Identification and Evaluation
Several leading organizations have successfully leveraged AI and ML to identify and evaluate strategic opportunities. For example, Netflix uses AI algorithms to analyze viewing patterns and customer feedback to identify trends and preferences. This insight informs their content acquisition and original production strategies, allowing Netflix to cater to diverse customer tastes and stay ahead of competitors. Similarly, Amazon leverages AI and ML for its recommendation engine, which not only enhances customer experience but also provides insights into consumer behavior and preferences. These insights inform Amazon's product development and strategic partnership decisions, driving continuous innovation and growth.
In the healthcare sector, companies like Roche are using AI and ML to accelerate drug discovery and development. By analyzing vast datasets of clinical trial results, genetic information, and patient records, AI models can identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy and safety profiles. This accelerates the R&D process, reduces costs, and improves the success rate of new drugs, providing a strategic advantage in the competitive pharmaceutical industry.
Moreover, financial services firms are using AI and ML to identify investment opportunities and manage risks. For instance, J.P. Morgan Chase employs AI to analyze market data, news, and financial reports to identify emerging investment trends and assess the risk of different assets. This enables the firm to make more informed investment decisions, optimize its portfolio, and deliver superior returns to its clients.
In conclusion, AI and ML are transforming the way organizations identify and evaluate strategic opportunities. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics, customer needs, and competitive landscapes. This enables them to make informed decisions, optimize their strategic planning processes, and maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving business environment.
In an ever-evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly faced with the challenge of ensuring their Strategy Deployment processes remain adaptable. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and achieving long-term success. The key to achieving this lies in understanding the dynamic nature of the business environment and integrating flexibility into the core of strategy deployment processes.
Building a Resilient Strategy Framework
The first step towards ensuring adaptability in strategy deployment processes is by building a resilient strategy framework. This framework should be designed to absorb and adapt to changes in the external environment. According to a study by McKinsey, organizations that regularly refresh their strategies and maintain strategic agility are more likely to sustain their performance over time. A resilient strategy framework includes a clear vision and flexible strategic objectives that can evolve as external conditions change. It also involves establishing a robust Strategic Planning process that incorporates scenario planning and stress testing to anticipate potential changes and prepare the organization to respond effectively.
Moreover, embedding flexibility into the strategic planning process allows organizations to pivot quickly in response to unforeseen events. This can be achieved through the adoption of a continuous planning cycle rather than a traditional annual planning process. Continuous planning enables organizations to adjust their strategies in real-time, ensuring that they remain relevant and effective. Additionally, leveraging technology and data analytics can enhance the organization's ability to monitor trends and identify signals of change, thereby informing strategic decisions and adjustments.
For instance, companies like Google and Amazon have demonstrated the effectiveness of maintaining flexible strategic frameworks. They continuously monitor the business environment and adjust their strategies accordingly, allowing them to capitalize on new opportunities and navigate challenges successfully.
Enhancing Organizational Agility
Organizational Agility is another critical component for ensuring the adaptability of strategy deployment processes. Agility enables an organization to respond swiftly to changes in the market, technology, and customer preferences. According to research by Deloitte, agile organizations can reduce their time to market by up to 50% and increase their employee engagement and customer satisfaction significantly. Achieving organizational agility requires a shift in culture, structure, and processes. It involves fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and risk-taking. Leaders play a crucial role in promoting this culture by encouraging experimentation and learning from failures.
Structurally, organizations can adopt more fluid and flexible organizational designs that facilitate cross-functional collaboration and quick decision-making. This might include the formation of multidisciplinary teams, flattening hierarchical structures, and implementing agile methodologies across the organization. Process-wise, streamlining operations and removing bureaucratic obstacles can significantly enhance agility. This includes simplifying approval processes, leveraging digital tools for collaboration, and automating routine tasks to free up resources for strategic initiatives.
Companies like Spotify and Netflix are prime examples of organizations that have embraced agility at their core. They have implemented agile methodologies not just in software development but across the entire organization, enabling them to adapt rapidly to changes in consumer behavior and technological advancements.
Embedding Continuous Learning and Innovation
Continuous Learning and Innovation are vital for ensuring that strategy deployment processes remain adaptable. In a rapidly changing business environment, what worked yesterday may not work tomorrow. Therefore, organizations must cultivate a culture of continuous learning where employees at all levels are encouraged to seek out new knowledge, skills, and competencies. According to a report by PwC, organizations that prioritize learning and development are 2.5 times more likely to be industry leaders in innovation and responsiveness to market changes.
Innovation should be embedded into the DNA of the organization, with processes and systems in place to support and encourage the generation of new ideas. This includes establishing innovation labs, hosting hackathons, and setting aside budgets for research and development. Moreover, organizations should foster an environment where failure is seen as an opportunity to learn and grow, rather than a setback. This approach encourages experimentation and allows organizations to discover new ways of doing things, which can be crucial for adapting to changes in the business environment.
3M is a notable example of an organization that has successfully embedded continuous learning and innovation into its culture. Through its "15% Time" policy, which allows employees to spend 15% of their time on projects of their choosing, 3M has developed numerous innovative products and maintained its competitive edge over the years.
In conclusion, ensuring that strategy deployment processes are adaptable to changes in the business environment requires a multifaceted approach. It involves building a resilient strategy framework, enhancing organizational agility, and embedding continuous learning and innovation into the organizational culture. By focusing on these areas, organizations can position themselves to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape successfully and sustain their competitive advantage over the long term.
Understanding what is the difference between strategic planning and tactical planning is crucial for any C-level executive aiming to steer their organization towards success. Strategic planning is the process of defining an organization's direction and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy. It involves setting long-term goals and determining the best approach to achieve these objectives. On the other hand, tactical planning is more focused on the short-term actions and resources needed to implement the strategies. It's about the day-to-day operations and the immediate steps required to move towards the strategic goals.
Strategic planning requires a high-level view and a deep understanding of the organization's mission, vision, and values. It's about looking at the big picture and positioning the organization for long-term success. This involves analyzing market trends, assessing strengths and weaknesses, and identifying opportunities and threats. The output of strategic planning is a framework that guides the organization in making decisions that align with its long-term objectives. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a robust strategic planning process that incorporates scenario planning and risk management to navigate the complexities of the global market.
Tactical planning, in contrast, is much more granular. It translates the broad strategies into actionable plans that can be executed in the short term. This includes setting departmental goals, allocating resources, and defining specific tasks. Tactical planning is about efficiency and effectiveness in achieving the strategic objectives. It requires a detailed understanding of the organization's operations and the ability to adapt to changes quickly. The focus is on performance management, operational excellence, and achieving quick wins that contribute to the strategic goals.
Key Differences in Framework and Approach
The framework and approach to strategic and tactical planning are fundamentally different. Strategic planning operates within a broader framework that considers the external environment, competitive dynamics, and long-term industry trends. It requires a visionary approach and the ability to make assumptions about the future. The strategic planning template involves setting objectives that are ambitious yet achievable, with a clear roadmap for reaching these goals over a multi-year horizon.
Tactical planning, on the other hand, works within a more confined framework that focuses on the internal capabilities of the organization. It's about optimizing current resources and processes to achieve the strategic objectives. The tactical planning template involves detailed action plans, schedules, and budgets that guide the day-to-day operations. It requires a hands-on approach and a focus on problem-solving and decision-making to overcome operational challenges.
While strategic planning sets the direction, tactical planning is about execution. Both are essential for the success of the organization, but they require different skill sets and mindsets. Strategic planning is more about leadership, culture, and innovation, while tactical planning is about management, execution, and control. The ability to balance and integrate these two types of planning is a key competency for C-level executives.
Real-World Examples and Insights
Consider the case of a global technology company undergoing a digital transformation. The strategic plan might involve repositioning the company to capitalize on emerging technologies and market trends, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. This would require a comprehensive analysis of the market, competitive positioning, and internal capabilities. The strategic framework would outline the long-term vision and goals, such as becoming a market leader in a new technology segment.
The tactical plan, in this scenario, would detail the specific projects, investments, and initiatives required to achieve the strategic objectives. This might include developing new products, entering new markets, or acquiring strategic partners. The tactical planning process would involve setting timelines, budgets, and performance metrics for these initiatives. It would also require coordinating across different departments and aligning resources with the strategic priorities.
In conclusion, understanding what is the difference between strategic planning and tactical planning is critical for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today's business environment. Strategic planning sets the direction and defines the long-term goals, while tactical planning focuses on the execution and the immediate steps required to achieve these goals. Both are essential, and the ability to integrate them effectively is a key determinant of organizational success. C-level executives must master both strategic and tactical planning to lead their organizations towards achieving their objectives.
Understanding how a vast demographic shift will reshape the world is crucial for C-level executives aiming to steer their organizations towards sustainable growth. The global population is aging, urbanization is on the rise, and migration patterns are changing. These shifts present both challenges and opportunities for global business strategies. As the demographic landscape transforms, so too must the frameworks and templates that guide strategic planning and execution.
One of the most significant demographic shifts is the aging population, particularly in developed economies. According to the United Nations, the number of people aged 60 years or older is expected to double by 2050. This aging demographic impacts workforce dynamics, consumer behavior, and healthcare demands. Organizations must adapt by reevaluating their product and service offerings to cater to an older consumer base. Additionally, workforce planning strategies need to incorporate flexible work arrangements and re-skilling programs to leverage the experience of older employees while attracting younger talent to replenish the workforce.
Urbanization is another key demographic trend, with the United Nations projecting that 68% of the world's population will live in urban areas by 2050. This shift has profound implications for how organizations approach market segmentation, supply chain logistics, and sustainability initiatives. Urban consumers tend to have different purchasing behaviors, favoring convenience, sustainability, and digital services. Companies must innovate to meet these demands, optimizing their supply chains for urban distribution and investing in digital transformation to enhance customer experiences.
Migration, both international and internal, is reshaping demographic profiles across the globe. This movement of people is creating multicultural societies that demand more diverse product and service offerings. Organizations need to develop a deeper understanding of these varied consumer preferences and adapt their marketing strategies accordingly. Moreover, the talent pool is becoming more diverse, requiring companies to embrace inclusivity and diversity in their hiring and management practices to attract and retain the best talent.
Strategic Implications and Actions
To navigate the demographic shifts effectively, organizations must incorporate demographic analysis into their Strategic Planning processes. This involves using data analytics to forecast demographic trends and assess their potential impact on market demand, labor supply, and regulatory environments. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Deloitte offer frameworks and tools that can help organizations analyze demographic data and integrate this insight into strategy development.
Adapting product and service offerings is essential to cater to changing consumer demographics. For instance, companies in the healthcare sector might focus on developing products and services for older adults, such as wearable health monitoring devices. Similarly, financial services organizations can offer retirement planning and wealth management services tailored to the needs of an aging population. Real-world examples include the shift by major consumer goods companies to develop products with easier-to-open packaging and marketing strategies that resonate with older consumers.
Investing in digital transformation is another critical strategy for addressing demographic shifts. Digital platforms and services can help organizations reach urban consumers, offer personalized experiences, and streamline operations. For example, e-commerce and mobile payment solutions are particularly effective in urban markets, where consumers value convenience and efficiency. Additionally, digital tools can facilitate remote work arrangements, helping organizations tap into a global talent pool and support a more diverse and inclusive workforce.
Conclusion
Demographic shifts are reshaping the global business landscape, presenting both challenges and opportunities. To remain competitive, organizations must understand these trends and integrate demographic insights into their strategic planning. This requires a proactive approach to adapting products and services, embracing digital transformation, and fostering an inclusive and diverse organizational culture. By doing so, organizations can not only navigate the challenges posed by demographic shifts but also capitalize on the opportunities they present to drive growth and innovation.
In summary, understanding and adapting to demographic shifts is not optional—it's imperative for long-term success. C-level executives must lead the charge by embedding demographic considerations into the core of their strategic frameworks and execution templates. The future belongs to organizations that can anticipate change, innovate, and adapt to the evolving needs of their customers, employees, and communities.
Aligning human resources with long-term strategic goals is critical for the sustained success and competitive advantage of any organization. This alignment ensures that the workforce is fully engaged and strategically leveraged to meet future challenges and achieve organizational objectives. The following strategies provide a roadmap for organizations looking to synchronize their human resources with their long-term strategic goals effectively.
Strategic Workforce Planning
Strategic Workforce Planning (SWP) is the cornerstone of aligning human resources with long-term strategic goals. SWP involves analyzing current workforce capabilities, identifying future workforce requirements based on strategic objectives, and developing strategies to bridge the gap. This process requires a deep understanding of the organization's strategic direction and the ability to forecast future talent needs. According to McKinsey, organizations that excel in strategic workforce planning can increase their productivity by up to 6% and their profitability by up to 5%.
Implementing SWP involves several key steps, including defining critical roles and skills needed for future success, assessing the current workforce against these requirements, and identifying gaps. Once gaps are identified, strategies such as targeted recruitment, employee development programs, and strategic redeployment can be employed to ensure the organization has the right talent in place to achieve its long-term goals.
Real-world examples of successful SWP include companies like IBM and Procter & Gamble, which have leveraged data analytics and forecasting tools to predict future talent needs and develop targeted training and recruitment strategies. These companies have not only improved their ability to meet strategic objectives but have also enhanced employee engagement and retention by providing clear career paths aligned with organizational goals.
Performance Management Alignment
Performance Management is another critical strategy for aligning human resources with long-term strategic goals. This involves setting individual employee goals that are directly linked to the organization's strategic objectives. By aligning employee performance metrics with the organization's broader goals, organizations can ensure that every member of the workforce is working towards the same objectives. A study by Deloitte found that organizations with aligned performance management processes are 3.5 times more likely to outperform their peers.
Effective performance management requires clear communication of strategic goals, the establishment of measurable and achievable individual targets, and regular feedback and performance reviews. It also involves recognizing and rewarding high performance that contributes to strategic objectives, thereby reinforcing the alignment between individual contributions and organizational goals.
An example of effective performance management alignment can be seen in Google's Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) framework. This framework ensures that employees at all levels of the organization are working towards clearly defined goals that align with Google's strategic priorities, fostering a high-performance culture that is closely aligned with long-term strategic goals.
Leadership Development and Succession Planning
Leadership Development and Succession Planning are essential for ensuring that an organization has the leadership capabilities required to achieve its long-term strategic goals. Developing leaders within the organization who have a deep understanding of the strategic vision and the skills to execute on it is crucial for sustained success. According to a report by BCG, companies with strong leadership and talent management practices see a 1.5 times higher growth in revenue and profit margins.
Organizations should focus on identifying high-potential employees and providing them with targeted development opportunities, including leadership training programs, mentorship, and rotational assignments across different areas of the organization. This not only prepares the next generation of leaders but also ensures that the organization has a deep bench of talent ready to step into critical roles as needed.
Companies like General Electric have long been recognized for their leadership development programs and succession planning processes. GE's commitment to developing leaders internally has enabled the company to navigate numerous market changes and strategic shifts successfully, demonstrating the value of aligning leadership development with long-term strategic goals.
Culture and Engagement
Finally, fostering a culture that supports the organization's strategic goals and actively engages employees in these goals is vital for alignment. An engaged workforce is more productive, more innovative, and more likely to stay with the organization. Gallup research indicates that highly engaged teams show a 21% increase in profitability. Cultivating a culture that aligns with strategic goals involves clear communication of the vision and values, as well as involving employees in the strategy development process.
Organizations can enhance alignment through regular communication about strategic goals, soliciting employee feedback, and involving employees in decision-making processes. This not only helps employees understand how their work contributes to the organization's success but also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment to the strategic vision.
Companies like Southwest Airlines have excelled in creating a culture that aligns with strategic goals. Southwest's focus on customer service and employee engagement is deeply embedded in the company's culture, driving its success in the highly competitive airline industry.
Aligning human resources with long-term strategic goals is not a one-time effort but a continuous process that requires commitment, strategic planning, and effective execution. By focusing on strategic workforce planning, performance management, leadership development, and culture and engagement, organizations can ensure that their human resources are fully aligned with their strategic objectives, driving sustained success and competitive advantage.
Fostering a culture that supports Agile Strategic Planning and rapid adaptation to change is crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in today's fast-paced business environment. This process involves cultivating a mindset that values flexibility, responsiveness, and continuous learning among all members of the organization. By implementing specific strategies and practices, organizations can create an environment that not only embraces change but also leverages it as an opportunity for growth and innovation.
Emphasizing Leadership Commitment and Role Modeling
Leadership plays a pivotal role in shaping and sustaining an organizational culture that is conducive to Agile Strategic Planning. Leaders must not only endorse agility and flexibility verbally but also demonstrate these values through their actions. This includes making rapid decisions, adapting leadership styles to be more collaborative and less hierarchical, and showing resilience in the face of setbacks. For instance, a study by McKinsey & Company highlights the importance of senior executives leading by example in fostering an agile culture. By actively participating in Agile practices and encouraging open communication, leaders can signal to the entire organization that adaptability is a valued and rewarded trait.
Moreover, leaders should invest in their own development to better guide their teams through change. This involves acquiring new skills relevant to Agile methodologies and understanding the dynamics of change management. Providing leaders with the tools and knowledge to navigate the complexities of today's business landscape is essential for ensuring that strategic planning remains flexible and responsive to market changes.
Finally, recognizing and rewarding behaviors that align with Agile principles can reinforce the desired culture. Leaders should establish recognition programs that celebrate innovation, risk-taking, and collaborative problem-solving. By valuing these behaviors, organizations can encourage more employees to embrace agility as a core component of their work ethic.
Building Organizational Capabilities for Flexibility and Speed
To support Agile Strategic Planning, organizations must develop capabilities that enable flexibility and rapid execution. This includes implementing Agile methodologies not only in software development teams but across the entire organization. For example, cross-functional teams can be empowered to make decisions quickly, without the need for extensive hierarchical approvals. Accenture's research on agility in business underscores the importance of such cross-functional teams in enhancing speed and efficiency, thereby enabling organizations to respond swiftly to emerging opportunities or threats.
Investing in technology is another critical aspect of building an agile organization. Digital tools and platforms can facilitate better collaboration, streamline processes, and provide real-time data for more informed decision-making. According to a report by Deloitte, leveraging digital technologies is key to achieving Operational Excellence and agility. Organizations that effectively use digital tools to support their strategic planning processes can adapt more quickly to changes in the external environment.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of continuous learning and development is essential for maintaining organizational agility. This means providing employees with opportunities to acquire new skills and knowledge that are relevant to the evolving business landscape. Encouraging experimentation and learning from failures are also important aspects of this learning culture. By doing so, organizations can ensure that their workforce remains adaptable and capable of supporting Agile Strategic Planning.
Encouraging Open Communication and Collaboration
Open communication and collaboration are foundational elements of an agile culture. Organizations should encourage the sharing of ideas and feedback across all levels, breaking down silos that can hinder agility. This can be facilitated through regular team meetings, open forums, and the use of collaborative tools that promote transparency and inclusivity. A study by Boston Consulting Group (BCG) on digital transformation success factors highlights the role of open communication in fostering an environment where innovation thrives.
Collaboration is equally important, as it brings together diverse perspectives and expertise that can lead to more innovative solutions. Organizations can promote collaboration by creating mixed-discipline teams for projects and initiatives, thereby leveraging the diverse skills and viewpoints of their workforce. This approach not only supports Agile Strategic Planning but also enhances problem-solving and creativity.
In addition, establishing clear channels for feedback and ensuring that it is acted upon can reinforce a culture of openness and trust. Employees who feel their input is valued are more likely to contribute their ideas and embrace change. This, in turn, supports the organization's ability to adapt quickly to new challenges and opportunities.
Implementing these strategies requires a concerted effort from all levels of the organization. By emphasizing leadership commitment, building organizational capabilities for flexibility, and encouraging open communication and collaboration, organizations can foster a culture that supports Agile Strategic Planning and rapid adaptation to change. This cultural transformation can be a significant competitive advantage, enabling organizations to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape with agility and resilience.
Strategic Planning in the face of rapid technological changes demands a proactive, agile, and foresighted approach. Organizations must not only adapt to current technological trends but also anticipate future shifts to maintain a competitive edge. This requires a blend of strategic foresight, operational flexibility, and a culture of continuous innovation. Below are strategies that can ensure Strategic Planning remains resilient amidst technological upheavals.
Embedding Flexibility into Strategic Planning
Traditional long-term planning models are often ill-suited to the fast-paced nature of technological advancement. Instead, organizations should adopt a more flexible approach to Strategic Planning. This involves setting broad, long-term goals while allowing for short-term objectives and tactics to evolve as new technologies emerge. A study by McKinsey emphasizes the importance of a dynamic approach to strategy in rapidly changing environments, suggesting that companies which regularly refresh their strategies can achieve up to a 33% higher profitability compared to those that don't.
To implement this, organizations can adopt rolling forecasts and flexible budgeting, moving away from the rigid annual planning cycles. This allows for the reallocation of resources in response to technological changes and market demands. Moreover, scenario planning plays a crucial role, enabling organizations to prepare for multiple future states by considering various technological trends and their potential impacts on the industry.
Additionally, adopting a 'test and learn' approach to new technologies can help organizations stay ahead. By piloting new technologies on a small scale, companies can assess their impact without committing extensive resources upfront. This iterative approach to innovation ensures that Strategic Planning is both responsive and resilient to technological shifts.
Strengthening Organizational Agility
Organizational agility is paramount in adapting to and capitalizing on technological changes. Agility in this context refers to the ability of an organization to rapidly change direction, scale operations up or down, and bring new products or services to market in response to technological advancements. According to a report by Deloitte, agile organizations can reduce their time to market by up to 50% and increase their employee engagement and productivity significantly.
Building an agile organization requires a shift in culture, processes, and structure. It involves empowering teams, flattening hierarchies, and fostering an environment where innovation and experimentation are encouraged. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, can be integrated into project management and product development processes to enhance responsiveness and flexibility.
Moreover, leveraging digital technologies for Operational Excellence is a critical aspect of enhancing agility. This includes automating processes, adopting cloud computing for scalability, and utilizing data analytics for informed decision-making. By embedding agility into the fabric of the organization, companies can ensure that their Strategic Planning processes are robust enough to handle the rapid pace of technological change.
Cultivating a Culture of Continuous Innovation
A culture that fosters continuous innovation is essential for organizations looking to thrive in a technology-driven landscape. This involves creating an environment where creativity is encouraged, failure is seen as a learning opportunity, and employees at all levels are engaged in identifying and implementing innovative solutions. According to PwC's Innovation Benchmark Report, companies that actively engage their entire organization in innovation efforts can increase their growth rate by up to three times compared to their peers.
Implementing structures and processes that support innovation is crucial. This can include setting up dedicated innovation labs, establishing cross-functional teams to explore new technologies, and implementing idea management systems to capture and evaluate suggestions from employees. Additionally, providing resources and time for employees to work on innovative projects can stimulate creative thinking and lead to breakthroughs in technology adoption and application.
Partnerships and collaborations with startups, academic institutions, and other organizations can also drive innovation. These alliances can provide access to new technologies, research, and talent. By fostering a culture of continuous innovation, organizations can ensure that their Strategic Planning processes are not only reactive to technological changes but are also proactively shaping the future of their industries.
In conclusion, ensuring that Strategic Planning is resilient to rapid technological changes requires a multifaceted approach. By embedding flexibility into planning processes, strengthening organizational agility, and cultivating a culture of continuous innovation, organizations can navigate the complexities of the digital age and emerge as leaders in their respective fields.
Effective strategy deployment and execution within an organization is a multifaceted process that requires meticulous planning, robust communication, and continuous monitoring. The success of these endeavors hinges not only on the strategies themselves but also on how they are implemented and brought to life within the organizational structure. This comprehensive approach ensures that strategic goals are not just theoretical ambitions but actionable pathways that lead to tangible outcomes.
Strategic Alignment and Planning
At the heart of effective strategy deployment is Strategic Alignment, ensuring that the organization's vision, mission, and core values are in sync with the strategic goals. This alignment is crucial for setting a clear direction and providing a unified purpose that guides decision-making at all levels. A study by McKinsey & Company highlights the importance of alignment, noting that organizations with highly aligned employees are more likely to be successful in achieving their strategic objectives. Strategic Planning involves not only defining goals and objectives but also setting priorities, allocating resources, and establishing timelines. This step is essential for creating a roadmap that outlines how the organization will move from its current state to the desired future state.
Effective communication plays a pivotal role in Strategic Planning. It ensures that all stakeholders are aware of the strategic goals, understand their roles in achieving them, and are committed to the organization's success. This involves not only disseminating information but also fostering an environment where feedback is encouraged and valued. By engaging employees in the planning process, organizations can build buy-in and enthusiasm for the strategic initiatives.
Another critical aspect of Strategic Planning is Risk Management. Organizations must identify potential obstacles and challenges that could derail their strategic goals and develop contingency plans to mitigate these risks. This proactive approach enables organizations to navigate uncertainties and adapt to changing circumstances without losing sight of their strategic objectives.
Performance Management and Measurement
Once the strategic plan is in place, Performance Management becomes crucial in ensuring that the organization is progressing towards its goals. This involves setting performance targets, monitoring progress, and providing regular feedback to employees. According to a report by Deloitte, organizations that effectively use performance management practices are more likely to outperform their peers in terms of revenue growth and profitability. Performance Measurement is an integral part of this process, providing the data needed to evaluate the effectiveness of the strategy and the efficiency of its implementation.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential tools in Performance Measurement. They provide a quantifiable measure of success and help organizations track their progress against strategic goals. However, it's important that KPIs are carefully selected to ensure they are aligned with the strategic objectives and provide meaningful insights into performance.
Feedback loops are another critical component of effective Performance Management. They allow organizations to collect input from employees, customers, and other stakeholders, which can be used to refine and adjust strategies as needed. This continuous improvement mindset ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to internal and external changes.
Change Management and Organizational Culture
Change Management is essential for facilitating the successful implementation of strategic initiatives. It involves preparing the organization for change, managing the transition process, and ensuring that changes are effectively integrated into the organization's operations. A study by Prosci found that projects with effective change management were six times more likely to meet their objectives than those without. This underscores the importance of managing the human side of change to ensure that employees are engaged and supportive of the strategic direction.
Organizational Culture plays a significant role in the success of strategy deployment and execution. A culture that promotes innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning can significantly enhance the organization's ability to implement strategic changes effectively. For instance, Google's culture of innovation and collaboration has been a key factor in its ability to continuously adapt and thrive in the rapidly changing digital landscape.
Leadership is also critical in shaping the organizational culture and driving the successful execution of strategic initiatives. Leaders must be champions of the strategy, embodying the values and behaviors they wish to see throughout the organization. They must also be effective communicators, able to articulate the vision and inspire their teams to achieve excellence. By leading by example, leaders can foster a culture that is aligned with the organization's strategic goals and conducive to achieving them.
Effective strategy deployment and execution require a comprehensive approach that encompasses strategic alignment and planning, performance management and measurement, and change management, all underpinned by a supportive organizational culture. By focusing on these critical steps, organizations can ensure that their strategic goals are not just aspirations but achievable realities that drive long-term success.
Understanding what is the problem statement in research is pivotal for any C-level executive looking to navigate through the complexities of today's business environment. A research problem statement is a concise description of an issue to be addressed or a condition to be improved upon. It identifies the gap between the current (problem) state and desired (goal) state of a process or product. In the context of business, this could range from operational inefficiencies, market share decline, to customer satisfaction issues. The problem statement serves as the foundation for any project, guiding the research framework and ensuring that the focus remains on addressing the identified issue.
Creating a compelling problem statement requires a deep understanding of the underlying issues affecting the organization. It should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This clarity is not just about having a clear direction for the research team but also about articulating the value proposition to stakeholders. For instance, a consulting firm like McKinsey or Bain might leverage data analytics to pinpoint the root cause of a decline in customer retention rates, framing a problem statement that guides the strategic planning process towards enhancing customer engagement and loyalty.
The significance of a well-formulated problem statement cannot be overstated. It not only sets the stage for the research but also helps in aligning team efforts towards a common goal. A clear problem statement acts as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring that the research remains focused and that the outcomes are actionable and directly tied to organizational objectives. It is a critical tool in the arsenal of any leader looking to drive strategic change, optimize operations, or innovate new products and services.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
Developing a robust framework for crafting a problem statement is essential for ensuring its effectiveness. The first step involves conducting a thorough analysis of the current situation to identify and understand the problem's dimensions. This could involve qualitative and quantitative research methods, including surveys, interviews, and data analysis. Consulting firms often employ proprietary methodologies to dissect complex issues, uncovering insights that inform the problem statement.
Once the problem is clearly understood, the next step is to articulate it in a way that is concise yet comprehensive. A good template to follow includes stating the problem, explaining its impact on the organization, and highlighting the benefits of solving it. This template ensures that the problem statement covers all critical aspects, making it a powerful tool for strategic decision-making.
Finally, the problem statement should be validated with stakeholders to ensure it aligns with broader organizational goals and has buy-in from key decision-makers. This step is crucial for ensuring the research directed by the problem statement is relevant, focused, and supported across the organization. Engaging stakeholders early on also facilitates smoother implementation of solutions down the line.
Real-World Examples
In the real world, problem statements have driven significant transformations within organizations. For example, a leading retailer facing declining sales might discover through research that the core issue is not product quality but customer experience. By framing a problem statement around improving the in-store experience, the retailer can focus its efforts on specific areas such as staff training, store layout, and customer service policies.
Another example could be a technology company struggling with product innovation. A well-defined problem statement might reveal that the root cause is not a lack of ideas but a siloed approach to product development. By focusing on enhancing cross-functional collaboration, the company can create a more conducive environment for innovation.
These examples underscore the importance of a clear, actionable problem statement in guiding organizations towards effective solutions. Whether it's improving customer satisfaction, driving operational efficiency, or fostering innovation, a well-crafted problem statement is a critical first step in the research process.
In conclusion, understanding and articulating what is the problem statement in research is a crucial skill for leaders in any organization. It sets the direction for strategic initiatives and ensures that efforts are concentrated on addressing the most pressing issues. By following a structured framework and leveraging real-world insights, executives can craft problem statements that are not only clear and focused but also aligned with organizational objectives and capable of driving meaningful change.
Creating a strategy document template is a critical step for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today's dynamic market environments. This document serves as a roadmap, guiding the organization through its strategic objectives, resource allocation, and the execution of its long-term vision. The importance of a well-crafted strategy document cannot be overstated—it aligns teams, informs stakeholders, and ensures that every facet of the organization is moving in the same direction towards achieving its goals.
At its core, a strategy document template should be designed to be both flexible and structured, allowing for adaptation to the organization's unique needs while maintaining a consistent approach to Strategy Development. The process of how to write a strategy document template involves a deep understanding of the organization's mission, vision, values, and strategic goals. It's about distilling complex ideas into actionable insights and clear directives that can be easily communicated across the organization. The template should serve as a blueprint, providing a framework that can be filled in with the specific details of the organization's strategic plan.
Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of clarity, conciseness, and relevance in strategy documents. They advocate for a structured approach that begins with an executive summary, followed by an analysis of the current state, a detailed description of the future state, and a clear action plan. This structure ensures that the strategy document is not only a planning tool but also a communication tool that can be used to engage and align stakeholders across the organization.
Key Components of a Strategy Document Template
When drafting a strategy document template, certain elements are non-negotiable. These components provide the skeleton upon which the strategic plan is built:
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of the strategic plan, offering a high-level insight into the organization's strategic objectives and how they will be achieved.
- Situation Analysis: This section delves into the current state of the organization, including an analysis of internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats (SWOT analysis).
- Strategic Objectives: Clearly defined goals that the organization aims to achieve over a specified timeframe, aligning with the overall mission and vision.
- Strategies and Tactics: The approach the organization will take to achieve its objectives, including specific tactics, resources required, and responsible parties.
- Implementation Plan: A detailed roadmap of how the strategies and tactics will be executed, including timelines, milestones, and key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Risk Management: An analysis of potential risks and contingencies to ensure the organization is prepared for unforeseen challenges.
This framework serves as a starting point, but it's crucial to tailor the template to the organization's specific context and strategic focus areas. For instance, a technology company undergoing Digital Transformation may emphasize Innovation and Leadership in its strategy document, while a manufacturing organization might focus on Operational Excellence and Supply Chain Optimization.
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of a well-structured strategy document. Take, for example, a global retail chain that successfully expanded into new markets by clearly outlining its market entry strategy, including detailed analysis, strategic objectives, and an implementation roadmap in its strategy document. This approach enabled the organization to align its internal teams, secure necessary resources, and execute its plan efficiently, ultimately achieving significant growth.
Best Practices for Writing a Strategy Document Template
To ensure the strategy document template is as effective as possible, there are several best practices to consider:
- Keep it concise: The strategy document should be succinct yet comprehensive enough to cover all critical aspects of the strategic plan. Avoid unnecessary jargon and focus on clear, direct language that is accessible to all stakeholders.
- Focus on alignment: Ensure that the strategic objectives align with the organization's mission and vision. This alignment is crucial for maintaining focus and ensuring that all efforts contribute to the overarching goals of the organization.
- Engage stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders in the strategy development process to gain buy-in and ensure that the plan reflects a wide range of perspectives and expertise. This collaborative approach enhances the plan's relevance and feasibility.
Additionally, leveraging insights from market research and consulting firms can provide valuable external perspectives and benchmarking data to inform the strategy development process. For instance, incorporating findings from Gartner or Forrester research can help validate strategic priorities and ensure they are grounded in industry trends and best practices.
In conclusion, creating a strategy document template is a critical step in the strategic planning process. It requires a careful balance between structure and flexibility, ensuring that the template serves as a practical tool for guiding the organization's strategic direction. By focusing on key components, adhering to best practices, and tailoring the template to the organization's unique needs, leaders can develop a robust framework that facilitates strategic alignment, informed decision-making, and successful execution of strategic initiatives.
In today's global business environment, geopolitical risks are increasingly influencing market dynamics, supply chains, and investment climates across industries. Companies that effectively adjust their Strategic Planning processes to better anticipate and manage these risks can secure a competitive advantage. This adjustment involves a multifaceted approach, including the integration of geopolitical risk assessment into strategic planning, enhancing organizational agility, and fostering strategic partnerships.
Integrating Geopolitical Risk Assessment into Strategic Planning
Geopolitical risk assessment should be a core component of the Strategic Planning process. This involves not only identifying potential geopolitical risks but also evaluating their potential impact on business operations and growth strategies. According to PwC's 22nd Annual Global CEO Survey, 73% of CEOs identified geopolitical uncertainty as a threat to their organization's growth. This statistic underscores the importance of incorporating geopolitical risk into strategic decision-making processes. Companies can achieve this by establishing a dedicated team or function focused on monitoring and analyzing geopolitical developments and their implications for the business. This team should work closely with strategic planners to ensure that insights are effectively integrated into the company's strategic framework.
Moreover, scenario planning is a critical tool for managing geopolitical risks. By developing and analyzing a range of plausible scenarios that could emerge from geopolitical tensions, companies can better prepare for various contingencies. This approach enables businesses to be more resilient and adaptable in the face of uncertainty. For instance, a company operating in an industry sensitive to trade policies might develop scenarios based on different outcomes of trade negotiations or regulatory changes. By preparing strategic responses for each scenario, the company can swiftly adjust its operations and strategies to mitigate adverse impacts.
Additionally, leveraging data analytics and intelligence tools can enhance the effectiveness of geopolitical risk assessment. Advanced analytics can help in identifying patterns and trends that may signal emerging risks, enabling companies to proactively adjust their strategies. For example, using predictive analytics to assess the likelihood of political instability in key markets can inform more strategic supply chain decisions, such as diversifying suppliers or establishing operations in more stable regions.
Enhancing Organizational Agility
Organizational agility is paramount in navigating the complexities of geopolitical risks. An agile organization can quickly adapt to changes in the geopolitical landscape, minimizing disruptions to its operations. This requires flexible strategic planning processes that allow for rapid decision-making and implementation. For example, adopting a rolling forecast approach to budgeting and planning can enable companies to adjust their financial and operational plans in response to emerging geopolitical risks.
Building cross-functional teams is another strategy to enhance agility. These teams bring together diverse expertise to address specific geopolitical challenges, facilitating more innovative and effective solutions. For instance, a cross-functional team comprising members from supply chain, legal, and market intelligence functions can collaboratively develop strategies to mitigate risks associated with new trade barriers or sanctions.
Investing in technology and digital capabilities also supports organizational agility. Digital platforms that enable real-time communication and collaboration can improve the speed and efficiency of response to geopolitical events. Additionally, technologies such as blockchain can offer solutions for enhancing supply chain transparency and security, critical factors in mitigating risks related to geopolitical disruptions.
Fostering Strategic Partnerships
Strategic partnerships can play a crucial role in managing geopolitical risks. By collaborating with local partners, companies can navigate regulatory environments more effectively and gain insights into local market dynamics. For example, a multinational corporation entering a new market might partner with a local firm to benefit from its understanding of the regulatory landscape and cultural nuances, reducing the risk of non-compliance or missteps in market entry strategies.
Moreover, partnerships with global organizations and think tanks specializing in geopolitical analysis can provide valuable intelligence and forecasting. These collaborations can enhance a company's ability to anticipate and prepare for geopolitical shifts. For instance, a technology firm might partner with a geopolitical risk consultancy to assess the implications of emerging technologies on global security and regulatory policies, informing its innovation and market strategies.
In conclusion, adjusting Strategic Planning processes to better anticipate and manage geopolitical risks is essential for companies operating in today's globalized economy. Integrating geopolitical risk assessment into strategic planning, enhancing organizational agility, and fostering strategic partnerships are key strategies for achieving this. By adopting these approaches, companies can not only mitigate risks but also identify new opportunities for growth and competitive differentiation.
Human Resources (HR) plays a pivotal role in aligning talent with the strategic needs of an organization, ensuring that the workforce is prepared and capable of executing the company's long-term vision. This alignment is critical for sustaining competitive advantage, driving innovation, and achieving Operational Excellence. In this context, HR's contribution to the Strategic Planning process is multifaceted, encompassing workforce planning, skill development, and organizational culture shaping, among others.
Strategic Workforce Planning
Strategic Workforce Planning is the cornerstone of aligning talent with future organizational needs. This process involves analyzing current workforce capabilities, forecasting future talent needs based on strategic objectives, and identifying the gaps between the present and the future. A report by McKinsey highlights the importance of a forward-looking approach to talent management, stating that organizations which actively engage in strategic workforce planning are better positioned to adapt to market changes, innovate, and maintain a competitive edge. To effectively contribute to Strategic Planning, HR must leverage data analytics to predict talent needs, considering factors such as retirement rates, skill evolution due to technological advancements, and external labor market trends.
HR can implement specific, actionable strategies to bridge the identified talent gaps. These may include targeted recruitment campaigns, internal training programs to upskill existing employees, and succession planning for critical roles. For instance, a global technology company facing a shortage of data scientists might launch an internal education program to train software engineers in data science, simultaneously addressing the talent gap and offering career development opportunities to its employees.
Moreover, HR should collaborate closely with other departments to ensure that workforce planning is fully integrated into the overall Strategic Planning process. This cross-functional collaboration ensures that talent strategies are not developed in isolation but are directly linked to business objectives and operational needs.
Building a Strategic Talent Pipeline
Developing a strategic talent pipeline is essential for ensuring the organization has access to the right skills at the right time. This involves not only identifying and recruiting top external talent but also nurturing internal talent to fill key positions. A study by Deloitte points out that organizations with robust talent pipelines are more agile, enabling them to respond more effectively to market demands and opportunities. HR plays a critical role in this process by establishing talent acquisition strategies that align with the organization's strategic direction and by fostering a culture of continuous learning and development.
To build a strategic talent pipeline, HR should focus on creating a compelling employer brand that attracts high-caliber candidates. This includes leveraging social media, professional networking platforms, and employee advocacy to showcase the organization's values, culture, and career opportunities. Furthermore, implementing comprehensive talent management programs that focus on leadership development, performance management, and employee engagement can help retain high-potential employees and prepare them for future leadership roles.
Real-world examples of successful talent pipeline development include Google's renowned internship program, which serves as a critical talent acquisition channel, and General Electric's leadership development programs, which have historically produced a significant number of the company's top executives. These examples underscore the importance of strategic investment in talent development as a means of securing the organization's future leadership and innovation capabilities.
Cultivating a Strategic Culture
Organizational culture plays a significant role in aligning talent with strategic objectives. A culture that fosters innovation, agility, and continuous improvement can significantly enhance an organization's ability to execute its strategy. According to a report by Bain & Company, companies with aligned culture and strategy experience higher levels of employee engagement and operational performance. HR is instrumental in shaping and nurturing this strategic culture through leadership development, recognition programs, and communication strategies.
Leadership development programs designed by HR should emphasize strategic thinking, decision-making, and change management skills, preparing leaders to drive the organization towards its strategic goals. Recognition programs, meanwhile, can reinforce behaviors and achievements that contribute to strategic objectives, promoting a culture of excellence and alignment.
Communication strategies are also vital. HR should ensure that all employees understand the organization's strategic vision, their role in achieving it, and how their work contributes to the bigger picture. This can be achieved through regular town hall meetings, strategic updates, and transparent communication channels. By fostering a culture that is in harmony with the organization's strategic objectives, HR can significantly enhance the organization's ability to achieve its goals.
In conclusion, HR's contribution to the Strategic Planning process is critical for ensuring talent alignment with future organizational needs. Through strategic workforce planning, building a strategic talent pipeline, and cultivating a strategic culture, HR can drive the organization towards achieving its long-term objectives, ensuring sustained competitive advantage and operational excellence.
In the current digital age, the importance of cybersecurity in Strategic Planning cannot be overstated. As companies become increasingly reliant on digital technologies, the potential impact of cyber threats on their operations, reputation, and bottom line has grown exponentially. Adjusting strategic planning to address cybersecurity involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing risk management, investment in technology and talent, and fostering a culture of security awareness.
Integrating Cybersecurity into Strategic Planning
The first step in adjusting strategic planning for cybersecurity is to integrate it as a core component of the Strategic Planning process. This integration requires a shift in mindset from viewing cybersecurity as a technical issue to understanding it as a strategic business challenge. Companies must evaluate their digital assets, identify potential threats, and assess their risk appetite. This assessment should inform the development of a cybersecurity strategy that aligns with the overall business objectives and is flexible enough to adapt to the evolving digital landscape. According to a report by McKinsey, companies that integrate cybersecurity into their strategic planning can reduce the impact of cyber attacks by up to 90%.
Effective integration also involves establishing clear lines of communication and responsibility for cybersecurity across the organization. This means involving key stakeholders from various departments—not just IT—in cybersecurity discussions. By doing so, companies can ensure that cybersecurity considerations are taken into account in decision-making processes at all levels. For instance, when launching a new product or entering a new market, the potential cybersecurity risks should be evaluated alongside financial and operational risks.
Moreover, strategic planning should include regular reviews and updates of the cybersecurity strategy to reflect new threats and technological advancements. This dynamic approach ensures that the company remains resilient in the face of an ever-changing cyber threat landscape. Regular training and drills can also help in preparing the organization to respond effectively to cyber incidents, minimizing damage and recovery time.
Investing in Cybersecurity Capabilities
Another critical aspect of adjusting strategic planning for cybersecurity is investing in the necessary capabilities to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. This includes not only technological solutions but also human talent. Cybersecurity technologies such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols are essential for protecting digital assets. However, these technologies need to be constantly updated and managed by skilled professionals. The global shortage of cybersecurity talent underscores the importance of investing in training and development programs to build an in-house team of cybersecurity experts.
Strategic partnerships can also play a key role in enhancing cybersecurity capabilities. Collaborating with specialized cybersecurity firms can provide access to advanced technologies and expertise that may be too costly or complex to develop internally. For example, cloud service providers often offer advanced security features that can help protect data more effectively than traditional on-premise solutions. These partnerships can also facilitate knowledge sharing and improve the company’s ability to respond to new threats.
Furthermore, companies should consider cybersecurity as a factor in their investment decisions. This includes evaluating the cybersecurity posture of potential partners, suppliers, and acquisition targets. A report by Deloitte highlighted that companies that conduct thorough cybersecurity due diligence during mergers and acquisitions can avoid significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Creating a Culture of Security Awareness
Adjusting strategic planning for cybersecurity also involves fostering a culture of security awareness throughout the organization. Employees are often the weakest link in a company’s cybersecurity defenses, with human error accounting for a significant portion of data breaches. Therefore, creating a culture where every employee understands their role in maintaining cybersecurity is crucial. This can be achieved through regular training programs, simulations of phishing attacks, and clear policies regarding data handling and password management.
Leadership plays a critical role in fostering this culture. Executives and managers should lead by example, adhering to security policies and demonstrating a commitment to cybersecurity. This top-down approach can help instill a sense of responsibility among employees and encourage them to take cybersecurity seriously. Additionally, recognizing and rewarding employees who contribute to improving the company’s cybersecurity can further reinforce the importance of this issue.
Finally, companies should engage with external stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and industry peers, to promote cybersecurity awareness. Sharing best practices and learning from others’ experiences can help raise the overall level of cybersecurity preparedness within the industry. For instance, participating in industry-wide cybersecurity drills can provide valuable insights into potential vulnerabilities and response strategies.
Adjusting strategic planning to address the increasing importance of cybersecurity is a complex but essential task. By integrating cybersecurity into strategic planning, investing in capabilities, and fostering a culture of security awareness, companies can protect their digital assets and ensure their long-term success in the digitally dependent world.
Performance management systems are essential tools for aligning the efforts of employees with the strategic objectives of an organization. To be effective, these systems must not only track and evaluate performance but also actively engage employees and motivate them towards achieving organizational goals. Designing such a system requires a comprehensive approach that integrates strategic planning, continuous feedback, and a culture of recognition and development.
Aligning Performance with Strategic Objectives
One of the first steps in designing an effective performance management system is ensuring that it is tightly aligned with the organization's strategic objectives. This involves setting clear, measurable goals at every level of the organization that directly contribute to the strategic aims. For instance, if an organization's strategic objective is to become the market leader in its sector within five years, individual and team goals should be set in a way that they collectively push towards achieving this aim. This might include targets related to innovation, customer satisfaction, market expansion, or operational efficiency.
To facilitate this alignment, organizations can adopt a Balanced Scorecard approach, a strategy performance management tool that can help managers to translate organizational objectives into performance metrics and targets. This framework ensures that the strategic objectives are translated into tangible actions and outcomes that can be measured and managed. For example, a study by Kaplan and Norton, who developed the Balanced Scorecard, showed that companies using this approach have seen a significant improvement in their performance because it ensures that all parts of the organization are working towards the same goals.
Moreover, technology plays a crucial role in aligning performance with strategic objectives. Performance management software can help in setting, tracking, and analyzing goals across the organization. These tools can provide real-time data and insights, making it easier for managers to adjust strategies and objectives as needed. According to Gartner, organizations that leverage performance management technology effectively are more likely to achieve their strategic objectives due to enhanced alignment and communication.
Fostering Employee Engagement through Continuous Feedback and Development
Employee engagement is critical for the success of any performance management system. Engaged employees are more productive, deliver higher quality work, and are less likely to leave the organization. To foster engagement, performance management systems must move beyond traditional annual reviews to incorporate continuous feedback and development opportunities. This approach helps employees understand how their work contributes to the organization's goals and provides them with the support they need to grow and succeed.
Continuous feedback mechanisms, such as regular one-on-one meetings, peer reviews, and real-time feedback tools, can provide employees with timely and constructive feedback. This not only helps in addressing issues as they arise but also promotes a culture of open communication and continuous improvement. According to Deloitte, organizations that have adopted a continuous feedback approach have seen an increase in employee engagement and productivity, as it helps employees feel valued and supported.
Furthermore, linking performance management with learning and development opportunities is essential for fostering engagement. Employees should have access to training, mentorship, and career development programs that help them build the skills needed to achieve their goals and advance their careers. This not only benefits the employees but also the organization, as it leads to a more skilled and motivated workforce. Accenture's research supports this, showing that organizations that invest in employee development see higher levels of engagement and performance.
Creating a Culture of Recognition and Accountability
A culture of recognition and accountability is fundamental to the success of a performance management system. Recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions reinforces positive behaviors and motivates others to perform at their best. This can be achieved through formal recognition programs, performance-based bonuses, and informal recognition practices, such as public acknowledgment in meetings or personal thank-you notes.
Accountability is equally important. Employees should be held accountable for their performance in a fair and consistent manner. This means setting clear expectations, providing the necessary resources and support, and addressing underperformance promptly and constructively. A culture of accountability ensures that employees understand the importance of their contributions and are motivated to achieve their best.
Real-world examples of organizations that have successfully implemented these principles include Google and Zappos. Google's performance management system emphasizes continuous feedback, peer reviews, and a strong focus on personal growth and development. Zappos, on the other hand, has created a unique culture of recognition and accountability, where employees are encouraged to take ownership of their work and celebrate each other's successes. These practices have not only contributed to high levels of employee engagement but have also driven these companies towards achieving their strategic objectives.
Performance management systems designed with strategic alignment, continuous feedback, and a culture of recognition and development at their core can significantly contribute to achieving organizational goals and fostering employee engagement. By focusing on these areas, organizations can create an environment where employees are motivated, engaged, and aligned with the strategic objectives, leading to improved performance and success.
Understanding what is true about the scope of a strong problem statement is crucial for any C-level executive aiming to steer their organization towards success. A well-defined problem statement acts as a guiding light for strategic planning, ensuring that every effort is aligned with solving the core issues at hand. It's not just about identifying a problem; it's about framing it in a way that directs resources, innovation, and efforts towards an effective and efficient resolution.
The scope of a strong problem statement should be precise enough to provide clear direction yet broad enough to allow for creative solutions. It must encapsulate the essence of the challenge the organization faces, without being so narrow that it limits potential strategies or so broad that it becomes vague and unactionable. A good problem statement serves as a framework for the strategy development process, enabling teams to brainstorm, innovate, and devise strategies that are directly relevant to the organization's core challenges.
In the world of consulting, frameworks play a significant role in defining the scope of a problem statement. Firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of structuring problem statements around measurable objectives and clear, impactful outcomes. This approach ensures that the problem statement is not just a description of an issue but a directive for action. It sets the stage for a strategic planning process that is focused, goal-oriented, and grounded in the reality of the organization's situation and capabilities.
Key Elements of a Strong Problem Statement
A strong problem statement should include several key elements that define its scope and ensure its effectiveness. First, it must clearly identify the issue at hand, using data and insights to underscore the importance of the problem. This might involve citing industry benchmarks or performance metrics that highlight the gap between the current state and desired outcomes. Second, the problem statement should articulate the impact of the issue on the organization's Strategic Planning, Operational Excellence, or other critical areas. This helps to prioritize the problem in the context of the organization's overall goals and objectives.
Third, a robust problem statement will outline the constraints and assumptions that frame the issue. This includes limitations on resources, time, or technology that could impact the solution. By defining these parameters upfront, the problem statement ensures that proposed strategies are realistic and feasible. Finally, the problem statement should hint at the potential benefits or opportunities that resolving the issue could unlock. This not only motivates the team but also aligns efforts with the broader objectives of Business Transformation and Performance Management.
Real-world examples demonstrate the power of a well-scoped problem statement. Consider a global retail chain that identified declining customer satisfaction as a critical issue. By framing the problem statement around specific customer experience metrics and linking it to sales performance and brand reputation, the organization was able to focus its efforts on targeted customer service improvements. This approach led to measurable improvements in customer satisfaction scores and a positive impact on sales, showcasing the effectiveness of a clearly defined problem statement.
Creating a Strong Problem Statement: A Template
Developing a strong problem statement requires a structured approach. A useful template might start with a concise description of the issue, followed by an explanation of why the issue matters, grounded in data and analysis. The next section should outline the impact of the problem on the organization's key performance indicators, followed by a discussion of the constraints and assumptions that shape the context of the problem.
This template serves as a starting point, but the real art lies in tailoring it to fit the unique context and challenges of your organization. It's about striking the right balance between specificity and flexibility, ensuring that the problem statement is both actionable and adaptable. Consulting firms often customize their frameworks to suit the specific needs of their clients, demonstrating the importance of a tailored approach.
In conclusion, the scope of a strong problem statement is a critical factor in the success of any strategic initiative. It defines the parameters of the problem, sets the direction for solution development, and ensures that efforts are aligned with the organization's broader goals. By crafting a clear, concise, and focused problem statement, leaders can mobilize their teams towards effective and impactful solutions, driving their organization towards Operational Excellence and strategic success.
Strategic Planning is a critical process that guides an organization's direction, prioritizes initiatives, allocates resources, and ensures that all stakeholders are aligned towards achieving the overarching goals. It is a comprehensive framework that encompasses understanding the current state, envisioning the future, and laying out a detailed roadmap to bridge the gap. The steps involved in Strategic Planning include goal setting, analysis, strategy formulation, strategy execution, and performance monitoring. Each step is crucial and requires meticulous attention to detail, rigorous analysis, and steadfast implementation to ensure organizational success.
The initial phase of Strategic Planning involves setting clear, achievable goals. This step is foundational, as it sets the direction for all subsequent efforts. Goals should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This ensures that the organization's objectives are clear and quantifiable, making it easier to track progress and make necessary adjustments. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of aligning these goals with the organization's mission and vision to ensure coherence and commitment across all levels of the organization. A common pitfall at this stage is setting overly ambitious goals without considering the practical constraints and resources available. To avoid this, organizations must conduct a thorough internal and external environment analysis to understand their capabilities and limitations.
Following goal setting, the next step is conducting a comprehensive analysis. This involves both internal analysis, such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), and external analysis, such as PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal). These analyses provide a clear picture of where the organization stands and the factors that could impact its strategy. According to Accenture, leveraging data analytics and market research at this stage can uncover valuable insights that can inform strategic decisions. It's critical to involve stakeholders from various departments to ensure a holistic view is captured. This collaborative approach not only enriches the analysis with diverse perspectives but also fosters a sense of ownership and alignment among team members.
With a solid understanding of the organization's current state and the external environment, the next step is strategy formulation. This involves translating the insights gained from the analysis into actionable strategies. The use of frameworks and templates can be particularly helpful in organizing thoughts and ensuring that strategies address the identified opportunities and challenges. Bain & Company highlights the importance of creating flexible strategies that can adapt to changing market conditions. This step should culminate in a strategic plan that outlines the priorities, initiatives, and resources required to achieve the set goals. It is essential for this plan to be realistic, considering the organization's capacity and resource constraints.
Executing the Strategy
Strategy execution is where many organizations face challenges. It involves translating the strategic plan into actionable tasks and ensuring that these are carried out effectively. Key to successful execution is clear communication of the plan and its objectives to all stakeholders. This ensures everyone understands their role in achieving the organization's goals. Deloitte emphasizes the importance of leadership in driving strategy execution, advocating for strong, committed leadership to guide the organization through this phase. Establishing a governance structure to oversee the execution process can help in monitoring progress and addressing any issues promptly.
Change management is another critical aspect of this step. As strategies often require changes in processes, systems, or behaviors, managing these changes effectively is crucial for minimizing resistance and ensuring smooth implementation. Tools and methodologies like Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model can be instrumental in guiding organizations through the complexities of change. Additionally, assigning responsibility and accountability for specific initiatives can enhance focus and drive towards completion.
Resource allocation is also a key consideration in strategy execution. Organizations must ensure that adequate resources—be it financial, human, or technological—are available and allocated efficiently to support the strategic initiatives. PwC advises on the importance of flexibility in resource allocation, suggesting that organizations should be prepared to shift resources as priorities change or new opportunities arise.
Monitoring Performance
The final step in the Strategic Planning process is monitoring performance. This involves establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the strategic goals and regularly reviewing progress against these metrics. Gartner recommends leveraging advanced analytics and business intelligence tools to track performance in real-time, allowing for timely adjustments. Regular performance reviews should be institutionalized, with a focus on learning and continuous improvement.
Feedback mechanisms are crucial at this stage. They provide insights into what is working and what is not, enabling organizations to pivot or adjust strategies as necessary. EY suggests incorporating both quantitative and qualitative feedback to get a comprehensive view of performance. Celebrating successes and learning from failures can help in maintaining momentum and morale.
In conclusion, effective implementation of each step of Strategic Planning is critical for organizational success. It requires a disciplined approach, rigorous analysis, strategic thinking, and robust execution. By setting clear goals, conducting thorough analyses, formulating actionable strategies, executing with precision, and monitoring performance diligently, organizations can navigate the complexities of today's business environment and steer towards long-term success.
Understanding the Circular Economy
The Circular Economy represents a fundamental shift from the traditional linear economy model of "take, make, dispose" to a more sustainable framework that emphasizes the reuse, sharing, repair, refurbishment, remanufacturing, and recycling of products and materials. This model not only aims to minimize waste but also to maximize the utilization of resources. For organizations looking to leverage the potential of the Circular Economy, understanding its principles is the first step. Strategic Planning must incorporate sustainability goals that align with the Circular Economy, focusing on designing products and processes that prioritize resource efficiency and waste reduction.
According to a report by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, companies that embrace the Circular Economy can unlock a $4.5 trillion economic opportunity by reducing waste, driving greater resource productivity, and capturing value from sectors such as circular supply chains and renewable energy. This highlights the importance for organizations to rethink and redesign their business models and operations in a way that aligns with circular principles.
Organizations can start by conducting a thorough analysis of their value chain to identify areas where circular economy principles can be applied. This might involve redesigning products for longer life spans, developing services that replace the need for physical products, or finding ways to recycle or repurpose waste into new products. Strategic Planning should also consider partnerships with other organizations to create closed-loop systems, where the output of one process becomes the input for another, thereby minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
Incorporating Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation play crucial roles in enabling the transition to a Circular Economy. Digital Transformation technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, and artificial intelligence (AI) can provide organizations with the tools they need to track and manage resources more efficiently, optimize product life cycles, and create more sustainable supply chains. For example, IoT devices can monitor the condition and usage of products, facilitating maintenance, repair, and refurbishment activities that extend product life spans and reduce waste.
Blockchain technology can enhance transparency and traceability in supply chains, making it easier for organizations to verify the sustainability credentials of their products and materials. This can be particularly important in sectors where the provenance of materials is a critical factor in sustainability, such as in the fashion industry or electronics manufacturing. AI and big data analytics can also help organizations to optimize their operations for sustainability, identifying patterns and insights that lead to more efficient use of resources.
Organizations should invest in Research and Development (R&D) to innovate new materials and processes that are designed for the Circular Economy. For instance, developing biodegradable materials or designing products for easier disassembly can significantly reduce environmental impact. Strategic Planning should allocate resources towards innovation that not only drives economic growth but also contributes to environmental sustainability.
Engaging Stakeholders and Building Ecosystems
Successful implementation of Circular Economy principles requires the engagement of a wide range of stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, regulators, and the broader community. Organizations need to communicate the benefits of the Circular Economy effectively, not just in terms of environmental impact but also in terms of economic and social benefits. This involves educating customers on the value of sustainable products and services and working with suppliers to ensure the sustainability of supply chains.
Building ecosystems is another critical aspect of leveraging the Circular Economy. This involves creating networks of partners that can collaborate to create closed-loop systems. For example, a manufacturer might partner with a recycling company to ensure that materials from used products are recovered and reused in new products. According to Accenture, collaboration across industries and sectors is key to unlocking the value of the Circular Economy, as it allows for the sharing of resources, knowledge, and technologies.
Organizations should also engage with policymakers to advocate for regulations and policies that support the Circular Economy. This can include incentives for sustainable practices, standards for recyclable materials, and regulations that encourage product stewardship. By actively participating in the development of a supportive regulatory environment, organizations can help to accelerate the transition to a Circular Economy.
In conclusion, adjusting Strategic Planning to leverage the potential of the Circular Economy requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses understanding and applying Circular Economy principles, incorporating technology and innovation, and engaging stakeholders and building ecosystems. By doing so, organizations can not only reduce their environmental impact but also unlock new economic opportunities and build a more sustainable future.
Integrating PEST analysis into strategic planning is a critical step for organizations aiming to identify new opportunities and navigate the complexities of the global business environment. This approach allows executives to systematically analyze Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors that could impact their organization's future growth and success. By leveraging PEST analysis, leaders can make informed decisions, anticipate market changes, and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Understanding the Role of PEST Analysis in Strategic Planning
PEST analysis serves as a comprehensive tool that helps organizations to scan their external macro-environment. The importance of incorporating PEST analysis into strategic planning cannot be overstated. It enables organizations to identify potential threats and opportunities in the external environment that could significantly affect their operations. By understanding these external factors, organizations can develop strategies that are more aligned with the current and future market conditions. This proactive approach not only helps in mitigating risks but also in seizing opportunities that competitors may overlook.
Strategic Planning, at its core, involves setting long-term goals and determining the best approach to achieve them. Incorporating PEST analysis into this process ensures that the strategies developed are not only robust but also resilient to external shocks. It provides a structured way for organizations to assess the landscape in which they operate, helping them to adjust their strategies in light of the findings. This dynamic approach to Strategic Planning is essential in today’s fast-paced and ever-changing business environment.
Moreover, PEST analysis facilitates a deeper understanding of market dynamics and consumer behavior, which are crucial for identifying new opportunities. By analyzing social trends, technological advancements, economic conditions, and political regulations, organizations can uncover untapped markets, new customer segments, and innovative product or service offerings. This strategic insight positions organizations to capitalize on changes in the external environment ahead of their competitors.
Integrating PEST Analysis into Strategic Planning Processes
To effectively integrate PEST analysis into Strategic Planning, organizations should begin by systematically gathering and analyzing information related to political, economic, social, and technological factors. This involves not only current data but also projections about future trends and developments. Once this analysis is complete, the findings should be incorporated into the strategic planning discussions, influencing the setting of objectives, the development of strategies, and the allocation of resources.
It is essential for organizations to establish a continuous process where PEST analysis is conducted at regular intervals or when significant external changes are anticipated. This ongoing process ensures that the organization's strategic plan remains relevant and responsive to the external environment. For instance, a sudden change in regulatory policies or a breakthrough technological innovation could necessitate a quick strategic pivot, underscoring the importance of agility in strategic planning.
Actionable insights from PEST analysis should be used to inform not only the overall corporate strategy but also functional strategies such as marketing, operations, and product development. For example, an economic downturn might prompt a shift towards more cost-effective product lines, while a social trend towards sustainability could lead to the development of eco-friendly products. By aligning strategies across the organization with insights derived from PEST analysis, organizations can ensure a cohesive and strategic response to external changes.
Real-World Examples of Successful PEST Integration
Consider the case of a leading technology company that leveraged PEST analysis to identify the opportunity for digital transformation services in the healthcare sector. By analyzing technological trends and regulatory changes, the company was able to anticipate the healthcare industry’s shift towards digital health records and telemedicine. This strategic insight allowed the company to pivot its offerings and capture a significant market share in a burgeoning industry.
Another example is a multinational retail corporation that used PEST analysis to navigate the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. By closely monitoring social and economic factors, the company quickly adapted its business model to focus on e-commerce and contactless delivery services. This strategic shift not only helped the company to survive during the pandemic but also positioned it for greater success in the post-pandemic world.
In conclusion, integrating PEST analysis into strategic planning is a powerful approach for identifying new opportunities and enhancing organizational resilience. By systematically analyzing the external environment and incorporating these insights into strategic planning processes, organizations can develop forward-looking strategies that are both agile and aligned with market conditions. This strategic agility is crucial for thriving in today’s complex and rapidly changing business landscape.
Digital transformation initiatives are critical for organizations aiming to maintain competitive advantage and adapt to the rapidly changing business landscape. Ensuring these initiatives align with the overall strategic goals is paramount for executives. This alignment ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, and the organization moves cohesively towards its long-term objectives. Below are specific, detailed, and actionable insights on how executives can ensure this alignment.
Establishing a Clear Strategic Vision
First and foremost, alignment begins with a clear strategic vision. This vision should articulate where the organization wants to be in the future and how digital transformation can facilitate this journey. Executives must ensure that this vision is communicated effectively across all levels of the organization. A study by McKinsey & Company highlights that companies with highly aligned digital strategies to their corporate strategies are twice as likely to achieve top-quartile financial performance than their peers. This underscores the importance of a well-articulated vision that serves as a north star for digital transformation efforts.
Moreover, the strategic vision should be revisited and updated regularly to reflect the fast-paced changes in technology and market dynamics. This dynamic approach allows the organization to remain agile and responsive to new opportunities and threats. Involving key stakeholders in the updating process ensures that the vision remains relevant and comprehensive.
Lastly, the strategic vision must be translated into actionable goals and metrics. This translation involves setting clear, measurable objectives for digital transformation initiatives that directly contribute to the strategic goals of the organization. Performance management systems should be updated to reflect these metrics, ensuring that progress can be monitored and managed effectively.
Integrating Digital Transformation into Strategic Planning
Integration of digital transformation initiatives into the overall strategic planning process is crucial. This integration ensures that digital transformation is not seen as a separate or isolated activity but as an integral part of the strategic direction of the organization. According to a report by PwC, organizations that successfully integrate their digital and corporate strategies report higher profitability and market share. This highlights the importance of embedding digital initiatives into the strategic planning process.
Executives should ensure that digital transformation is considered in all aspects of strategic planning, including market analysis, competitive positioning, and resource allocation. This comprehensive approach ensures that digital initiatives are fully aligned with the strategic objectives and can leverage the organization's core competencies.
Furthermore, cross-functional teams should be established to oversee the integration of digital transformation into strategic planning. These teams, comprising members from IT, operations, finance, and other relevant departments, can ensure that digital initiatives are developed and implemented in a way that supports the overall strategic goals. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and ensures that digital transformation initiatives are grounded in the organization's strategic objectives.
Promoting a Culture of Alignment and Innovation
Culture plays a significant role in aligning digital transformation initiatives with strategic goals. A culture that values alignment, innovation, and continuous learning is essential for the successful integration of digital strategies. According to Deloitte, organizations with a strong digital culture are more likely to achieve high performance in their digital transformation efforts. This culture encourages experimentation, learning from failures, and continuous improvement, all of which are critical for aligning digital initiatives with strategic goals.
Executives can promote such a culture by leading by example, demonstrating a commitment to digital transformation, and its alignment with the organization's strategic objectives. Recognition and rewards for teams that successfully integrate digital initiatives with strategic goals can also reinforce the importance of alignment.
Additionally, training and development programs focused on digital skills and strategic thinking can help build the necessary competencies across the organization. These programs should emphasize the importance of alignment and provide tools and frameworks for integrating digital initiatives with strategic planning. By investing in the development of their people, organizations can ensure that their teams are equipped to drive digital transformation in a way that aligns with their strategic objectives.
Leveraging Data and Analytics for Strategic Alignment
Data and analytics play a critical role in aligning digital transformation initiatives with strategic goals. By leveraging data, executives can gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiencies. These insights can inform strategic decisions and ensure that digital transformation initiatives are focused on areas that offer the highest strategic value. According to Gartner, data-driven organizations are more likely to excel in their digital transformation efforts and achieve competitive advantage.
Investing in advanced analytics and business intelligence tools can enable organizations to analyze vast amounts of data and generate actionable insights. These tools can help identify opportunities for digital innovation that align with strategic objectives and assess the impact of digital initiatives on key performance indicators.
Moreover, establishing a data governance framework is essential for ensuring the quality, security, and accessibility of data. This framework supports effective decision-making and enables the organization to leverage data as a strategic asset. By prioritizing data and analytics, organizations can ensure that their digital transformation initiatives are aligned with their strategic goals and are positioned for success.
In conclusion, ensuring alignment between digital transformation initiatives and overall strategic goals requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses clear strategic visioning, integration into strategic planning, promoting a culture of alignment and innovation, and leveraging data and analytics. By following these actionable insights, executives can lead their organizations towards successful digital transformation that is fully aligned with their strategic objectives.
Strategic planning plays a pivotal role in maximizing shareholder value, especially in volatile markets. This process involves setting priorities, focusing energy and resources, strengthening operations, ensuring employees and other stakeholders are working toward common goals, and assessing and adjusting the organization's direction in response to a changing environment. It is a disciplined effort that produces fundamental decisions and actions that shape and guide what an organization is, who it serves, what it does, and why it does it, with a focus on the future.
The Importance of Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning is crucial for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of volatile markets successfully. It allows organizations to anticipate future challenges and opportunities, enabling them to be proactive rather than reactive. In a study by McKinsey & Company, it was found that companies with strategic planning processes that are more sophisticated and adaptive to market changes tend to outperform their peers in terms of revenue growth and profitability. This is because strategic planning helps in aligning the organization's resources with its strategic objectives, ensuring that all efforts are directed towards achieving long-term goals that enhance shareholder value.
Moreover, Strategic Planning facilitates better risk management. By identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them, organizations can protect their assets and ensure sustainable growth. This is particularly important in volatile markets where unexpected events can have significant impacts on the organization's performance. Effective Strategic Planning also involves scenario planning, which prepares the organization for different possible futures, enhancing its resilience and agility.
Additionally, Strategic Planning plays a critical role in Performance Management. It establishes a clear framework for evaluating the organization's performance, setting benchmarks, and implementing corrective measures to address any deviations from the strategic goals. This continuous loop of planning, execution, evaluation, and adjustment is essential for maintaining operational excellence and maximizing shareholder value in the face of market volatility.
Aligning Strategy with Market Realities
One of the key aspects of Strategic Planning is its ability to align the organization's strategy with the realities of the market. This requires a deep understanding of the market dynamics, customer needs, competitive landscape, and technological advancements. For instance, Accenture's research highlights the importance of Digital Transformation as a strategic priority for organizations looking to enhance their competitiveness and shareholder value in rapidly evolving markets. By integrating digital technology into all areas of the organization, companies can improve their operational efficiency, customer experience, and innovation capabilities.
Strategic Planning also emphasizes the importance of Leadership and Culture in executing the strategy effectively. Leaders play a crucial role in communicating the vision, motivating employees, and driving change. A strong organizational culture that supports innovation, accountability, and continuous improvement is essential for the successful implementation of the strategy. This alignment between strategy, leadership, and culture is critical for achieving operational excellence and long-term success.
In the context of volatile markets, Strategic Planning must also include a focus on Innovation. This involves not only the development of new products and services but also the exploration of new business models and revenue streams. For example, companies like Amazon and Netflix have continuously innovated their business models to adapt to changing market conditions, thereby sustaining their growth and enhancing shareholder value. Strategic Planning enables organizations to foster a culture of innovation, where creative thinking and experimentation are encouraged, and failures are viewed as learning opportunities.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Real-world examples further illustrate the importance of Strategic Planning in maximizing shareholder value. Apple Inc., under the leadership of Steve Jobs and now Tim Cook, has exemplified how a clear strategic vision, combined with innovative products and a strong brand, can create immense shareholder value, even in the face of market volatility. Apple's focus on innovation, quality, and customer experience has allowed it to remain a leader in the technology industry.
Another example is Microsoft's pivot towards cloud computing and subscription services under CEO Satya Nadella. This strategic shift was driven by the recognition of changing market demands and the declining growth in the PC market. By realigning its strategy to focus on cloud services, Microsoft not only revitalized its growth but also significantly increased its market value, demonstrating the power of strategic agility in volatile markets.
In conclusion, Strategic Planning is indispensable for organizations aiming to maximize shareholder value in volatile markets. It provides a structured approach to navigating uncertainty, aligning resources with strategic objectives, and fostering a culture of innovation and resilience. By effectively planning and executing their strategies, organizations can achieve sustainable growth and long-term success, even in the face of rapid market changes.
Defining a research problem statement is a critical step in aligning an organization's strategic planning goals with actionable insights. The crux of "what is the problem statement in research" lies in its ability to succinctly describe the issues that need addressing to achieve desired outcomes. This process requires a deep understanding of the organization's current position, its strategic objectives, and the gaps that exist between the current state and future aspirations. A well-crafted problem statement acts as a compass, guiding the research towards generating relevant data and insights that support strategic decision-making.
For C-level executives, the emphasis should be on leveraging a structured framework to articulate the problem statement. This involves conducting a thorough analysis of internal and external environments, utilizing tools such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) or PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental) analyses. These analyses help in identifying key issues that are critical to the organization's success. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG advocate for a hypothesis-driven approach to problem-solving, which begins with a clear and concise problem statement. This approach ensures that the research is focused and aligned with the strategic goals of the organization.
The development of a problem statement should not occur in a vacuum. It requires collaboration across departments and levels within the organization to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities. Engaging with stakeholders through interviews, workshops, and surveys can provide diverse perspectives that enrich the problem statement. Furthermore, examining case studies and industry reports from authoritative sources such as Gartner or Forrester can offer insights into how similar challenges have been addressed, providing a solid foundation for crafting a robust problem statement.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
A systematic framework is essential for crafting a problem statement that is both effective and aligned with strategic planning goals. The first step in this framework involves identifying and articulating the gap between the current state and the desired future state. This gap analysis highlights the areas where research is needed to inform strategy development and decision-making. Following this, it is crucial to prioritize the issues identified based on their impact on the organization's strategic objectives. This prioritization ensures that the research focuses on the most critical areas.
After identifying and prioritizing the issues, the next step is to formulate the problem statement. A powerful problem statement is clear, concise, and focused, outlining the specific issues that the research will address. It should also imply the potential benefits that solving the problem will bring to the organization. Utilizing a template or guideline from reputable consulting firms can help ensure that the problem statement meets these criteria. For instance, templates provided by firms like Accenture or Deloitte often include prompts or questions designed to refine and focus the problem statement.
The final step in the framework is validation. Before proceeding with the research, it is imperative to validate the problem statement with key stakeholders. This validation process ensures that the problem statement accurately reflects the strategic goals and priorities of the organization. It also provides an opportunity to make adjustments based on feedback, ensuring that the research is targeted and relevant. Engaging with stakeholders during this phase not only builds consensus but also fosters a sense of ownership over the research process and its outcomes.
Real-World Applications
Consider the example of a global retail chain facing declining sales. By applying the framework outlined above, the organization identified that the root cause of the decline was not product quality or pricing, but rather a misalignment between their in-store experience and the evolving expectations of their customer base. The problem statement focused on understanding these changing customer expectations and identifying strategies to enhance the in-store experience. This clear, focused problem statement guided the research, which ultimately informed a successful strategy for revamping the in-store experience, leading to a significant increase in sales.
In another instance, a technology company struggling with high employee turnover utilized this framework to craft a problem statement centered around understanding the factors contributing to turnover and identifying strategies for improving employee retention. The research informed by this problem statement led to the implementation of a comprehensive employee engagement program, which significantly reduced turnover rates and improved organizational performance.
In conclusion, crafting an effective research problem statement is a critical step in aligning research efforts with an organization's strategic planning goals. By following a structured framework and engaging with stakeholders throughout the process, organizations can ensure that their research is focused, relevant, and impactful. Real-world examples demonstrate the power of a well-defined problem statement in guiding successful research and strategy development efforts. As organizations navigate an increasingly complex and dynamic business environment, the ability to articulate and address relevant research problems will be a key driver of strategic success.
Strategic financial planning is a cornerstone of long-term organizational growth and stability. It provides a roadmap for how an organization can achieve its financial goals and objectives, aligning resources with strategic priorities. This process involves the development of financial models, forecasts, and scenarios that help leaders make informed decisions about investments, cost management, and revenue generation. By integrating financial planning into the strategic management process, organizations can ensure that they are not only reacting to market changes but also proactively shaping their future.
One critical aspect of strategic financial planning is its ability to enhance decision-making. With a robust financial plan, C-level executives have access to data-driven insights that inform strategic choices, from mergers and acquisitions to new market entry and product development. This planning process involves rigorous analysis of financial data, market trends, and competitor performance, providing a comprehensive view of the organization's financial health and competitive position. By leveraging these insights, executives can prioritize investments, allocate resources more effectively, and mitigate risks, driving sustainable growth and long-term stability.
Moreover, strategic financial planning fosters alignment across the organization. By establishing clear financial targets and metrics, organizations can ensure that all departments and teams are working towards the same goals. This alignment is crucial for executing strategy and achieving operational excellence. Financial plans act as a communication tool, bridging the gap between strategy and execution, and ensuring that everyone understands the financial implications of their actions. Through regular updates and reviews, financial planning keeps the organization agile, responsive to changes in the external environment, and focused on key priorities.
Framework for Strategic Financial Planning
Developing a strategic financial planning framework involves several key steps. Initially, organizations must define their strategic objectives, identifying what they aim to achieve in the long term. This vision sets the direction for financial planning, guiding the allocation of resources and investments. Next, a detailed analysis of the current financial situation is essential, including an assessment of revenue streams, cost structures, and capital allocation. This analysis provides a baseline for measuring progress and identifying areas for improvement.
The next step in the framework is scenario planning and forecasting. Organizations must model various financial scenarios, considering different market conditions, competitive actions, and internal changes. This approach allows organizations to anticipate potential challenges and opportunities, planning for a range of outcomes. By preparing for uncertainty, organizations can remain resilient in the face of volatility and adapt their strategies as needed.
Finally, performance management is a critical component of the strategic financial planning framework. This involves setting key performance indicators (KPIs), monitoring progress against financial targets, and adjusting plans based on actual performance. Regular reviews of financial performance enable organizations to stay on track, make necessary corrections, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Performance management ensures that financial planning is not a one-time exercise but a continuous process that drives strategic execution and organizational success.
Real-World Examples and Consulting Insights
Leading consulting firms, such as McKinsey & Company and Bain & Company, have highlighted the importance of strategic financial planning through various client engagements. For instance, McKinsey's work with a global manufacturing company involved developing a comprehensive financial planning process that aligned with the company's strategic growth initiatives. By implementing a robust framework for financial planning and analysis, the company was able to identify underperforming units, reallocate capital to high-growth areas, and significantly improve its overall financial performance.
Bain & Company's insights into financial planning emphasize the role of digital transformation in enhancing financial forecasting and scenario planning. Through the adoption of advanced analytics and digital tools, organizations can achieve greater accuracy in their financial models, respond more quickly to market changes, and drive more informed decision-making. This digital approach to financial planning enables organizations to leverage data for competitive advantage, optimizing their financial strategies in real-time.
In conclusion, strategic financial planning is critical for long-term growth and stability. It enhances decision-making, fosters organizational alignment, and enables continuous adaptation to changing market conditions. By following a structured framework and leveraging insights from consulting firms, organizations can develop effective financial plans that support strategic objectives and drive sustainable success. Whether through traditional methods or digital transformation, strategic financial planning remains a key pillar of organizational excellence and competitive positioning.
Strategic planning processes are the backbone of any successful organization, guiding it towards achieving its long-term objectives. When designed effectively, these processes can significantly enhance customer experience and satisfaction, a critical determinant of an organization's growth and sustainability. In today's highly competitive business environment, understanding and implementing strategies that prioritize the customer can set an organization apart from its competitors.
Understanding Customer Needs through Strategic Planning
At the core of enhancing customer experience and satisfaction is the deep understanding of customer needs and expectations. Strategic planning must start with a comprehensive market analysis, leveraging data analytics and customer feedback to gain insights into customer behavior and preferences. Organizations like McKinsey & Company emphasize the importance of a customer-centric approach in strategic planning, advocating for the use of advanced analytics to predict customer trends and behaviors. By integrating customer insights into the strategic planning process, organizations can develop targeted strategies that address specific customer needs, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Furthermore, strategic planning should involve the alignment of organizational goals with customer expectations. This means setting clear, measurable objectives that focus on enhancing the customer experience, such as reducing response times, improving product quality, or offering personalized services. Performance management systems should be designed to track and measure the success of these objectives, ensuring that the organization remains focused on its customer-centric goals.
Engaging customers directly in the strategic planning process can also provide valuable insights and foster a sense of ownership and loyalty among customers. This can be achieved through customer advisory boards, feedback surveys, and forums that allow customers to voice their opinions and suggestions. By actively listening to customers and incorporating their feedback into strategic decisions, organizations can ensure that their strategies are aligned with customer needs and expectations.
Integrating Digital Transformation into Strategic Planning
Digital transformation has become a critical component of strategic planning, offering new opportunities to enhance customer experience and satisfaction. Organizations must embrace digital technologies to streamline operations, improve customer interactions, and deliver personalized customer experiences. For instance, Accenture's research highlights the role of digital platforms in enabling organizations to provide seamless, omnichannel experiences that meet customers' expectations for convenience and accessibility.
Investing in customer relationship management (CRM) systems, mobile applications, and AI-driven chatbots can significantly improve the efficiency and quality of customer service, leading to higher satisfaction levels. These technologies can also provide organizations with valuable customer data and insights, enabling them to tailor their products and services to meet specific customer needs.
Moreover, strategic planning should consider the integration of digital technologies into product development and innovation processes. This involves leveraging customer data to drive innovation and develop new products and services that meet evolving customer needs. By adopting a digital-first approach in strategic planning, organizations can stay ahead of technological trends and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Building a Customer-Centric Culture
A customer-centric culture is essential for enhancing customer experience and satisfaction. Strategic planning processes should include initiatives aimed at building and reinforcing a culture that prioritizes the customer in every aspect of the organization's operations. Leadership plays a crucial role in modeling customer-centric behaviors and embedding them into the organization's values and practices.
Training and development programs should be implemented to equip employees with the skills and knowledge needed to deliver exceptional customer service. These programs should emphasize the importance of empathy, active listening, and problem-solving in creating positive customer interactions. Additionally, reward and recognition systems should be aligned with customer satisfaction metrics, incentivizing employees to prioritize customer needs and contribute to the overall customer experience.
Finally, continuous improvement processes should be integrated into the strategic planning framework, ensuring that the organization remains agile and responsive to changing customer expectations. This involves regularly reviewing and updating strategies based on customer feedback and market trends, fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability. By prioritizing continuous improvement, organizations can sustain high levels of customer satisfaction and build long-term relationships with their customers.
In conclusion, designing strategic planning processes with a focus on enhancing customer experience and satisfaction requires a comprehensive approach that integrates customer insights, digital transformation, and a customer-centric culture. By prioritizing the customer in every aspect of strategic planning, organizations can achieve sustainable growth and a competitive advantage in the market.
Understanding what a strategic plan in business entails is crucial for any C-level executive aiming to steer their organization towards long-term success. At its core, a strategic plan is a comprehensive framework designed to outline an organization's vision, mission, and the strategies that will be employed to achieve these objectives over a specified period. This plan serves as a roadmap, guiding decision-making processes and resource allocation to ensure alignment with overarching goals. It is not merely a document but a dynamic tool that requires regular updates and revisions to reflect the changing business environment and organizational priorities.
The development of a strategic plan involves a meticulous process of analysis, including both internal and external environment assessments. This process enables an organization to identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis) and to craft strategies that leverage its unique capabilities to capitalize on market opportunities while mitigating risks. The strategic planning process typically encompasses setting long-term objectives, determining the most effective actions to achieve these goals, and allocating resources accordingly. A well-articulated strategic plan provides clarity and direction, fostering a sense of purpose and unity among employees.
Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of aligning the strategic plan with the digital transformation and innovation initiatives within an organization. In today’s fast-paced digital world, incorporating technology-driven strategies into the strategic plan is non-negotiable for maintaining relevance and achieving competitive differentiation. The strategic plan should, therefore, be flexible enough to adapt to technological advancements and market shifts, ensuring the organization remains agile and resilient in the face of disruption.
Key Components of a Strategic Plan
A strategic plan comprises several key components, each playing a critical role in the plan's overall effectiveness. The vision statement is a cornerstone, articulating a clear and inspirational long-term goal for the organization. Following closely is the mission statement, which defines the organization's purpose and its core values, guiding daily operations and decision-making. Objectives, both long-term and short-term, are specific, measurable goals that the organization aims to achieve, serving as milestones towards realizing the vision.
Strategy development is another crucial element, involving the formulation of actionable strategies to achieve the set objectives. This requires a deep understanding of the organization's internal capabilities and the external environment. Performance management systems are then put in place to track progress, measure outcomes, and ensure accountability. Lastly, the strategic plan must include a risk management framework to identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans, safeguarding the organization against unforeseen challenges.
Effective strategic planning also demands a robust governance structure to oversee the plan's implementation. This involves assigning roles and responsibilities, establishing clear lines of communication, and creating mechanisms for regular review and adjustment of the plan. A dynamic and responsive governance framework ensures the strategic plan remains relevant and aligned with the organization's evolving needs and objectives.
Implementing the Strategic Plan
Implementation is where many organizations face challenges. It requires meticulous planning, unwavering commitment, and a culture that embraces change. Leadership plays a pivotal role in this phase, driving the strategic initiatives forward and rallying the organization around the shared vision. Clear communication is critical to ensure that all stakeholders understand their roles and the importance of their contributions to the strategic objectives.
Change management is an integral part of the implementation process. It involves preparing the organization for the changes that come with executing the strategic plan, managing resistance, and ensuring a smooth transition. This often requires training programs to equip employees with the necessary skills and knowledge, as well as mechanisms to provide feedback and address concerns.
Monitoring and evaluation are also key to successful implementation. This involves setting up key performance indicators (KPIs) and regular reporting mechanisms to track progress against the strategic objectives. Data-driven insights gained from this process inform decision-making, allowing for course corrections and adjustments to the strategy as needed. Organizations must remain agile, ready to pivot their strategies in response to performance feedback and external changes.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a leading technology company that attributed its market dominance to its rigorous strategic planning process. By closely aligning its strategic plan with innovation and customer-centric strategies, the company was able to anticipate market trends and rapidly adapt its offerings, outpacing competitors and achieving sustained growth.
Another example is a global retail giant that leveraged its strategic plan to expand into new markets. Through careful analysis and strategic partnerships, the company executed a plan that capitalized on emerging market opportunities while mitigating risks associated with international expansion. This strategic approach enabled the company to quickly gain a foothold in new territories, driving revenue growth and expanding its global presence.
In conclusion, a strategic plan in business is a fundamental tool that guides an organization towards achieving its long-term vision and objectives. By providing a clear framework for decision-making and resource allocation, a strategic plan helps organizations navigate the complexities of the business environment, adapt to change, and achieve sustainable growth. C-level executives must therefore prioritize strategic planning, ensuring it is comprehensive, agile, and aligned with the organization's core values and objectives.
Understanding how to reduce inflation in a country requires a multifaceted approach that combines monetary policy, fiscal discipline, and structural reforms. Inflation, the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, can erode purchasing power and destabilize economies if left unchecked. For C-level executives and policymakers, the challenge is not only to mitigate inflation but also to do so in a way that sustains long-term economic growth and stability.
Monetary policy is often the first line of defense against rising inflation. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, can influence inflation by adjusting interest rates. Raising interest rates can help cool an overheating economy by making borrowing more expensive, which in turn can reduce spending and investment. However, this strategy must be employed judiciously, as overly aggressive rate hikes can lead to recession. The balance here is delicate, and timing is crucial. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Deloitte often emphasize the importance of data-driven decision-making in this context, advocating for a strategic approach to monetary tightening that is responsive to economic indicators.
Fiscal policy also plays a critical role in managing inflation. Government spending and taxation influence the amount of money circulating in the economy. By reducing government spending or increasing taxes, a country can decrease the total demand for goods and services, thereby putting downward pressure on prices. This strategy, however, must be balanced against the potential for negative impacts on economic growth and employment. Strategic Planning in this arena involves crafting policies that achieve the dual objectives of controlling inflation and supporting sustainable economic development.
Structural reforms are another key component of a comprehensive strategy to combat inflation. These reforms can include measures to increase market efficiency, improve regulatory frameworks, and enhance labor market flexibility. By increasing productivity and competition, structural reforms can help stabilize prices over the long term. For instance, deregulation in certain sectors can lead to increased competition and lower prices for consumers. Consulting giants like Accenture and PwC often work with governments to design and implement these reforms, leveraging their global expertise to tailor strategies to the specific needs of each country.
Implementing Technology and Innovation
Technology and innovation offer powerful tools for fighting inflation. Digital Transformation can lead to significant gains in Operational Excellence and productivity, which in turn can help control costs and prices. For example, advancements in supply chain management can reduce logistical costs, while automation can lower production costs. Organizations must prioritize Innovation as a core component of their strategy to combat inflation, leveraging technology to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
Moreover, the adoption of digital currencies and blockchain technology can provide central banks with new mechanisms for implementing monetary policy. These technologies can offer more direct control over the money supply and improve the effectiveness of policy measures. However, the integration of these technologies requires careful planning and risk management to avoid unintended consequences.
The role of data analytics in managing inflation cannot be overstated. By harnessing the power of big data, organizations and governments can gain insights into inflationary trends and develop more targeted interventions. Performance Management systems, powered by advanced analytics, can help policymakers monitor the impact of their actions in real-time and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Global Collaboration and Policy Coordination
In today's interconnected world, no country operates in isolation. Global economic dynamics can have a profound impact on national inflation rates. As such, international collaboration and policy coordination are essential for effectively managing inflation. Multilateral organizations, such as the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, play a crucial role in facilitating this cooperation, offering frameworks for dialogue and joint action.
Exchange rate policies are a prime example of an area where international coordination can be particularly beneficial. By working together to avoid competitive devaluations, countries can help stabilize global financial markets and mitigate inflationary pressures. Additionally, sharing best practices and lessons learned can accelerate the adoption of effective inflation control measures across countries.
Ultimately, reducing inflation in a country requires a comprehensive and coordinated approach that leverages monetary policy, fiscal discipline, structural reforms, and technological innovation. It demands strategic foresight, data-driven decision-making, and international cooperation. For C-level executives and policymakers, the challenge is to implement these strategies in a way that not only addresses inflation but also lays the foundation for sustainable economic growth and prosperity. By adopting a holistic and adaptive framework, countries can navigate the complexities of inflation management and secure a stable economic future.
Understanding how a vast demographic shift will reshape the world is crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in the upcoming decades. The global population is aging, birth rates in many countries are declining, and migration patterns are altering the demographic landscape significantly. These shifts have profound implications for market demand, labor forces, and consumer preferences. To stay ahead, strategic planning must evolve beyond traditional models to incorporate these demographic realities.
Firstly, organizations must refine their market analysis frameworks to include demographic trends. This involves not just looking at current customer demographics but projecting future changes and understanding their implications. For example, an aging population may indicate a growing market for healthcare services, retirement planning, and leisure activities targeted at older adults. On the other hand, countries with a youth bulge may see increased demand for education, entry-level employment opportunities, and digital entertainment. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Deloitte have emphasized the importance of demographic analysis in strategy development, highlighting how shifts in age, migration, and urbanization patterns necessitate a reevaluation of market opportunities and risks.
Secondly, workforce planning needs to adapt to these demographic shifts. As the working-age population shrinks in many developed countries, organizations may face talent shortages. This calls for a dual strategy of investing in automation and digital transformation to increase productivity, alongside developing more attractive employment propositions for both the existing workforce and potential migrants. Furthermore, with a more diverse workforce, companies must enhance their focus on inclusivity and flexibility to cater to a wider range of needs and preferences. Real-world examples include global corporations that have revamped their HR policies to offer flexible working conditions, lifelong learning opportunities, and comprehensive health and wellness programs.
Lastly, innovation in product and service offerings must take into account the changing needs and preferences of a demographically shifting world. This could mean designing products that are more accessible to older users, leveraging technology to meet the demands of tech-savvy younger generations, or tailoring products and marketing strategies to the cultural nuances brought about by increased global migration. The template for success in this area involves continuous market research, agile development processes, and a willingness to pivot strategies based on evolving demographic insights.
Framework for Adapting to Demographic Shifts
To effectively adapt to these demographic changes, organizations should employ a comprehensive framework that encompasses market analysis, workforce planning, and innovation. This framework should be dynamic, allowing for regular updates as new demographic data becomes available. Key components include:
- Detailed demographic forecasting to anticipate market needs and workforce trends.
- An agile strategic planning process that can quickly respond to new insights.
- Investment in technology and automation to mitigate workforce challenges.
- Enhanced focus on diversity and inclusion to attract and retain a broad talent pool.
- Continuous innovation in product and service offerings to meet changing consumer preferences.
Implementing this framework requires a commitment from the top down, with C-level executives playing a pivotal role in championing these changes. It also demands collaboration across departments to ensure that demographic insights are integrated into all aspects of strategic planning and operations.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Several leading organizations have already begun to adjust their strategies in response to demographic shifts. For instance, a multinational healthcare company has shifted its product development focus towards non-invasive monitoring devices and telehealth services, anticipating the needs of an aging global population. Similarly, a tech giant has launched digital literacy programs targeting older adults, recognizing the expanding market segment this demographic represents.
In the realm of workforce management, companies like Accenture and Google have set benchmarks for inclusivity and flexibility, offering remote work options, part-time roles, and comprehensive benefits that appeal to a diverse and changing workforce. These measures not only address current demographic challenges but also position these organizations as attractive employers for the future.
Adapting to demographic shifts is not optional for organizations aiming to remain competitive in the coming decades. It requires a proactive approach, leveraging detailed data analysis, strategic foresight, and a willingness to innovate. By recognizing how a vast demographic shift will reshape the world, organizations can turn potential challenges into opportunities for growth and development.
Developing a Business Plan and Strategic Planning are two critical, yet distinct, processes that organizations undertake to ensure their long-term success and operational effectiveness. While they are interconnected, each serves a different purpose and requires a unique approach for maximum effectiveness.
Understanding the Differences
The development of a Business Plan is fundamentally about detailing the operational and financial objectives of an organization and the specific plans to achieve these goals. It is a document that outlines an organization's vision, mission, and the tactical measures needed to attain its financial projections. Business Plans are often used to secure investment or loans and serve as a roadmap for internal management to guide growth and development. They typically cover a shorter time frame, usually one to three years, and are more detailed in the financial and operational planning aspects.
Strategic Planning, on the other hand, focuses on setting long-term goals and determining the actions and resources required to achieve them. It involves a deep analysis of the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis) to craft strategies that will enable it to compete effectively in its market. Strategic Planning is more about the direction in which an organization needs to move to achieve long-term success and sustainability. It is broader in scope, often encompassing a three to five-year horizon, or even longer.
While a Business Plan might be more focused on the "how" of reaching immediate operational goals, Strategic Planning is concerned with the "what" and "why" of an organization's long-term direction. Both are crucial for an organization's success but require different approaches and considerations.
Approaching Business Plan Development
To develop an effective Business Plan, organizations should start by conducting a thorough market analysis to understand their industry, competitors, and target market deeply. This analysis should inform the development of clear, measurable objectives that align with the organization's financial goals and operational capabilities. It's essential to be realistic about what can be achieved and to outline detailed strategies for sales, marketing, operations, and finance that are aligned with these objectives.
Financial projections are a critical component of any Business Plan. These should include detailed forecasts for income, cash flows, and balance sheets, grounded in realistic assumptions about the market and the organization's capacity. According to a report by McKinsey, organizations that regularly update their financial forecasts and assumptions tend to outperform their peers significantly, highlighting the importance of dynamic financial planning.
Finally, the Business Plan should be reviewed and updated regularly. The market conditions, competitive landscape, and internal capabilities of an organization can change rapidly, necessitating adjustments to the plan. This dynamic approach ensures that the organization remains on track to achieve its objectives and can adapt to new opportunities or challenges as they arise.
Approaching Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning requires a broad, long-term view and should start with a clear articulation of the organization's vision and mission. These foundational elements provide the direction for the strategic objectives and the overall plan. Engaging stakeholders across the organization in this process ensures that the plan is comprehensive and aligns with the broader goals of the organization.
An effective Strategic Planning process involves a rigorous analysis of the external and internal environment of the organization. Tools like SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and Porter's Five Forces can provide valuable insights into the market dynamics, regulatory landscape, and competitive pressures. This analysis helps in identifying strategic opportunities and threats and is critical for developing a resilient strategy that can adapt to changes in the business environment.
Implementation and monitoring are where many Strategic Plans fail to deliver. Setting up clear metrics for success and regular review points is crucial. According to Bain & Company, organizations that effectively align their strategic planning process with their execution and use a balanced scorecard for performance management significantly increase their chances of success. Regularly revisiting the strategy, engaging in scenario planning, and being prepared to pivot as necessary are key components of a dynamic Strategic Planning process.
In practice, the development of a Business Plan and Strategic Planning are intertwined processes. For example, Amazon's approach to continuously evolving its business model while maintaining a clear long-term vision demonstrates the importance of aligning detailed operational planning with a broader strategic framework. Similarly, Apple's focus on innovation and customer experience underpins both its strategic direction and its operational priorities, illustrating how these planning processes can reinforce each other for maximum effectiveness.
Creating an effective strategic planning presentation is crucial for leaders aiming to communicate their vision and roadmap for the organization's future. This task demands a blend of analytical rigor, strategic insight, and compelling storytelling. The goal is to not only present a plan but to inspire action, align stakeholders, and set the stage for implementation. To achieve this, executives must leverage a structured framework, grounded in consulting best practices, while also personalizing the approach to resonate with their specific audience.
At the outset, it's essential to establish a clear understanding of the strategic context. This involves a thorough analysis of internal capabilities and external opportunities and threats. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of leveraging data-driven insights to inform strategy development. A strategic planning presentation should begin with a succinct overview of the market dynamics, highlighting key trends, challenges, and opportunities. This sets the stage for a compelling narrative that explains why change is necessary and what the organization stands to gain.
The core of the presentation should articulate the strategic vision and objectives. This is where a well-defined framework comes into play. Utilize a template that breaks down the strategy into manageable components—such as goals, key initiatives, and performance metrics. This approach not only clarifies the strategy but also facilitates easier digestion and recall by the audience. Each strategic objective should be linked to specific actions and outcomes, demonstrating a clear path from the current state to the desired future state. Real-world examples of successful strategic transformations can be powerful in illustrating these points and providing a model for what's possible.
Finally, the presentation must address implementation. This includes outlining the governance structure, resource allocation, and timelines. It's critical to present a realistic and detailed plan for how the strategy will be executed. This section should also cover risk management and contingency planning, acknowledging potential challenges and how they will be mitigated. The aim is to leave the audience with confidence in the feasibility of the plan and the organization's capacity to execute it effectively.
Engaging Your Audience
Knowing how to make a strategic planning presentation engaging is as important as the content itself. Start by tailoring the presentation to your audience. C-level executives, for instance, will appreciate a focus on high-level outcomes and strategic fit, while operational teams might value detailed action plans and role-specific implications. Use storytelling techniques to weave a narrative that connects emotionally with the audience, making the strategic vision feel not only logical but also inspiring.
Visual aids are another critical element. Charts, graphs, and infographics can convey complex information more effectively than text-heavy slides. However, it's important to balance visual elements with content to avoid overwhelming the audience. Consulting firms often use a "less is more" approach, selecting a few impactful visuals to support key points. This helps to maintain focus and facilitates a clearer understanding of the strategy.
Interactivity can also enhance engagement. Encourage questions and discussions throughout the presentation to foster a sense of ownership and alignment among stakeholders. This dialogue can provide valuable feedback and insights, which can be used to refine and improve the strategic plan.
Measuring Success
An often-overlooked aspect of strategic planning presentations is setting the stage for ongoing performance management. It's not enough to launch a strategy; its success depends on continuous monitoring and adaptation. Include a section on how progress will be measured, detailing the key performance indicators (KPIs) and review mechanisms that will be used. This not only underscores the organization's commitment to the strategy but also establishes accountability.
Consulting leaders like Deloitte and PwC stress the importance of a dynamic approach to strategy execution. This involves regular strategy reviews and adjustments based on performance data and changing market conditions. By incorporating this mindset into the presentation, leaders can demonstrate strategic agility and the ability to pivot as necessary to achieve strategic objectives.
In conclusion, crafting an effective strategic planning presentation requires a balance of analytical depth, strategic clarity, and engaging storytelling. By following a structured framework, tailoring the message to the audience, and emphasizing implementation and performance management, leaders can inspire confidence and drive strategic action. Remember, the ultimate goal is not just to present a plan, but to mobilize the organization towards a shared vision of success.
Ensuring alignment between Digital Transformation initiatives and overarching Strategic Goals is a critical challenge for executives today. Digital Transformation is not just about adopting new technologies but about reimagining existing business models, processes, and strategies to drive innovation and efficiency. However, without a clear alignment with the organization's Strategic Goals, these initiatives can lead to wasted resources, misaligned priorities, and missed opportunities.
Establishing a Clear Vision and Strategic Framework
The first step in aligning Digital Transformation initiatives with Strategic Goals is to establish a clear vision and strategic framework. This involves defining what Digital Transformation means for the organization and how it supports the broader business objectives. A strategic framework should articulate the key drivers of transformation, such as customer experience, operational efficiency, or innovation, and map these drivers to specific business outcomes.
According to McKinsey, organizations that succeed in digital transformation are those that have a clear definition of their transformation’s objectives. McKinsey’s research also shows that companies with successful transformations have a clear narrative that is well communicated across the organization. This narrative not only outlines the vision but also the strategic importance of the transformation in achieving the organization's long-term goals.
Leadership plays a critical role in developing and communicating this vision. Executives must be actively involved in the Strategic Planning process, ensuring that the Digital Transformation initiatives are not just technology projects but strategic business initiatives that are integral to the organization's future success.
Aligning Organizational Structures and Governance
To ensure alignment between Digital Transformation initiatives and Strategic Goals, organizations must also align their structures and governance models. This means integrating Digital Transformation into the core strategic planning and decision-making processes, rather than treating it as a separate or parallel effort. A cross-functional steering committee or a dedicated Digital Transformation office can help oversee the alignment of digital initiatives with strategic objectives.
Accenture highlights the importance of governance in ensuring that digital investments are aligned with business priorities. Their research suggests that organizations with strong governance frameworks are more likely to report successful Digital Transformation outcomes. This involves establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability for Digital Transformation efforts, ensuring that these initiatives have the necessary oversight and direction to stay aligned with strategic goals.
Moreover, fostering a culture of collaboration across business units and functions is essential. Digital Transformation often requires changes across different parts of the organization. By breaking down silos and encouraging cross-functional teams to work together, organizations can ensure that Digital Transformation initiatives are integrated into the broader business strategy and contribute to shared goals.
Measuring Success and Adapting to Change
Another critical aspect of aligning Digital Transformation initiatives with Strategic Goals is establishing metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that reflect both digital and strategic objectives. These metrics should be designed to measure the impact of Digital Transformation on the organization's strategic priorities, such as growth, customer satisfaction, or operational efficiency.
Gartner emphasizes the importance of measurement in Digital Transformation success. Their research indicates that organizations that define and monitor the right metrics are more likely to achieve the desired outcomes from their Digital Transformation efforts. This includes not only traditional financial metrics but also more nuanced indicators of digital maturity, such as digital revenue growth, customer engagement levels, or innovation rates.
However, it is also important for organizations to remain flexible and adaptable. The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and what may seem like a strategic priority today could change tomorrow. Regularly reviewing and adjusting Digital Transformation initiatives in response to new information, market trends, or changes in strategic direction is crucial. This agility allows organizations to pivot as needed and ensures that Digital Transformation efforts remain aligned with the overarching Strategic Goals.
Real-World Examples
Many leading organizations have successfully aligned their Digital Transformation initiatives with their Strategic Goals. For example, Walmart’s investment in e-commerce and digital technologies was directly aligned with its strategic goal of expanding its market share and improving customer experience. By integrating digital initiatives into its core business strategy, Walmart was able to significantly enhance its online presence and compete more effectively with digital-first retailers.
Similarly, General Electric’s (GE) Digital Transformation, centered around its Predix platform, was closely aligned with its strategic goal of leading in the industrial internet. GE integrated digital capabilities across its product lines and services, leveraging data and analytics to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and create new revenue streams. This strategic alignment enabled GE to position itself as a leader in the digital industrial space.
In conclusion, aligning Digital Transformation initiatives with overarching Strategic Goals requires a clear vision, aligned organizational structures and governance, measurable outcomes, and the agility to adapt to change. By focusing on these key areas, executives can ensure that their Digital Transformation efforts drive meaningful business outcomes and contribute to the long-term success of the organization.
Integrating Virtual Reality (VR) into an organization's operations or customer service is not merely about adopting new technology; it's about embracing a transformative tool that can redefine the competitive landscape. The strategic planning for VR integration requires a comprehensive approach that aligns with the organization's overall objectives, leverages competitive advantages, and anticipates the future direction of the industry.
Understanding the Strategic Importance of VR
The first step in planning for VR integration is recognizing its strategic importance. VR technology has moved beyond gaming and entertainment, proving its value in training, education, product development, and customer engagement across various industries. For instance, in healthcare, VR is used for surgical training and patient therapy, offering a risk-free environment for practitioners and a comforting space for patients. In retail, VR enables customers to visualize products in a 3D space, enhancing their purchasing confidence and satisfaction. Acknowledging VR's potential to revolutionize business models, improve operational efficiency, and create unique customer experiences is crucial for strategic planning.
Organizations must conduct a thorough market analysis to understand the current and potential applications of VR in their industry. This involves examining competitors' strategies, identifying customer needs and expectations, and assessing the technological landscape. By doing so, organizations can pinpoint where VR can add the most value, whether in designing new products, improving service delivery, or creating immersive marketing campaigns.
Strategic planning for VR also requires an evaluation of the organization's readiness to adopt this technology. This includes assessing the existing technological infrastructure, the skills and competencies of the workforce, and the organization's culture towards innovation. A gap analysis can help identify areas that need development or investment to support VR integration effectively.
Developing a VR Integration Roadmap
Once the strategic importance of VR is understood, the next step is to develop a VR integration roadmap. This plan should outline the specific goals and objectives of VR adoption, aligned with the organization's broader strategic aims. Whether the goal is to enhance product design, streamline operations, or offer groundbreaking customer experiences, it must be clearly defined and measurable.
The roadmap should detail the stages of VR integration, from pilot projects and proof of concepts to full-scale implementation. Starting with small, manageable projects can help the organization learn and adapt, reducing the risks associated with new technology adoption. For example, a retailer might first introduce VR in a single store to refine the customer experience before rolling it out across all locations.
Investment in the necessary technology and skills development is a critical component of the VR integration roadmap. This includes not only the VR hardware and software but also the training programs for employees to effectively use and support the technology. Partnerships with VR technology providers and specialized consultants can accelerate the learning curve and ensure the organization has access to the latest innovations and best practices.
Ensuring Organizational Alignment and Support
For VR integration to be successful, it must have the support and alignment of the entire organization. This starts with leadership commitment to champion the initiative, allocate resources, and foster a culture of innovation. Leaders should communicate the strategic importance of VR, its expected benefits, and how it fits into the organization's future vision to garner support from all levels of the organization.
Change management is a critical aspect of ensuring organizational alignment and support for VR integration. This involves preparing the workforce for the changes, addressing concerns and resistance, and building the necessary skills and competencies. Engaging employees early in the process, involving them in pilot projects, and providing opportunities for feedback can facilitate a smoother transition.
Finally, measuring the impact of VR integration is essential for demonstrating its value and guiding future investments. Organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) related to VR objectives, such as improved operational efficiency, increased sales, or enhanced customer satisfaction. Regular monitoring and reporting on these KPIs will help assess the effectiveness of VR initiatives and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, strategically planning for the integration of VR into operations or customer service is a multifaceted process that requires a deep understanding of the technology's potential, a clear roadmap for implementation, and strong organizational alignment and support. By carefully considering these elements, organizations can harness the power of VR to transform their operations, differentiate themselves in the market, and deliver unparalleled customer experiences.
Understanding the ecosystem in the context of strategic business management is pivotal for any C-level executive aiming to navigate the complexities of today's market dynamics. An ecosystem strategic model refers to the framework that organizations use to analyze, design, and implement strategies that leverage the relationships and interdependencies within their business ecosystem. This ecosystem comprises various stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, competitors, and other entities that directly or indirectly influence the organization's ability to create and capture value.
The concept of an ecosystem strategic model moves beyond traditional strategic planning, emphasizing the importance of collaborative and adaptive approaches. In this model, the focus shifts from competing against rivals in a zero-sum game to fostering a network of partnerships and alliances that can enhance innovation, efficiency, and market reach. The key is to determine the ecosystem strategic model that aligns with the organization's goals, capabilities, and market position, enabling it to thrive amidst the complexities of the digital age.
Frameworks and templates for ecosystem strategy development often include mapping the ecosystem to identify key players and their roles, assessing the value each entity brings, and identifying potential opportunities for collaboration or co-opetition (cooperative competition). Consulting firms like McKinsey and Accenture have highlighted the significance of digital ecosystems, for instance, in enabling organizations to offer more comprehensive solutions through partnerships, thereby driving growth and enhancing customer experiences. These insights underscore the need for a strategic approach that is both holistic and flexible, capable of adapting to changes within the ecosystem.
Key Components of an Ecosystem Strategic Model
When looking to determine the ecosystem strategic model that best suits an organization, several key components must be considered. First and foremost, understanding the ecosystem's structure is essential. This involves identifying the various stakeholders, their roles, and the nature of their interactions. It's about mapping out the ecosystem to visualize how value flows within it and where the organization fits within this structure.
Second, strategy development within an ecosystem context requires a clear articulation of the organization's value proposition to the ecosystem. This goes beyond traditional value propositions to customers, focusing on what the organization brings to the ecosystem as a whole—be it innovation, market access, or operational excellence. The goal is to position the organization as an indispensable player within the ecosystem.
Lastly, governance mechanisms are crucial for managing relationships within the ecosystem. These mechanisms can range from formal contractual agreements to more informal collaborative arrangements. They serve to align interests, manage conflicts, and facilitate the co-creation of value among ecosystem participants. Effective governance ensures that the ecosystem remains resilient and adaptable to changes in the market or technology landscape.
Implementing an Ecosystem Strategy
Implementation of an ecosystem strategic model requires a shift in mindset from a focus on internal capabilities to an outward-looking, collaborative approach. Organizations must be willing to share insights, resources, and even revenues with ecosystem partners to co-create value. This often involves investing in digital platforms and technologies that enable seamless collaboration and data sharing among ecosystem participants.
Moreover, leadership and culture play a critical role in the successful adoption of an ecosystem strategy. Leaders must champion a vision of collaboration and openness, fostering a culture that values partnership and collective success over individual achievement. This cultural shift can be challenging but is essential for organizations looking to thrive in complex ecosystems.
Real-world examples of successful ecosystem strategies abound. Tech giants like Apple and Amazon have built extensive ecosystems around their products and services, leveraging partnerships with app developers, content creators, and third-party retailers to offer unparalleled value to customers. These examples highlight the potential of ecosystem strategies to drive innovation, scale, and customer satisfaction in today's interconnected world.
In conclusion, understanding what is the ecosystem and determining the ecosystem strategic model is crucial for organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of the modern market. By focusing on collaboration, adaptability, and co-creation of value, organizations can position themselves for sustained success in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Understanding why we need to plan is critical for any organization aiming for long-term success and adaptability. Strategic planning, a disciplined effort to produce fundamental decisions and actions shaping an organization's future, is a cornerstone of sustainable growth. It provides a framework for organizations to set priorities, allocate resources, and ensure that stakeholders are working toward common goals. In today's rapidly changing business environment, the absence of a strategic plan can leave an organization directionless, vulnerable to external pressures, and unable to capitalize on opportunities.
Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of strategic planning in navigating the complexities of global markets and technological advancements. A strategic plan acts as a roadmap, guiding an organization through its growth phases while allowing for real-time adjustments in response to market dynamics. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining relevance and achieving operational excellence. Moreover, strategic planning facilitates risk management by identifying potential threats and opportunities, enabling organizations to prepare and respond effectively rather than reactively.
The process of strategic planning involves setting objectives, analyzing competitive dynamics, and defining strategic initiatives. This structured approach ensures that every aspect of the organization is aligned with its overall strategy, from financial management to talent development. By establishing clear metrics for success and regularly reviewing progress, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. This alignment between strategy and execution is what ultimately drives long-term success and competitive positioning in the market.
Frameworks and Templates in Strategic Planning
Frameworks and templates play a pivotal role in the strategic planning process, offering a structured approach to strategy development and implementation. Consulting firms often provide proprietary models that help organizations analyze their situation, identify strategic options, and make informed decisions. For example, the use of SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis or the Boston Consulting Group Matrix enables organizations to evaluate their position and focus their efforts on areas with the highest potential for growth and impact.
Adopting a proven strategic planning template ensures that critical elements are not overlooked and that the planning process is conducted systematically. This consistency is vital for organizations with complex operations or those operating in multiple markets. It allows for the standardization of strategic planning activities across different departments and geographies, ensuring that all parts of the organization are aligned with the overarching strategy.
Moreover, these frameworks facilitate communication and collaboration among stakeholders by providing a common language and reference points. This is essential for securing buy-in and ensuring that the strategic plan is executed effectively. By leveraging these tools, organizations can enhance their strategic agility, enabling them to pivot quickly in response to changes in the external environment.
Real-World Examples of Strategic Planning Success
Several leading organizations attribute their long-term success and adaptability to rigorous strategic planning. For instance, Apple's approach to innovation and market expansion is underpinned by a clear strategic plan that focuses on creating high-quality products and entering new markets judiciously. This strategic discipline has allowed Apple to maintain its market leadership and continue to grow in a highly competitive industry.
Another example is Amazon, which has successfully diversified its business portfolio through strategic planning. By identifying and entering into new markets such as cloud computing and e-commerce fulfillment, Amazon has not only increased its revenue streams but also enhanced its resilience against market fluctuations. These strategic moves were the result of careful planning and analysis, demonstrating the power of strategic planning in driving business transformation and long-term success.
In conclusion, strategic planning is indispensable for any organization aiming to thrive in today's dynamic business environment. It provides a framework for decision-making, promotes alignment and efficiency, and enhances an organization's ability to adapt and innovate. By leveraging strategic planning frameworks and templates, and learning from real-world success stories, organizations can navigate the complexities of the market and achieve sustainable growth. The question of why we need to plan is answered by the tangible benefits that strategic planning brings to organizations, making it a critical component of effective management and leadership.
Organizational culture plays a pivotal role in the successful integration of sustainability into Strategic Planning. It serves as the bedrock upon which strategies for sustainability are built, communicated, and implemented. The culture of an organization influences how sustainability initiatives are perceived, valued, and adopted by its members. This integration requires a shift in mindset from viewing sustainability as an add-on or compliance requirement to seeing it as a core component of the organization's identity and strategy.
Understanding the Role of Organizational Culture
Organizational culture is the collection of values, expectations, and practices that guide and inform the actions of all team members. It is the social glue that binds the organization together. When it comes to integrating sustainability into Strategic Planning, the culture of an organization can either act as a catalyst or a barrier. A culture that promotes innovation, flexibility, and long-term thinking is more likely to successfully integrate sustainability because these values align with the principles of sustainable development. Conversely, a culture that prioritizes short-term gains and has rigid processes may resist the changes required for sustainable integration.
For instance, a McKinsey report highlights the importance of aligning sustainability with the core business strategy and embedding it into the organizational culture. The report suggests that sustainability should be seen not just as a way to mitigate risks or comply with regulations, but as an opportunity to innovate, create value, and build competitive advantage. This perspective shift requires a cultural transformation that values sustainability as a key driver of business success.
Moreover, leadership plays a critical role in shaping the organizational culture to embrace sustainability. Leaders who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through their decisions, investments, and communications help cultivate a culture that values and prioritizes sustainable practices. This top-down approach is essential for embedding sustainability into the fabric of the organization.
Strategic Planning and Sustainability Integration
Strategic Planning is a systematic process for envisioning a desired future and translating this vision into broadly defined goals or objectives and a sequence of steps to achieve them. When sustainability is integrated into Strategic Planning, it ensures that sustainable development principles guide decision-making processes at all levels of the organization. This integration requires a clear understanding of how sustainability impacts the organization's strategic goals, operations, and stakeholder relationships.
According to a report by the Boston Consulting Group (BCG), companies that effectively integrate sustainability into their core business strategy can unlock significant value, including enhanced brand reputation, increased operational efficiencies, and improved risk management. The report emphasizes the need for organizations to align their sustainability efforts with their strategic priorities and to embed sustainability considerations into all aspects of their strategic planning process.
The integration of sustainability into Strategic Planning also involves setting clear sustainability goals, developing metrics to measure progress, and establishing accountability mechanisms. This requires a cultural shift towards transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement. Organizations that successfully navigate this shift are better positioned to respond to the evolving expectations of customers, investors, and regulators regarding sustainability.
Real-World Examples of Successful Integration
Several leading organizations have demonstrated how a strong organizational culture can facilitate the successful integration of sustainability into Strategic Planning. For example, Patagonia, a company renowned for its commitment to environmental sustainability, has embedded this commitment into every aspect of its operations and strategic planning. Patagonia's culture of responsibility towards the planet guides its product design, supply chain decisions, and customer engagement strategies. This alignment between culture and strategy has not only enhanced Patagonia's brand reputation but also contributed to its financial success.
Another example is Unilever, a global consumer goods company, which has placed sustainability at the heart of its business strategy. Unilever's Sustainable Living Plan aims to decouple the company's growth from its environmental footprint, while increasing its positive social impact. This ambitious plan is supported by a culture that values sustainability, innovation, and long-term value creation. Unilever's leadership in sustainability has been recognized by its inclusion in the Dow Jones Sustainability Index, a testament to the successful integration of sustainability into its strategic planning and organizational culture.
In conclusion, the role of organizational culture in the successful integration of sustainability into Strategic Planning cannot be overstated. A culture that values sustainability, innovation, and long-term thinking is essential for organizations looking to embed sustainable development principles into their strategic planning processes. Leadership commitment, clear sustainability goals, and alignment between sustainability and strategic priorities are key factors in this integration. As demonstrated by companies like Patagonia and Unilever, when sustainability is deeply embedded in the organizational culture, it can drive innovation, enhance brand reputation, and create long-term value for both the organization and society.
Formulating an effective research problem statement is a critical first step in the research process, laying the groundwork for all subsequent research activities. It serves as a concise encapsulation of the issue that the research aims to address, guiding the research strategy and influencing the design of the research framework. An effectively crafted problem statement not only clarifies the research objectives but also ensures alignment with the organization's strategic goals, making it a pivotal element in the success of any research project.
The process of how to formulate a problem statement in research begins with a thorough understanding of the context and the specific issue at hand. This requires a deep dive into existing literature, market trends, and organizational data to identify gaps in knowledge or unaddressed challenges that the research could tackle. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of leveraging data analytics and industry insights to pinpoint these gaps accurately. For instance, a report by Gartner might reveal emerging trends in consumer behavior that are not yet fully understood, presenting an opportunity for research.
Once the initial exploration is complete, the next step involves articulating the problem in a clear, concise, and specific manner. A well-defined problem statement should outline the scope of the research, the objectives, and the potential impact of the findings. It should be direct and to the point, avoiding any ambiguity that could mislead the research direction. The use of a structured framework or template can be invaluable in this phase, helping to organize thoughts and ensure that all critical elements of the problem statement are addressed.
It is also essential for the problem statement to be relevant and significant to the organization's strategic objectives. This alignment ensures that the research efforts are not only academically interesting but also practically valuable, offering insights that can drive decision-making and strategy development. The problem statement should make a compelling case for why the research is necessary, highlighting the potential benefits and implications of the findings for the organization.
Key Components of a Research Problem Statement
A robust research problem statement typically includes several key components. First, it should start with a background that sets the stage for the problem, providing context and highlighting the relevance of the issue. This background should be grounded in factual data and insights from authoritative sources, establishing the foundation for the research.
The next component is the statement of the problem itself, which should be articulated clearly and succinctly. This statement should identify the specific gap in knowledge or unmet need that the research aims to address. It is crucial to be precise in defining the problem, avoiding broad or vague descriptions that could dilute the focus of the research.
Finally, the problem statement should outline the objectives of the research, specifying what the study aims to achieve. These objectives should be SMART—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound—providing a clear roadmap for the research process. Additionally, the statement should hint at the potential implications of the research findings, underscoring the importance of the study and its potential impact on the organization.
Real-World Examples and Frameworks
In the realm of consulting, the use of frameworks and templates is commonplace for structuring problem statements. For instance, the PESTEL analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal) is often employed to explore external factors that could influence the research problem. Similarly, the SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) can help in identifying internal and external aspects relevant to the problem statement.
Consider the example of a retail organization facing declining sales. Through initial research and data analysis, it might uncover that the drop is significantly pronounced in its online sales channel. The problem statement could then focus specifically on identifying the factors contributing to the decline in online sales, with objectives centered around understanding consumer behavior, evaluating the effectiveness of current marketing strategies, and exploring potential technological solutions.
Another example could be a healthcare provider looking to improve patient satisfaction scores. By leveraging patient feedback and industry benchmarks, the organization can formulate a problem statement focused on identifying the key drivers of patient dissatisfaction and developing strategies to address these issues.
In conclusion, crafting an effective research problem statement is a nuanced process that requires a strategic approach, deep understanding of the organization's goals, and a clear vision of the research's potential impact. By following a structured framework and incorporating specific, detailed, and actionable insights, organizations can set the stage for meaningful research that drives strategic decision-making and fosters innovation.
Hoshin Kanri, also known as Policy Deployment, is a strategic planning process that aligns an organization's functions and activities with its strategic objectives. It emphasizes a coherent direction that combines the efforts of all employees, from top management to front-line workers, towards achieving long-term goals. Measuring the effectiveness of Hoshin Kanri in achieving strategic objectives involves a multi-faceted approach, focusing on both the process and the outcomes.
Setting Clear Metrics and Targets
The first step in measuring the effectiveness of Hoshin Kanri is to establish clear, measurable objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with the strategic goals. These metrics should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For instance, if a strategic objective is to improve customer satisfaction, relevant KPIs might include Net Promoter Score (NPS) or customer satisfaction scores (CSAT). It's important that these metrics are communicated clearly to all levels of the organization to ensure alignment and focus.
Organizations can track progress against these metrics using a balanced scorecard approach, which provides a comprehensive view of performance across different areas of the business. This method allows leaders to see how well the strategic objectives are being met and where adjustments may be needed. For example, Accenture has highlighted the importance of balanced scorecards in providing a holistic view of organizational performance, enabling better strategic decision-making.
Furthermore, setting interim milestones is crucial for long-term objectives. These milestones serve as checkpoints to assess progress and make necessary adjustments. This iterative process ensures that the organization remains agile and can respond to changes in the external environment or internal performance issues.
Engagement and Alignment Across the Organization
Another key aspect of measuring the effectiveness of Hoshin Kanri is assessing the level of engagement and alignment across the organization. This involves evaluating how well the strategic objectives have been communicated and whether employees understand their role in achieving these goals. Surveys and feedback mechanisms can be valuable tools for gauging employee alignment and engagement. For instance, regular pulse surveys can provide insights into whether employees feel they are contributing to the strategic objectives and if they understand the direction in which the organization is headed.
Alignment workshops and cross-functional team meetings are also effective in ensuring that all departments and teams are working towards the same goals. These forums allow for the sharing of ideas, addressing of concerns, and clarification of roles and responsibilities. PwC has emphasized the importance of alignment in strategy execution, noting that organizations with high levels of alignment and collaboration are more likely to achieve their strategic objectives.
Additionally, leadership plays a critical role in fostering alignment and engagement. Leaders must be champions of the Hoshin Kanri process, consistently communicating the strategic objectives and how each team and individual contributes to these goals. Leadership commitment is essential for maintaining focus and momentum towards achieving strategic objectives.
Continuous Improvement and Learning
Measuring the effectiveness of Hoshin Kanri is not only about assessing outcomes but also about evaluating the process itself. Continuous improvement is a core principle of Hoshin Kanri, and organizations should regularly review and refine their strategic planning and execution processes. This includes analyzing what worked well, what didn't, and why. For example, a retrospective analysis might reveal that certain objectives were not achieved due to unrealistic time frames or insufficient resources, leading to adjustments in future planning cycles.
Learning from both successes and failures is crucial. Organizations should foster a culture that values feedback and learning, where employees feel empowered to share their insights and suggestions for improvement. This culture of continuous learning can be facilitated through after-action reviews, lessons learned sessions, and innovation workshops. Deloitte has highlighted the importance of a learning culture in driving organizational agility and resilience, enabling organizations to adapt and thrive in a rapidly changing environment.
Finally, leveraging technology and data analytics can significantly enhance the measurement of Hoshin Kanri's effectiveness. Advanced analytics and business intelligence tools can provide real-time insights into performance against strategic objectives, identify trends, and predict potential roadblocks. This data-driven approach enables more informed decision-making and strategic adjustments, ensuring that the organization remains on track towards achieving its long-term goals.
In conclusion, measuring the effectiveness of Hoshin Kanri in achieving strategic objectives requires a comprehensive approach that includes setting clear metrics and targets, ensuring engagement and alignment across the organization, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement and learning. By focusing on both the outcomes and the process, organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of strategic execution and achieve sustainable success.
Developing a comprehensive business strategy plan is essential for aligning with long-term organizational goals. This process requires a deep understanding of what a business strategy plan entails, a robust framework for strategy development, and the application of best practices from consulting leaders. A business strategy plan outlines the actions and decisions an organization must take to reach its objectives and fulfill its mission. It serves as a roadmap, guiding the organization through the complexities of its operating environment while focusing on future growth and sustainability.
The first step in crafting a comprehensive business strategy plan involves conducting a thorough analysis of the organization's current state, including its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis). This analysis provides a solid foundation for understanding the internal and external factors that could impact the organization's ability to achieve its long-term goals. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of this diagnostic phase, as it highlights critical areas for improvement and potential market opportunities.
Following the initial analysis, the next step is to define clear, measurable objectives that align with the organization's vision and mission. These objectives should be ambitious yet achievable, with specific timelines for accomplishment. Setting these goals requires input from all levels of the organization to ensure buy-in and to reflect the collective ambition of the team.
Once objectives are set, the organization must develop a strategic framework to achieve these goals. This framework includes identifying the key initiatives, resources, and investments needed to move the needle. It also involves outlining the roles and responsibilities of different teams and individuals, ensuring accountability across the organization. A well-defined framework acts as a template that guides decision-making and prioritization of efforts.
Implementing the Strategy
With a clear strategy in place, the focus shifts to implementation. This phase is often where organizations face the most challenges, as it requires meticulous planning, effective change management, and ongoing performance management. According to Accenture, successful strategy implementation hinges on the organization's ability to adapt to change and to maintain alignment between strategy and execution.
Implementation plans should detail the specific actions, timelines, and resources required to achieve each strategic objective. This includes establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and to identify areas needing adjustment. Regular progress reviews are essential, allowing leadership to stay informed and to make data-driven decisions.
Effective communication throughout the organization is critical during this phase. Leaders must ensure that all team members understand their roles in executing the strategy and how their work contributes to the organization's overall goals. This fosters a culture of accountability and collaboration, driving collective efforts towards achieving strategic objectives.
Monitoring and Adapting the Strategy
A business strategy plan is not a set-and-forget document. It requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to remain relevant in a rapidly changing business environment. This means regularly reviewing the organization's strategic performance against its objectives and making necessary adjustments to the plan.
Technological advancements, market shifts, and competitive dynamics can all necessitate changes to the strategy. Organizations must remain agile, ready to pivot their strategies in response to these external pressures. For instance, digital transformation initiatives have become a top priority for many organizations, driven by the need to enhance operational efficiency and to meet evolving customer expectations.
Finally, it's crucial to foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within the organization. Encouraging employees to contribute ideas and to challenge the status quo can uncover new opportunities for growth and efficiency. This culture acts as a catalyst for sustaining long-term strategic success, ensuring the organization remains competitive and aligned with its long-term goals.
In conclusion, developing a comprehensive business strategy plan is a dynamic, ongoing process that requires careful planning, execution, and adaptation. By understanding the components of a successful strategy, implementing it effectively, and remaining adaptable, organizations can ensure alignment with their long-term goals and achieve sustained success.
Developing a robust strategic plan is a critical endeavor for any organization aiming to align its operations with long-term goals. The process requires a deep understanding of the organization's current position, its desired future state, and the steps necessary to bridge the gap between the two. This journey involves several key steps, each demanding meticulous attention to detail and strategic foresight.
The first step in how to develop a strategic plan involves conducting a comprehensive analysis of the organization's internal and external environments. This analysis, often encapsulated by a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) framework, provides a solid foundation for understanding the organization's current capabilities, market position, and external factors influencing its operations. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of this analysis as it helps in identifying critical areas for improvement and potential growth opportunities. It's not just about looking inward but also understanding the broader market dynamics, customer needs, and competitive forces at play.
Following the initial analysis, setting clear, measurable, and achievable goals is paramount. These goals should be directly aligned with the organization's vision and mission, ensuring that every strategic initiative undertaken contributes to the broader objectives. This step requires a delicate balance between ambition and realism, pushing the organization to stretch its capabilities while remaining achievable. Performance Management frameworks come into play here, providing a template for tracking progress against these goals and ensuring accountability throughout the organization.
With a clear understanding of the organization's current state and desired future, the next step involves crafting a detailed strategy to achieve these goals. This involves identifying specific initiatives, allocating resources efficiently, and establishing timelines for execution. Strategy Development is not a one-size-fits-all process; it requires customization to fit the unique needs and context of the organization. Consulting firms often utilize bespoke frameworks to guide this process, ensuring that the strategy is comprehensive, actionable, and aligned with the organization's long-term vision.
Engaging Stakeholders and Building Consensus
Strategic planning is not an isolated exercise; it requires the active involvement and buy-in of stakeholders across the organization. From C-level executives to frontline employees, everyone's engagement is crucial for the successful implementation of the strategic plan. This step involves transparent communication of the strategic vision, goals, and the rationale behind specific strategic initiatives. Building consensus is key to overcoming resistance to change and ensuring that everyone is aligned towards the common objectives.
Moreover, stakeholder engagement provides valuable insights and perspectives that can refine and enhance the strategic plan. It fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation, encouraging employees to contribute ideas and solutions that align with the strategic objectives. Consulting firms like Deloitte and PwC highlight the importance of leveraging diverse perspectives in strategic planning to uncover hidden opportunities and mitigate potential risks.
Effective communication strategies are essential in this phase, utilizing various channels and tools to reach different segments of the organization. Whether through town hall meetings, workshops, or digital platforms, the goal is to ensure that the strategic plan is understood, embraced, and actively supported by all stakeholders.
Implementing the Strategy
With a well-defined strategic plan and stakeholder consensus, the focus shifts to implementation. This phase is where the rubber meets the road, translating strategic objectives into concrete actions. It requires meticulous planning, coordination, and monitoring to ensure that initiatives are executed as planned. Project management methodologies and tools are critical in this phase, providing the structure and discipline needed to manage complex initiatives across different parts of the organization.
Change Management also plays a crucial role in this phase, addressing the human and cultural aspects of implementing new strategies. Resistance to change is a natural phenomenon in any organization, but with effective leadership and communication, it can be managed and mitigated. Leaders must champion the strategic plan, demonstrating commitment and resilience in the face of challenges. They should also recognize and celebrate early wins, building momentum and reinforcing the value of the strategic initiatives.
Finally, a robust Performance Management system is essential for tracking progress, measuring results, and making necessary adjustments to the strategy. This involves setting up key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with strategic goals, regularly reviewing performance data, and being agile in responding to deviations from the plan. Continuous monitoring and evaluation ensure that the strategic plan remains relevant and effective in achieving the organization's long-term objectives.
Adapting and Evolving the Strategy
In today's fast-paced and ever-changing business environment, strategic plans cannot be static. They must be dynamic, capable of adapting to new information, market trends, and organizational changes. This requires an ongoing process of strategic review and adjustment, ensuring that the strategy remains aligned with the organization's goals and the external environment.
Leadership plays a critical role in this process, fostering a culture of agility and continuous improvement. They must encourage open dialogue about the strategy's effectiveness, be willing to challenge assumptions, and make tough decisions to pivot or adjust the strategy as needed. This agility ensures that the organization can respond effectively to opportunities and threats, maintaining its strategic direction and achieving long-term success.
Incorporating feedback mechanisms and learning loops into the strategic planning process allows the organization to learn from its experiences, both successes and failures. This learning informs future strategic decisions, making the organization more resilient and adaptable in the face of uncertainty. Consulting firms advocate for this adaptive approach to strategic planning, emphasizing the importance of flexibility, learning, and resilience in achieving sustainable growth and success.
Developing a robust strategic plan is a comprehensive process that requires careful analysis, clear goal setting, strategic thinking, stakeholder engagement, effective implementation, and continuous adaptation. By following these steps and leveraging insights from consulting frameworks and real-world examples, organizations can create a strategic plan that aligns with their long-term goals, navigates the complexities of the modern business environment, and drives sustainable success.
Understanding the difference between Strategic Planning and Tactical Planning is crucial for any organization aiming to achieve long-term goals. Strategic Planning involves setting the overall direction and priorities of the organization, focusing on long-term objectives and the allocation of resources to achieve these goals. It is about defining where the organization wants to be in the future and establishing a clear vision. This high-level planning is typically done by top executives and board members who consider external and internal factors that could impact the organization's success.
Tactical Planning, on the other hand, translates the broad strategies into specific, actionable steps that can be taken in the short term. It involves the development of detailed plans to achieve parts of the strategic plan within various departments or units of the organization. Tactical planning is more about the "how" of reaching targets within the framework set by the strategic plan. It is often the responsibility of middle managers to develop and implement these plans, ensuring that the day-to-day operations align with the overarching strategic objectives.
The distinction between these two types of planning is not just academic but has real-world implications for how an organization prioritizes its activities, allocates its resources, and measures its progress. Without a clear strategic plan, tactical efforts can become disjointed and ineffective. Conversely, without robust tactical planning, even the most visionary strategic plan can fail to materialize. Thus, understanding what is the difference between strategic planning and tactical planning is essential for effective management and leadership.
Framework and Template in Strategic and Tactical Planning
In the realm of Strategic and Tactical Planning, frameworks and templates play a vital role in guiding the thought processes and actions of management teams. A Strategic Planning framework might include analyses such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) or PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental), helping leaders to assess their organization's position and potential. These frameworks provide a structured approach to strategy development, ensuring that all relevant factors are considered.
Tactical Planning, in contrast, benefits from templates that outline specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities. For example, a project management template can help break down strategic objectives into manageable tasks, assigning each to different team members with deadlines and milestones. This level of detail is crucial for the execution phase, ensuring that every team member understands their role in achieving the strategic objectives.
Consulting firms often emphasize the importance of customizing these frameworks and templates to fit the unique needs of each organization. There is no one-size-fits-all approach in strategic or tactical planning. The context, culture, and specific challenges of the organization should shape the planning process. This customization is where the expertise of seasoned consultants can be invaluable, providing insights and adaptations that align with best practices while meeting the specific needs of the organization.
Real World Examples
Consider the case of a global retail chain embarking on a Digital Transformation initiative. The Strategic Planning phase involved defining the vision for the transformation, understanding how digital technology could enhance customer experience, and identifying key areas for investment. This high-level planning required input from senior leadership and external experts to align with the organization's long-term goals.
The Tactical Planning phase for this initiative, however, involved creating detailed project plans for the rollout of new online platforms, training programs for staff to improve digital literacy, and timelines for technology adoption in stores. Middle management played a crucial role in executing these plans, ensuring that each store was ready to implement the new systems and processes.
Another example can be seen in the healthcare sector, where an organization might strategize to become the leader in patient care quality over the next decade. Strategic Planning would involve setting this vision, identifying key performance indicators for quality care, and allocating resources to research and development. Tactical Planning would then detail the implementation of new patient care protocols, training for staff on these protocols, and the integration of new technology to monitor patient outcomes.
In both examples, the synergy between Strategic and Tactical Planning is evident. The strategic plan sets the direction and priorities, while tactical plans deal with the realization of these objectives. This dual approach ensures that the organization not only knows where it wants to go but also has a concrete plan to get there, making the distinction between strategic and tactical planning a cornerstone of effective management.
Understanding what is tactical planning in business is crucial for C-level executives who are tasked with navigating their organizations through the ever-evolving market dynamics. Tactical planning, in essence, involves the development of short-term actions and strategies that are designed to achieve the more immediate goals of an organization. These plans are typically focused on a timeframe of one to three years and are more detailed and specific than strategic plans, which outline the long-term vision and objectives of an organization. Tactical planning is about translating the broad strokes of strategic planning into actionable steps that can be implemented and measured for effectiveness.
The framework for tactical planning requires a deep dive into the operational aspects of an organization. It examines the resources available—such as human capital, technology, and financial assets—and determines the best way to deploy these resources to meet strategic objectives. This process often involves a series of steps including setting short-term goals, identifying the necessary actions to achieve these goals, allocating resources, and establishing timelines for completion. The aim is to create a template that guides decision-making and action at the operational level, ensuring that every department and team is aligned with the organization's overarching strategy.
Consulting firms like McKinsey and Bain often emphasize the importance of a robust tactical planning process as a critical component of overall strategic management. They argue that without tactical planning, even the most visionary strategies can flounder, as there is no clear path to their realization. This underscores the need for C-level executives to not only be visionaries but also pragmatists who can bridge the gap between strategy and execution. By focusing on tactical planning, leaders can ensure that their organizations are not just dreamers but doers, capable of adapting to changes and seizing opportunities in the short term.
Key Elements of Tactical Planning
At the heart of tactical planning lies a set of key elements that ensure its effectiveness. Firstly, goal setting is paramount. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This clarity helps in crafting strategies that are directly tied to achieving these goals. Secondly, resource allocation is critical. It involves determining what resources are needed, in what quantity, and where they should be deployed to maximize impact. Lastly, performance monitoring and control mechanisms are essential. They provide the feedback loop necessary to adjust plans based on real-world results and organizational learning.
Another vital element is the integration of cross-functional teams. Tactical planning is not the sole purview of senior management but involves collaboration across departments. This ensures that plans are realistic and take into account the capabilities and limitations of different parts of the organization. Furthermore, risk management is integrated into tactical planning, identifying potential obstacles and developing contingency plans to mitigate these risks.
Effective communication is also a cornerstone of successful tactical planning. It ensures that everyone in the organization understands the goals, their role in achieving them, and the progress being made. This fosters a culture of accountability and alignment, which are crucial for the successful implementation of tactical plans.
Implementing Tactical Plans
Implementation of tactical plans requires a disciplined approach. It starts with the clear articulation of plans to all stakeholders, ensuring that everyone understands the objectives and their role in achieving them. This is followed by the execution of the plan, where the focus is on following the established timeline and adjusting as necessary based on performance metrics and feedback.
Leadership plays a critical role in this phase, providing the direction, support, and resources needed to overcome challenges. They must also foster a culture that values agility and flexibility, allowing the organization to adapt to unforeseen changes without losing sight of its goals. Moreover, celebrating short-term wins is important for maintaining momentum and morale.
In conclusion, tactical planning is a dynamic and essential process that bridges the gap between strategic vision and operational reality. It requires a detailed understanding of the organization's capabilities, a clear set of goals, and the flexibility to adapt to changes. For C-level executives, mastering the art of tactical planning is not just about ensuring the organization's survival in the short term but positioning it for long-term success in an increasingly complex and competitive environment.
Understanding what a business strategy plan is, involves recognizing it as a comprehensive document that outlines an organization's direction, objectives, and the actions required to achieve these goals. This strategic blueprint serves as a roadmap for decision-making and resource allocation, ensuring that all efforts are aligned with the overarching vision. A well-crafted business strategy plan not only delineates where an organization is going but also how it will get there, making it an indispensable tool for C-level executives.
In the realm of consulting, frameworks play a crucial role in the development of a business strategy plan. These frameworks offer a structured approach to analyzing challenges, identifying opportunities, and formulating strategies. For instance, consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG have popularized tools such as the SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and the PESTLE analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental), which help organizations in crafting strategies that are both resilient and adaptive to market dynamics.
The importance of a robust business strategy plan is underscored by its capacity to guide an organization through periods of uncertainty. For example, during the digital transformation wave that is reshaping industries, a strategic plan that incorporates digital strategies can position an organization to capitalize on new technologies and customer behaviors. This proactive stance on adaptation and innovation is what separates market leaders from followers.
Key Components of a Business Strategy Plan
A comprehensive business strategy plan encompasses several key components, each serving a specific purpose in the strategic planning process. At the core, the plan should define the organization's mission, vision, and core values, which provide a foundation for all strategic decisions. Following this, a detailed analysis of the current state of the organization, including an assessment of internal capabilities and external market conditions, is essential. This analysis enables leaders to identify strategic gaps and opportunities.
Another critical component is the setting of strategic objectives and goals. These should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to ensure that they are clear and actionable. Additionally, the strategy plan must outline the initiatives and projects that will be undertaken to achieve these goals, including timelines, responsibilities, and required resources. This level of detail transforms the strategic vision into actionable steps, making it possible to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
Risk management is also a vital element of a business strategy plan. It involves identifying potential risks that could derail the plan and developing mitigation strategies to address them. This proactive approach to risk ensures that the organization is prepared for uncertainties and can navigate challenges more effectively.
Implementing a Business Strategy Plan
Implementation is where many organizations face challenges. A strategy, no matter how well-crafted, is only as good as its execution. Therefore, a critical phase of the business strategy plan is outlining a clear implementation framework. This includes establishing governance structures, such as a strategy office or steering committee, to oversee the execution of the plan. It also involves communicating the strategy throughout the organization to ensure alignment and buy-in from all levels.
Performance management is another key aspect of implementation. This involves setting up KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and regular review processes to monitor progress towards strategic objectives. These metrics provide a quantifiable measure of success and help in identifying areas where adjustments may be needed. Real-time data and analytics play a significant role in this process, enabling decision-makers to make informed adjustments to the strategy in response to internal and external changes.
Change management is also integral to successful implementation. Strategic plans often require significant changes in processes, systems, and behaviors. Effective change management strategies, including training, communication, and support, are necessary to overcome resistance and ensure that the organization can successfully transition to the new strategic direction.
Real-World Examples and Success Stories
Several organizations have successfully implemented business strategy plans that have driven significant growth and transformation. For example, a leading technology company leveraged its strategic plan to pivot from hardware to software and services, capturing new market opportunities and driving revenue growth. This shift was underpinned by a detailed strategic plan that outlined new business models, investment in digital capabilities, and a cultural shift towards innovation.
Another example is a global retailer that implemented a strategic plan focused on customer experience and digital transformation. By integrating online and offline channels, investing in data analytics, and optimizing its supply chain, the retailer was able to enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, leading to improved financial performance.
These examples underscore the value of a well-conceived and effectively implemented business strategy plan. By providing a clear direction, actionable steps, and a framework for adaptation, a strategic plan enables organizations to navigate complexity and achieve sustainable growth.
Aligning Strategy Development with Global Sustainability Goals requires a comprehensive approach that integrates sustainability into the core of strategic planning and execution. This involves understanding the global sustainability agenda, recognizing the business implications of sustainability challenges, and leveraging opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage. The following sections outline how organizations can effectively align their Strategy Development with global sustainability goals.
Understanding Global Sustainability Goals
Global sustainability goals, notably the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), provide a universal framework for addressing pressing environmental, social, and economic challenges. These goals encompass a broad range of objectives, including climate action, clean energy, responsible consumption, and social equity. For organizations, understanding these goals is the first step in aligning their strategies with global sustainability objectives. This requires a comprehensive assessment of how an organization’s operations, products, and services impact these goals and identifying areas where improvements can be made. A report by McKinsey emphasizes the importance of businesses understanding their role in contributing to the SDGs and suggests that aligning business strategies with these goals can unlock economic opportunities worth billions of dollars.
Organizations should conduct a materiality assessment to identify the sustainability issues that are most relevant to their business and stakeholders. This involves engaging with stakeholders, including customers, employees, investors, and communities, to understand their concerns and expectations regarding sustainability. By prioritizing these issues in their Strategy Development, organizations can focus their efforts where they can have the greatest impact and create the most value.
Moreover, integrating sustainability into the Strategic Planning process requires a shift in perspective. Organizations must move beyond viewing sustainability as a compliance or risk management issue and instead see it as a driver of innovation, growth, and competitive advantage. This shift in perspective is critical for developing strategies that are not only aligned with global sustainability goals but also contribute to long-term business success.
Leveraging Sustainability for Competitive Advantage
Aligning Strategy Development with global sustainability goals offers organizations the opportunity to innovate, differentiate, and create value. Sustainable practices can lead to cost savings through improved resource efficiency, reduced waste, and enhanced operational efficiency. For example, a study by Accenture found that companies that integrate sustainability into their core business strategy achieve above-average performance in their respective industries. These companies are not only able to reduce costs but also drive innovation by developing new products and services that meet the growing demand for sustainable solutions.
Moreover, sustainability can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Consumers are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on companies’ environmental and social practices. By demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, organizations can attract and retain customers who are looking for brands that align with their values. This can also help organizations tap into new markets and customer segments that prioritize sustainability.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a critical factor in attracting and retaining talent. Employees, particularly millennials and Gen Z, are increasingly seeking employers that share their values and are making tangible efforts to address global sustainability challenges. By embedding sustainability into their culture and operations, organizations can position themselves as employers of choice and build a motivated, engaged workforce that is committed to achieving sustainability goals.
Implementing Sustainability in Strategy Development
To effectively integrate sustainability into Strategy Development, organizations must establish clear sustainability objectives and metrics. This involves setting ambitious yet achievable targets for reducing environmental impact, improving social outcomes, and driving economic growth. Organizations should also incorporate sustainability metrics into their performance management systems to track progress and hold leaders accountable for results.
Collaboration and partnerships are essential for achieving sustainability goals. Organizations should seek opportunities to collaborate with suppliers, customers, industry peers, NGOs, and governments to drive systemic change. This can involve participating in industry consortia, engaging in public-private partnerships, and supporting policy initiatives that advance sustainability objectives. By working together, organizations can leverage their collective expertise and resources to address complex sustainability challenges more effectively.
In conclusion, aligning Strategy Development with global sustainability goals is not only a moral imperative but also a strategic opportunity. Organizations that successfully integrate sustainability into their strategic planning and execution can drive innovation, enhance competitive advantage, and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable world. This requires a comprehensive approach that involves understanding global sustainability goals, leveraging sustainability for competitive advantage, and implementing sustainability in Strategy Development through clear objectives, collaboration, and accountability.
Strategic Planning is a critical tool that organizations can leverage to navigate the complexities of remote and hybrid work models. In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the shift towards remote work has accelerated, presenting both opportunities and challenges for organizations worldwide. Strategic Planning enables organizations to align their resources, technologies, and workforce to adapt to these new work models effectively. This process involves setting clear objectives, analyzing internal and external environments, and developing strategies to achieve organizational goals while mitigating risks associated with remote and hybrid work environments.
Understanding the Impact of Remote and Hybrid Work Models
The transition to remote and hybrid work models has fundamentally altered how organizations operate. A report by McKinsey highlighted that over 20% of the workforce could work remotely three to five days a week as effectively as they could if working from an office. This shift has implications for organizational structure, culture, and operational processes. Strategic Planning helps organizations to reassess their operational models and identify areas that require adjustment or enhancement to support remote work. For example, it may necessitate the adoption of new technologies for communication and collaboration or the redesign of performance management systems to accommodate remote workers.
Moreover, remote and hybrid work models have emphasized the importance of digital transformation. Organizations must ensure that their digital infrastructure can support the increased demand for virtual collaboration tools and cybersecurity measures. Strategic Planning plays a crucial role in identifying the digital capabilities required to support these work models and in developing a roadmap for digital transformation. This includes evaluating current technology stacks, identifying gaps, and prioritizing investments in technologies that facilitate remote work, such as cloud computing, collaboration platforms, and advanced security protocols.
Additionally, these work models pose challenges to maintaining organizational culture and employee engagement. Strategic Planning allows organizations to develop strategies to preserve company culture in a virtual environment, such as virtual team-building activities and regular communication channels that promote inclusivity and connectivity among remote employees. It also involves creating policies that support work-life balance and mental health, which are critical for sustaining employee engagement in remote and hybrid settings.
Enhancing Operational Excellence and Performance Management
Operational Excellence is another critical area where Strategic Planning can help organizations navigate the challenges of remote and hybrid work models. This involves optimizing business processes to improve efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. For remote and hybrid work models, this may include streamlining communication processes, adopting agile methodologies, and implementing tools for project management and collaboration. Strategic Planning enables organizations to identify process improvements that can enhance productivity and ensure that remote teams can work effectively and cohesively.
Performance Management is also significantly impacted by remote and hybrid work models. Traditional performance metrics and supervision methods may not be effective in a remote setting. Organizations need to redefine performance indicators that reflect the outcomes and productivity of remote work. Strategic Planning helps in developing a performance management framework that is suited to remote and hybrid work environments. This includes setting clear expectations, focusing on outcomes rather than activities, and utilizing technology to track and evaluate performance. Moreover, it emphasizes the importance of continuous feedback and communication to ensure that remote employees remain aligned with organizational goals and expectations.
Furthermore, Strategic Planning aids in identifying training and development needs to equip managers and employees with the skills required to thrive in remote and hybrid work environments. This includes training on remote leadership, virtual collaboration, and time management. By investing in skill development, organizations can enhance their capacity to manage remote teams effectively and ensure that employees are equipped to meet the challenges of remote work.
Leveraging Data and Analytics for Informed Decision Making
Data and Analytics play a pivotal role in Strategic Planning, especially in the context of remote and hybrid work models. By leveraging data, organizations can gain insights into the effectiveness of remote work arrangements, employee productivity, and engagement levels. For instance, analyzing data on work patterns and employee feedback can help organizations identify challenges and areas for improvement in their remote work policies and practices. Strategic Planning involves using these insights to make informed decisions about work models, technology investments, and employee support initiatives.
Moreover, data analytics can help organizations in forecasting and scenario planning. This is particularly important in a rapidly changing work environment, where organizations must be prepared to adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Strategic Planning uses data to model various scenarios and their potential impacts on the organization. This enables organizations to develop contingency plans and strategies that are resilient to changes in the work environment.
In conclusion, Strategic Planning is a vital tool for organizations looking to navigate the challenges of remote and hybrid work models. By focusing on operational excellence, performance management, and leveraging data for informed decision-making, organizations can develop strategies that support effective remote work, enhance employee engagement, and maintain organizational culture. Through careful planning and execution, organizations can turn the challenges of remote and hybrid work into opportunities for innovation, growth, and competitive advantage.
Fostering a risk-aware culture within an organization is crucial for achieving strategic objectives. This involves embedding risk management into the very fabric of the organization, ensuring that every decision and action considers potential risks and their implications. By doing so, organizations can not only mitigate losses but also identify and capitalize on opportunities that risks may present. The strategies to foster such a culture are multifaceted, involving leadership commitment, comprehensive risk management frameworks, and continuous education and communication.
Leadership Commitment and Tone at the Top
Leadership commitment plays a pivotal role in fostering a risk-aware culture. The "tone at the top" set by senior management and the board of directors is critical. Leaders must not only talk about the importance of risk management but also walk the talk by integrating risk considerations into strategic planning and decision-making processes. For instance, a study by Deloitte highlighted that organizations with engaged boards that regularly discuss risk and strategy are more likely to achieve operational and financial performance targets. Leaders should demonstrate through their actions that understanding and managing risk is everyone's responsibility, not just that of the risk management department.
Furthermore, leaders should establish clear risk management policies and objectives that align with the organization's strategic goals. This includes defining risk appetite and tolerance levels, which set the boundaries for risk-taking. By doing so, leaders can ensure that the organization pursues opportunities that are within its risk capacity and contributes to the achievement of strategic objectives. It is also essential for leaders to recognize and reward risk-aware behaviors among employees, thereby reinforcing the importance of risk management in the organizational culture.
Real-world examples of leadership commitment can be seen in organizations that have successfully navigated crises. For instance, during the financial crisis of 2008, organizations that had strong risk management practices led by committed leaders were better positioned to manage the downturn and recover more quickly than their peers. These organizations had leaders who regularly engaged in risk discussions and made strategic decisions with a clear understanding of the risks involved.
Comprehensive Risk Management Frameworks
Developing and implementing a comprehensive risk management framework is another strategy to foster a risk-aware culture. Such frameworks provide a structured approach to identifying, assessing, managing, and monitoring risks across the organization. According to PwC, a well-designed risk management framework can help organizations align risk appetite and strategy, enhance risk response decisions, and reduce operational surprises and losses. The framework should be integrated into the organization's overall strategic and operational planning processes, ensuring that risk management is not an afterthought but a fundamental part of planning and execution.
The risk management framework should include mechanisms for risk identification and assessment, such as risk registers and risk assessments, which help in systematically identifying and evaluating risks. It should also define risk response strategies, including avoidance, mitigation, transfer, and acceptance, and establish clear roles and responsibilities for risk management. This ensures that everyone in the organization knows their part in managing risks. Moreover, the framework should promote continuous monitoring of risks and the effectiveness of risk management strategies, allowing for timely adjustments in response to changing risk landscapes.
An example of effective use of a risk management framework is seen in the technology sector, where companies face rapid changes and high levels of uncertainty. Companies like Google and Amazon have embedded risk management into their innovation processes, enabling them to take calculated risks in developing new products and entering new markets, while also being prepared to manage potential failures.
Continuous Education and Communication
Continuous education and communication are essential for fostering a risk-aware culture. Organizations should invest in regular training and development programs to enhance employees' understanding of risk management principles and practices. This includes training on how to identify and assess risks, the importance of risk management in achieving strategic objectives, and the specific risk management tools and processes used by the organization. Accenture's research indicates that organizations with ongoing risk management education programs are more adept at identifying and responding to risks proactively, thereby enhancing their resilience and competitive advantage.
Effective communication is also crucial in fostering a risk-aware culture. This involves not only disseminating information about risks and risk management practices but also creating open channels for feedback and discussion about risk-related issues. Organizations should encourage a culture where discussing risks is seen as a positive contribution to the organization's success, rather than a negative or fear-based discussion. This can be achieved through regular risk management meetings, updates in internal newsletters, and forums for sharing lessons learned from risk events.
A notable example of effective communication and education is seen in the healthcare industry, where organizations face a wide range of risks, from patient safety to data security. Hospitals that have implemented comprehensive risk management education programs for their staff, including simulations and drills, have seen significant improvements in risk identification and management, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced liability.
In conclusion, fostering a risk-aware culture is a multifaceted endeavor that requires commitment from leadership, comprehensive risk management frameworks, and continuous education and communication. By adopting these strategies, organizations can embed risk management into their culture, thereby supporting the achievement of strategic objectives and enhancing overall resilience.
What is the key attribute of a strong problem statement in the realm of business management? This question is pivotal for C-level executives navigating the complexities of strategic planning, digital transformation, and operational excellence. A robust problem statement acts as the north star for any project, guiding all strategic and operational decisions. It succinctly describes the issue that needs to be addressed, providing a clear direction for the organization. The key attribute of a strong problem statement is its specificity. It should be precise and articulate enough to define the scope of the problem without ambiguity, enabling the organization to devise a focused strategy for resolution.
Specificity in a problem statement ensures that the organization can measure its progress towards solving the issue. It allows for the setting of clear, achievable objectives and the allocation of resources in a manner that directly contributes to resolving the identified problem. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a well-defined problem statement in strategy development and execution. They argue that a specific problem statement helps in breaking down complex issues into manageable parts, making it easier for teams to tackle them effectively. This approach not only streamlines the problem-solving process but also enhances team alignment and focus.
Moreover, a specific problem statement facilitates better communication across all levels of the organization. It ensures that everyone, from the executive team to the front-line employees, understands what the organization is up against. This clarity is crucial for fostering an environment of collaboration and innovation, as it encourages individuals to contribute ideas and solutions that are directly relevant to the issue at hand. In this context, specificity acts as a filter, ensuring that the organization's efforts are concentrated on what truly matters, thereby maximizing the impact of its strategic initiatives.
Framework for Crafting a Strong Problem Statement
Developing a strong problem statement requires a structured approach. A widely recognized framework involves identifying the situation, the complication, and the question. This template ensures that the problem statement covers all critical aspects of the issue, providing a comprehensive overview that guides the organization's strategic response. The situation describes the current state or context in which the problem exists. The complication highlights the specific issue or challenge that disrupts the status quo. Finally, the question specifies what needs to be addressed to overcome the complication.
This framework encourages leaders to delve deep into the problem, promoting a thorough analysis that uncovers the root cause of the issue. Consulting giants such as Accenture and Deloitte advocate for this analytical approach, arguing that understanding the underlying factors contributing to a problem is essential for developing effective solutions. By applying this framework, organizations can craft problem statements that are not only specific but also grounded in a deep understanding of the issue at hand.
Real-world examples underscore the effectiveness of this approach. Consider the case of a leading retail chain struggling with declining sales. By applying the framework, the company identified online competition as the complication affecting its traditional in-store sales model. The problem statement thus formulated focused on how to enhance the in-store customer experience to compete effectively with online retailers. This specificity in defining the problem enabled the company to channel its efforts towards developing innovative solutions, such as personalized shopping experiences and in-store digital enhancements, driving a turnaround in its sales performance.
Actionable Insights for Implementation
To leverage the full potential of a strong problem statement, organizations should integrate it into their strategic planning and execution processes. This involves regularly revisiting and refining the problem statement as the situation evolves. Market dynamics and internal factors can shift, necessitating adjustments to ensure the problem statement remains relevant and aligned with the organization's strategic objectives.
Additionally, fostering a culture that values clarity and specificity in problem definition is crucial. Encouraging teams to articulate problems clearly and concisely can enhance problem-solving efficiency across the organization. This cultural shift can be facilitated through training and by setting examples at the leadership level. Leaders who consistently demonstrate the importance of specific, well-defined problem statements in their strategic decision-making processes set a precedent for the rest of the organization to follow.
Finally, leveraging external expertise can provide valuable perspectives that enhance the specificity and relevance of problem statements. Consulting firms, with their broad experience across industries and functions, can offer insights that internal teams might overlook. Engaging with consultants to review and refine problem statements can ensure that they accurately capture the essence of the issue, providing a solid foundation for strategic and operational planning.
In conclusion, the key attribute of a strong problem statement in business management is specificity. A specific problem statement provides a clear, focused lens through which an organization can view its challenges, enabling it to devise targeted strategies for effective resolution. By adopting a structured framework for crafting problem statements and integrating these into their strategic processes, organizations can enhance their problem-solving capabilities, driving improved performance and competitive positioning in their respective markets.
Scenario planning is a strategic planning tool that allows organizations to explore and prepare for several possible futures. By incorporating scenario planning into strategic decision-making processes, organizations can better navigate the complexities and uncertainties of the business environment. This approach not only enhances strategic agility but also improves risk management and fosters innovation.
Enhances Strategic Agility
Strategic Agility is paramount in today's fast-paced and unpredictable business environment. Scenario planning equips organizations with the ability to swiftly adapt to changes by having pre-thought strategies for various possible futures. According to a report by McKinsey, companies that regularly engage in scenario planning are quicker to react to disruptions and can pivot their strategies more smoothly than those that do not. This is because scenario planning forces organizations to consider a wide range of outcomes and prepare for them, reducing the time needed to respond when changes occur. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, organizations that had considered scenarios involving global health crises were better positioned to adapt their operations and strategies quickly, minimizing disruptions to their business.
Furthermore, scenario planning enhances decision-making processes by providing a structured framework for evaluating the implications of different strategic choices. This helps in identifying potential risks and opportunities associated with each scenario, enabling leaders to make more informed decisions. By considering various future states, organizations can develop flexible strategies that can be adjusted as more information becomes available or as circumstances change.
Additionally, scenario planning fosters a culture of strategic thinking and continuous learning within the organization. It encourages leaders and employees to think beyond the current state and consider long-term implications of their decisions. This mindset is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and achieving sustainable growth in an ever-changing business landscape.
Improves Risk Management
Risk Management is a critical aspect of strategic planning, and scenario planning significantly enhances an organization's ability to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. By considering a broad spectrum of possible futures, organizations can identify potential threats that might not be apparent through traditional risk management approaches. For example, PwC's Global Risk, Uncertainty, and Crisis Management survey highlights that organizations employing scenario planning are better at identifying emergent risks and responding to them proactively. This proactive stance on risk management can save organizations from potential financial losses and reputational damage.
Scenario planning also helps in the prioritization of risks based on their likelihood and potential impact on the organization. This prioritization enables organizations to allocate resources more effectively, focusing on preparing for high-impact risks. Moreover, by regularly updating scenarios and risk assessments, organizations can stay ahead of emerging risks and adjust their risk management strategies accordingly.
In addition to identifying and mitigating risks, scenario planning also enables organizations to spot opportunities that arise from uncertainty. For instance, a scenario that considers the impact of new technologies might reveal opportunities for innovation and new business models. By integrating scenario planning into risk management processes, organizations can turn potential threats into opportunities, strengthening their competitive advantage.
Fosters Innovation
Innovation is a key driver of growth and competitive advantage, and scenario planning plays a vital role in fostering an innovative culture within organizations. By exploring a variety of future scenarios, organizations can uncover unexpected opportunities for innovation. For example, Accenture's research on innovation highlights that companies that engage in scenario planning are more likely to identify disruptive technologies and market trends before their competitors. This early identification allows organizations to invest in innovation and development activities that capitalize on these trends, positioning them as leaders in their respective fields.
Scenario planning also encourages creative thinking and problem-solving among employees. By involving a diverse group of stakeholders in the scenario planning process, organizations can leverage different perspectives and expertise, leading to more innovative ideas and solutions. This collaborative approach to strategic planning not only enhances the quality of the scenarios developed but also fosters a culture of innovation and collaboration within the organization.
Moreover, scenario planning provides a safe framework for testing new ideas and strategies. Organizations can simulate the outcomes of innovative initiatives within different scenarios, allowing them to assess the feasibility and potential impact of these initiatives without taking on significant real-world risks. This ability to experiment and learn from hypothetical outcomes is invaluable for driving innovation and achieving long-term success.
Incorporating scenario planning into strategic decision-making processes offers organizations a robust framework for navigating uncertainty, enhancing strategic agility, improving risk management, and fostering innovation. By preparing for multiple future states, organizations can better position themselves to respond to changes, capitalize on opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth.
Strategic Planning is a critical process for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today's business environment successfully. It involves a systematic approach to setting long-term goals, identifying the actions needed to achieve those goals, and allocating resources to execute those actions effectively. Understanding what Strategic Planning entails and the steps involved in Strategic Planning is essential for C-level executives who are tasked with steering their organizations towards sustainable growth and operational excellence.
At its core, Strategic Planning requires a deep dive into the organization's current state, including its mission, vision, and core values, to ensure that the strategy aligns with the overarching objectives. This alignment is crucial for maintaining focus and ensuring that every aspect of the organization is working towards the same goals. The process begins with a thorough analysis of internal and external factors that could impact the organization's ability to achieve its objectives. This includes evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis), a tool widely recognized and utilized across consulting firms like McKinsey, BCG, and Bain for its effectiveness in strategic assessment.
Following the initial assessment, the next step involves defining clear, measurable goals and objectives that are both ambitious and achievable. Setting these goals requires a careful balance between aiming for growth and innovation while being realistic about the organization's capabilities and market conditions. This stage often involves scenario planning and forecasting, methodologies that help organizations anticipate future trends and prepare for various contingencies. Consulting firms such as Accenture and Deloitte frequently emphasize the importance of this forward-looking approach in their strategic planning frameworks.
The development of a strategy to achieve the set goals is where the rubber meets the road. This involves identifying the specific initiatives, projects, and actions required to move the organization forward. It requires a deep understanding of the organization's resources, including human, financial, and technological assets, and how these can be best utilized or augmented to support the strategy. The creation of a strategic plan template can facilitate this process, providing a structured approach to organizing and prioritizing initiatives. This template should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the organization's internal or external environment, a principle that consulting giants like PwC and EY advocate for in their approach to Strategic Planning.
Implementation and Execution
With a clear strategy in place, the focus shifts to implementation and execution. This step is often where many organizations face challenges, as it requires meticulous planning, effective communication, and unwavering commitment from all levels of the organization. Leadership plays a pivotal role in this phase, driving the strategy forward, championing change, and ensuring that the organization's culture supports the strategic objectives. Real-world examples demonstrate that organizations with strong, committed leadership are more likely to successfully implement their strategic plans.
Effective communication is another critical component of successful strategy implementation. This involves not just cascading information down through the organization but also ensuring that there is a two-way flow of communication. Feedback mechanisms should be in place to capture insights from across the organization, allowing for adjustments to the strategy as needed. Consulting firms like KPMG and Oliver Wyman highlight the importance of agility in the implementation phase, with the ability to pivot and adapt being key to navigating unforeseen challenges.
Monitoring progress and measuring performance against predefined metrics is essential to ensure that the organization is on track to achieve its strategic goals. This involves setting up a robust performance management system that can provide real-time data and insights into how well the strategy is being executed. Regular review meetings should be scheduled to assess progress, celebrate successes, and address any areas where the organization may be falling short. Adjustments to the strategy or implementation plan may be necessary based on these reviews, underscoring the need for a dynamic approach to Strategic Planning.
Continuous Improvement
The final step in the Strategic Planning process is continuous improvement. In today's fast-paced business environment, resting on laurels is not an option. Organizations must continually assess their strategy and execution to identify areas for enhancement. This requires a culture of innovation, where employees at all levels are encouraged to propose new ideas and improvements. Consulting leaders like Bain and BCG often stress the importance of embedding a continuous improvement mindset within the strategic planning framework to ensure long-term success.
Continuous improvement also involves staying abreast of industry trends and technological advancements. Organizations must be willing to evolve their strategies in response to changes in the market or competitive dynamics. This agility can be the difference between staying ahead of the curve or falling behind. Leveraging insights from market research firms like Gartner and Forrester can provide valuable perspectives on emerging trends and technologies that could impact the strategic direction of the organization.
In conclusion, Strategic Planning is a comprehensive process that requires careful analysis, clear goal setting, strategic execution, and continuous improvement. By following these steps, organizations can ensure that they are well-positioned to achieve their long-term objectives and navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape. The role of C-level executives in this process cannot be overstated, as their vision, leadership, and commitment are critical to the successful implementation and sustainability of the strategic plan.
Integrating climate change and environmental sustainability into Strategic Planning is not just a moral imperative but also a strategic one. As the effects of climate change become increasingly unavoidable, organizations must adapt their strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on new opportunities. This integration involves a comprehensive approach, encompassing risk management, innovation, and leadership, to ensure long-term resilience and sustainability.
Incorporating Environmental Sustainability into Corporate Strategy
Strategic Planning must prioritize environmental sustainability to ensure long-term viability and compliance with evolving regulations. This involves conducting a thorough Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) analysis to identify how climate-related risks can impact operations, supply chains, and market positioning. For instance, a McKinsey report highlights the importance of incorporating ESG factors into strategic decision-making to enhance value creation and resilience. Organizations should develop a Sustainability Vision that aligns with their overall corporate strategy, setting clear, measurable goals for reducing carbon footprints, enhancing resource efficiency, and promoting sustainable practices.
Embedding sustainability into the core business strategy requires a shift in mindset from viewing environmental regulations as constraints to seeing them as drivers of innovation. For example, companies like Unilever and Patagonia have successfully integrated sustainability into their business models, resulting in enhanced brand loyalty and competitive advantage. These organizations have set ambitious sustainability goals, leveraging eco-friendly materials, and processes, while also engaging consumers and stakeholders in their sustainability journey.
Moreover, leveraging technology and innovation is crucial for achieving sustainability objectives. Digital Transformation initiatives, such as the use of AI for energy efficiency or blockchain for supply chain transparency, can drive significant improvements in environmental performance. Organizations should also consider partnerships with startups, NGOs, and academic institutions to foster innovation in sustainability solutions.
Risk Management and Climate Change
Climate change introduces a range of risks that organizations must manage, from physical risks due to extreme weather events to transition risks associated with shifting to a low-carbon economy. A comprehensive Risk Management strategy that incorporates climate change is essential for resilience. This involves not only identifying and assessing the potential impacts of climate change on the organization's operations but also developing strategies to mitigate these risks. For instance, PwC's Global Risk Management Survey emphasizes the importance of integrating climate risk into the overall risk management framework, suggesting that organizations that proactively manage climate risks are better positioned to adapt and thrive.
Adaptation strategies may include diversifying supply chains to reduce vulnerability to extreme weather events, investing in resilient infrastructure, and developing contingency plans. Transition risks can be managed by gradually shifting towards more sustainable business practices, such as reducing reliance on fossil fuels and investing in renewable energy sources. This not only mitigates risks but also positions the organization to capitalize on new opportunities in the green economy.
Furthermore, transparent reporting on climate risks and sustainability efforts is becoming increasingly important for stakeholders, including investors, customers, and regulatory bodies. Organizations should adopt frameworks such as the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) to enhance their reporting practices, thereby improving transparency and accountability.
Leadership, Culture, and Stakeholder Engagement
Leadership commitment is paramount in driving sustainability and climate change initiatives. Leaders must champion these efforts, embedding them into the organization's culture and operations. This requires not only setting a strategic vision for sustainability but also inspiring and mobilizing the entire organization towards this goal. Training and development programs can equip employees with the knowledge and skills needed to contribute to sustainability objectives, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
Stakeholder engagement is another critical component. Organizations must actively engage with customers, suppliers, regulators, and the community to align sustainability efforts with stakeholder expectations and needs. This can enhance reputation, build trust, and foster collaboration on sustainability initiatives. For example, engaging suppliers in sustainability efforts can drive improvements in environmental performance across the supply chain, while community engagement initiatives can support local sustainability goals and enhance social license to operate.
Finally, organizations should leverage sustainability reporting and communication to highlight their achievements and learnings in addressing climate change and environmental sustainability. This not only demonstrates commitment and progress to stakeholders but also encourages a culture of continuous improvement and innovation in sustainability practices.
In conclusion, incorporating climate change and environmental sustainability into Strategic Planning is essential for organizations aiming to remain competitive and resilient in the face of global environmental challenges. Through a comprehensive approach that integrates sustainability into corporate strategy, risk management, and organizational culture, while actively engaging stakeholders, organizations can navigate the complexities of climate change, turning challenges into opportunities for innovation and growth.
Crafting a comprehensive strategy document is a critical step for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today’s market dynamics. A well-structured strategy document serves as a roadmap, guiding an organization through its Strategic Planning process, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned with the organization's long-term goals and objectives. Understanding how to write a strategy document template is essential for C-level executives who are tasked with steering their organizations towards success. This guide provides a detailed framework, incorporating insights from leading consulting firms, to assist in creating an effective strategy document.
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary sets the stage for the strategy document. It should concisely outline the organization’s vision, mission, and the key strategies that will be employed to achieve the defined goals. This section is not merely an introduction but a powerful statement that encapsulates the essence of the strategic plan. It should be compelling enough to engage the reader and provide a clear snapshot of what the document will cover. The Executive Summary is often the most read section of the strategy document, making it crucial for capturing the essence of the strategic direction in a succinct manner.
Given its importance, the Executive Summary must be written with clarity and precision. It should highlight the main objectives and strategies without delving into too much detail. The aim is to provide a high-level overview that entices stakeholders to delve deeper into the document. This section should also reflect the organization's commitment to its goals and its readiness to adapt to changing market conditions.
Real-world examples, such as those from successful strategy deployments by leading firms, can be instrumental in illustrating the potential impact of a well-crafted Executive Summary. These examples not only serve as a benchmark but also inspire confidence among stakeholders about the strategic direction proposed.
Strategic Objectives and Goals
Defining clear, measurable objectives and goals is fundamental to any strategic plan. This section should articulate what the organization aims to achieve in the short, medium, and long term. Objectives should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This framework ensures that goals are not only clear and actionable but also aligned with the overall vision and mission of the organization.
Each objective should be accompanied by a set of strategies that outline how these goals will be achieved. This includes identifying the resources required, the timeline for implementation, and the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure success. Providing a detailed action plan adds credibility to the strategic objectives and demonstrates a clear path forward.
Consulting firms often emphasize the importance of aligning strategic objectives with the organization's core competencies and market opportunities. This alignment ensures that the organization is not only playing to its strengths but also positioning itself effectively in the market to capture growth opportunities. Real-world case studies from consulting practices can offer valuable insights into how strategic objectives can be structured to drive growth and innovation.
Market Analysis and Insights
A thorough market analysis is crucial for understanding the environment in which the organization operates. This section should provide an in-depth look at market trends, customer needs, and competitive dynamics. A comprehensive market analysis informs the strategic direction by highlighting opportunities for growth and areas of potential risk.
The insights gained from the market analysis should be used to refine the organization's strategic objectives and strategies. This includes identifying key market segments, understanding customer preferences, and analyzing competitor strategies. The goal is to leverage this analysis to create a competitive strategy that capitalizes on market opportunities while mitigating risks.
Leading consulting firms often use sophisticated analytical tools and frameworks to conduct market analysis. Incorporating data-driven insights into the strategy document strengthens the strategic plan by grounding it in empirical evidence. This approach not only enhances the credibility of the strategy but also ensures that decision-making is informed by the latest market intelligence.
Implementation Plan
The Implementation Plan is where the strategy is translated into actionable steps. This section should outline the specific initiatives, projects, and actions that will be undertaken to achieve the strategic objectives. It is important to assign clear responsibilities, set realistic timelines, and allocate the necessary resources for each initiative.
Effective implementation requires careful planning and coordination across the organization. This includes establishing a governance structure to oversee the execution of the strategy, defining the roles and responsibilities of team members, and setting up mechanisms for monitoring progress and addressing challenges.
Consulting firms often highlight the importance of flexibility in the implementation plan. The ability to adapt to changes in the market or within the organization is crucial for maintaining strategic agility. Real-world examples demonstrate how organizations that incorporate flexibility into their implementation plans are better positioned to respond to unforeseen challenges and capitalize on new opportunities.
Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Risk Management is an essential component of strategic planning. This section should identify potential risks to the strategic plan and outline measures to mitigate these risks. A comprehensive risk management plan includes both internal and external risks, ranging from operational challenges to market volatility.
Contingency planning is equally important. It provides a framework for responding to unforeseen events or challenges that could impact the implementation of the strategy. Having a well-thought-out contingency plan ensures that the organization can quickly adapt and maintain momentum towards achieving its strategic objectives.
Best practices from consulting firms suggest that a proactive approach to risk management and contingency planning can significantly enhance the resilience of the strategic plan. By anticipating potential obstacles and preparing for them in advance, organizations can navigate uncertainties more effectively and sustain their strategic momentum.
Crafting a comprehensive strategy document is a complex but critical process for guiding an organization towards its strategic objectives. By incorporating these key elements into a strategy document template, C-level executives can ensure that their strategic planning is effective, actionable, and aligned with the organization's long-term vision and goals.
Hoshin Kanri, also known as Policy Deployment, is a methodological approach that ensures an organization's strategic goals are consistently communicated and effectively aligned across all levels. This process not only facilitates a unified direction but also enhances the organization's ability to achieve its long-term objectives through systematic planning, implementation, and review.
Strategic Alignment through Hoshin Planning
The core of Hoshin Kanri lies in its unique ability to bridge the gap between strategic intentions and operational realities. It starts with the development of a strategic vision that is then broken down into specific, actionable objectives. These objectives are not just top-down directives but are formulated through a collaborative process involving input from various levels of the organization. This inclusive approach ensures that the strategic goals are aligned with the operational capabilities and realities of the organization, making them more achievable and relevant.
One of the key features of Hoshin Kanri is the "catchball" process. This iterative dialogue between different levels of the organization ensures that goals, strategies, and tactics are understood, refined, and agreed upon by all. It's a process of negotiation and consensus-building that helps in aligning the strategic goals with the operational activities. The catchball process not only facilitates alignment but also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment towards the goals across the organization.
Moreover, Hoshin Kanri emphasizes the importance of monitoring and reviewing progress towards strategic goals. Regular review meetings are held to assess the progress, identify any deviations from the plan, and make necessary adjustments. This continuous feedback loop ensures that the organization remains agile and can adapt to changing circumstances, keeping the strategic goals relevant and achievable.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Many leading organizations have successfully implemented Hoshin Kanri to align their strategic goals across different levels. For example, Toyota, a pioneer in adopting Hoshin Kanri, has demonstrated how effective alignment of strategic goals can lead to operational excellence and sustained competitive advantage. Toyota's approach to Hoshin Kanri involves a rigorous process of cascading objectives from the top management down to the shop floor, ensuring that every employee understands their role in achieving the strategic goals.
Another example is Intel, which adopted a modified version of Hoshin Kanri to drive its strategic transformation. Intel's "Objectives and Key Results" (OKR) framework is inspired by the principles of Hoshin Kanri and focuses on setting clear, measurable goals that are aligned across the organization. This approach has helped Intel in achieving alignment and focus, driving growth and innovation.
These examples highlight the versatility and effectiveness of Hoshin Kanri in facilitating strategic alignment across different organizational contexts. Whether it's manufacturing, technology, or any other sector, Hoshin Kanri provides a structured framework for aligning strategic goals with operational activities.
Implementing Hoshin Kanri for Strategic Alignment
Implementing Hoshin Kanri requires a systematic approach and a commitment to continuous improvement. The first step is to clearly define the strategic goals and ensure they are communicated across the organization. This involves not just top-down communication but engaging with employees at all levels to gather input and build consensus around the goals.
The next step is to use the catchball process to refine and align the goals with operational activities. This requires open communication channels and a culture of trust and collaboration. Leaders play a crucial role in facilitating this process, ensuring that there is clarity and alignment at every level.
Finally, it is crucial to establish a robust system for monitoring progress and reviewing the alignment of strategic goals. This involves setting up regular review meetings, using performance metrics to assess progress, and being open to making adjustments to the plan as needed. Continuous monitoring and review are essential for maintaining alignment and achieving the strategic goals.
In conclusion, Hoshin Kanri offers a comprehensive framework for aligning strategic goals across different levels of an organization. Through its systematic approach to planning, implementation, and review, Hoshin Kanri ensures that strategic goals are not just aspirational but are actionable and aligned with the operational realities of the organization. Implementing Hoshin Kanri can lead to improved strategic focus, operational excellence, and enhanced organizational performance.
In today's rapidly evolving market, organizations are constantly challenged to reassess their resource allocations to ensure they remain on the cutting edge. A common question that arises among C-level executives is, "What new business resources are you lack in?" This query underscores the ongoing struggle to identify and fill gaps within an organization's arsenal to maintain or enhance its strategic position. The resources in question span across various domains, including technology, human capital, and strategic frameworks, each playing a pivotal role in the organization's success.
One critical area where organizations often find themselves lacking is in the realm of Digital Transformation. Despite the buzz around digitalization, many organizations struggle to effectively integrate advanced technologies such as AI, machine learning, and blockchain into their operations. The gap isn't just in the technology itself but in the expertise required to harness its potential fully. A report by McKinsey highlights that one of the key barriers to successful digital transformation is the lack of digital talent. This gap in digital skills and expertise can significantly hinder an organization's ability to innovate and stay ahead of the curve.
Another significant resource gap lies in Strategic Planning and Execution. Many organizations possess a strategic vision but fall short in execution. This discrepancy often stems from a lack of robust frameworks and templates that guide the translation of strategy into actionable steps. Consulting giants like Bain & Company and BCG have emphasized the importance of a solid strategic framework that encompasses not only the development of strategy but also its implementation. Without such frameworks, organizations risk misalignment between their strategic objectives and operational activities, leading to suboptimal performance and missed opportunities.
Furthermore, the landscape of Risk Management has evolved, with new threats emerging that many organizations are ill-equipped to handle. Cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and compliance risks are just a few examples of the complex challenges that require specialized resources. The expertise to navigate these risks is often lacking, leaving organizations vulnerable to potentially devastating impacts. Accenture's research underscores the importance of proactive risk management strategies and the need for organizations to bolster their capabilities in this area to protect their interests and ensure continuity.
Identifying Resource Gaps
To effectively address the question of what new business resources are lacking, organizations must first conduct a comprehensive assessment of their current capabilities versus the demands of their strategic objectives. This process involves a deep dive into all aspects of the organization, from its operational processes to its organizational culture. One effective method is the SWOT analysis, which helps in identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. However, beyond traditional methods, leveraging advanced analytics and benchmarking against industry standards can provide deeper insights into specific areas of deficiency.
Once gaps have been identified, prioritizing them becomes crucial. Not all gaps are created equal, and resources should be allocated to areas that will drive the most significant impact on the organization's strategic goals. This prioritization should be a dynamic process, with regular reviews to adjust to changing market conditions and organizational objectives. Consulting firms often advocate for a structured approach to this process, utilizing strategic frameworks to ensure a balanced allocation of resources that supports both short-term needs and long-term ambitions.
Addressing these gaps requires a multifaceted strategy. For technological deficiencies, partnerships with tech firms or investments in training and development programs can be effective. When it comes to strategic planning and execution, adopting proven frameworks and templates from reputable consulting firms can provide a solid foundation. For risk management, developing in-house expertise or collaborating with specialized firms can enhance an organization's resilience. Each of these strategies requires not just financial investment but also a commitment to cultural and organizational change.
Implementing Solutions
Implementation of strategies to fill resource gaps should be approached with a clear plan and accountability mechanisms. Setting clear milestones and KPIs ensures that efforts are measurable and aligned with the organization's strategic objectives. It also involves fostering a culture of continuous improvement, where feedback is actively sought and used to refine strategies over time. Leadership plays a critical role in this process, not only in setting the direction but also in championing the changes across the organization.
Moreover, leveraging external expertise through consulting partnerships can accelerate the process of addressing resource gaps. Consultants bring a wealth of experience and can provide tailored solutions that fit the unique needs of the organization. They can also facilitate the transfer of knowledge and skills, building internal capabilities that sustain long-term growth.
In conclusion, identifying and addressing what new business resources you lack in is a continuous process that requires vigilance, strategic thinking, and adaptability. By focusing on areas such as digital transformation, strategic planning and execution, and risk management, organizations can close critical gaps that hinder their progress. Through a combination of internal assessments, prioritization, and strategic partnerships, organizations can bolster their resources, ensuring they are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of today's business environment.
Understanding how offshoring benefits the United States requires a deep dive into the economic frameworks and strategic planning that underpin this business model. At its core, offshoring allows U.S. organizations to leverage global talent and cost efficiencies, driving down operational costs and enhancing competitiveness on the global stage. This strategy, when executed effectively, can lead to significant economic benefits, including job creation in higher-value sectors, an uptick in domestic investment, and a stronger balance of trade.
One of the primary advantages of offshoring is its impact on cost reduction and efficiency improvement. Organizations can access labor markets where the cost of labor is significantly lower than in the U.S., without compromising on quality. This cost saving can be redirected towards R&D, marketing, and other core activities that enhance the organization's market position and innovation capacity. Furthermore, the global exposure organizations gain through offshoring can lead to new market opportunities, driving revenue growth and strategic expansion.
Moreover, offshoring can act as a catalyst for domestic job creation in unexpected ways. As organizations save on operational costs and reinvest in their core business areas, there's often a need for more sophisticated roles in the home country, such as product development, marketing, and strategic planning. These roles typically offer higher wages and require higher skill levels, contributing to the upskilling of the domestic workforce and fostering a more vibrant, innovation-driven economy.
Economic Resilience and Global Integration
Offshoring also plays a crucial role in enhancing the economic resilience of the United States. By diversifying operations across different geographical locations, organizations can mitigate risks associated with local economic downturns, political instability, or natural disasters. This strategic diversification ensures continuity of operations and safeguards against disruptions, contributing to the overall stability of the U.S. economy.
In addition, engaging in offshoring fosters deeper integration into the global economy. This integration is not just about financial flows but also involves the exchange of ideas, culture, and innovation. Such cross-pollination can lead to breakthrough innovations and strengthen the United States' position as a global leader in technology, finance, and other key sectors. The framework for global trade and investment becomes more robust as U.S. organizations play an active role in the global marketplace, benefiting from and contributing to international economic growth.
Furthermore, the strategic relocation of certain business processes can help U.S. organizations focus on their core competencies, thereby enhancing productivity and operational excellence. This focus is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in an increasingly complex and dynamic global market. Offshoring, when part of a well-considered strategy, allows for an optimization of resources that can lead to significant performance improvements and market leadership.
Challenges and Strategic Considerations
While the benefits of offshoring are substantial, it's important for organizations to navigate the associated challenges with a strategic mindset. Issues such as cultural differences, quality control, and intellectual property risks require a comprehensive risk management strategy. Effective communication, robust legal frameworks, and a deep understanding of the local market are essential for mitigating these risks and maximizing the benefits of offshoring.
Successful offshoring also depends on the organization's ability to maintain a balance between cost savings and ethical considerations. The public and regulatory scrutiny around offshoring practices demands a transparent and socially responsible approach. Organizations must ensure fair labor practices and environmental sustainability in their offshoring locations to maintain their reputation and operational integrity.
In conclusion, offshoring offers a strategic template for U.S. organizations to enhance their competitiveness, innovate, and grow in the global market. The economic benefits extend beyond the organization, contributing to job creation, economic resilience, and the strategic positioning of the United States in the global economy. However, realizing these benefits requires a nuanced understanding of the complexities involved and a commitment to strategic planning, ethical practices, and continuous improvement. Consulting with experts and leveraging a framework that aligns with the organization's long-term vision and values is crucial for success in this endeavor.
At the heart of strategic planning and decision-making lies the problem statement, a critical component that sets the stage for clear, actionable insights. What is the key attribute of a strong problem statement? It's specificity. A well-crafted problem statement provides a laser-focused description of the issue at hand, ensuring that the organization's leadership can align on the challenge before diving into solution mode. This precision is not just about identifying what the problem is, but also understanding its scope, its impact on the organization, and the urgency with which it needs to be addressed.
Frameworks and templates from top consulting firms underscore the importance of specificity in problem statements. For instance, McKinsey & Company's approach to problem-solving emphasizes the need to break down the problem into manageable parts, a task that becomes significantly more feasible with a specific problem statement. This precision allows for a more effective allocation of resources, ensuring that efforts are concentrated on the most critical aspects of the problem. Moreover, a specific problem statement facilitates the measurement of progress, as it establishes clear metrics for success.
Strategy development, therefore, begins with a clear understanding of the problem. This clarity is not just about what is wrong, but also why it matters. The key attribute of a strong problem statement lies in its ability to not only define the problem but also to articulate its significance to the organization's overall objectives. This specificity in understanding the problem's impact guides strategic planning, ensuring that the solutions proposed are not just effective but also aligned with the organization's long-term goals.
Importance of Clarity and Conciseness
Clarity and conciseness in a problem statement go hand in hand with specificity. A clear problem statement avoids ambiguity, making it easy for all stakeholders to understand the issue without room for misinterpretation. This clarity is crucial in rallying the organization around a common goal, facilitating a cohesive approach to addressing the challenge. Additionally, conciseness ensures that the problem statement is direct and to the point, avoiding unnecessary complexity that can dilute focus and impede understanding.
In the realm of consulting, clarity and conciseness are prized attributes. Consulting firms like Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and Bain & Company often stress the importance of being able to articulate a problem in a straightforward manner. This skill is not just about effective communication; it's about ensuring that the strategic planning process is grounded in a common understanding of what needs to be achieved. A concise problem statement acts as a north star, guiding the decision-making process and keeping the organization's efforts aligned with the strategic objectives.
Real-world examples abound where clarity and conciseness in problem statements have led to successful outcomes. Take, for example, a major retail chain facing declining sales. By articulating the problem as "a significant year-over-year decline in sales due to outdated inventory management practices," the organization can immediately focus on the core issue. This clarity and conciseness enable a targeted approach to strategic planning, focusing efforts on revamping inventory management practices to address the sales slump.
Alignment with Organizational Goals
A strong problem statement must also align with the organization's overarching goals. This alignment ensures that the efforts to solve the problem are in service of the organization's strategic objectives, rather than being a distraction or a misallocation of resources. It's about ensuring that the problem, once solved, moves the organization closer to its long-term vision.
Consulting frameworks often emphasize the importance of this alignment. For instance, Accenture's strategy development framework includes an assessment of how well the problem statement aligns with the organization's strategic priorities. This step is crucial in ensuring that the solutions developed are not just effective in isolation but are also contributing to the broader objectives of the organization.
Consider the example of a technology company looking to undergo a Digital Transformation. If the problem statement is framed as "the need to modernize IT infrastructure to support growth," it directly aligns with the organizational goal of scaling operations. This alignment ensures that the strategic planning and decision-making processes are focused on not just solving the immediate problem but also facilitating long-term growth and resilience.
In conclusion, the key attribute of a strong problem statement in the context of strategic planning and decision-making is specificity. However, it's the combination of specificity with clarity, conciseness, and alignment with organizational goals that truly makes a problem statement effective. These components ensure that the problem is understood, actionable, and relevant, laying a solid foundation for successful strategy development and implementation.
Strategic planning in business is the process of defining an organization's direction and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy. It involves setting goals, determining actions to achieve the goals, and mobilizing resources to execute the actions. A well-formulated strategic plan provides a framework that gives an organization a competitive edge, drives long-term growth, and ensures its sustainability in a rapidly changing market environment.
For C-level executives, understanding what strategic planning in business entails is crucial. It's not merely about having a vision for the future but about creating a detailed roadmap that aligns with the organization's core values, mission, and long-term objectives. This roadmap should be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the market yet robust enough to guide the organization through uncertainty. The strategic planning process involves an in-depth analysis of internal and external factors, including market trends, competition, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This analysis provides the foundation for Strategy Development, which is critical for maintaining a competitive edge.
Implementing a strategic plan requires a disciplined approach and commitment across all levels of the organization. It's about making strategic choices and allocating resources where they will create the most value. This often means making tough decisions—such as divesting from non-core areas and focusing on core competencies. The strategic planning process also involves setting Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and ensure that the organization is on track to achieving its goals. Performance Management systems play a crucial role in this aspect, providing the necessary data to inform decision-making and strategy adjustments.
Frameworks and Templates in Strategic Planning
Frameworks and templates serve as invaluable tools in the strategic planning process. They provide a structured approach to analyzing the organization's current state, defining strategic priorities, and mapping out the path to achieving long-term objectives. Popular frameworks such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis, PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental) analysis, and Porter's Five Forces model offer strategic insights that help in identifying opportunities and threats in the external environment, as well as assessing internal capabilities and resources.
Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG have developed their proprietary strategic planning frameworks that are widely adopted across industries. These frameworks not only facilitate strategy development but also help in aligning the organization's vision with actionable initiatives. For example, McKinsey's Three Horizons of Growth framework assists organizations in balancing their portfolio of initiatives across immediate, medium-term, and long-term horizons, ensuring sustained growth and innovation.
Using a strategic planning template can streamline the process, ensuring that all critical elements are addressed. A good template will guide executives through the steps of setting strategic objectives, analyzing the environment, formulating strategies, and defining action plans. It acts as a checklist, ensuring that the strategic plan is comprehensive and cohesive. The template also facilitates communication of the strategic plan to stakeholders, making it easier to garner support and align efforts across the organization.
Driving Long-Term Growth through Strategic Planning
Strategic planning is pivotal in driving long-term growth for organizations. It enables leaders to set a clear direction, prioritize investments, and allocate resources efficiently. By focusing on strategic objectives and leveraging core competencies, organizations can explore new markets, innovate, and create value for customers and stakeholders. Strategic planning also plays a critical role in risk management, allowing organizations to anticipate potential challenges and devise contingency plans.
Real-world examples underscore the value of strategic planning in driving growth. Companies like Apple and Amazon have leveraged strategic planning to diversify their product lines and enter new markets, resulting in exponential growth. Their success can be attributed to a deep understanding of market dynamics, customer needs, and the ability to innovate continually. These organizations exemplify how strategic planning, coupled with execution excellence, can result in a significant competitive edge and long-term growth.
Moreover, strategic planning facilitates digital transformation, a key driver of growth in today's economy. By incorporating digital strategies into the overall strategic plan, organizations can harness technology to improve operations, enhance customer experiences, and create new business models. Digital transformation requires a strategic approach, aligning technology initiatives with business objectives to drive growth and innovation.
Strategic planning in business is not a one-time exercise but an ongoing process that requires constant review and adaptation. The rapidly changing business environment demands that organizations remain agile, adjusting their strategies in response to market shifts, technological advancements, and competitive pressures. A robust strategic plan, supported by a solid framework and actionable insights, is essential for organizations aiming to achieve long-term growth and maintain a competitive edge. By prioritizing strategic planning, C-level executives can ensure their organizations are well-positioned to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Market analysis plays a crucial role in the development of a business plan within the Strategic Planning process. It provides a comprehensive understanding of the market environment in which an organization operates, including insights into customer needs, market trends, competitive landscape, and regulatory frameworks. This in-depth knowledge is essential for making informed decisions and formulating strategies that are realistic, achievable, and aligned with the organization's goals.
Understanding Market Demand and Customer Needs
At the heart of every successful business plan is a deep understanding of market demand and customer needs. Market analysis helps organizations identify who their potential customers are, what they need, and how these needs might evolve over time. This is critical for Product Development, Innovation, and creating value propositions that resonate with the target market. For instance, a report by McKinsey & Company highlighted how consumer behavior shifts have accelerated digital adoption across industries, suggesting that organizations need to rapidly adapt their product offerings and go-to-market strategies to stay relevant.
Furthermore, market analysis enables organizations to segment their market based on various criteria such as demographics, psychographics, and behavior, allowing for more targeted and effective marketing strategies. This segmentation can lead to the development of specialized products or services, tailored marketing messages, and more efficient allocation of resources. A study by Bain & Company showed that companies that excel in segmentation and targeted marketing can achieve significantly higher growth rates compared to their competitors.
Additionally, understanding customer needs and market demand aids in forecasting future trends, which is essential for long-term Strategic Planning. Organizations can use this information to anticipate changes in consumer behavior, technological advancements, or shifts in the competitive landscape, and adjust their business plans accordingly.
Competitive Analysis and Strategic Positioning
Another critical aspect of market analysis is competitive analysis, which involves evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of current and potential competitors. This analysis provides valuable insights into the competitive dynamics of the market, including market share, growth strategies, product offerings, and go-to-market strategies. For example, a report by Boston Consulting Group (BCG) emphasized the importance of competitive analysis in identifying market gaps and opportunities for differentiation, which can be a key driver of competitive advantage.
Through competitive analysis, organizations can identify their Unique Selling Propositions (USPs) and position themselves strategically in the market. This involves making informed decisions on pricing, distribution channels, marketing strategies, and product features. A well-executed competitive analysis not only helps in understanding the external competitive environment but also assists in internal benchmarking, setting realistic goals, and measuring performance against industry standards.
Real-world examples of successful strategic positioning abound. For instance, Apple Inc. has consistently used market and competitive analysis to position itself as a leader in innovation, quality, and customer experience. This strategic positioning has enabled Apple to command premium pricing and maintain a loyal customer base, despite intense competition in the technology sector.
Regulatory Environment and Risk Management
Market analysis also involves understanding the regulatory environment of the industry in which an organization operates. This is crucial for Risk Management, compliance, and ensuring that the business plan is not only viable but also legally sound. For instance, organizations in the healthcare sector must navigate a complex web of regulations regarding patient privacy, data security, and product approvals. A report by Deloitte highlighted how regulatory changes are among the top concerns for healthcare executives, underlining the importance of incorporating regulatory analysis into the Strategic Planning process.
Moreover, market analysis helps organizations identify potential risks and uncertainties in the market, such as economic downturns, technological disruptions, or changes in consumer behavior. By understanding these risks, organizations can develop contingency plans and strategies to mitigate them. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies that had thoroughly analyzed their market and identified potential risks were better prepared to adapt to the sudden shifts in market demand and supply chain disruptions.
In conclusion, market analysis is an indispensable component of the Strategic Planning process and business plan development. It provides the foundational knowledge necessary for making informed decisions, identifying opportunities for growth, and navigating the complexities of the market. Organizations that invest in thorough market analysis are better equipped to develop robust business plans that are realistic, strategic, and aligned with their long-term objectives.
Mitigating rising national inflation rates is a complex challenge that requires a multifaceted approach. Inflation can erode purchasing power, destabilize markets, and create uncertainty in economic environments. However, strategic planning initiatives can play a pivotal role in combating these effects. By implementing targeted strategies, organizations can contribute to a broader effort to stabilize and reduce inflation within a country. This discussion will delve into several strategic initiatives that can effectively mitigate rising national inflation rates, focusing on frameworks and templates derived from consulting and strategy best practices.
Firstly, enhancing productivity through Digital Transformation is a critical strategy. In an era where technology drives market dynamics, investing in digital tools and platforms can significantly increase operational efficiency. For instance, automating manual processes reduces labor costs and increases output, which can help in keeping prices stable. A report by McKinsey highlights that organizations leveraging digital technologies can see a productivity increase of up to 25%. This is not just about cutting costs but about reimagining processes to deliver more value at lower costs, thereby contributing to inflation control.
Secondly, Supply Chain Optimization is vital. Inflation often feeds on supply chain bottlenecks. By applying a robust framework for Supply Chain Management, organizations can ensure the smooth flow of goods and services, preventing shortages that can lead to price hikes. Techniques such as demand forecasting, inventory management, and supplier diversification can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Real-world examples include companies like Toyota, which has mastered the art of Just-In-Time inventory, significantly reducing holding costs and thus contributing to lower end-product prices.
Lastly, fostering Innovation and R&D can lead to the development of cost-effective products and services. By prioritizing innovation, organizations can find new ways to deliver value without contributing to inflationary pressures. This could involve developing new materials, processes, or technologies that lower the cost of production. For example, the renewable energy sector is continuously innovating to produce cheaper, more efficient energy solutions that can replace more expensive, traditional energy sources, thereby reducing costs for consumers and businesses alike.
Implementing Cost-Control Measures
Adopting cost-control measures is another effective strategy for combating inflation. This involves a detailed analysis of all operational expenses and identifying areas where efficiencies can be gained. Strategies such as zero-based budgeting, where every expense must be justified for each new period, can lead to significant cost reductions. Consulting giants like Bain & Company have advocated for this approach, noting that it can lead to a more disciplined financial management culture within an organization.
Moreover, renegotiating contracts with suppliers to lock in prices for extended periods can shield an organization from short-term price fluctuations. This strategy requires a proactive approach to procurement and a keen understanding of market dynamics. By leveraging long-term contracts, organizations can achieve more predictable cost structures, which is crucial for pricing stability.
Additionally, energy efficiency measures can significantly reduce operational costs, particularly in manufacturing and logistics. Implementing energy-saving technologies and practices not only reduces costs but also aligns with sustainability goals. For example, companies like Amazon have invested heavily in renewable energy projects to power their operations, which helps in controlling operational costs and mitigating inflationary pressures.
Price Stability Initiatives
Price stability initiatives are essential in the fight against inflation. One effective approach is the implementation of dynamic pricing strategies that adjust prices based on real-time market conditions. While this may seem counterintuitive, it can actually prevent sudden spikes in demand that lead to inflation. By using sophisticated algorithms, organizations can modulate prices to manage demand effectively without contributing to inflationary trends.
Another strategy is to invest in customer education and transparency. By communicating the reasons behind price adjustments and demonstrating a commitment to fair pricing, organizations can maintain customer loyalty and prevent market panic that can exacerbate inflationary pressures. For instance, companies like Unilever have adopted transparent pricing strategies that explain cost structures to consumers, fostering trust and understanding.
Finally, developing alternative products or services that meet the same needs at lower costs can provide consumers with options that do not contribute to inflation. This requires a deep understanding of consumer needs and a commitment to innovation. By offering alternatives, organizations can play a direct role in controlling inflation, ensuring that consumers have access to affordable options.
In conclusion, mitigating rising national inflation rates requires a concerted effort from organizations across various sectors. By focusing on Digital Transformation, Supply Chain Optimization, Innovation, Cost-Control Measures, and Price Stability Initiatives, organizations can contribute significantly to reducing inflation. These strategies, rooted in consulting and strategic planning best practices, offer a comprehensive template for addressing one of the most pressing economic challenges of our time.
Linking Performance Management to Strategic Planning is a critical process for ensuring organizational alignment and achieving long-term success. This integration enables organizations to translate their strategic objectives into measurable outcomes, ensuring that every team and individual's efforts contribute directly to the overarching goals. The alignment between Performance Management and Strategic Planning is not just about setting targets but creating a culture that embraces continuous improvement, accountability, and strategic focus.
One of the first steps in linking these two critical areas is the development of a clear and comprehensive Strategic Plan. This plan should not only outline the long-term vision and goals of the organization but also identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure success. According to a study by Bain & Company, organizations that effectively align their strategy and their performance metrics are 1.95 times more likely to achieve above-average results. This highlights the importance of not only setting strategic goals but also defining how success towards these goals will be measured.
Once the Strategic Plan and KPIs are established, the next step is to integrate these into the Performance Management system. This involves setting individual and team objectives that are directly linked to the strategic goals. For example, if a strategic objective is to increase market share by 10% within three years, then sales and marketing teams will have specific targets related to customer acquisition and retention. This direct linkage ensures that everyone in the organization understands how their work contributes to the strategic objectives, fostering a sense of purpose and direction.
Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
For Performance Management to effectively support Strategic Planning, organizations must cultivate a culture of continuous improvement. This involves regular reviews of both individual and team performance against the set objectives and the strategic goals. A study by Deloitte revealed that organizations with continuous performance management processes were 34% more likely to report successful innovation. Continuous improvement is not just about identifying areas for improvement but also recognizing and celebrating achievements, which in turn motivates teams and individuals to strive for excellence.
Implementing regular feedback loops is a key component of fostering this culture. Feedback should be timely, specific, and constructive, focusing on how individuals and teams can better align their efforts with the strategic objectives. This process encourages open communication and collaboration, which are essential for identifying and addressing any misalignments or challenges that may arise.
Moreover, training and development play a crucial role in supporting continuous improvement. Organizations should invest in programs that help employees develop the skills and knowledge needed to contribute effectively to the strategic goals. This includes not only technical skills but also soft skills such as leadership, communication, and strategic thinking. By investing in employee development, organizations not only enhance their ability to achieve their strategic objectives but also demonstrate a commitment to their workforce, which can improve engagement and retention.
Utilizing Technology and Data Analytics
In today's digital age, technology and data analytics are powerful tools that can enhance the alignment between Performance Management and Strategic Planning. Advanced analytics and business intelligence platforms can provide real-time insights into performance metrics, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions. For instance, a report by McKinsey & Company emphasizes the importance of leveraging big data and analytics to drive strategic decision-making and improve organizational performance.
Technology can also streamline the Performance Management process, making it easier to set, track, and review objectives. Many organizations are adopting performance management software that integrates with their strategic planning tools, allowing for seamless alignment and communication across the organization. This not only improves efficiency but also ensures that performance data is accurate and up-to-date, which is crucial for effective decision-making.
Furthermore, data analytics can identify trends and patterns that may impact the organization's ability to achieve its strategic goals. By analyzing performance data in the context of external market and industry trends, organizations can anticipate challenges and opportunities, allowing them to adapt their strategies and objectives as needed. This proactive approach to Performance Management and Strategic Planning can give organizations a competitive edge, enabling them to respond swiftly to changes in the business environment.
Real-World Examples
One notable example of successful alignment between Performance Management and Strategic Planning is Google. The technology giant uses a combination of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and continuous feedback to ensure that individual efforts are directly contributing to the company's strategic goals. This approach has not only helped Google achieve remarkable growth and innovation but also fostered a culture of transparency and accountability.
Another example is Intel, which has long used a similar OKR framework to align its Performance Management with its strategic objectives. This clarity and focus have been instrumental in Intel's ability to navigate the rapidly changing technology landscape and maintain its position as a market leader.
In conclusion, linking Performance Management to Strategic Planning is essential for organizational alignment and success. By setting clear strategic objectives, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, leveraging technology and data analytics, and learning from real-world examples, organizations can ensure that their Performance Management processes effectively support their strategic goals. This alignment not only drives organizational performance but also enhances employee engagement and competitiveness in the dynamic business environment.
Strategic planning is a critical component in steering organizations towards long-term success and sustainability. In today's rapidly evolving market landscape, integrating sustainable practices into strategic planning is not just an ethical choice but a business imperative that significantly enhances shareholder value. This integration focuses on creating economic value that also contributes positively to society and the environment, aligning with the broader expectations of consumers, investors, and regulators.
Driving Financial Performance through Sustainability
At the core of enhancing shareholder value through sustainable practices is the direct impact on financial performance. A study by McKinsey & Company highlighted that organizations with high ratings for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors have a lower cost of debt and equity; and companies that lead in sustainability practices are 33% more likely to generate higher profitability. This is because sustainable practices often lead to operational efficiencies, reduced waste, and improved energy efficiency, directly reducing costs and improving margins. Furthermore, sustainability-driven innovation can open new markets and revenue streams, from sustainable products and services to green technologies.
Investors are increasingly focusing on sustainability as a criterion for investment decisions. ESG funds are attracting high inflows, with assets under management in sustainable funds reaching $1.65 trillion in 2020, according to Bloomberg. This shift in investor preference underscores the importance of integrating sustainable practices into strategic planning to attract investment and enhance shareholder value. Companies that fail to adopt sustainable practices risk divestment and a decrease in their stock price, directly affecting shareholder value.
Moreover, regulatory pressures around the world are intensifying, with governments implementing policies and regulations to encourage or mandate sustainable practices. Organizations that proactively incorporate sustainability into their strategic planning are better positioned to navigate these regulatory changes, avoiding potential fines and benefiting from incentives for sustainable operations. This proactive approach not only protects but also enhances shareholder value by ensuring long-term viability and access to capital.
Building Brand Value and Competitive Advantage
Sustainable practices significantly contribute to building a strong, positive brand image, which is a critical asset in today’s competitive market. Consumers are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on a company’s environmental and social impact, with Nielsen reporting that 66% of consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable brands. This consumer preference for sustainability can be leveraged through strategic planning to differentiate an organization's brand, create a loyal customer base, and secure a competitive advantage. The alignment of brand values with consumer values not only drives sales but also enhances overall brand value, contributing to shareholder wealth.
In addition to consumer preferences, sustainability also plays a crucial role in talent attraction and retention. A study by Deloitte found that millennials and Gen Z, who are rapidly becoming the dominant force in the workforce, prefer to work for companies that prioritize sustainability. By integrating sustainable practices into the core of strategic planning, organizations can attract top talent, reduce turnover rates, and improve employee engagement and productivity. This not only reduces costs associated with hiring and training but also drives innovation and performance, further enhancing shareholder value.
Competitive advantage also comes from innovation in products, services, and processes driven by sustainability. Companies like Tesla have revolutionized industries by making sustainability a core part of their value proposition, disrupting traditional markets and setting new standards. Strategic planning that prioritizes sustainability fosters a culture of innovation, enabling organizations to stay ahead of market trends and regulatory requirements, and to seize opportunities in the green economy.
Enhancing Risk Management and Resilience
Integrating sustainable practices into strategic planning enhances an organization's ability to manage risks and build resilience. Environmental risks, such as climate change, resource scarcity, and natural disasters, present significant challenges to long-term business operations. By adopting sustainable practices, organizations can mitigate these risks, ensuring business continuity and protecting shareholder value. For example, investing in renewable energy sources not only reduces carbon footprint but also secures energy supply, protecting the organization from fluctuations in fossil fuel prices and availability.
Social risks, including labor practices and community relations, are also critical. Organizations that fail to address these issues face reputational damage, legal challenges, and potential disruptions to their operations. Strategic planning that includes comprehensive sustainability frameworks can help organizations anticipate and mitigate these social risks, ensuring stable and ethical operations.
Finally, sustainability enhances financial resilience. Organizations that are perceived as sustainable are more likely to attract and retain investors, secure favorable loan terms, and have access to a wider range of financing options. This financial resilience is crucial in navigating economic downturns and market volatility, protecting and enhancing shareholder value in the long term.
In conclusion, integrating sustainable practices into strategic planning is not merely a trend but a fundamental approach to enhancing shareholder value. Through improved financial performance, brand value, competitive advantage, and risk management, sustainability becomes a powerful lever for long-term success and resilience. Organizations that recognize and act on this will not only lead in their markets but also contribute positively to society and the environment, creating a legacy of value that extends beyond financial metrics.
Creating a plan on a page in PowerPoint is a strategic exercise that condenses complex ideas into a digestible, visually engaging format. This approach is particularly valuable for C-level executives who need to quickly grasp the essence of a strategy without getting bogged down in details. A well-crafted one-page plan can serve as a powerful tool for communicating strategic objectives, action items, and key metrics to stakeholders across the organization. In this context, PowerPoint offers a versatile platform for designing a concise, impactful plan that aligns with the organization's goals and priorities.
The first step in creating a plan on a page in PowerPoint is to select the right template. While PowerPoint provides a range of default templates, consulting firms often develop custom frameworks tailored to specific strategic planning processes. These frameworks are designed to capture essential elements such as Strategic Planning, Digital Transformation, and Operational Excellence in a coherent structure. When choosing a template, consider the key messages you want to convey and select a design that facilitates clear, logical presentation of these points. For instance, a SWOT analysis template can be effective for highlighting strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, while a timeline template may be better suited for outlining key milestones in a Strategy Development initiative.
Once you have selected an appropriate template, the next step is to distill your strategy into its core components. This involves a rigorous process of synthesis, where you identify the most critical elements of your plan and articulate them in a clear, concise manner. Consulting firms often employ a hierarchy of objectives, starting with high-level strategic goals and drilling down to specific tactics and metrics. This approach ensures that every element of the plan is aligned with the overarching objectives of the organization. It is essential to prioritize clarity and brevity in this process, focusing on what truly matters to the organization's success.
Visual elements play a crucial role in enhancing the readability and impact of your plan. Use charts, graphs, and infographics to illustrate key points and make data more accessible. Color coding can be used to differentiate between different strategic themes or priorities, making it easier for viewers to navigate the plan. Additionally, incorporating icons or images can help to break up text and add visual interest. Remember, the goal is to create a document that can be quickly scanned and understood, so avoid clutter and ensure that each visual element serves a clear purpose.
Aligning with Organizational Goals
Alignment with organizational goals is paramount when crafting a plan on a page in PowerPoint. This requires a deep understanding of the organization's strategic direction and the ability to translate this into actionable insights. Begin by reviewing the organization's mission, vision, and strategic priorities. Then, ensure that each component of your plan directly supports these objectives. This alignment is critical for securing buy-in from senior leadership and ensuring that the plan resonates with stakeholders across the organization.
Consulting firms often emphasize the importance of stakeholder engagement in the strategic planning process. Engaging key stakeholders early on can provide valuable insights and foster a sense of ownership over the plan. This collaborative approach can also help to identify potential roadblocks and ensure that the plan is realistic and achievable. When presenting your plan, be prepared to discuss how it aligns with the organization's goals and how it will be implemented in practice. This includes outlining specific action items, assigning responsibilities, and establishing metrics for tracking progress.
Metrics and KPIs are essential for measuring the success of your plan. Choose metrics that are directly linked to your strategic objectives and that provide clear indicators of progress. These could include financial metrics, customer satisfaction scores, or operational efficiency measures. Make sure to include these metrics in your one-page plan, using visual elements like dashboards or scorecards to present them in an easily digestible format. This not only helps to keep the organization focused on key outcomes but also enables quick adjustments to the plan as needed.
Best Practices for Effective Communication
Effective communication is key to the success of any strategic plan. When creating a plan on a page in PowerPoint, it's important to use language that is clear, direct, and free of jargon. This ensures that the plan is accessible to a broad audience, including those who may not have a deep background in the subject matter. Additionally, consider the narrative flow of your presentation. The plan should tell a compelling story, starting with the context and rationale for the strategy, followed by the objectives, action items, and expected outcomes.
Feedback is a critical component of the strategic planning process. After presenting your plan, solicit feedback from stakeholders to gauge their understanding and buy-in. This can be done through formal presentations, one-on-one meetings, or digital communication channels. Be open to constructive criticism and willing to make adjustments based on this feedback. The goal is to create a living document that evolves in response to changing circumstances and new insights.
In conclusion, creating a plan on a page in PowerPoint requires a thoughtful approach that balances clarity, conciseness, and visual appeal. By selecting the right template, distilling your strategy into its core components, and aligning with organizational goals, you can develop a powerful tool for strategic communication. Remember to engage stakeholders, measure progress with relevant metrics, and be open to feedback. With these best practices, you can create a one-page plan that effectively communicates your strategic vision and drives organizational success.
Crafting a research problem statement is a critical step in the strategic planning initiatives of any organization. This statement not only sets the stage for the entire research process but also guides the direction of strategic efforts. It is a concise description of the issue that needs to be addressed, providing a clear focus for research and strategy development. The formulation of a compelling problem statement is pivotal in aligning organizational resources towards a common goal and ensuring that the strategic planning process is grounded in reality.
When considering how to formulate a problem statement in research, it's essential to start with a deep understanding of the organization's current state, its objectives, and the challenges it faces. This involves a thorough analysis of internal and external environments, leveraging frameworks and tools commonly used in consulting practices. A well-defined problem statement should articulate the gap between the current situation and the desired future state, highlighting the importance of addressing the issue at hand. It should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), providing a solid foundation for developing actionable strategies.
The first step in crafting a problem statement involves identifying and articulating the core issue. This requires a comprehensive review of existing data, insights from market research, and consultations with key stakeholders. For instance, consulting giants like McKinsey and Bain emphasize the importance of leveraging data analytics and stakeholder interviews to uncover underlying problems that may not be immediately apparent. By synthesizing this information, organizations can pinpoint specific challenges that are hindering performance or growth.
Key Elements of a Problem Statement
Several key elements are crucial when formulating a problem statement for strategic planning initiatives. First and foremost, clarity is paramount. The statement should be straightforward, avoiding any ambiguity that could lead to misinterpretation. It's about getting to the heart of the issue without getting bogged down in technical jargon or overly complex explanations. A clear problem statement enables all stakeholders to have a common understanding of what needs to be addressed.
Secondly, the problem statement must be rooted in factual evidence. It should draw on real-world data, industry benchmarks, and insights from authoritative sources. For example, market research firms like Gartner and Forrester provide valuable data that can help validate the significance of the problem. This evidence-based approach ensures that the problem statement is not just a hypothesis but a reflection of actual challenges facing the organization.
Lastly, the problem statement should explicitly state the impact of the problem on the organization. This includes potential risks, missed opportunities, and the overall effect on strategic objectives. By quantifying the impact, the problem statement makes a compelling case for why the issue cannot be ignored. It serves as a rallying point for mobilizing resources and driving change.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
To systematically approach the formulation of a problem statement, organizations can adopt a structured framework. This framework should begin with a situation analysis, followed by problem identification, and culminating in the articulation of the problem statement. Consulting firms often use templates and tools to facilitate this process, ensuring a comprehensive and methodical approach.
The situation analysis involves gathering and analyzing relevant data, including competitive analysis, customer feedback, and performance metrics. This stage is about painting a detailed picture of the current landscape within which the organization operates. Following this, problem identification focuses on distilling the information gathered into key issues that require attention. This step may involve prioritizing problems based on their urgency and impact on the organization.
The final step is the actual formulation of the problem statement. This involves crafting a concise statement that encapsulates the essence of the identified problem. The statement should be specific enough to guide research and strategy development but flexible enough to accommodate new insights as they emerge. A well-formulated problem statement acts as a north star, guiding the strategic planning process and ensuring that efforts are focused on addressing the most critical issues.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a leading retail chain facing declining sales. Through a comprehensive analysis, it was identified that the core issue was not product quality or pricing but an outdated digital presence compared to competitors. The problem statement focused on the need to revamp the digital strategy to enhance online customer engagement and sales. This clear articulation of the problem guided the strategic planning process, resulting in targeted initiatives that successfully addressed the issue.
In another example, a global manufacturing company utilized a problem statement to highlight inefficiencies in its supply chain operations. By clearly stating the problem and its impact on delivery times and customer satisfaction, the organization was able to prioritize investments in supply chain optimization technologies. These examples underscore the power of a well-crafted problem statement in driving strategic change and achieving desired outcomes.
In conclusion, formulating a problem statement is a critical step in strategic planning initiatives. It requires clarity, evidence-based analysis, and a focus on impact. By adopting a structured framework and drawing on real-world examples, organizations can ensure that their strategic planning efforts are both effective and aligned with their overarching goals.
Running a strategic planning workshop requires meticulous preparation, sharp focus, and a clear understanding of the desired outcomes. For C-level executives tasked with steering their organizations towards new horizons, these workshops are not just meetings but pivotal moments that can define future paths. The essence of how to run a strategic planning workshop effectively lies in its ability to align team members, crystallize strategic objectives, and lay down actionable plans. This process, when executed with precision, can transform abstract visions into tangible roadmaps that propel an organization forward.
Initiating the workshop with a well-defined framework is crucial. This framework serves as the blueprint around which discussions are structured and outcomes are measured. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a robust framework that encompasses market analysis, competitive dynamics, and internal capabilities assessment. A comprehensive framework ensures that the workshop covers all critical aspects of strategy development, from identifying growth opportunities to addressing potential threats. Moreover, leveraging a proven template can streamline the process, making it more efficient and focused.
Engagement and participation are key to a successful strategic planning workshop. Facilitators must employ techniques to ensure active involvement from all participants, fostering an environment where ideas can be freely exchanged and debated. This includes breaking down hierarchical barriers and encouraging contributions from all levels of the organization. Tools such as SWOT analysis, scenario planning, and role-playing can be instrumental in stimulating discussion and generating innovative solutions. The goal is to emerge from the workshop with a clear set of strategic initiatives, prioritized according to their potential impact and feasibility.
Pre-Workshop Preparation
Success in a strategic planning workshop begins long before the actual event. Pre-workshop preparation involves identifying the right participants, setting clear objectives, and ensuring that all necessary data and resources are available. Selecting participants is a strategic decision in itself; including a mix of leadership and key stakeholders from various departments ensures diverse perspectives and expertise. This diversity enriches the discussion and contributes to more comprehensive strategic insights.
Setting clear objectives for the workshop is another critical step. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They guide the agenda and keep discussions focused, preventing the workshop from veering off course. Additionally, gathering relevant data, market research, and competitive intelligence beforehand equips participants with the information needed to make informed decisions. This preparation phase is the foundation upon which a productive workshop is built.
Communication plays a vital role in pre-workshop preparation. Participants should be briefed on the objectives, agenda, and their expected contributions. Providing pre-reading materials or conducting pre-workshop surveys can also help in warming up participants to the workshop's themes, ensuring that they come prepared to engage deeply with the subject matter. This level of preparation sets the stage for a workshop that is not only productive but also energizing and inspiring for all involved.
Executing the Workshop
The day of the workshop is where strategy meets action. Starting with a clear articulation of the workshop's goals sets the tone for the day. It's important to manage time effectively, allocating sufficient blocks for brainstorming, discussion, and decision-making. Facilitators must be adept at guiding conversations, ensuring that discussions remain on topic and that every voice is heard. This may involve playing devil's advocate or challenging assumptions to deepen the analysis and enrich the outcomes.
Breakout sessions can be an effective way to tackle specific themes or issues in smaller groups. These sessions allow for more focused discussions and can generate more detailed strategic initiatives. It's essential to regroup after these sessions to share insights and integrate them into the broader strategic framework. The use of digital tools and platforms can enhance collaboration, allowing for real-time polling, feedback, and documentation of ideas.
Wrapping up the workshop requires summarizing key takeaways, agreeing on next steps, and assigning responsibilities. This closure ensures that the momentum generated during the workshop translates into concrete actions. Setting deadlines and establishing accountability mechanisms are critical to maintaining progress. Follow-up sessions to review progress can help keep initiatives on track and adjust plans as necessary, ensuring that the strategic planning workshop translates into meaningful change for the organization.
Post-Workshop Follow-Up
Effective strategic planning doesn't end with the workshop. The real test of a workshop's success is in the implementation of the strategies developed. Immediate follow-up is crucial to maintain the momentum. This includes distributing a comprehensive summary of the workshop outcomes, action items, and assigned responsibilities to all participants and relevant stakeholders. Ensuring that this information is communicated clearly and promptly helps keep everyone aligned and focused on the objectives.
Establishing a timeline for reviewing progress towards the strategic initiatives is also vital. Regular check-ins provide opportunities to assess progress, address challenges, and make necessary adjustments. These reviews keep the strategy dynamic, allowing the organization to adapt to changes in the external environment or internal capabilities.
Finally, measuring the impact of the strategic initiatives is essential for validating the effectiveness of the strategic planning process. This involves setting key performance indicators (KPIs) and benchmarks that align with the strategic objectives defined during the workshop. Tracking these metrics over time provides valuable insights into the strategy's execution and outcomes, informing future strategic planning efforts and ensuring continuous improvement in the organization's strategic management practices.
In conclusion, running an effective strategic planning workshop demands thorough preparation, active engagement, and diligent follow-up. By adhering to these principles, C-level executives can ensure that their strategic planning workshops are not just another meeting but a catalyst for transformation and growth within their organizations.
Developing a comprehensive annual operating plan (AOP) is a critical exercise for any organization aiming to align its strategic goals with operational execution. This process involves a detailed roadmap that outlines the financial and operational goals for the year, setting the stage for how resources will be allocated to meet these objectives. The importance of a well-structured AOP cannot be overstated—it serves as a guiding star for decision-making throughout the fiscal year, ensuring that all departments are moving in harmony towards the organization's overarching goals.
The first step in how to make an annual operating plan is to ensure a deep understanding of the organization's strategic objectives. This requires a thorough analysis of the previous year's performance, market trends, and the competitive environment. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Bain often emphasize the need for a data-driven approach in this phase, leveraging analytics to identify areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. This foundation supports the development of realistic, achievable goals that are directly tied to the organization's strategic vision.
Next, the creation of a robust framework is essential. This framework should outline the key components of the AOP, including revenue targets, expense budgets, key initiatives, and performance metrics. A common practice among leading organizations is to use a template that standardizes the planning process across all departments, ensuring consistency and facilitating easier consolidation at the corporate level. This template approach not only streamlines the planning process but also aids in the communication of the plan to stakeholders, making it easier to rally the organization around the common goals.
Finally, the integration of risk management into the AOP is crucial. In today's volatile business environment, plans must be flexible and resilient, capable of adapting to unexpected challenges. Incorporating scenario planning and stress testing can help organizations anticipate potential obstacles and devise contingency plans. This proactive approach to risk management ensures that the organization can maintain operational continuity and meet its objectives, even when faced with unforeseen circumstances.
Best Practices for AOP Development
One of the best practices in developing an annual operating plan is to foster cross-functional collaboration. The most successful plans are those that are co-created with input from various departments, ensuring that the plan is comprehensive and takes into account the diverse perspectives within the organization. This collaborative approach not only improves the quality of the AOP but also enhances buy-in from key stakeholders, making implementation more seamless.
Another critical practice is the establishment of clear, measurable KPIs (Key Performance Indicators). These indicators should be directly linked to the strategic objectives of the organization and should serve as a dashboard for monitoring progress throughout the year. Regular review meetings should be scheduled to assess performance against these KPIs, allowing for timely adjustments to the plan as needed. This iterative process ensures that the organization remains agile and can respond effectively to changes in the internal or external environment.
Additionally, leveraging technology can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the AOP process. Many organizations now use advanced planning software that facilitates real-time collaboration, scenario analysis, and performance tracking. These tools not only streamline the planning process but also provide valuable insights that can inform decision-making, ultimately leading to better outcomes for the organization.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a global technology firm that implemented a dynamic AOP process, integrating market intelligence and competitive analysis into their strategic planning. By using a data-driven approach, the firm was able to identify high-growth areas and allocate resources more effectively, resulting in a significant increase in market share.
Another example is a leading consumer goods company that adopted a collaborative planning approach, involving stakeholders from across the organization in the AOP development. This inclusive strategy not only improved the accuracy of the plan but also fostered a sense of ownership among employees, driving higher levels of engagement and execution excellence.
Lastly, a healthcare organization leveraged advanced planning software to enhance its AOP process, enabling more effective scenario planning and performance tracking. This technology-driven approach allowed the organization to quickly adapt to changing regulations and market conditions, ensuring sustained operational efficiency and continued growth.
In conclusion, developing a comprehensive annual operating plan is a multifaceted process that requires strategic thinking, cross-functional collaboration, and a focus on execution. By following the practices outlined above and leveraging real-world insights, organizations can create effective AOPs that drive operational excellence and strategic alignment. Remember, the goal of the AOP is not just to set targets but to create a living document that guides the organization through the complexities of the business landscape, ensuring agility, resilience, and sustained success.
Integrating Agile methodologies into the Strategic Planning process of a startup can significantly enhance its adaptability and responsiveness to market changes. Agile, primarily known for its success in software development, focuses on iterative progress, collaboration, and customer feedback. By applying these principles to business plan development, startups can create a more dynamic and flexible approach to achieving their long-term objectives.
Understanding Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies involve breaking down projects into small, manageable units, known as sprints, which are subject to regular reassessment and adaptation. This approach contrasts with traditional methods that often rely on extensive upfront planning and a rigid execution path. The key benefits of Agile include increased adaptability, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced team productivity. According to a report by the Project Management Institute, organizations that embrace Agile methodologies are more likely to achieve success in their projects than those that do not.
To integrate Agile into business plan development, startups should begin by defining clear, yet flexible, goals. These goals should be revisited and refined through regular intervals, allowing the organization to pivot as necessary based on feedback and market developments. Additionally, fostering a culture that values collaboration, both within the team and with external stakeholders, is crucial. This ensures that diverse perspectives are considered in the decision-making process, thereby enhancing the robustness of the strategic plan.
Moreover, leveraging tools and technologies that support Agile practices can facilitate more effective collaboration and project management. For instance, digital boards and project management software enable real-time tracking of progress and issues, allowing for swift adjustments. This technological integration not only streamlines the process but also ensures transparency and accountability among team members.
Practical Steps to Agile Integration
To effectively integrate Agile methodologies into business plan development, startups should follow a structured approach. Firstly, the organization should conduct a thorough market analysis to understand the needs and preferences of their target customer segment. This step is crucial for defining value propositions that are both compelling and adaptable. Following this, the startup should develop a minimum viable product (MVP) or service offering, which can be rapidly launched to gather initial customer feedback.
Subsequently, based on the insights gained, the organization can iterate on its offering and strategic plan. This iterative process should be guided by key performance indicators (KPIs) that are aligned with the organization's strategic goals. Regular review meetings should be scheduled to assess progress, identify challenges, and adjust plans as necessary. This approach not only ensures that the organization remains aligned with its strategic objectives but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
It is also important for startups to cultivate partnerships and collaborations that can provide additional resources and insights. For example, working with industry experts or joining startup accelerators can offer valuable mentoring and networking opportunities. These relationships can be instrumental in navigating market complexities and accelerating growth.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
One notable example of a startup that successfully integrated Agile methodologies into its business plan development is Spotify. The music streaming service adopted an Agile model known as "Squads and Tribes," which allowed it to rapidly innovate and respond to user preferences. This approach enabled Spotify to quickly become a leader in the highly competitive music streaming industry.
Another example is Dropbox, which used Agile principles to iterate on its product offering based on user feedback. This focus on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction was key to the company's growth and success in the cloud storage market. Dropbox's ability to rapidly adapt its strategic plan in response to user needs and market trends was a significant factor in its scalability and resilience.
These examples illustrate the effectiveness of integrating Agile methodologies into business plan development. By embracing flexibility, continuous improvement, and customer-centricity, startups can navigate the uncertainties of the market more effectively and achieve sustainable growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating Agile methodologies into the business plan development process can significantly enhance a startup's adaptability and responsiveness. By adopting an iterative approach, fostering collaboration, and leveraging technology, organizations can create dynamic strategic plans that are capable of evolving with the market. Practical steps such as conducting thorough market analysis, developing MVPs, and cultivating strategic partnerships are essential in this integration process. Real-world examples like Spotify and Dropbox demonstrate the potential of Agile methodologies to drive innovation and success in the competitive startup landscape. Ultimately, the key to effective Agile integration lies in the organization's commitment to continuous improvement and customer-centricity.
Integrating ethical considerations into Strategic Planning is paramount for organizations aiming to achieve sustainable success. Ethical practices foster trust among stakeholders, enhance brand reputation, and mitigate risks associated with legal and compliance issues. In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, where stakeholders are increasingly valuing corporate responsibility, embedding ethics into strategic frameworks is not just advisable but essential.
Establishing an Ethical Framework
The first step in integrating ethical considerations into Strategic Planning is the establishment of a robust ethical framework. This framework serves as the foundation upon which all strategic decisions are made. It should clearly define the organization's core ethical principles, values, and standards of behavior expected from all employees. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Deloitte emphasize the importance of aligning this framework with the organization's mission, vision, and strategic objectives to ensure coherence and relevance across all levels of decision-making.
Developing this framework involves a comprehensive analysis of the organization's internal and external environments to identify ethical risks and opportunities. It also requires engagement with stakeholders to understand their expectations and concerns regarding ethical behavior. Once established, the framework should be communicated effectively throughout the organization, ensuring that it is understood and embraced by all employees.
Actionable steps include conducting ethics training programs, establishing clear reporting mechanisms for ethical concerns, and incorporating ethical performance indicators into Performance Management systems. Real-world examples include companies like Patagonia and Ben & Jerry's, which have embedded ethical considerations into their strategic planning processes, resulting in strong brand loyalty and competitive advantage.
Integrating Ethics into Strategy Development
Once the ethical framework is in place, the next step is to integrate these considerations into the Strategy Development process. This integration ensures that ethical considerations are not an afterthought but a fundamental aspect of strategic decision-making. It involves evaluating strategic options through the lens of the ethical framework to ensure that chosen strategies are not only viable but also align with the organization's ethical standards.
Consulting firms such as Boston Consulting Group (BCG) and Bain & Company advocate for the use of ethical decision-making models and tools during the Strategy Development phase. These models help in assessing the ethical implications of strategic choices and in making informed decisions that balance profitability with ethical considerations. For example, a template for ethical decision-making might include criteria such as stakeholder impact analysis, long-term versus short-term benefits, and alignment with core values.
Practical steps for integration include incorporating ethics into SWOT analysis, risk management processes, and scenario planning. By doing so, organizations can identify potential ethical risks and opportunities early in the planning process, allowing for proactive rather than reactive management. Companies like Starbucks and Unilever provide exemplary cases of how integrating ethics into strategic planning can drive innovation and create value for both the organization and society.
Operationalizing Ethical Strategies
The final step in integrating ethical considerations into Strategic Planning is operationalizing ethical strategies. This involves translating strategic plans into actionable policies, procedures, and initiatives that embed ethical considerations into the day-to-day operations of the organization. It requires a concerted effort to ensure that the ethical framework is not only a guiding principle for strategy but also for operational execution.
Key to this process is the alignment of organizational structures, processes, and systems with the ethical framework. This might involve revising performance metrics, incentive schemes, and reporting structures to ensure they encourage ethical behavior. Consulting firms like Accenture and PwC highlight the importance of leveraging technology and data analytics to monitor compliance with ethical standards and measure the impact of ethical initiatives on organizational performance.
Implementing ethical strategies effectively requires strong leadership commitment and a culture that values ethics and integrity. Leaders must model ethical behavior and make it clear that ethical considerations are a priority in decision-making. Furthermore, organizations should foster an environment where employees feel empowered to raise ethical concerns without fear of retaliation. Examples of companies that have successfully operationalized ethical strategies include Salesforce, which has been recognized for its ethical leadership and commitment to social responsibility.
Integrating ethical considerations into Strategic Planning is a complex but rewarding endeavor. It requires a systematic approach, starting with the establishment of an ethical framework, followed by the integration of ethics into Strategy Development, and culminating in the operationalization of ethical strategies. By adhering to these best practices, organizations can ensure that their strategic planning processes not only drive financial success but also contribute positively to society and the environment. The benefits of such an approach—ranging from enhanced brand reputation to improved stakeholder relationships—are well documented and significant, underscoring the importance of ethics in strategic planning for today’s leaders.
In the rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are increasingly turning to the gig economy and freelance talent to drive innovation, flexibility, and competitive advantage. Strategic Planning plays a critical role in enabling organizations to effectively integrate and capitalize on this burgeoning workforce. By leveraging freelance talent, organizations can access a wide array of skills and expertise on-demand, optimize costs, and increase agility in response to changing market demands. However, to truly benefit from this shift, a deliberate approach rooted in Strategic Planning is essential.
Understanding the Gig Economy Landscape
The first step in capitalizing on the gig economy is to understand its landscape and potential impact on your organization. The gig economy encompasses a diverse range of freelance workers, from creative professionals and IT experts to consultants and temporary hires. According to a report by McKinsey, independent workers comprise approximately 20% to 30% of the working-age population in the United States and the EU-15. This significant portion of the workforce represents a vast pool of talent that organizations can tap into. Strategic Planning requires a deep dive into the specific skills and types of freelance talent that align with the organization's current and future needs. This involves analyzing workforce trends, identifying skill gaps, and forecasting future talent requirements.
Organizations must also assess the legal and operational implications of integrating freelance talent. This includes understanding the regulatory environment, tax implications, and the need for flexible contract management systems. Strategic Planning should address these considerations to ensure a seamless integration of freelance workers into the organization's workforce.
Strategic Talent Acquisition and Management
Once the organization has a clear understanding of the gig economy landscape, the next step is to develop a Strategic Talent Acquisition plan. This plan should outline how the organization will attract, engage, and retain freelance talent. Key components include creating attractive value propositions for freelancers, leveraging technology platforms for talent acquisition, and developing onboarding processes that ensure freelancers can quickly and effectively contribute to organizational goals.
Performance Management is another critical aspect of leveraging freelance talent. Unlike traditional employees, freelancers require a different approach to performance evaluation and management. Organizations should establish clear performance metrics, regular feedback mechanisms, and flexible reward systems that recognize the unique contributions of freelance workers. This not only helps in maintaining high levels of motivation among freelancers but also ensures alignment with organizational objectives.
Leveraging Technology for Integration and Collaboration
Technology plays a pivotal role in enabling effective collaboration between freelance talent and permanent staff. Digital platforms and collaboration tools can facilitate seamless communication, project management, and knowledge sharing. Organizations should invest in technology solutions that support remote work, ensure data security, and integrate freelancers into the organization's workflow and culture. For example, adopting cloud-based project management tools and communication platforms can help in creating a cohesive work environment that fosters collaboration and innovation.
Moreover, Strategic Planning should also consider the development of proprietary platforms or the use of existing freelance management systems. These platforms can help in streamlining the process of sourcing, managing, and paying freelance talent. By automating administrative tasks and providing real-time visibility into freelance activities, organizations can enhance operational efficiency and focus on core strategic initiatives.
In conclusion, the gig economy presents a significant opportunity for organizations to enhance their agility, access specialized skills, and drive innovation. However, capitalizing on this opportunity requires a strategic approach that encompasses understanding the gig economy landscape, strategic talent acquisition and management, and leveraging technology for integration and collaboration. By embedding these elements into their Strategic Planning, organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of the gig economy and harness the full potential of freelance talent.
Scenario planning is a strategic tool that allows organizations to explore and prepare for multiple future environments, particularly useful in navigating the complex and often unpredictable landscape of regulatory changes. In industries where regulation plays a significant role, such as finance, healthcare, energy, and telecommunications, the ability to anticipate and adapt to regulatory shifts is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage and operational resilience.
Understanding Scenario Planning
At its core, scenario planning involves identifying a set of plausible futures based on a combination of known facts, expected trends, and potential surprises. This process enables organizations to "rehearse" responses to various regulatory scenarios, ensuring that when changes occur, they are not caught off guard. It is not about predicting the future but preparing for it, by developing flexible strategies that can be adapted as the regulatory environment evolves.
Effective scenario planning requires a deep understanding of the current regulatory landscape, an assessment of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that could influence future regulations, and a clear grasp of the organization's strategic objectives. It also involves engaging a broad range of stakeholders, including regulatory experts, industry analysts, and frontline employees, to gain diverse perspectives on potential regulatory changes and their implications.
Organizations can leverage insights from consulting firms like McKinsey & Company, which has emphasized the importance of scenario planning in helping businesses navigate uncertainty. By systematically analyzing different regulatory scenarios and their potential impacts, companies can identify key risks and opportunities, prioritize strategic initiatives, and allocate resources more effectively.
Strategic Implementation of Scenario Planning
To implement scenario planning effectively, organizations should start by defining a set of 3-5 plausible regulatory scenarios. These scenarios should cover a wide range of possibilities, from minor adjustments in existing regulations to major overhauls that could disrupt the industry. For each scenario, the organization should develop a detailed analysis of the potential impacts on its operations, market position, and competitive landscape.
Next, organizations must develop strategic responses to each scenario. This involves identifying the actions that would be necessary to mitigate risks and seize opportunities under each regulatory environment. Strategies might include diversifying product lines, investing in new technologies, forming strategic partnerships, or lobbying for favorable regulatory outcomes. The key is to ensure that these strategies are flexible and can be adjusted as more information becomes available.
Finally, scenario planning should be integrated into the organization's ongoing strategic planning and risk management processes. This means regularly updating scenarios based on new information, monitoring the regulatory landscape for signs of change, and conducting "war games" to test the organization's preparedness for different regulatory outcomes. By making scenario planning a continuous process, organizations can stay one step ahead of regulatory changes and maintain their agility in a dynamic environment.
Real-World Examples
One notable example of scenario planning in action is the financial services industry's response to the Dodd-Frank Act in the United States. Anticipating a range of possible regulatory changes, banks and financial institutions used scenario planning to prepare for new compliance requirements, assess the impact on their business models, and explore strategic options for maintaining profitability. As a result, many were able to adapt more quickly to the new regulatory environment, gaining a competitive edge over less prepared rivals.
In the energy sector, companies have used scenario planning to navigate the uncertainties surrounding climate change and environmental regulation. For instance, a leading oil and gas company developed scenarios ranging from "business as usual" to "rapid transition" to a low-carbon economy. This approach helped the company identify strategic investments in renewable energy and carbon capture technologies, positioning it for success in a variety of regulatory futures.
Scenario planning is a powerful tool for navigating regulatory changes, offering organizations a structured approach to anticipating and responding to the uncertainties of the future. By systematically analyzing different regulatory scenarios, developing flexible strategies, and integrating scenario planning into their strategic processes, organizations can enhance their resilience, agility, and competitive advantage in an ever-changing regulatory landscape.
Developing a comprehensive strategic business plan is critical for organizations aiming to align their operations with long-term goals and secure a strong market position. This process involves a deep dive into the organization's current status, its aspirations, and the strategies that will bridge the gap between the present and the future. A strategic business plan acts as a roadmap, guiding the organization through the complexities of growth, competition, and change. It encompasses an analysis of internal capabilities, market trends, and potential challenges, laying out a clear path for achieving strategic objectives.
The first step in crafting a strategic business plan is conducting a thorough situation analysis. This includes a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis to identify internal and external factors that could impact the organization's ability to reach its goals. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of understanding the market dynamics, customer needs, and competitive forces to inform strategic decision-making. This foundational work helps in pinpointing where the organization stands and in which direction it should head.
Following the situation analysis, setting clear, measurable objectives is paramount. These objectives should be ambitious yet achievable, serving as milestones towards the realization of the organization's vision. Performance Management frameworks come into play here, offering tools to track progress and ensure that every department's efforts are aligned with the overarching strategy. This alignment is crucial for maintaining focus and cohesion across the organization as it moves forward.
Strategy formulation is the core of the strategic business plan. This involves selecting the strategic initiatives that will drive the organization towards its goals. It's about making choices on where to compete, how to differentiate, and what resources will be required. A well-defined strategy acts as a template guiding decision-making and resource allocation, ensuring that the organization's actions are coherent and directly contribute to achieving long-term objectives.
Framework for Strategic Planning
A robust framework is essential for effective strategic planning. It provides a structured approach, ensuring that all critical aspects of the plan are addressed systematically. One popular framework is the Balanced Scorecard, which looks at the organization from four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Process, and Learning & Growth. This holistic view ensures that the strategy is balanced and considers both short-term performance and long-term capability building.
Another key element of the framework is the integration of Digital Transformation initiatives. In today's fast-paced environment, leveraging technology can provide a significant boost in operational efficiency and customer engagement. Consulting giants like Accenture and Deloitte highlight the role of digital tools in enabling better data analysis, enhancing communication, and automating processes, which are all vital for executing a strategic plan successfully.
Risk Management is also an integral part of the strategic planning framework. It involves identifying potential risks that could derail the plan and developing mitigation strategies. This proactive approach ensures that the organization is prepared for uncertainties and can adapt its strategy as needed, maintaining resilience in the face of challenges.
Executing the Strategic Business Plan
Execution is where many organizations stumble. It requires meticulous planning, effective communication, and unwavering discipline. The strategic business plan should outline the specific actions, timelines, and responsibilities to ensure clarity and accountability. Leadership plays a critical role in this phase, driving the strategy forward, motivating the team, and making tough decisions when necessary.
Change Management is a critical aspect of execution. As the organization embarks on its strategic initiatives, it will inevitably encounter resistance. A structured approach to managing change, focusing on communication, training, and support, can facilitate a smoother transition and higher adoption rates. Real-world examples demonstrate that organizations that excel in change management are more likely to achieve their strategic objectives.
Finally, continuous monitoring and adjustment are essential. The market and external environment are always changing, and the strategic business plan must be flexible enough to adapt. Regularly reviewing performance against objectives, gathering feedback, and making necessary adjustments ensures that the strategy remains relevant and effective. This iterative process keeps the organization agile, allowing it to respond to new opportunities and threats as they arise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, developing a comprehensive strategic business plan is a multifaceted process that requires careful analysis, strategic thinking, and diligent execution. By following a structured framework, setting clear objectives, and remaining adaptable, organizations can align their efforts with their long-term goals and achieve a strong market position. The journey is complex and challenging, but with the right approach, leadership, and commitment, it is undoubtedly achievable.
Managing limited resources to achieve personal goals is a critical challenge faced by leaders and executives across industries. The essence of this challenge lies in the strategic allocation of available resources—time, money, and human capital—to maximize outcomes and drive personal and organizational success. The key to navigating this landscape is adopting a strategic framework that prioritizes efficiency, adaptability, and focused goal-setting.
In the realm of consulting, frameworks and templates serve as the bedrock for strategy development and decision-making. A well-structured framework for managing limited resources begins with a clear articulation of personal goals. These goals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). Once goals are defined, the next step involves conducting a thorough resource audit to identify what is available, what is lacking, and what can be optimized. This process mirrors the strategic planning exercises conducted by top-tier consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG, where resources are meticulously mapped against strategic objectives to identify gaps and opportunities.
After identifying available resources and aligning them with personal goals, the next step is prioritization. Not all goals are created equal, and not all will contribute equally to personal or organizational advancement. Prioritization involves assessing the impact of each goal against the resource investment required, using a cost-benefit analysis approach. This method ensures that resources are allocated to goals with the highest potential return on investment, a principle that is deeply ingrained in the operational excellence strategies of leading organizations. Furthermore, leveraging technology and automation can play a pivotal role in maximizing resource efficiency, a strategy that has been central to digital transformation initiatives across sectors.
Adaptability is another critical component of managing limited resources effectively. Market conditions, organizational priorities, and personal circumstances can evolve, necessitating a flexible approach to goal achievement. This entails regularly reviewing and adjusting goals and resource allocations in response to changing dynamics, a practice that underscores the importance of agility in leadership and strategic planning. Real-world examples of this include executives at tech startups who pivot their business models in response to user feedback or market trends, thereby optimizing their use of limited resources to achieve strategic objectives.
Implementing a Resource Management Framework
To operationalize the management of limited resources, a structured framework is essential. This framework should begin with goal setting, followed by resource auditing, prioritization, and the implementation of technology and automation solutions where applicable. Regular review sessions to assess progress and adapt plans are also crucial. This template mirrors the strategic planning processes used by consulting firms to guide organizations in achieving operational excellence and strategic goals.
For instance, adopting project management and resource allocation tools can provide a granular view of where resources are being spent and highlight areas of inefficiency. Additionally, time management techniques, such as the Eisenhower Matrix, can help in prioritizing tasks based on urgency and importance, ensuring that limited time resources are focused on activities that directly contribute to goal attainment.
Another actionable insight is the leveraging of networks and partnerships to extend one's resource pool. This approach is frequently observed in the strategy development phases of startups and scale-ups, where resources are inherently limited. Collaborating with partners can provide access to additional skills, funding, or technologies without the need for significant upfront investment, thereby accelerating the achievement of personal goals within the constraints of limited resources.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Consider the example of a tech startup operating in the competitive landscape of Silicon Valley. Despite having limited financial resources, the leadership team focused on strategic partnerships with larger tech firms to gain access to advanced technologies and market channels. This strategic move, often highlighted in case studies by consulting firms like Accenture and Capgemini, showcases how limited resources can be managed effectively to reach personal and organizational goals.
In another instance, a non-profit organization aimed at improving literacy rates among underprivileged children utilized volunteer networks and digital platforms to maximize its reach and impact. By leveraging digital transformation strategies to optimize their limited resources, they were able to achieve significant improvements in literacy rates without substantial increases in budget. This example underscores the power of innovation and strategic resource management in achieving lofty goals with constrained resources.
Ultimately, managing limited resources to achieve personal goals requires a strategic, disciplined approach that emphasizes efficiency, prioritization, and adaptability. By employing a structured framework, leveraging technology, and embracing strategic partnerships, individuals can maximize their resource utilization and achieve their goals, even in the face of limitations. These principles, drawn from the playbook of consulting and strategy development, offer a robust template for personal and organizational success.
Developing a strategic roadmap in Excel is a critical task for any organization aiming to streamline its business planning and execution processes. Excel, with its versatile features, offers a robust platform for creating a detailed and actionable strategic roadmap. This guide provides a framework and actionable insights on how to build a roadmap in Excel, tailored for C-level executives seeking to drive their organizations toward Operational Excellence and Strategic Planning success.
Firstly, understanding the importance of a strategic roadmap is crucial. It serves as a visual representation that outlines the key steps an organization needs to take to achieve its strategic goals. Excel allows for the customization and flexibility needed to adapt this roadmap as strategies evolve. The process begins with defining clear, measurable objectives that align with the organization's overarching goals. This alignment ensures that every action taken contributes directly to the broader vision, making the roadmap not just a planning tool, but a critical component of Strategy Development.
Next, gathering and organizing relevant data is a foundational step in building your roadmap in Excel. This involves collecting data on market trends, internal performance metrics, and competitive analysis. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Bain emphasize the importance of data-driven decision-making in strategic planning. Utilizing Excel's analytical tools, such as pivot tables and conditional formatting, can help highlight key insights and patterns that will inform the strategic direction. This phase is about laying the groundwork for informed decision-making, ensuring that the roadmap is built on a solid foundation of empirical evidence and strategic analysis.
Once the objectives are set and the data is organized, the next step is to design the roadmap template in Excel. This involves setting up a timeline, defining milestones, and identifying the key initiatives required to reach those milestones. Excel's flexibility allows for the creation of a dynamic template that can be easily updated as initiatives progress or as priorities shift. It's important to keep the template clear and user-friendly, with visual elements like Gantt charts or timelines to provide a snapshot of the roadmap at a glance. This visual representation is crucial for keeping all stakeholders aligned and focused on the organization's strategic goals.
Implementing the Roadmap
With the strategic roadmap template in place, the focus shifts to implementation. This involves assigning responsibilities, setting deadlines, and establishing metrics for success. Excel's tracking capabilities come into play here, allowing for real-time monitoring of progress against the roadmap. It's essential to establish a cadence of regular reviews and updates to the roadmap. These reviews serve as checkpoints to assess progress, make necessary adjustments, and ensure that the organization remains on track to achieve its strategic objectives.
Effective communication is another critical aspect of implementing the strategic roadmap. All relevant stakeholders should have access to the roadmap and understand their role in its execution. Excel facilitates this by enabling the sharing of the roadmap document, either directly or through integration with other Microsoft Office applications. This ensures that everyone involved is working from the same plan and can collaborate effectively towards common goals.
Risk management is an integral part of the implementation process. Identifying potential risks and incorporating contingency plans into the roadmap can help mitigate these risks. Excel's analytical tools can be used to model various scenarios and their potential impact on the roadmap. This proactive approach to risk management is vital for maintaining the integrity of the strategic plan and ensuring that the organization can navigate any challenges that arise.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Roadmap
Continuous monitoring and adjustment of the strategic roadmap are essential for its success. Excel's capabilities allow for the creation of dashboards that provide a real-time view of progress against strategic objectives. These dashboards can be customized to highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) and other metrics that are critical for the organization's success. Regularly reviewing these metrics ensures that the organization can quickly respond to changes in the internal or external environment.
Adjustments to the roadmap may be necessary as new opportunities or challenges emerge. Excel's flexibility allows for easy updates to the roadmap, ensuring that it remains relevant and aligned with the organization's strategic goals. This iterative process of monitoring, reviewing, and adjusting the roadmap is a hallmark of agile and responsive strategic planning.
In conclusion, building a strategic roadmap in Excel requires a structured approach that begins with clear objective setting, followed by data gathering and template design. Implementing the roadmap with a focus on communication, risk management, and continuous monitoring ensures that the organization stays on course to achieve its strategic goals. Excel's versatility and analytical capabilities make it an invaluable tool in this process, providing a dynamic platform for strategic planning and execution.
Emerging technologies are fundamentally reshaping the landscape of Strategic Planning, offering unprecedented opportunities for companies to enhance their decision-making processes, gain competitive advantages, and foster innovation. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can access deeper insights, predict future trends more accurately, and execute their strategies more effectively.
Utilizing Big Data and Analytics for Informed Decision Making
One of the most significant ways companies can enhance their Strategic Planning processes is through the utilization of Big Data and Analytics. These technologies enable businesses to process vast amounts of data, uncover hidden patterns, and gain insights that were previously inaccessible. For instance, by analyzing customer data, companies can identify emerging market trends, predict customer behaviors, and tailor their strategies to meet evolving demands. According to a report by McKinsey, companies that leverage customer behavior insights outperform peers by 85% in sales growth and more than 25% in gross margin. This demonstrates the critical role of data analytics in driving strategic decisions and achieving superior performance.
Moreover, predictive analytics can significantly improve risk management by forecasting potential market shifts and identifying threats before they materialize. This proactive approach allows companies to adjust their strategies in real-time, mitigating risks and capitalizing on opportunities. For example, in the financial sector, firms use predictive models to assess credit risk, detect fraudulent activities, and optimize investment portfolios, thereby enhancing their strategic agility and operational resilience.
Furthermore, Big Data and Analytics facilitate Performance Management by enabling companies to track and measure the effectiveness of their strategic initiatives. Through advanced analytics tools, businesses can set, monitor, and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) in real-time, making data-driven adjustments to their strategies to ensure alignment with their objectives.
Adopting Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Strategic Insights
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming Strategic Planning by providing companies with the ability to simulate and predict future scenarios with remarkable accuracy. These technologies can analyze complex datasets, identify patterns, and generate predictive models that help decision-makers anticipate market changes and customer needs. For example, AI-powered tools can forecast demand for products and services, enabling companies to optimize their supply chain operations and inventory management.
AI and ML also enhance strategic decision-making by automating routine tasks, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic activities. For instance, AI algorithms can automate the analysis of competitive intelligence, providing regular updates on competitors’ strategies, market positioning, and performance. This continuous flow of insights supports a dynamic Strategic Planning process, where strategies can be adapted in response to changing market conditions.
Moreover, AI-driven scenario planning tools allow companies to explore various strategic options and assess their potential impacts under different conditions. This capability is invaluable for Risk Management, as it enables organizations to prepare for a range of outcomes and develop contingency plans. A notable example is the use of AI by pharmaceutical companies to simulate clinical trial outcomes, significantly accelerating the drug development process and improving strategic decision-making in R&D investments.
Leveraging Digital Twins for Operational Excellence and Innovation
Digital Twins technology, which creates virtual replicas of physical systems, processes, or products, offers another avenue for enhancing Strategic Planning. By simulating the performance of products or operations in a virtual environment, companies can identify inefficiencies, test changes, and predict outcomes without the risks and costs associated with real-world experimentation. This capability is particularly beneficial for Operational Excellence, as it allows for continuous improvement and optimization of processes.
For instance, in the manufacturing sector, Digital Twins are used to model production lines and supply chains, enabling companies to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and predict the impact of changes on production capacity and delivery times. This not only improves operational efficiency but also supports strategic initiatives by providing a clear understanding of operational capabilities and constraints.
Furthermore, Digital Twins facilitate innovation by offering a safe and cost-effective environment for testing new products, services, and business models. Companies can explore disruptive technologies and approaches, assess their feasibility, and refine their strategies before implementation in the real world. This approach to innovation management ensures that strategic planning is informed by practical insights and grounded in realistic assessments of technological and market potential.
In conclusion, emerging technologies such as Big Data and Analytics, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, and Digital Twins are revolutionizing the field of Strategic Planning. By harnessing these technologies, companies can enhance their decision-making processes, gain deeper insights into market trends and customer behaviors, improve risk management, and drive operational excellence and innovation. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly play an increasingly critical role in shaping the strategic agendas of forward-thinking organizations.
Understanding how offshoring benefits the United States requires a nuanced appreciation of the global business landscape and the strategic imperatives driving organizational decisions. Offshoring, the practice of relocating certain business functions or processes to countries where costs are lower, has been a pivotal strategy for U.S. organizations aiming to maintain competitiveness and enhance profitability. This approach not only capitalizes on cost differentials but also taps into global talent pools, fostering innovation and operational excellence.
Cost reduction is often the most cited advantage of offshoring. By leveraging lower labor costs in countries such as India, China, or the Philippines, U.S. organizations can significantly decrease their operational expenses. This is not merely about minimizing expenses but also about reallocating resources towards core competencies and strategic initiatives. Such a reallocation allows for an enhanced focus on Research and Development (R&D), marketing, and customer engagement strategies that are pivotal for long-term growth and sustainability.
Moreover, offshoring opens doors to global markets, providing U.S. organizations with a strategic foothold in emerging economies. This presence is not just beneficial for tapping into new customer bases but also for understanding and adapting to global market dynamics. The insights gained from operating in diverse markets can be invaluable for Strategy Development, enabling organizations to anticipate and respond to international trends and demands more effectively.
Enhancing Competitive Strategy through Offshoring
Offshoring can be a cornerstone for refining an organization's Competitive Strategy. By offshoring non-core functions, U.S. organizations can concentrate on areas where they can offer unique value propositions. This strategic focus is essential for differentiation and for sustaining a competitive edge in today's fast-paced business environment. Furthermore, access to a global talent pool through offshoring can accelerate innovation. The diverse perspectives and skills that international teams bring to the table can spur creativity, leading to breakthrough products and services.
Another strategic advantage is the agility and flexibility that offshoring provides. In an era where market conditions and consumer preferences change rapidly, the ability to scale operations up or down without significant capital investment or long-term commitments can be a game-changer. This operational flexibility allows U.S. organizations to respond more swiftly to market demands, regulatory changes, and technological advancements.
Offshoring also plays a critical role in Digital Transformation initiatives. By collaborating with offshore partners who have specialized expertise in digital technologies, U.S. organizations can accelerate their digital journeys. This collaboration can range from software development to data analytics and cybersecurity, covering a broad spectrum of digital capabilities that are essential for modernizing operations and delivering enhanced customer experiences.
Implementing a Successful Offshoring Framework
For offshoring to be truly beneficial, it must be approached with a strategic framework in mind. This involves careful planning, partner selection, and ongoing management to ensure alignment with the organization's overall strategy. A well-structured offshoring strategy should include clear objectives, performance metrics, and a governance model to manage the relationship with offshore partners effectively.
Consulting firms like McKinsey and Deloitte have emphasized the importance of aligning offshoring strategies with organizational goals and risk management practices. They advocate for a template that not only focuses on cost savings but also evaluates the impact on customer satisfaction, innovation capabilities, and operational resilience. This holistic approach ensures that offshoring contributes positively to the organization's strategic objectives and long-term vision.
Real-world examples of successful offshoring abound. Many leading U.S. technology firms have established R&D centers in countries like India and China, not just for cost savings but also to leverage local talent for innovation. These centers have become integral to the organizations' global innovation ecosystems, contributing significantly to product development and technological advancements.
Conclusion
In summary, offshoring offers U.S. organizations a multitude of strategic advantages, from cost reduction and access to global talent pools to enhanced operational flexibility and innovation. However, realizing these benefits requires a strategic, well-executed approach that aligns with the organization's broader objectives. By adopting a comprehensive framework for offshoring, U.S. organizations can not only optimize their operations but also position themselves for sustained growth and success in the global marketplace.
Creating a compelling problem statement is a critical step in the Strategic Planning process. It sets the stage for identifying and addressing key issues that an organization faces. A well-crafted problem statement provides a clear, concise description of the challenges to be solved and serves as a foundation for developing effective strategies. The question of "what are the key elements of a problem statement pdf" is frequently raised by C-level executives who understand the importance of getting this step right in the strategic planning documentation. This document should act as a framework that guides the subsequent analysis and strategy formulation phases.
The first essential component of a problem statement is a clear, specific description of the issue at hand. It should succinctly summarize the problem without diving into unnecessary details. This requires a deep understanding of the situation, often necessitating thorough consulting and analysis. For instance, a problem statement in the context of Digital Transformation might focus on the organization's current technological limitations and the impact on market competitiveness. The key here is to be as precise as possible about the problem's nature, scope, and implications.
Another critical element is the rationale behind addressing the problem. This section should articulate why the problem matters to the organization and its stakeholders. It often includes a discussion on the potential consequences of inaction, supported by data and insights from reputable sources like McKinsey or Gartner. For example, a problem statement related to Operational Excellence might highlight inefficiencies costing the organization millions annually, backed by industry benchmarks. This part of the problem statement makes a compelling case for why the issue cannot be ignored.
Context and Constraints
Understanding the context in which the problem exists is another vital component. This includes the internal and external factors that contribute to the problem or could influence the solution. For instance, a problem statement focused on Risk Management might consider regulatory changes, market volatility, or technological advancements. It's about painting a picture of the environment surrounding the issue, providing a backdrop against which the problem and its potential solutions can be evaluated.
Constraints are also a crucial part of the problem statement. These are the limitations within which any solution must be developed and implemented. Constraints can be financial, technological, regulatory, or cultural within the organization. Acknowledging these upfront helps in setting realistic expectations and guides the strategy development process. For example, a template for addressing Performance Management issues might need to consider budgetary constraints or existing IT infrastructure limitations.
The inclusion of these elements ensures that the problem statement is grounded in reality and considers the broader context. It helps in identifying feasible solutions that are not just effective but also practical given the organization's specific circumstances. This approach fosters innovation within boundaries, encouraging creative solutions that are also viable.
Goals and Objectives
Clearly defined goals and objectives are essential components of a problem statement. These should articulate what the organization aims to achieve by addressing the problem. Setting these objectives provides direction for the strategic planning process and criteria against which potential solutions can be evaluated. For instance, a problem statement for a strategy aimed at Innovation might set a goal to enter new markets or develop new products within a specific timeframe.
These goals should be SMART—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. They act as a benchmark for success, enabling the organization to measure progress and make adjustments as needed. For example, a goal to "increase market share by 10% within two years through digital channels" provides a clear target for the organization's Digital Transformation efforts.
Establishing these objectives also helps in aligning the organization's resources and efforts towards a common aim. It ensures that all departments and teams understand what they are working towards and how their contributions fit into the larger picture. This alignment is crucial for effective Strategy Development and implementation.
Actionable Insights and Next Steps
The final key element of a problem statement is the outline of actionable insights and potential next steps. This part bridges the gap between identifying the problem and beginning the journey towards a solution. It suggests a framework for the analysis and strategy formulation phases that follow. While it does not provide the solution itself, it sets the stage for the detailed work that will lead to resolving the issue.
This section might include recommendations for initial research, potential areas for innovation, or preliminary steps towards Change Management. For example, a problem statement addressing Leadership challenges might recommend a leadership assessment or a culture survey as a starting point. These insights guide the organization on where to focus its efforts initially.
By including these components, a problem statement becomes a powerful tool in Strategic Planning. It not only defines the problem but also outlines why it matters, the context and constraints around it, what success looks like, and how to start addressing it. This comprehensive approach ensures that the organization is well-prepared to tackle its challenges head-on, with a clear direction and understanding of what needs to be done. Crafting such a problem statement requires careful thought and analysis but is a critical step in setting the stage for successful Strategy Development and implementation.
Understanding what is a strategic business plan is crucial for C-level executives aiming to steer their organizations towards long-term success. At its core, a strategic business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines an organization's long-term goals and the strategies it will employ to achieve them. This plan serves as a roadmap, guiding the organization through the complexities of its operating environment while ensuring that all efforts are aligned with its overarching objectives.
A strategic business plan is more than just a tool for securing funding or satisfying board members. It is an essential component of effective Strategy Development, serving as a framework that informs decision-making processes at every level of the organization. By clearly defining objectives, setting performance targets, and outlining the resources required to achieve these goals, a strategic business plan enables organizations to navigate through market uncertainties with greater agility and confidence.
The development of a strategic business plan involves a thorough analysis of the organization's internal and external environments. This includes evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis), understanding market dynamics, and identifying key drivers of change. The insights gained from this analysis are then used to craft strategies that leverage the organization's core competencies to capitalize on market opportunities and mitigate potential risks.
Key Components of a Strategic Business Plan
A strategic business plan typically includes several key components that provide a clear and actionable roadmap for the organization. These components often encompass:
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview of the strategic plan, including the organization's mission, vision, and key strategic objectives.
- Market Analysis: An in-depth look at the organization's operating environment, including market trends, customer needs, and competitive positioning.
- Strategy and Implementation: Detailed descriptions of the strategies the organization will pursue to achieve its objectives, including specific initiatives, timelines, and responsible parties.
- Financial Plan: A projection of the financial outcomes expected from implementing the strategic plan, including revenue forecasts, budget allocations, and investment requirements.
- Risk Management: An analysis of potential risks that could impact the strategic plan's success and the measures in place to mitigate these risks.
Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring that the strategic business plan is both comprehensive and actionable. By addressing these areas, organizations can develop a robust framework that aligns resources and efforts towards achieving desired outcomes.
Moreover, the strategic business plan must be a living document, subject to regular review and adjustments as market conditions and organizational priorities evolve. This dynamic approach allows organizations to remain responsive to changes and maintain strategic agility in a rapidly changing business environment.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
Several leading organizations have demonstrated the power of effective strategic business planning. For example, technology giants like Apple and Google have consistently leveraged strategic planning to navigate market shifts and drive innovation. By clearly articulating their strategic objectives and aligning their resources accordingly, these companies have maintained their positions as industry leaders, despite the fast-paced nature of the tech sector.
In the consulting world, firms such as McKinsey & Company and Boston Consulting Group (BCG) emphasize the importance of strategic business planning in their advisory services. These firms help clients across industries to develop and implement strategic plans that foster growth, enhance operational efficiency, and build resilience against market disruptions. Through their expertise, these consulting firms have aided countless organizations in transforming strategic plans from mere documents into actionable drivers of success.
Implementing a strategic business plan requires commitment, discipline, and a willingness to adapt. Organizations that excel in this area often exhibit strong leadership, a culture of continuous improvement, and an unwavering focus on their strategic objectives. These qualities, combined with a well-crafted strategic business plan, enable organizations to achieve sustainable growth and long-term success in an increasingly competitive and complex business landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a strategic business plan is an indispensable tool for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today's business environment. By providing a clear framework for strategic decision-making, aligning resources with objectives, and fostering a culture of agility and innovation, a strategic business plan empowers organizations to achieve their long-term goals. As the business world continues to evolve, the importance of strategic planning will only grow, making it essential for C-level executives to master the art and science of strategic business planning.
Crafting a problem statement that aligns with Strategic Planning objectives is a critical step for any organization aiming to tackle issues in a structured and effective manner. A well-defined problem statement acts as a guiding light for strategy development, ensuring that efforts are directed towards addressing the core issues that hinder organizational growth and efficiency. Understanding "what does a problem statement look like" within the context of strategic planning involves delving into the specifics of the organization's challenges, goals, and the environment in which it operates.
A problem statement should succinctly describe the issue at hand, its impact on the organization, and the potential benefits of resolving it. This clarity is paramount for C-level executives who need to make informed decisions quickly. The statement should not only highlight the problem but also encapsulate the urgency and significance of addressing it. Crafting such a statement requires a deep understanding of the organization's Strategic Planning objectives, as well as the ability to distill complex issues into a clear, actionable framework.
To ensure alignment with Strategic Planning objectives, the problem statement must be rooted in a thorough analysis of the organization's internal and external environments. This involves leveraging frameworks and methodologies from top consulting firms like McKinsey or Bain, which emphasize the importance of a data-driven approach to understanding strategic challenges. For instance, a SWOT analysis can provide insights into the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, serving as a foundational element for the problem statement.
Moreover, the problem statement must be flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances while remaining focused on the long-term Strategic Planning objectives. This balance is crucial for maintaining strategic direction and ensuring that the organization remains responsive to emerging challenges and opportunities. The use of a well-crafted problem statement as a part of the strategic framework facilitates a focused approach to Strategy Development, Performance Management, and Change Management.
Key Elements of a Problem Statement in Strategic Planning
When asking "what does a problem statement look like," it's essential to consider the key elements that constitute an effective statement. First and foremost, it must clearly define the problem in a way that is understandable to all stakeholders. This involves avoiding jargon and ensuring that the statement is grounded in reality, reflecting the actual challenges faced by the organization.
Secondly, the problem statement should establish the scope of the issue. This includes specifying the areas of the organization affected, the processes involved, and the timeframe over which the problem has developed. A precise scope helps in focusing the Strategic Planning efforts and prevents the dilution of resources across too broad an area.
Lastly, the problem statement should articulate the impact of the problem on the organization's Strategic Planning objectives. This could involve quantifying the problem in terms of financial loss, customer impact, or operational inefficiency. By linking the problem directly to the organization's objectives, the statement underscores the importance of addressing the issue and sets the stage for developing targeted strategies.
Real-World Examples and Application
Consider a global retail organization facing declining sales due to changing consumer behaviors and increased competition from e-commerce platforms. A problem statement for this organization might look like: "Over the past two years, our organization has experienced a 10% decline in in-store sales, significantly impacting our market share and profitability. This trend threatens our long-term Strategic Planning objectives of market leadership and financial growth. Addressing this issue requires a strategic shift towards Digital Transformation and an enhanced online customer experience."
This statement clearly defines the problem, establishes its scope, and links it to the organization's Strategic Planning objectives. It also sets the stage for a strategic response that involves embracing Digital Transformation, a priority for many organizations navigating the challenges of the digital economy.
In conclusion, crafting a problem statement that aligns with Strategic Planning objectives is a critical skill for leaders. It requires a deep understanding of the organization's strategic goals, the ability to analyze complex situations, and the clarity to articulate challenges in a way that mobilizes the organization towards effective solutions. By focusing on the key elements of a problem statement and applying real-world examples, leaders can ensure that their Strategic Planning efforts are both focused and impactful.
Scenario Planning is a strategic tool that organizations use to envision and prepare for multiple future possibilities, ensuring resilience and flexibility in the face of potential disruptions. This method involves identifying and analyzing various future scenarios, including best-case, worst-case, and most likely scenarios, to develop strategic responses. By considering a wide range of possible futures, organizations can better anticipate changes, mitigate risks, and seize opportunities.
Understanding Scenario Planning
Scenario Planning starts with the identification of external forces and trends that could impact the organization. These might include technological advances, regulatory changes, economic shifts, or social trends. The goal is to understand how these forces could interact to create different future business environments. Organizations often engage in Environmental Scanning and SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to gather necessary insights. This process helps in identifying Critical Uncertainties—those factors with the potential to have significant impacts on the organization's strategy but whose outcomes are highly unpredictable.
Once critical uncertainties are identified, organizations develop a range of scenarios that represent different ways these uncertainties could unfold in the future. Each scenario tells a coherent story about a possible future state, including details about how market conditions, customer preferences, and competitive landscapes might evolve. This approach allows organizations to "rehearse" responses to various future events, enhancing their Strategic Agility. The scenarios are not predictions but rather plausible and divergent futures that challenge the organization's assumptions and expand its thinking.
Strategic Planning then involves aligning the organization's strategy with these scenarios. This might include developing flexible strategies that can succeed across multiple scenarios or creating contingent strategies that can be quickly deployed if certain indicators suggest a particular scenario is becoming more likely. This approach helps organizations to be more adaptive and resilient, reducing the risk of being caught off-guard by future disruptions.
Applying Scenario Planning in Practice
One actionable insight for implementing Scenario Planning is to establish a dedicated team or task force responsible for overseeing the scenario development process. This team should include members from various functional areas within the organization to ensure a comprehensive understanding of potential impacts. Engaging external experts or consultants can also provide valuable perspectives and help challenge internal assumptions.
The scenario development process typically involves workshops or brainstorming sessions where participants explore different future possibilities. Techniques such as trend analysis, impact analysis, and cross-impact analysis can be used to understand the relationships between different forces and how they might combine to create future scenarios. Organizations can then use tools like scenario matrices to organize and prioritize these scenarios based on their likelihood and potential impact on the organization.
After developing scenarios, the next step is to analyze the implications of each scenario for the organization's strategy. This involves identifying opportunities and threats within each scenario and assessing the organization's readiness to respond. Strategic options are then developed, which might include diversifying product lines, investing in new technologies, or building strategic partnerships. These strategies are then stress-tested against each scenario to ensure they are robust and flexible enough to succeed in a variety of future states.
Real-World Examples of Scenario Planning
A notable example of Scenario Planning in action is the global energy company Royal Dutch Shell. In the 1970s, Shell used Scenario Planning to anticipate the possibility of a Middle Eastern oil embargo, a scenario that many competitors considered unlikely. When the 1973 oil crisis occurred, Shell was better prepared than its competitors, allowing it to navigate the crisis more effectively. Shell's use of Scenario Planning has been credited with helping it become one of the largest energy companies in the world.
Another example is the multinational technology company Microsoft. In the early 2000s, Microsoft engaged in Scenario Planning to explore the future of computing. This process helped Microsoft anticipate the rise of cloud computing and the decline of traditional software licensing models. As a result, Microsoft invested heavily in developing its Azure cloud platform, which has become a significant growth driver for the company.
These examples illustrate the power of Scenario Planning in helping organizations navigate uncertainty and change. By systematically exploring different future scenarios, organizations can develop more resilient and flexible strategies, positioning themselves to thrive in an ever-changing business environment.
Formulating an effective problem statement is a critical step in guiding strategic planning initiatives within any organization. It serves as the foundation for identifying, analyzing, and addressing key issues that hinder organizational performance or growth. A well-crafted problem statement not only clarifies the issue at hand but also aligns the team's focus and sets the stage for innovative solutions. In the realm of strategic planning, understanding what is problem statement in research is paramount for C-level executives who aim to steer their organizations towards success.
The essence of a problem statement in the context of strategic planning lies in its ability to succinctly summarize the challenges or opportunities facing the organization. It should encapsulate the core of the issue, its impact on the organization, and the potential benefits of addressing it. Crafting such a statement requires a deep understanding of the organization's current state, its strategic objectives, and the external environment. This involves gathering and analyzing data, consulting with stakeholders, and leveraging insights from past initiatives. The goal is to create a statement that is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), providing a clear direction for the strategic planning process.
Developing a robust framework for formulating a problem statement is crucial. This framework should guide the executive team through a structured process of identifying key issues, understanding their root causes, and assessing their impact on the organization's strategic goals. Consulting firms often employ various strategic analysis tools, such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis, PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental) analysis, and Porter's Five Forces, to facilitate this process. These tools help in distilling complex information into actionable insights, enabling executives to articulate problem statements that are both comprehensive and precise.
Key Components of an Effective Problem Statement
An effective problem statement should include several key components. First, it must clearly define the issue, avoiding generalizations and focusing on specific challenges or opportunities. This specificity aids in understanding the scope and scale of the problem. Second, it should highlight the implications of the problem on the organization's operations, strategic goals, or stakeholder value. This helps in prioritizing the issue within the broader strategic context. Lastly, a good problem statement should hint at the potential benefits or outcomes of solving the problem, setting the stage for ideation and solution development.
For instance, a problem statement focusing on declining market share might detail the extent of the decline, its impact on revenue and profitability, and the potential gains from reversing this trend. This level of detail and clarity ensures that the strategic planning process is focused and goal-oriented. Additionally, incorporating data and insights from authoritative sources, such as market research firms or industry analyses, can further strengthen the problem statement by grounding it in reality.
It's also important to note that the problem statement is not static. As the strategic planning process unfolds, new information may emerge that necessitates revising the problem statement. This iterative approach ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to changing circumstances, allowing for the refinement of strategies and initiatives as needed.
Utilizing a Template for Problem Statement Development
Utilizing a template can streamline the development of a problem statement. Such a template typically includes sections for describing the issue, its impact, and the desired state or outcomes. This structured approach ensures that all relevant aspects of the problem are considered and articulated clearly. Consulting firms often provide customized templates as part of their strategy development toolkit, tailored to the specific needs and challenges of the organization.
For example, a template might prompt executives to first describe the issue in quantitative terms, such as "a 15% decline in customer retention rate over the past year." Following this, the template could guide them to explore the impact of this issue, perhaps on customer lifetime value or brand reputation. Finally, the template would encourage the articulation of a desired outcome, like "reversing the decline to achieve a 10% improvement in retention within 18 months." This methodical approach ensures that the problem statement is not only clear and concise but also aligned with the organization's strategic objectives.
In conclusion, crafting an effective problem statement is a critical first step in the strategic planning process. It requires a deep understanding of the organization's challenges and opportunities, a structured approach to problem identification and analysis, and the ability to articulate the issue in a way that is clear, concise, and actionable. By focusing on the key components of a problem statement and utilizing a template for its development, C-level executives can ensure that their strategic planning initiatives are grounded in reality and geared towards meaningful outcomes.
Crafting a comprehensive annual operating plan (AOP) is a critical exercise for any organization aiming to align its operational activities with strategic goals. This process requires meticulous planning, a deep understanding of the organization's strategic vision, and an ability to translate long-term objectives into actionable, short-term operational plans. The AOP serves as a roadmap, guiding the organization through the fiscal year, ensuring that every department's efforts contribute to the overarching strategic objectives.
The first step in developing an effective AOP is to conduct a thorough review of the previous year's performance. This involves analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs), financial results, and progress towards strategic goals. Insights from this review will highlight areas of success and identify opportunities for improvement. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Deloitte emphasize the importance of this retrospective analysis as a foundation for forward-looking planning. This stage also involves re-evaluating the organization's strategic goals to ensure they remain relevant and achievable within the current market context.
Following the review, the next step is to set clear, measurable objectives for the upcoming year. These objectives should be closely aligned with the organization's strategic goals and should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Each department within the organization should then develop its own set of objectives that contribute to the overall goals. This alignment ensures that every team's efforts are directed towards common outcomes, fostering a sense of unity and purpose across the organization.
Finally, the AOP must include detailed action plans for achieving the set objectives. This involves outlining specific initiatives, assigning responsibilities, setting timelines, and allocating resources. A robust framework for monitoring progress and performance against the plan is also essential. Regular review meetings should be scheduled to assess progress, address challenges, and make necessary adjustments to the plan. This iterative process ensures that the organization remains agile and can respond effectively to unforeseen challenges or opportunities.
Best Practices for AOP Development
Engaging stakeholders throughout the AOP development process is crucial. This ensures buy-in and commitment from all levels of the organization, from the C-suite to frontline employees. Effective communication plays a key role here, with clear articulation of the strategic goals, the rationale behind them, and the expected contributions from each department. This collaborative approach not only enhances the quality of the AOP but also fosters a culture of accountability and transparency.
Another best practice is to leverage technology in the planning process. Advanced analytics and business intelligence tools can provide valuable insights into market trends, customer behavior, and operational efficiencies. These insights can inform more accurate forecasting, risk assessment, and scenario planning. Consulting giants like Accenture and PwC advocate for the integration of digital tools in strategic planning processes to enhance data-driven decision-making and operational agility.
Incorporating risk management into the AOP is also essential. This involves identifying potential internal and external risks that could impact the organization's ability to achieve its objectives. For each identified risk, the plan should outline mitigation strategies and contingency plans. This proactive approach to risk management ensures that the organization is well-prepared to navigate uncertainties and maintain operational resilience.
Utilizing Frameworks and Templates
A structured framework can significantly streamline the AOP development process. Many consulting firms offer proprietary frameworks that guide organizations through the planning process, ensuring that all critical aspects are considered. These frameworks typically encompass market analysis, strategic goal setting, operational planning, resource allocation, and performance monitoring. Utilizing such a framework ensures a comprehensive and systematic approach to AOP development.
Templates can also be valuable tools in the AOP development process. They provide a standardized format for presenting the plan, ensuring consistency and clarity. Templates can facilitate the integration of plans across departments, enabling a more cohesive and aligned operational strategy. They also save time and reduce the risk of omitting critical information.
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of these practices. Organizations that have adopted a structured framework and utilized templates for their AOP development often report improved strategic alignment, enhanced operational efficiency, and better financial performance. These organizations are also better positioned to adapt to changes in the market, leveraging their strategic agility to maintain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, developing a comprehensive annual operating plan is a complex but essential process that requires careful analysis, strategic alignment, and detailed planning. By following best practices and leveraging frameworks and templates, organizations can enhance their strategic execution and operational efficiency. Engaging stakeholders, incorporating technology, and integrating risk management are also key to developing an effective AOP. With a well-crafted AOP, organizations can navigate the fiscal year with confidence, poised to achieve their strategic goals and drive sustainable growth.
Creating an effective strategic plan is a critical step for any organization aiming to achieve long-term success. The process involves a systematic approach to setting goals, determining actions to achieve those goals, and mobilizing resources to execute the actions. A well-crafted strategic plan not only outlines where an organization is going and the actions needed to make progress but also how it will know if it is successful. In the realm of consulting, firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of aligning the strategic plan with the organization's core values and mission to ensure sustainable growth.
At the heart of how to do a strategic plan is the framework used to guide the process. A robust framework incorporates an analysis of the internal and external environment, setting strategic priorities, and defining key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress. Consulting giants often advocate for frameworks that are flexible yet comprehensive, allowing organizations to adapt to changing market dynamics while staying focused on their long-term vision. The use of a template can streamline the strategic planning process, ensuring that all critical elements are considered and that the plan is communicated effectively across the organization.
Strategy development should be a collaborative process that involves input from various levels of the organization. This inclusivity ensures that the strategic plan is realistic and grounded in the operational realities of the organization. Additionally, engaging employees in the strategy development process can foster a sense of ownership and commitment to the organization's goals, which is crucial for successful implementation. The role of leadership in driving the process cannot be overstated; they must champion the plan and lead by example to instill a strategic mindset throughout the organization.
Key Components of a Strategic Plan
The strategic planning process can be daunting, but breaking it down into key components can make it more manageable. First and foremost, a clear articulation of the organization's mission, vision, and core values sets the foundation for the strategic direction. This step ensures that the strategic plan aligns with the overarching purpose of the organization and reflects its identity.
Conducting a thorough SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) is another critical component. This analysis provides insight into the organization's current position relative to its competitors and the external environment. It helps in identifying strategic priorities and areas where the organization needs to innovate or improve. Consulting firms often leverage their vast industry knowledge to assist organizations in conducting a comprehensive SWOT analysis.
Setting strategic objectives is the next step. These objectives should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to ensure they are clear and actionable. For each objective, developing a set of initiatives or strategies to achieve them is essential. This includes identifying the resources required, assigning responsibilities, and establishing timelines for completion. Performance management systems play a crucial role in monitoring progress and ensuring accountability throughout the implementation phase.
Implementing and Monitoring the Strategic Plan
Implementation is where many organizations face challenges. A strategic plan is only as good as its execution. Effective implementation requires detailed action plans, including timelines, resource allocation, and defined responsibilities. Change management practices are critical during this phase to address resistance and ensure a smooth transition. Regular communication and updates on progress can help maintain momentum and keep the organization aligned with the strategic goals.
Monitoring and evaluating the progress of the strategic plan is vital for its success. This involves setting up a system to track performance against the defined KPIs and making adjustments as necessary. Organizations should conduct regular strategy reviews to assess what is working and what is not. This iterative process allows for continuous improvement and ensures that the strategic plan remains relevant in a rapidly changing business environment.
Real-world examples demonstrate the importance of flexibility and adaptation in strategic planning. For instance, companies like Amazon and Google have excelled by continuously refining their strategies based on market feedback and emerging trends. Their ability to pivot and innovate has been key to maintaining a competitive edge in the digital era.
In summary, creating an effective strategic plan requires a systematic approach, a flexible yet comprehensive framework, and active engagement from all levels of the organization. By focusing on these critical elements and leveraging best practices from consulting experts, organizations can develop a strategic plan that drives sustainable growth and long-term success.
Understanding what is the statement of the problem in business management is pivotal for any C-level executive. It lays the groundwork for identifying, articulating, and ultimately resolving the challenges an organization faces. A well-defined problem statement serves as a compass, guiding strategic planning, operational improvements, and innovation efforts. It encapsulates the essence of the issue at hand, providing a clear direction for the development of a framework and strategy to address it. In the realm of consulting, the articulation of a problem statement is often the first step in the engagement process, setting the stage for effective solution design and implementation.
A problem statement in business management is not merely a description of an issue; it is a precise articulation that captures the gap between the current state and the desired future state of an organization. It outlines the boundaries of the problem, identifies the stakeholders affected, and quantifies the impact on the organization. Crafting a compelling problem statement requires a deep understanding of the organization's strategic objectives, its operational realities, and the external environment in which it operates. This clarity is not just about identifying what is wrong; it is about framing the problem in a way that mobilizes resources, galvanizes leadership, and aligns efforts across the organization.
From a strategic standpoint, a problem statement acts as a catalyst for change. It challenges the status quo and compels an organization to think critically about its Strategy Development, Operational Excellence, and Innovation capabilities. For instance, a well-structured problem statement can illuminate the need for Digital Transformation in an organization lagging behind in technology adoption. By precisely defining the problem—such as "Our current technology infrastructure is inadequate to meet the growing demand for digital services, resulting in a 20% customer churn rate"—leadership can prioritize investments, rally the organization around a common goal, and measure progress against specific benchmarks.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
Developing a robust problem statement requires a structured approach. Consulting firms often employ a template or framework to ensure comprehensiveness and clarity. The first step involves gathering and analyzing data to understand the problem's dimensions. This might include financial analysis, customer feedback, competitive benchmarking, and operational metrics. Next, the problem must be contextualized within the organization's strategic objectives—how does it impact the organization's ability to achieve its goals?
The second step is to articulate the problem in a concise, yet comprehensive manner. This includes describing the current state, the desired future state, and the barriers to achieving that state. The language used should be direct and jargon-free, making the problem statement accessible to all stakeholders. Finally, the problem statement should conclude with a question or a challenge, inviting solutions and encouraging a proactive approach to problem-solving.
For example, a consulting project might begin with a problem statement like, "Despite a 15% increase in sales volume, our profit margins have declined by 10% over the last fiscal year due to inefficiencies in our supply chain operations. How can we redesign our supply chain to improve profitability?" This statement clearly outlines the problem, its impact on the organization, and sets the stage for identifying potential solutions.
Real-World Application and Impact
In practice, a well-defined problem statement has the power to transform an organization. Take, for instance, a global retail chain that recognized a decline in in-store sales while its online competitors were flourishing. By articulating a problem statement that focused on the need to enhance the in-store customer experience to compete effectively in the digital age, the organization was able to prioritize investments in technology, training, and store layout redesigns. This strategic clarity led to a measurable improvement in customer satisfaction and sales performance.
Another example involves a manufacturing company struggling with product quality issues that were affecting customer satisfaction and brand reputation. The problem statement highlighted the gap between the current quality control processes and the industry best practices, leading to a comprehensive review and overhaul of the quality management system. This focused effort not only resolved the immediate quality issues but also instilled a culture of continuous improvement across the organization.
Ultimately, the value of a problem statement in business management cannot be overstated. It is the linchpin that connects strategic vision with operational reality, ensuring that efforts are directed towards the most pressing challenges. For C-level executives, mastering the art of crafting and leveraging problem statements is essential for driving organizational change, fostering innovation, and achieving sustained performance improvement. By adopting a disciplined approach to problem statement development, leaders can ensure that their organizations are well-positioned to navigate the complexities of the modern business environment.
The rise of social entrepreneurship presents a transformative shift in the global business landscape, compelling traditional organizations to rethink their Strategic Planning processes. Social entrepreneurship, characterized by ventures that prioritize social and environmental goals alongside financial returns, has gained significant momentum. This movement not only challenges the conventional profit-centric business model but also introduces new paradigms for innovation, stakeholder engagement, and value creation. As a result, corporate strategic planning must evolve to incorporate these dimensions, ensuring competitiveness and relevance in an increasingly conscientious market.
Integration of Social Objectives into Corporate Strategy
One of the primary implications for corporate strategic planning is the need to integrate social objectives into the core corporate strategy. This integration goes beyond corporate social responsibility (CSR) as a peripheral activity, making social impact a central component of the organization's mission and competitive strategy. For instance, a report by McKinsey highlights that companies integrating social goals into their business model can unlock new markets and drive sustainable growth. This approach requires a deep understanding of the social and environmental issues relevant to the business and the development of innovative solutions that address these challenges while generating economic value.
Strategic planning processes must therefore incorporate tools and frameworks that enable the identification and assessment of social impact opportunities. This might include adopting social return on investment (SROI) metrics, engaging in stakeholder dialogues to understand community needs, and leveraging partnerships with social enterprises. Companies like Patagonia and Ben & Jerry's serve as exemplars, having embedded social and environmental activism into their brand identity and business operations, thus creating a competitive edge through differentiation and customer loyalty.
Moreover, the strategic planning process must be agile enough to respond to the dynamic nature of social issues and stakeholder expectations. This agility can be fostered through continuous environmental scanning, scenario planning, and the incorporation of feedback mechanisms that allow for the iterative refinement of social impact strategies.
Collaboration and Ecosystem Engagement
The rise of social entrepreneurship also underscores the importance of collaboration and ecosystem engagement in corporate strategic planning. Traditional competitive strategies based on zero-sum assumptions are increasingly inadequate in addressing complex social and environmental challenges. Instead, organizations must adopt a more collaborative stance, seeking partnerships with social entrepreneurs, NGOs, government agencies, and even competitors to co-create solutions that have a broader societal impact.
For example, Accenture's research on ecosystem orchestration emphasizes the value of collaborative platforms that bring together diverse stakeholders to innovate and scale solutions to pressing global issues. This approach not only amplifies impact but also enables organizations to share risks and resources, access new capabilities, and tap into collective intelligence. Unilever's partnership with various NGOs and social enterprises to source sustainable raw materials is a case in point, demonstrating how ecosystem collaboration can support both social objectives and business goals.
Strategic planning must therefore prioritize the identification and cultivation of partnership opportunities, the development of shared goals and metrics for success, and the establishment of governance structures that facilitate effective collaboration and mutual accountability.
Adaptation of Business Models and Value Propositions
Finally, the emergence of social entrepreneurship compels organizations to adapt their business models and value propositions to meet the expectations of a more socially and environmentally conscious market. This adaptation might involve innovating new products or services that address social issues, reconfiguring supply chains to enhance sustainability, or adopting business practices that promote economic inclusion and diversity.
Gartner's insights on business model innovation suggest that organizations must be willing to experiment with new approaches, such as circular economy models or impact investing frameworks, to create value in ways that align with societal goals. IKEA's investments in renewable energy and its initiatives to design products with circular principles in mind exemplify how companies can reinvent themselves to thrive in a social entrepreneurship-driven market.
Strategic planning processes must facilitate this adaptation by incorporating sustainability and social impact assessments into product development, market analysis, and business model design. This requires a shift in mindset from viewing social and environmental considerations as constraints to seeing them as sources of innovation and growth opportunities.
The rise of social entrepreneurship represents a paradigm shift that requires organizations to rethink their strategic planning processes. By integrating social objectives into corporate strategy, engaging in collaborative ecosystems, and adapting business models and value propositions, organizations can navigate this shift successfully. This approach not only ensures their long-term viability but also contributes to the creation of a more sustainable and equitable global economy.
Understanding what is allocation of resources in economics is pivotal for C-level executives aiming to align their organization's resource allocation with strategic planning goals. In the context of economics, resource allocation involves distributing available resources among various competing needs and projects within an organization to maximize efficiency and achieve strategic objectives. This process requires a meticulous approach to decision-making, leveraging both quantitative analysis and qualitative judgment to ensure that resources such as capital, labor, and time are utilized in the most effective manner possible.
Strategic planning serves as the foundation for effective resource allocation. It outlines the organization's vision, goals, and the strategies required to achieve them. However, aligning resources with these strategic goals demands a robust framework that can guide the allocation process. Consulting firms such as McKinsey and BCG advocate for a structured approach to resource allocation that involves setting clear priorities, analyzing current resource distributions, and continuously monitoring and adjusting allocations based on performance and changing market conditions. This strategic alignment ensures that the organization's resources are focused on high-priority initiatives that drive growth and innovation.
To optimize resource allocation, organizations must adopt a dynamic and flexible approach. Traditional budgeting processes often fall short in today's fast-paced business environment, where agility and responsiveness are key. Instead, adopting a zero-based budgeting approach or implementing rolling forecasts can provide the flexibility needed to reallocate resources swiftly in response to new opportunities or threats. This ensures that the organization remains aligned with its strategic goals while adapting to market dynamics.
Framework for Strategic Resource Allocation
Developing a framework for strategic resource allocation starts with a deep understanding of the organization's strategic goals and the critical drivers of success. This framework should include a comprehensive analysis of the current resource allocation and its effectiveness in supporting strategic objectives. Tools and templates from consulting practices can be invaluable in this process, offering structured methodologies for evaluating and prioritizing resource allocation across projects and departments.
Key elements of a successful resource allocation framework include setting clear criteria for investment decisions, establishing a governance structure to oversee the allocation process, and implementing a performance management system to track the outcomes of resource allocations. This framework ensures that decision-making is grounded in strategic objectives and that there is accountability for the efficient use of resources. Moreover, it facilitates a culture of continuous improvement, where lessons learned from past allocation decisions inform future strategies.
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of a well-structured resource allocation framework. Companies like Google and Amazon have excelled in aligning their resource allocation with strategic planning goals, focusing on innovation and customer satisfaction. These organizations continuously evaluate their resource allocations, making adjustments to invest in new technologies and markets that support their long-term strategic objectives. Their success underscores the importance of a flexible and strategic approach to resource allocation.
Implementing a Strategic Resource Allocation Process
Implementing a strategic resource allocation process requires a shift in mindset from a static, annual budgeting cycle to a more dynamic, strategic planning approach. This involves moving beyond mere financial considerations to include strategic priorities in the decision-making process. A template for strategic resource allocation might include stages such as strategic goal setting, resource analysis, allocation decision-making, implementation, and monitoring and review.
Effective implementation also hinges on the organization's ability to foster a culture of transparency and accountability. This means clearly communicating the strategic goals and the rationale behind resource allocation decisions to all stakeholders. Engaging cross-functional teams in the allocation process encourages collaboration and ensures that diverse perspectives are considered, leading to more informed and effective allocation decisions.
Moreover, leveraging technology can significantly enhance the resource allocation process. Advanced analytics and business intelligence tools enable organizations to analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends, forecast future needs, and measure the impact of resource allocations on strategic goals. These technologies facilitate a data-driven approach to resource allocation, allowing executives to make more informed decisions and swiftly adjust allocations in response to changing circumstances.
Conclusion
Optimizing resource allocation to align with strategic planning goals is a complex but essential task for C-level executives. It requires a deep understanding of what is allocation of resources in economics, a robust framework for strategic decision-making, and a commitment to continuous improvement. By adopting a dynamic and strategic approach to resource allocation, organizations can ensure that their resources are effectively utilized to achieve their long-term objectives. Success in this endeavor not only drives operational efficiency and innovation but also positions the organization for sustainable growth in an ever-changing business landscape.
Developing a successful strategic plan is a critical endeavor for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today’s business environment. The process involves a series of structured steps and components, designed to align the organization's resources with its vision and goals. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to do a strategic plan, tailored for C-level executives seeking actionable insights.
The first step in strategic planning is to define the organization's mission, vision, and core values. This foundational phase sets the stage for all subsequent planning activities. The mission statement clarifies the organization's purpose, the vision statement outlines its long-term aspirations, and core values guide behavior and decision-making. Engaging stakeholders during this phase ensures alignment and fosters a sense of ownership across the organization.
Following the establishment of these foundational elements, conducting a thorough external and internal analysis is crucial. Tools such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental) analyses provide insights into the organization's operating environment. This step identifies critical issues that the strategic plan must address, including emerging market trends, regulatory changes, and competitive dynamics. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a data-driven approach in this phase to accurately capture the organization's strategic context.
With a clear understanding of the internal and external landscape, the next step is to develop strategic objectives and goals. These should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART). Setting these objectives requires a delicate balance between ambition and realism, ensuring they are challenging yet achievable. This phase often involves scenario planning to anticipate future changes and adapt strategies accordingly.
Framework and Template Design
Creating a strategic planning framework and template is essential for organizing the plan's components coherently. The framework serves as a blueprint, outlining the key areas of focus, such as Market Expansion, Digital Transformation, Operational Excellence, and Innovation. Each area should have a dedicated section in the template, detailing the objectives, strategies, action plans, and performance metrics. This structured approach ensures comprehensive coverage of all critical aspects of the organization's strategy.
The template should also include a timeline for implementation, assigning clear responsibilities to team members. This promotes accountability and facilitates the tracking of progress against milestones. Utilizing a standardized template across the organization enhances consistency in strategic planning efforts and simplifies communication of the strategic plan to stakeholders.
Consulting firms often advocate for the inclusion of a risk management plan within the strategic planning template. This involves identifying potential risks to the strategic objectives and developing mitigation strategies. Incorporating risk management from the outset ensures that the organization is prepared to address challenges proactively, rather than reactively.
Execution and Monitoring
With the strategic plan developed, the focus shifts to execution. This phase is about translating the strategic objectives into actionable initiatives and projects. It requires effective Change Management to align the organization's culture, processes, and resources with the strategic goals. Leadership plays a pivotal role in driving the execution, providing direction, and motivating the team to achieve the set objectives.
Monitoring and evaluating the progress of the strategic plan is critical to its success. This involves establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for each strategic objective and regularly reviewing performance against these metrics. Performance management systems and dashboards are valuable tools for tracking progress and identifying areas requiring adjustment. Regular strategy review meetings should be scheduled to assess the plan's effectiveness and make necessary revisions.
Finally, fostering a culture of continuous improvement is essential for sustaining strategic success. Organizations should encourage feedback from all levels and be willing to adapt their strategies in response to new insights and changing market conditions. This iterative approach to strategic planning ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to opportunities and challenges.
Developing a successful strategic plan is a comprehensive process that requires careful consideration of the organization's vision, a thorough analysis of its internal and external environment, and a structured framework for execution and monitoring. By following these steps and components, organizations can ensure that their strategic plan is not only well-designed but also effectively implemented, driving them towards their long-term goals.
Crafting a strategic problem statement is pivotal in steering an organization towards its objectives. A well-defined problem statement serves as the compass for strategy development, guiding teams through the maze of operational challenges towards effective solutions. The essence of a good problem statement lies in its clarity, conciseness, and capability to galvanize action. It is not merely a statement of an issue but a framework for focusing efforts and resources efficiently.
In the realm of consulting, where precision and impact are paramount, crafting a strategic problem statement is a foundational step in the advisory process. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of articulating a problem statement that is both specific and actionable. This clarity enables organizations to align their strategies with the problem at hand, ensuring that every initiative taken is a step towards resolution. A good problem statement acts as a lens, focusing the organization's efforts on what truly matters, thereby optimizing resource allocation and maximizing impact.
Moreover, a robust problem statement is instrumental in rallying stakeholders around a common goal. It transcends the boundaries of departments and functions, fostering a unified approach to problem-solving. In this context, the problem statement becomes more than a sentence—it becomes a rallying cry that mobilizes and inspires action across the organization. The specificity of the problem statement ensures that all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the issue, which in turn, facilitates collaboration and innovation in developing solutions.
Framework for Crafting a Strategic Problem Statement
Developing a strategic problem statement requires a structured approach. A useful template to consider involves three key elements: the issue, its impact, and the potential for improvement. Firstly, the issue should be described in a manner that is both specific and verifiable. Vague statements lead to vague solutions. Secondly, the impact of the issue on the organization's objectives should be clearly articulated. This includes quantifying the problem in terms of cost, time, or quality, wherever possible. Lastly, the statement should hint at the potential for improvement, suggesting that the problem is solvable and that solutions can lead to significant benefits for the organization.
This framework ensures that the problem statement is grounded in reality, focusing on tangible issues rather than abstract challenges. It also ensures that the problem is relevant to the organization's objectives, making it a worthy focus for strategic efforts. Consulting firms often stress the importance of this relevance, as it ensures that solving the problem will lead to meaningful advancements towards the organization's goals.
Utilizing this template, executives can craft problem statements that are not only clear and specific but also inherently strategic. This strategic nature ensures that the problem statement is directly tied to the organization's broader objectives, making it a powerful tool in strategy development and execution.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a leading retail chain struggling with declining sales. A strategic problem statement for this organization might be, "Sales have declined by 15% over the past two quarters due to an outdated product mix and inadequate online presence, impacting profitability and market share. There is an opportunity to reverse this trend by revitalizing the product line and enhancing digital marketing efforts." This statement clearly outlines the issue, its impact, and the potential for improvement, providing a solid foundation for strategic action.
In another example, a technology firm facing high employee turnover might define their problem as, "Employee turnover has increased by 25% year-over-year, primarily in the tech department, leading to increased recruitment costs and loss of institutional knowledge. Addressing the root causes of dissatisfaction and improving retention strategies presents an opportunity to enhance operational excellence and innovation." This problem statement highlights a specific issue, quantifies its impact, and suggests a path forward, making it an effective tool for strategic planning.
These examples illustrate how a well-crafted problem statement can guide an organization in identifying and addressing critical issues. By focusing on the specifics of the problem, its impact on the organization, and the potential for improvement, executives can ensure that their strategic efforts are both targeted and impactful. In today's fast-paced business environment, the ability to articulate and address problems efficiently is a key driver of success. A strategic problem statement is not just a sentence; it's a blueprint for action.
In conclusion, understanding what is a good problem statement is crucial for any organization aiming to align its strategic efforts with its objectives. By employing a structured framework and focusing on specificity, impact, and potential for improvement, organizations can craft problem statements that not only define the problem but also mobilize the organization towards effective solutions. In the journey towards achieving operational excellence and strategic goals, a well-defined problem statement is an indispensable tool.
Developing a strategic plan PDF that effectively aligns an organization requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various critical components. This document serves as a roadmap for achieving long-term goals, aligning team efforts, and ensuring that every part of the organization is moving in the same direction. To create a strategic plan that is both actionable and aligned with organizational goals, certain key elements must be included.
Firstly, an executive summary is essential. This section provides a high-level overview of the strategic plan, outlining the organization's vision, mission, and key objectives. It sets the tone for the document and gives stakeholders a clear understanding of what the organization aims to achieve. The executive summary must be concise yet informative, offering a snapshot of the strategic direction without delving into the specifics of implementation.
Secondly, a situation analysis is critical. This involves a thorough examination of the organization's current state, including an analysis of internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats (SWOT analysis). Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a data-driven approach to this analysis, leveraging market research and competitive intelligence to inform strategic decisions. This section should also include a stakeholder analysis, identifying key groups affected by the strategic plan and their respective interests and concerns.
Lastly, clear goals and objectives need to be defined. These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting clear goals provides direction and enables the organization to measure progress over time. It's also important to outline the strategies and actions that will be taken to achieve these goals, including resource allocation, timelines, and responsible parties. This section is the core of the strategic plan, guiding the organization's efforts towards achieving its long-term vision.
Strategic Framework and Implementation Plan
The strategic framework provides the structure for executing the strategic plan. It translates the organization's vision and goals into actionable strategies and initiatives. A well-designed framework includes prioritized initiatives, resource allocation, and performance metrics. It's crucial to ensure that the framework is flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances while remaining focused on the organization's long-term goals.
Implementation planning is another key component. This involves setting detailed action plans for each strategic initiative, including timelines, milestones, and responsible parties. Consulting firms like Accenture and Deloitte highlight the importance of a robust implementation plan in ensuring that strategic initiatives are executed effectively and efficiently. This section should also address risk management, identifying potential challenges and contingencies to mitigate these risks.
Performance management is integral to the implementation plan. This involves establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress towards strategic goals. Regular review and reporting mechanisms should be in place to monitor performance, allowing for adjustments to the plan as needed. Effective performance management ensures that the organization remains on track to achieve its strategic objectives.
Leadership, Culture, and Change Management
Leadership commitment is crucial for the success of any strategic plan. Leaders must be fully engaged in the strategy development process and committed to its implementation. They play a key role in communicating the vision and goals to the entire organization, inspiring and motivating employees to align their efforts with the strategic plan. Leadership also involves making tough decisions and allocating resources where they are most needed to achieve strategic objectives.
Organizational culture plays a significant role in the successful implementation of a strategic plan. A culture that is aligned with the organization's strategic goals fosters innovation, collaboration, and a sense of ownership among employees. Consulting firms like Bain and EY stress the importance of aligning culture with strategy to achieve operational excellence. This includes reinforcing values and behaviors that support the strategic objectives and addressing any cultural barriers to change.
Effective change management is essential to ensure that strategic initiatives are embraced by the organization. This involves preparing the organization for change, managing the transition process, and reinforcing changes to make them stick. Change management strategies should be integrated into the strategic plan to address resistance and ensure that employees are supported throughout the process. This ensures that the organization can adapt to new directions and achieve its strategic goals.
In conclusion, developing a strategic plan PDF that effectively aligns an organization requires careful consideration of several key components. From setting a clear vision and goals to implementing a robust framework and managing change, each element plays a critical role in ensuring the strategic plan's success. By incorporating these components, organizations can develop a strategic plan that not only guides them towards their long-term objectives but also ensures alignment and engagement across the organization.
Understanding the nuances of a problem statement is crucial for the strategic planning process. It sets the stage for identifying the right solutions and crafting a roadmap that aligns with the organization's objectives. The clarity and precision of a problem statement can significantly impact the effectiveness of strategy development and implementation. To enhance strategic planning, it's essential to articulate the key elements of a problem statement. This involves a deep dive into what are the 5 elements of a problem statement, providing a comprehensive framework for leaders to address challenges systematically.
The first element of a problem statement is the identification of the issue. This requires a clear and concise description of the problem, focusing on the symptoms that signal its existence. It's not just about stating the problem but understanding its manifestations within the organization. For instance, a decline in sales is a symptom; the problem could be an outdated product line or ineffective marketing strategies. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of distinguishing between symptoms and root causes in their strategic planning frameworks.
Secondly, the impact of the problem on the organization needs to be quantified. This involves analyzing how the issue affects operational efficiency, profitability, market position, and customer satisfaction. Quantifying the impact provides a tangible basis for prioritizing strategic initiatives. It turns abstract problems into concrete challenges that require immediate attention. Accenture's research highlights that organizations that excel in problem identification and impact analysis are more likely to outperform their peers in terms of revenue growth and market share.
Understanding the Context
The third element is understanding the context within which the problem exists. This includes the internal and external factors that contribute to the problem's persistence. Internal factors could be related to organizational culture, processes, or resources, while external factors might include market dynamics, regulatory changes, or technological advancements. A thorough context analysis helps in identifying the levers that can be pulled to address the problem. Deloitte's strategy consultants often use SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis as a template to understand the context better.
Additionally, understanding the context requires an appreciation of the stakeholders involved or affected by the problem. This includes employees, customers, suppliers, and regulators. Their perspectives can provide valuable insights into the problem's nuances and potential solutions. Engaging with stakeholders can also foster a culture of transparency and collaboration, essential for successful change management.
Moreover, the context also sets the stage for benchmarking against best practices or competitors. This can reveal gaps in performance or capabilities that need to be addressed. Real-world examples from organizations that have successfully navigated similar challenges can serve as a guide and inspiration for strategy formulation.
Goals and Objectives
The fourth element revolves around defining clear, specific goals and objectives that the solution should achieve. This goes beyond merely solving the problem; it involves setting a vision for what success looks like. Goals should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) and aligned with the organization's overall strategic objectives. This alignment ensures that solving the problem contributes to the broader mission and vision of the organization.
Setting goals and objectives also involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure success. These metrics provide a quantifiable means of tracking progress and evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented solutions. Bain & Company's Performance Management framework emphasizes the importance of linking KPIs to strategic objectives to ensure that efforts are focused on the most impactful areas.
Furthermore, defining goals and objectives helps in prioritizing resources and efforts. It ensures that the organization's time, talent, and capital are invested in initiatives that promise the highest return in terms of solving the problem and advancing strategic goals.
Actionable Solutions and Evaluation
The fifth element focuses on identifying actionable solutions and setting up an evaluation mechanism. Solutions should be practical, feasible, and tailored to the organization's context. They should address the root causes of the problem, not just its symptoms. This requires a creative approach to problem-solving, leveraging insights from data analysis, stakeholder feedback, and benchmarking. Consulting firms like EY and KPMG offer a variety of problem-solving frameworks and templates that can be adapted to different organizational contexts.
Implementing solutions also requires a detailed action plan that outlines the steps, timelines, responsibilities, and resources required. This plan serves as a roadmap for execution, ensuring that all team members are aligned and accountable. Oliver Wyman's Change Management framework highlights the importance of a structured approach to implementation, including regular monitoring and adjustment based on feedback and results.
Finally, setting up an evaluation mechanism is critical for assessing the effectiveness of the solutions. This involves collecting and analyzing data on the predefined KPIs, comparing results against objectives, and making adjustments as necessary. Continuous evaluation ensures that the organization remains agile and responsive to changes, optimizing strategies for maximum impact. In conclusion, articulating the key elements of a problem statement enhances the strategic planning process by providing a clear, structured approach to addressing challenges. By focusing on these five elements, leaders can ensure that their strategies are grounded in reality, aligned with organizational goals, and capable of delivering tangible results.
The role of the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) has evolved significantly over the past decade, transitioning from a purely financial focus to a broader strategic partner within the organization. Today, CFOs play a pivotal role in shaping the strategic direction and driving long-term growth initiatives. Understanding how a CFO influences strategic decisions is crucial for C-level executives aiming to harness the full potential of their financial leadership.
At the heart of strategic influence, CFOs leverage financial data and analytics to inform decision-making processes. This involves not just historical financial performance but also predictive analytics to forecast future trends and potential scenarios. By providing a data-driven framework for strategic planning, CFOs enable the organization to make informed decisions about where to allocate resources for optimal growth. This approach ensures that investments are aligned with the organization's strategic goals and are likely to yield the highest return on investment.
Furthermore, CFOs bring a unique perspective to risk management. In today's volatile business environment, identifying and mitigating risks is a critical component of strategic planning. CFOs assess financial risks, such as currency fluctuations, interest rates, and credit risks, as well as broader operational risks that could impact the organization's financial health. By integrating risk management into the strategic planning process, CFOs ensure that the organization is not only pursuing growth opportunities but also protecting itself against potential setbacks.
Another area where CFOs exert significant influence is in capital structure optimization. Decisions regarding debt, equity, and reinvestment are crucial for funding growth initiatives and achieving long-term financial sustainability. CFOs develop strategies to manage the organization's capital efficiently, ensuring that it has the financial flexibility to pursue opportunities while maintaining a healthy balance sheet. This strategic approach to financial management supports sustainable growth and enhances shareholder value.
Driving Digital Transformation
In the digital age, CFOs play a leading role in driving digital transformation initiatives. With a deep understanding of both financial and operational processes, CFOs are uniquely positioned to identify areas where technology can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and open new revenue streams. By championing digital initiatives, CFOs help the organization stay competitive in a rapidly changing business environment.
Implementing new technologies often requires significant investment, and the CFO's involvement ensures that these investments are aligned with the organization's strategic objectives. Whether it's adopting cloud computing, leveraging big data analytics, or exploring artificial intelligence, CFOs develop a financial framework that supports these initiatives. This not only includes calculating the expected return on investment but also involves developing a funding strategy that balances short-term costs with long-term benefits.
Moreover, digital transformation often requires a cultural shift within the organization. CFOs, with their cross-functional visibility, are well-placed to lead change management efforts, ensuring that teams are equipped and motivated to adopt new technologies. This leadership role extends beyond the finance function, influencing the organization's overall approach to innovation and technology adoption.
Enhancing Performance Management
Performance management is another critical area where CFOs influence strategic decisions. By developing a comprehensive performance management framework, CFOs ensure that the organization's strategic objectives are translated into actionable metrics and KPIs. This allows for real-time monitoring of progress against goals, enabling agile decision-making in response to changing market conditions.
CFOs also play a key role in aligning performance incentives with strategic objectives. This involves designing compensation and reward systems that motivate employees to achieve targets that support the organization's long-term goals. By closely linking performance management with strategic planning, CFOs help create a high-performance culture that is focused on delivering results.
Additionally, CFOs use performance management data to identify areas for operational improvement. This might involve streamlining processes, reducing costs, or reallocating resources to higher-value activities. Through continuous performance optimization, CFOs drive efficiency and effectiveness across the organization, supporting sustainable growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the influence of a CFO on strategic decisions extends far beyond traditional financial management. By providing a framework for data-driven decision-making, managing risk, optimizing capital structure, driving digital transformation, and enhancing performance management, CFOs play a crucial role in shaping the organization's strategic direction and ensuring its long-term success. As organizations navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape, the strategic insight and leadership of the CFO are more valuable than ever.
Crafting a compelling problem statement in business management is a critical step in the strategic planning process. It sets the stage for identifying and articulating the core issues that an organization faces, guiding the development of effective strategies and solutions. A well-defined problem statement not only captures the essence of the challenges at hand but also serves as a rallying point for the team, focusing efforts and resources on what truly matters.
In the realm of consulting, the ability to distill complex business scenarios into a succinct problem statement is highly valued. Consultants from leading firms such as McKinsey and BCG often employ a structured framework to ensure clarity and precision. This framework typically involves a deep dive into the organization's current state, identifying the gap between where the organization is and where it wants to be, and articulating the obstacles standing in the way.
For C-level executives, the stakes are high. A problem statement is not just an academic exercise; it's a strategic tool. It must be actionable, specific, and grounded in data. According to Gartner, organizations that clearly define their problems can accelerate decision-making processes by up to 50%. This underscores the importance of crafting a problem statement that not only diagnoses the problem but also points towards potential solutions.
Key Components of a Problem Statement
A robust problem statement in business management should include several key components. First, it must succinctly describe the issue, focusing on the symptoms of the problem as experienced by the organization. This requires a keen understanding of the organization's operations, market position, and competitive environment.
Second, the statement should detail the impact of the problem. This involves quantifying the problem's effects on the organization, whether in terms of financial loss, market share erosion, or diminished customer satisfaction. Providing concrete data here lends credibility to the urgency of the issue.
Lastly, the problem statement should hint at the potential for improvement. This doesn't mean offering a solution within the statement itself but rather suggesting that a solution exists and is worth pursuing. This component is crucial for motivating stakeholders and rallying support for the strategic planning process.
Utilizing a Framework
When approaching how to statement of the problem, employing a structured framework can be incredibly beneficial. Consulting firms often use templates and methodologies designed to extract the most pertinent information and organize it in a logical, compelling manner. These frameworks typically guide the executive through a series of questions or prompts, focusing on the nature of the problem, its impacts, and the context in which it exists.
One popular framework involves the following steps: Define the problem, Analyze the root causes, Estimate the impact, and Describe the solution landscape. This approach not only helps in crafting a clear problem statement but also in laying the groundwork for the subsequent strategy development phase.
Frameworks and templates are not one-size-fits-all. Each organization's situation is unique, and the framework should be adapted to fit the specific context and challenges of the organization. However, the discipline of following a structured approach ensures that all relevant aspects of the problem are considered.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a global retail chain experiencing declining sales. The problem statement might focus on the mismatch between the organization's product offerings and evolving consumer preferences, underscored by a data-driven analysis of sales trends and market research.
In another example, a technology firm facing high employee turnover might articulate a problem statement centered around the challenges of maintaining a competitive compensation package and fostering a positive corporate culture. Here, employee engagement surveys and industry benchmarking data would provide the foundation for the statement.
Each of these examples illustrates the importance of specificity, data reliance, and a clear indication that a solution is achievable. Crafting an effective problem statement is the first step in a journey towards organizational improvement. It requires a deep understanding of the business, a structured approach, and a commitment to action. For C-level executives, mastering this skill is essential for driving their organizations forward in an increasingly complex and competitive environment.
In the rapidly evolving business environment, strategic planning is not just beneficial; it's a necessity for driving growth and ensuring sustainability. C-level executives are constantly on the lookout for resources that can streamline this process, offering a competitive edge in strategy formulation and execution. Understanding what resources you can use to enhance your strategic planning efforts is crucial. This includes leveraging frameworks, consulting insights, strategy templates, and digital tools, all designed to provide a structured approach to planning and decision-making.
Frameworks are foundational to strategic planning, offering a structured methodology for analyzing challenges, identifying opportunities, and setting actionable goals. Renowned consulting firms such as McKinsey & Company and Boston Consulting Group (BCG) have developed various strategic frameworks that have been widely adopted across industries. For instance, McKinsey's Growth Pyramid and BCG's Growth-Share Matrix provide organizations with a lens through which they can evaluate their business units or product lines, facilitating focused investment decisions and resource allocation. These frameworks not only guide organizations in developing their strategies but also in monitoring their execution, ensuring alignment with the overarching goals.
Consulting insights, on the other hand, offer a rich repository of knowledge and expertise gleaned from industry leaders and market analysis. Firms like Deloitte and PwC publish extensive research and case studies that delve into emerging trends, operational best practices, and innovative strategies across sectors. By tapping into these insights, organizations can benchmark their performance, identify gaps in their strategic planning, and uncover new opportunities for growth. These insights also provide a global perspective, enabling organizations to anticipate market shifts and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Strategy templates serve as a practical tool in the strategic planning process, offering a blueprint for organizations to follow. These templates range from comprehensive strategic plans to specific models like SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis, PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental) analysis, and OKRs (Objectives and Key Results). Templates help in organizing thoughts, presenting data coherently, and ensuring that all critical aspects of strategy development are addressed. They also promote consistency in the planning process across different departments or business units, facilitating better communication and alignment within the organization.
Utilizing Digital Tools for Strategic Planning
Digital transformation has introduced a plethora of tools that significantly enhance the strategic planning process. Software solutions for Performance Management, Risk Management, and Business Transformation are now indispensable for organizations aiming to stay ahead. Tools like Balanced Scorecard software enable organizations to translate their vision and strategy into a set of performance indicators that provide a framework for strategic management and operational feedback. Similarly, risk management tools help in identifying potential threats to the strategy's success and developing mitigation plans.
Collaboration tools have also become essential, especially in the context of remote work and global teams. Platforms such as Microsoft Teams or Slack facilitate seamless communication and collaboration, ensuring that all team members are aligned with the strategic goals and can contribute effectively. Additionally, project management tools like Asana or Trello provide a visual overview of strategic projects, tracking progress against milestones and deadlines, which is critical for timely execution.
Moreover, data analytics and business intelligence tools offer organizations the ability to analyze vast amounts of data, deriving insights that inform strategic decisions. Tools like Tableau or Power BI enable executives to visualize data trends, performance metrics, and market analysis, making it easier to identify areas for improvement or investment. The ability to quickly adapt strategies based on real-time data has become a significant factor in maintaining a competitive stance in today's dynamic markets.
Engaging with Industry Peers and Thought Leaders
Networking with industry peers and engaging with thought leaders through conferences, workshops, and professional forums can provide invaluable insights into strategic planning practices. These interactions offer a platform for exchanging ideas, discussing challenges, and learning from the experiences of others. Organizations can gain fresh perspectives on strategy development, implementation, and monitoring, which can be particularly beneficial for overcoming specific hurdles or innovating within their strategic approach.
Professional associations and industry groups often host events and publish materials that highlight best practices, emerging trends, and case studies of successful strategy execution. Participation in these forums not only broadens an organization's knowledge base but also fosters partnerships and collaborations that can be instrumental in achieving strategic objectives.
In conclusion, leveraging a combination of frameworks, consulting insights, strategy templates, digital tools, and engaging with the broader business community are essential resources for strategic planning. These resources provide a structured approach to strategy development, enable data-driven decision-making, and foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. By effectively utilizing these tools, organizations can enhance their strategic planning efforts, driving growth and ensuring long-term sustainability in an increasingly complex and competitive environment.
Understanding and articulating a clear "statement of the problem" is paramount in the strategic planning process. This foundational step is not merely an academic exercise but a critical component that guides the direction of an organization's strategy development and implementation. A well-defined problem statement serves as a compass, ensuring that the strategic planning process is aligned with the organization's core challenges and objectives.
In the realm of strategic planning, the "statement of the problem" acts as a bridge between the current state of affairs and the envisioned future state. It succinctly describes the issues or opportunities that the organization intends to address. Crafting an effective problem statement requires a deep understanding of the organization's internal and external environments, including market dynamics, competitive pressures, and internal capabilities. This understanding is often derived from rigorous analysis and consultation with key stakeholders across the organization.
Consulting firms such as McKinsey and Bain emphasize the importance of a structured approach to defining the problem statement. These firms advocate for frameworks that guide the identification and articulation of the problem. A commonly used framework involves stating the issue, its impact on the organization, and the potential benefits of addressing it. This structured approach ensures that the problem statement is comprehensive, focused, and actionable. It also facilitates alignment among stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is working towards a common goal.
Key Components of an Effective Problem Statement
An effective statement of the problem is clear, concise, and specific. It should articulate the issue in a manner that is understandable to all stakeholders, without resorting to jargon or overly technical language. The statement should also quantify the problem, if possible, to provide a clear scope of the issue. This could involve specifying the financial impact, the market share decline, or the customer satisfaction drop that the problem is causing.
Moreover, the problem statement should be relevant to the strategic goals of the organization. It must align with the overall vision and mission, serving as a stepping stone towards achieving long-term objectives. This alignment ensures that the strategic planning process remains focused on what is truly important to the organization, rather than being sidetracked by peripheral issues.
Finally, an actionable problem statement is one that implicitly suggests a direction for solution development. While it does not prescribe specific solutions, it frames the problem in a way that guides the subsequent strategy formulation and decision-making processes. This characteristic is crucial for maintaining momentum in the strategic planning process and for ensuring that the problem statement leads to tangible improvements.
Integrating the Problem Statement into Strategic Planning
The integration of the problem statement into the strategic planning process is a critical step that requires careful consideration. One effective approach is to use the problem statement as the foundation for a SWOT analysis—identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the problem. This analysis can then inform the development of strategic objectives and initiatives designed to address the problem.
Another approach involves using the problem statement to prioritize resources and focus areas. In a resource-constrained environment, organizations must make tough choices about where to allocate their time, money, and effort. A clear and compelling problem statement helps to justify these allocations, ensuring that resources are directed towards the most critical issues.
Throughout the strategic planning process, it is important to revisit and potentially revise the problem statement. As the organization gains a deeper understanding of the issue and its context, the initial problem statement may need refinement. This iterative approach ensures that the strategic planning process remains relevant and aligned with the organization's evolving needs and circumstances.
Real-World Application
Consider the case of a global retail chain experiencing declining sales and market share. By defining a clear problem statement—such as "Declining sales and market share due to inadequate digital presence and evolving consumer preferences"—the organization can focus its strategic planning efforts on addressing these specific issues. This problem statement highlights the need for a digital transformation and a reevaluation of the customer value proposition.
The organization can then use this problem statement to guide its SWOT analysis, strategy development, and resource allocation. For instance, it might prioritize investments in e-commerce platforms and customer experience initiatives. By keeping the problem statement at the forefront of its strategic planning process, the organization ensures that its efforts are concentrated on addressing the most pressing challenges.
In conclusion, a well-defined statement of the problem is a critical component of the strategic planning process. It provides clarity, focus, and direction, ensuring that the organization's strategic efforts are aligned with its most significant challenges and opportunities. By following a structured approach to defining and integrating the problem statement, organizations can enhance their strategic planning process and improve their overall strategic outcomes.
Integrating sustainability into the Strategic Planning process of an organization requires a comprehensive approach to measurement that aligns with both long-term objectives and immediate operational goals. The success of sustainability initiatives is not only about reducing environmental impact but also about enhancing economic performance and societal contributions. To effectively measure this success, organizations must adopt a multi-dimensional set of metrics that reflect the broad scope of sustainability.
Environmental Impact Metrics
One of the primary facets of sustainability initiatives is their environmental impact. Organizations are increasingly looking to reduce their carbon footprint, minimize waste, and conserve natural resources. Metrics in this category include Carbon Footprint, Water Usage, Waste Reduction, and Energy Efficiency. For instance, a report by McKinsey & Company highlights the importance of measuring the carbon footprint not just in direct operations but across the entire supply chain to understand the full scope of an organization's environmental impact. This comprehensive approach helps in identifying areas for improvement and in implementing more effective sustainability strategies.
Energy Efficiency, measured through metrics such as energy consumption per unit of production, can reveal insights into operational improvements that simultaneously reduce costs and environmental impact. Waste Reduction metrics, on the other hand, focus on the percentage decrease in waste generated through operational changes and recycling efforts. These metrics are actionable and directly correlate to both sustainability goals and operational efficiency.
Water Usage is another critical metric, especially for organizations in water-intensive industries. Tracking reductions in water use not only contributes to sustainability goals but also mitigates risk associated with water scarcity. The use of these environmental impact metrics enables organizations to monitor progress, make informed decisions, and report on sustainability efforts in a manner that is transparent and accountable to stakeholders.
Economic Performance Metrics
While environmental metrics are crucial, the economic performance of sustainability initiatives is equally important. Metrics such as Cost Savings from Sustainability Initiatives, Return on Investment (ROI) of Sustainability Projects, and Revenue Generated from Sustainable Products or Services offer a clear picture of the financial benefits of integrating sustainability into strategic planning. According to a report by Boston Consulting Group (BCG), companies that lead in sustainability practices tend to outperform their peers financially, indicating a strong correlation between sustainability and economic performance.
Cost Savings from Sustainability Initiatives can be measured by tracking reductions in energy costs, waste disposal fees, and water usage costs. These savings directly impact the bottom line, making them compelling metrics for stakeholders. ROI of Sustainability Projects further quantifies the financial returns on investments in sustainability, providing a clear indicator of the value these initiatives bring to the organization.
Additionally, Revenue Generated from Sustainable Products or Services highlights the market demand for sustainability and its contribution to the organization's growth. This metric not only measures economic success but also reflects the organization's alignment with consumer values and market trends towards sustainability.
Societal Contribution Metrics
Sustainability initiatives also have a significant societal impact, which can be measured through metrics such as Community Engagement, Employee Engagement in Sustainability Initiatives, and Contribution to Local Economies. A study by Deloitte indicates that organizations with high levels of employee engagement in sustainability efforts see improvements in morale, retention, and productivity, underscoring the importance of measuring and fostering this engagement.
Community Engagement metrics focus on the organization's efforts to involve local communities in sustainability initiatives, such as through volunteer programs or local environmental projects. These efforts not only contribute to societal well-being but also strengthen the organization's relationship with the community.
Contribution to Local Economies, measured by metrics such as job creation in sustainable sectors or investments in local sustainability projects, reflects the organization's role in promoting economic development within the context of sustainability. This broader societal impact is an essential component of the overall success of sustainability initiatives, demonstrating the organization's commitment to creating value beyond its immediate operational and financial objectives.
In conclusion, measuring the success of sustainability initiatives within the Strategic Planning process requires a balanced set of metrics that encompass environmental impact, economic performance, and societal contribution. By adopting these metrics, organizations can ensure that their sustainability efforts are effective, measurable, and aligned with their strategic objectives. Real-world examples from leading consulting firms underscore the importance of these metrics in driving meaningful sustainability outcomes and enhancing overall organizational performance.
Understanding what is the first step in the strategic planning process is crucial for any organization aiming to align its operations with long-term goals effectively. This initial phase sets the tone for the entire strategic planning journey, ensuring that subsequent actions are guided by a clear, well-defined purpose. The cornerstone of this process involves establishing a solid framework that encapsulates the organization's vision, mission, and core values. This framework serves not only as a beacon for guiding strategic decisions but also as a benchmark against which the organization's progress can be measured.
Before diving into the specifics of strategic planning, it's imperative for C-level executives to grasp the importance of a comprehensive situational analysis. This involves a thorough examination of the organization's internal and external environments. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the value of leveraging tools such as SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis to gain insights into the organization's current state and its position within the broader market context. This analytical approach ensures that the strategic planning process is grounded in reality, with a clear understanding of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Actionable insights derived from the situational analysis inform the development of a strategy that is both ambitious and attainable. This strategy should outline the key objectives that the organization aims to achieve in the long term, broken down into manageable, quantifiable targets. Establishing these objectives early in the strategic planning process enables the organization to design a roadmap that is not only aligned with its overarching goals but also adaptable to changing market dynamics. This level of clarity and foresight is essential for maintaining strategic focus and direction over time.
Building a Robust Strategic Framework
The creation of a strategic framework is an essential step in the strategic planning process. This framework provides a structured template for mapping out the organization's future direction. It should encapsulate the organization's vision for the future, its mission that defines its purpose, and the core values that guide its operations and decision-making processes. A well-articulated framework serves as the foundation upon which all strategic initiatives are built, ensuring consistency and alignment across the organization.
Consulting firms often advise on the importance of involving key stakeholders in the development of the strategic framework. This collaborative approach ensures buy-in from those who will be instrumental in implementing the strategy, fostering a sense of ownership and commitment across the organization. Moreover, it allows for a diversity of perspectives, enriching the strategic planning process with insights from different areas of the business.
Once the strategic framework is in place, it acts as a reference point for all subsequent planning activities. It guides the setting of strategic priorities and the allocation of resources, ensuring that efforts are concentrated on areas of greatest impact. This strategic alignment is critical for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization's operations, driving it towards the achievement of its long-term goals.
Implementing a Situational Analysis
Conducting a situational analysis is a critical step that precedes the formulation of any strategic plan. This comprehensive analysis allows an organization to take stock of its current situation, identifying strengths to build upon, weaknesses to address, opportunities to seize, and threats to mitigate. The insights gained from this analysis are invaluable in informing the strategic direction of the organization.
Tools like SWOT analysis, PESTLE (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental) analysis, and Porter's Five Forces are commonly used by organizations to conduct a thorough situational analysis. These tools help in painting a detailed picture of the organization's internal capabilities and external environment. The objective data and insights provided by these analyses are crucial for making informed strategic decisions.
The role of data in this phase cannot be overstated. In today's data-driven world, leveraging analytics to understand market trends, customer behavior, and competitive dynamics is a game-changer. Organizations that effectively analyze and interpret data can anticipate market shifts and adapt their strategies accordingly, staying one step ahead in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
Conclusion
Initiating the strategic planning process with a clear understanding of what is the first step is paramount for any organization aiming to achieve its long-term goals. By establishing a solid strategic framework and conducting a comprehensive situational analysis, organizations can ensure that their strategic planning efforts are both effective and aligned with their overarching objectives. These initial steps lay the groundwork for a strategic plan that is realistic, actionable, and adaptable, positioning the organization for success in the years to come.
Understanding the ecosystem in which an organization operates is crucial for developing a robust Strategic Planning process that ensures sustainable growth and a strong position in the market. The term "ecosystem" refers to the complex network of suppliers, customers, competitors, and other stakeholders that interact within a particular industry or market. A strategic model that leverages this ecosystem can enable organizations to identify new opportunities, innovate, and respond more effectively to changes in the market.
The first step in leveraging an ecosystem strategic model is to thoroughly understand what is the ecosystem your organization is a part of. This involves mapping out the various entities that influence your market, including direct and indirect competitors, suppliers, distributors, and customers. It also means understanding the regulatory environment, technological advancements, and social trends that could impact your organization. This comprehensive view helps in identifying potential partners or channels that can be exploited for growth and innovation.
Once the ecosystem has been mapped out, the next step is to determine the ecosystem strategic model that best suits your organization's goals and capabilities. This framework should outline how your organization can interact with different entities within the ecosystem to create value. For example, consulting firms like McKinsey and Accenture often highlight the importance of collaboration and co-creation with partners to accelerate Digital Transformation and innovation. This could involve forming strategic alliances, investing in startups, or participating in industry consortia.
Implementing an ecosystem strategic model requires a shift in mindset from a traditional competitive strategy to one that emphasizes collaboration and mutual benefits. It involves identifying key players in the ecosystem that can help your organization to achieve its Strategic Planning objectives, and figuring out how to engage with them effectively. This might mean sharing resources, aligning on standards, or working together on marketing initiatives. The goal is to enhance the overall value of the ecosystem, which in turn, benefits all participants.
Key Components of an Ecosystem Strategic Model
To effectively leverage an ecosystem strategic model, certain key components must be considered. These include:
- Value Creation: Identify how your organization can contribute to and derive value from the ecosystem. This could be through innovative products, services, or business models that address unmet needs within the ecosystem.
- Strategic Partnerships: Determine which relationships are most critical to your success and focus on building strong, mutually beneficial partnerships. These partnerships can provide access to new markets, technologies, and expertise.
- Agility and Adaptability: The ecosystem is constantly evolving, so it’s essential for organizations to remain agile and adaptable. This means being able to quickly respond to new opportunities or threats within the ecosystem.
For instance, tech giants like Apple and Google have masterfully created and leveraged their ecosystems, not just by developing innovative products but also by creating platforms that enable other businesses to thrive. Apple’s App Store and Google’s Android Market are prime examples of how these organizations have managed to create immense value for themselves and their ecosystem partners.
Implementing the Strategy
Implementation of an ecosystem strategic model involves careful planning and execution. Start by developing a clear strategy that outlines your objectives within the ecosystem and identifies the key players you need to engage with. This strategy should be integrated into your overall Strategic Planning process and supported by top management.
Next, focus on building the capabilities needed to thrive in an ecosystem environment. This may include investing in new technologies, developing new skill sets among your workforce, or establishing processes that facilitate collaboration and innovation. It’s also important to establish metrics and KPIs to measure the success of your ecosystem strategy.
Finally, communication is key. Ensure that all stakeholders within the ecosystem are aligned on goals, roles, and expectations. This requires regular dialogue and transparency, as well as a willingness to adjust course as the ecosystem evolves.
In summary, leveraging an ecosystem strategic model can provide organizations with a powerful framework for Strategic Planning that goes beyond traditional competitive strategies. By understanding the ecosystem, determining the right strategic model, and focusing on value creation, strategic partnerships, and agility, organizations can enhance their growth prospects and secure a strong position in the market. Real-world examples from leading consulting firms and market leaders underscore the effectiveness of this approach, making it an essential consideration for any forward-thinking C-level executive.
Identifying what new business resources your organization lacks is pivotal for steering towards your strategic objectives. In the rapidly evolving market dynamics, staying ahead requires not just a keen understanding of your current capabilities but also an acute awareness of the gaps that might hinder your progress. This analysis delves into the critical areas where organizations typically find themselves wanting, offering a framework for assessment and action that is both comprehensive and actionable.
First and foremost, a common shortfall in many organizations is in the realm of Digital Transformation. Despite the buzz around digital for the past decade, a surprising number of organizations still lag in implementing robust digital strategies. This gap is not just in technology infrastructure but also in digital literacy among the workforce and the integration of digital into the core strategic planning processes. Consulting giants like McKinsey and Accenture have highlighted how digital leaders outperform their peers by focusing on speed, agility, and cross-functional collaboration. The lack of a coherent digital strategy can lead to missed opportunities in market penetration, customer engagement, and operational efficiency.
Another critical area often overlooked is Talent Management and Development. In the quest for operational excellence, the human element can sometimes be neglected. Yet, the capability and motivation of your workforce are paramount in executing any strategy. Organizations frequently find themselves lacking in specialized skills, particularly in areas like data analytics, user experience design, and cybersecurity. Furthermore, the cultural aspect of talent management—nurturing a culture of innovation, leadership, and continuous learning—is often underemphasized. This oversight can stifle innovation and reduce the organization's ability to adapt to change swiftly.
Risk Management and Resilience Planning also emerge as areas where gaps are commonly found. In an era where disruptions are the norm rather than the exception, the ability to anticipate, mitigate, and recover from setbacks is crucial. Many organizations find their risk management frameworks reactive rather than proactive, lacking in both scope and depth. This deficiency not only exposes the organization to potential crises but also hampers its ability to seize opportunities that come with market fluctuations. A robust risk management strategy, informed by thorough market and internal analysis, is essential for sustaining growth and stability.
Strategic Planning and Execution
At the heart of many organizational challenges is the gap in Strategic Planning and Execution. Crafting a strategy is one thing; executing it effectively is another. The disconnect between these two phases can be attributed to a lack of clear communication, inadequate resource allocation, and insufficient performance monitoring. A strategy might look perfect on paper but fail miserably in practice if the organization lacks the resources—be it financial, human, or technological—to implement it. Consulting firms often emphasize the importance of a detailed execution plan that aligns with the organization's overall objectives and capabilities.
Moreover, the pace at which market conditions and consumer preferences change requires organizations to be more agile in their strategic planning processes. This agility is often hampered by rigid structures and processes that are not conducive to quick pivots or adjustments. The template for strategic planning needs to be flexible yet robust, allowing for quick decisions and adjustments without losing sight of the long-term goals.
Additionally, Performance Management systems within many organizations are not aligned with the strategic objectives. There is a frequent disconnect between what is measured and what truly matters for achieving strategic goals. Performance indicators need to be directly linked to strategic objectives, ensuring that all efforts are geared towards the same end goals. Without this alignment, resources might be wasted on activities that do not contribute to the organization's strategic objectives.
Innovation and Market Adaptation
Innovation is the lifeblood of any organization aiming to not just survive but thrive in today's competitive environment. However, fostering an innovative culture and adapting to market changes are areas where many organizations fall short. The lack of a systematic approach to innovation—be it through R&D, partnerships, or internal innovation programs—can leave organizations playing catch-up with more agile competitors. Real-world examples abound of organizations that failed to adapt to technological and market shifts, highlighting the critical nature of this gap.
Moreover, the process of market adaptation is often slow due to bureaucratic decision-making processes and a lack of customer-centricity in strategy development. Organizations need to embed customer insights into their strategic planning process, ensuring that strategies are responsive to changing customer needs and preferences. This customer-centric approach should be supported by a robust framework for gathering and analyzing customer data, enabling informed decision-making.
Lastly, the integration of sustainability into the core strategy remains a gap for many. As consumers and regulatory bodies increasingly demand sustainable practices, organizations lacking in this area risk not just reputational damage but also potential regulatory penalties and missed market opportunities. A strategic approach to sustainability can also unlock new markets and innovation opportunities, making it a critical area for resource allocation and development.
In conclusion, identifying and addressing the gaps in what new business resources you lack is crucial for achieving your strategic objectives. By focusing on areas such as Digital Transformation, Talent Management, Risk Management, Strategic Planning and Execution, and Innovation and Market Adaptation, organizations can build a more resilient and competitive posture in the market. The journey towards closing these gaps begins with a thorough assessment, followed by a strategic and focused effort to marshal the necessary resources towards areas of deficiency.
Understanding the components of a problem statement is crucial for any C-level executive aiming to steer their organization towards Strategic Planning and Operational Excellence. A well-crafted problem statement acts as a compass for strategy development, guiding teams through the complexities of project management and decision-making. The essence of what are the parts of the statement of the problem lies in its ability to succinctly summarize the issue at hand, its implications, and the potential benefits of solving it. This foundation is not just a starting point; it's a framework that aligns the organization's efforts towards a common goal.
The first component of a problem statement is the description of the problem itself. This should not only outline the issue in clear and concise terms but also delve into the specifics of how it affects the organization. It's not enough to state that sales are declining; a robust problem statement would specify the rate of decline, the segments most affected, and the potential reasons behind this trend. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Bain emphasize the importance of grounding this description in data and factual analysis, ensuring that the problem is not based on assumptions but on verifiable evidence.
Following the problem description, the next part focuses on the consequences or implications if the problem remains unresolved. This section should paint a vivid picture of the future state, detailing the potential losses in revenue, market share, or operational efficiency. It's a projection that should resonate with every stakeholder, making the case for why addressing the problem cannot be delayed. This urgency is what transforms a problem statement from a mere observation into a call to action.
Identifying Stakeholders and Requirements
Integral to the problem statement is the identification of key stakeholders. These are the individuals or groups who are directly or indirectly affected by the problem and its resolution. Stakeholders can range from internal teams and employees to external partners, customers, and even regulatory bodies. Understanding their perspectives and needs is vital for crafting a solution that is not only effective but also broadly accepted across the organization. This part of the statement ensures that the strategy development process is inclusive, taking into account the diverse impacts of the problem and its potential solutions.
Alongside stakeholder identification, defining the requirements for a successful solution is another critical component. This goes beyond merely stating the desired outcome; it involves setting clear, measurable objectives that the solution must achieve. Whether it's improving customer satisfaction scores, increasing operational efficiency by a certain percentage, or achieving cost reductions, these requirements set the benchmarks for success. They provide a template against which the effectiveness of the proposed solution can be evaluated, ensuring that the resolution aligns with the organization's Strategic Planning goals.
Moreover, these requirements must be realistic and achievable, reflecting a deep understanding of the organization's capabilities and constraints. They serve as a bridge between the current state, as outlined in the problem description, and the envisioned future state, guiding the organization through the transformation process. This clarity is essential for maintaining focus and momentum, avoiding the common pitfall of pursuing solutions that are either too ambitious or too detached from the organization's reality.
Proposing a Path Forward
The final part of a problem statement is arguably the most forward-looking: proposing a path forward. This doesn't mean detailing the solution in its entirety—that's a task for the subsequent strategy and planning phases. Instead, this component is about outlining a high-level approach or framework for tackling the problem. It might hint at Digital Transformation, Operational Excellence initiatives, or a shift in market focus as potential strategies. The key is to present a direction that resonates with the urgency and significance of the problem, offering a glimpse into the strategic thinking that will guide the organization's efforts.
This section should also underscore the benefits of addressing the problem, not just in terms of avoiding negative consequences but in seizing new opportunities. It's about framing the problem-solving process as a catalyst for innovation, leadership development, and competitive positioning. By doing so, the problem statement becomes a rallying point for the organization, a source of motivation that drives collective action towards a common goal.
In conclusion, crafting a comprehensive problem statement is a critical first step in addressing any organizational challenge. It requires a deep understanding of the issue, its implications, the stakeholders involved, and the outcomes desired. By breaking down the problem into these constituent parts and approaching it with a strategic, data-driven mindset, leaders can set the stage for meaningful change. The problem statement is not just a diagnostic tool; it's a strategic asset that, when leveraged effectively, can guide an organization through its most complex challenges towards a brighter, more successful future.
Integrating Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) into the Strategic Planning frameworks of organizations is not just a moral imperative but also a strategic one. Research from McKinsey & Company has shown that companies in the top quartile for ethnic and cultural diversity on executive teams were 36% more likely to experience above-average profitability than companies in the fourth quartile. This statistic underscores the significant impact that DEI can have on an organization's bottom line. To harness this potential, organizations must adopt specific, detailed, and actionable strategies that embed DEI into the very fabric of their strategic planning.
Embedding DEI Goals into Corporate Strategy
One of the most effective strategies for enhancing DEI within strategic planning frameworks is the explicit inclusion of DEI goals within the corporate strategy. This involves setting clear, measurable objectives related to diversity, equity, and inclusion that align with the overall strategic goals of the organization. For instance, an organization might set a goal to achieve a certain percentage of minority leadership positions within a specific timeframe. This approach ensures that DEI is not seen as a separate initiative but as an integral part of the strategic planning process.
To operationalize these goals, organizations can adopt a Balanced Scorecard approach, where DEI objectives are included as one of the key perspectives. This allows for the integration of DEI metrics alongside financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth metrics, ensuring a holistic approach to strategy execution. Companies like Accenture have successfully implemented this approach, leading to significant improvements in their DEI outcomes.
Moreover, embedding DEI goals into corporate strategy requires commitment from top leadership. Leaders must communicate the importance of these goals, model inclusive behavior, and hold the organization accountable for achieving them. Leadership commitment is crucial for creating a culture that values diversity, equity, and inclusion and for driving the strategic changes needed to achieve DEI objectives.
Leveraging Data and Analytics for DEI
Another critical strategy is leveraging data and analytics to inform DEI efforts. Organizations can collect and analyze data on workforce composition, recruitment, retention, and promotion rates by demographic categories to identify areas for improvement. This data-driven approach allows organizations to set specific, targeted goals and to measure progress over time. For example, Google publishes an annual diversity report that provides transparency into its workforce diversity and outlines its strategies for improving DEI.
Advanced analytics and artificial intelligence tools can also be used to identify unconscious bias in recruitment and promotion processes. By analyzing patterns in historical hiring and promotion data, organizations can identify biases in job descriptions, recruitment practices, or performance evaluations. This enables them to implement corrective measures to ensure a more equitable process. Companies like PwC have developed AI-driven tools to help organizations identify and mitigate unconscious bias in their talent processes.
Furthermore, leveraging data and analytics for DEI extends beyond internal processes. Organizations can also analyze customer data to ensure that their products and services are accessible and relevant to diverse customer groups. This not only enhances DEI within the organization but also drives business growth by tapping into new markets and customer segments.
Creating Inclusive Cultures
Finally, enhancing DEI within strategic planning frameworks requires creating cultures that are truly inclusive. This means going beyond diversity in hiring to ensure that all employees feel valued, included, and able to contribute to their fullest potential. Ernst & Young (EY) emphasizes the importance of an inclusive culture in its DEI strategy, focusing on creating an environment where diverse perspectives are valued and where everyone has the opportunity to succeed.
Organizations can promote inclusivity by providing diversity and inclusion training for all employees, establishing employee resource groups (ERGs) for underrepresented groups, and implementing mentorship programs that support the development of diverse talent. These initiatives not only support the personal and professional development of employees but also contribute to a more inclusive and innovative organizational culture.
In addition, organizations must ensure that their policies and practices support equity and inclusion. This includes everything from flexible working arrangements to support work-life balance, to equitable compensation practices, to robust anti-discrimination policies. By creating an environment that supports diversity, equity, and inclusion at every level, organizations can unlock the full potential of their workforce and drive strategic success.
In conclusion, enhancing DEI within strategic planning frameworks requires a comprehensive approach that includes setting explicit DEI goals, leveraging data and analytics, and creating inclusive cultures. By adopting these strategies, organizations can not only improve their DEI outcomes but also drive innovation, enhance employee engagement, and improve financial performance.
In the fast-paced world of C-level management, staying ahead of the curve is not just an option—it's a necessity. The question then arises: "What are some resources you can use to ensure your organization remains at the forefront of its industry?" The answer lies in leveraging a variety of essential business management resources, from cutting-edge consulting frameworks to comprehensive strategy templates. These tools are not just about maintaining status quo; they are about propelling your organization to new heights.
Consulting firms such as McKinsey, BCG, and Bain have long been the gold standard for strategic insights and frameworks. These organizations excel in distilling complex business challenges into manageable, actionable strategies. For C-level executives looking to refine their Strategy Development or Operational Excellence, accessing case studies or industry reports from these firms can provide unparalleled insights. Moreover, many of these consulting giants offer proprietary tools and frameworks that can significantly streamline the strategic planning process. For instance, McKinsey's Three Horizons of Growth framework can be instrumental in guiding long-term innovation planning.
Digital Transformation is another area where resources from top consulting firms and market research giants like Gartner and Forrester become invaluable. These organizations not only offer a bird's-eye view of the latest technological trends but also provide detailed analyses on how these trends can be applied within specific industries. Gartner's Hype Cycle, for example, is a fantastic tool for C-level executives to gauge the maturity and adoption rates of emerging technologies. Leveraging such resources can help organizations stay ahead of the curve in integrating new technologies into their operations.
Risk Management and Performance Management are areas that require constant vigilance and adaptability. Here, templates and frameworks from consulting firms can offer a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks. Similarly, performance management tools can help in setting clear KPIs, monitoring progress, and implementing corrective measures as needed. These resources not only ensure that the organization is protected against potential threats but also that it is always aligned with its strategic objectives.
Leadership and Culture
At the heart of every successful organization is a strong Leadership team and a culture that promotes innovation and excellence. Resources aimed at enhancing Leadership skills and cultivating a positive organizational culture can be found in a variety of formats, including executive coaching services, leadership development programs, and culture transformation frameworks. For example, Deloitte's CulturePath offers a science-based approach to culture change, helping organizations to diagnose their cultural landscape and implement effective change strategies.
Moreover, the importance of continuous learning cannot be overstated for C-level executives. Participating in leadership forums, attending industry conferences, and enrolling in executive education programs are all effective ways to stay updated on the latest management theories and practices. These experiences not only provide valuable insights but also offer opportunities to network with peers and thought leaders in the field.
Finally, internal resources such as employee feedback mechanisms and cross-functional teams can be instrumental in fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement. Encouraging open communication and collaboration across departments can lead to more innovative solutions and a more agile organization.
Implementing Change and Innovation
Change Management and Innovation are critical components of any organization's long-term success. Utilizing frameworks and methodologies from consulting firms can help in systematically approaching change and ensuring that innovation efforts are aligned with the organization's strategic goals. For instance, Kotter's 8-Step Process for Leading Change is a widely recognized framework that provides a step-by-step approach to implementing successful change initiatives.
In addition to consulting resources, leveraging technology platforms for project management and collaboration can significantly enhance the efficiency of change and innovation processes. Tools such as Asana, Trello, and Slack facilitate seamless communication and coordination among team members, regardless of their physical location. These platforms can be particularly useful in managing cross-functional projects and ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and informed.
Lastly, fostering a culture that embraces change and encourages experimentation is crucial. This can be achieved through mechanisms such as innovation labs, hackathons, and incentive programs for innovative ideas. By creating an environment where employees feel empowered to experiment and take risks, organizations can cultivate a strong pipeline of innovative solutions and maintain their competitive edge.
In conclusion, C-level executives have a plethora of resources at their disposal to drive their organizations forward. From leveraging the insights and frameworks of top consulting firms to embracing technology and fostering a culture of leadership and innovation, the key is to remain adaptable and continuously seek out new tools and methodologies. By doing so, executives can ensure their organizations not only survive but thrive in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Understanding the key elements of a problem statement in the context of business management is crucial for any C-level executive aiming to steer their organization towards success. A well-crafted problem statement acts as the foundation for any strategic initiative, guiding the direction of consulting efforts and ensuring that the focus remains on addressing the core issues at hand. In essence, it sets the stage for effective strategy development, operational improvements, and long-term organizational resilience.
The first key element of a problem statement is a clear, concise description of the issue. This should go beyond merely stating symptoms, diving deep into the underlying causes. It's about articulating the problem in a way that it becomes tangible and quantifiable. For instance, instead of saying "sales are declining," a more effective problem statement would specify "a 20% quarter-over-quarter decline in sales due to emerging competitive technologies and changing customer preferences." This precision not only aids in understanding the scope but also in measuring the impact and success of any implemented solutions.
Another critical component is the relevance of the problem to the organization's strategic objectives. A problem statement should align with the broader goals, whether it's achieving Operational Excellence, driving Digital Transformation, or enhancing Customer Experience. This alignment ensures that solving the problem will have a meaningful impact on the organization's overall performance and strategic direction. It also helps in securing buy-in from stakeholders by demonstrating how addressing the issue supports the organization's core priorities.
The third essential element is the identification of stakeholders affected by the problem. This includes both internal and external parties, from employees and management to customers and partners. Understanding who is impacted and how provides insights into the problem's reach and the potential ramifications of not addressing it. It also helps in tailoring the solution to meet the needs of those most affected, thereby increasing the likelihood of successful adoption and implementation.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
Developing a robust framework for creating a problem statement is vital. Many consulting firms, including McKinsey and BCG, advocate for a structured approach that involves several steps. Initially, it requires gathering and analyzing data to understand the problem's dimensions fully. This is followed by synthesizing the information to identify patterns or root causes. The use of a template or checklist can ensure that all critical aspects of the problem are considered and addressed.
Next, the problem statement should be tested for clarity and relevance. This can involve seeking feedback from key stakeholders to ensure that the statement resonates and is understood. It's also an opportunity to refine the statement, making it as specific and actionable as possible. The goal is to have a problem statement that not only defines the issue but also points towards potential solutions.
Finally, the problem statement should be documented and communicated effectively. This often takes the form of a PDF or presentation that can be shared across the organization and with external partners. The document serves as a reference point for all subsequent strategic and operational planning, ensuring that efforts remain aligned with solving the identified problem.
Real-World Application
In practice, the power of a well-formulated problem statement is evident in numerous case studies across industries. For example, a retail organization facing declining foot traffic might frame their problem statement around the need to enhance in-store customer experience in the face of increasing online shopping options. This clear articulation of the problem would then drive efforts in digital integration, staff training, and store layout redesigns.
Similarly, a financial services firm grappling with digital disruption might define their problem in terms of needing to accelerate digital transformation to meet changing customer expectations for online banking services. This problem statement focuses the organization's efforts on technology upgrades, process automation, and digital literacy training for staff.
In conclusion, crafting a precise and actionable problem statement is a critical first step in addressing any organizational challenge. It requires a deep understanding of the issue, its relevance to the organization's goals, and the stakeholders involved. By following a structured framework and incorporating the key elements discussed, C-level executives can ensure that their strategic initiatives are grounded in a solid understanding of the problems they aim to solve. This approach not only facilitates effective problem-solving but also drives organizational growth and resilience in an ever-changing business landscape.
PEST analysis, an acronym for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological analysis, is a strategic tool used to evaluate the external macro-environmental factors that might impact an organization. This framework is pivotal in the strategic planning process, especially in mitigating risks that could potentially derail an organization's objectives. By scrutinizing the external environment through the PEST lens, organizations can preemptively identify potential threats and opportunities, enabling them to devise robust strategies that are both resilient and adaptable.
Understanding PEST Analysis in Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning is a critical process for any organization aiming to secure a competitive advantage in its industry. The incorporation of PEST analysis into this process ensures that the organization does not operate in a vacuum but rather takes into account the broader macro-environmental variables. This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the market dynamics and potential hurdles that could impact the organization's growth trajectory. For instance, a shift in regulatory policies (Political factor) or a sudden economic downturn (Economic factor) can significantly affect the organization's operations. By leveraging the PEST framework, organizations can develop contingency plans that are both flexible and resilient.
Consulting firms such as McKinsey & Company and Boston Consulting Group (BCG) emphasize the importance of incorporating frameworks like PEST into the strategic planning process. These firms argue that a thorough external analysis not only aids in risk mitigation but also helps in identifying new market opportunities. This dual focus ensures that organizations are not merely reactive but are proactively shaping their strategic direction in alignment with external changes.
Furthermore, the PEST analysis serves as a template for continuous environmental scanning. This ongoing process ensures that the organization remains vigilant and responsive to changes in the external environment, thereby safeguarding its strategic interests and ensuring long-term sustainability.
PEST Analysis in Mitigating Risks
Risk Management is an integral component of Strategic Planning. The PEST framework plays a crucial role in identifying potential risks that could impact the organization's ability to achieve its strategic objectives. By analyzing each segment of the PEST analysis, organizations can uncover risks related to political instability, economic fluctuations, social trends, and technological advancements. For example, the advent of disruptive technologies (Technological factor) can render existing products or services obsolete, posing a significant risk to the organization's market position.
Actionable insights derived from PEST analysis enable organizations to devise strategies that mitigate these risks. For instance, an organization might diversify its investment portfolio in response to economic uncertainties or invest in research and development to stay ahead of technological disruptions. Consulting firms like Accenture and Deloitte provide guidance to organizations on how to integrate these insights into their strategic planning process, ensuring that risk mitigation strategies are both effective and aligned with the organization's overall strategic goals.
Real-world examples abound of organizations that have successfully navigated external challenges by incorporating PEST analysis into their strategic planning. For instance, companies in the renewable energy sector closely monitor political and regulatory developments to anticipate changes in environmental policies. This proactive approach enables them to adjust their strategies accordingly, securing a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
PEST Analysis as a Strategic Tool
The value of PEST analysis as a strategic tool cannot be overstated. It provides a structured approach for organizations to analyze the external environment systematically. This comprehensive analysis is crucial for Strategy Development, ensuring that the organization's strategic initiatives are both relevant and resilient in the face of external challenges. The PEST framework also facilitates a deeper understanding of the market dynamics, enabling organizations to position themselves strategically within their industry.
Consulting firms play a pivotal role in helping organizations leverage the PEST framework effectively. Through their expertise, they guide organizations in conducting thorough PEST analyses, interpreting the findings, and integrating these insights into the Strategic Planning process. This collaborative approach ensures that organizations are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the external environment, thereby enhancing their strategic decision-making process.
In conclusion, PEST analysis is an indispensable tool in the arsenal of strategic planning. It not only aids in Risk Management but also enhances the organization's ability to adapt and thrive in an ever-changing external environment. By incorporating the PEST framework into their strategic planning process, organizations can ensure that they are well-prepared to face the challenges and seize the opportunities that lie ahead.
In the realm of Strategic Planning, crafting a precise and actionable problem statement is paramount. This critical element serves as the north star for guiding organizations through complex challenges and towards their strategic objectives. Understanding what elements make up a problem statement—and selecting all that apply—is essential for C-level executives embarking on the journey of Strategy Development, Change Management, or any form of Business Transformation. A well-constructed problem statement not only clarifies the issue at hand but also aligns stakeholders and sets the stage for innovative solutions.
At its core, a problem statement should succinctly describe the issue that needs to be addressed, its impact on the organization, and the potential benefits of solving it. However, to be truly effective in the context of strategic planning, it must go beyond this basic framework. It should incorporate a clear understanding of the current state, the desired future state, and the gaps that exist between the two. This requires a deep dive into the organization's internal and external environments, leveraging data and insights to paint an accurate picture of the situation.
Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of grounding problem statements in factual evidence and strategic insight. They advocate for a data-driven approach, where decisions are informed by market research, competitive analysis, and customer feedback. This not only enhances the credibility of the problem statement but also ensures that the strategic planning process is anchored in reality, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Key Components of a Problem Statement
When considering what elements make up a problem statement, select all that apply from the following components:
- Clear, Concise Description of the Problem: The statement should pinpoint the issue in a straightforward manner, avoiding jargon and ambiguity. It's about getting to the heart of the matter quickly and clearly.
- Context and Background: Providing a snapshot of the situation helps to frame the problem within the larger strategic landscape of the organization. This includes historical data, current challenges, and any previous attempts at resolution.
- Stakeholder Impact: Detailing who is affected by the problem and how it underscores the urgency and relevance of finding a solution. This can range from internal stakeholders like employees to external ones like customers or shareholders.
- Quantifiable Data: Supporting the problem statement with relevant data and statistics strengthens its validity. This could include financial losses, customer churn rates, market share declines, or other measurable indicators of the problem's impact.
- Desired Outcome: Articulating what success looks like provides a target for the strategic planning process. This should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
This template serves as a comprehensive framework for C-level executives to ensure that all critical aspects of the problem are considered. It's not just about identifying the problem but also understanding its nuances and the ripple effects it has across the organization.
Real-world examples underscore the importance of a well-crafted problem statement in strategic planning. Consider a global retailer facing declining sales due to changing consumer behaviors and increased competition. By framing the problem statement around these specific challenges, incorporating market analysis and consumer trends, the organization can focus its strategic planning efforts on innovation and customer engagement strategies that directly address the root causes of the decline.
Implementing the Problem Statement in Strategic Planning
With a robust problem statement in hand, the next step is integrating it into the strategic planning process. This involves translating the problem statement into actionable goals and objectives, developing strategies to achieve them, and implementing a plan of action. The problem statement acts as a guidepost throughout this process, ensuring that efforts remain focused on addressing the core issue.
Strategy development must be iterative and flexible, allowing for adjustments as new information becomes available or as circumstances change. This agility is crucial for maintaining alignment with the problem statement's objectives. Regular review and assessment against the problem statement ensure that the organization remains on track and can make informed decisions about strategic direction.
Consulting firms often stress the importance of communication and stakeholder engagement in this process. A clearly communicated problem statement fosters a shared understanding of the challenges and objectives, facilitating collaboration and buy-in across the organization. This collective focus on a common goal is instrumental in driving successful strategic outcomes.
In conclusion, the formulation of a problem statement is a critical first step in effective Strategic Planning. By incorporating the key elements outlined above, C-level executives can ensure that their strategic initiatives are both focused and aligned with the organization's broader goals. This not only enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of the planning process but also positions the organization for sustainable success in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Understanding the allocation of resources in economics is pivotal for any C-level executive striving for organizational excellence. At its core, resource allocation involves distributing available resources among various competing needs or projects within an organization. This process is fundamental to strategic planning, operational efficiency, and ultimately, achieving organizational goals. The essence of what is allocation of resources in economics lies in making decisions that maximize the effectiveness of resources in terms of meeting the organization's objectives while minimizing waste and inefficiencies.
Frameworks and templates provided by leading consulting firms such as McKinsey or Bain offer a structured approach to resource allocation. These methodologies often emphasize the importance of aligning resource allocation with the organization's strategic objectives, a practice that ensures resources are directed towards areas with the highest potential for impact. Moreover, advanced analytics and data-driven insights play a crucial role in informing these decisions, allowing leaders to allocate resources more effectively based on empirical evidence rather than intuition or historical precedents.
Actionable insights into resource allocation often involve a rigorous assessment of the organization's current resource utilization, identifying areas of underperformance or overinvestment. This process might include a thorough analysis of financial data, operational metrics, and market trends to pinpoint opportunities for reallocating resources in a manner that supports strategic growth initiatives or operational improvements. For instance, shifting investment from low-growth areas to fund digital transformation projects that promise higher returns and improved customer satisfaction.
Strategic Frameworks in Resource Allocation
In the realm of strategic planning, the allocation of resources is a critical exercise that demands a well-structured framework. Consulting giants like BCG and McKinsey advocate for frameworks that facilitate a holistic view of the organization's strategic priorities, ensuring that resource allocation decisions are tightly aligned with long-term objectives. These frameworks typically involve stages of assessment, prioritization, allocation, and monitoring, each critical for ensuring that resources are optimally deployed.
The prioritization stage, for example, requires a meticulous evaluation of projects and initiatives based on their potential to contribute to strategic goals. This often involves leveraging tools such as weighted scoring models or return on investment (ROI) analyses to objectively assess each initiative's value proposition. Following this, resources are allocated in a manner that prioritizes high-impact projects while considering the organization's capacity and constraints.
Monitoring and reallocation form the final stages of the strategic framework, where the effectiveness of resource allocation decisions is continually assessed. This involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and conducting regular reviews to ensure that resources are being used as intended and are delivering the expected outcomes. Adjustments are made as necessary to address any misalignments or to respond to changing market conditions, ensuring that the organization remains agile and responsive in its resource allocation strategy.
Real-World Applications and Challenges
Real-world examples of effective resource allocation abound in sectors ranging from technology to healthcare. For instance, a leading tech company might allocate significant resources towards research and development (R&D) to fuel innovation and maintain its competitive edge. This decision reflects a strategic prioritization of innovation as a key driver of growth and market leadership.
However, the process of resource allocation is not without its challenges. One of the primary obstacles organizations face is the resistance to change, particularly when reallocating resources away from traditional areas or projects that are no longer aligned with strategic objectives. Overcoming this resistance requires strong leadership, clear communication, and the ability to demonstrate the rationale and benefits of reallocation decisions.
Another challenge lies in the dynamic nature of the market and the need for organizations to remain flexible in their allocation strategies. This necessitates a continuous reassessment of priorities and the willingness to pivot resource allocation in response to emerging trends, technological advancements, or shifts in consumer behavior. Organizations that excel in this aspect often employ a dynamic resource allocation model that allows for rapid reallocation in alignment with changing strategic priorities.
In conclusion, the allocation of resources in economics is a critical component of strategic management, requiring a structured framework, data-driven insights, and a dynamic approach to adapt to market changes. By embracing these principles, C-level executives can ensure their organizations are well-positioned to capitalize on opportunities and drive sustained growth and success.
Understanding what is the first step in the strategic planning process is crucial for any C-level executive aiming to steer their organization towards success. This initial phase sets the tone for the entire strategy development journey, ensuring that the foundation is robust and well-defined. In the realm of strategic planning, this foundational step is often identified as the establishment of a clear, actionable mission and vision statement. These statements not only articulate the organization's core objectives and aspirations but also serve as a guiding star for all subsequent strategic decisions and initiatives.
Before diving into the complexities of market analysis, goal setting, or strategy formulation, it's imperative for leaders to take a step back and reflect on the fundamental purpose and long-term ambitions of their organization. This involves a thorough introspection and dialogue among key stakeholders to distill the essence of what the organization stands for and where it aspires to be in the future. Crafting a compelling mission statement requires a deep understanding of the organization's unique value proposition, core competencies, and the impact it seeks to make on its customers, employees, and the broader community.
Moreover, the vision statement extends beyond the present, projecting a future state where the organization has achieved its highest aspirations. It's a source of inspiration and motivation, providing a clear picture of what success looks like. Both these elements are critical in aligning the organization's strategic initiatives and ensuring that every action taken is a step towards realizing that envisioned future. Without a well-defined mission and vision, strategic planning can become a directionless exercise, lacking focus and coherence.
Importance of Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders in the initial stages of the strategic planning process is another critical aspect that cannot be overlooked. Stakeholder engagement involves consulting with and considering the perspectives of those who have a vested interest in the organization's success, including employees, customers, investors, and partners. This collaborative approach not only enriches the strategic planning process with diverse insights but also fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among stakeholders, enhancing the likelihood of successful strategy implementation.
Consulting firms like McKinsey and Deloitte emphasize the value of stakeholder engagement as a means to uncover hidden opportunities, anticipate potential challenges, and build a consensus around the strategic direction. This process often uncovers invaluable insights that can significantly impact the strategic priorities of the organization. For instance, direct feedback from customers can reveal emerging needs and preferences, while employees might highlight operational inefficiencies or innovation opportunities that senior management might overlook.
Furthermore, engaging stakeholders early on ensures that the mission and vision statements are not just reflective of the leadership's aspirations but resonate with all segments of the organization. This collective buy-in is crucial for the seamless execution of strategic initiatives, as it minimizes resistance and fosters a culture of collaboration and shared purpose.
Setting the Strategic Framework
Once the mission and vision statements are established and stakeholder insights have been integrated, the next step is to develop a strategic framework that will guide the organization through the strategy development process. This framework serves as a template, outlining the key components of the strategic plan, including strategic objectives, key performance indicators (KPIs), and the strategic initiatives designed to achieve these objectives. It provides a structured approach to strategy formulation, ensuring that all efforts are aligned with the overarching goals of the organization.
Many consulting firms offer proprietary strategic planning frameworks that are designed to facilitate this process. For example, frameworks like the Balanced Scorecard or McKinsey's 7S model provide a comprehensive approach to assessing and aligning various aspects of the organization's operations with its strategic goals. These tools not only help in identifying the strategic priorities but also in mapping out the action plans required to achieve them.
In conclusion, the first step in the strategic planning process involves establishing a clear and compelling mission and vision statement, engaging stakeholders to gather diverse insights, and setting a strategic framework that will guide the organization through the subsequent phases of strategy development. This foundational step is critical in ensuring that the strategic plan is both ambitious and achievable, aligning the organization's efforts towards a common goal and paving the way for sustainable growth and success.
Crafting a strategic problem statement is a critical first step in guiding organizational planning and decision-making. A well-defined problem statement serves as a compass for strategy development, ensuring that every decision aligns with the organization's overarching goals. This requires a deep understanding of the current challenges, clear articulation of the desired future state, and identification of the gaps that exist between these two points. In the realm of consulting, frameworks for developing a problem statement are considered foundational tools, enabling leaders to dissect complex issues into manageable parts.
The process begins with identifying and articulating the core issue. This involves gathering and analyzing data to understand the root cause of the problem. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of leveraging both quantitative and qualitative data to paint a comprehensive picture of the situation. This step is not about jumping to solutions but rather ensuring a thorough understanding of the problem landscape. It's about asking the right questions—what is happening, why is it happening, and what are the implications if it remains unaddressed?
Next, the focus shifts to clearly defining the problem in a concise statement. This statement should encapsulate the essence of the issue without being overly complex. The art of crafting this statement lies in striking a balance between specificity and breadth. It should be specific enough to guide focused analysis and decision-making but broad enough to not preclude potential innovative solutions. A template often used in strategy consulting involves stating the problem, its impact on the organization, and the urgency or importance of addressing it.
Finally, the problem statement must be actionable. It should serve as a call to action, prompting the organization to mobilize resources towards a solution. This means framing the problem in a way that it is solvable within the constraints and capabilities of the organization. Consulting firms often advise using a framework that outlines the scope of the problem, the stakeholders involved, and the potential levers for change. This approach ensures that the problem statement is not just a diagnosis but a roadmap for action.
Framework for Developing a Problem Statement
Developing a strategic problem statement requires a structured approach. A widely recognized framework involves the following steps: identification, articulation, and actionability. Each step is crucial and builds upon the previous one to ensure a comprehensive and effective problem statement.
In the identification phase, leaders must immerse themselves in the ecosystem of the problem. This means going beyond surface-level symptoms to understand underlying causes. Tools such as SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and PESTLE analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, Environmental) are invaluable in this phase. They help leaders to contextualize the problem within the broader market and internal organizational dynamics.
Articulation involves distilling the insights gained during the identification phase into a clear, concise statement. This statement should encapsulate the essence of the problem, why it matters, and the potential impact of solving it. Effective articulation requires a blend of analytical rigor and storytelling. The goal is to craft a narrative that resonates with stakeholders and galvanizes them into action.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a global retail chain facing declining sales. The initial problem statement might focus on the symptom: "Sales have declined by X% over the last Y months." However, a strategic problem statement, developed through a rigorous framework, would delve deeper: "Sales have declined due to a combination of changing consumer preferences, increased competition from e-commerce platforms, and an outdated store format. Addressing this issue is critical to reversing the sales trend and ensuring the company's long-term viability."
In another example, a technology firm struggling with slow digital transformation might initially frame their problem as a lack of new technology adoption. A more strategic problem statement, however, would identify underlying issues such as cultural resistance, misaligned incentives, and skill gaps. It would then articulate these findings in a way that highlights the urgency and potential strategies for overcoming these barriers.
These examples underscore the importance of a well-crafted problem statement. It's not merely an academic exercise but a strategic tool that guides decision-making and action. By following a structured framework, leveraging both data and narrative, and focusing on actionability, organizations can ensure that their problem statement serves as a powerful catalyst for change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, developing a strategic problem statement is a critical skill for leaders seeking to navigate complex challenges. By following a structured framework, leveraging diverse data sources, and focusing on clarity and actionability, organizations can transform their problem statements into powerful tools for strategic planning and decision-making. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the ability to articulate and address core issues effectively will remain a key differentiator for successful organizations.
Strategic Planning in the era of the sharing economy requires a fundamental shift in how organizations traditionally view value creation, competition, and asset utilization. The sharing economy, characterized by the sharing of access to goods and services facilitated by community-based online platforms, has disrupted industries across the globe. Organizations must adapt their Strategic Planning processes to not only survive but thrive in this new economic landscape. This adaptation involves rethinking resource allocation, embracing technological innovation, and fostering a culture of collaboration and openness.
Understanding the Sharing Economy
The sharing economy is built on the premise of maximizing asset utilization and fostering community-centric platforms where individuals and organizations can lend, rent, or share their resources with others. This model challenges traditional business models by prioritizing access over ownership. According to a report by PwC, the sharing economy is projected to grow from $15 billion in 2014 to $335 billion by 2025. This rapid growth indicates a significant shift in consumer behavior and presents both opportunities and challenges for Strategic Planning.
Organizations must first understand the principles underlying the sharing economy—such as trust, community, and sustainability—to effectively incorporate them into their Strategic Planning. This involves analyzing market trends, consumer preferences, and technological advancements that facilitate the sharing economy. For instance, leveraging big data analytics can provide insights into consumer behavior and preferences, enabling organizations to identify opportunities for sharing economy models in their operations or offerings.
Moreover, embracing the sharing economy principles requires organizations to reassess their value propositions. The focus shifts from selling products or services to offering access and experiences. This necessitates a reevaluation of marketing strategies, customer engagement practices, and even product development processes to align with the values of the sharing economy.
Adapting Strategic Planning Processes
To incorporate the principles of the sharing economy into Strategic Planning, organizations need to adapt their approach to strategy formulation and execution. This includes fostering a culture of innovation, redefining competitive advantage, and embracing flexibility in operational models. For example, embracing collaborative consumption models can lead to the development of new revenue streams and cost reduction strategies through more efficient asset utilization.
Strategic alliances and partnerships become crucial in the sharing economy. Organizations should seek to partner with technology platforms, community organizations, and even competitors to create shared value. Airbnb’s partnership with local governments to collect and remit taxes is an example of how collaborative approaches can address regulatory challenges and create mutually beneficial outcomes. Similarly, automotive companies like BMW and Daimler have formed partnerships to create mobility services, recognizing the shift towards shared transportation models.
Risk Management also takes on a new dimension in the sharing economy. Organizations must navigate regulatory uncertainties, data security concerns, and reputational risks associated with sharing models. Strategic Planning should include robust risk assessment frameworks that evaluate the potential impacts of sharing economy initiatives and incorporate mitigation strategies. This includes investing in cybersecurity measures, developing clear policies for data privacy, and engaging in transparent communication with stakeholders.
Leveraging Technology for Competitive Advantage
Technology is a critical enabler of the sharing economy. Organizations must invest in digital platforms, mobile applications, and data analytics tools to facilitate the sharing of resources and enhance customer experiences. For example, leveraging blockchain technology can provide secure and transparent ways to facilitate transactions in the sharing economy, building trust among users.
Moreover, digital transformation initiatives should be aligned with Strategic Planning to ensure that technology investments support the overall strategic objectives of the organization. This includes developing digital capabilities that enable rapid adaptation to market changes, personalization of customer experiences, and efficient management of shared resources.
Finally, organizations must recognize that the sharing economy is not just a technological trend but a shift towards more sustainable and community-oriented business models. This requires a long-term commitment to innovation, collaboration, and social responsibility. Strategic Planning should incorporate sustainability goals and metrics to measure the impact of sharing economy initiatives on environmental, social, and economic outcomes.
Real World Examples
Several organizations have successfully adapted their Strategic Planning to incorporate the principles of the sharing economy. For instance, IKEA has ventured into furniture leasing, recognizing the growing consumer preference for access over ownership. This strategic move not only aligns with sustainability goals but also opens new revenue streams for the company.
Similarly, Ford has transformed from a traditional automotive manufacturer to a mobility services provider. Through its Ford Smart Mobility plan, the company is exploring car sharing, ride sharing, and other mobility services that reflect the principles of the sharing economy. This strategic pivot demonstrates how organizations can leverage their core competencies in new and innovative ways to remain competitive in a rapidly changing economic landscape.
In conclusion, adapting Strategic Planning to incorporate the principles of the sharing economy requires a comprehensive understanding of the new economic model, a willingness to embrace technological innovation, and a commitment to collaboration and sustainability. By doing so, organizations can unlock new opportunities for growth, enhance their competitive advantage, and contribute to a more sustainable and inclusive economy.
Understanding what defines a good problem statement in business management is crucial for C-level executives aiming to steer their organizations toward success. A well-crafted problem statement acts as the north star for strategic planning, guiding teams through the complexities of problem-solving and decision-making processes. It sets the stage for innovation, operational excellence, and, ultimately, achieving organizational goals.
A good problem statement in business management is clear, concise, and specific. It should succinctly describe the issue that needs to be addressed, without veering into unnecessary detail or ambiguity. This clarity helps in aligning team efforts and resources towards a common objective. Moreover, it should be rooted in verifiable data or insights, making it actionable and measurable. This specificity aids in the formulation of strategies and the assessment of their effectiveness post-implementation.
Furthermore, an effective problem statement is forward-looking, highlighting not just the current challenges but also the potential impact on future operations and opportunities. It should inspire a sense of urgency and importance, motivating stakeholders to rally behind a solution. In essence, a good problem statement serves as a foundational element in the strategic planning process, enabling organizations to navigate challenges with precision and purpose.
Framework for Crafting a Good Problem Statement
The development of a good problem statement can be guided by a structured framework. This involves initially identifying and understanding the core issue at hand. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of distinguishing symptoms from root causes. A deep dive into the underlying factors contributing to a problem ensures that the statement addresses the core issue rather than its manifestations.
Once the core issue is identified, the next step is to articulate the problem in a way that encapsulates its scope and impact. This requires a balance between being too broad, which can dilute focus, and too narrow, which might overlook interconnected issues. A well-defined problem statement should also outline the consequences of inaction, providing a compelling case for why the issue warrants attention and resources.
Finally, incorporating a sense of feasibility into the problem statement is key. It should not only define what the problem is but also hint at the possibility of its resolution. This doesn't mean proposing a solution within the statement but rather ensuring that the problem is framed in a way that suggests it can be effectively tackled. This aspect of the problem statement is crucial for securing buy-in from stakeholders and setting the stage for strategic problem-solving efforts.
Real World Examples and Actionable Insights
In the realm of Digital Transformation, for instance, a good problem statement might focus on the specific challenges an organization faces in integrating new technologies with legacy systems. It would detail the operational inefficiencies, potential revenue losses, or customer satisfaction issues arising from this challenge. By grounding the problem statement in real, quantifiable impacts, leaders can better prioritize initiatives and resources.
Actionable insights play a pivotal role in refining problem statements. For example, data analytics might reveal that a decline in customer satisfaction scores is linked to slow response times in customer service. This insight helps in crafting a problem statement that not only highlights the symptom (declining satisfaction scores) but also points to a specific operational issue (response times) that needs addressing.
In conclusion, crafting a good problem statement is both an art and a science. It requires a deep understanding of the issue, a strategic approach to defining it, and the ability to communicate its importance compellingly. By following a structured framework and leveraging actionable insights, C-level executives can ensure that their organizations are equipped to tackle challenges head-on, driving towards operational excellence and strategic success.
Understanding what is meant by a problem statement in research is crucial for any organization looking to embark on a research initiative. A well-defined problem statement acts as a compass, guiding the strategic planning process and ensuring that research efforts are aligned with the organization's overarching goals. It is the cornerstone upon which the entire research project is built, providing clarity and focus to the research team. In the context of strategic planning, a clear problem statement helps in identifying the specific issues that need to be addressed, thereby facilitating a more targeted and effective approach to research.
From a consulting perspective, crafting a precise problem statement is akin to setting the stage for successful strategy development. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a well-articulated problem statement as it lays the groundwork for the research framework. This framework then informs the development of a strategy that is both actionable and aligned with the organization's objectives. A problem statement serves not just as a statement of intent but as a strategic tool that sharpens the focus of research initiatives, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and that the research outcomes are actionable and directly relevant to the organization's strategic goals.
The role of a problem statement extends beyond the initial stages of research. It is a dynamic component of the research process, continually guiding and refining the research strategy as new information and insights are uncovered. This adaptability ensures that the research initiative remains focused and relevant, even as the external business environment changes. The ability to pivot and refine research objectives in response to emerging trends or data is a critical aspect of maintaining strategic agility. Therefore, a well-defined problem statement is not just a starting point but a constant reference that guides strategic planning and execution throughout the research process.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
Developing a problem statement that is both precise and aligned with strategic objectives requires a structured approach. A useful template involves starting with a clear identification of the issue at hand, followed by its implications for the organization, and concluding with a question or hypothesis that the research will address. This template ensures that the problem statement is comprehensive, covering not just the "what" but also the "why" and the "how" of the research initiative.
Consulting firms often utilize a framework that begins with a deep dive into the organization's current state, including its challenges and opportunities. This analysis is critical in identifying the underlying issues that need to be addressed through research. Following this, the problem statement is refined through iterative discussions with key stakeholders, ensuring that it is aligned with both the strategic objectives of the organization and the realities of the operational environment. This collaborative approach not only enhances the relevance of the problem statement but also ensures buy-in from key stakeholders, a crucial factor for the successful execution of research initiatives.
Moreover, the use of a structured framework for developing a problem statement encourages a disciplined approach to research. It compels the research team to critically evaluate the scope and objectives of the research initiative, ensuring that they are both realistic and strategically significant. This disciplined approach is essential for maintaining focus and ensuring that the research initiative does not deviate from its intended strategic objectives. By providing a clear direction and purpose, a well-defined problem statement enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of research efforts.
Real-World Applications and Benefits
In practice, organizations across various industries have leveraged well-defined problem statements to drive successful research initiatives. For example, in the healthcare sector, a leading hospital used a clear problem statement to guide its research on reducing patient wait times. The problem statement focused on the specific issue of long wait times, its impact on patient satisfaction, and the need for operational improvements. This clarity of purpose enabled the research team to develop targeted strategies that significantly improved patient flow and satisfaction.
Similarly, a technology company used a well-articulated problem statement to focus its research on improving user experience for its flagship product. The problem statement clearly outlined the issues users were facing, the potential impact on customer retention, and the need for innovative solutions. This focused approach to research resulted in the development of a series of enhancements that dramatically improved user satisfaction and loyalty.
The benefits of a well-defined problem statement extend beyond the successful completion of research initiatives. Organizations that employ this strategic tool enjoy improved decision-making, as the research outcomes are directly aligned with strategic objectives. Additionally, a clear problem statement ensures that research efforts are more likely to lead to actionable insights, thereby enhancing the organization's ability to respond effectively to challenges and opportunities. In essence, a well-defined problem statement is not just a component of the research process; it is a strategic asset that enhances the organization's overall strategic planning and execution capabilities.
In conclusion, the importance of a well-defined problem statement in research cannot be overstated. It is a critical tool that enhances strategic planning, ensures the alignment of research initiatives with organizational goals, and facilitates the efficient allocation of resources. By providing a clear focus and direction, a well-articulated problem statement enables organizations to navigate the complexities of the research process and achieve meaningful, actionable outcomes. As such, understanding and leveraging this tool is essential for any organization looking to enhance its strategic planning and execution through research.
Technology has become a critical enabler in ensuring that Performance Management systems within organizations are not only efficient but also aligned with strategic goals. The advent of sophisticated software and analytical tools has transformed traditional Performance Management, making it more dynamic, real-time, and closely tied to organizational strategy. This transformation is crucial for organizations aiming to maintain a competitive edge in the fast-paced business environment.
Real-Time Feedback and Goal Adjustment
One of the significant ways technology enhances Performance Management is through the provision of real-time feedback and the facilitation of agile goal setting. Traditional Performance Management processes often relied on annual reviews, which are no longer sufficient in today’s fast-moving business world. With technology, managers and employees can receive immediate feedback on their performance, allowing for quick adjustments and continuous improvement. This real-time capability ensures that employees' efforts are always aligned with the strategic goals of the organization. For instance, platforms like Workday and SuccessFactors enable managers to set, track, and update goals quickly, ensuring alignment with changing organizational priorities.
Moreover, technology facilitates the collection and analysis of performance data, enabling managers to identify trends, strengths, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach to Performance Management ensures that decisions are based on objective information rather than subjective opinions. According to a report by Deloitte, organizations that use analytics in their Performance Management processes are twice as likely to report improvements in employee engagement and organizational performance.
Furthermore, technology enables the customization of Performance Management processes to fit the unique needs of different teams or departments within an organization. This flexibility ensures that Performance Management is relevant and aligned with the specific strategic goals of each part of the organization, thereby enhancing overall effectiveness.
Enhancing Employee Engagement and Ownership
Technology also plays a crucial role in enhancing employee engagement and ownership of Performance Management. Engaged employees are more likely to be committed to the organization's strategic goals and put in the effort required to achieve them. Modern Performance Management tools facilitate more frequent and meaningful interactions between employees and managers, moving beyond the traditional annual review to continuous dialogue. This ongoing communication helps in aligning individual goals with the strategic objectives of the organization, thereby fostering a sense of ownership among employees towards achieving those goals.
Additionally, technology enables the implementation of recognition and reward systems that are closely linked to performance metrics. For example, platforms like Bonusly allow organizations to implement peer-to-peer recognition programs that are tied to specific achievements or milestones, which can be directly linked to strategic goals. This not only motivates employees but also reinforces the importance of aligning individual efforts with organizational objectives.
Employee engagement is further enhanced by providing employees with access to their performance data, allowing them to self-monitor and adjust their efforts in real-time. This empowerment leads to increased motivation and commitment to achieving strategic goals. A study by Gartner found that organizations that effectively leverage technology to engage employees in Performance Management see a 14% increase in team performance and a 24% increase in employee performance.
Facilitating Learning and Development
Another critical aspect of aligning Performance Management with strategic goals is the focus on learning and development. Technology facilitates the identification of skill gaps and the delivery of personalized learning experiences to address these gaps. This ensures that employees are not only performing well in their current roles but are also developing the skills needed to contribute to future strategic objectives. Learning Management Systems (LMS) like Cornerstone OnDemand and LinkedIn Learning provide platforms for delivering targeted training programs, tracking progress, and measuring the impact of learning on performance.
Moreover, technology enables the integration of learning and development activities with Performance Management processes, making it easier for managers to identify development needs based on performance data and to recommend appropriate learning interventions. This integrated approach ensures that learning and development are directly aligned with strategic goals, thereby enhancing the overall effectiveness of Performance Management.
Additionally, the use of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning in learning and development can provide predictive insights into future skill requirements. This allows organizations to proactively prepare their workforce for upcoming strategic challenges, ensuring that Performance Management is not only about meeting current goals but also about future-proofing the organization.
In conclusion, technology significantly enhances the effectiveness of Performance Management in aligning with strategic goals through real-time feedback and goal adjustment, enhancing employee engagement and ownership, and facilitating learning and development. By leveraging technology, organizations can ensure that their Performance Management processes are dynamic, data-driven, and aligned with their strategic objectives, thereby driving organizational success in the competitive business landscape.
Creating a strategic plan on a single PowerPoint slide is an art form that demands clarity, conciseness, and a deep understanding of your audience's needs. In the fast-paced world of C-level executives, the ability to distill complex strategies into a one-page overview is invaluable. This approach not only facilitates quick decision-making but also ensures that key stakeholders are aligned with the organization's strategic direction. Here, we delve into best practices for developing a strategic one-page plan in PowerPoint, drawing on insights from leading consulting firms and leveraging years of experience in strategy development and executive communication.
Firstly, understanding the framework for how to create a plan on a page in PowerPoint is crucial. The framework should encompass all critical elements of your strategy, including objectives, key results, initiatives, and metrics for success. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of starting with a clear objective that aligns with the organization's overall vision. From there, breaking down the strategy into actionable components—what needs to be achieved (objectives), how success will be measured (key results), what will be done to get there (initiatives), and how progress will be tracked (metrics)—is essential. This structured approach ensures that your one-page plan is not only comprehensive but also actionable.
Moreover, the choice of template and design plays a significant role in how effectively your message is communicated. A cluttered or overly complex template can detract from the clarity of your strategy. Opt for simplicity and visual appeal, using clear headings, bullet points, and icons to represent different sections of your plan. Color coding can also be a powerful tool to differentiate between various components or priorities within your strategy. Remember, the goal is to make your one-page plan as intuitive and easy to grasp as possible for busy executives who often have limited time to absorb detailed information.
Additionally, incorporating real-world examples and data can significantly enhance the credibility and impact of your strategic plan. Citing authoritative sources or case studies from renowned consulting firms can provide valuable context and demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of your proposed initiatives. For instance, if your strategy includes a digital transformation component, referencing a successful case study from Accenture or Deloitte can lend weight to your recommendations and help convince stakeholders of the need for change.
Key Elements to Include
When crafting your one-page strategic plan, certain elements are non-negotiable. These include:
- Executive Summary: Start with a concise summary that captures the essence of your strategy, including the overarching goal and key priorities.
- Strategic Objectives: Clearly articulate the main objectives that your organization aims to achieve, ensuring they are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART).
- Action Plan: Detail the specific initiatives or projects that will be undertaken to achieve each objective, including responsible teams or individuals and timelines.
- Performance Metrics: Define how success will be measured for each objective, including both qualitative and quantitative metrics.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks or challenges that could impede progress and outline strategies for mitigation.
This structured approach ensures that your plan is not only comprehensive but also actionable and aligned with the organization's strategic goals.
Best Practices for Effective Communication
Effective communication is key to ensuring your one-page plan resonates with C-level executives. Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon that might obfuscate your message. Visual aids, such as charts and graphs, can be incredibly effective in illustrating trends, comparisons, and projections. However, it's important to use them judiciously to avoid overwhelming your audience. Each visual element should serve a clear purpose and enhance the understanding of your strategic plan.
Furthermore, tailoring your presentation to the specific interests and concerns of your audience can significantly increase its impact. For instance, if your audience is particularly focused on Operational Excellence, highlight how your strategy will improve efficiency and reduce costs. This level of customization demonstrates a deep understanding of your audience's priorities and can make your strategic plan more compelling.
In conclusion, developing a strategic one-page plan in PowerPoint requires a balance of comprehensive content, clear and effective communication, and visually appealing design. By following these best practices, you can create a powerful tool that facilitates strategic alignment, decision-making, and execution across your organization. Remember, the ultimate goal is to convey a complex strategy in a simple, digestible format that resonates with C-level executives and drives your organization forward.
Understanding "what is the statement of the problem" in the context of strategic planning is pivotal for C-level executives focused on steering their organizations toward sustainable growth and operational excellence. A well-defined problem statement acts as a north star, guiding the strategic planning process by clearly identifying the issues that need resolution. This clarity is crucial for aligning team efforts, optimizing resource allocation, and setting realistic goals. In essence, it transforms abstract challenges into tangible objectives that can be systematically addressed.
In the realm of strategic planning, a problem statement serves as a foundational element that informs decision-making and strategy development. It provides a concise description of the gap between the current state and the desired future state, highlighting the obstacles that prevent the organization from achieving its strategic goals. Crafting a compelling problem statement requires a deep understanding of the organization's internal and external environments, including market dynamics, competitive pressures, and internal capabilities. This understanding enables leaders to pinpoint the root causes of issues rather than merely addressing symptoms.
The process of defining a problem statement should be rigorous and analytical, leveraging data and insights from across the organization. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a data-driven approach to problem identification and solution development. By grounding the problem statement in empirical evidence, leaders can ensure that their strategic initiatives are focused on addressing the most impactful challenges. This evidence-based approach also facilitates buy-in from stakeholders across the organization, as it demonstrates a commitment to informed decision-making.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
A structured framework can significantly enhance the effectiveness of a problem statement in guiding strategic planning efforts. The first step in this framework involves conducting a comprehensive analysis of the organization's current state, including its performance metrics, competitive positioning, and market trends. This analysis should be rooted in data collected from reliable sources, including market research firms like Gartner and Forrester, to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Following the initial analysis, the next step is to identify the specific challenges or opportunities that the organization faces. This requires a critical examination of the internal and external factors that influence the organization's performance. Consulting firms often use tools like SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis and PESTEL (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, Legal) analysis to facilitate this examination. The insights gained from these analyses are instrumental in articulating a clear and focused problem statement.
Once the challenges have been identified, the final step in the framework is to distill these insights into a concise problem statement. This statement should articulate the core issue in a way that is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Crafting a problem statement that adheres to these criteria ensures that it can effectively guide the strategic planning process, from strategy development to implementation and performance management.
Real-World Application and Benefits
The application of a well-defined problem statement in strategic planning can be illustrated through real-world examples. For instance, a leading retail organization facing declining sales in a highly competitive market used a clear problem statement to pivot its strategy towards digital transformation. By accurately identifying the root causes of its sales decline—such as outdated technology infrastructure and changing consumer behaviors—the organization was able to focus its strategic planning efforts on initiatives that directly addressed these issues, resulting in a successful turnaround.
The benefits of utilizing a problem statement in strategic planning are manifold. It not only ensures that strategic initiatives are aligned with the organization's overarching goals but also enhances decision-making efficiency and effectiveness. A clear problem statement acts as a filter, helping leaders prioritize initiatives based on their potential impact on the identified problem. This prioritization is critical in today's fast-paced business environment, where resources are limited and the cost of misalignment can be significant.
In conclusion, the role of a problem statement in strategic planning cannot be overstated. It is a powerful tool that enables organizations to navigate the complexities of the business landscape with focus and precision. By adopting a structured approach to defining and utilizing problem statements, leaders can drive their organizations toward desired outcomes with greater confidence and clarity. The journey from problem identification to strategic execution becomes more manageable, and ultimately, more successful.
Creating an annual operating plan is a critical process that requires meticulous planning, strategic foresight, and a deep understanding of an organization's goals, resources, and market dynamics. This comprehensive guide aims to provide C-level executives with a robust framework for developing an effective annual operating plan that aligns with their organization's strategic objectives. By leveraging industry insights and actionable steps, leaders can ensure their organizations are well-positioned for success in the upcoming fiscal year.
At the core of an effective annual operating plan is a clear articulation of the organization's strategic priorities. This involves a thorough analysis of the internal and external factors that could impact the organization's performance, including market trends, competitive dynamics, and regulatory changes. Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of aligning strategic planning with operational execution to drive organizational agility and resilience. A well-defined strategy serves as the foundation for setting operational goals, allocating resources, and defining key performance indicators (KPIs) that will guide the organization's efforts throughout the year.
Developing a detailed and actionable framework is the next step in crafting an annual operating plan. This framework should outline the specific initiatives and projects that will be undertaken to achieve the strategic goals, along with timelines, responsible parties, and required resources. Utilizing a template can streamline this process, ensuring consistency and clarity across the organization. It's essential to incorporate flexibility into the plan to adapt to unforeseen challenges and opportunities. Regular reviews and adjustments based on performance data and market feedback will help maintain alignment with the strategic objectives and operational realities.
Effective communication and stakeholder engagement are paramount throughout the planning and execution phases. An annual operating plan is not just a document for senior management; it's a roadmap that guides the entire organization. Clear, concise, and consistent communication ensures that everyone understands their role in achieving the plan's objectives. Engaging employees, customers, and other stakeholders in the planning process can provide valuable insights, foster buy-in, and drive collective effort towards common goals. This collaborative approach can significantly enhance the plan's effectiveness and the organization's overall performance.
Key Components of an Annual Operating Plan
An annual operating plan comprises several key components, each contributing to the overall effectiveness of the plan. These components include:
- Strategic Objectives: Clearly defined goals that align with the organization's long-term vision and mission.
- Operational Goals: Specific, measurable targets that translate the strategic objectives into actionable plans.
- Resource Allocation: Detailed plans for deploying financial, human, and technological resources to support the operational goals.
- Risk Management: Identification of potential risks and development of mitigation strategies to ensure the plan's success.
- Performance Metrics: KPIs and other metrics to monitor progress, measure success, and guide decision-making throughout the year.
These components are interrelated and must be carefully balanced to create a cohesive and effective plan. For instance, resource allocation decisions should be informed by the strategic objectives and operational goals, while risk management strategies should be integrated into all aspects of the plan to safeguard against potential disruptions.
Moreover, the choice of performance metrics is critical. They should not only reflect the organization's strategic priorities but also be realistic, measurable, and directly linked to the actions and outcomes they are intended to influence. This ensures accountability and motivates all levels of the organization to contribute to the plan's success.
Implementing the Annual Operating Plan
Implementation is where strategy translates into action. It requires disciplined execution, continuous monitoring, and agile management. Leaders must be proactive in addressing challenges, seizing opportunities, and making necessary adjustments to the plan. This agility is crucial in today's fast-paced and unpredictable business environment.
Technology plays a pivotal role in facilitating effective implementation. Digital tools and platforms can enhance collaboration, streamline processes, and provide real-time data for informed decision-making. For example, project management software can help track progress against goals, while analytics platforms can offer insights into performance trends and areas for improvement.
Finally, fostering a culture of accountability and continuous improvement is essential for the successful implementation of the annual operating plan. This involves setting clear expectations, providing regular feedback, and recognizing achievements. Encouraging a culture of innovation and experimentation can also drive operational excellence and strategic growth. By embracing these principles, organizations can not only achieve their annual objectives but also strengthen their competitive position and long-term sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating an annual operating plan is a complex but essential process that requires strategic thinking, detailed planning, and effective execution. By following a structured framework, engaging stakeholders, and leveraging technology, organizations can develop a plan that aligns with their strategic objectives and positions them for success. Continuous monitoring, agile management, and a culture of accountability and improvement are key to navigating challenges and capitalizing on opportunities throughout the year. With a well-crafted annual operating plan, organizations can achieve operational excellence, drive strategic growth, and build a resilient and agile business ready to thrive in the dynamic global marketplace.
Crafting a compelling problem statement is a critical step in strategic planning for any organization. It sets the stage for identifying the most pressing issues that need resolution and guides the strategic direction. A well-defined problem statement acts as a North Star, keeping the organization's efforts aligned towards a common goal. It is not merely a statement of an existing issue but a clear, concise articulation of the challenges that hinder the organization's progress towards its strategic objectives.
The first key element of a problem statement in strategic planning is specificity. A vague or overly broad problem statement will not serve its purpose. It must precisely describe the issue at hand, avoiding generalizations and focusing on specific aspects that are problematic. This requires a deep dive into the organization's performance metrics, operational processes, and market position to identify the exact barriers to success. Consulting firms often emphasize the importance of data-driven insights to achieve this level of specificity. For instance, a McKinsey report on strategic decision-making underscores the value of leveraging analytics to pinpoint areas of underperformance that need strategic intervention.
Another crucial component is relevance. The problem statement must be directly linked to the organization's core strategic goals. It should reflect an understanding of how the identified issue impacts the organization's ability to achieve its objectives, whether it's market expansion, customer satisfaction, innovation, or financial health. This alignment ensures that the strategic planning process is focused on overcoming hurdles that are critical to the organization's success. It also facilitates the prioritization of resources and efforts towards solving the most impactful problems.
Lastly, the problem statement should be actionable. It must not only describe the problem but also imply the potential for solutions. This means framing the problem in a way that invites exploration of strategic options and alternatives. An actionable problem statement encourages a proactive approach to strategy development, focusing on opportunities for improvement rather than merely lamenting over challenges. It sets the stage for ideation, encouraging the team to think creatively about how to overcome the obstacles identified.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
Developing a problem statement that is specific, relevant, and actionable requires a structured approach. A useful framework involves the following steps:
- Begin with a thorough analysis of the organization's current state, including performance metrics, competitive positioning, and market trends. This analysis should be grounded in reliable data and insights from reputable sources.
- Identify the gap between the current state and the organization's strategic objectives. This involves pinpointing the specific issues that are preventing progress towards these goals.
- Articulate the problem in a clear, concise statement that encapsulates the essence of the challenge. The statement should be direct and to the point, avoiding any ambiguity.
This framework serves as a template for organizations to systematically approach the task of defining their problem statement. It ensures that the statement is grounded in a solid understanding of the organization's strategic context and is focused on issues that are critical to its success.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a leading retail chain facing declining sales. Their problem statement might focus on the specific challenge of increasing online competition and changing consumer behaviors, which are directly relevant to their strategic goal of market leadership. By framing the problem in terms of specific, actionable issues, the organization can then explore strategic options such as digital transformation, customer experience enhancement, or operational efficiency improvements.
In another example, a technology firm struggling with slow innovation cycles might craft a problem statement centered on the need to accelerate product development to stay ahead of rapid technological changes. This highlights the relevance of the issue to the firm's strategic objective of maintaining a competitive edge through innovation. The problem statement thus becomes a catalyst for exploring strategies focused on process optimization, culture change, or investment in new technologies.
In conclusion, a well-crafted problem statement is a foundational element of effective strategic planning. It requires specificity, relevance, and actionability to truly serve its purpose. By following a structured framework and drawing on real-world examples, organizations can ensure that their problem statement accurately captures the challenges they face and sets the stage for strategic success.
Understanding what is meant by problem statement in research is crucial for any organization looking to tackle issues effectively and efficiently. A problem statement is a concise description of an issue to be addressed or a condition to be improved upon. It identifies the gap between the current (problem) state and desired (goal) state of a process or product. By focusing on the facts, the problem statement provides a clear understanding of the issue which needs to be solved.
In the realm of consulting, crafting a compelling problem statement is foundational to the strategy development process. It sets the stage for the entire project, guiding the research framework and influencing the strategic planning efforts. A well-defined problem statement is not just a statement of the problem but a clear, specific description of the issue that is to be addressed. It includes the impact of the problem on the organization, quantifies the gap between the current and desired states, and may also suggest a direction for the solution. This precision is vital for aligning team efforts and ensuring that the research is directed towards tangible outcomes.
Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a robust problem statement in driving effective solutions. It acts as a compass for the research, ensuring that the focus remains on addressing the core issue rather than getting sidetracked by peripheral concerns. The problem statement is also a critical communication tool, helping to ensure that all stakeholders have a unified understanding of the problem at hand. This clarity is essential for mobilizing resources and galvanizing the organization towards a common goal.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
Developing a problem statement requires a structured approach to ensure that it is both informative and actionable. A commonly used framework involves several key components: the identification of the problem, the impact of the problem, and the potential solution space. This framework ensures that the problem statement is comprehensive and focused on actionable insights.
The first step in this framework is to clearly define the problem, including how it was discovered and why it is a priority for the organization. This involves gathering and analyzing data to quantify the problem's impact and scope. The next step is to articulate the impact of the problem on the organization. This could include financial losses, decreased customer satisfaction, or internal inefficiencies. By quantifying the impact, the problem statement underscores the urgency and importance of addressing the issue.
Finally, while the problem statement primarily focuses on the issue at hand, it should also hint at the potential solution space without prescribing a specific solution. This encourages creative thinking and problem-solving within the strategic planning and research phases. The inclusion of potential solution spaces helps to frame the problem in a way that is conducive to ideation and innovation.
Real-World Examples
Consider a global retail chain experiencing declining sales in several key markets. Their problem statement might read: "Over the past two years, our organization has seen a 10% decline in sales across five major markets, leading to a significant impact on overall profitability. This decline is attributed to both increased competition and changing consumer behaviors. Addressing this issue requires a strategic review of our market positioning and consumer engagement strategies to identify and implement corrective actions."
In another example, a technology firm might be facing challenges with product development cycles that are longer than industry standards. Their problem statement could be: "Our product development cycle is 30% longer than the industry average, resulting in delayed market entry and lost revenue opportunities. This issue stems from inefficiencies in our development and testing phases. A comprehensive analysis of our processes and benchmarks against industry standards is needed to identify and rectify the root causes."
Utilizing the Problem Statement in Research
The problem statement is not just a formative step in the research process; it is a guiding light throughout the project lifecycle. It helps in maintaining focus, ensuring that the research efforts are always aligned with the core issue. The problem statement also aids in the development of a research strategy, serving as a reference point for methodological decisions, data collection, and analysis.
In the context of consulting, the problem statement is often revisited and refined as more information becomes available. This iterative process ensures that the research remains relevant and focused on addressing the most pressing issues facing the organization. It is a dynamic tool that adapts to the evolving understanding of the problem and the research findings.
Moreover, the problem statement plays a crucial role in stakeholder engagement. By clearly articulating the issue, its impacts, and the potential solution space, it helps to build consensus and rally the organization around the research efforts. This is particularly important in complex projects where buy-in from multiple stakeholders is critical for success.
In conclusion, understanding what is meant by problem statement in research is fundamental for any organization looking to address challenges strategically and effectively. It is the cornerstone of the research process, providing direction, focus, and a framework for action. By crafting a clear, concise, and actionable problem statement, organizations can ensure that their research efforts are well-positioned to deliver meaningful and impactful solutions.
Managing limited resources to achieve both organizational and personal goals is a common challenge faced by executives worldwide. The key to optimizing these resources lies in strategic planning, a discipline that, when executed effectively, can turn constraints into opportunities for growth and innovation. The strategic planning process involves setting objectives, analyzing competitive dynamics, and allocating resources in a way that aligns with the organization's long-term vision. This approach not only ensures that limited resources are utilized efficiently but also helps in identifying areas where investments can yield the highest returns.
One effective framework for managing limited resources is the Priority Matrix, which helps executives categorize tasks based on urgency and importance. This tool is instrumental in decision-making, allowing leaders to focus on activities that align closely with their strategic objectives while deferring or delegating less critical tasks. Additionally, the adoption of a Zero-Based Budgeting (ZBB) approach forces managers to justify every dollar spent, ensuring that resources are allocated to initiatives that are essential to achieving key goals. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Bain have highlighted the effectiveness of ZBB in driving cost discipline and reallocating resources towards more strategic areas.
Moreover, leveraging technology and digital transformation initiatives can significantly enhance an organization's ability to do more with less. Automation of routine tasks, for example, frees up valuable resources that can be redirected towards more strategic initiatives. Similarly, adopting cloud-based solutions can reduce the need for significant capital investments in IT infrastructure, allowing for a more agile allocation of resources. These strategies not only optimize the use of limited resources but also foster a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within the organization.
Strategic Resource Allocation
Strategic Resource Allocation is critical in ensuring that limited resources are managed effectively to reach personal and organizational goals. This process involves a deep dive into the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis) to identify where resources can be most effectively deployed. By aligning resource allocation with strategic priorities, executives can ensure that their organization remains focused on its core competencies while avoiding the dispersion of efforts across too many fronts.
Implementing a robust Performance Management system is another vital component of strategic resource allocation. By setting clear KPIs and regularly reviewing performance against these metrics, executives can ensure that resources are being utilized in areas that contribute most significantly to the organization's success. This approach not only enhances accountability but also provides a clear template for measuring the impact of resource allocation decisions.
Real-world examples abound of organizations that have successfully optimized limited resources through strategic planning. For instance, a global retailer applied a strategic resource allocation framework to revamp its supply chain, resulting in significant cost savings and improved delivery times. By focusing on core areas that directly impacted customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, the retailer was able to achieve its organizational goals despite the constraints of limited resources.
Leveraging Partnerships and Collaborations
In an era where innovation and speed to market are critical, leveraging partnerships and collaborations can be a game-changer for organizations looking to optimize limited resources. Strategic alliances with other organizations can provide access to new markets, technologies, and expertise without the need for substantial capital investment. This approach not only accelerates growth but also spreads the risk associated with new initiatives.
Consulting giants like Accenture and Deloitte have underscored the value of ecosystems and partnerships in driving digital transformation and innovation. By collaborating with startups, technology providers, and even competitors, organizations can tap into a wealth of resources and capabilities that would otherwise be beyond their reach. This strategy is particularly effective in industries where technological advancements are rapidly changing the competitive dynamics.
Ultimately, the ability to manage limited resources effectively is a critical competency for today's executives. By employing strategic planning methods, leveraging technology, and fostering partnerships, leaders can optimize these resources to achieve both organizational and personal goals. The journey towards resource optimization requires a disciplined approach to strategic planning, a willingness to embrace change, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Through these efforts, executives can turn the challenge of limited resources into an opportunity for strategic advantage and long-term success.
Defining a problem statement that aligns with Strategic Planning goals is a critical step in ensuring that an organization's efforts are directed towards meaningful and impactful outcomes. The key elements of a problem statement serve as a compass, guiding the strategic initiatives and ensuring that every action taken contributes towards the overarching objectives of the organization. In the realm of consulting, where precision and clarity are paramount, a well-crafted problem statement is the foundation upon which successful strategy development and execution are built.
At the core, the problem statement should succinctly articulate the issue at hand, its implications for the organization, and the potential benefits of addressing it. This requires a deep understanding of the organization's current state, including its internal capabilities and external environment. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Bain emphasize the importance of leveraging data and analytics to inform this understanding, ensuring that the problem statement is rooted in reality and not in assumption. This data-driven approach not only enhances the accuracy of the problem statement but also aligns it more closely with the organization's strategic goals.
Furthermore, the problem statement must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). This SMART framework ensures that the problem statement is not just a vague description of an issue but a clear and actionable challenge that the organization can address. For example, instead of stating "increase revenue," a SMART problem statement would specify "increase revenue by 10% within the next fiscal year through expansion into the Asian market." This level of specificity guides the strategic planning process, ensuring that the goals set are aligned with the problem statement and, by extension, with the organization's strategic objectives.
Framework for Crafting a Problem Statement
Developing a problem statement that is both effective and strategic requires a structured approach. Consulting firms often utilize a template or framework to ensure consistency and comprehensiveness in problem statement development. This typically involves several key steps, starting with the identification of the issue. This step goes beyond merely stating the problem; it involves a deep dive into understanding the root causes and the factors contributing to the issue. This is where leveraging industry insights and benchmarks can be particularly valuable, providing a context for the problem within the broader market dynamics.
The next step in the framework involves articulating the impact of the problem on the organization. This is where quantification comes into play, translating the issue into tangible metrics such as lost revenue, decreased market share, or increased operational costs. By quantifying the impact, the problem statement becomes more compelling, making a stronger case for why addressing the issue should be a strategic priority.
Finally, the framework requires outlining the potential benefits and opportunities that resolving the problem would bring to the organization. This forward-looking perspective is crucial for aligning the problem statement with the organization's strategic goals. It shifts the focus from the problem itself to the strategic outcomes that solving the problem would enable, such as entering new markets, enhancing customer satisfaction, or improving operational efficiency.
Real-World Examples
Consider the case of a global retail chain that identified a significant drop in customer retention rates. By applying a structured framework, the organization was able to craft a problem statement that not only highlighted the issue but also outlined the strategic implications of failing to address it. The problem statement focused on the potential to increase customer lifetime value and market share by improving customer engagement and satisfaction strategies. This clear and strategic problem statement guided the organization's strategic planning, resulting in targeted initiatives that successfully reversed the trend in customer retention.
In another example, a technology company facing stiff competition in innovation used a well-defined problem statement to steer its strategic planning towards more aggressive research and development efforts. The problem statement highlighted the gap between the current product offerings and the evolving market needs, quantifying the potential revenue loss and the opportunity cost of inaction. This strategic problem statement became the catalyst for a comprehensive innovation strategy that propelled the company to a leadership position in its market.
In conclusion, a well-crafted problem statement is a critical tool in aligning strategic planning with organizational goals. By focusing on the key elements of a problem statement, leveraging a structured framework, and drawing on real-world examples, organizations can ensure that their strategic planning efforts are both effective and impactful. The precision, clarity, and strategic focus of the problem statement set the direction for the organization's strategic initiatives, ensuring that every effort contributes towards the achievement of the overarching goals.
Scenario planning plays a crucial role in preparing organizations for unexpected market shifts by enabling them to anticipate possible future scenarios and develop strategic responses. This approach helps organizations to navigate through uncertainties with greater agility and resilience. In an era where market dynamics are increasingly volatile, the ability to foresee and adapt to potential changes can provide a significant competitive advantage.
Understanding Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is a strategic planning method that organizations use to create a variety of long-term plans based on different assumptions about the future. It involves identifying trends, uncertainties, and potential future events to visualize various plausible future environments. This method allows organizations to test their strategies against multiple scenarios to ensure flexibility and preparedness for any market condition. Unlike traditional forecasting, which often relies on linear projections based on past data, scenario planning acknowledges the complexity and unpredictability of future events, making it a vital tool for strategic risk management.
According to a report by McKinsey & Company, companies that regularly engage in scenario planning are better positioned to navigate crises and recover more quickly. This is because scenario planning enhances an organization's ability to anticipate changes, assess risks, and seize opportunities in a timely manner. By understanding potential future contexts, organizations can develop strategic options that are robust across a range of scenarios, thereby minimizing the risk of strategic missteps.
Effective scenario planning requires a deep understanding of the external environment, including economic, political, technological, and social factors. It also demands a clear grasp of the organization's capabilities and strategic objectives. By aligning scenario planning with strategic goals, organizations can ensure that their strategic responses are both proactive and aligned with their long-term vision.
Scenario Planning in Action
Real-world examples of scenario planning underscore its value in preparing for unexpected market shifts. For instance, during the financial crisis of 2008, companies that had engaged in scenario planning were able to respond more swiftly and effectively than their counterparts. These organizations had already considered extreme market conditions in their strategic planning, enabling them to make informed decisions quickly, such as adjusting their investment strategies or operational models to mitigate risks.
Another example can be found in the energy sector, where companies like Royal Dutch Shell have long used scenario planning to navigate the volatile oil market. Shell’s scenario planning exercises have helped it to anticipate significant shifts in the energy market, such as the rise of renewable energy and changing geopolitical landscapes. This foresight has allowed Shell to adapt its business model and investment priorities ahead of its competitors, demonstrating the strategic value of scenario planning in ensuring long-term resilience and competitiveness.
Similarly, in the technology sector, scenario planning enables companies to prepare for rapid changes in technology trends and consumer behavior. By considering scenarios that encompass various technological advancements and market responses, tech companies can develop more agile and innovative strategies, ensuring they remain at the forefront of digital transformation.
Implementing Scenario Planning
To effectively implement scenario planning, organizations should begin by identifying key drivers of change that could impact their industry. This involves a thorough analysis of external forces and internal capabilities. Engaging a wide range of stakeholders in this process can provide diverse perspectives and enhance the comprehensiveness of the scenarios developed.
Once key drivers are identified, organizations can develop a set of plausible scenarios that represent different futures. Strategies should then be tested against these scenarios to identify potential vulnerabilities and opportunities. This process not only aids in strategic decision-making but also helps in building a culture of agility and continuous learning within the organization.
Finally, scenario planning should be integrated into the organization's ongoing strategic planning process. This ensures that it is not a one-time exercise but a continuous effort that informs strategic decisions on a regular basis. By regularly updating scenarios and strategic responses, organizations can maintain their preparedness for unexpected market shifts, ensuring long-term sustainability and success.
In conclusion, scenario planning is an essential strategic tool for preparing organizations for unexpected market shifts. It enables organizations to anticipate changes, assess risks, and seize opportunities, thereby enhancing their resilience and competitive advantage. By incorporating scenario planning into their strategic processes, organizations can navigate the uncertainties of the future with confidence and agility.
Understanding what is tactical planning in business is crucial for any C-level executive aiming to enhance their organization's strategic planning process. Tactical planning refers to the process of taking a company's strategic plan and breaking it down into specific, short-term actions and plans. These actions are designed to achieve parts of the larger strategic objectives. This approach allows for a more focused execution of strategy, ensuring that every part of the organization is aligned towards the common goals.
Tactical planning serves as a bridge between the high-level strategic vision and the day-to-day operations of the organization. It translates broad strategic goals into actionable plans that can be implemented by teams across the organization. This level of planning is essential for operational excellence, as it provides a clear framework for decision-making and prioritization. By defining specific steps, resources, and timelines, tactical planning makes it easier for managers to guide their teams effectively towards achieving strategic objectives.
Moreover, tactical planning introduces a layer of accountability and performance management into the strategic planning process. By setting clear targets and KPIs for tactical initiatives, organizations can monitor progress and make adjustments as needed. This iterative process ensures that the strategy remains relevant and responsive to changes in the external environment. It also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, where lessons learned from tactical execution can inform future strategic planning cycles.
Integrating Tactical Planning into Strategic Planning
To effectively integrate tactical planning into the strategic planning process, organizations should adopt a structured framework. This framework should outline how strategic objectives will be broken down into tactical plans, who will be responsible for executing these plans, and how progress will be measured. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG often emphasize the importance of a clear, actionable template for this integration, ensuring that strategic and tactical planning are seamlessly connected.
One approach is to use a cascading objectives framework, where strategic goals are translated into departmental and individual objectives. This ensures that every team and employee understands their role in achieving the strategic vision. Regular review meetings can then be used to assess progress, identify challenges, and adjust plans as necessary. This approach not only enhances alignment and execution but also promotes engagement by involving employees in the strategic process.
Another key aspect is the use of technology to support tactical planning and execution. Digital tools can provide real-time visibility into progress, facilitate communication across teams, and enable data-driven decision-making. For example, project management software can help track the completion of tactical initiatives, while analytics platforms can measure their impact on strategic objectives. Leveraging technology in this way can significantly increase the efficiency and effectiveness of tactical planning.
Real-World Examples of Successful Tactical Planning
Consider the case of a global retail chain that used tactical planning to drive its digital transformation strategy. By breaking down the strategic goal into specific digital initiatives—such as launching an e-commerce platform, implementing a mobile payment system, and using data analytics for customer insights—the organization was able to execute its strategy in a focused and efficient manner. Each initiative had a clear plan with defined timelines, responsibilities, and metrics for success, enabling the company to achieve its digital transformation objectives ahead of schedule.
Another example is a manufacturing company that applied tactical planning to improve its supply chain resilience. The strategic objective was to reduce dependency on single-source suppliers. The tactical plan included identifying alternative suppliers, developing dual-sourcing capabilities, and increasing inventory levels of critical components. By executing these tactical initiatives, the company was able to mitigate supply chain risks and improve its operational flexibility.
In conclusion, tactical planning plays a critical role in enhancing the strategic planning process. It provides a detailed roadmap for execution, ensures alignment across the organization, and introduces accountability and performance management into strategy implementation. By adopting a structured framework and leveraging technology, organizations can effectively integrate tactical planning into their strategic planning efforts. Real-world examples from various industries demonstrate the value of tactical planning in achieving strategic objectives and driving organizational success.
When C-level executives ponder over the question, "How long is a strategic plan?" the answer is not one-size-fits-all. The optimal timeframe for a strategic plan to ensure alignment with long-term goals and market dynamics is typically three to five years. This period allows an organization to navigate through immediate challenges while setting the stage for sustainable growth. Strategic Planning, in its essence, is a framework designed to guide an organization through its future endeavors, adapting to changes in the market environment and leveraging opportunities for innovation and growth.
Consulting giants like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of flexibility within strategic plans. The rapidly changing business environment, influenced by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences, demands that organizations remain agile. A strategic plan that is too rigid or too long-term may fail to accommodate these inevitable changes, rendering it ineffective. Therefore, a three to five-year plan provides a balance between long-term vision and the agility to adapt to new information or market conditions.
Moreover, this timeframe aligns with the strategic planning cycles of many leading organizations, which revisit and revise their strategies at regular intervals. This iterative process ensures that the strategy remains relevant and aligned with the external market and internal capabilities. It's a template for success in today's volatile business environment, where the only constant is change.
Key Components of a Strategic Plan
A strategic plan is more than just a document; it's a roadmap for an organization's future. It encompasses several key components, including vision and mission statements, strategic objectives, and action plans. These elements provide a clear direction and a framework for decision-making. The plan should also include performance indicators to measure progress and a mechanism for regular review and adjustment.
Consulting firms often stress the importance of aligning the strategic plan with the organization's core values and culture. This alignment ensures that the strategy is not only feasible but also sustainable over the long term. It fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among employees, which is crucial for successful implementation. The strategic plan should be communicated effectively throughout the organization, with clear roles and responsibilities defined.
Action plans are critical for translating strategic objectives into tangible outcomes. They outline the specific steps needed to achieve each objective, including resource allocation, timelines, and responsible parties. This level of detail is essential for operationalizing the strategy and ensuring accountability. Regular progress reviews and adjustments to the action plans keep the strategy on track and responsive to changes in the internal and external environment.
Adapting to Market Dynamics
The ability to adapt to market dynamics is a critical aspect of strategic planning. Organizations must remain vigilant, continuously scanning the external environment for trends, threats, and opportunities. This proactive approach enables them to anticipate changes and adjust their strategies accordingly. Digital Transformation, for example, is a trend that has significantly impacted many industries, requiring organizations to adapt their strategies to remain competitive.
Risk Management is another important consideration. A strategic plan should identify potential risks to the organization and outline strategies to mitigate them. This forward-thinking approach not only protects the organization but also positions it to take advantage of opportunities that may arise from changes in the market.
Real-world examples demonstrate the importance of adaptability in strategic planning. Companies like Amazon and Netflix have successfully navigated significant market changes by continuously evolving their strategies. Their ability to anticipate and respond to consumer preferences and technological advancements has been key to their sustained growth and success.
Conclusion
In summary, the optimal timeframe for a strategic plan is three to five years. This period allows for a balance between long-term vision and the flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions. A strategic plan should include clear objectives, action plans, and mechanisms for regular review and adjustment. It should also align with the organization's culture and values, ensuring widespread commitment and effective implementation. Finally, an organization's ability to adapt to market dynamics and manage risks is critical for the success of its strategic plan. By following these guidelines, C-level executives can develop a strategic plan that positions their organization for long-term growth and success.
Creating a roadmap in Excel for strategic business planning is a critical task for C-level executives aiming to steer their organizations towards success. Excel, with its versatile functionality, serves as a powerful tool to visualize the trajectory of business initiatives, aligning them with the overarching strategic goals. This guide provides a comprehensive approach on how to build a roadmap in Excel, tailored for the no-nonsense C-level executive seeking actionable insights.
Firstly, understanding the framework of your roadmap is essential. A roadmap in Excel starts with defining the strategic objectives that your organization aims to achieve. These objectives could range from Digital Transformation, Operational Excellence, to Performance Management. The next step involves breaking down these objectives into specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. This granularity enables a clearer vision of the steps necessary to achieve the strategic objectives. Consulting firms like McKinsey and Bain emphasize the importance of aligning these goals with the organization's core capabilities and market opportunities to ensure they are realistic and impactful.
Once the framework is established, the next step is to create the Excel template. Excel offers a variety of templates that can be customized to suit your organization's needs. However, creating a bespoke template allows for greater flexibility. Start by setting up a timeline across the top of the spreadsheet, typically in months or quarters, depending on the length of your strategic plan. Then, list the strategic objectives and their corresponding SMART goals in the first column. Utilize Excel's conditional formatting to create a color-coded system that visually represents the status of each goal—such as not started, in progress, and completed. This visual representation aids in quickly identifying areas that require attention.
Integrating milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) into your roadmap is crucial for tracking progress. Milestones mark significant achievements or phases in the strategic plan, serving as checkpoints to evaluate progress. KPIs, on the other hand, provide a quantifiable measure of success. For each goal, define relevant KPIs that align with the strategic objectives. Excel's charting features can be leveraged to create dashboards that offer a dynamic view of these metrics, enabling real-time decision-making based on data-driven insights.
Best Practices for Roadmap Management
Effective roadmap management involves regular review and adaptation. The business environment is constantly evolving, and so should your strategic plan. Schedule quarterly reviews to assess the progress against the roadmap. These reviews offer the opportunity to make necessary adjustments, whether it's reallocating resources, reprioritizing goals, or pivoting strategies in response to unforeseen challenges. Consulting giants like Deloitte and PwC advocate for agile strategic planning, emphasizing the importance of flexibility and responsiveness to change.
Collaboration across departments is another key aspect of successful roadmap execution. Ensure that the roadmap is accessible to all relevant stakeholders and encourage regular updates and feedback. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, driving collective effort towards achieving the strategic objectives. Excel's sharing and co-authoring features facilitate this collaborative process, allowing multiple users to view and edit the roadmap in real-time.
Lastly, leveraging technology to enhance the functionality of your Excel roadmap can provide a competitive edge. Advanced Excel users can integrate macros and VBA scripts to automate updates and generate reports, saving valuable time and reducing the risk of human error. Additionally, consider integrating Excel with project management tools and platforms for a more comprehensive view of strategic initiatives and their alignment with the overall business plan.
Real-World Application
Consider the example of a multinational corporation undergoing a Digital Transformation. The organization's roadmap in Excel detailed the strategic objectives, such as automating key processes and enhancing digital customer experiences. Each objective was broken down into SMART goals, with specific timelines and responsible teams assigned. The roadmap utilized conditional formatting to highlight progress and integrated KPIs to measure the impact of digital initiatives on customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Through quarterly reviews, the organization identified bottlenecks in the implementation process and was able to quickly reallocate resources to address these challenges. Collaboration tools within Excel enabled cross-functional teams to provide updates and feedback, ensuring that all departments were aligned with the Digital Transformation strategy. The use of macros automated the reporting process, allowing executives to focus on strategic decision-making rather than manual data management.
In summary, building a roadmap in Excel requires a clear framework, a customized template, and effective management practices. By following these guidelines, C-level executives can create a dynamic tool that aligns strategic objectives with actionable plans, driving their organization towards success. Remember, the key to a successful roadmap is not just in its creation but in its execution and adaptability to change.
Creating a strategic planning presentation that resonates with C-level executives requires a deep understanding of the organization's goals, challenges, and the competitive environment it operates in. To ensure executive buy-in and alignment, the presentation must be more than just a collection of slides; it needs to tell a compelling story, grounded in data and insights, that outlines a clear path forward for the organization. This involves a careful blend of analytical rigor, strategic foresight, and persuasive storytelling.
At the core of any effective strategic planning presentation is a well-defined framework that guides the narrative. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of structuring presentations around a logical flow that moves from diagnosing the current state of the organization to proposing a strategic vision and actionable steps to achieve it. This typically involves an analysis of internal strengths and weaknesses, an assessment of external opportunities and threats, and a detailed discussion of strategic initiatives designed to capitalize on these insights. Incorporating relevant data and case studies can help to substantiate the strategy and make the case more compelling to a skeptical executive audience.
Another critical element is the alignment of the strategic plan with the organization's broader objectives and values. This means not only demonstrating how the proposed strategy will drive financial performance and operational excellence but also how it aligns with the organization's mission and culture. Highlighting this alignment can help to secure executive buy-in by showing that the strategy is not just about achieving short-term gains but is also about building a sustainable competitive position that reflects the organization's core values. To this end, including testimonials or endorsements from key stakeholders within the organization can add credibility and emotional weight to the presentation.
Utilizing a Robust Strategic Framework
Incorporating a robust strategic framework is non-negotiable in crafting a presentation that commands attention and fosters alignment. The use of a proven framework—such as Porter's Five Forces, the BCG Matrix, or the McKinsey 7S Framework—provides a structured approach to analyzing the organization's situation and crafting a strategy. These frameworks offer a template for systematically breaking down complex issues into manageable components, making it easier to communicate the rationale behind strategic decisions. Moreover, leveraging these established frameworks can lend additional credibility to the presentation, as they are widely recognized and respected among business leaders.
However, it's crucial to adapt these frameworks to the specific context of the organization. This might involve customizing the analysis to focus on the most relevant factors or combining elements from multiple frameworks to capture the nuances of the organization's strategic challenges. Tailoring the framework in this way helps to ensure that the presentation speaks directly to the executives' concerns and priorities, making it more likely that they will see the value in the proposed strategy.
Furthermore, the strategic framework should be used not only to diagnose and analyze but also to propose specific, actionable initiatives. This means moving beyond general recommendations to outline concrete steps the organization can take to implement the strategy, including timelines, resource allocations, and key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring success. By providing a clear action plan, the presentation can help to demystify the strategy and make it feel more attainable, increasing the likelihood of executive buy-in.
Communicating with Clarity and Conviction
The ability to communicate complex ideas with clarity and conviction is perhaps the most critical skill in ensuring a strategic planning presentation resonates with C-level executives. This requires a careful balance between providing enough detail to substantiate the strategy and maintaining a high-level focus that keeps the audience engaged. Using clear, concise language and avoiding unnecessary jargon can help to make the presentation more accessible and persuasive.
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in enhancing the clarity and impact of the presentation. Well-designed charts, graphs, and diagrams can help to illustrate key points and make complex data more digestible. However, it's important to use visual aids judiciously and ensure that they support the narrative rather than distracting from it. Each visual element should have a clear purpose and be directly tied to the strategic message being conveyed.
Finally, delivering the presentation with confidence and enthusiasm is essential. This involves not just mastering the material but also engaging with the audience, anticipating their questions, and being prepared to defend the strategy with data and insights. The goal is to not only inform but also inspire the executives, convincing them that the proposed strategy is not only viable but also essential for the organization's success. By combining a strong strategic framework with clear communication and a compelling delivery, the presentation can achieve the desired outcome of securing executive buy-in and alignment.
Understanding what is included in an annual operating plan is pivotal for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of today's business environment effectively. The annual operating plan serves as a roadmap, translating strategic goals into actionable objectives and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to drive growth and operational excellence. This comprehensive document should not only outline the financial targets but also encompass various critical components that align with the organization's strategic vision.
At its core, the annual operating plan must include a detailed financial budget. This budget covers projected revenue, expenses, cash flow, and capital expenditure. It's a financial compass that guides the organization through fiscal discipline, ensuring that all departments operate within their means while striving to achieve broader financial goals. Consulting giants like McKinsey & Company emphasize the importance of a robust financial plan that is both realistic and flexible, allowing organizations to adapt to market changes swiftly.
Another essential element is the sales and marketing strategy. This section outlines the approaches the organization will employ to achieve its revenue targets. It includes detailed plans for product launches, marketing campaigns, sales strategies, and customer acquisition and retention. The effectiveness of this component is often measured by its ability to not only reach but exceed sales targets, thereby contributing significantly to the organization's financial health.
Operational plans are also critical, detailing the day-to-day activities required to maintain and improve business operations. This includes production schedules, supply chain management strategies, quality control measures, and customer service protocols. Operational excellence is a key driver of customer satisfaction and loyalty, which in turn, impacts the organization's bottom line.
Human Resources and Talent Management
Human resources and talent management are integral to the annual operating plan. This section focuses on workforce planning, talent acquisition, training and development, and performance management. An organization's ability to attract, retain, and develop talent directly influences its capacity for innovation, productivity, and competitive positioning. Consulting firms like Deloitte often highlight the correlation between effective talent management strategies and organizational performance.
Succession planning and leadership development are also crucial components. They ensure the organization has a pipeline of skilled leaders ready to take on critical roles, thereby safeguarding the organization's future. This forward-thinking approach to talent management fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptability.
Diversity and inclusion initiatives should also be woven into the fabric of the annual operating plan. These programs are not just about social responsibility—they're a strategic imperative. Research has shown that diverse teams are more innovative and make better decisions, leading to improved financial performance.
Risk Management and Compliance
Risk management and compliance are non-negotiable elements of an effective annual operating plan. This section identifies potential risks—financial, operational, strategic, and compliance-related—and outlines strategies to mitigate these risks. A proactive approach to risk management not only protects the organization from potential threats but also prepares it to respond swiftly and effectively should issues arise.
Compliance with local, national, and international laws and regulations is also paramount. The plan should detail the organization's approach to compliance, including monitoring systems, training programs, and audit processes. In today's global business environment, non-compliance can result in significant financial penalties and damage to the organization's reputation.
Technology and digital transformation initiatives are increasingly becoming a cornerstone of the annual operating plan. Organizations must outline their strategy for leveraging technology to improve operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. This includes investments in new technologies, digital transformation projects, and cybersecurity measures.
Performance Metrics and Monitoring
Lastly, the annual operating plan must include a framework for performance management and monitoring. This involves setting clear, measurable objectives for each department and outlining the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to track progress. Regular reviews and adjustments are necessary to ensure the organization remains on track to achieve its strategic goals.
Performance management systems should be designed to foster a culture of accountability and continuous improvement. They provide the data needed to make informed decisions, celebrate successes, and address areas of concern promptly.
Incorporating these critical components into the annual operating plan ensures that the organization is well-positioned to execute its strategy effectively. It's a comprehensive approach that aligns financial targets with operational capabilities, talent management, risk mitigation, and performance monitoring. By focusing on these areas, organizations can navigate the complexities of the business landscape and drive sustainable growth.
Understanding why we need to plan is fundamental to achieving sustained success in any organization. Strategic planning serves as the compass for an organization, guiding its direction and ensuring that it navigates through the complexities of the market with a clear purpose. It is not merely about setting goals but about systematically aligning resources, capabilities, and actions with long-term objectives and the external environment. This alignment is crucial for organizations to not only survive but thrive in today's fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape.
A well-crafted strategic plan acts as a framework that informs decision-making processes and prioritizes initiatives. It enables organizations to proactively identify opportunities for growth and areas of potential risk, ensuring that they are not merely reacting to external pressures but are prepared and positioned to capitalize on them. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of a robust strategic planning process in driving performance management and operational excellence. These processes help organizations to remain agile, adapting their strategies in response to market dynamics while maintaining a steadfast focus on their core objectives.
Moreover, strategic planning is essential for effective resource allocation. In an era where financial and human resources are often limited, organizations must make judicious decisions about where to invest. A strategic plan, developed through a rigorous strategy development process, provides a template for these decisions, ensuring that resources are allocated to initiatives that are most likely to drive growth and create value. This prioritization is critical for achieving efficiency and maximizing return on investment, thereby ensuring the financial health and sustainability of the organization.
Driving Innovation and Change
Innovation is at the heart of growth and sustainability for any organization. Strategic planning fosters an environment where innovation can flourish by setting a clear vision and objectives that encourage creative thinking and experimentation. It provides a structured yet flexible framework within which new ideas can be tested and implemented, ensuring that innovation is not left to chance but is a deliberate outcome of the organization's strategic focus. Consulting giants like Accenture and Deloitte highlight how strategic planning is integral to embedding innovation into the organizational culture, making it a continuous process rather than a one-off event.
Change management is another critical aspect that benefits from strategic planning. Organizations are constantly faced with the need to adapt to new technologies, regulatory changes, and shifting customer expectations. A strategic plan equips leaders with the insights and direction needed to navigate these changes successfully. It outlines the steps necessary to achieve transformational goals, from digital transformation to cultural shifts, ensuring that every action is aligned with the broader vision. This alignment is crucial for minimizing resistance and ensuring that change initiatives are embraced and effectively implemented across the organization.
Furthermore, strategic planning plays a pivotal role in leadership and talent development. By defining clear strategic objectives, organizations can identify the skills and competencies required to achieve these goals. This clarity allows for targeted leadership development programs and talent management strategies that are aligned with the organization's future needs. As a result, organizations are better equipped to foster a leadership pipeline that is capable of driving the organization forward in alignment with its strategic vision.
Enhancing Performance and Accountability
Performance management is another area where strategic planning proves indispensable. By setting clear, measurable objectives, organizations can better monitor progress and performance against these goals. This process not only facilitates timely adjustments to strategies and tactics but also enhances accountability at all levels of the organization. Leaders and teams understand what is expected of them and how their contributions align with the organization's strategic objectives, fostering a culture of performance and excellence.
Risk management is inherently tied to strategic planning. In identifying and prioritizing objectives, organizations must also assess the potential risks associated with achieving these goals. This assessment allows for the development of mitigation strategies that are integrated into the overall strategic plan. Consulting firms like PwC and EY advocate for a proactive approach to risk management, where risks are not only identified and assessed but are managed as an integral part of the strategic planning process. This approach ensures that organizations are not caught off-guard by unforeseen events but are prepared to manage risks effectively, safeguarding their assets and ensuring long-term sustainability.
In conclusion, the question of why do we need to plan is answered by the myriad benefits that strategic planning brings to an organization. From driving innovation and managing change to enhancing performance and ensuring effective risk management, strategic planning is the linchpin of sustainable success. It provides a structured yet flexible framework that guides organizations through the complexities of the modern business environment, ensuring they are well-positioned to capitalize on opportunities and navigate challenges. In essence, strategic planning is not just about setting a direction; it's about creating a roadmap for achieving excellence and sustainability in a constantly evolving landscape.
Ensuring that a problem statement is comprehensive and aligns with an organization's strategic planning objectives is a critical step in the framework of effective management and decision-making. What is true about the scope of a strong problem statement is that it serves as a foundation for identifying, analyzing, and solving critical issues that impede an organization's ability to achieve its goals. A well-crafted problem statement should succinctly describe the issue at hand, its impact on the organization, and the potential benefits of resolving it. This clarity is paramount for aligning teams and resources towards a common objective, ensuring that efforts are not wasted on misaligned or low-impact activities.
To begin with, the development of a strong problem statement requires a deep understanding of the organization's strategic objectives. This involves a comprehensive analysis of the current state of affairs, identifying gaps between the current and desired states, and understanding the implications of these gaps on the organization's ability to achieve its goals. Consulting firms like McKinsey and BCG emphasize the importance of aligning problem statements with strategic objectives to ensure that solutions are not only effective but also contribute to the long-term success of the organization. For instance, if an organization's strategic objective is Digital Transformation, the problem statement should directly address the barriers or challenges preventing progress in this area.
Furthermore, the scope of a strong problem statement extends beyond merely stating the problem. It includes a clear articulation of the issue's context, the stakeholders involved, and the urgency of addressing the problem. Utilizing a structured framework or template can aid in ensuring that all relevant aspects of the problem are considered. For example, the "5 Whys" technique can help drill down to the root cause of a problem, while a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) can provide a broader understanding of the internal and external factors that influence the issue. This comprehensive approach ensures that the problem statement is not only aligned with strategic objectives but is also actionable and measurable.
Actionable insights are crucial for the implementation phase. A strong problem statement should guide the development of a strategy for addressing the issue, including setting clear, measurable objectives, identifying required resources, and establishing a timeline for achieving results. This strategic approach ensures that the organization can track progress and make adjustments as necessary, ultimately leading to the successful resolution of the problem.
Aligning Problem Statements with Strategic Planning Objectives
To ensure that problem statements are aligned with strategic planning objectives, organizations must adopt a holistic approach to strategy development. This involves engaging stakeholders across various levels of the organization to gather diverse perspectives and insights. Leadership plays a critical role in this process, providing the vision and direction necessary to guide the alignment of problem statements with strategic objectives. Effective communication is also essential, ensuring that all team members understand the strategic goals of the organization and how their efforts contribute to achieving these goals.
Real-world examples demonstrate the importance of alignment. For instance, a leading retail organization facing declining sales might frame its problem statement around enhancing customer experience and engagement as part of its broader strategy for Digital Transformation. By focusing on this specific aspect, the organization can direct its resources and efforts towards initiatives that are most likely to drive sales and improve customer satisfaction, such as optimizing its online platform or implementing personalized marketing strategies.
In practice, consulting firms often use specific templates and tools to facilitate the alignment of problem statements with strategic objectives. These tools help organizations systematically analyze their challenges and develop targeted, strategic responses. For example, the use of a strategy map can help visualize the connection between strategic objectives and the specific problems that need to be addressed, ensuring that all efforts are coherent and aligned towards the same end goal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the scope of a strong problem statement is critical for ensuring that an organization's efforts are aligned with its strategic planning objectives. By clearly defining the problem, its context, and its impact on the organization, and by aligning it with strategic objectives, organizations can focus their resources on high-impact initiatives that drive progress towards their goals. The use of structured frameworks, templates, and tools, along with effective leadership and communication, can facilitate this alignment, leading to more effective problem-solving and strategic decision-making.
The main purpose of strategic planning is to set an organization on a path towards achieving its long-term goals and objectives. This process involves a deep dive into understanding both the internal and external environments in which the organization operates. Strategic planning serves as a framework that guides decision-making and resource allocation, ensuring that all actions are aligned with the overarching vision and goals of the organization. It's not just about setting goals; it's about creating a viable roadmap for achieving them, which involves careful consideration of the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis).
In the realm of consulting, experts often emphasize the importance of strategic planning as a critical tool for ensuring organizational sustainability and growth. A well-crafted strategic plan not only outlines where an organization wants to go but also how it's going to get there. This involves setting clear, measurable objectives, identifying key initiatives, and establishing timelines for execution. The strategy development process is iterative, requiring regular reviews and adjustments to stay relevant in a rapidly changing business environment. This adaptability is crucial for navigating the complexities of today's market dynamics.
Moreover, strategic planning acts as a communication tool that aligns the entire organization. By clearly articulating the organization's vision and strategy, leaders can rally their teams around common goals, fostering a sense of purpose and direction. This alignment is essential for driving operational excellence and achieving strategic objectives. In essence, strategic planning is not just about plotting a course for the future; it's about creating a cohesive, agile organization that can adapt and thrive amidst uncertainty.
Key Components of a Strategic Plan
A strategic plan typically encompasses several key components, including vision and mission statements, core values, SWOT analysis, strategic objectives, action plans, and performance metrics. Each element plays a crucial role in providing a comprehensive blueprint for the organization's future. The vision and mission statements define the organization's purpose and aspirations, setting the tone for its strategic direction. Core values, on the other hand, articulate the principles that guide the organization's behavior and decision-making.
Conducting a SWOT analysis is a fundamental step in strategic planning, as it helps organizations identify critical factors that could impact their ability to achieve their goals. This analysis informs the development of strategic objectives, which are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that move the organization closer to its vision. Action plans detail the steps needed to achieve these objectives, including resource allocation, timelines, and responsibilities.
Finally, performance metrics are essential for monitoring progress and evaluating the effectiveness of the strategic plan. These metrics provide a quantifiable means of tracking achievements and identifying areas for improvement. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the strategic plan based on these metrics ensures that the organization remains on track to achieve its long-term objectives. The strategic planning process, therefore, is not a one-time event but a dynamic, ongoing cycle of planning, execution, evaluation, and refinement.
Real-World Examples of Strategic Planning Success
Several leading organizations attribute their success to rigorous strategic planning. For instance, technology giants like Apple and Google have leveraged strategic planning to navigate the complexities of the digital landscape, driving innovation and maintaining market leadership. Apple's focus on design, user experience, and ecosystem integration has been central to its strategic plan, enabling it to revolutionize multiple industries, from computing to telecommunications and entertainment. Google's strategic plan emphasizes continuous innovation, data-driven decision-making, and a culture that encourages experimentation, allowing it to dominate the search engine market and expand into new areas like cloud computing and autonomous vehicles.
Another example is Amazon, which has used strategic planning to evolve from an online bookstore into a global e-commerce and cloud computing powerhouse. Amazon's strategic plan has focused on customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and diversification into new markets and services. This approach has enabled Amazon to achieve remarkable growth and disrupt various industries, including retail, logistics, and media.
In conclusion, the main purpose of strategic planning is to provide a structured approach to achieving an organization's long-term vision and objectives. By offering a clear framework for decision-making and action, strategic planning enables organizations to navigate the complexities of the business environment, adapt to change, and achieve sustainable growth. Whether through setting clear objectives, aligning organizational efforts, or driving operational excellence, strategic planning is an indispensable tool for any organization looking to thrive in today's competitive landscape.
Defining a problem statement is a critical first step in the strategic planning process. It sets the stage for a clear, focused direction that aligns an organization's resources, capabilities, and strategies towards addressing a specific challenge or seizing an opportunity. Understanding what does statement of the problem mean in this context is essential for C-level executives who are tasked with steering their organizations through increasingly complex and volatile business environments. A well-articulated problem statement acts as a compass, guiding the strategic planning process by ensuring that all efforts are concentrated on a defined issue, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the plan.
A problem statement serves as a framework for strategic planning. It helps in identifying the gap between the current state and the desired future state, making it easier for leaders to formulate strategies that are both relevant and focused. This clarity is crucial for mobilizing resources efficiently and for setting priorities that align with the organization's overarching goals. Consulting firms often emphasize the importance of a succinct problem statement in strategy development, as it helps in breaking down complex issues into manageable parts. This segmentation allows for a more structured approach to tackling challenges, making the strategic planning process more efficient and effective.
Moreover, a well-defined problem statement facilitates better communication and alignment within the organization. It ensures that everyone, from top-level executives to front-line employees, understands the specific challenge or opportunity the organization is facing. This shared understanding is critical for fostering an environment of collaboration and for ensuring that all actions taken are in service of addressing the core issue. The use of a common framework and template in articulating the problem statement can further enhance this alignment, making it easier for teams across different functions to work together towards a common goal.
Real-World Application and Benefits
In practice, organizations that invest time in crafting a precise problem statement often see a more streamlined strategic planning process. For example, a global retailer facing declining sales in a specific region used a problem statement to zero in on the root causes—ranging from supply chain inefficiencies to local market competition. This focus allowed the retailer to tailor its strategies specifically to address these issues, resulting in a turnaround in sales figures. The problem statement acted as a catalyst for targeted action, demonstrating its value in translating complex challenges into actionable strategies.
Additionally, the process of defining a problem statement encourages a culture of critical thinking and innovation within the organization. It prompts leaders and teams to question assumptions, analyze data, and explore various perspectives before arriving at the core issue. This approach not only leads to a more effective strategic plan but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability. In a business landscape where change is the only constant, this culture is invaluable for maintaining competitive agility.
From a consulting perspective, firms like McKinsey and BCG have long advocated for the use of structured problem-solving frameworks that begin with a clear problem statement. These frameworks are instrumental in helping organizations across industries—from healthcare to technology—identify and articulate their key challenges. The insights generated through this process are often the foundation for innovative strategies that drive significant business transformation.
Implementing an Effective Problem Statement
To implement an effective problem statement, organizations should start by gathering and analyzing relevant data to understand the scope and specifics of the challenge or opportunity. This step involves engaging with various stakeholders to gain diverse perspectives and insights. Following this, leaders should use a template or framework to distill the information into a concise statement that clearly articulates the issue without being overly broad or narrow. This balance is crucial for maintaining focus without limiting potential strategic options.
Once the problem statement is defined, it should be communicated throughout the organization to ensure alignment and buy-in. This communication is not a one-time event but an ongoing conversation that keeps the problem statement at the forefront of strategic planning efforts. Regular reviews and updates to the problem statement may be necessary as the organization progresses towards its goals and as external conditions evolve. This iterative process ensures that the strategic plan remains relevant and focused on addressing the most pressing issues facing the organization.
In conclusion, defining a problem statement is a pivotal step in enhancing the effectiveness of strategic planning. It provides a clear focus, facilitates alignment and collaboration, and fosters a culture of critical thinking and innovation. By investing the time and effort to articulate a precise problem statement, organizations can ensure that their strategic planning efforts are both efficient and impactful, driving meaningful business transformation in the process.
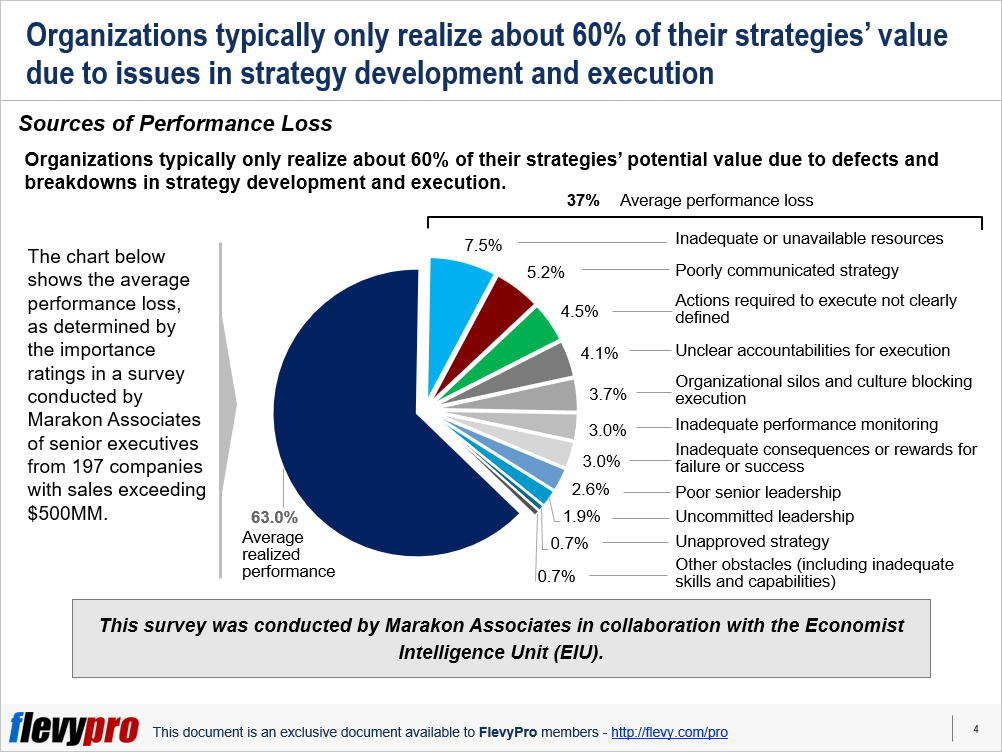
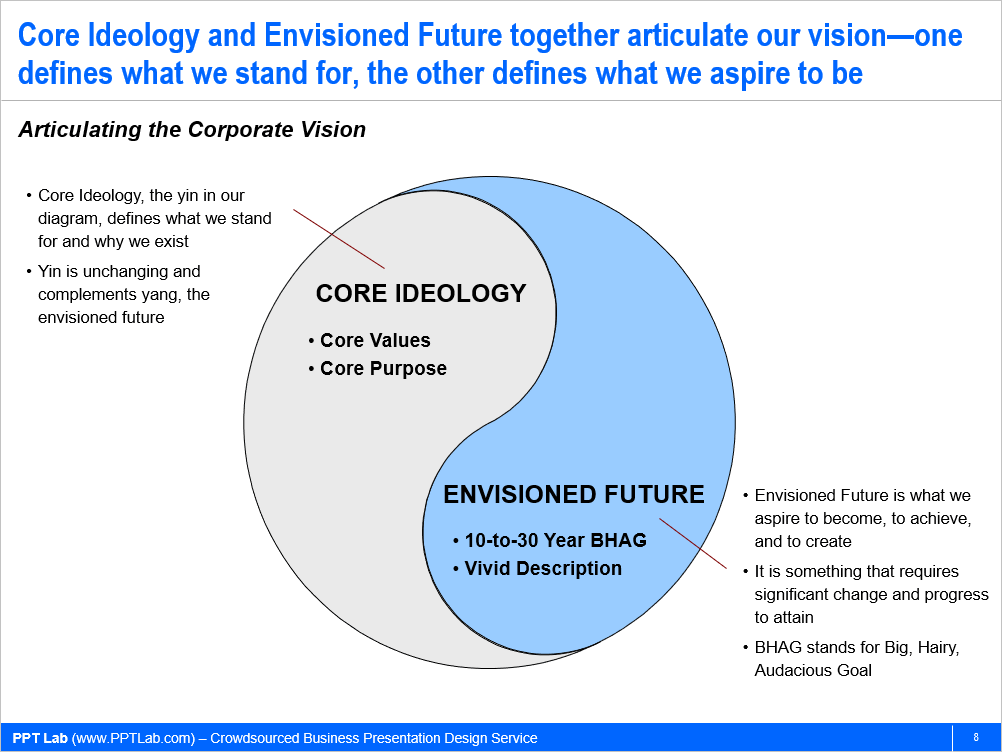
 Tesla's mission statement is: "to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy." This statement is concise and captures the essence of Tesla:
Tesla's mission statement is: "to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy." This statement is concise and captures the essence of Tesla: