Strategic Management (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 133 Slides
STRATEGY DEVELOPMENT PPT DESCRIPTION
—— Strategic Management
— Introduction to Strategic Management
Introduction, Meaning, and Definition: Strategic management is the process of formulating, implementing, and evaluating strategies to achieve organizational objectives. It involves setting goals, analyzing the competitive environment, and ensuring the organization moves in the right direction.
Need for Strategic Management: Organizations need strategic management to navigate complex environments, anticipate changes, and adapt accordingly. It provides a roadmap for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
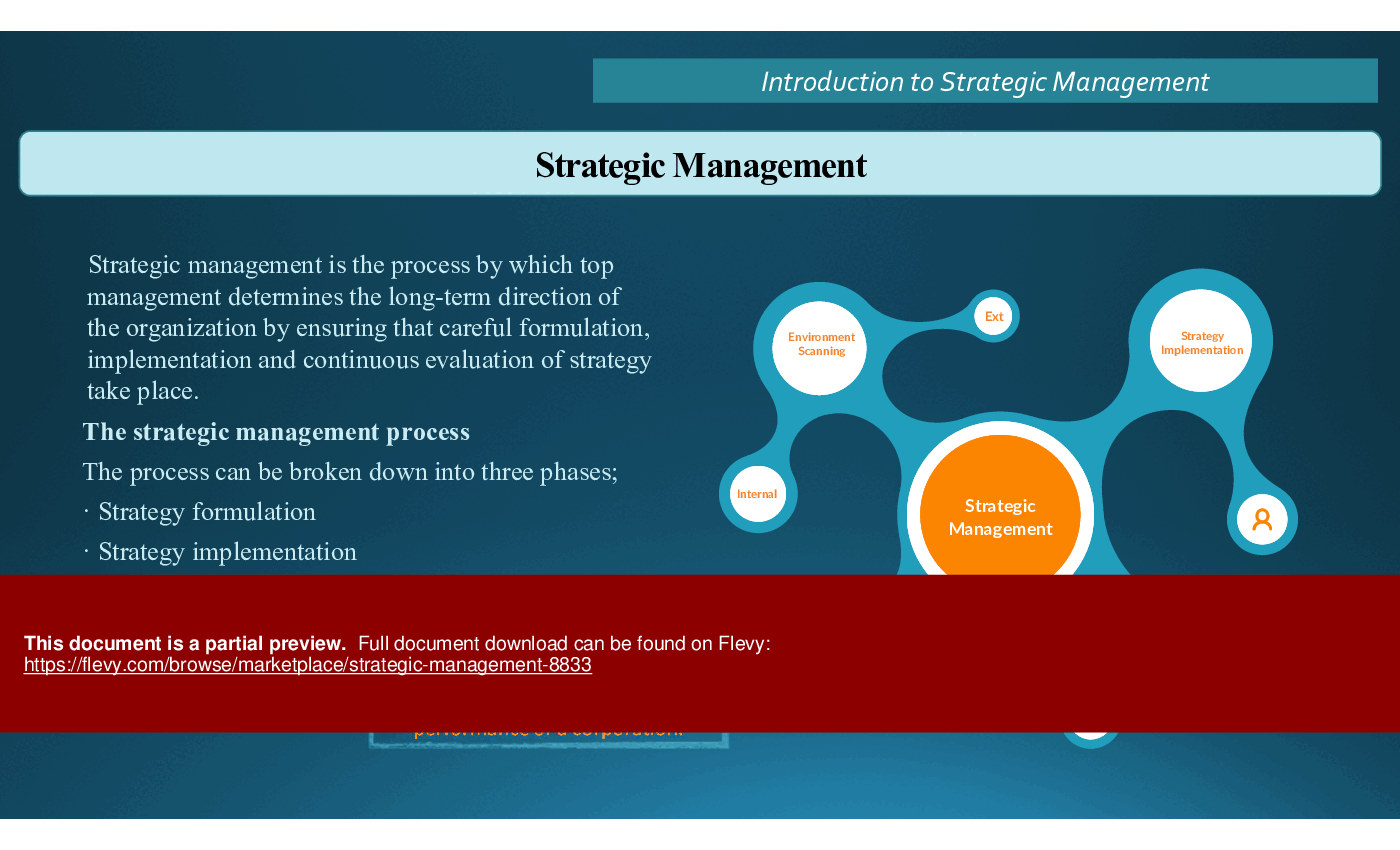
Process of Strategic Management: The process includes:
1. Defining the vision, mission, and objectives.
2. Conducting an environmental appraisal.
3. Formulating strategy.
4. Implementing strategy.
5. Evaluating and controlling strategy.
Strategic Decision Making: This involves choosing the best course of action among various alternatives to achieve organizational goals.
Strategic Management Approaches: Various approaches include the classical approach, evolutionary approach, processual approach, and systemic approach, each providing a different perspective on how strategies should be developed and executed.
— Strategy Evaluation
Strategy Evaluation and Control: This step ensures that strategies are effectively implemented and are achieving desired outcomes. It involves setting performance standards, measuring actual performance, and taking corrective actions.
Operational Control: Focuses on day-to-day operations to ensure that organizational activities align with strategic goals.
Overview of Management: Effective strategy evaluation requires a comprehensive understanding of management principles, including planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
Focus on Key Result Areas: Emphasizing areas that significantly impact organizational success, such as financial performance, customer satisfaction, internal processes, and learning and growth.
— Environmental Appraisal
The Concept of Environment: The external and internal factors that influence an organization's strategy.
The Company and Its Environment: Understanding the interaction between the company and its external environment is crucial for strategic planning.
Porter's Five Forces Model: A tool for analyzing the competitive environment, including the threat of new entrants, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry.
Scanning the Environment: Identifying and monitoring external factors that could impact the organization.
Technological, Social, Cultural, Demographic, Political, Legal, and Other Environmental Forces: Each of these factors must be analyzed to understand their potential impact on the organization.
Internal Analysis: Assessing the organization's internal resources, capabilities, and competencies.
Competitive Advantage and Value Chain Analysis: Identifying activities that create value and provide a competitive edge.
SWOT Analysis: Analyzing the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to inform strategic decisions.
— Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning Process: Involves defining the strategy, setting goals, and determining the actions to achieve them.
Levels of Strategy:
• Corporate Level Strategy: Overall scope and direction of the organization.
• Business Level Strategy: How the organization competes in particular markets.
• Functional Level Strategy: Specific actions within departments to support business level strategies.
Strategic Alternatives: Various strategic directions including stability, expansion, merger, retrenchment, and restructure strategies.
Competitive Analysis: Assessing the strengths and weaknesses of competitors to identify opportunities and threats.
— Implementation of Strategy
Aspects of Strategy Implementation: Involves putting the strategy into action through projects, procedures, and structural adjustments.
Project and Procedural Implementation: Managing specific initiatives and ensuring procedures align with strategic goals.
Structural Implementation: Adjusting the organizational structure to support the strategy.
Organizational Design and Change: Ensuring the organization is designed to facilitate strategic objectives and managing change effectively.
Organizational Systems: Implementing systems that support strategic goals.
Behavioral Implementation: Aligning organizational behavior with strategic goals through leadership and corporate culture.
Leadership Implementation: Ensuring leaders drive and support strategic initiatives.
Corporate Culture: Cultivating a culture that supports the organization's strategy.
— Strategy Evaluation
Strategy Evaluation and Control: Continuously monitoring and assessing the strategy to ensure it meets organizational objectives.
Operational Control: Ensuring daily operations align with strategic goals.
Overview of Management: Effective strategy evaluation relies on sound management practices.
Focus on Key Result Areas: Prioritizing areas critical to strategic success to ensure the organization remains on track.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 133-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Strategic Management PPTX presentation provides a comprehensive overview of strategic management concepts, processes, and decision-making frameworks. Developed by experts with extensive consulting backgrounds at McKinsey, Deloitte, and Capgemini, this presentation is designed for corporate executives, integration leaders, and consultants. It equips users with the knowledge to navigate competitive landscapes, formulate effective strategies, and implement them successfully. Download this expert-ready presentation to enhance your strategic management capabilities.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to align organizational goals with strategic initiatives
• Integration leaders managing mergers or acquisitions
• Consultants advising clients on strategic planning and execution
• Business unit managers responsible for implementing strategic objectives
• Teams involved in competitive analysis and market positioning
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to define organizational direction
• In workshops focused on competitive analysis and market entry strategies
• When preparing for executive decision-making meetings
• For training sessions on strategic management frameworks and methodologies
Learning Objectives
• Define strategic management and its significance in achieving organizational goals
• Build a comprehensive strategic plan that aligns with business objectives
• Establish effective decision-making processes for strategic initiatives
• Identify and analyze competitive forces using frameworks like Porter’s Five Forces
• Develop skills for conducting SWOT analysis to assess internal and external factors
• Implement strategies effectively while monitoring progress and making adjustments
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Strategic Management (page 1)
• Process of Strategic Management (page 5)
• Strategic Decision Making (page 10)
• Environmental Appraisal (page 15)
• Porter’s Five Forces Model (page 25)
• SWOT Analysis (page 35)
• Strategic Planning Process (page 45)
• Implementation of Strategy (page 55)
• Strategy Evaluation and Control (page 65)
Primary Topics Covered
• Strategic Management - The process by which top management determines the long-term direction of the organization through careful formulation, implementation, and evaluation of strategies.
• Environmental Scanning - A systematic process of collecting and analyzing information about external and internal factors affecting the organization.
• SWOT Analysis - A framework for identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to inform strategic planning.
• Porter’s Five Forces - A model for analyzing the competitive forces within an industry to assess its attractiveness and profitability.
• Strategic Planning - The process of defining an organization’s vision, mission, and objectives, and determining the actions needed to achieve them.
• Strategy Implementation - The execution of strategic plans through resource allocation, structural adjustments, and operational changes.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Strategic planning template for defining vision, mission, and objectives
• SWOT analysis framework for assessing internal and external factors
• Porter’s Five Forces analysis tool for evaluating industry competitiveness
• Environmental scanning checklist for identifying key external influences
• Strategy implementation roadmap for tracking progress and milestones
• Evaluation and control framework for measuring strategy effectiveness
Slide Highlights
• Overview of strategic management concepts and definitions
• Detailed breakdown of the strategic management process phases
• Visual representation of Porter’s Five Forces and their implications
• Examples of SWOT analysis in real-world scenarios
• Step-by-step guide to the strategic planning process
• Key metrics for evaluating strategy performance
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Strategic Management (60 minutes)
• Overview of strategic management concepts
• Discussion on the importance of strategic alignment
• Group activity: Identifying organizational strengths and weaknesses
Environmental Appraisal and Competitive Analysis (90 minutes)
• Presentation on environmental scanning techniques
• Workshop on conducting a SWOT analysis
• Group exercise: Applying Porter’s Five Forces to a case study
Strategy Formulation and Implementation (90 minutes)
• Defining strategic objectives and key results
• Developing an implementation plan with timelines
• Role-playing exercise: Navigating strategic decision-making scenarios
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the strategic planning template to reflect your organization’s unique vision and mission
• Adjust the SWOT analysis framework to focus on specific market conditions and internal capabilities
• Incorporate industry-specific examples into the Porter’s Five Forces analysis
• Modify the implementation roadmap to align with your organization’s operational structure and resource availability
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of leadership in strategic management
• The impact of corporate culture on strategy implementation
• Techniques for effective communication during strategy execution
• Methods for fostering cross-functional collaboration in strategic initiatives
Topic FAQ
What are the typical phases of a strategic management process I should plan for?
Strategic management generally follows 5 phases: defining vision, mission and objectives; conducting an environmental appraisal; formulating strategy; implementing the strategy; and evaluating and controlling outcomes. Each phase focuses on specific activities from analysis to execution, ending with evaluation and control across 5 steps.How do I conduct a SWOT analysis that actually informs strategy?
A SWOT starts by cataloguing internal strengths and weaknesses, then mapping external opportunities and threats. Use findings to prioritize strategic options and identify capability gaps to address during implementation; a formal SWOT analysis framework helps structure inputs and outputs for decision-making and planning.How can Porter’s Five Forces help assess industry attractiveness for a new market entry?
Porter’s Five Forces examines the threat of new entrants, buyer and supplier bargaining power, threat of substitutes, and competitive rivalry to gauge profitability and barriers to entry. Use it to identify levers for differentiation or pricing strategy when evaluating an industry’s competitiveness with the 5 forces model.What features matter most when selecting a ready-made strategic planning toolkit?
Look for tools that map the full strategy lifecycle: templates for vision/mission/objectives, environmental scanning checklists, competitive analysis tools (e.g., Porter’s Five Forces), SWOT frameworks, implementation roadmaps, and evaluation metrics. The Strategic Management deck explicitly includes these templates and tools for end-to-end planning.How much time should I allocate for a strategy workshop using slide-based materials?
A focused workshop can be structured into shorter modules; the sample agenda allocates 60 minutes for introduction, 90 minutes for environmental appraisal and competitive analysis, and 90 minutes for strategy formulation and implementation planning — totaling roughly 4 hours across 3 modules.I need to align business unit goals with corporate strategy — which tools should I use?
Start with the strategic planning template to define vision, mission, and objectives at both corporate and BU levels, use environmental scanning and SWOT to surface gaps, then build an implementation roadmap and monitoring metrics. The Strategic Management presentation provides these templates, including a strategic planning template and SWOT framework.What methods are effective for monitoring and controlling strategy implementation?
Effective monitoring uses an evaluation and control framework with clear performance standards, regular measurement of actual performance, and corrective actions tied to key result areas. Operational control ensures daily activities align with strategy while strategic control reviews overall effectiveness using an evaluation and control framework.Are ready-made strategy templates cost-effective for small consulting projects?
Ready-made templates can save preparation time and provide structure for consistent deliverables, reducing billable hours spent on slide design and methodology setup. The Strategic Management package bundles multiple tools and templates to support planning, analysis, and implementation, with 6 templates and tools included.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is strategic management?
Strategic management is the process by which an organization defines its direction and makes decisions on allocating resources to pursue this direction effectively.
How do I conduct a SWOT analysis?
A SWOT analysis involves identifying internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats, to inform strategic planning and decision-making.
What is the purpose of environmental scanning?
Environmental scanning helps organizations identify external factors that could impact their operations, allowing them to adapt and respond proactively to changes in the business landscape.
How can Porter’s Five Forces model be applied?
Porter’s Five Forces model can be used to assess the competitive dynamics of an industry, helping organizations understand their market position and identify potential strategic moves.
What are the key components of a strategic plan?
A strategic plan typically includes the organization’s vision, mission, objectives, strategies for achieving those objectives, and a framework for monitoring progress.
How often should a strategic plan be reviewed?
Strategic plans should be reviewed periodically, typically annually or quarterly, to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with changing market conditions.
What is the difference between strategic control and operational control?
Strategic control focuses on evaluating the effectiveness of the overall strategy and making adjustments as needed, while operational control monitors day-to-day activities to ensure they align with established plans.
How can I ensure successful strategy implementation?
Successful strategy implementation requires clear communication, adequate resource allocation, alignment of organizational structure, and ongoing monitoring of progress against objectives.
Glossary
• Strategic Management - The process of defining an organization’s direction and making decisions on resource allocation.
• SWOT Analysis - A framework for identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
• Environmental Scanning - The process of collecting and analyzing information about external and internal factors.
• Porter’s Five Forces - A model for analyzing industry competitiveness.
• Strategic Planning - The process of defining an organization’s vision, mission, and objectives.
• Strategy Implementation - The execution of strategic plans through resource allocation and operational changes.
• Strategic Control - Monitoring and adjusting the overall strategy based on performance outcomes.
• Operational Control - Ensuring day-to-day activities align with established plans.
• Competitive Advantage - The attributes that allow an organization to outperform its competitors.
• Corporate Culture - The values and behaviors that shape how an organization operates.
• Leadership Implementation - The role of leaders in guiding and influencing the execution of strategies.
• Key Result Areas (KRAs) - Strategic sectors where the business aims to achieve strong outcomes.
Source: Best Practices in Strategy Development, Strategy Deployment & Execution PowerPoint Slides: Strategic Management PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting