Poka Yoke - Mistake Proofing Presentation (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + Zip archive file (ZIP) 50 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Develop simple mistake proofing devices
MISTAKE-PROOFING PPT DESCRIPTION
This presentation has 50 slides and comprises of the following:
Introduction to Mistake Proofing in the Workplace
Identification of activities for improvement
Methods associated with controlling and reducing mistakes
Implementing changes in the workplace
Workplace projects
Also included with this document is a bonus zip of 41 Lean documents (includes templates, case studies, articles, posters, charts, and more).
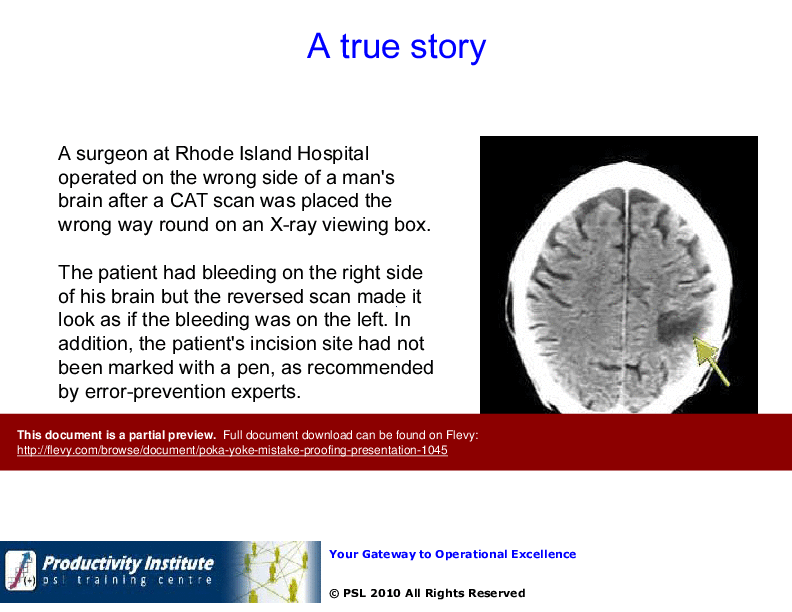
This comprehensive Poka Yoke – Mistake Proofing Presentation dives deep into the critical aspects of error prevention. It includes real-world examples and case studies that illustrate the devastating impact of mistakes, such as the Rhode Island Hospital incident. The presentation emphasizes the importance of zero defects, urging organizations to adopt a culture of perfection where defects are neither created nor tolerated.
The PPT also categorizes errors into learning gaps, memory gaps, inconsistencies, application errors, and omissions. Each category is paired with practical strategies for prevention, ensuring that your team can identify and mitigate potential errors before they escalate. Critical control points and variation analysis are highlighted as essential tools for maintaining consistency and quality in your processes.
Involving the team is crucial for generating more ideas and improving processes. The presentation outlines the benefits of leveraging prior knowledge and skills, considering all skill levels, and achieving a higher success rate. Mistake-proofing techniques like replacement and detection are detailed, showcasing how automation and sensors can enhance reliability and error identification.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 50-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Poka Yoke – Mistake Proofing Presentation is a comprehensive training resource designed to enhance operational excellence through effective error prevention strategies. Developed by a recognized leader in Lean methodologies, this presentation equips teams with the knowledge to identify and eliminate defects in processes, ultimately driving towards zero defects. Participants will learn how to implement mistake-proofing techniques that foster a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that quality is built into processes rather than inspected out.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Quality Assurance Managers focused on reducing defects and improving process reliability
• Operations Managers seeking to enhance efficiency and minimize waste
• Team Leaders responsible for implementing Lean methodologies in their departments
• Continuous Improvement Professionals aiming to drive cultural change within their organizations
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During Lean training sessions to introduce mistake-proofing concepts
• In workshops aimed at identifying process improvement opportunities
• When launching initiatives focused on quality enhancement and defect reduction
Learning Objectives
• Define the principles of mistake-proofing and its importance in operational excellence
• Identify sources of defects and variability within processes
• Develop strategies for implementing mistake-proofing techniques effectively
• Analyze critical control points in workflows to enhance quality assurance
• Create a culture of continuous improvement through team involvement and engagement
• Monitor and validate the effectiveness of implemented mistake-proofing measures
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Mistake Proofing in the Workplace (page 3)
• Identification of Activities for Improvement (page 5)
• Methods for Controlling and Reducing Mistakes (page 7)
• Implementing Changes in the Workplace (page 10)
• Workplace Projects (page 12)
• Tools and Templates (page 15)
Primary Topics Covered
• Defects and Their Impact - Defects can account for 20-40% of production costs, emphasizing the need for effective mistake-proofing strategies.
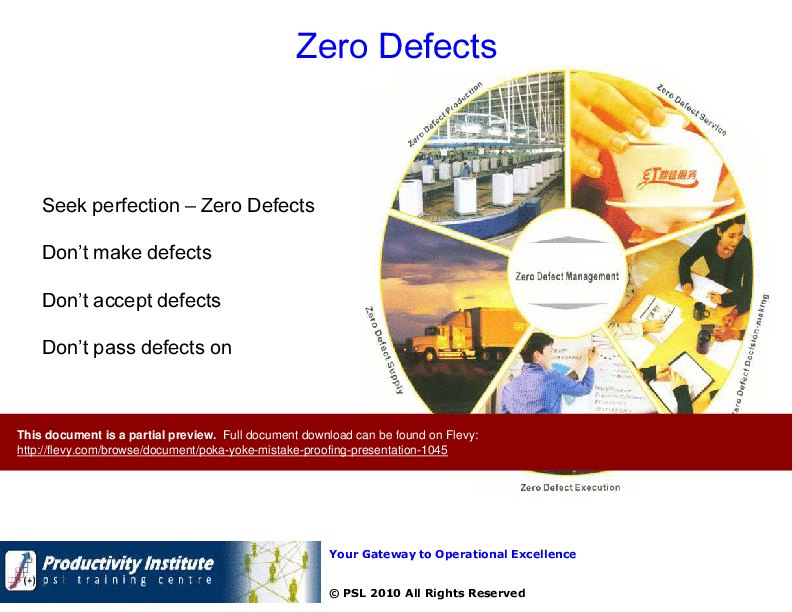
• Zero Defects Philosophy - Aiming for zero defects involves not making, accepting, or passing on defects, fostering a culture of quality.
• Critical Control Points - Identifying points in processes where controls can prevent defects is essential for effective mistake-proofing.
• Categories of Error - Understanding the various sources of non-conformance helps in developing targeted prevention strategies.
• Mistake Proofing Techniques - Techniques such as elimination, prevention, and detection are explored to minimize errors in processes.
• Continuous Improvement - Emphasizing the need for ongoing monitoring and improvement to sustain quality outcomes.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Improvement Opportunity Sheet for identifying potential areas for mistake-proofing
• Action Plan template for implementing and tracking mistake-proofing initiatives
• Validation strategy framework to ensure processes achieve “Right First Time, Every Time” results
• Project evidence documentation to support the implementation of mistake-proofing measures
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the Zero Defects philosophy and its significance in operational excellence
• Case study illustrating the consequences of not implementing mistake-proofing measures
• Visual representation of the journey towards defect-free processes
• Step-by-step guide for error-proofing through practical examples and techniques
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Mistake Proofing (60 minutes)
• Overview of mistake-proofing concepts and principles
• Group discussion on current defect challenges in participants' areas
Techniques for Implementation (90 minutes)
• Interactive session on mistake-proofing techniques and their applications
• Group activity to develop a mistake-proofing plan for a selected process
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement (60 minutes)
• Strategies for monitoring the effectiveness of implemented measures
• Discussion on fostering a culture of continuous improvement within teams
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the presentation to include specific case studies relevant to your organization’s processes
• Modify templates to reflect your company’s terminology and operational standards
• Incorporate industry-specific examples to enhance relatability and engagement
Secondary Topics Covered
• Human factors and their impact on error rates
• The role of team involvement in successful mistake-proofing initiatives
• Techniques for designing processes that facilitate error prevention
• Strategies for training staff on mistake-proofing principles and practices
Topic FAQ
What are the main topics covered in a typical mistake-proofing training deck?
A typical mistake-proofing training deck covers introduction to mistake proofing, identification of activities for improvement, methods for controlling and reducing mistakes, implementing changes, workplace projects, and tools/templates. In this presentation those topics are organized across pages 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, and 15.What mistake-proofing techniques should I expect to learn and apply?
Common techniques include elimination, prevention, detection, and facilitation, with additional tactics like replacement and use of automation or sensors to improve reliability. The presentation links these techniques to monitoring and validation approaches and documents them alongside the Validation strategy framework.How do you identify critical control points where errors can be prevented?
Identify critical control points by analysing workflow steps for variability and non-conformance, mapping where defects originate or propagate, and documenting findings to prioritise controls. The materials recommend using an Improvement Opportunity Sheet to capture and assess those points.I need to run a mistake-proofing workshop for my team — what agenda should I follow?
A practical agenda begins with an introduction to mistake-proofing (60 minutes), then techniques and hands-on planning (90 minutes), and finishes with monitoring and continuous improvement discussion (60 minutes). Flevy's Poka Yoke - Mistake Proofing Presentation includes a suggested workshop agenda with these time blocks of 60, 90, and 60 minutes.How much time and what resources are typically needed to train staff on mistake-proofing?
The sample workshop agenda totals about 210 minutes (3.5 hours) and uses a slide deck plus practical templates and case studies. Flevy's Poka Yoke - Mistake Proofing Presentation supplies the slide content, templates, and a bonus ZIP of 41 Lean documents to support training.What should I look for when buying a mistake-proofing training deck or toolkit?
Look for a slide deck that includes practical templates (Improvement Opportunity Sheet, Action Plan), a Validation strategy, real-world case studies, a workshop agenda, and supplemental reference documents; also note author credentials such as development by a certified LSS Master Black Belt. An Action Plan template is a key inclusion.How does mistake-proofing help an organisation pursue a Zero Defects philosophy?
Mistake-proofing focuses on designing processes so defects are not made, accepted, or passed on by identifying critical control points and applying elimination, prevention, and detection techniques. This builds quality into processes and supports the Zero Defects philosophy through ongoing monitoring and validation.For a small team, what deliverables should I expect from a purchased mistake-proofing deck to justify implementation effort?
A purchasable deck should provide a ready-to-run slide set, templates for identifying and tracking improvements, case studies, and supplemental reference material to run workshops and implement changes. Flevy's Poka Yoke - Mistake Proofing Presentation provides a 50-slide deck plus a ZIP of 41 Lean documents and templates.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is mistake-proofing?
Mistake-proofing, or Poka Yoke, refers to techniques that help prevent errors in processes by designing systems that make it impossible to make mistakes.
How can I identify defects in my processes?
Start by analyzing your workflow to pinpoint areas of variability and non-conformance. Utilize tools like the Improvement Opportunity Sheet to document findings.
What are critical control points?
Critical control points are specific steps in a process where controls can be applied to prevent defects from occurring. Identifying these points is crucial for effective mistake-proofing.
What techniques can be used for mistake-proofing?
Techniques include elimination, prevention, detection, and facilitation, each aimed at reducing the likelihood of errors in processes.
How do I implement mistake-proofing in my workplace?
Begin by identifying potential error sources, prioritize them, and develop a plan using the provided templates to implement mistake-proofing strategies.
What is the role of continuous improvement in mistake-proofing?
Continuous improvement ensures that processes are regularly evaluated and enhanced, maintaining high-quality standards and adapting to new challenges.
How can I engage my team in mistake-proofing efforts?
Involve team members in identifying defects and developing solutions, fostering a sense of ownership and collaboration in the process.
What resources are available for further learning?
Recommended readings and resources are provided in the presentation, including websites and books focused on mistake-proofing and Lean methodologies.
Glossary
• Poka Yoke - A Japanese term meaning "mistake-proofing," aimed at preventing errors in processes.
• Zero Defects - A quality management philosophy that strives for no defects in products or services.
• Critical Control Points - Specific points in a process where controls can be applied to prevent defects.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to enhance products, services, or processes over time.
• Error-Proofing Techniques - Methods used to design processes that minimize the potential for errors.
• Defect - An imperfection or deficiency in a product or service that fails to meet quality standards.
• Non-Conformance - Failure to meet specified requirements or standards in a process.
• Action Plan - A detailed plan outlining steps to achieve specific goals or improvements.
• Improvement Opportunity Sheet - A tool for identifying areas where processes can be enhanced.
• Validation Strategy - A plan for testing and confirming that processes meet quality standards.
• Team Involvement - Engaging team members in the process of identifying and solving problems.
• Human Factors - Elements related to human behavior that can impact the effectiveness of processes.
Source: Best Practices in Mistake-Proofing PowerPoint Slides: Poka Yoke - Mistake Proofing Presentation PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, OpEx Academy NZ