Network Security - Transport Layer Security (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 81 Slides
CYBER SECURITY PPT DESCRIPTION
In this presentation, we'll explore three crucial aspects of modern digital security and communication. We'll begin with Networks, discussing their various types (LAN, WAN, MAN, PAN) and the essential components like routers and switches that keep them operational. Next, we'll delve into Crypto Basics, covering key concepts such as encryption, decryption, hash functions, and digital signatures, all fundamental for protecting data. Finally, we'll focus on Transport Layer Security (TLS), a vital protocol ensuring secure communication over networks through encryption, authentication, and data integrity. Together, these topics highlight the interconnected nature of secure digital interactions.
Networks
A network is a collection of interconnected devices that communicate with each other to share resources and data. These devices, known as nodes, can be anything from computers and servers to smartphones and IoT devices. Networks can be classified based on their size and scope into several types:
1. Local Area Network (LAN): A network that covers a small geographical area, typically within a single building or campus. It is characterized by high data transfer rates and low latency.
2. Wide Area Network (WAN): Extends over a large geographical area, often composed of multiple LANs connected through public or private networks.
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): Spans a city or a large campus, bridging multiple LANs.
4. Personal Area Network (PAN): A small network used for connecting personal devices, usually within a range of a few meters.
The fundamental components of a network include routers, switches, and access points. Routers direct data packets between networks, switches connect devices within a LAN, and access points enable wireless connectivity.
Crypto Basics
Cryptography is the science of securing communication and data through the use of mathematical techniques. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation. Key concepts in cryptography include:
1. Encryption: The process of converting plaintext into ciphertext using an algorithm and a key. It can be symmetric (same key for encryption and decryption) or asymmetric (public and private keys).
2. Decryption: The reverse process of encryption, converting ciphertext back into readable plaintext.
3. Hash Functions: Generate a fixed-size hash value from input data, used for verifying data integrity. Common algorithms include SHA-256 and MD5.
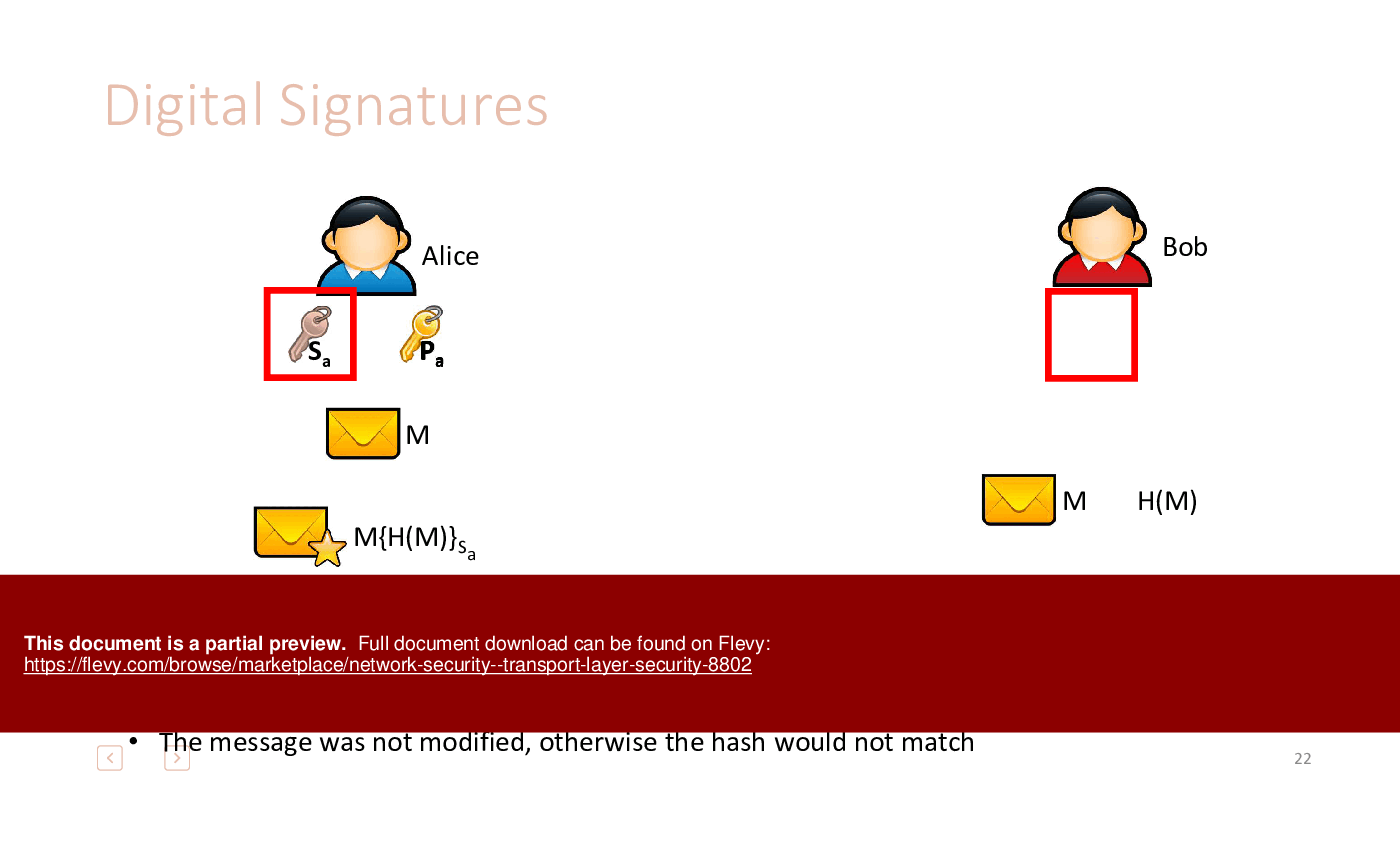
4. Digital Signatures: Provide a way to verify the authenticity and integrity of a message or document using a private key to sign and a public key to verify.
Cryptographic techniques are foundational to securing communications, protecting sensitive data, and enabling trust in digital transactions.
Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide secure communication over a computer network. It ensures data privacy and integrity between communicating applications. Key aspects of TLS include:
1. Encryption: TLS encrypts the data transmitted between the client and server, preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
2. Authentication: TLS uses certificates to authenticate the identity of the communicating parties, typically through a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
3. Integrity: By employing message authentication codes (MACs), TLS ensures that data has not been altered during transmission.
TLS operates at the transport layer of the OSI model and is widely used in securing web communications (HTTPS), email (SMTPS), and other internet services. The protocol has undergone several iterations, with TLS 1.3 being the most recent version, offering improved security and performance.
In conclusion, networks form the backbone of modern digital communication, cryptography provides the tools to secure this communication, and Transport Layer Security (TLS) ensures that the data transmitted across these networks remains private and untampered.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 81-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation on Network Security focuses on Transport Layer Security (TLS), a critical protocol for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authentication of data exchanged over networks. Developed by a team of experts with extensive consulting experience, this deck provides a comprehensive overview of security principles, cryptographic techniques, and the operational mechanisms of TLS. Users will gain insights into the importance of security properties such as confidentiality, integrity, and authentication, as well as practical knowledge on implementing TLS in real-world applications.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• IT Security Professionals responsible for network security protocols
• System Administrators managing secure communications
• Compliance Officers ensuring adherence to security standards
• Developers implementing secure applications
• Consultants advising on cybersecurity measures
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During security training sessions for IT staff
• When developing or updating security policies
• For workshops focused on implementing TLS in applications
• In discussions about improving organizational cybersecurity posture
Learning Objectives
• Define key security properties relevant to network communications
• Understand the fundamentals of cryptography and its role in security
• Identify the mechanisms of Transport Layer Security (TLS)
• Analyze the structure and purpose of X.509 certificates
• Evaluate the importance of Certificate Authorities (CAs) in establishing trust
• Recognize common vulnerabilities and attacks associated with TLS
• Implement best practices for securing network communications
Table of Contents
• Defining Security (page 3)
• Security Properties (page 4)
• Confidentiality (page 5)
• Integrity (page 6)
• Authenticity (page 7)
• Availability (page 8)
• Non-repudiation (page 9)
• Authentication (page 10)
• Cryptography is Fundamental (page 12)
• Symmetric Key Crypto (page 13)
• Public Key Cryptography (page 16)
• SSL/TLS Overview (page 30)
• Goals of TLS (page 31)
• Certificate Authorities (page 33)
• Problems with TLS (page 42)
Primary Topics Covered
• Defining Security - Security encompasses policies and mechanisms designed to protect data and resources against unauthorized access and attacks.
• Security Properties - Key properties include confidentiality, integrity, authenticity, availability, and non-repudiation, which are essential for secure communications.
• Confidentiality - Ensures that data is accessible only to authorized entities, often achieved through cryptographic methods.
• Integrity - Guarantees that data remains unaltered during transmission, utilizing techniques like hash functions and HMAC.
• Authenticity - Establishes the identity of the sender, often verified through digital signatures and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
• Transport Layer Security (TLS) - A protocol that provides secure communication over a computer network, replacing the older SSL protocol.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Security policy framework template for defining organizational security measures
• TLS implementation checklist for secure communications
• X.509 certificate management guide for maintaining trust
• Risk assessment template for evaluating TLS vulnerabilities
• Incident response plan for addressing TLS-related security breaches
Slide Highlights
• Overview of security properties and their implications for network communications
• Detailed explanation of the TLS handshake process and its components
• Visual representation of the role of Certificate Authorities in establishing trust
• Analysis of common TLS vulnerabilities and recommended mitigations
• Case studies illustrating real-world applications of TLS and security best practices
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Network Security (30 minutes)
• Overview of security principles and their relevance
• Discussion on the importance of TLS in modern communications
Understanding TLS (60 minutes)
• In-depth exploration of the TLS protocol
• Hands-on demonstration of TLS implementation
Certificate Management (45 minutes)
• Overview of X.509 certificates and their role in security
• Best practices for managing certificates and working with CAs
Common Vulnerabilities and Mitigations (45 minutes)
• Analysis of known TLS vulnerabilities
• Strategies for securing communications against attacks
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the security policy framework to align with organizational goals and compliance requirements
• Update the TLS implementation checklist based on specific application needs and infrastructure
• Modify the incident response plan to reflect organizational protocols and communication channels
Secondary Topics Covered
• Cryptographic hash functions and their applications
• Differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption
• The role of public key infrastructure in secure communications
• Challenges associated with certificate revocation and management
• Overview of common TLS attacks and their implications
FAQ
What is Transport Layer Security (TLS)?
TLS is a cryptographic protocol designed to provide secure communication over a computer network, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authentication.
How does TLS ensure data confidentiality?
TLS uses encryption techniques to ensure that data transmitted between clients and servers is only accessible to authorized parties.
What are the main components of a TLS handshake?
The TLS handshake includes the ClientHello and ServerHello messages, certificate exchange, and the establishment of a session key for encryption.
What is the role of a Certificate Authority (CA)?
A CA is a trusted entity that issues digital certificates, verifying the identity of the certificate holder and enabling secure communications.
What are common vulnerabilities associated with TLS?
Common vulnerabilities include man-in-the-middle attacks, weak cipher suites, and implementation bugs that can compromise security.
How can organizations mitigate TLS vulnerabilities?
Organizations can implement best practices such as regular updates, using strong cipher suites, and performing thorough security audits.
What is the significance of X.509 certificates?
X.509 certificates are used to establish a chain of trust in TLS communications, containing the public key and identity of the certificate holder.
What is perfect forward secrecy?
Perfect forward secrecy is a property of certain key exchange protocols that ensures session keys are not compromised even if the private key is compromised.
How often should certificates be renewed?
Certificates should be renewed regularly, ideally with short lifetimes to minimize the risk of compromise.
Glossary
• Transport Layer Security (TLS) - A protocol for secure communication over a computer network.
• Certificate Authority (CA) - An entity that issues digital certificates to verify identities.
• X.509 Certificate - A standard format for public key certificates.
• Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) - A framework for managing digital certificates and public-key encryption.
• Confidentiality - The property that ensures data is accessible only to authorized entities.
• Integrity - The assurance that data has not been altered during transmission.
• Authenticity - The verification of the identity of the sender of a message.
• Non-repudiation - The assurance that someone cannot deny the validity of their signature on a document or message.
• Cryptographic Hash Function - A function that converts input data into a fixed-size string of characters, which is typically a hash value.
• Symmetric Key Cryptography - A type of encryption where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption.
• Asymmetric Key Cryptography - A type of encryption that uses a pair of keys, one public and one private.
• Man-in-the-Middle Attack - A security breach where an attacker intercepts communication between 2 parties.
• Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) - A property of secure communication protocols that ensures session keys are not compromised even if the private key is compromised.
• Certificate Revocation List (CRL) - A list of certificates that have been revoked before their expiration date.
• Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) - A protocol for checking the revocation status of a digital certificate.
• Weak Cipher Suite - A set of cryptographic algorithms that are considered insecure.
• Implementation Bug - A flaw in the code that can lead to security vulnerabilities.
• Digital Signature - A mathematical scheme for verifying the authenticity and integrity of a message.
• Authentication - The process of verifying the identity of a person or device.
• Availability - The property that ensures data and resources are accessible when needed.
Source: Best Practices in Cyber Security PowerPoint Slides: Network Security - Transport Layer Security PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting