DESCRIPTION
Complete KPIs for Sales and Marketing Managers
Contents
1. KPIs Sales Manager
2. KPIs Marketing Manager
3. KPIs Corporate Planning Manager
4. KPIs Business Development Manager
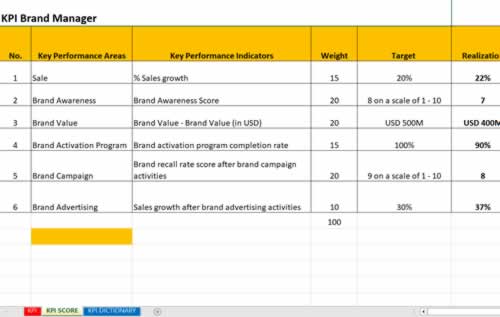
5. KPIs Brand Manager
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable measurements used to gauge a company's overall long-term performance. KPIs specifically help determine a company's strategic, financial, and operational achievements, especially compared to those of other businesses within the same sector. They can also be used to judge progress or achievements against a set of benchmarks or past performance.
1. Key performance indicators (KPIs) measure a company's success vs. a set of targets, objectives, or industry peers.
2. KPIs can be financial, including net profit (or the bottom line, net income), revenues minus certain expenses, or the current ratio (liquidity and cash availability).
3. Customer-focused KPIs generally center on per-customer efficiency, customer satisfaction, and customer retention.
4. Process-focused KPIs aim to measure and monitor operational performance across the organization.
5. Businesses generally measure and track KPIs through analytics software and reporting tools.
Key performance indicators are used in business to judge performance and progress toward specific, measurable goals. They may be compared to:
1. A predetermined benchmark
2. Other competitors within the industry
3. The performance of the business over time
Also referred to as key success indicators (KSIs), KPIs vary between companies and between industries, depending on performance criteria. For example, a software company striving to attain the fastest growth in its industry may consider year-over-year (YOY) revenue growth as its chief performance indicator. Conversely, a retail chain might place more value on same-store sales as the best KPI metric for gauging growth.
At the heart of KPIs lie data collection, storage, cleaning, and synthesizing. The KPI data is gathered and compared to whatever target has been set. The results of that comparison then are analyzed and used to draw conclusions about how well current systems, or recent changes to those systems, are working to achieve the department or business's goals. This lets management know whether the current systems are effective or whether to make changes to improve those outcomes and meet future goals.
The goal of KPIs is to communicate results succinctly to allow management to make more informed strategic decisions. They are often measured using analytics software and reporting tools.
Most KPIs fall into four broad categories. Each category has its own characteristics, time frame, and level of business that is likely to use it. Different KPIs may also be used by different departments within the same business.
1. Strategic
Strategic KPIs are usually the most high-level. These types of KPIs may indicate how a company is doing, although they don't provide much information beyond a high-level snapshot. Executives are most likely to use strategic KPIs. Examples include return on investment, profit margin, and total company revenue.
2. Operational
Operational KPIs are focused on a tight time frame. These KPIs measure how a company is doing month over month, or sometimes day over day, by analyzing different processes, segments, or geographical locations. Operational KPIs are often used by managing staff and to analyze questions that are derived from analyzing strategic KPIs. For example, if an executive notices that company-wide revenue has decreased, they may investigate which product lines are struggling.
3. Functional
Functional KPIs hone in on specific departments or functions within a company. For example, a finance department may keep track of how many new vendors they register within their accounting information system each month. A marketing department measures how many clicks each email distribution receives.
Regards,
UJ Consulting
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form.
Source: Complete KPIs for Sales and Marketing Managers () Document, UJ Consulting
THERE ARE 5 PRODUCTS IN THIS BUNDLE:
|
|
KPI Brand Manager
Contents
1. Key Performance Indicator (KPI) Brand Manager
2. KPI Brand Manager Score
3. KPI Brand Manager Dictionary
KPI stands for key... [read more]
Individual Price: $25.00
|
|
|
KPI Business Development Manager
Contents
1. KPI Business Development Manager
2. KPI Business Development Manager Score
3. KPI Business Development Manager... [read more]
Individual Price: $25.00
|
|
|
KPI Corporate Planning Manager
Contents
1. KPI Corporate Planning Manager
2. KPI Corporate Planning Manager Score
3. KPI Corporate Planning Manager Dictionary
KPI... [read more]
Individual Price: $25.00
|
|
|
KPI Marketing Manager
Contents
1. KPI Marketing Manager
2. KPI Score
3. KPI Dictionary
KEY PERFORMANCE INDICATOR
KPI stands for key performance indicator, a... [read more]
Individual Price: $25.00
|
|
|
KPI Sales Manager
Contents
1. KPI Sales Manager
2. KPI Score
3. KPI Dictionary
KPI stands for key performance indicator, a quantifiable measure of performance over time... [read more]
Individual Price: $25.00
|