Complete Guide to Post-merger Integration (PMI) (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 106 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Provides a structured 5-phase approach to the complex and cumbersome PMI process.
- Provides a framework to setting up the IMO, along with the core roles and responsibilities.
- Provides actionable checklists and insights into 12 integration functional areas.
POST-MERGER INTEGRATION PPT DESCRIPTION
Post-merger Integration (PMI), also known as M&A Integration, is a highly complex process. The bringing together of 2 distinct organizations experiencing change, while ensuring operations continues as usual is a challenge that can never be underestimated.
The PMI transition process often requires meticulous coordination across multiple functions to protect deal value and maintain business continuity. Executives must also navigate cultural alignment and stakeholder expectations to build a cohesive new entity.
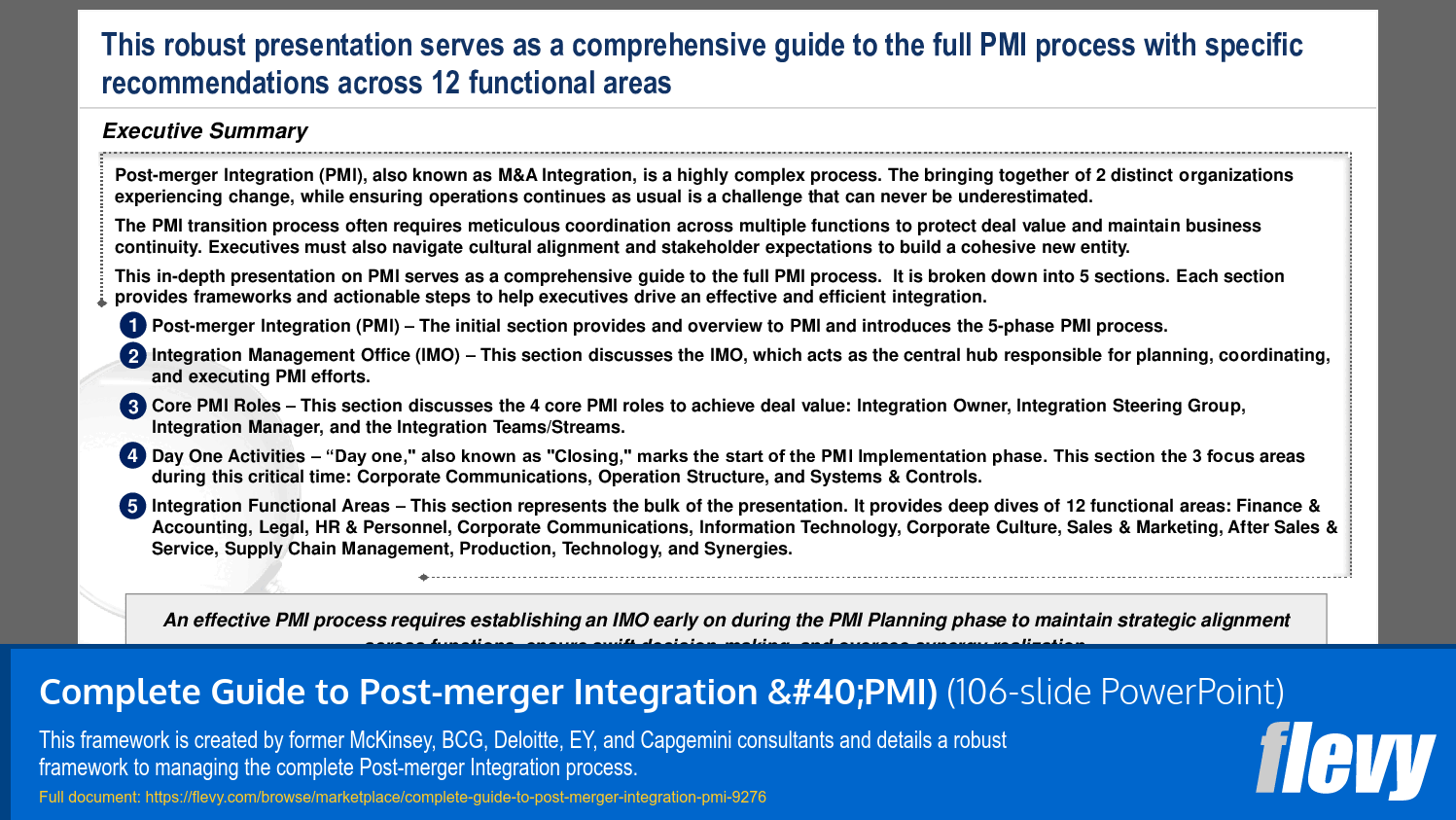
This in-depth PowerPoint presentation on PMI serves as a comprehensive guide to the full PMI process. It is broken down into 5 sections. Each section provides frameworks and actionable steps to help executives drive an effective and efficient integration.
Post-merger Integration (PMI)
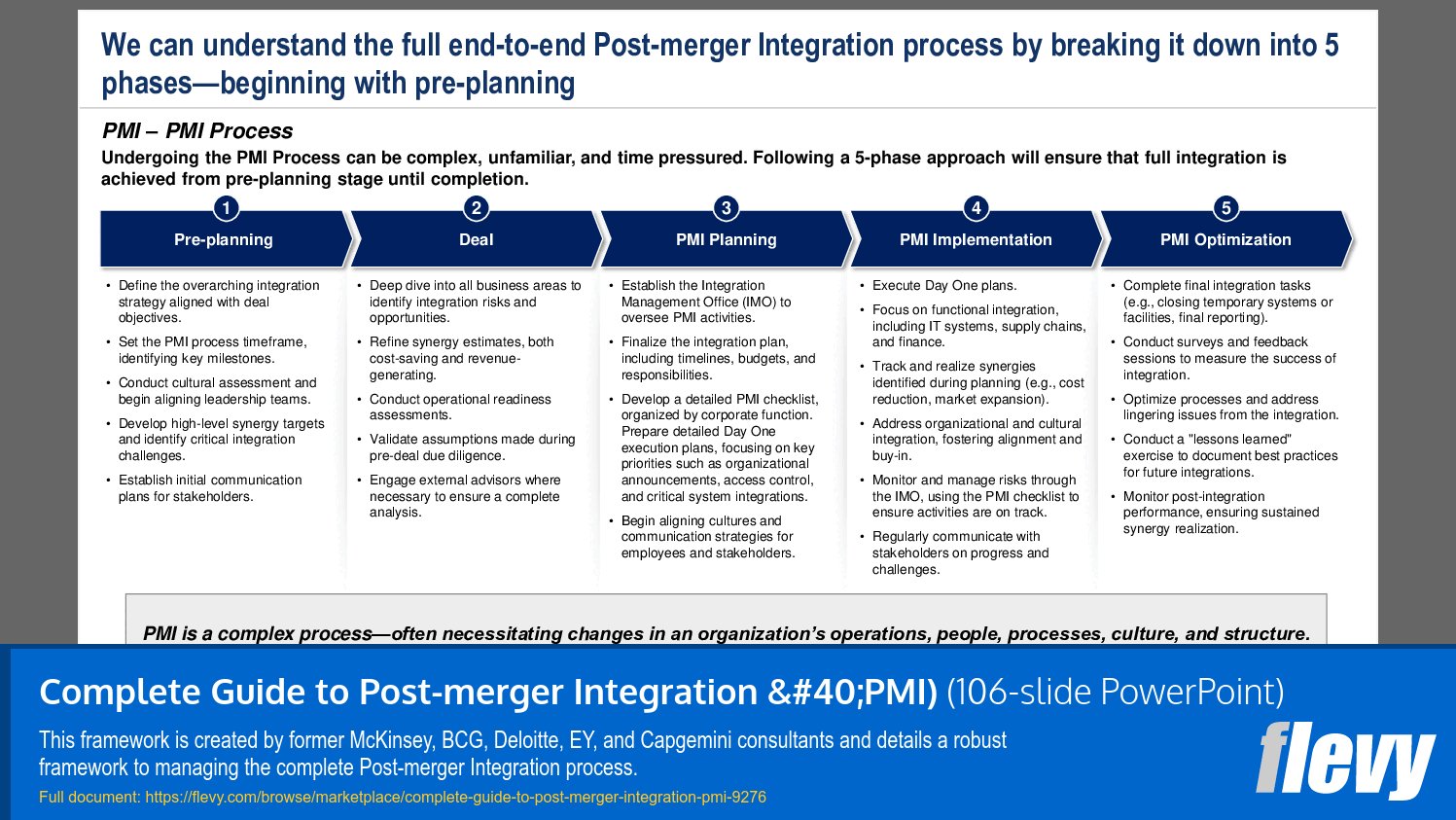
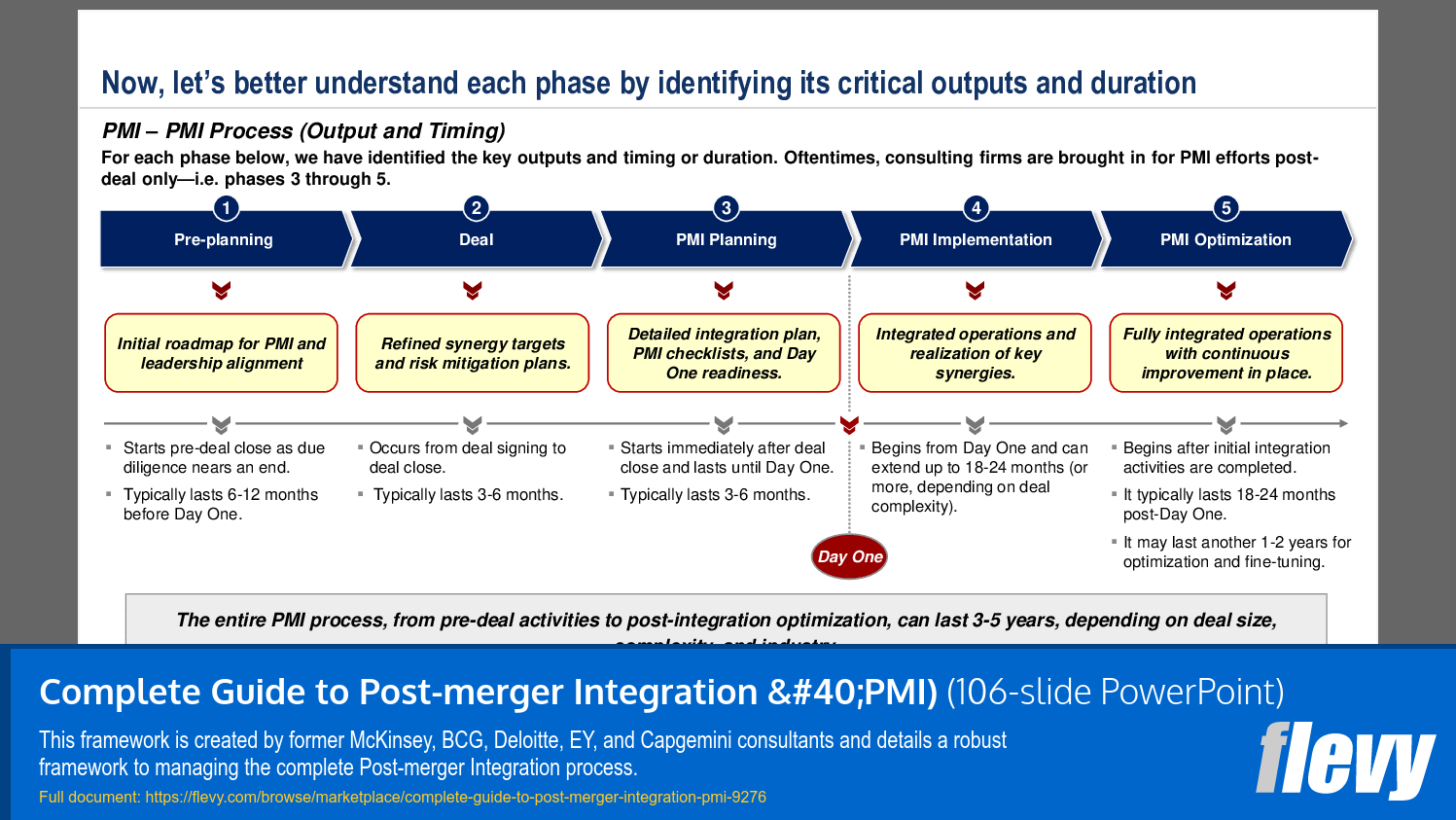
The initial section provides and overview to PMI and introduces the 5-phase PMI process:
1. Pre-planning – Establishes the strategic foundation by defining integration goals, identifying potential synergies, and outlining critical milestones.
2. Deal – Conducts due diligence, refines synergy estimates, and finalizes transaction terms to ensure alignment with overall business objectives.
3. PMI Planning – Sets up the Integration Management Office (IMO), defines roles and responsibilities, and lays out detailed plans for functional and cultural integration.
4. PMI Implementation – Executes Day One readiness activities, tracks synergies, and addresses organizational and cultural integration in real time.
5. PMI Optimization – Completes remaining integration tasks, assesses outcomes, and streamlines processes to sustain long-term performance and synergy realization.
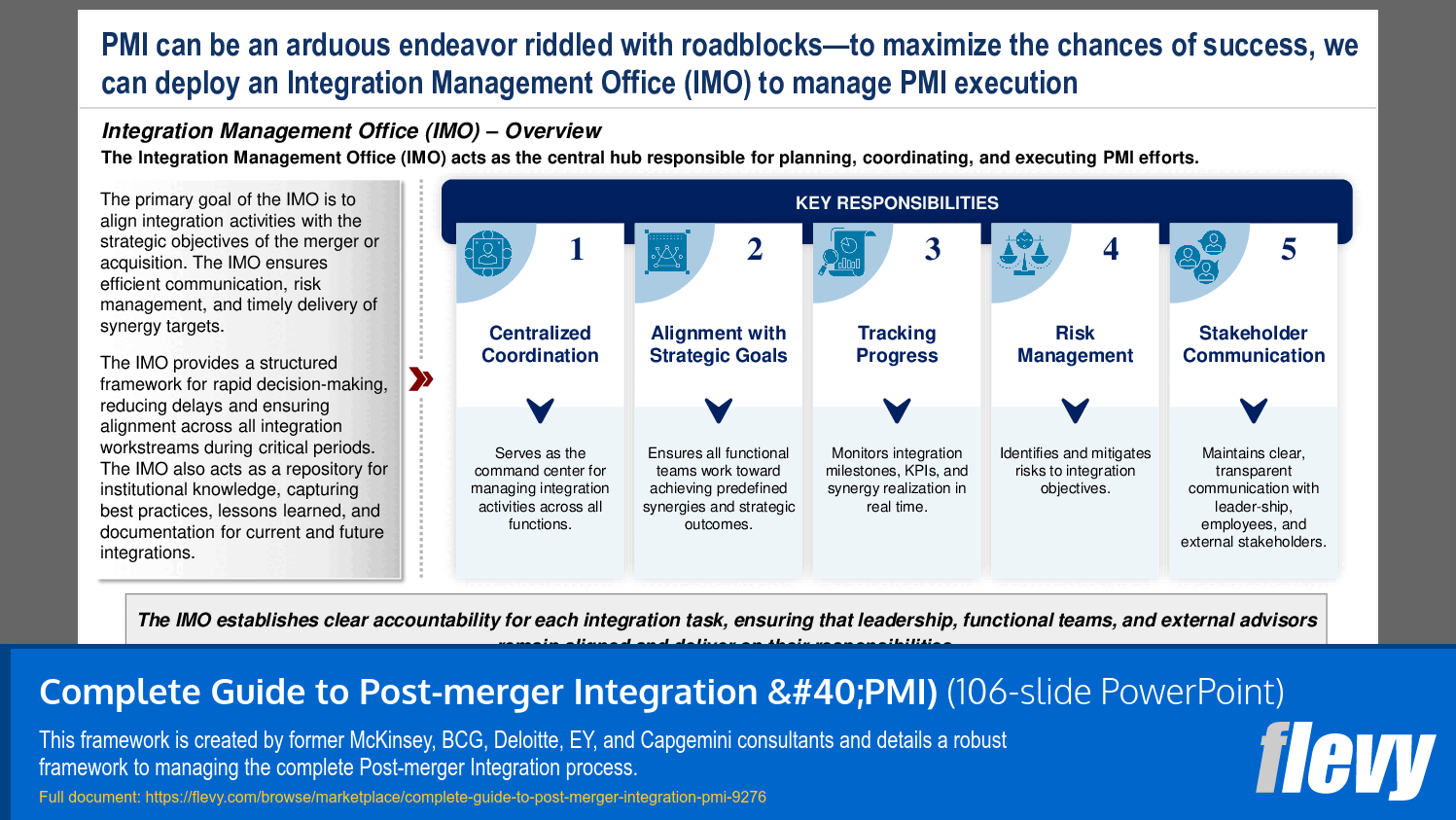
Integration Management Office (IMO)
This section discusses the IMO, which acts as the central hub responsible for planning, coordinating, and executing PMI efforts. An effective PMI process requires establishing an IMO early on (during the PMI Planning phase) to maintain strategic alignment across functions, ensure swift decision-making, and oversee synergy realization.
The primary goal of the IMO is to align integration activities with the strategic objectives of the merger or acquisition. The IMO ensures efficient communication, risk management, and timely delivery of synergy targets.
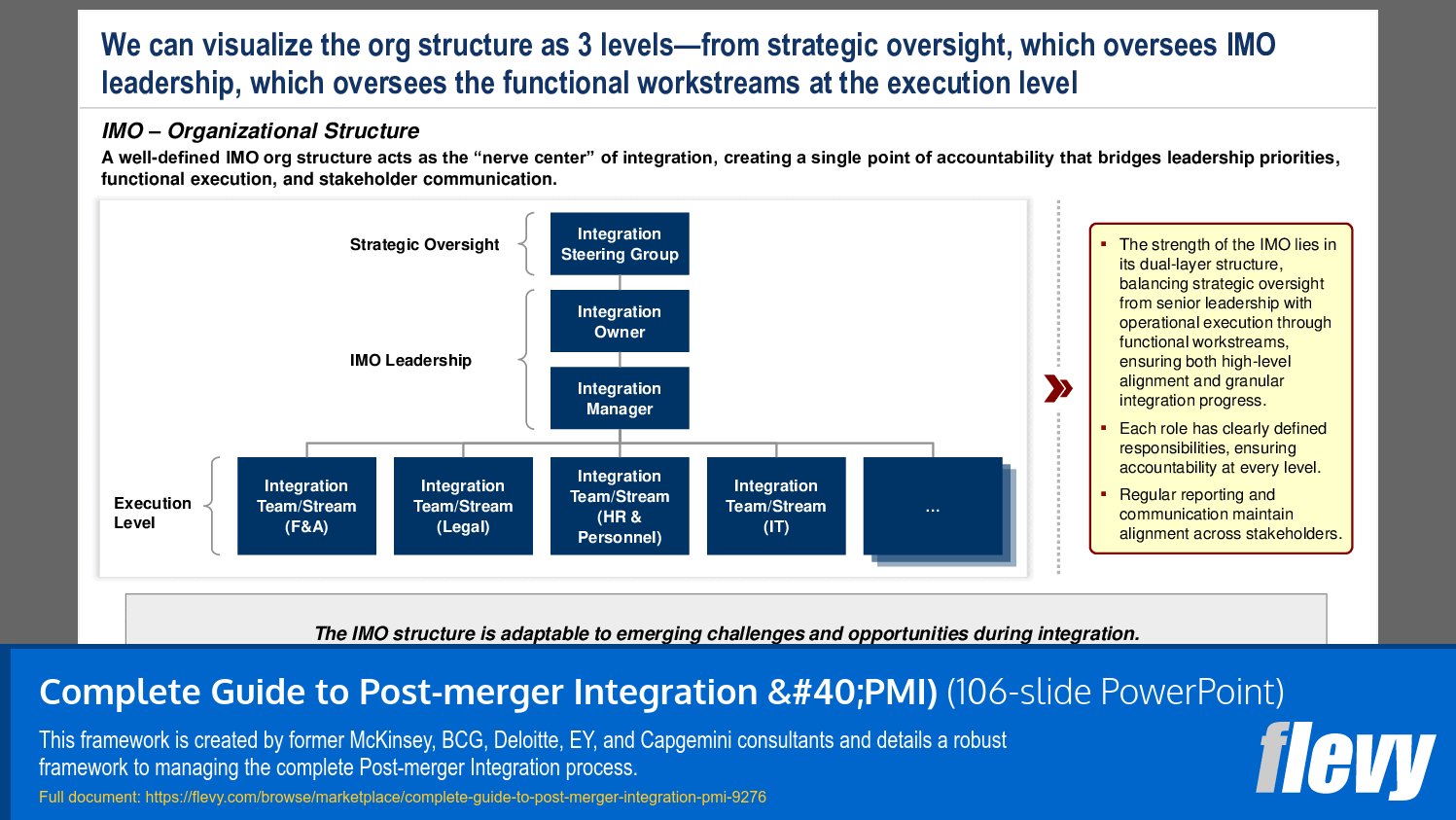
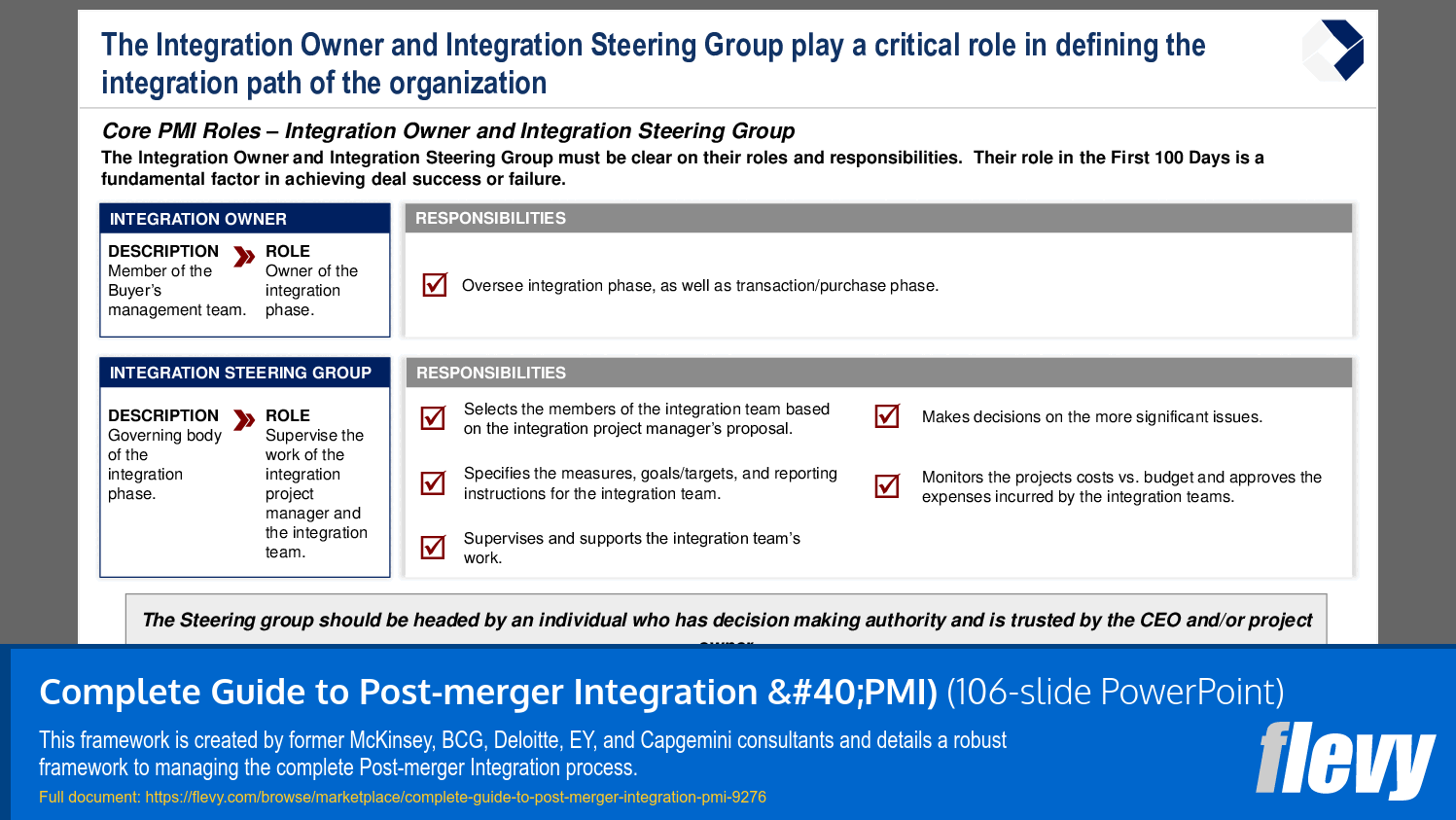
Core PMI Roles
This section discusses the 4 core PMI roles to achieve deal value:
1. Integration Owner
2. Integration Steering Group
3. Integration Manager
4. the Integration Teams/Streams
Day One Activities
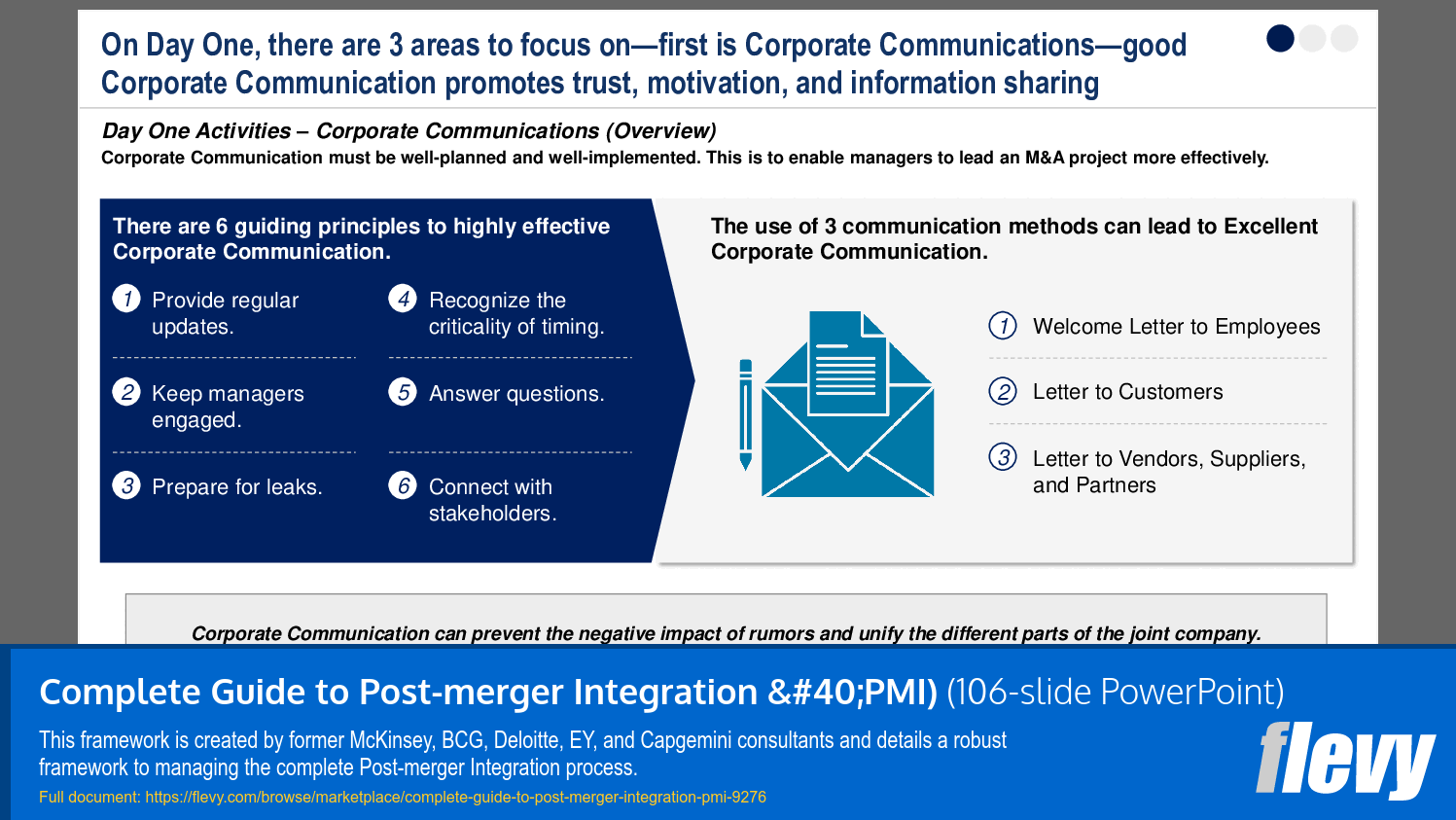
"Day one," also known as "Closing," marks the start of the PMI Implementation phase. This section the 3 focus areas during this critical time:
1. Corporate Communications
2. Operation Structure
3. Systems & Controls
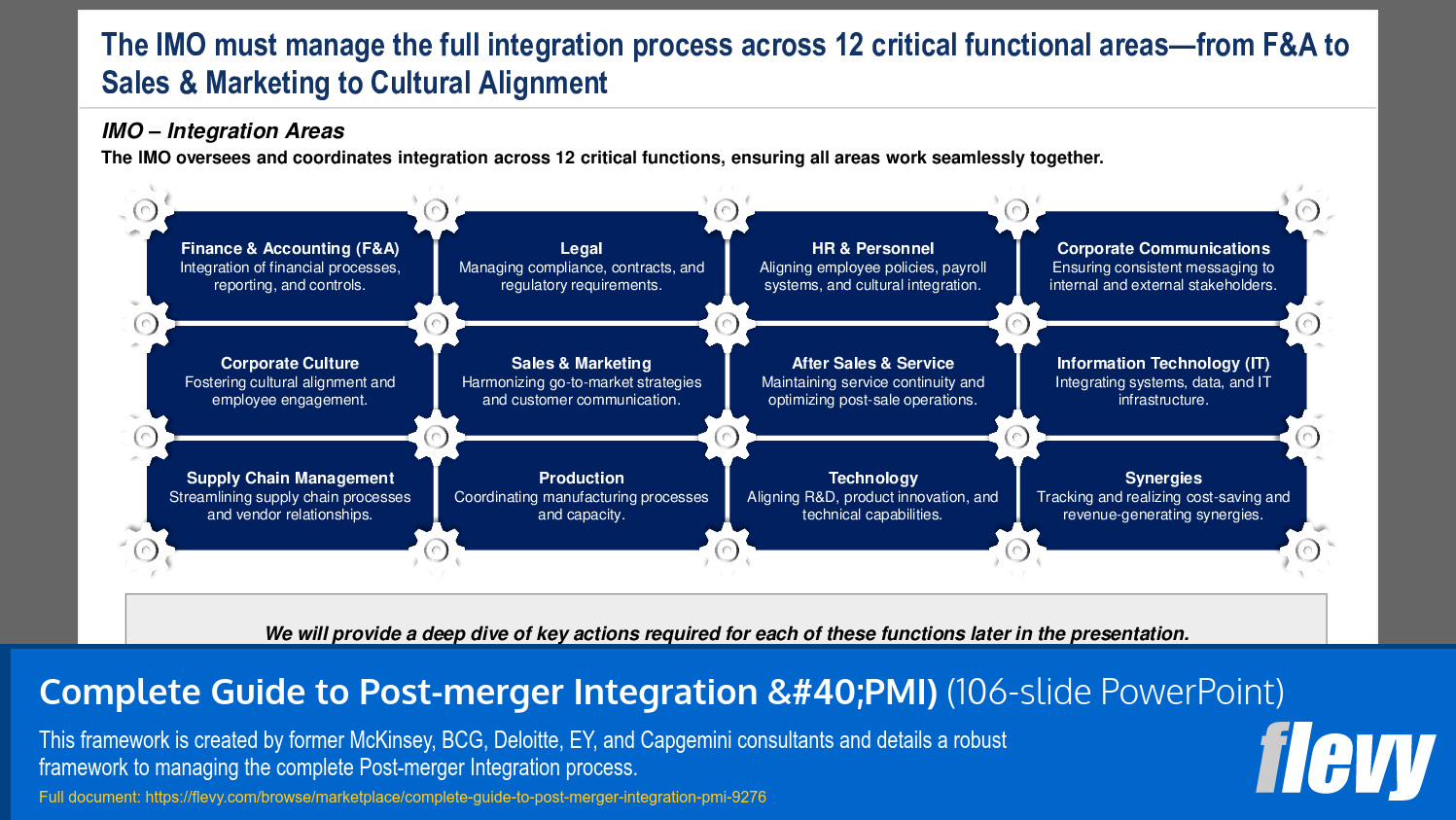
Integration Functional Areas
This section represents the bulk of the presentation. It provides deep dives of 12 functional areas:
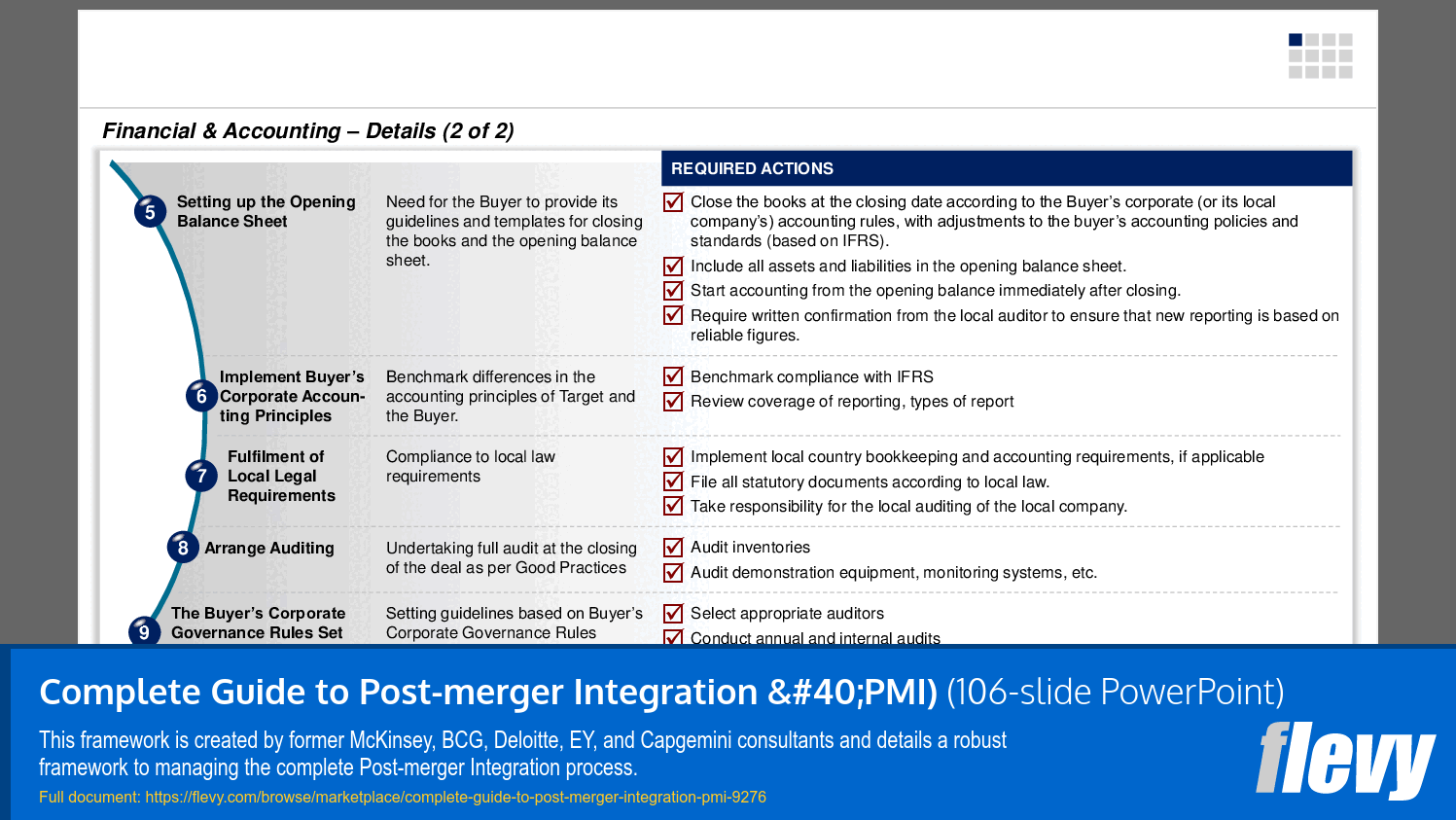
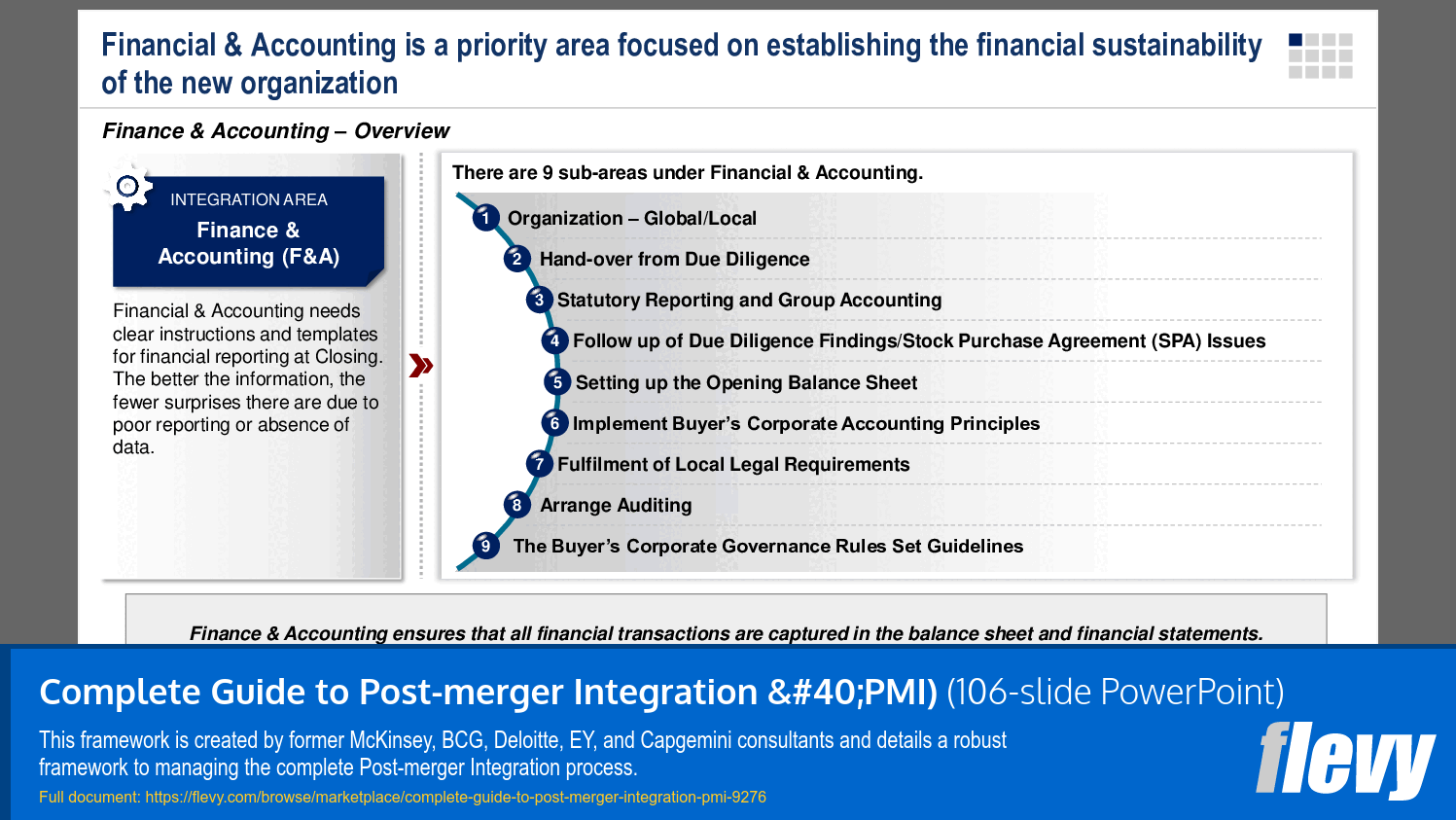
1. Finance & Accounting
2. Legal
3. HR & Personnel
4. Corporate Communications
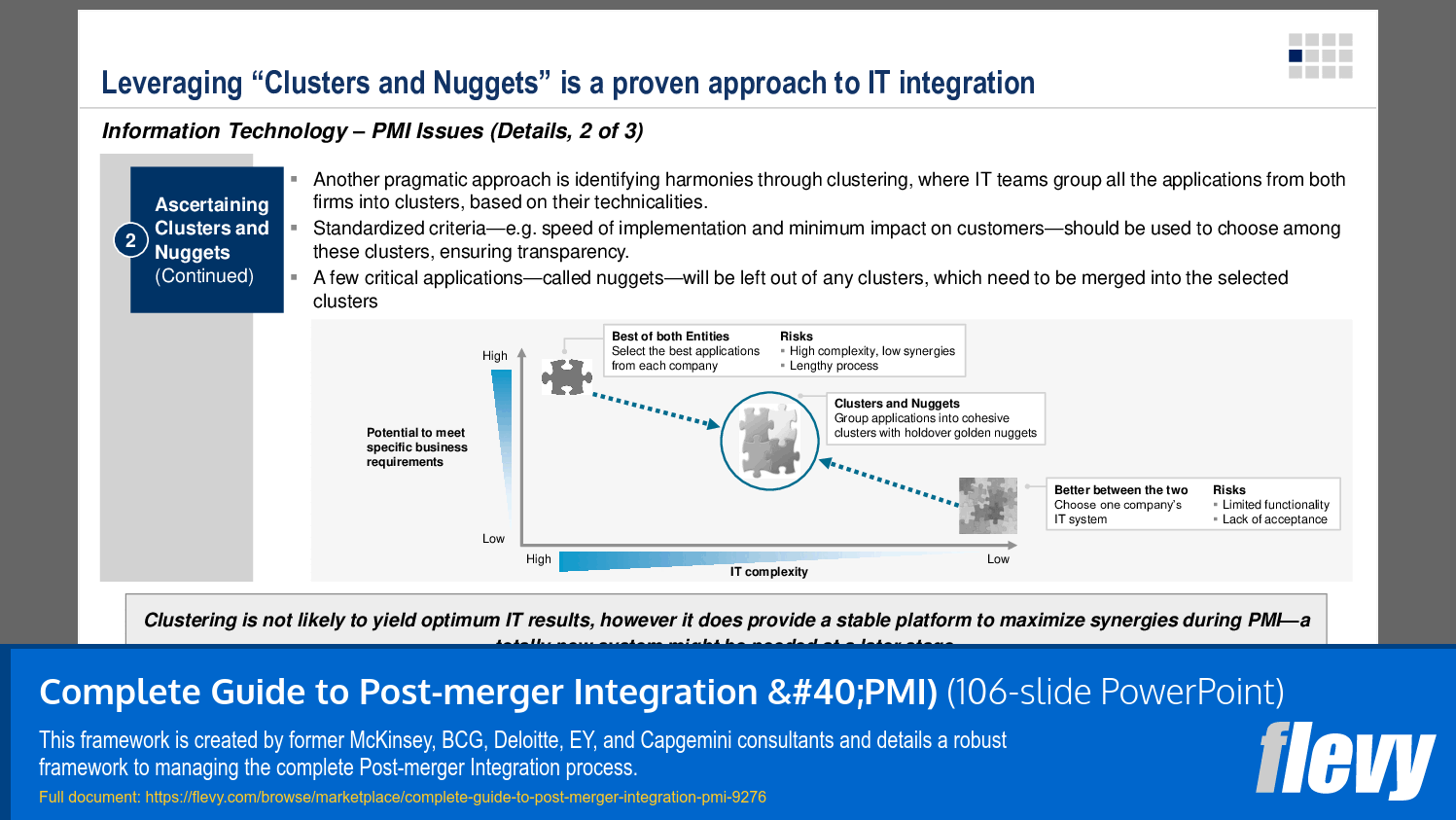
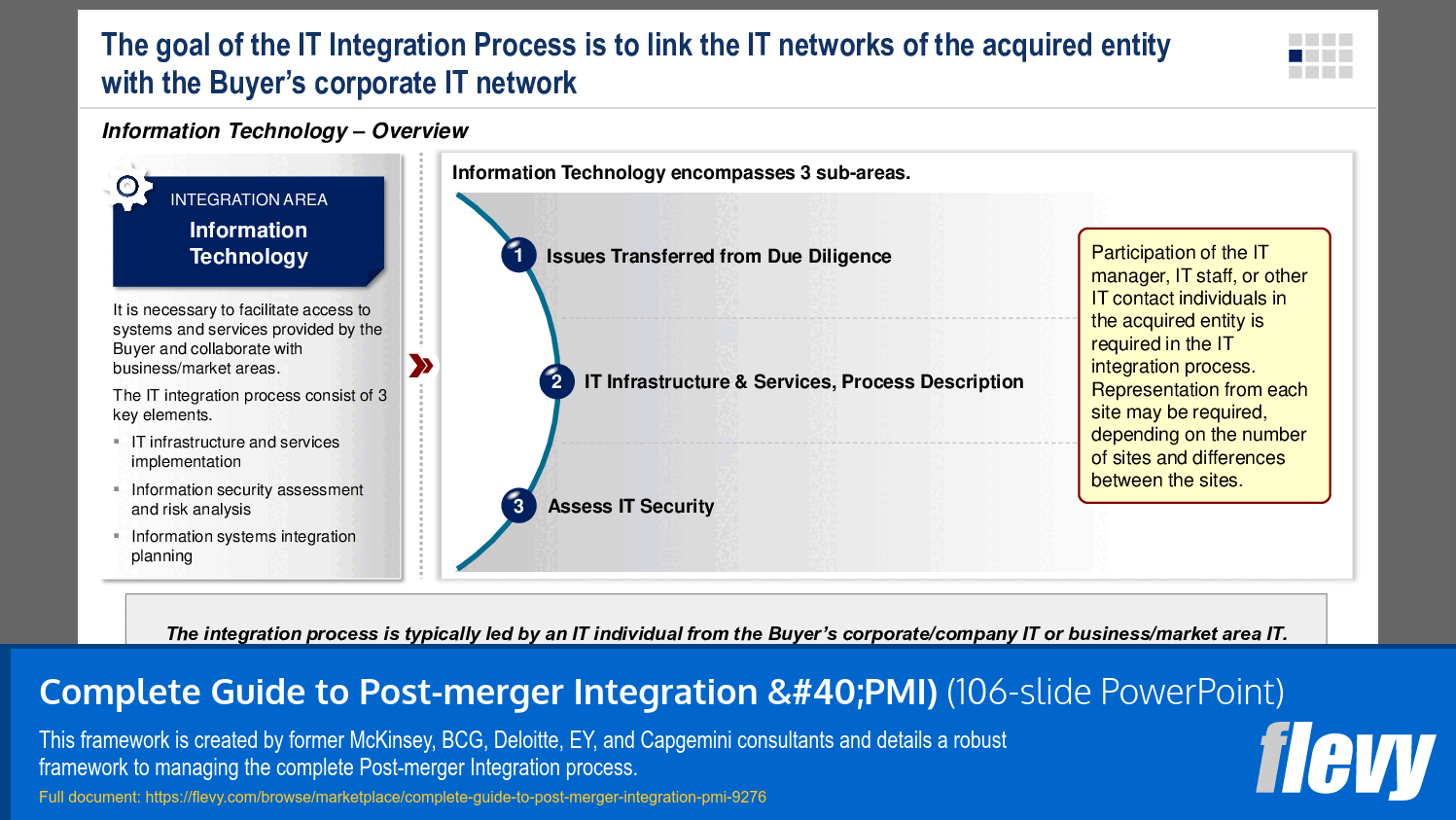
5. Information Technology
6. Corporate Culture
7. Sales & Marketing
8. After Sales & Service
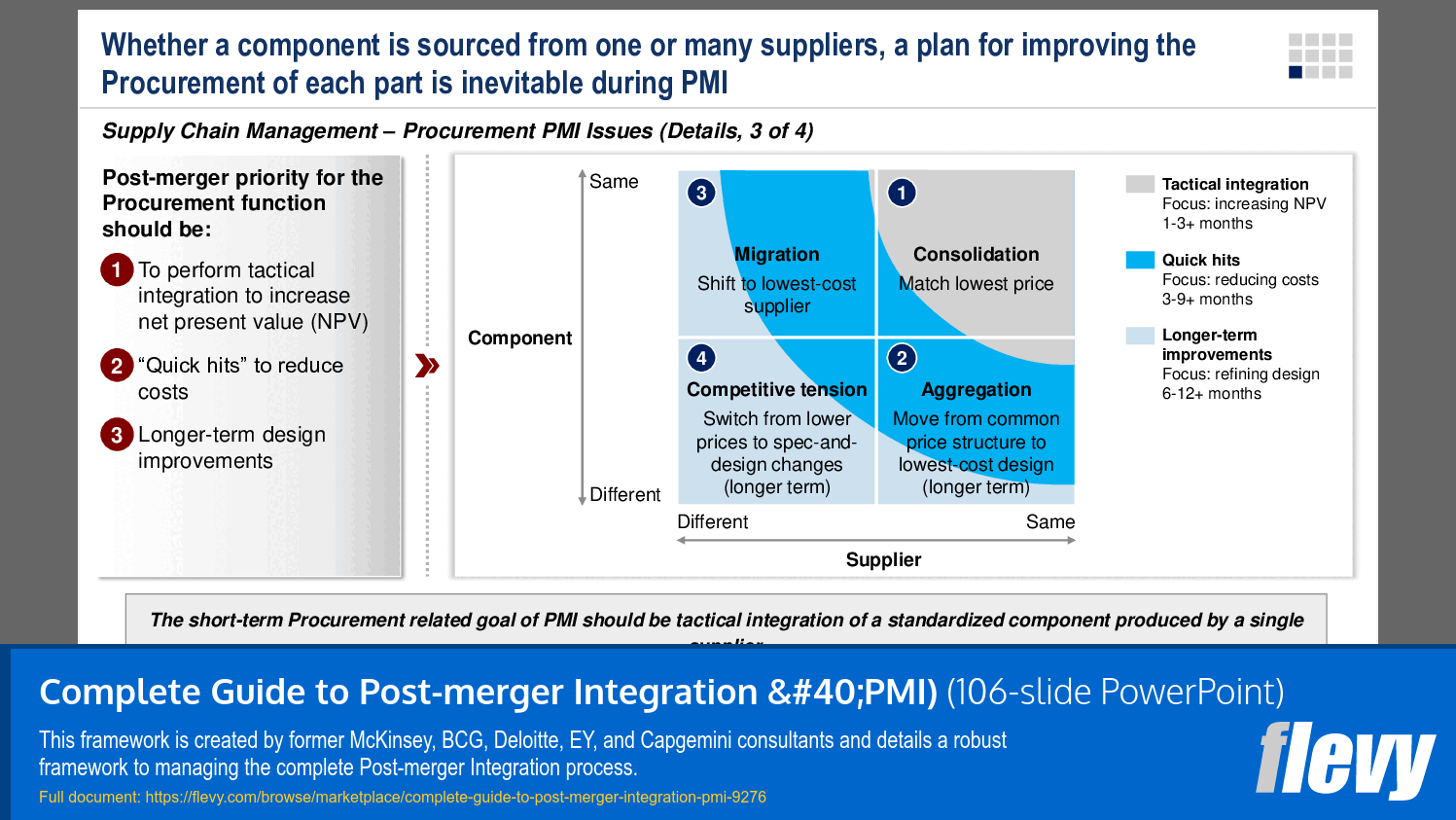
9. Supply Chain Management
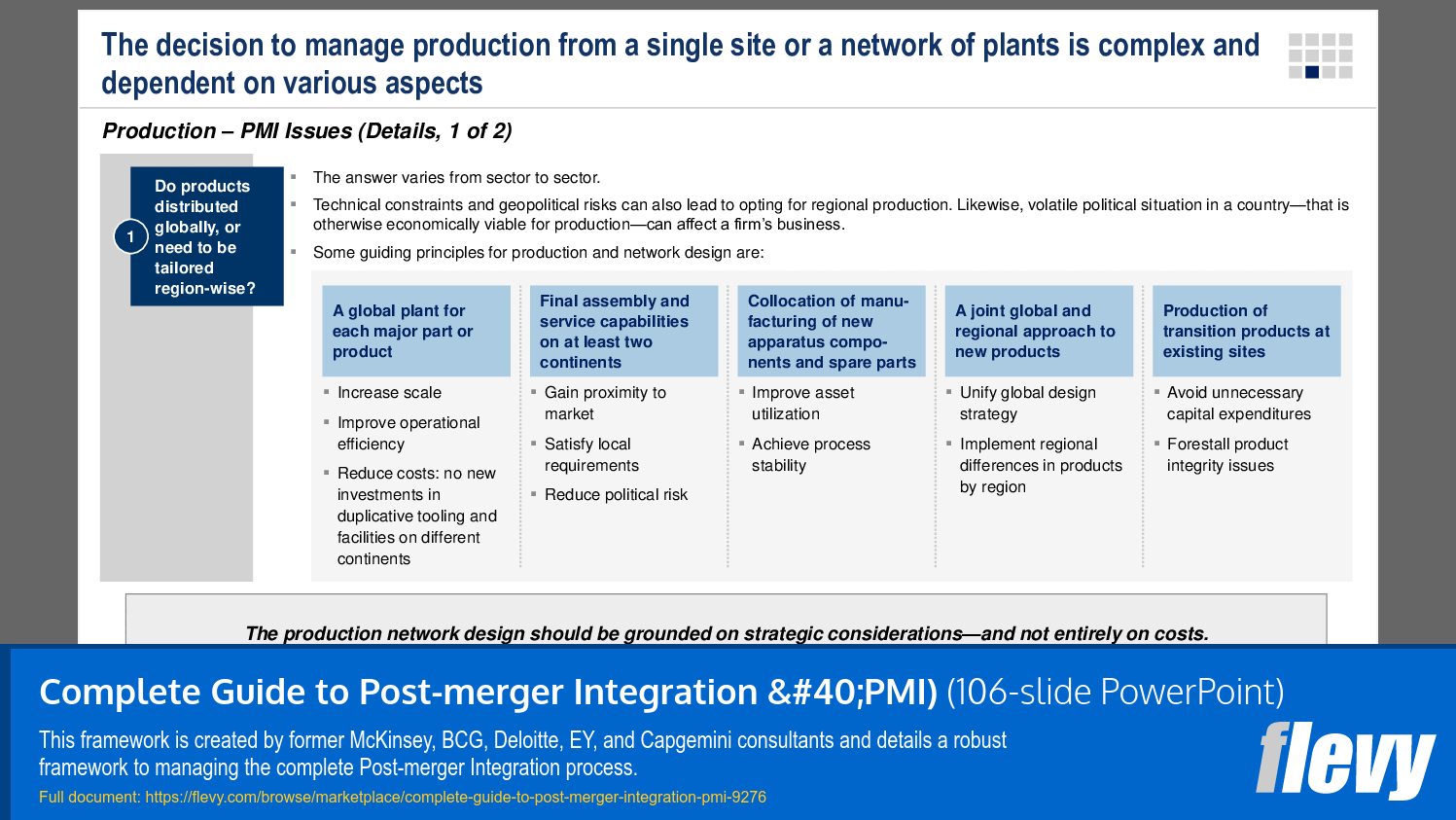
10. Production
11. Technology
12. Synergies
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 106-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
Post-merger Integration (PMI), also known as M&A Integration, is a complex process that involves merging 2 distinct organizations while ensuring operational continuity. This presentation serves as a comprehensive guide to the PMI process, detailing frameworks and actionable steps necessary for effective integration. It is structured into 5 key sections: an overview of PMI, the role of the Integration Management Office (IMO), core PMI roles, critical Day One activities, and an in-depth exploration of twelve functional areas. The PMI process requires meticulous planning and coordination to capture synergies and maintain business continuity.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives overseeing mergers and acquisitions.
• Integration leaders responsible for executing PMI strategies.
• Consultants advising on M&A integration processes.
• Functional team leaders managing specific integration areas like HR, IT, and Finance.
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During pre-merger planning to align integration strategies with business objectives.
• At the onset of Day One activities to ensure smooth operational transitions.
• Throughout the PMI process to track progress and address integration challenges.
Learning Objectives
• Define the PMI process and its significance in M&A success.
• Establish an Integration Management Office (IMO) to oversee integration efforts.
• Identify core PMI roles and their responsibilities in achieving integration goals.
• Execute Day One activities effectively to ensure operational readiness.
• Analyze twelve functional areas to optimize integration outcomes.
• Develop strategies for capturing synergies and enhancing organizational performance.
Table of Contents
• Executive Summary (page 4)
• Post-merger Integration (PMI) (page 5)
• Integration Management Office (IMO) (page 12)
• Core PMI Roles (page 20)
• Day One Activities (page 28)
• Integration Functional Areas (page 38)
Primary Topics Covered
• Post-merger Integration Overview - PMI is the process following a merger or acquisition, focusing on aligning 2 organizations to maximize synergies and maintain operational continuity.
• Integration Management Office (IMO) - The IMO acts as the central hub for planning and executing PMI activities, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives.
• Core PMI Roles - Key roles include the Integration Owner, Integration Steering Group, Integration Manager, and Integration Teams, each responsible for specific aspects of the integration.
• Day One Activities - Critical focus areas during Day One include Corporate Communications, Operational Structure, and Systems & Controls to ensure a smooth transition.
• Integration Functional Areas - Detailed examination of twelve functional areas, including Finance, HR, IT, and Sales & Marketing, to identify integration challenges and opportunities.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• PMI process checklist for tracking integration activities.
• Communication templates for Day One announcements.
• Integration planning templates for functional areas.
• Risk management frameworks for identifying and mitigating integration risks.
• Performance tracking dashboards for monitoring synergy realization.
• Documentation guidelines for maintaining compliance and governance.
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the PMI process and its 5 phases.
• Structure and responsibilities of the Integration Management Office (IMO).
• Key roles and their impact on integration success.
• Day One focus areas and critical actions.
• In-depth analysis of functional areas and their integration strategies.
Potential Workshop Agenda
Integration Strategy Alignment Session (90 minutes)
• Discuss overarching integration goals and objectives.
• Identify key stakeholders and their roles in the integration process.
• Review integration timelines and milestones.
Day One Execution Planning Session (120 minutes)
• Develop detailed plans for Corporate Communications and Operational Structure.
• Assign responsibilities for Systems & Controls implementation.
• Establish a feedback mechanism for Day One activities.
Functional Integration Review (60 minutes)
• Evaluate integration progress across key functional areas.
• Identify challenges and opportunities for synergy realization.
• Adjust integration plans based on feedback and performance metrics.
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the PMI process checklist to reflect specific organizational needs and integration goals.
• Adjust communication templates to align with corporate branding and messaging strategies.
• Modify integration planning templates to incorporate unique functional requirements and timelines.
• Update risk management frameworks to address industry-specific challenges and compliance issues.
• Personalize performance tracking dashboards to reflect key performance indicators relevant to the integration.
Secondary Topics Covered
• Governance structures for integration oversight.
• Cultural alignment strategies to facilitate smooth transitions.
• Change management practices to address employee concerns.
• Legal considerations and compliance requirements during integration.
• Technology integration strategies to enhance operational efficiency.
Topic FAQ
What are the standard phases of a post-merger integration process?
A common PMI lifecycle is organized into 5 phases: Pre-planning (define goals and synergies), Deal (due diligence and finalize terms), PMI Planning (establish IMO and roles), PMI Implementation (Day One readiness and execution), and PMI Optimization (complete remaining tasks and sustain synergies), ending with 5 phases.What is the Integration Management Office (IMO) and when should it be set up?
The IMO is the central hub for planning, coordinating, and executing PMI activities; it ensures alignment with strategic objectives, manages communication, risk, and synergy tracking. The guidance recommends establishing the IMO early during the PMI Planning phase.Which activities should be prioritized for Day One readiness?
Day One priorities focus on Corporate Communications to stakeholders, Operational Structure to define reporting and roles, and Systems & Controls to ensure transactional and operational continuity. Templates and checklists for these Day One actions are included as practical deliverables.How should I assess the value of PMI templates before purchasing?
Evaluate whether templates cover IMO setup, governance roles, Day One communications, functional integration planning, risk management, and performance tracking. Confirm adaptability to your branding and timelines and whether they include concrete tools like an integration checklist and performance tracking dashboards.I’m leading HR integration after an acquisition — what are the immediate planning steps?
Prioritize alignment with the IMO and integration governance, prepare Day One corporate communications for employees, assess cultural alignment and change management needs, and use HR-specific integration planning templates to map roles, policies, and personnel actions relevant to the HR & Personnel functional area.How long does a typical PMI effort take and what influences the timeline?
PMI duration varies with deal complexity and integration challenges; typical timelines span multiple years. The document notes PMI can last anywhere from 3 to 5 years depending on complexity, governance clarity, and the scope of functional integration tasks.What governance roles are essential for managing a PMI program?
Core PMI governance roles include an Integration Owner (executive sponsor), an Integration Steering Group for strategic decisions, an Integration Manager overseeing day-to-day execution, and multiple Integration Teams or Streams responsible for functional deliverables such as finance, IT, HR, and operations.Where can I find ready-made PMI slide decks and templates for planning and Day One execution?
Flevy’s Complete Guide to Post-merger Integration is a 106-slide PowerPoint (PPTX) that provides PMI process checklists, communication templates for Day One, integration planning templates for functional areas, risk management frameworks, and performance tracking dashboards in a downloadable format.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the primary goal of Post-merger Integration?
The primary goal of PMI is to maximize synergies and ensure that the merger or acquisition achieves its predicted value while maintaining operational continuity.
What role does the Integration Management Office (IMO) play?
The IMO serves as the central hub for coordinating and executing PMI efforts, ensuring alignment with strategic objectives and effective communication across functional areas.
What are the critical focus areas on Day One?
On Day One, critical focus areas include Corporate Communications, Operational Structure, and Systems & Controls to ensure a seamless transition.
How long does the PMI process typically last?
The PMI process can last anywhere from 3 to 5 years, depending on the complexity of the deal and the integration challenges faced.
What are some common challenges during PMI?
Common challenges include lack of clear leadership, resistance to change, misalignment of strategic objectives, and inadequate resources.
How can organizations ensure effective communication during integration?
Establishing a robust communication framework that includes regular updates, stakeholder engagement, and clear messaging is essential for effective communication during integration.
What are the key roles involved in the PMI process?
Key roles include the Integration Owner, Integration Steering Group, Integration Manager, and Integration Teams, each responsible for specific aspects of the integration.
What functional areas are typically involved in the PMI process?
Functional areas involved in PMI include Finance & Accounting, HR & Personnel, IT, Sales & Marketing, Corporate Communications, and Supply Chain Management.
How can organizations capture synergies during integration?
Organizations can capture synergies by identifying cost-saving opportunities, enhancing revenue generation, and optimizing operational efficiencies across integrated functions.
What is the significance of cultural alignment in PMI?
Cultural alignment is crucial for ensuring employee engagement, minimizing resistance to change, and fostering a cohesive organizational identity post-merger.
Glossary
• Post-merger Integration (PMI) - The process of combining 2 organizations after a merger or acquisition.
• Integration Management Office (IMO) - The central body responsible for overseeing PMI activities.
• Synergies - The additional value created through the combination of 2 organizations.
• Day One - The first day of operational integration following a merger or acquisition.
• Integration Owner - The executive responsible for the overall integration strategy.
• Integration Manager - The individual overseeing the day-to-day execution of the integration plan.
• Integration Teams - Functional groups tasked with specific integration activities.
• Cultural Alignment - The process of harmonizing the values and practices of merging organizations.
• Stakeholders - Individuals or groups affected by the merger or acquisition.
• Due Diligence - The investigation conducted prior to a merger or acquisition to assess risks and opportunities.
• Change Management - Strategies implemented to facilitate the transition during integration.
• Governance Structure - The framework for decision-making and accountability during PMI.
• Operational Structure - The arrangement of roles and responsibilities within the merged organization.
• Risk Management - The process of identifying and mitigating potential issues during integration.
• Communication Plan - A strategy for disseminating information to stakeholders during the integration process.
• Functional Areas - Specific departments involved in the integration, such as Finance, HR, IT, etc.
• Transition Services Agreement (TSA) - A contract outlining services provided by one party to another during the transition period.
• Integration Checklist - A tool used to track progress and ensure all necessary steps are completed during PMI.
• Performance Metrics - Measures used to evaluate the success of the integration process.
POST-MERGER INTEGRATION PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Post-merger Integration PowerPoint Slides: Complete Guide to Post-merger Integration (PMI) PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting