Cybersecurity Sorcery Cube (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 34 Slides
CYBER SECURITY PPT DESCRIPTION
In this comprehensive presentation, we delve into the core concepts of cybersecurity, exploring the multidimensional McCumber Cube and its three dimensions: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. We discuss the fundamental principles of the CIA Triad, emphasizing the importance of protecting data confidentiality, ensuring data integrity, and maintaining data availability. Additionally, we examine the different states of data – at rest, in transit, and in use – and analyze cybersecurity countermeasures, including preventive, detective, corrective, and deterrent measures. Furthermore, we introduce the ISO Cybersecurity Model as a framework for managing information security risks, providing organizations with a systematic approach to safeguarding their assets.
1. The Cybersecurity Sorcery Cube:
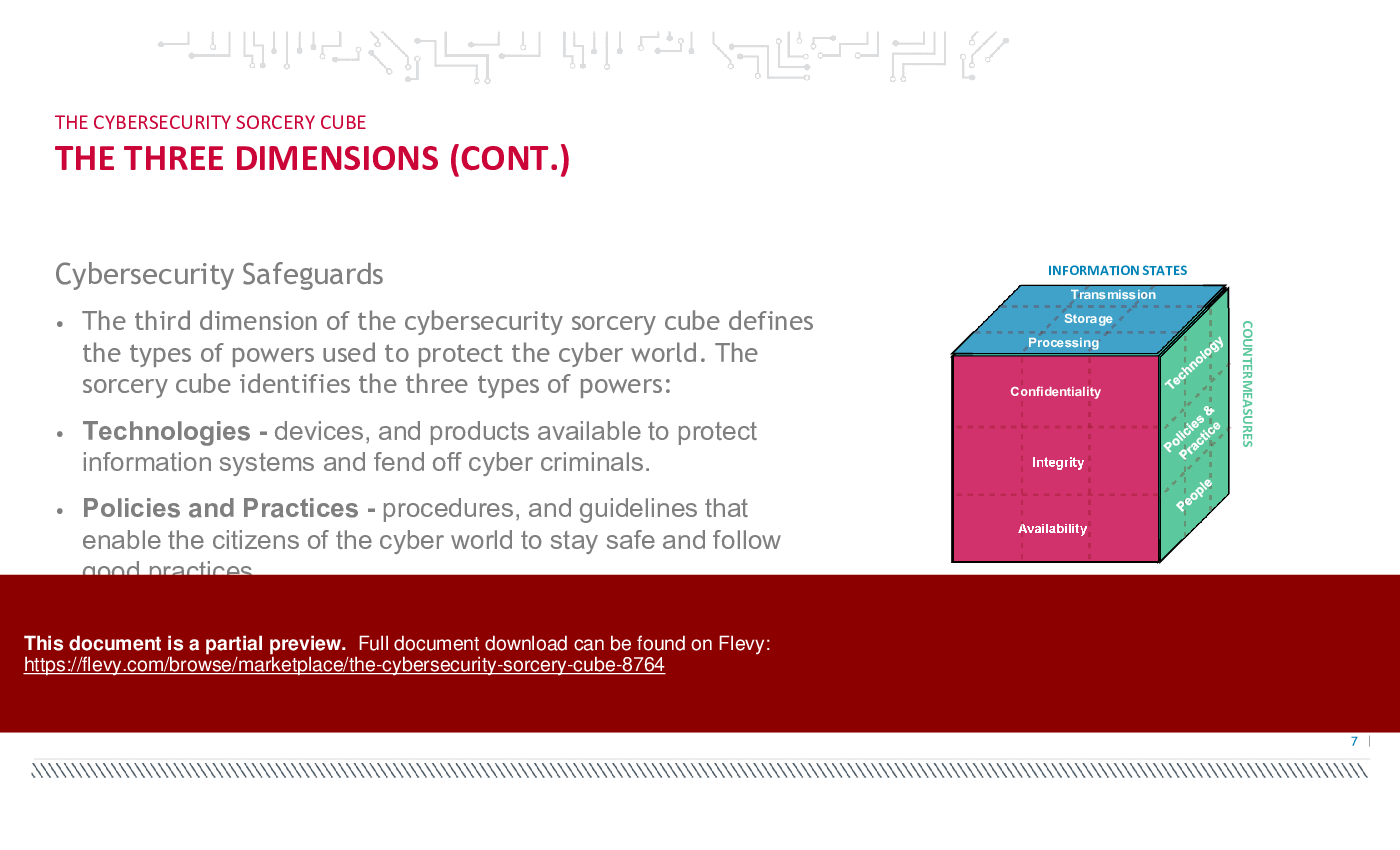
The McCumber Cube is a multidimensional model used to analyze and understand the various aspects of information security. It consists of three dimensions: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Confidentiality refers to protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and unaltered. Availability ensures that information and resources are accessible and usable when needed. These dimensions intersect to form different areas within the cube, representing different security concerns and priorities. Understanding and addressing these dimensions is essential for developing effective cybersecurity strategies.
2. CIA TRIAD:
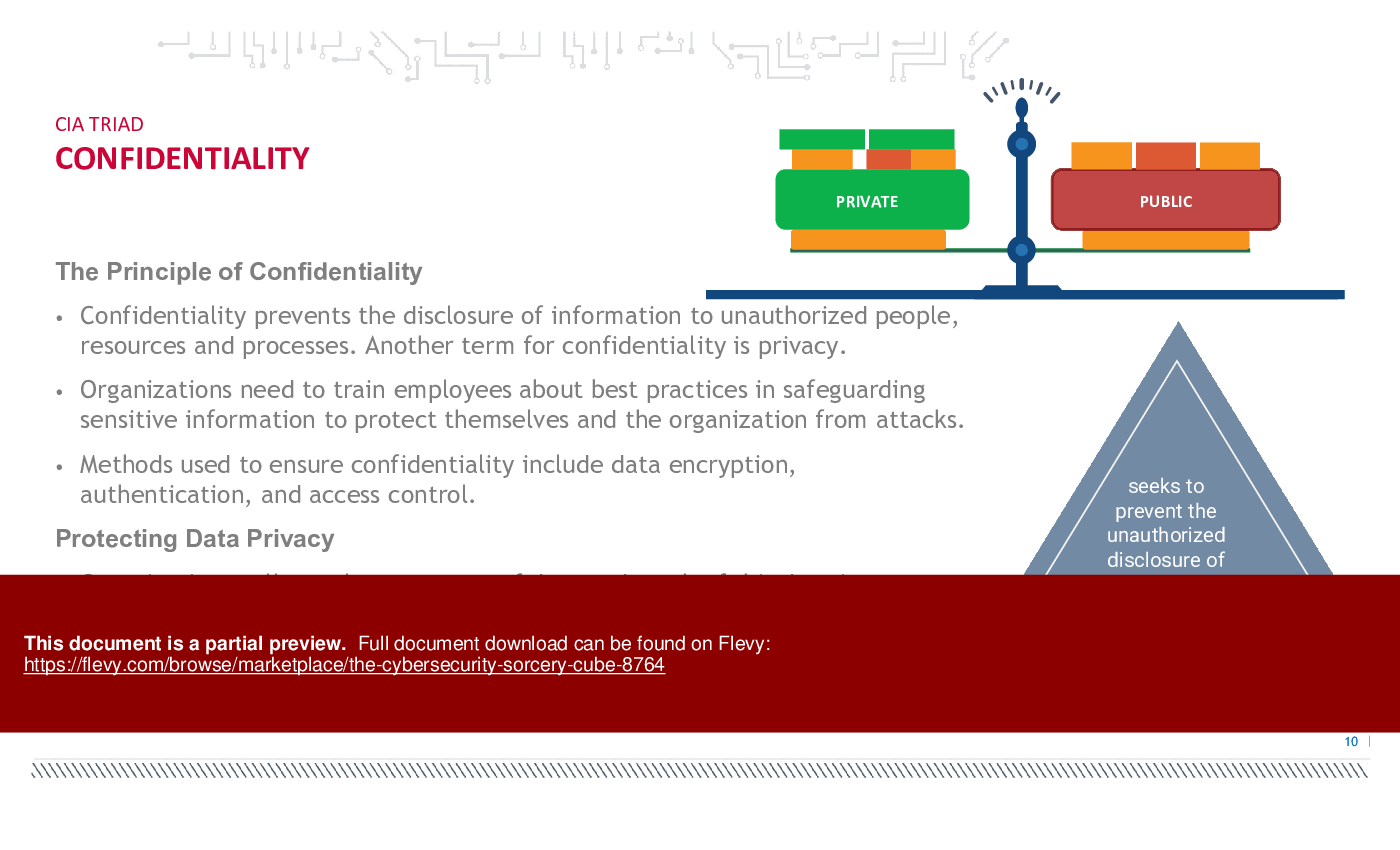
The CIA Triad is a fundamental concept in information security that consists of three principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Confidentiality ensures that information is only accessible to authorized individuals or entities and is not disclosed to unauthorized parties. Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and unaltered throughout its lifecycle. Availability ensures that information and resources are accessible and usable when needed by authorized users. These principles form the foundation of information security practices and are used to guide the implementation of security controls and measures to protect data and systems from various threats and risks.
3. States of Data:
Data can exist in three states: at rest, in transit, and in use. Data at rest refers to data that is stored in a storage medium, such as databases, files, or archives. Data in transit refers to data that is being transmitted over a network or between systems, such as emails, file transfers, or network communications. Data in use refers to data that is being processed or accessed by an application or system, such as data being manipulated in memory or displayed on a screen. Understanding the different states of data is important for implementing appropriate security controls and measures to protect data throughout its lifecycle.
4. Cybersecurity Countermeasures:
Cybersecurity countermeasures are measures taken to protect systems, networks, and data from cyber threats and attacks. There are various types of cybersecurity countermeasures, including preventive, detective, corrective, and deterrent measures. Preventive measures aim to prevent security incidents from occurring by implementing controls such as firewalls, antivirus software, and access controls. Detective measures aim to detect security incidents and breaches as they occur or shortly after, using tools such as intrusion detection systems and security monitoring. Corrective measures aim to respond to and mitigate the impact of security incidents, such as incident response and recovery plans. Deterrent measures aim to discourage attackers from targeting a system or organization by implementing measures such as security awareness training and security policies.
5. IT Security Management Framework:
The ISO Cybersecurity Model, also known as ISO/IEC 27001, is a widely recognized framework for managing information security risks. It provides a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, and managing security risks to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information assets. The framework consists of a set of policies, procedures, and controls that organizations can implement to establish, maintain, and continuously improve their information security management systems. It includes various components such as risk assessment, security controls, monitoring and measurement, and continual improvement. By adopting the ISO Cybersecurity Model, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to information security and enhance their ability to protect sensitive information and systems from cyber threats.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Cyber Security PowerPoint Slides: Cybersecurity Sorcery Cube PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting