Network Security - Key Concepts (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 87 Slides
CYBER SECURITY PPT DESCRIPTION
In this comprehensive presentation, we explore the dynamic landscape of Network Security, addressing critical topics such as the current state of cybersecurity, threat actors, malware, common network attacks, IP vulnerabilities, TCP and UDP vulnerabilities, IP services, network security best practices, and cryptography. We delve into the evolving tactics of threat actors, the diverse range of malware types, and the intricate vulnerabilities inherent in network protocols and services. Additionally, we outline essential network security best practices and highlight the vital role of cryptography in safeguarding data integrity and confidentiality. This presentation equips audiences with essential knowledge to navigate and mitigate modern cyber threats.
Current State of Cybersecurity:
The current state of cybersecurity is marked by a continuous battle between defenders and attackers. As organizations increasingly rely on digital technologies, the attack surface has expanded, leading to a rise in cyber threats and data breaches. Vectors of data loss include various attack methods such as phishing, ransomware, insider threats, and supply chain attacks. Cybercriminals target sensitive data for financial gain, espionage, or disruption, exploiting vulnerabilities in networks, systems, and applications.
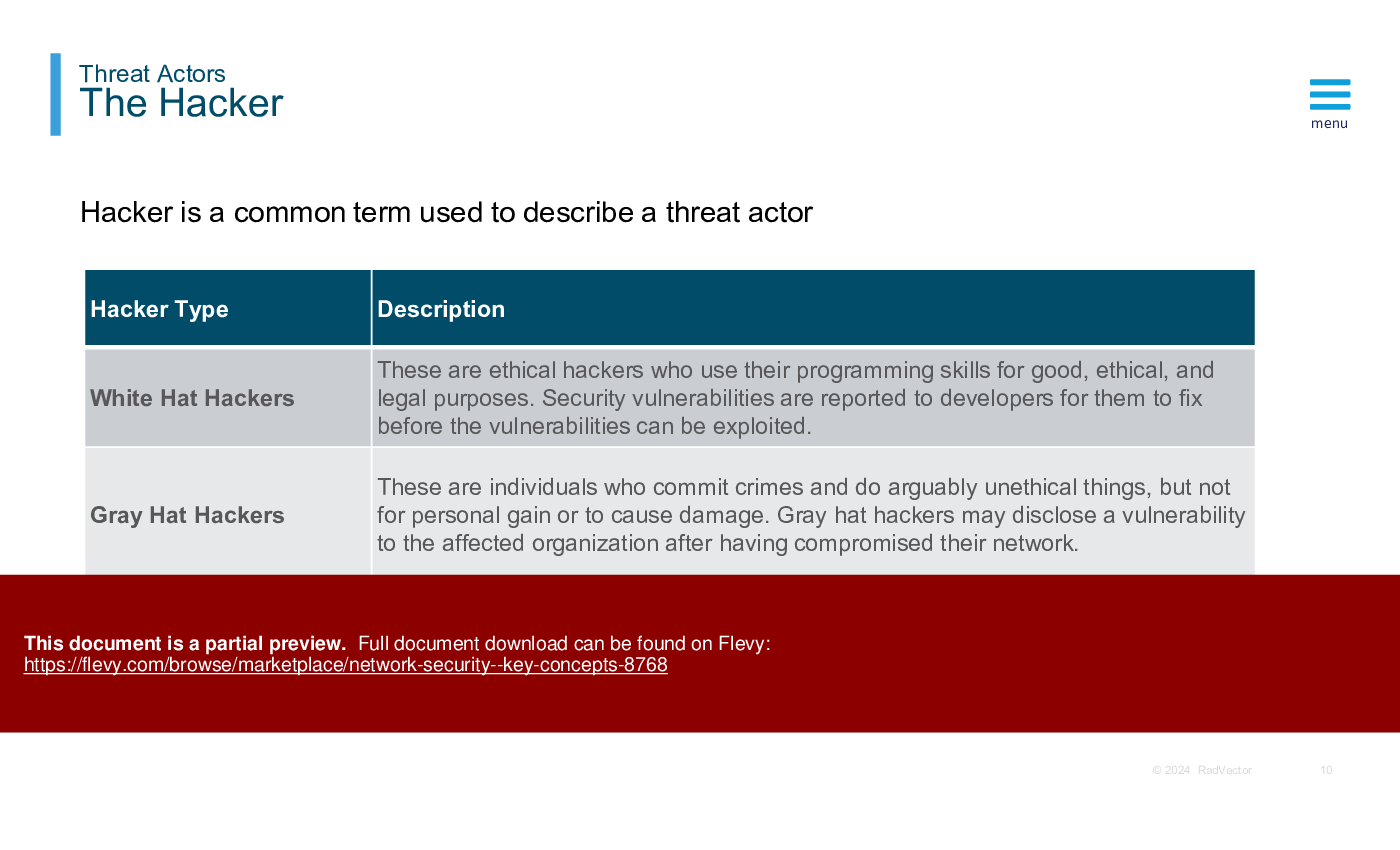
Threat Actors:
Threat actors employ a variety of tools and techniques to exploit networks and compromise data. These tools include malware, ransomware, exploit kits, phishing emails, social engineering tactics, and advanced persistent threats (APTs). Threat actors often use a combination of these tools to gain unauthorized access to networks, steal sensitive information, disrupt operations, or extort ransom payments.
Malware:
Malware encompasses a wide range of malicious software designed to infiltrate and damage computers and networks. Common types of malware include viruses, worms, Trojans, spyware, adware, and ransomware. Each type of malware has its own characteristics and methods of propagation, but they all pose significant risks to cybersecurity and data integrity.
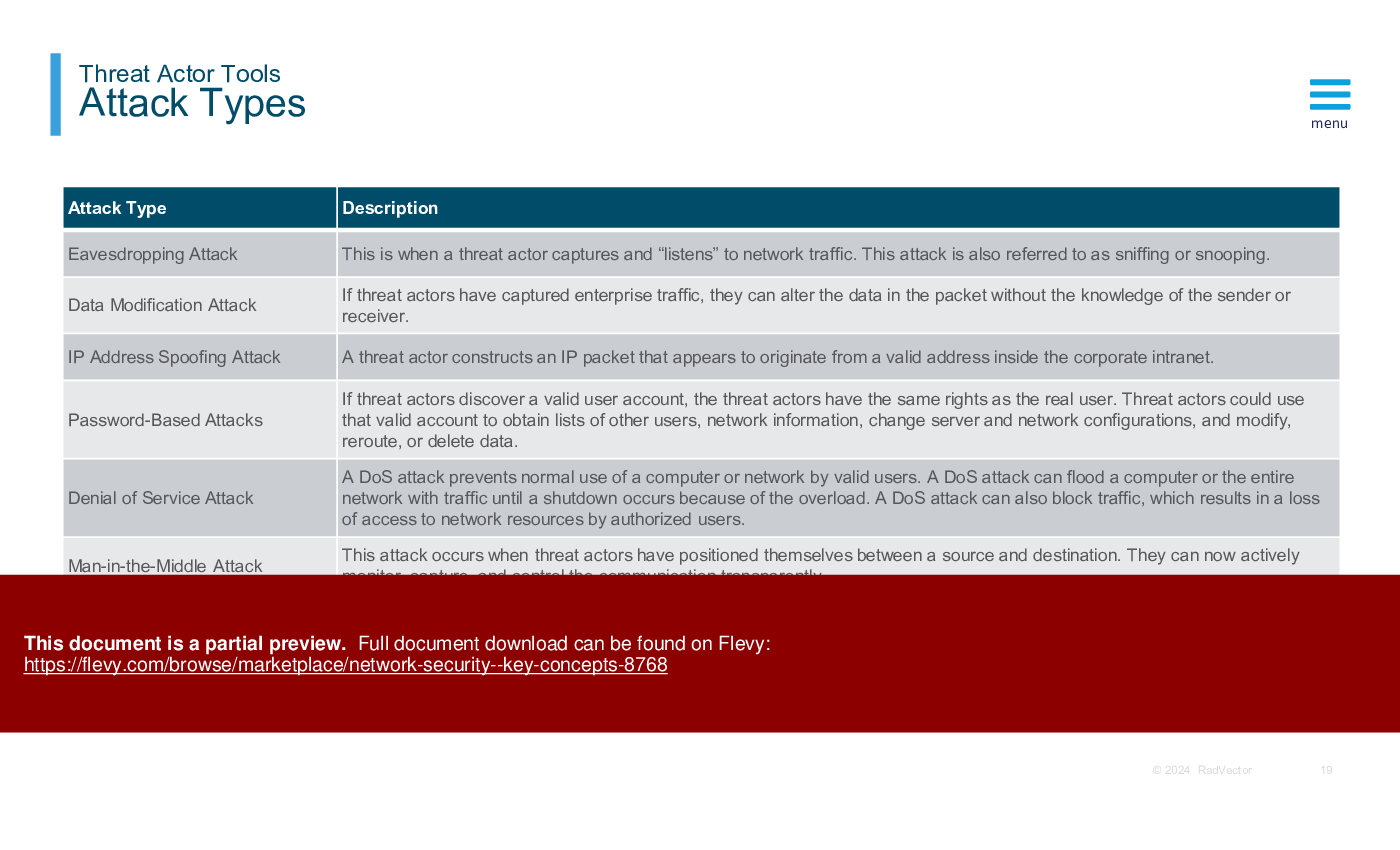
Common Network Attacks:
Common network attacks target vulnerabilities in network protocols, services, and devices to gain unauthorized access or disrupt operations. These attacks include Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, packet sniffing, and DNS spoofing. These attacks can lead to network downtime, data theft, or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
IP Vulnerabilities and Threats:
Threat actors exploit vulnerabilities in the Internet Protocol (IP) to compromise networks and systems. These vulnerabilities may include insecure configurations, weak authentication mechanisms, or outdated software. Threat actors can exploit IP vulnerabilities to launch various attacks, such as IP spoofing, IP fragmentation attacks, or IP address hijacking, to gain unauthorized access or disrupt network operations.
TCP and UDP Vulnerabilities:
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are common network protocols used for communication between devices on the Internet. Threat actors exploit vulnerabilities in TCP and UDP to launch attacks such as TCP SYN flooding, TCP reset attacks, UDP flooding, or UDP amplification attacks. These attacks can overload network resources, degrade network performance, or disrupt service availability.
IP Services:
IP services, such as Domain Name System (DNS), Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), are essential for network communication and management. However, threat actors can exploit vulnerabilities in these services to gain unauthorized access, intercept traffic, or launch attacks. For example, DNS cache poisoning, DHCP spoofing, or SNMP enumeration can be used to compromise network security and integrity.
Network Security Best Practices:
Implementing network security best practices is essential for protecting against cyber threats and data breaches. These practices include regular security assessments and audits, patch management, access control, encryption, network segmentation, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), security awareness training, and incident response planning. By following these best practices, organizations can mitigate risks and strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.
Cryptography:
Cryptography is a crucial component of cybersecurity that involves securing data through encryption, decryption, and authentication processes. Common cryptographic processes include symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, hashing, digital signatures, and key exchange protocols. These processes are used to protect data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity in transit and at rest. By employing cryptographic techniques, organizations can ensure the confidentiality of sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access or tampering.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Cyber Security PowerPoint Slides: Network Security - Key Concepts PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting