Foundations of Artificial Intelligence (AI) (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 108 Slides
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE PPT DESCRIPTION
Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Neural Networks: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
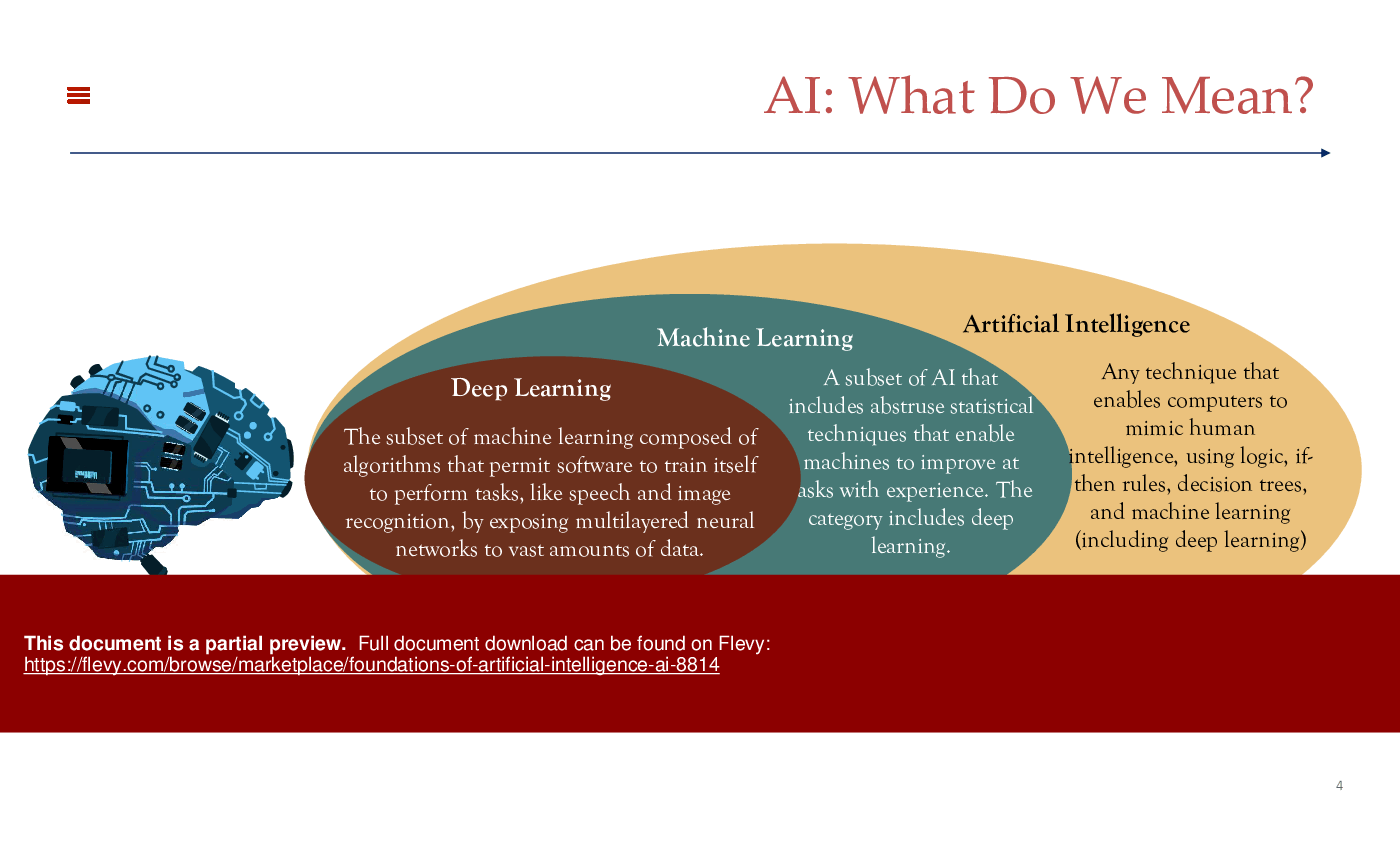
In this presentation, we will explore the core pillars of artificial intelligence (AI): Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Neural Networks (NN). These technologies are driving innovations across various industries, transforming how we interact with machines and data.
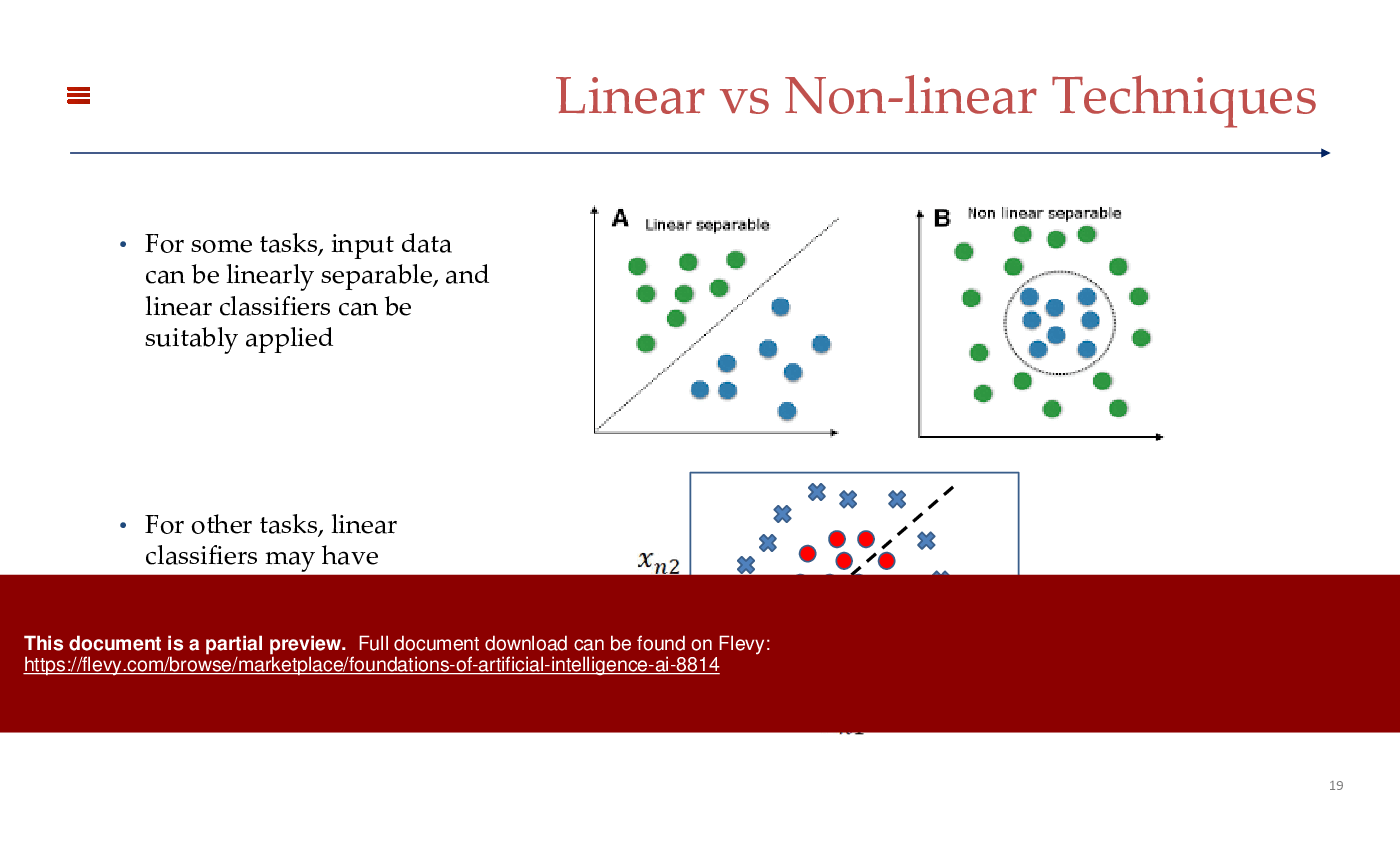
Machine Learning (ML)
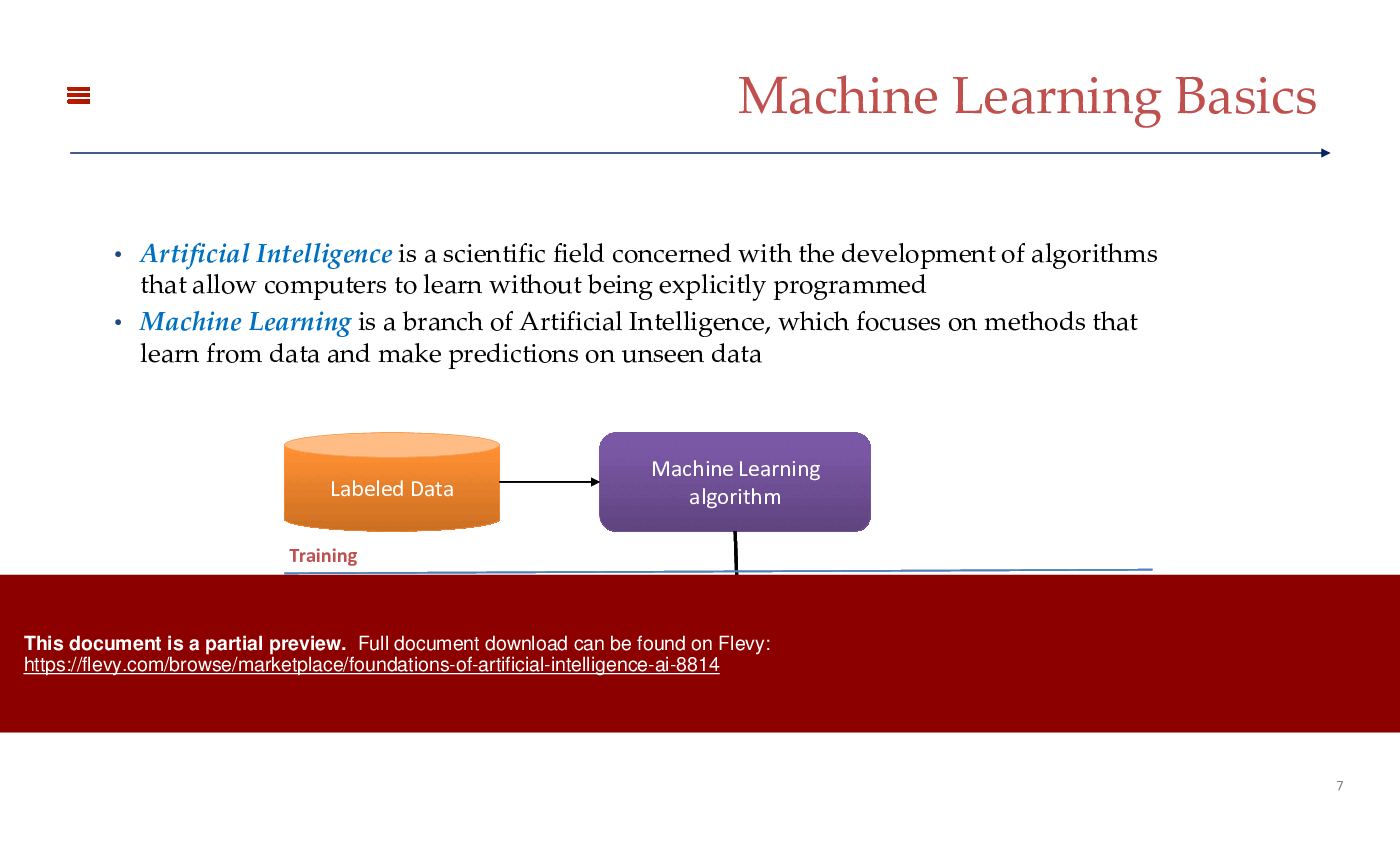
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that enable computers to learn from and make decisions based on data. Unlike traditional programming, where rules are explicitly coded, ML algorithms identify patterns and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed for the task. Common applications of ML include spam filtering, recommendation systems, and predictive analytics. There are three main types of ML:
1. Supervised Learning: Algorithms are trained on labeled data, making predictions based on input-output pairs.
2. Unsupervised Learning: Algorithms analyze and identify patterns in unlabeled data.
3. Reinforcement Learning: Algorithms learn optimal actions through trial and error, receiving rewards or penalties.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning is a specialized subset of ML that utilizes neural networks with many layers (hence "deep"). These deep neural networks are capable of learning and modeling complex patterns in large datasets. DL has revolutionized fields such as image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving. Key to DL's success is its ability to automatically extract features from raw data, reducing the need for manual feature engineering.
Neural Networks (NN)
Neural Networks are the foundation of DL and an essential part of ML. Inspired by the human brain, NNs consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized in layers. Each neuron processes input and passes the output to the next layer. Through training, neural networks adjust the weights of connections to minimize prediction errors. There are several types of neural networks:
1. Feedforward Neural Networks: The simplest type, where information flows in one direction from input to output.
2. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Primarily used for image processing, leveraging convolutional layers to capture spatial hierarchies.
3. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): Suitable for sequential data like time series and text, with connections that form directed cycles.
Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Neural Networks are the bedrock technologies driving the AI revolution. Their ability to analyze vast amounts of data and uncover insights is transforming industries, enabling advancements that were once thought impossible. By understanding and leveraging these technologies, we can develop intelligent systems that enhance our lives and drive future innovations.
This comprehensive presentation equips decision-makers with a solid understanding of AI fundamentals, including practical applications and methodologies. It emphasizes the importance of leveraging these technologies to drive innovation and operational efficiency across various sectors.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 108-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Foundations of Artificial Intelligence (AI)" presentation provides a comprehensive overview of AI, focusing on machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks. Developed by a team of experts with extensive consulting backgrounds, this PPTX equips corporate executives and consultants with the foundational knowledge necessary to understand and implement AI technologies. The presentation covers essential concepts, including supervised and unsupervised learning, neural network architectures, and training methodologies, enabling users to grasp the intricacies of AI and its applications in various sectors.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to understand AI fundamentals for strategic decision-making
• Integration leaders responsible for implementing AI solutions within their organizations
• Consultants advising clients on AI adoption and implementation strategies
• Data scientists and analysts looking to enhance their knowledge of machine learning and neural networks
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During AI strategy workshops to establish a foundational understanding among stakeholders
• In training sessions for teams transitioning to AI-driven projects
• As a reference guide for discussions on AI technologies and their applications
Learning Objectives
• Define key concepts of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning
• Differentiate between supervised and unsupervised learning techniques
• Identify various neural network architectures and their applications
• Explain the training processes for neural networks, including gradient descent and regularization methods
• Analyze the role of activation functions in neural networks
• Evaluate the effectiveness of different machine learning algorithms
Table of Contents
• Machine Learning Basics (page 6)
• Areas of Machine Learning (page 8)
• Supervised Learning Techniques (page 10)
• Unsupervised Learning Techniques (page 11)
• Introduction to Deep Learning (page 26)
• Neural Network Architectures (page 93)
• Training Neural Networks (page 53)
Primary Topics Covered
• Machine Learning Basics - An introduction to the field of AI, emphasizing algorithms that enable computers to learn from data without explicit programming.
• Supervised Learning - Techniques that utilize labeled data for training models, including classification and regression methods.
• Unsupervised Learning - Approaches that identify patterns in unlabeled data, such as clustering and dimensionality reduction.
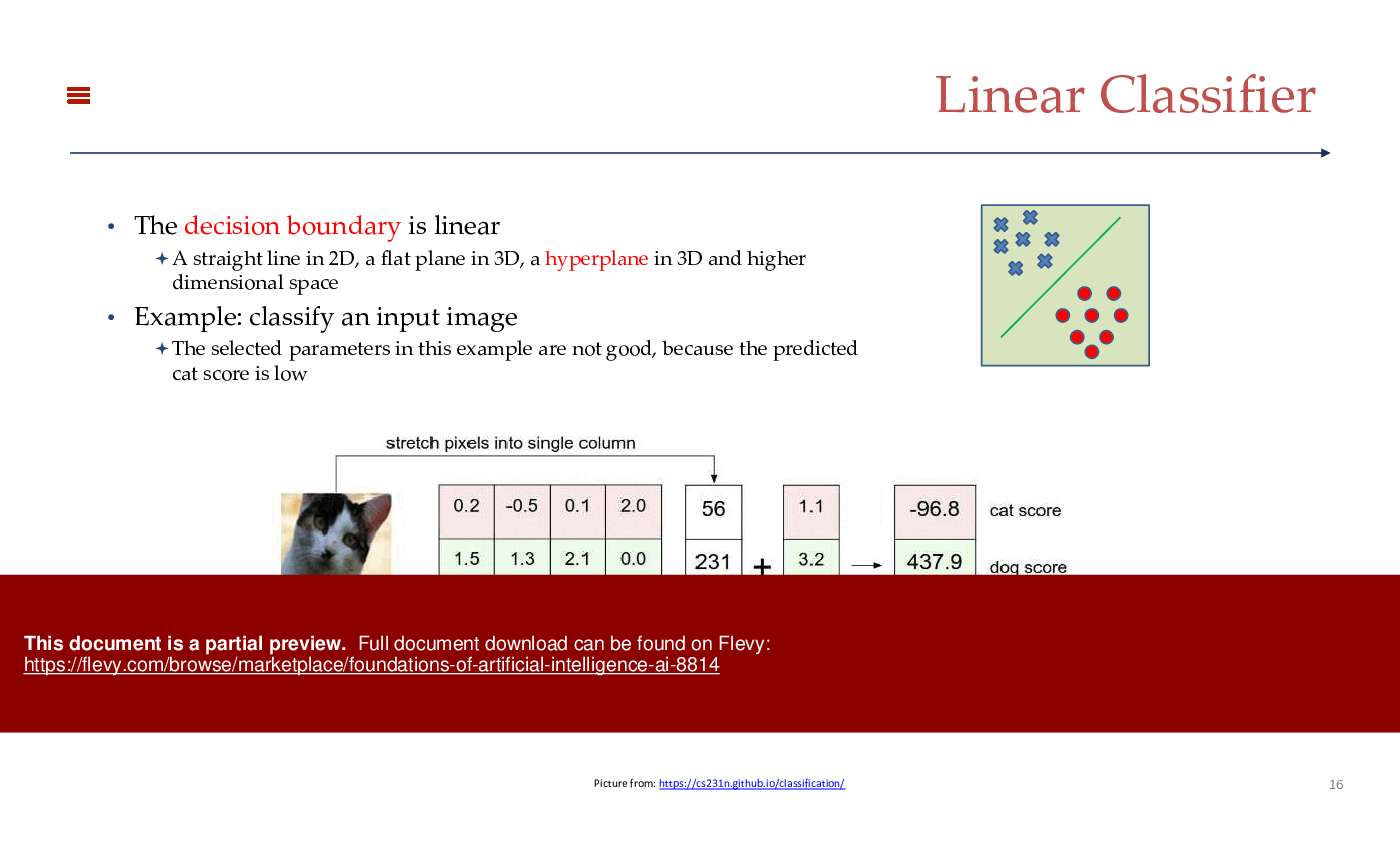
• Deep Learning - A subfield of machine learning that employs multi-layered neural networks to learn complex data representations.
• Neural Network Architectures - Overview of various architectures, including convolutional and recurrent neural networks, tailored for specific tasks.
• Training Neural Networks - Methods for optimizing neural networks, including gradient descent, loss functions, and regularization techniques.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Machine learning algorithm templates for supervised and unsupervised learning
• Neural network architecture diagrams for visual representation of different models
• Training process flowcharts for implementing gradient descent and backpropagation
• Activation function comparison charts for evaluating performance in neural networks
• Regularization technique guidelines to prevent overfitting in models
Slide Highlights
• Overview of machine learning basics, outlining the distinctions between supervised and unsupervised learning
• Detailed explanation of supervised learning techniques, including support vector machines and decision trees
• Visual representation of neural network architectures, showcasing convolutional and recurrent networks
• Step-by-step breakdown of the training process for neural networks, including gradient descent and backpropagation
• Insights into activation functions and their impact on model performance
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to AI and Machine Learning (60 minutes)
• Discuss the fundamentals of AI and its importance in modern business
• Explore the differences between machine learning, deep learning, and traditional programming
Hands-on Session on Supervised Learning Techniques (90 minutes)
• Review various supervised learning algorithms and their applications
• Engage in practical exercises to implement classification and regression models
Deep Learning and Neural Networks Overview (60 minutes)
• Introduce deep learning concepts and neural network architectures
• Analyze case studies showcasing successful deep learning applications
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the presentation by incorporating industry-specific examples relevant to your organization
• Adjust the depth of technical content based on the audience's familiarity with AI concepts
• Include case studies or success stories from your organization to illustrate practical applications of AI
Secondary Topics Covered
• Reinforcement learning and its applications in AI
• The impact of big data on machine learning and AI development
• Ethical considerations in AI implementation
• Future trends in AI technology and its implications for businessesDocument FAQ
What is the difference between machine learning and deep learning?
Machine learning encompasses a range of algorithms that allow computers to learn from data, while deep learning is a subset of machine learning that utilizes multi-layered neural networks for more complex data representation.
What are the main types of supervised learning?
Supervised learning primarily includes classification and regression techniques, where models are trained on labeled data to make predictions.
How do neural networks learn?
Neural networks learn through a process called training, where they adjust their weights and biases based on the input data and the corresponding output, using algorithms like gradient descent.
What is overfitting in machine learning?
Overfitting occurs when a model learns the noise in the training data instead of the underlying pattern, resulting in poor performance on unseen data. Regularization techniques can help mitigate this issue.
What are activation functions, and why are they important?
Activation functions determine the output of a neuron in a neural network, introducing non-linearity into the model, which is crucial for learning complex patterns in data.
How does gradient descent work?
Gradient descent is an optimization algorithm used to minimize the loss function by iteratively adjusting the model parameters in the direction of the steepest descent.
What is the role of regularization in training neural networks?
Regularization techniques, such as weight decay and dropout, are used to prevent overfitting by adding a penalty for large weights or randomly dropping units during training.
What are some common applications of AI in business?
AI is used in various applications, including predictive analytics, customer service automation, fraud detection, and personalized marketing strategies.
Glossary
• Artificial Intelligence (AI) - Techniques enabling computers to mimic human intelligence.
• Machine Learning (ML) - A branch of AI focused on algorithms that learn from data.
• Deep Learning (DL) - A subset of ML using multi-layered neural networks for complex data representation.
• Neural Networks (NN) - Computational models inspired by the human brain, used for pattern recognition.
• Supervised Learning - Learning from labeled data to make predictions.
• Unsupervised Learning - Discovering patterns in unlabeled data.
• Activation Function - A mathematical function that determines the output of a neuron.
• Gradient Descent - An optimization algorithm for minimizing the loss function.
• Overfitting - A modeling error due to excessive complexity, leading to poor generalization.
• Regularization - Techniques to prevent overfitting by adding constraints to the model.
• Support Vector Machine (SVM) - A supervised learning algorithm for classification tasks.
• Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) - A type of NN primarily used for image data.
• Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) - A type of NN designed for sequential data processing.
• Loss Function - A function that measures the difference between predicted and actual outcomes.
• Hyper-parameter - Parameters that are set before the learning process begins, influencing model training.
• Clustering - An unsupervised learning technique for grouping similar data points.
• Dimensionality Reduction - Techniques for reducing the number of features in a dataset while preserving important information.
• Ensemble Learning - Combining multiple models to improve performance.
• Cross-Validation - A technique for assessing how the results of a statistical analysis will generalize to an independent dataset.
• Dropout - A regularization technique that randomly drops units during training to prevent overfitting.
• Batch Normalization - A technique to improve training speed and stability by normalizing layer inputs.
Source: Best Practices in Artificial Intelligence PowerPoint Slides: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence (AI) PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting