Entrepreneurial Decision Making and the Effect on Business Models (PDF)
PDF document 21 Pages
DECISION MAKING PDF DESCRIPTION
In this paper we review the results of an empirical research of a number of organisations. The research shows a difference in the evaluation of a business model of an organization by the entrepreneur and by the researchers. It shows, based on an extensive list of questions, the decision to be taken on strategic level differs by entrepreneurs compared with the decision to be taken by researchers based on the same set of questions. The paper goes into the field of entrepreneurs and the factors why they drive their own business like they do and how they gather data and process this data to prepare for a decision on strategic level. The paper describes how cognitive possibilities of the entrepreneur, biases and heuristics, experience and type of personality influence the decision making process. Finally future implications are mentioned as how to influence the process of decision making at strategic level by entrepreneurs in order to be able to have a more objective decision process based on facts rather than on gut feeling.
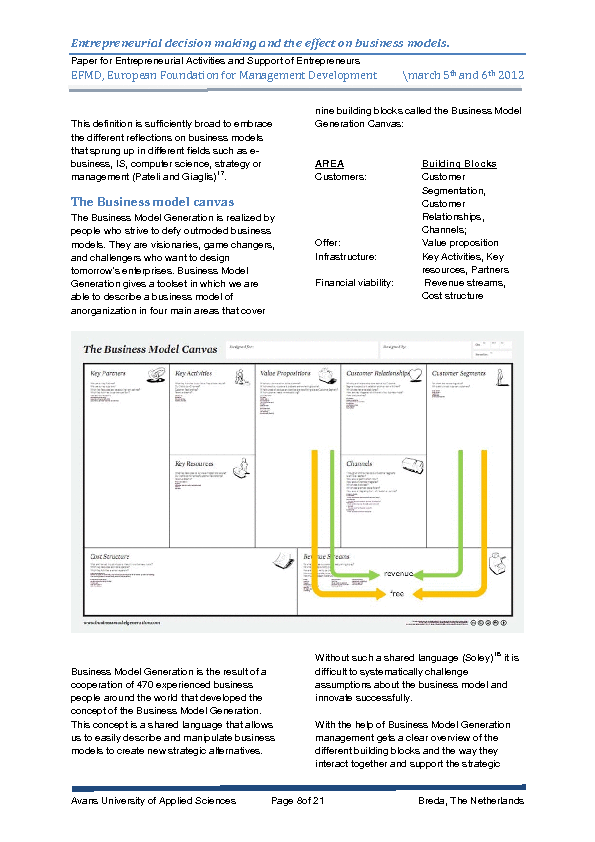
Researchers and authors have been supporting entrepreneurs in their development of their business and the challenges they have to cope within the current economic situation. Using methods and techniques such as Business Model Generation of Osterwalder and Pigneur business models of organizations are mapped in nine different building blocks. Together they are called the Canvas of the business model. Included in the methodology an extensive questionnaire helps to evaluate the business model and the result is a swot of the business model of the organization. Both researchers and entrepreneurs themselves thev filled out this questionnaire resulting in two evaluations of the same business model. To be able to have a good understanding of these evaluations the results of the questionnaire are placed in a simple spreadsheet. To get a clear view of the difference of the two evaluations both evaluations were put together is a third simple spreadsheet. With this graphical overview the differences in the evaluation from the researchers compared with the entrepreneurs became very clear.
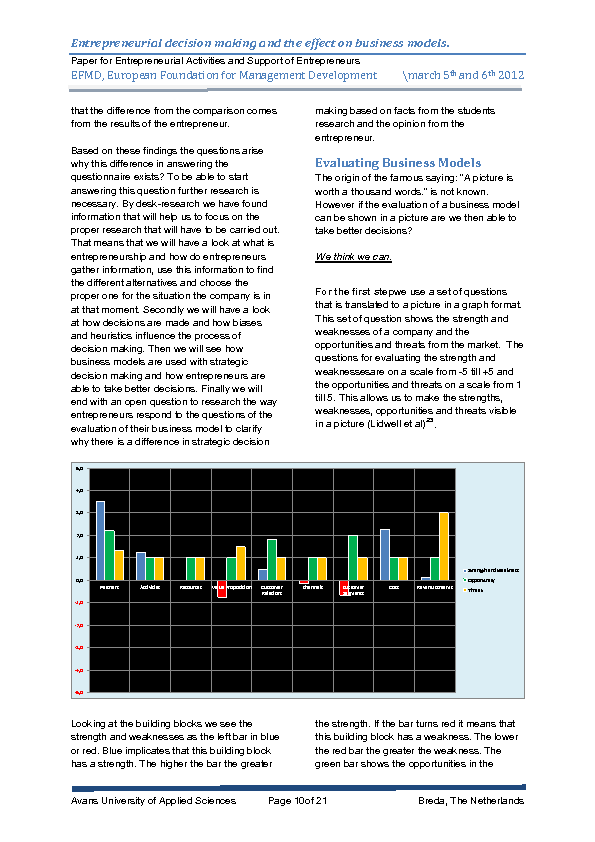
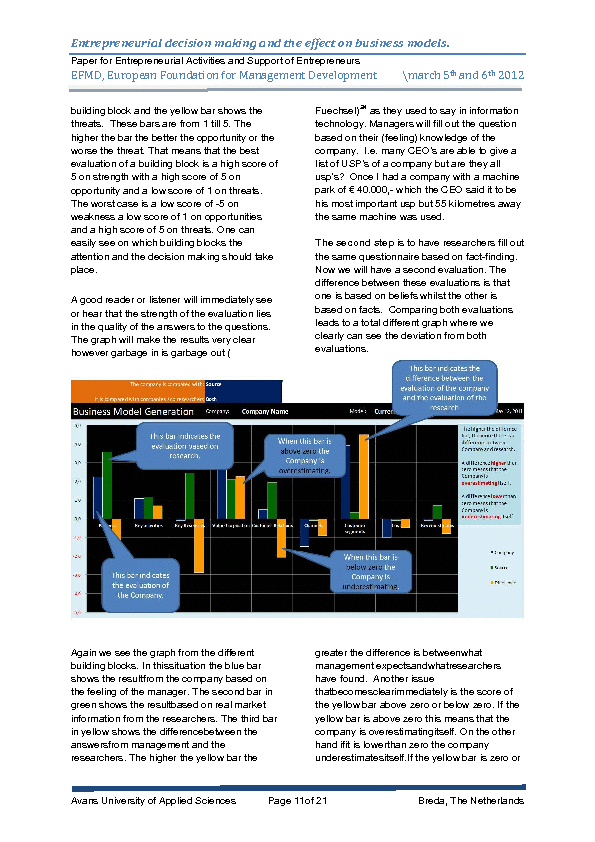
The authors therefore questioned themselves why there could be such a big difference in the evaluations. In one specific example form a company in the metal industry a remarkable difference showed in the two evaluations. Choices to be made on strategic lever for the company should be price raise and cost reduction based on the evaluation of the entrepreneur. Using the same questionnaire the researchers came with a total different advice on strategic level. The researchers showed very clear that there advice was in the area of channels and customer relationships. When looking to these two building blocks of the canvas of Business Model Generation the comparison showed a 180 degrees opposite result. In the first situation together with the current bad economic situation the chance of surviving this crisis with price raises and cost reduction is much lower than invest in customer relationships and the channels to inform and reach them. It is also known that in bad economic situations a counter-cyclical investment can give a company a greater chance of continuity. In the search of an explanation concerning this bi gap the authors researched by desk-research how a decision making process works with entrepreneurs. The most important factors that influence the decision making process of entrepreneurs appears to be a number of susceptible factors. Before we go into these factors it should be clear what an entrepreneurs does in his decision making process. A decision making process consists of three different steps from data gathering, data interpreting and the final decision. Data gathering an taking decisions is a clear process where the interpretation of the data that should lead to information and knowledge is not.
Looking at the factors that in the end make up the interpretation of data and the situation to take a decision the first one is how the entrepreneur will get the proper data on which to decide. Once this information from ICT systems appears to be incorrect the entrepreneur will never rely on that system again. Secondly it shows that in the current information overload entrepreneurs must have the capabilities to select and combine all the data that is available. Too much data from different sources can lead to the maximum entrepreneurs can handle and transcends in certain situations the cognitive possibilities of the entrepreneur. The third factor the entrepreneur takes into account are the biases that the entrepreneur has and influence the decision to make. In uncertain situations entrepreneurs do not follow a logical set of rules to decide what to do. They more rely on biases that give them the idea to be certain about the decision to take. Heuristics, as the next factor is closely related to the biases entrepreneurs use in their decision making process. Based on past experience entrepreneurs tend to decide in the same way they did in an earlier decision making process. However past situations are mostly not the same as current situations and therefore entrepreneurs can make wrong decision using their heuristics. People tend to react based on the personality. This is the fifth factor why entrepreneurs take decisions like they do. More important is the personality off entrepreneurs in stressful situations. One cannot control the behavior and falls back on the personality and reacts based on this personality.
The decision making process is influenced by the factors mentioned above. Entrepreneurs take decisions to reach future success for their company or themselves. Included they look at the different risks involved to reach this future success. Entrepreneurs within a complex situation or with partly unknown circumstances will take decisions based on routine like they did before. This can be very risky because the former circumstances are mostly not the same as the current and therefore a past decision can work out differently in a present situation. Entrepreneurs with a lot of job experience take decisions based on intuition. This means that the person in this situation has the possibility to mull over the issue over a night?s sleep and then come up with a decision. Waking up means that the rational mind takes over the unconscious mind that was mulling over the subject and can take a decision.
Knowing the different factors that make up the decision making process of entrepreneurs a very interesting question remains unanswered. Can the gap between the entrepreneurial decision making process and the researchers decision making process be reduced or even closed. Therefore a new empirical research is started at Avans University in order to discover how researchers and knowledge institutions are able to support the decision making process of entrepreneurs.
We would really encourage entrepreneurs to take part in this further research.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Decision Making, Entrepreneurship PDF: Entrepreneurial Decision Making and the Effect on Business Models PDF (PDF) Document, marijnmulders