Building Resilience Toolkit (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) + Word (DOCX) 712 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Offers tools and strategies to build organizational resilience and navigate uncertainty effectively.
- Includes templates for developing comprehensive crisis management and business continuity plans.
- Equips leaders with resources to foster a culture of resilience within their teams.
BUSINESS RESILIENCE PPT DESCRIPTION
Curated by McKinsey-trained Executive
Boost Your Business Resilience with the Ultimate Toolkit: A Comprehensive Resource
In today's rapidly changing business environment, resilience is more critical than ever. The Complete Business Resilience Toolkit offers everything you need to build and sustain a resilient organization. With over 710+ slides and a 70+ page Word file, this comprehensive toolkit covers every aspect of resilience, from foundational theories to practical applications.
CONTENT OVERVIEW
• Introduction to Resilience in Business
• The Foundations of Resilience
• Dealing with Pressure & Change
• Causes of Lack of Resilience
• Factors for Building Resilience
• Using Motivation to Build Resilience
• Time Management as a Resilience Tool
• Developing Self-Awareness for Resilience
• Energy Management for Resilience
• Stress Management for Resilience
• Relaxation Techniques for Resilience
• The Role of Teamwork in Resilience
• Understanding the Behavior Cycle in Business
• The Role of Emotional Intelligence (EI) in Resilience
• Factors Affecting Your Attitude Toward Resilience
• Managing Pressure for Resilience
• Tips for Building Resilience in Business
Templates for Resilience Planning
• Resilience Strategy Template
• Business Continuity Plan Template
• Crisis Management Plan Template
• Scenario Planning Template
• Risk Assessment Template
• Stress Management Plan Template
• Work-Life Balance Template
• Self-Awareness Development Template
• Team Resilience Building Template
• Leadership Resilience Plan Template
• Organizational Resilience Roadmap Template
• Emotional Intelligence Development Template
• Behavior Cycle Management Template
• Feedback Loop Template
• Trust Building Plan Template
• Conflict Resolution Strategy Template
• Communication Plan Template
• Supportive Work Environment Design Template
• Performance and Well-being Tracking Template
• Decision-Making Framework Template
• Relaxation Schedule Template
• Mindfulness Integration Template
• Growth Mindset Development Template
• Positive Attitude Maintenance Template
• Pressure Management Framework Template
• Stress-Resilient Workplace Design Template
• Organizational Resilience Culture Template
• Continuous Improvement Plan Template
Worksheets and Exercises for Building Resilience
• Self-Reflection Worksheet
• Mindfulness Practice Worksheet
• Emotional Awareness Exercise
• Cognitive Distortion Identification Worksheet
• Positive Self-Talk Worksheet
• Behavior Tracking Worksheet
• Gratitude Practice Worksheet
• Stress Trigger Identification Worksheet
• Empathy Development Exercise
• Resilience Assessment Worksheet
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Understanding the Importance of Resilience in Business
Resilience in a business context refers to the ability of an organization to withstand, adapt to, and recover from challenges. This concept goes beyond mere survival; it's about emerging from adversity stronger and more capable than before. The importance of resilience has never been more apparent, especially in the face of global trends such as technological disruption, economic uncertainty, and the increasing complexity of the business environment.
1.1 Overview of Resilience in Business
Resilience is not a new concept, but its relevance in the modern business environment has grown significantly. Historically, businesses focused on stability and predictability. However, with the advent of globalization, digital transformation, and volatile markets, the need for resilience has become paramount.
1.1.1 Definition of Resilience: At its core, resilience is the capacity to recover quickly from difficulties. In business, it involves preparing for disruptions, maintaining critical operations during a crisis, and adapting to new circumstances post-crisis.
1.1.2 Importance of Resilience in Business: Resilience is essential for ensuring business continuity, protecting employee well-being, and maintaining a competitive edge. Resilient organizations are better equipped to manage risks, seize opportunities, and sustain long-term growth.
1.1.3 Historical Perspective: Evolution of Resilience in Business: The concept of resilience has evolved from risk management and crisis response to a broader, more proactive approach that encompasses organizational culture, leadership, and strategic planning.
The Foundations of Resilience
Building resilience starts with understanding its theoretical foundations and the characteristics that define resilient individuals and organizations.
2.1 Theoretical Foundations of Resilience
2.1.1 Psychological Resilience: Concepts and Theories – Psychological resilience refers to an individual's ability to mentally and emotionally cope with a crisis or return to pre-crisis status quickly. This concept is grounded in theories of stress and coping, which emphasize the importance of adaptability and mental flexibility.
2.1.2 Organizational Resilience: Frameworks and Models – Organizational resilience involves a structured approach to identifying risks, developing response strategies, and fostering a culture that supports resilience. Frameworks such as the Resilience Wheel and the Adaptive Cycle provide models for understanding and enhancing organizational resilience.
2.1.3 The Role of Systems Thinking in Resilience: Systems thinking emphasizes the interconnections within an organization. By understanding how different parts of a business interact, leaders can develop more effective strategies for building resilience.
2.2 Key Characteristics of Resilient Individuals and Organizations
Resilience is characterized by adaptability, persistence, and a proactive approach to challenges.
2.2.1 Adaptability and Flexibility: The ability to pivot and adjust strategies in response to changing conditions is a hallmark of resilience.
2.2.2 Persistence and Determination: Resilient organizations and individuals persist through challenges, maintaining focus on long-term goals even in the face of adversity.
2.2.3 Emotional Stability and Composure: Maintaining emotional control during crises helps individuals and teams make better decisions and reduces the likelihood of panic-driven mistakes.
2.2.4 Proactive Attitude and Preparedness: Resilient businesses don't just react to crises—they anticipate them and prepare accordingly.
Dealing with Pressure and Change
Change is a constant in the business world, and the ability to manage pressure and navigate change is essential for resilience.
3.1 Understanding Business Pressure
3.1.1 Sources of Pressure in the Workplace: Common sources include tight deadlines, high performance expectations, and interpersonal conflicts. Recognizing these sources is the first step in developing strategies to manage them.
3.1.2 The Impact of Pressure on Decision Making: Pressure can cloud judgment, leading to rushed decisions that may not be in the best long-term interest of the business.
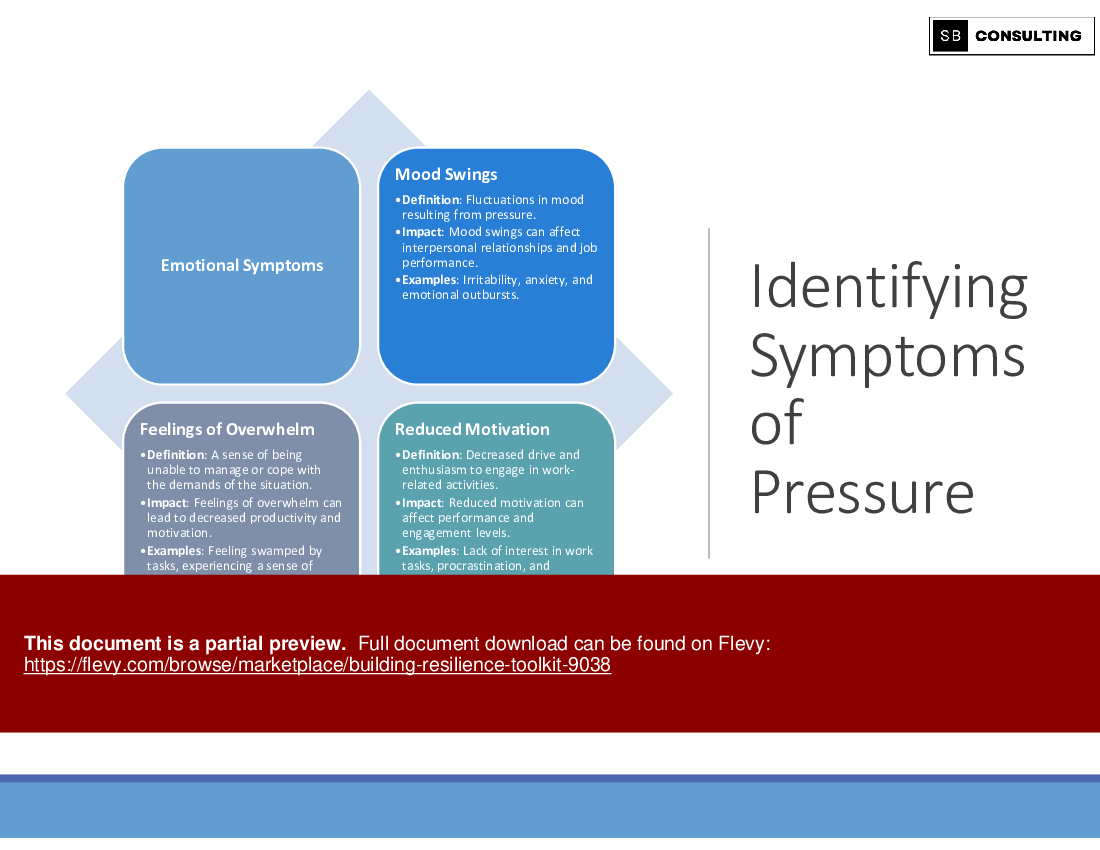
3.1.3 Identifying Symptoms of Pressure: Recognizing the signs of stress in oneself and others is crucial for early intervention and preventing burnout.
3.2 The Nature of Change in Business
3.2.1 Types of Organizational Change: Change can be strategic, structural, process-related, or cultural. Each type requires different strategies for management and adaptation.
3.2.2 The Change Curve and Emotional Responses: The change curve describes the emotional stages individuals go through during change, from shock and denial to acceptance and commitment.
3.2.3 Resistance to Change: Causes and Solutions: Resistance often stems from fear of the unknown or a perceived threat to job security. Effective communication and involvement in the change process can help mitigate resistance.
3.3 Strategies for Managing Pressure
3.3.1 Cognitive Behavioral Approaches: Techniques such as cognitive restructuring help individuals challenge and change negative thought patterns that contribute to stress.
3.3.2 Mindfulness and Pressure Management: Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, can reduce stress and improve focus, making it easier to handle pressure.
3.3.3 Developing a Pressure-Resilient Mindset: A resilient mindset involves viewing challenges as opportunities for growth rather than threats.
3.4 Navigating Change Effectively
3.4.1 Change Management Principles: Effective change management involves clear communication, stakeholder engagement, and a structured approach to implementing change.
3.4.2 Communication Strategies During Change: Open and transparent communication is key to reducing uncertainty and gaining buy-in from employees during change.
3.4.3 Supporting Teams Through Change: Providing support through training, resources, and emotional encouragement helps teams adapt to change more effectively.
Causes of Lack of Resilience
Understanding the barriers to resilience is essential for addressing them.
4.1 Identifying Signs of Low Resilience
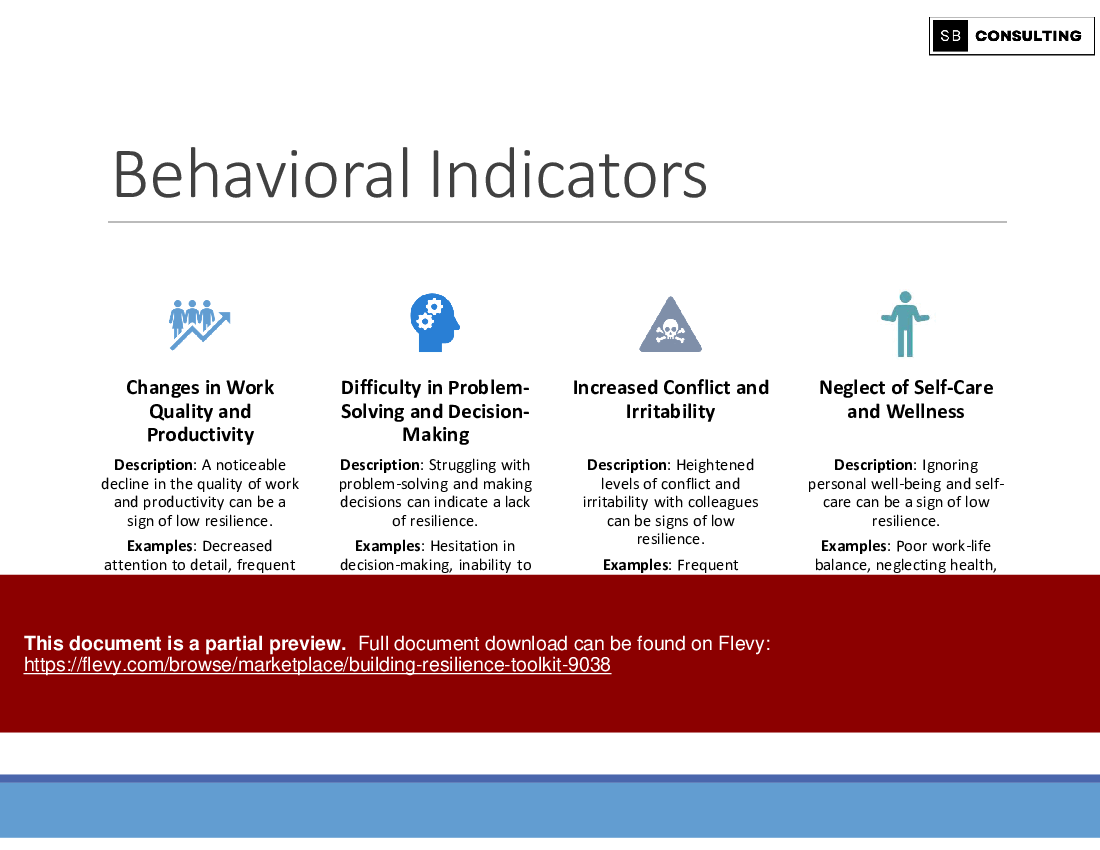
4.1.1 Behavioral Indicators: Low resilience often manifests in behaviors such as avoidance, excessive worry, and difficulty making decisions.
4.1.2 Psychological and Emotional Signs: Anxiety, depression, and chronic stress are common indicators of low resilience.
4.1.3 Organizational Symptoms of Low Resilience: High employee turnover, low morale, and resistance to change are signs that an organization may lack resilience.
4.2 Common Causes of Resilience Erosion
4.2.1 Chronic Stress and Burnout: Prolonged exposure to stress without adequate recovery can erode resilience over time.
4.2.2 Lack of Control and Uncertainty: Feeling powerless in the face of challenges undermines resilience.
4.2.3 Poor Organizational Culture: A toxic work environment can drain energy and motivation, making it difficult to maintain resilience.
4.2.4 Inadequate Support Systems: Without strong support networks, individuals and organizations are less able to bounce back from adversity.
4.3 The Role of External and Internal Stressors
4.3.1 External Factors: Economic downturns, technological disruptions, and social changes are external stressors that can impact resilience.
4.3.2 Internal Factors: Leadership style, organizational culture, and internal processes play a significant role in determining an organization's resilience.
4.3.3 The Interplay Between External and Internal Stressors: Resilience is often compromised when internal vulnerabilities intersect with external pressures.
Factors for Building Resilience
Building resilience requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both personal and organizational factors.
5.1 Personal Factors Influencing Resilience
5.1.1 Growth Mindset and Resilience: A growth mindset, which emphasizes learning and development, is crucial for personal resilience.
5.1.2 Emotional Regulation Skills: The ability to manage emotions effectively is a key component of resilience.
5.1.3 Physical Well-being and Resilience: Good physical health supports mental and emotional resilience.
5.1.4 Social Support Networks: Strong relationships provide emotional support and practical assistance during tough times.
5.2 Organizational Factors Supporting Resilience
5.2.1 Leadership Commitment to Resilience: Leaders who prioritize resilience set the tone for the entire organization.
5.2.2 Fostering a Positive Organizational Culture: A culture that encourages collaboration, innovation, and support enhances resilience.
5.2.3 Developing Resilient Teams: Resilient teams are characterized by strong communication, trust, and a shared sense of purpose.
5.2.4 Systems and Processes for Resilience: Robust systems and processes that support adaptability and continuous improvement are essential for organizational resilience.
5.3 The Role of Leadership in Resilience Building
5.3.1 Resilient Leadership Characteristics: Resilient leaders demonstrate adaptability, emotional intelligence, and a commitment to their team's well-being.
5.3.2 Leadership Behaviors that Foster Resilience: Encouraging open communication, providing resources for stress management, and leading by example are key behaviors.
5.3.3 Coaching and Mentoring for Resilience: Leaders who act as coaches and mentors help develop resilience in their teams by providing guidance and support.
Building a Resilience Culture
Creating a culture of resilience requires commitment and consistent effort.
6.1 Defining a Resilience Culture
6.1.1 Characteristics of a Resilient Culture: A resilient culture is characterized by adaptability, continuous learning, and a proactive approach to challenges.
6.1.2 Benefits of a Resilient Culture: Organizations with a resilient culture are more likely to thrive in the face of adversity and maintain a competitive edge.
6.1.3 Challenges in Creating a Resilient Culture: Resistance to change, entrenched behaviors, and lack of leadership support can hinder efforts to build a resilient culture.
6.2 Strategies for Developing a Resilient Culture
6.2.1 Promoting Open Communication: Encouraging open and honest communication helps identify issues early and fosters trust.
6.2.2 Encouraging Continuous Learning and Innovation: A culture that values learning and innovation is better equipped to adapt to change.
6.2.3 Implementing Employee Well-being Programs: Supporting employees' physical and mental health is crucial for maintaining resilience.
6.2.4 Celebrating Success and Learning from Failures: Recognizing achievements and learning from setbacks reinforces a resilient mindset.
6.3 Role of HR in Building a Resilient Culture
6.3.1 Recruitment and Selection for Resilience: Hiring individuals who demonstrate resilience can strengthen the organization's overall resilience.
6.3.2 Training and Development Programs: Providing training in resilience skills, such as stress management and adaptability, supports a resilient workforce.
6.3.3 Performance Management and Resilience: Performance management systems that reward resilience behaviors encourage a resilient culture.
Developing a Resilience Strategy
A well-crafted resilience strategy is essential for guiding an organization through challenges.
7.1 Steps in Developing a Resilience Strategy
7.1.1 Assessing Current Resilience Levels: Conducting a resilience audit helps identify strengths and areas for improvement.
7.1.2 Setting Resilience Goals and Objectives: Clear goals and objectives provide direction and focus for resilience efforts.
7.1.3 Identifying Key Risks and Vulnerabilities: Understanding potential risks and vulnerabilities is essential for developing effective resilience strategies.
7.1.4 Developing Resilience Initiatives and Action Plans: Initiatives should address identified risks and support the overall resilience goals of the organization.
7.2 Integrating Resilience into Organizational Strategy
7.2.1 Aligning Resilience with Business Objectives: Resilience efforts should support and enhance the organization's strategic objectives.
7.2.2 Embedding Resilience into Daily Operations: Integrating resilience into standard operating procedures ensures it becomes a part of the organizational DNA.
7.2.3 Monitoring and Evaluating Resilience Efforts: Regular monitoring and evaluation help track progress and make necessary adjustments to resilience strategies.
Tools and Templates for Building Resilience
The Building Resilience Business Toolkit includes a range of tools and templates to support resilience efforts.
8.1 Resilience Assessment Tools
8.1.1 Resilience Audits and Surveys: These tools help assess the current level of resilience in individuals, teams, and the organization as a whole.
8.1.2 Risk Assessment Templates: Templates for identifying and assessing risks help prioritize resilience efforts.
8.1.3 Employee Well-being Checklists: These checklists support efforts to monitor and improve employee well-being, a key component of resilience.
8.2 Planning and Implementation Templates
8.2.1 Resilience Action Plan Templates: These templates guide the development of action plans for enhancing resilience.
8.2.2 Crisis Management Plans: Pre-prepared templates for crisis management ensure quick and effective responses to unexpected events.
8.2.3 Business Continuity Plans: Continuity planning templates help ensure that critical operations can continue during and after a disruption.
8.3 Training and Development Resources
8.3.1 Resilience Training Modules: Pre-designed training modules cover topics such as stress management, adaptability, and leadership resilience.
8.3.2 Team-Building Exercises for Resilience: Exercises designed to build trust, communication, and collaboration among team members enhance team resilience.
8.3.3 Leadership Development Resources: Resources focused on developing resilient leadership skills are crucial for driving resilience throughout the organization.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Learning from others' experiences provides valuable insights into resilience building.
9.1 Case Studies of Resilient Organizations
9.1.1 Case Study: Resilience in the Face of Economic Downturn: This case study examines how a major corporation successfully navigated a severe economic downturn by implementing a comprehensive resilience strategy.
9.1.2 Case Study: Navigating Technological Disruption: This case study explores how a tech company adapted to rapid technological changes, maintaining its market position through innovation and resilience.
9.1.3 Case Study: Building Resilience After a Crisis: This case study details how an organization recovered from a major crisis, emerging stronger and more resilient.
9.2 Best Practices for Building Resilience
9.2.1 Proactive Risk Management: Organizations that proactively identify and manage risks are better prepared to handle disruptions.
9.2.2 Fostering a Resilience Culture: Best practices include promoting a culture of learning, adaptability, and continuous improvement.
9.2.3 Integrating Resilience into Leadership Development: Developing resilient leaders is a critical component of organizational resilience.
Conclusion: The Path Forward for Resilience
In an increasingly complex and unpredictable business environment, resilience is not just an option but a necessity. The Building Resilience Business Toolkit provides the resources, tools, and strategies needed to cultivate resilience at every level of your organization. By embracing resilience, businesses can not only survive challenges but thrive in the face of adversity.
Investing in resilience is an investment in the future. With the right approach, tools, and mindset, your organization can navigate uncertainty, seize new opportunities, and achieve long-term success. Whether you are a business leader, manager, or team member, this comprehensive toolkit offers the insights and practical resources needed to build a more resilient and successful organization.
Key Words:
Strategy & Transformation, Growth Strategy, Strategic Planning, Strategy Frameworks, Innovation Management, Pricing Strategy, Core Competencies, Strategy Development, Business Transformation, Marketing Plan Development, Product Strategy, Breakout Strategy, Competitive Advantage, Mission, Vision, Values, Strategy Deployment & Execution, Innovation, Vision Statement, Core Competencies Analysis, Corporate Strategy, Product Launch Strategy, BMI, Blue Ocean Strategy, Breakthrough Strategy, Business Model Innovation, Business Strategy Example, Corporate Transformation, Critical Success Factors, Customer Segmentation, Customer Value Proposition, Distinctive Capabilities, Enterprise Performance Management, KPI, Key Performance Indicators, Market Analysis, Market Entry Example, Market Entry Plan, Market Intelligence, Market Research, Market Segmentation, Market Sizing, Marketing, Michael Porter's Value Chain, Organizational Transformation, Performance Management, Performance Measurement, Platform Strategy, Product Go-to-Market Strategy, Reorganization, Restructuring, SWOT, SWOT Analysis, Service 4.0, Service Strategy, Service Transformation, Strategic Analysis, Strategic Plan Example, Strategy Deployment, Strategy Execution, Strategy Frameworks Compilation, Strategy Methodologies, Strategy Report Example, Value Chain, Value Chain Analysis, Value Innovation, Value Proposition, Vision Statement, Corporate Strategy, Business Development, Busienss plan pdf, business plan, PDF, Biusiness Plan DOC, Bisiness Plan Template, PPT
NOTE:Our digital products are sold on an "as is" basis, making returns and refunds unavailable post-download. Please preview and inquire before purchasing. Please contact us before purchasing if you have any questions! This policy aligns with the standard Flevy Terms of Usage.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
Source: Best Practices in Business Resilience PowerPoint Slides: Building Resilience Toolkit PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, SB Consulting