Structured Problem Solving & Hypothesis Generation (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 34 Slides
PROBLEM SOLVING PPT DESCRIPTION
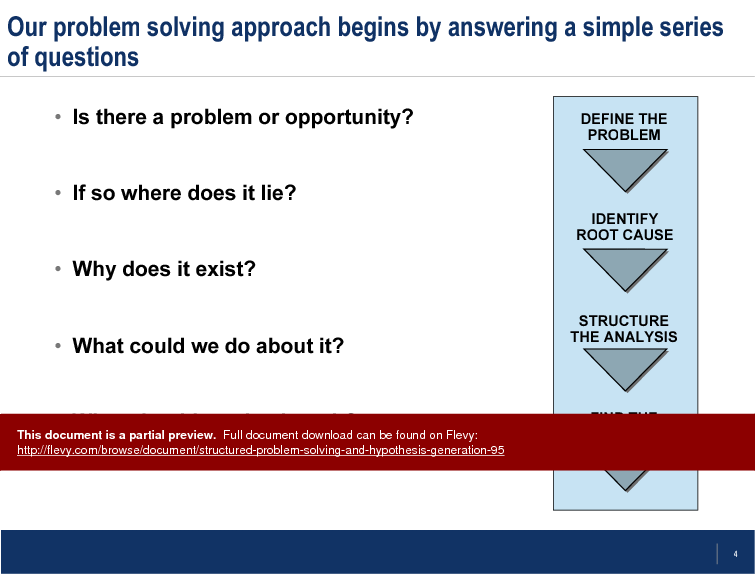
This training PPT presentation provides a comprehensive approach to structured problem solving, starting with the identification of whether a problem or opportunity exists.
It guides you through pinpointing the exact location of the issue, understanding its root causes, and exploring potential solutions. The methodology ensures that all aspects of the problem are thoroughly examined, leading to more effective and sustainable outcomes.
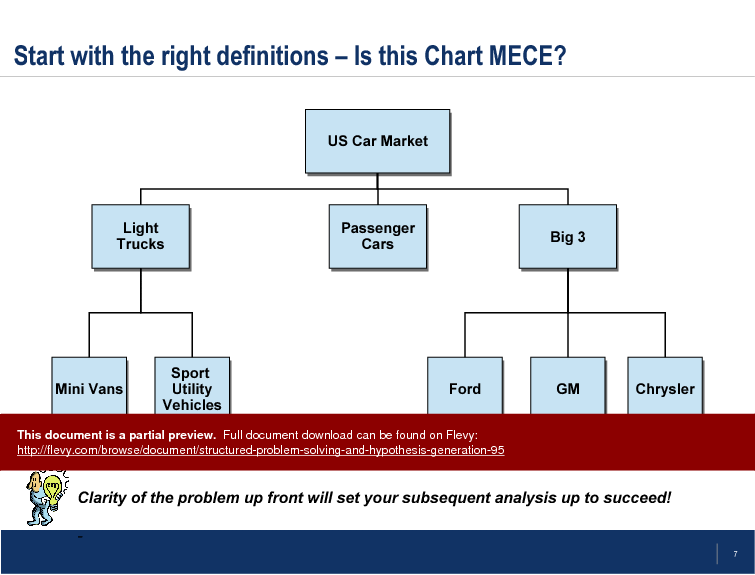
The presentation emphasizes the importance of MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) frameworks to ensure clarity and precision in problem definition. By categorizing elements such as the US car market into distinct, non-overlapping segments, it ensures that no critical factors are overlooked. This clarity is crucial for setting up a robust analysis and avoiding common pitfalls in problem-solving processes.
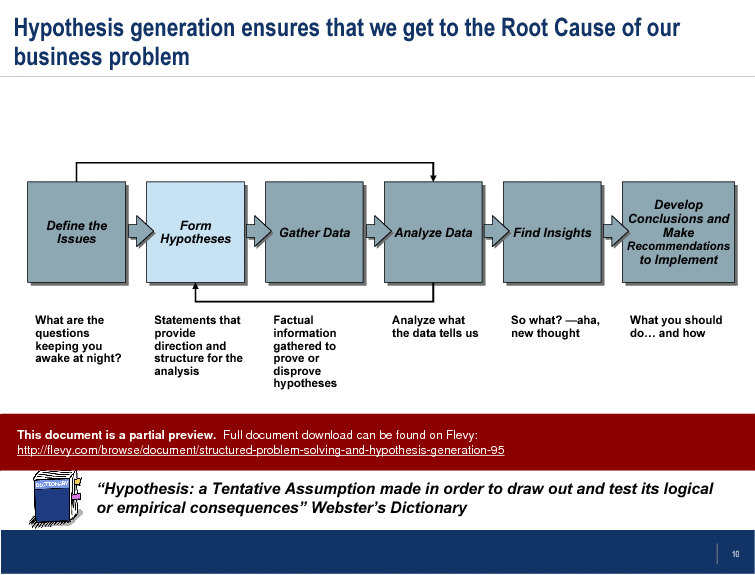
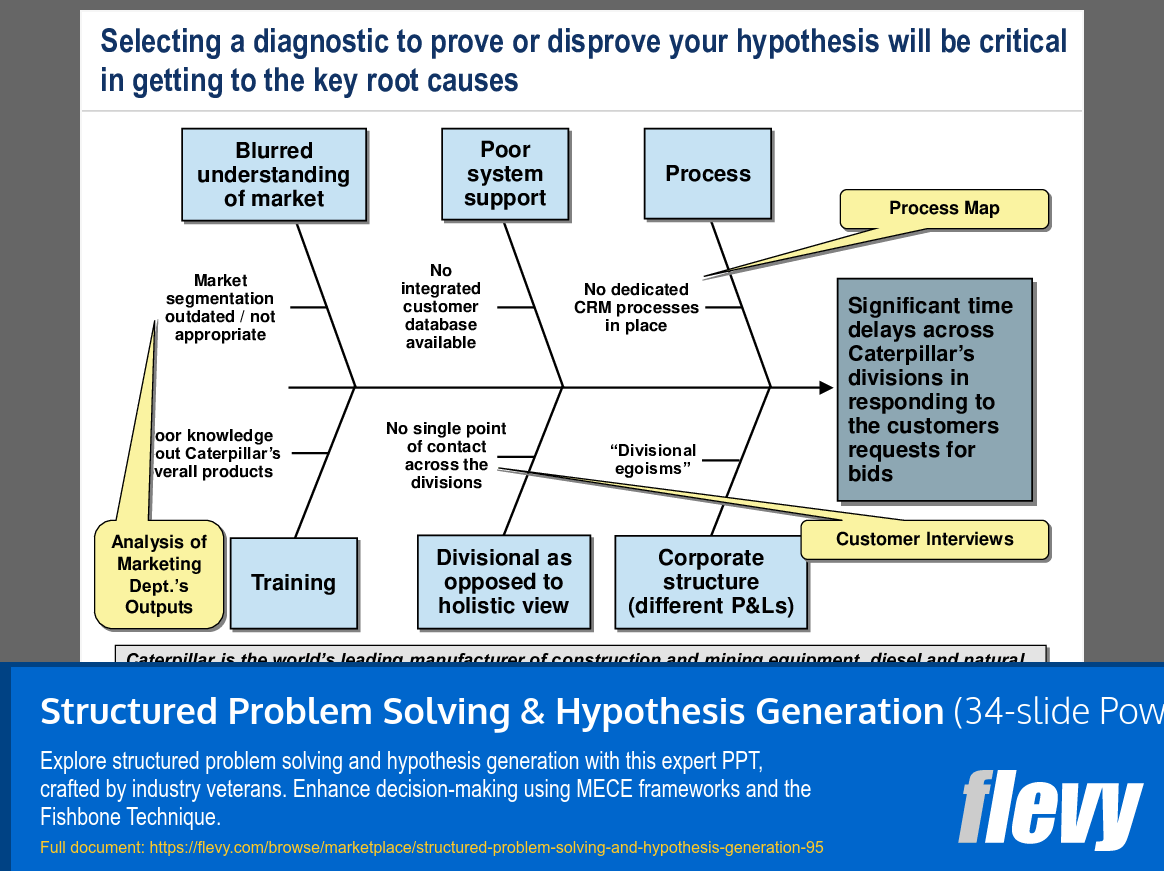
Hypothesis generation is a key focus, with detailed steps on forming, testing, and validating hypotheses. The document outlines how to gather and analyze data to either prove or disprove initial assumptions. This iterative process is designed to uncover deep insights and drive informed decision-making. The inclusion of real-world examples, such as Caterpillar’s market challenges, illustrates the practical application of these techniques.
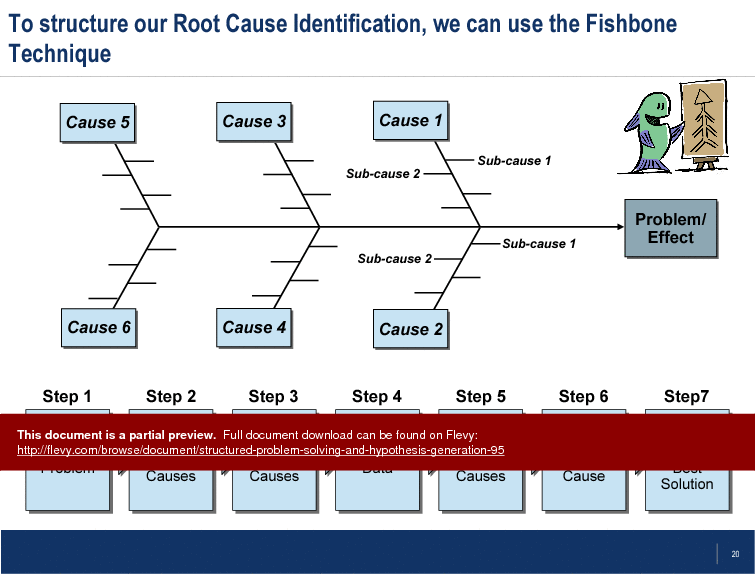
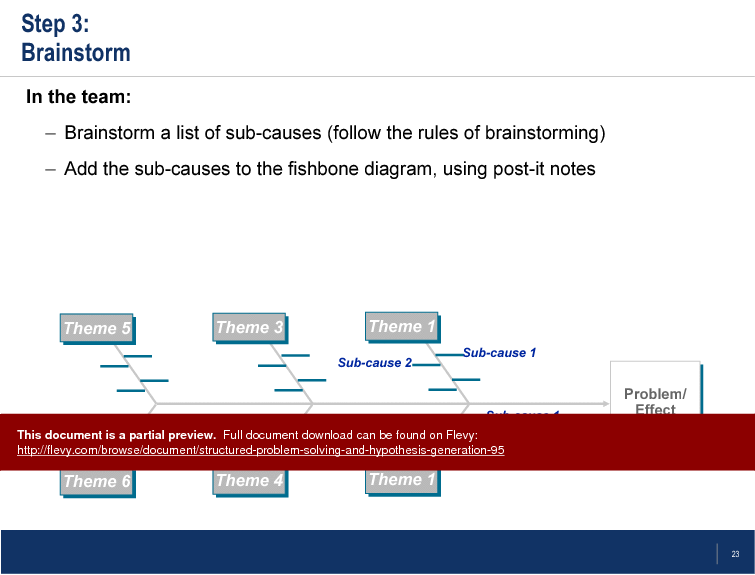
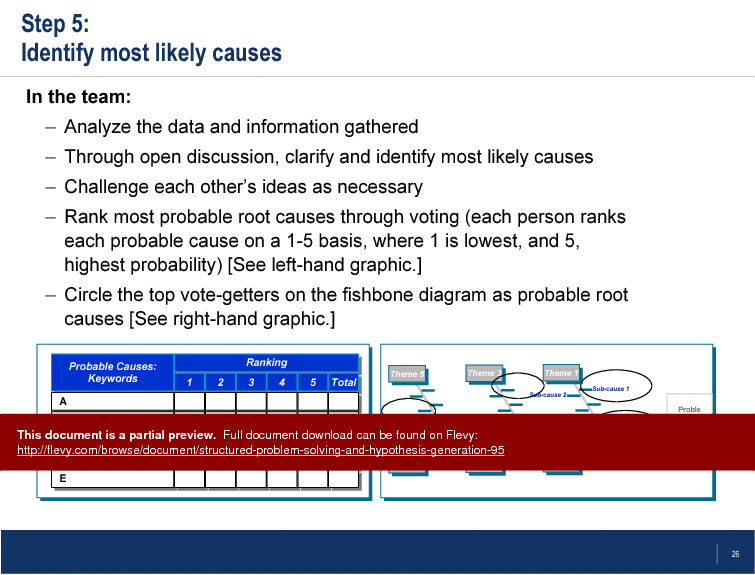
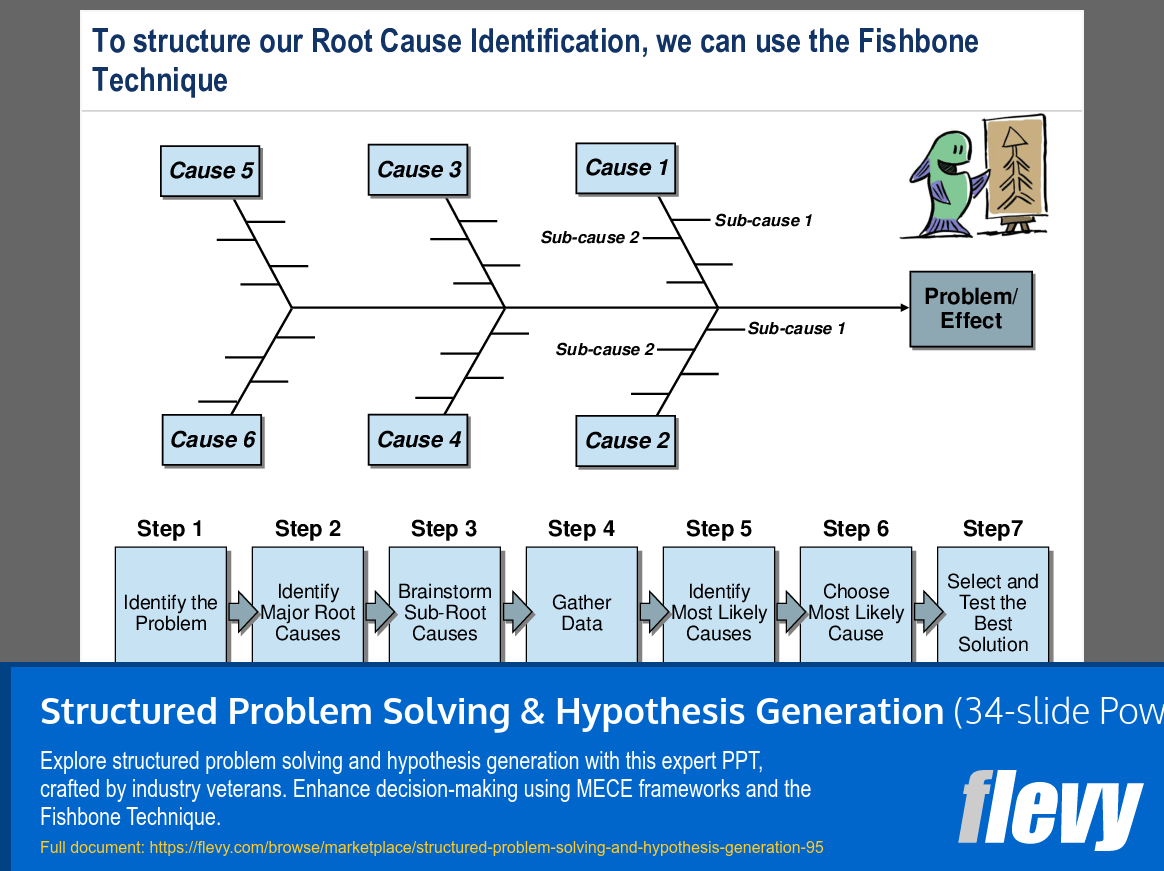
The Fishbone Technique is highlighted as a valuable tool for root cause identification. By visually mapping out causes and sub-causes, teams can systematically explore all potential factors contributing to a problem. This structured approach facilitates thorough brainstorming and prioritization of the most likely root causes, ensuring that solutions are targeted and effective.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 34-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation on Structured Problem Solving & Hypothesis Generation is crafted in a consulting-grade format, comparable to McKinsey, Bain, or BCG-quality materials (not affiliated). It provides a systematic approach to identifying and addressing business problems through structured thinking and hypothesis generation. Users will learn to define problems clearly, generate hypotheses about root causes, and utilize the Fishbone Technique for structured analysis. This deck equips corporate executives and consultants with the tools needed to enhance decision-making and problem-solving capabilities.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to improve decision-making processes
• Consultants aiming to enhance client problem-solving frameworks
• Project managers responsible for diagnosing and resolving project issues
• Team leaders facilitating brainstorming and analysis sessions
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to define and analyze key business challenges
• In workshops aimed at developing actionable solutions to complex problems
• When conducting root cause analysis for operational inefficiencies
Learning Objectives
• Define the problem clearly to facilitate effective analysis
• Develop hypotheses to explore potential root causes
• Structure analysis using logical frameworks and the Fishbone Technique
• Gather and analyze data to validate or invalidate hypotheses
• Generate actionable recommendations based on insights derived from analysis
• Communicate findings effectively using logical pyramids
Table of Contents
• What Is Structured Problem Solving? (page 2)
• How Do We Define the Problem? (page 3)
• How Do We Generate Hypotheses About the Root Cause of a Problem? (page 4)
• How Do We Structure Our Hypotheses Using the Fishbone Approach? (page 20)
• Key Points About Structured Problem Solving and Hypothesis Generation (page 34)
• Helpful Hints for Effective Problem Solving (page 35)
Primary Topics Covered
• Structured Problem Solving - A formal approach to organizing thought processes to identify and solve business problems effectively.
• Defining the Problem - Techniques to clarify the problem statement, ensuring a focused analysis.
• Hypothesis Generation - The process of forming educated guesses to explore potential root causes of identified issues.
• Fishbone Technique - A structured method for identifying and categorizing root causes, breaking down complex problems into manageable components.
• Data Gathering and Analysis - Strategies for collecting and analyzing data to validate hypotheses and inform decision-making.
• Logical Pyramids - A communication tool that structures information for clarity and impact, aiding in the presentation of findings.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Problem definition templates to guide clarity in identifying issues
• Hypothesis generation frameworks to facilitate structured thinking
• Fishbone diagrams for visualizing root cause analysis
• Data collection checklists for effective information gathering
• Logical pyramid templates for presenting findings succinctly
Slide Highlights
• Overview of structured problem-solving principles and their importance
• Step-by-step breakdown of the Fishbone Technique for root cause analysis
• Examples illustrating the application of hypothesis generation in real-world scenarios
• Visual aids demonstrating the logical pyramid structure for effective communication
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Structured Problem Solving (30 minutes)
• Overview of structured problem-solving principles
• Discussion on the importance of defining problems clearly
Hypothesis Generation Session (60 minutes)
• Brainstorming potential hypotheses
• Group activity on formulating and testing hypotheses
Root Cause Analysis Workshop (90 minutes)
• Introduction to the Fishbone Technique
• Team exercise to identify root causes of a sample problem
Customization Guidance
• Adapt the problem definition templates to align with specific organizational contexts
• Tailor the Fishbone diagrams to reflect industry-specific challenges
• Modify data gathering strategies based on available resources and tools
Secondary Topics Covered
• Importance of clarity in problem statements
• Techniques for effective brainstorming and idea generation
• Strategies for validating hypotheses through data analysis
• Best practices for collaborative problem-solving
Topic FAQ
What are the core steps in a structured problem-solving process?
A structured problem-solving process begins with a clear problem definition, followed by hypothesis generation, structuring hypotheses (for example with a Fishbone), gathering and analyzing data to validate or invalidate hypotheses, and producing recommendations communicated via logical pyramids. These steps culminate in communication using logical pyramids.How does hypothesis generation typically work in a consulting-style approach?
Hypothesis generation starts with forming educated guesses about root causes through targeted questioning and brainstorming, then prioritizing hypotheses for testing and validating them with data. The described method emphasizes iterative testing and validation using hypothesis generation frameworks and data analysis tools.When is the Fishbone Technique most useful for root cause analysis?
The Fishbone Technique is useful when teams need to categorize and break down complex problems into causes and sub-causes for systematic exploration. It helps surface multiple contributing factors during brainstorming and is provided as Fishbone diagrams in the presentation on page 20.How should I define a problem clearly so analysis is effective?
Define a problem by articulating scope, outcome metrics, and boundaries using MECE principles to avoid overlap or omission. Use focused problem definition templates to ensure clarity on where the issue lies and what success looks like, leveraging the included problem definition templates.What should I look for when choosing a structured problem-solving template or toolkit?
Choose a toolkit that offers clear problem-definition templates, hypothesis-generation frameworks, visual root-cause tools (Fishbone), data-collection checklists, and communication templates (logical pyramids), plus example workflows or workshop agendas to operationalize the approach; look specifically for data collection checklists.How quickly can a team adopt a purchased PPT toolkit for a workshop?
A team can adopt the toolkit to run an initial workshop within a few hours using the provided agenda and templates. The product includes a sample agenda with timed sessions such as a 30-minute introduction, a 60-minute hypothesis session, and a 90-minute root cause workshop.How should I weigh cost versus value when buying problem-solving templates?
Assess value by estimating internal hours saved in structuring problems, running workshops, and producing executive-ready outputs. Compare that to the purchase cost and check the presence of practical artifacts like problem definition templates, Fishbone diagrams, and data collection checklists to quantify potential time savings.I need to diagnose operational inefficiencies—what framework should I use first?
Begin with a precise problem definition framed with MECE principles, then generate hypotheses about likely root causes and use a Fishbone to organize potential contributors. Follow with targeted data gathering to validate hypotheses, using the Fishbone Technique as the primary diagnostic tool.How can I structure a hypothesis generation workshop for my team?
Structure the workshop with a brief framing session, timed brainstorming using targeted questions, hypothesis prioritization, and rapid testing plans. Use the presentation’s suggested Hypothesis Generation Session format and templates to guide activities, including a recommended 60-minute hypothesis session.Can structured problem-solving techniques improve executive communication of findings?
Yes. Communicating via logical pyramids organizes conclusions and supporting arguments in a top-down, succinct way that executives can follow. Use logical pyramid templates to turn validated hypotheses and data into a clear executive narrative, employing the included logical pyramid templates.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is structured problem solving?
Structured problem solving is a formal approach that organizes thinking to identify and address business challenges effectively.
How do I define a problem clearly?
Defining a problem involves articulating the issue in a way that facilitates understanding and analysis, often using frameworks like MECE.
What is the Fishbone Technique?
The Fishbone Technique is a visual tool used to identify and categorize potential root causes of a problem, breaking down complex issues into manageable parts.
How can I generate effective hypotheses?
Effective hypotheses can be generated by asking targeted questions, brainstorming with team members, and validating assumptions through data.
What role does data analysis play in this process?
Data analysis is crucial for validating or disproving hypotheses, providing evidence to support conclusions and recommendations.
How can I communicate findings effectively?
Using logical pyramids helps structure information clearly, making it more memorable and impactful for stakeholders.
What are the key steps in root cause analysis?
Key steps include identifying the problem, brainstorming causes, gathering data, and selecting the most likely root cause for resolution.
Why is collaboration important in problem-solving?
Collaboration brings diverse perspectives and expertise, enhancing the quality of analysis and the effectiveness of solutions developed.
Glossary
• Structured Problem Solving - A formal method for organizing thought processes to tackle business issues.
• Hypothesis - A tentative assumption made to explore potential causes of a problem.
• Fishbone Technique - A visual tool for identifying and categorizing root causes of issues.
• Data Analysis - The process of examining data to draw conclusions and inform decision-making.
• Logical Pyramid - A communication structure that organizes information for clarity and impact.
• Root Cause - The fundamental reason for a problem, which must be addressed to resolve the issue effectively.
• MECE - Mutually Exclusive and Comprehensively Exhaustive; a principle for structuring information clearly.
• Brainstorming - A collaborative technique for generating ideas and solutions without initial criticism.
• Diagnostic - A method or tool used to analyze and identify the causes of a problem.
• Stakeholder - An individual or group with an interest in the outcome of a project or issue.
• Sub-Cause - A secondary factor contributing to a primary cause of a problem.
• KPI - Key Performance Indicator; a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives.
• Trendline - A line indicating the general course or tendency of a set of data points.
• Gap Analysis - A method for assessing the differences between current performance and desired outcomes.
• Pilot Test - A trial run of a solution to evaluate its effectiveness before full implementation.
• Stakeholder Engagement - The process of involving individuals or groups who may be affected by or have an interest in a project.
• Control Chart - A statistical tool used to monitor the performance of a process over time.
• Process Map - A visual representation of the steps involved in a process.
• Customer Interviews - Conversations with customers to gather insights and feedback on products or services.
• Analysis of Outputs - The examination of results produced by a process to evaluate effectiveness.
PROBLEM SOLVING PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Problem Solving, Hypothesis Generation, MECE, Bain PowerPoint PowerPoint Slides: Structured Problem Solving & Hypothesis Generation PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, Process Consulting