Manufacturing Strategy: Make vs. Buy (PowerPoint PPT Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPT) 25 Slides FlevyPro Document
MANUFACTURING PPT DESCRIPTION
Internal manufacturing of a product versus procurement from external supplier sources is a difficult decision requiring careful and thorough assessment of multiple elements. The assessment includes organization's core competencies, business strategy, manufacturing strategy, internal capacity, resource limitations, demand fluctuations, time-to-market, and improved returns, among others. Top management has to negotiate the trade-offs between the make or buy alternatives.
Procurement from external sources liberates the organization's resources, cuts investment demands, increases flexibility and return on capital. However, there are associated quality and supply risks involved with this strategy. In contrast, "in-house manufacturing" employs internal capacity, absorb fixed costs, and safeguard intellectual property. Nevertheless, the "make" approach entails unwarranted complexities, and avert resources and focus away from more important strategic priorities.
This PowerPoint presentation on Manufacturing Strategy provides a comprehensive framework to help organizational leadership answer the make vs. buy question by evaluating their manufacturing network and strategies, developing an assessment criteria, detailed implementation process, and tactics for executing the framework.
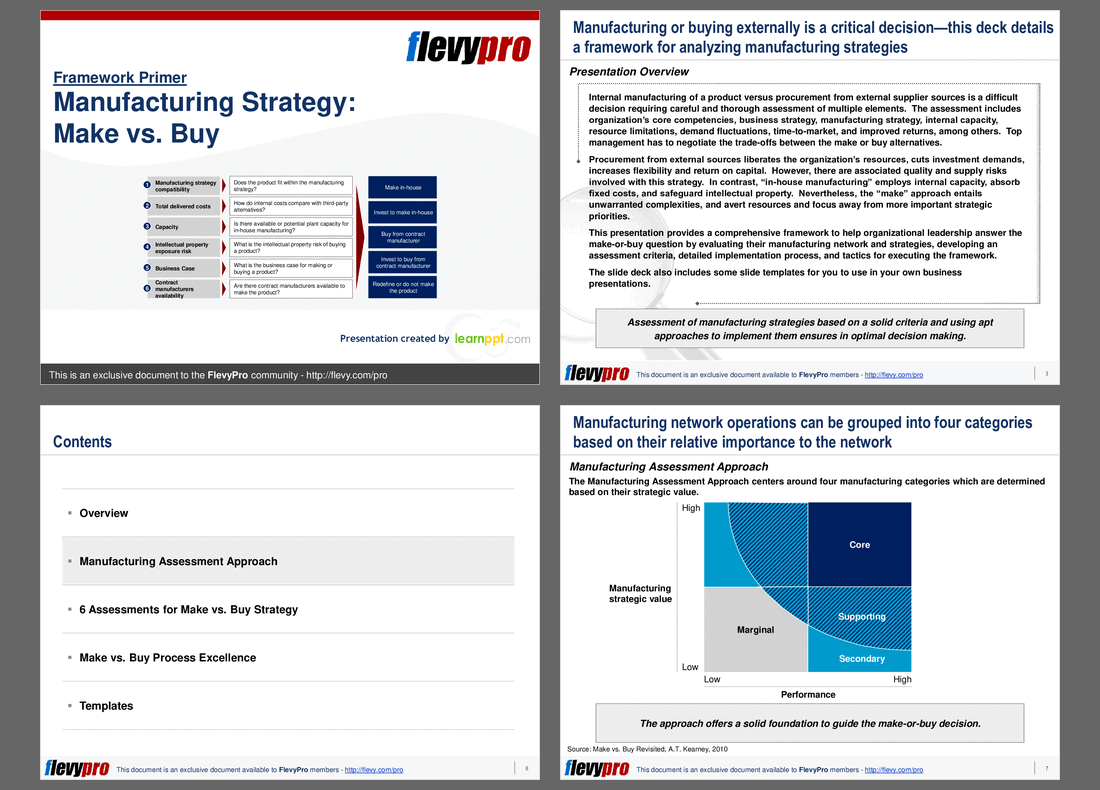
There are 6 broad assessments to evaluate when making the make vs. buy decision:
1. Manufacturing Strategy compatibility – Does the product fit within our Manufacturing Strategy?
2. Total delivered costs – How do internal costs compare with third-party alternatives?
3. Capacity – Is there available or potential plant capacity for in-house manufacturing?
4. Intellectual Property exposure risk – What is the Intellectual Property risk of buying a product?
5. Business Case development – What is the Business Case for making vs. buying a product?
6. Contract manufacturers availability – Are there actually contract manufacturers available to make the product?
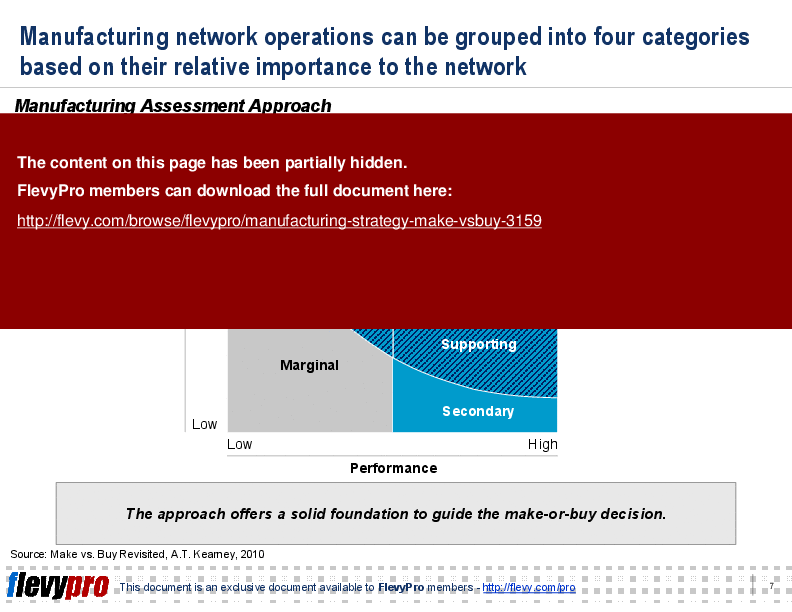
This framework also breaks down the 6 attributes to enable a successful make-or-buy process. These attributes allow for a company to establish a workable and consistent make-or-buy process.
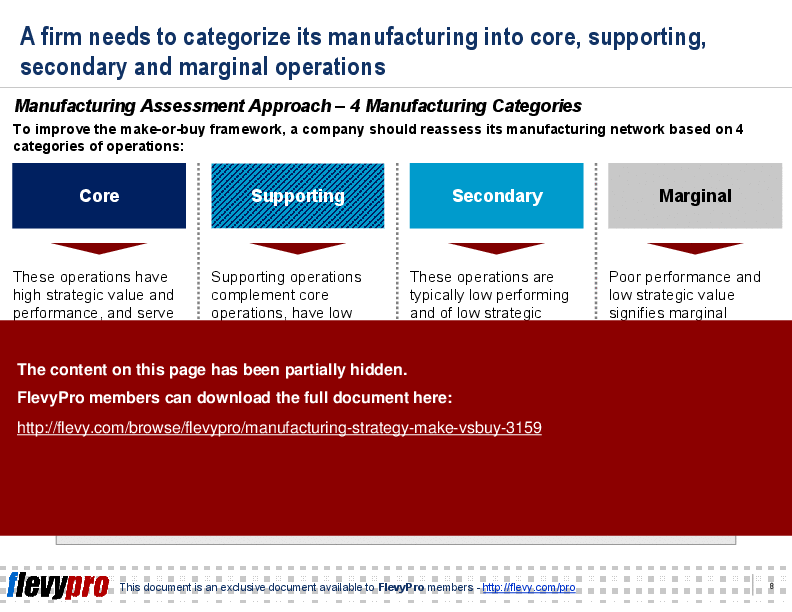
The Manufacturing Strategy PPT also includes some slide templates that depict the 4 Manufacturing Categories and Make vs. Buy Assessment Criteria for you to use in your own business presentations.
The presentation categorizes manufacturing operations into core, supporting, secondary, and marginal, providing a structured approach to decision-making. It also includes templates for assessing strategic value and performance, aiding in the practical application of the framework.
Got a question about this document? Email us at flevypro@flevy.com.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 25-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The "Manufacturing Strategy: Make vs. Buy" presentation provides a structured framework for organizations to evaluate their manufacturing strategies. It addresses the critical decision of whether to produce in-house or procure from external suppliers. The framework emphasizes the importance of assessing various factors, including core competencies, capacity, and cost implications. By utilizing this presentation, executives can make informed decisions that align with their business strategies and operational capabilities, ultimately optimizing resource allocation and enhancing operational efficiency.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives involved in strategic decision-making for manufacturing.
• Operations managers overseeing production and supply chain processes.
• Financial analysts assessing cost implications of manufacturing decisions.
• Consultants advising organizations on manufacturing strategy and optimization.
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions focused on manufacturing capabilities.
• When evaluating potential shifts in production strategy due to market changes.
• In workshops aimed at aligning manufacturing decisions with business objectives.
Learning Objectives
• Define the key elements of the make vs. buy decision framework.
• Assess the compatibility of products with the manufacturing strategy.
• Evaluate total delivered costs for in-house production versus external procurement.
• Analyze internal capacity and its implications for manufacturing decisions.
• Identify intellectual property risks associated with outsourcing.
• Develop a comprehensive business case for manufacturing decisions.
• Determine the availability of contract manufacturers for specific products.
Table of Contents
• Overview (page 3)
• Manufacturing Assessment Approach (page 7)
• 6 Assessments for Make vs. Buy Strategy (page 10)
• Make vs. Buy Process Excellence (page 15)
• Templates (page 19)
Primary Topics Covered
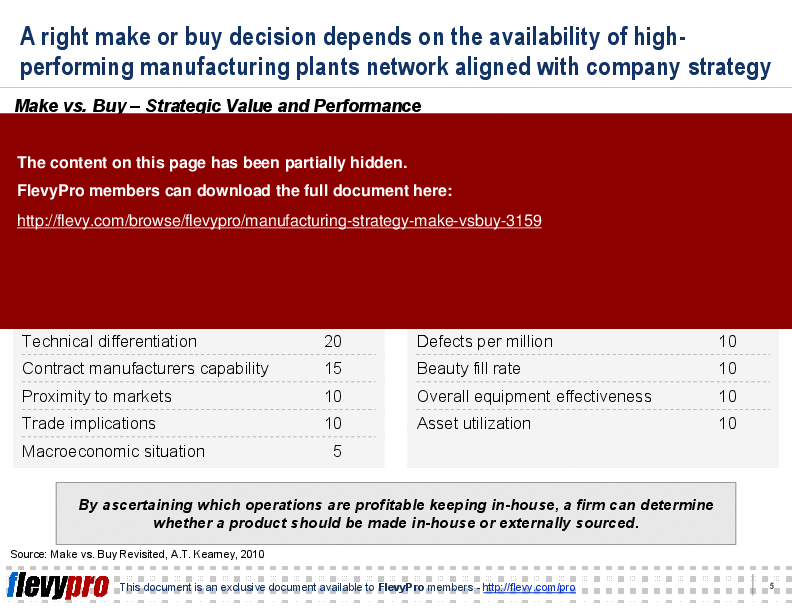
• Manufacturing Strategy Compatibility - Evaluates whether a product aligns with the organization's overall manufacturing strategy, guiding the decision to make or buy.
• Total Delivered Costs - Compares internal manufacturing costs with third-party alternatives to determine the most cost-effective option.
• Capacity - Assesses available plant capacity for in-house manufacturing against projected demand to inform production decisions.
• Intellectual Property Exposure Risk - Analyzes the risks associated with outsourcing manufacturing and the potential impact on intellectual property.
• Business Case Development - Guides the creation of a detailed business case for making or buying a product, considering all relevant factors.
• Contract Manufacturers Availability - Evaluates the availability and capabilities of third-party manufacturers to meet production needs.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• Make vs. Buy assessment criteria template for evaluating manufacturing decisions.
• Cost comparison models to analyze internal versus external manufacturing costs.
• Capacity assessment tools to evaluate plant capabilities against demand projections.
• Intellectual property risk assessment framework for outsourcing decisions.
• Business case development templates for presenting make vs. buy options.
• Contract manufacturer evaluation checklist to assess potential partners.
Slide Highlights
• Overview of the make vs. buy decision framework, emphasizing critical assessment areas.
• Visual representation of manufacturing categories based on strategic value and performance.
• Detailed assessment criteria for evaluating the make vs. buy decision.
• Framework for developing a comprehensive business case for manufacturing choices.
Potential Workshop Agenda
Make vs. Buy Strategy Session (90 minutes)
• Introduce the make vs. buy framework and its importance.
• Discuss key assessments and their implications for decision-making.
• Break into groups to analyze specific case studies using the framework.
Assessment Criteria Review (60 minutes)
• Review the assessment criteria for make vs. buy decisions.
• Discuss real-world applications and challenges faced by participants.
• Develop action plans for implementing the framework in participants' organizations.
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the assessment criteria to reflect specific industry standards and practices.
• Adjust cost comparison models to include unique internal cost structures.
• Incorporate organizational terminology and metrics into the templates provided.
Secondary Topics Covered
• Risk management strategies for outsourcing manufacturing.
• Trends in contract manufacturing and their implications for strategy.
• Case studies of successful make vs. buy decisions in various industries.
• Best practices for ongoing evaluation of manufacturing strategies.
Topic FAQ
What are the core assessments I should run in a manufacturing make-versus-buy review?
A standard review covers 6 core assessments: manufacturing strategy compatibility, total delivered costs, capacity, intellectual property exposure risk, business case development, and contract manufacturers availability. These 6 assessments form the basis for consistent make-or-buy decisions and are presented as the framework’s primary components.How should total delivered costs be compared when choosing to make or buy?
Total delivered cost comparison requires tallying internal manufacturing costs and comparing them with third-party quotes while accounting for logistics, quality, and other delivered-cost elements. Use cost comparison models to capture fixed and variable costs and to compare internal versus external options with a cost comparison model.What role does plant capacity play in deciding to produce internally or outsource?
Capacity determines whether existing or adjustable plant throughput can meet projected demand without excessive capital investment; it influences timing, cost, and time-to-market trade-offs. Capacity assessment tools help quantify available versus required output when evaluating make-versus-buy options.How can I assess intellectual property exposure before outsourcing manufacturing?
Assess IP exposure by reviewing legal protections, contractual safeguards, and compliance in potential manufacturing locations, and by mapping what proprietary knowledge would be shared. The presentation includes an intellectual property risk assessment framework for structured evaluation.What should a buyer look for in a make-versus-buy toolkit when working within a tight budget and timeline?
Prioritize concise slide decks and reusable templates that reduce build time: assessment criteria, cost comparison models, capacity tools, IP risk framework, business case templates, and a supplier checklist. A toolkit packaged as a slide deck of 25 slides can shorten preparation time.Are templates worth purchasing versus building models from scratch for make-versus-buy analysis?
Templates standardize evaluation, ensure consistent criteria across products, and accelerate business-case development; typical deliverables include make-vs-buy assessment criteria, cost comparison models, capacity tools, and business case development templates to support repeatable analysis.How do I evaluate and shortlist contract manufacturers during a make-versus-buy process?
Conduct market research to identify suppliers, then assess their capabilities, capacity, quality standards, and alignment with production needs using a contract manufacturer evaluation checklist to score and compare candidates for suitability.After a merger or major market change, how often should we reevaluate our manufacturing strategy?
Manufacturing strategy should be reassessed in response to significant market changes and as part of periodic strategic reviews; a common cadence recommended in practice is every 2 to 3 years to ensure alignment with demand and capabilities.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is the primary purpose of the make vs. buy framework?
The framework helps organizations systematically evaluate whether to manufacture products in-house or procure them from external suppliers, considering various strategic and operational factors.
How can the total delivered costs be effectively assessed?
By comparing internal manufacturing costs with quotes from external suppliers, organizations can identify the most cost-effective option while factoring in logistics and quality considerations.
What factors should be considered when assessing capacity?
Organizations should evaluate current plant capacity against projected demand and consider potential adjustments to existing production lines or processes.
Why is intellectual property exposure a concern in outsourcing?
Outsourcing manufacturing can increase the risk of intellectual property theft or misuse, making it essential to assess legal protections and compliance in the manufacturing location.
What is included in a comprehensive business case for manufacturing decisions?
A business case should outline the operational and financial implications of making or buying a product, including cost analyses, resource requirements, and potential risks.
How do I determine the availability of contract manufacturers?
Conduct market research to identify potential subcontractors, assess their capabilities, and evaluate their alignment with your production needs and quality standards.
How often should the manufacturing strategy be reevaluated?
Organizations should reassess their manufacturing strategies every 2 to 3 years or when significant market changes occur that could impact production decisions.
What are the benefits of using templates provided in the presentation?
Templates streamline the assessment process, ensuring consistency and thoroughness in evaluating make vs. buy decisions across different products and scenarios.
Glossary
• Make vs. Buy - A strategic decision framework for determining whether to produce in-house or procure from external suppliers.
• Total Delivered Costs - The complete cost of producing a product, including all associated expenses.
• Capacity - The maximum output that a manufacturing facility can produce within a given timeframe.
• Intellectual Property Exposure - The risk of losing proprietary information when outsourcing manufacturing.
• Business Case - A document outlining the rationale for a specific business decision, including costs and benefits.
• Contract Manufacturers - External companies that produce goods on behalf of another company.
• Manufacturing Strategy Compatibility - The alignment of a product with the overall manufacturing strategy of an organization.
• Assessment Criteria - Standards used to evaluate options in the make vs. buy decision-making process.
• Performance Metrics - Quantitative measures used to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing operations.
• Risk Management - The process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with business decisions.
• Supply Chain Flexibility - The ability of a supply chain to adapt to changes in demand or supply conditions.
• Operational Efficiency - The ability to deliver products or services in the most cost-effective manner without compromising quality.
• Strategic Value - The importance of a manufacturing operation in contributing to the organization's overall goals and objectives.
• Market Dynamics - The forces that impact the supply and demand of products in a market.
• Resource Allocation - The distribution of resources among various projects or business units.
• Quality Standards - The criteria that products must meet to ensure they are fit for use.
• Time-to-Market - The time taken from product conception to market launch.
• Demand Fluctuations - Variations in consumer demand for products over time.
• Core Competencies - The unique strengths and abilities that give an organization a competitive advantage.
• Fixed Costs - Expenses that do not change with the level of production or sales.
• Variable Costs - Costs that vary directly with the level of production.
MANUFACTURING PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Manufacturing PowerPoint Slides: Manufacturing Strategy: Make vs. Buy PowerPoint (PPT) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting
Did you need more documents?
Consider a FlevyPro subscription from $39/month. View plans here.
For $10.00 more, you can download this document plus 2 more FlevyPro documents. That's just $13 each.