Six Sigma (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 72 Slides
SIX SIGMA PROJECT PPT DESCRIPTION
Six Sigma
1. Explain Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at improving the quality of processes by identifying and eliminating defects and minimizing variability. Developed by Motorola in the 1980s and popularized by General Electric, Six Sigma uses statistical tools and techniques to achieve process improvement. The goal is to reduce the defect rate to fewer than 3.4 defects per million opportunities, which corresponds to a sigma level of 6, ensuring a high level of quality and consistency.
2. Explain the Steps in Implementing Six Sigma
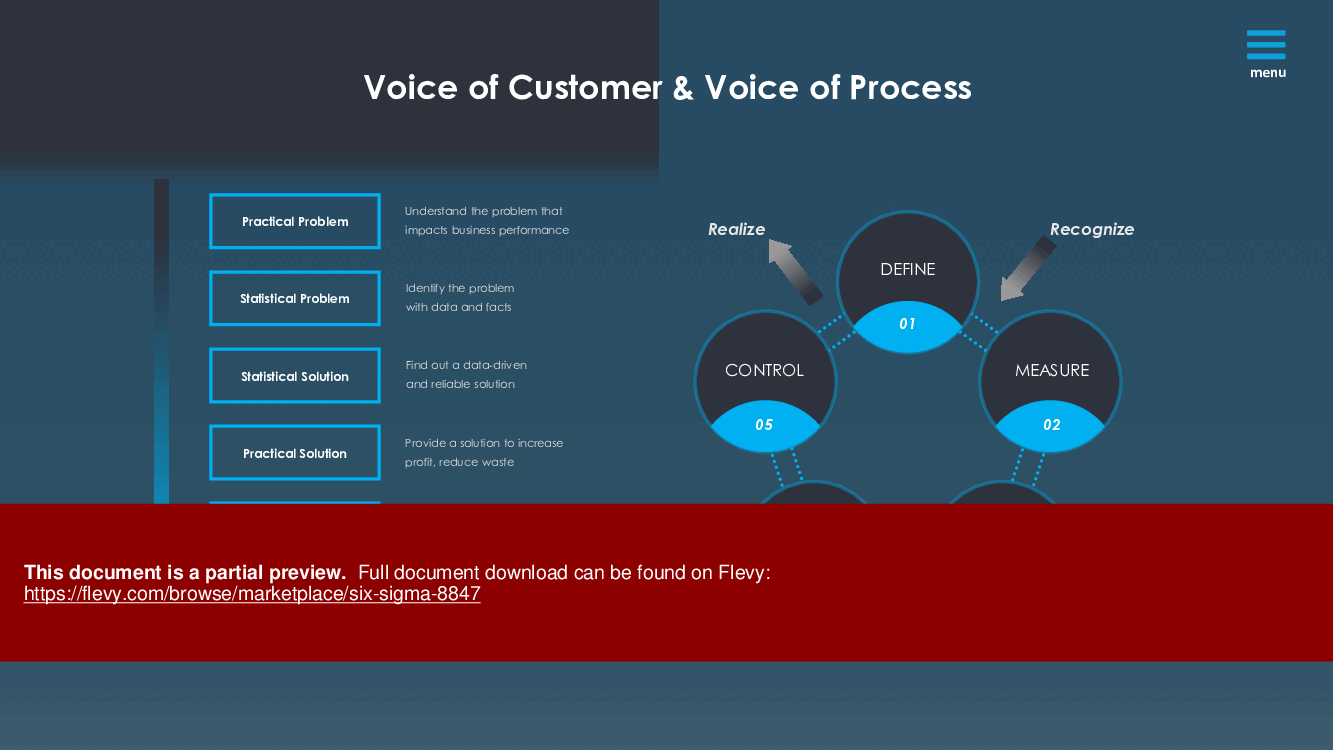
Six Sigma implementation follows structured methodologies, primarily DMAIC, DMADV, and DFSS:
• DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control)
• Define: Identify the problem or project goals.
• Measure: Collect data to establish baselines.
• Analyze: Identify root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
• Improve: Develop and implement solutions.
• Control: Monitor the improvements to sustain gains.
• DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify)
• Define: Define project goals and customer requirements.
• Measure: Quantify customer needs and specifications.
• Analyze: Develop design alternatives and select the best option.
• Design: Design the process or product to meet customer requirements.
• Verify: Test and validate the design before full-scale implementation.
• DFSS (Design for Six Sigma)
• This approach focuses on designing products and processes that meet Six Sigma quality levels from the outset. It often incorporates methodologies like DMADV to ensure robust and high-quality designs.
3. Discuss the Six Sigma Program
A Six Sigma program involves more than just applying the methodologies; it requires a cultural shift within the organization. Key components include:
• Leadership Commitment: Strong support from top management to foster a culture of quality and continuous improvement.
• Training and Certification: Employees are trained and certified at different levels (Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, Master Black Belt) based on their expertise and role in Six Sigma projects.
• Project Selection: Careful selection of projects that align with strategic goals and have the potential for significant impact.
• Team-Based Approach: Cross-functional teams collaborate to identify and solve quality issues.
• Continuous Improvement: Ongoing efforts to improve processes, products, and services using Six Sigma tools and techniques.
Six Sigma is a powerful methodology for improving quality and efficiency. By following structured approaches like DMAIC, DMADV, and DFSS, organizations can systematically eliminate defects and enhance performance. A successful Six Sigma program requires commitment, training, and a focus on continuous improvement to achieve and sustain high-quality standards.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 72-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
The Six Sigma presentation from RadVector provides a comprehensive overview of the Six Sigma methodology, focusing on its application in process improvement and defect reduction. Developed by a team of experts with extensive experience in consulting, this training deck equips corporate executives and integration leaders with the tools necessary to implement Six Sigma strategies effectively. The presentation covers key methodologies such as DMAIC, DMADV, and DFSS, enabling users to enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction while minimizing costs and waste.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives seeking to improve process quality and efficiency
• Integration leaders responsible for implementing Six Sigma methodologies
• Quality assurance teams focused on defect reduction and process optimization
• Project managers overseeing process improvement initiatives
• Training and development teams designing Six Sigma training programs
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions to align Six Sigma initiatives with business objectives
• In training workshops aimed at educating staff on Six Sigma principles and practices
• When analyzing current processes to identify areas for improvement
• For project kick-offs focused on implementing Six Sigma methodologies
Learning Objectives
• Define the core principles and methodologies of Six Sigma
• Build a structured approach to process improvement using DMAIC and DMADV
• Establish metrics for measuring process capability and performance
• Identify critical to quality (CTQ) attributes that impact customer satisfaction
• Analyze and reduce process variation to enhance operational efficiency
• Create a sustainable Six Sigma culture within the organization
Table of Contents
• Introduction to Six Sigma (page 3)
• Key Concepts of Six Sigma (page 5)
• Six Sigma Methodologies: DMAIC and DMADV (page 10)
• Implementation Strategies for Six Sigma (page 15)
• Tools and Techniques in Six Sigma (page 20)
• Case Studies and Examples (page 25)
• Conclusion and Next Steps (page 30)
Primary Topics Covered
• Six Sigma Overview - An introduction to the Six Sigma methodology and its significance in process improvement.
• DMAIC Methodology - A structured approach for improving existing processes through defined steps: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control.
• DMADV Methodology - A framework for designing new processes or products that meet customer needs while ensuring quality.
• Critical to Quality (CTQ) - Identification of the attributes that are most important to customers and essential for quality improvement.
• Statistical Tools - Overview of the statistical methods and tools used in Six Sigma to analyze and improve processes.
• Lean Six Sigma - Integration of Lean principles with Six Sigma to enhance efficiency by eliminating waste.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• DMAIC project charter template for defining project goals and scope
• CTQ analysis template for identifying customer requirements
• Process mapping tools for visualizing workflows and identifying inefficiencies
• Control charts for monitoring process performance over time
• Training materials for educating staff on Six Sigma principles
• Implementation roadmap for guiding Six Sigma projects from initiation to completion
Slide Highlights
• Overview of Six Sigma principles emphasizing the importance of quality and customer satisfaction
• Visual representation of the DMAIC process illustrating each step in detail
• Case study examples showcasing successful Six Sigma implementations in various industries
• Statistical analysis tools and their applications in process improvement
• Comparison of Six Sigma with other methodologies like Lean and Kaizen
Potential Workshop Agenda
Introduction to Six Sigma (60 minutes)
• Overview of Six Sigma principles and methodologies
• Discussion on the importance of quality in business
DMAIC Deep Dive (90 minutes)
• Detailed exploration of each DMAIC phase
• Group activities to practice applying DMAIC to real-world scenarios
Tools and Techniques Workshop (60 minutes)
• Hands-on training on Six Sigma tools such as control charts and process mapping
• Case study analysis to reinforce learning
Implementation Planning Session (90 minutes)
• Development of a Six Sigma implementation plan tailored to organizational needs
• Identification of key stakeholders and resources required for success
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the DMAIC templates to reflect specific organizational processes and goals
• Adjust training materials to align with the existing knowledge level of staff
• Incorporate company-specific examples and case studies to enhance relevance
• Modify the implementation roadmap to fit the unique timeline and resources of the organization
Secondary Topics Covered
• The role of leadership in fostering a Six Sigma culture
• Integration of Six Sigma with other quality management frameworks
• Techniques for sustaining improvements over time
• The impact of Six Sigma on customer satisfaction and business performance
Topic FAQ
What are the main phases of DMAIC and how are they used in process improvement?
DMAIC is a five-step, data-driven problem-solving cycle used to improve existing processes: Define the problem and goals, Measure baseline performance, Analyze root causes, Improve the process with targeted solutions, and Control to sustain gains. The method is organized into Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control (5 phases).How does DMADV differ from DMAIC when designing new processes or products?
DMADV is oriented to design rather than improvement: Define project goals and customer needs, Measure customer requirements, Analyze design options, Design the process or product to meet specs, and Verify performance through testing. DMADV is Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify.Which statistical tools are commonly applied in Six Sigma projects?
Six Sigma commonly applies statistical analysis and statistical process control tools to quantify variation and monitor performance. Typical methods cited include process mapping, statistical analysis software, and control charts for ongoing monitoring, with control charts used to track stability and variation.What should I look for when buying a Six Sigma training deck or toolkit?
Look for clear coverage of DMAIC/DMADV/DFSS, ready templates (project charter, CTQ analysis), process-mapping artifacts, control charts, and a suggested implementation roadmap and workshop agenda. Flevy's Six Sigma explicitly lists a DMAIC project charter template.How much time and internal resources are suggested for a basic Six Sigma workshop?
The product provides a sample agenda combining introduction, a DMAIC deep dive, tools training, and implementation planning; the listed sessions total about 5 hours across modules, including a 90-minute DMAIC deep dive.I need to cut defect rates on a manufacturing line—what Six Sigma tools should I start with?
Begin with CTQ analysis to identify what customers value, map the current process to spot waste and variation, collect data to establish baselines, perform root-cause analysis, then implement SPC and control charts to monitor defect rates. Start with a CTQ analysis template and control charts.Can Six Sigma be integrated with Lean practices, and how would that look in a project?
Yes. Integration combines Six Sigma’s statistical defect-reduction focus with Lean’s waste-elimination tools to improve flow and reduce non-value activities. A project would add waste-mapping and flow improvement to standard Six Sigma analysis, reflecting a Lean Six Sigma approach.Are prebuilt templates and control charts useful for internal Six Sigma projects?
Prebuilt templates provide ready artifacts to define scope, capture CTQs, map processes, and monitor performance, reducing setup time and standardizing documentation. Flevy's Six Sigma includes templates such as a DMAIC project charter template.Document FAQ
These are questions addressed within this presentation.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at improving process quality by identifying and eliminating defects, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
How does DMAIC work?
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a structured approach used to improve existing processes by systematically addressing issues and implementing solutions.
What is the difference between DMAIC and DMADV?
DMAIC is used for improving existing processes, while DMADV is focused on designing new processes or products that meet customer needs.
What tools are used in Six Sigma?
Common tools include process mapping, control charts, statistical analysis software, and quality function deployment (QFD).
How can Six Sigma benefit my organization?
Implementing Six Sigma can lead to reduced defects, improved efficiency, lower costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
What training is required for Six Sigma?
Training typically includes foundational knowledge of Six Sigma principles, methodologies, and tools, often culminating in certification as a Green Belt or Black Belt.
How do I start a Six Sigma project?
Begin by defining the project scope, identifying key stakeholders, and using the DMAIC framework to guide the process.
What metrics should I track in a Six Sigma project?
Key metrics include defect rates, process capability indices, and customer satisfaction scores.
Glossary
• Six Sigma - A methodology focused on process improvement and defect reduction.
• DMAIC - A structured problem-solving process for improving existing processes.
• DMADV - A methodology for designing new processes or products.
• CTQ (Critical to Quality) - Attributes that are essential for meeting customer needs.
• Lean - A methodology focused on eliminating waste and improving efficiency.
• Control Chart - A statistical tool used to monitor process performance over time.
• Quality Function Deployment (QFD) - A tool for translating customer requirements into technical specifications.
• Process Mapping - A visual representation of workflows to identify inefficiencies.
• Variation - The degree of deviation in a process from its intended outcome.
• Defect - Any instance where a product or service fails to meet customer expectations.
• Statistical Process Control (SPC) - A method of quality control that uses statistical methods to monitor and control a process.
• Black Belt - A trained Six Sigma professional who leads projects and trains others.
• Green Belt - A Six Sigma practitioner who supports project teams and implements process improvements.
• Lean Six Sigma - A combined approach that integrates Lean manufacturing principles with Six Sigma methodologies.
• Benchmarking - The process of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests.
• Root Cause Analysis - A method for identifying the underlying causes of defects or problems.
• Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) - A systematic approach for evaluating processes to identify where and how they might fail.
• Voice of the Customer (VoC) - The process of capturing customers' expectations, preferences, and aversions.
• Continuous Improvement - Ongoing efforts to improve products, services, or processes.
Source: Best Practices in Six Sigma Project PowerPoint Slides: Six Sigma PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, RadVector Consulting