Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Opportunities (across Value Chain) (PowerPoint PPTX Slide Deck)
PowerPoint (PPTX) 44 Slides
BENEFITS OF THIS POWERPOINT DOCUMENT
- Provides over 100+ RPA opportunities across the Value Chain, which can lead to significant cost savings and productivity gains.
- Allows you to prioritize your RPA projects by corporate function or formulate a cross-functional RPA Strategy.
- Lay the foundation to your Digital Transformation Program with targeted RPA initiatives.
VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS PPT DESCRIPTION
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots and Artificial Intelligence to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks that are typically performed by humans, thereby allowing employees to focus on more value-add, strategic work.
RPA not only reduces the need for human intervention in mundane tasks, but also allows organizations to strategically reallocate their human resources towards activities that require human judgment, creativity, and interpersonal skills. This shift can lead to innovation and a stronger competitive position. Furthermore, for employees, it improves job satisfaction and productivity.
For organizations pursuing Digital Transformation, RPA is typically the lowest hanging fruit. RPA opportunities are relatively easy to identify and deploy; and potential results are high impact and easily measurable. RPA allows organizations to digitize and automate processes at a foundational level, setting the stage for more advanced technologies like AI and machine learning, which can further enhance decision-making and operational efficiencies.
Specific RPA benefit areas include:
Cost Reduction – Significantly lowers operational costs by automating routine tasks.
Productivity & Efficiency Gains – Increases workflow speed and productivity by eliminating human error and delays.
Scalability – Facilitates the easy scaling of operations to handle increased workload without additional investment.
Improved Accuracy – Ensures high precision and consistency in task execution, reducing the risk of errors.
Employee Satisfaction – Frees up employees from monotonous tasks, allowing them to engage in more meaningful and strategic activities.
Compliance & Control – Enhances compliance with regulations by providing a clear, consistent, and auditable trail of actions.
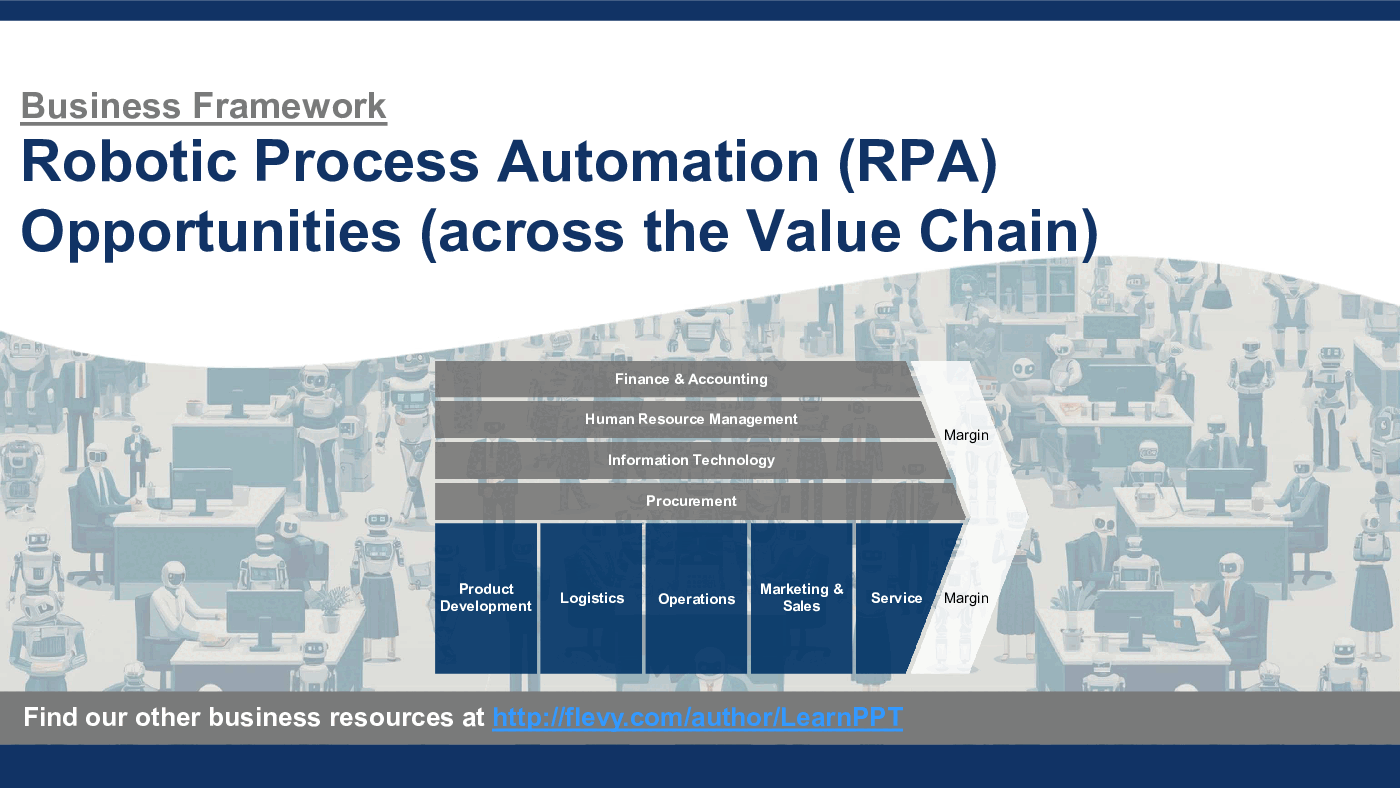
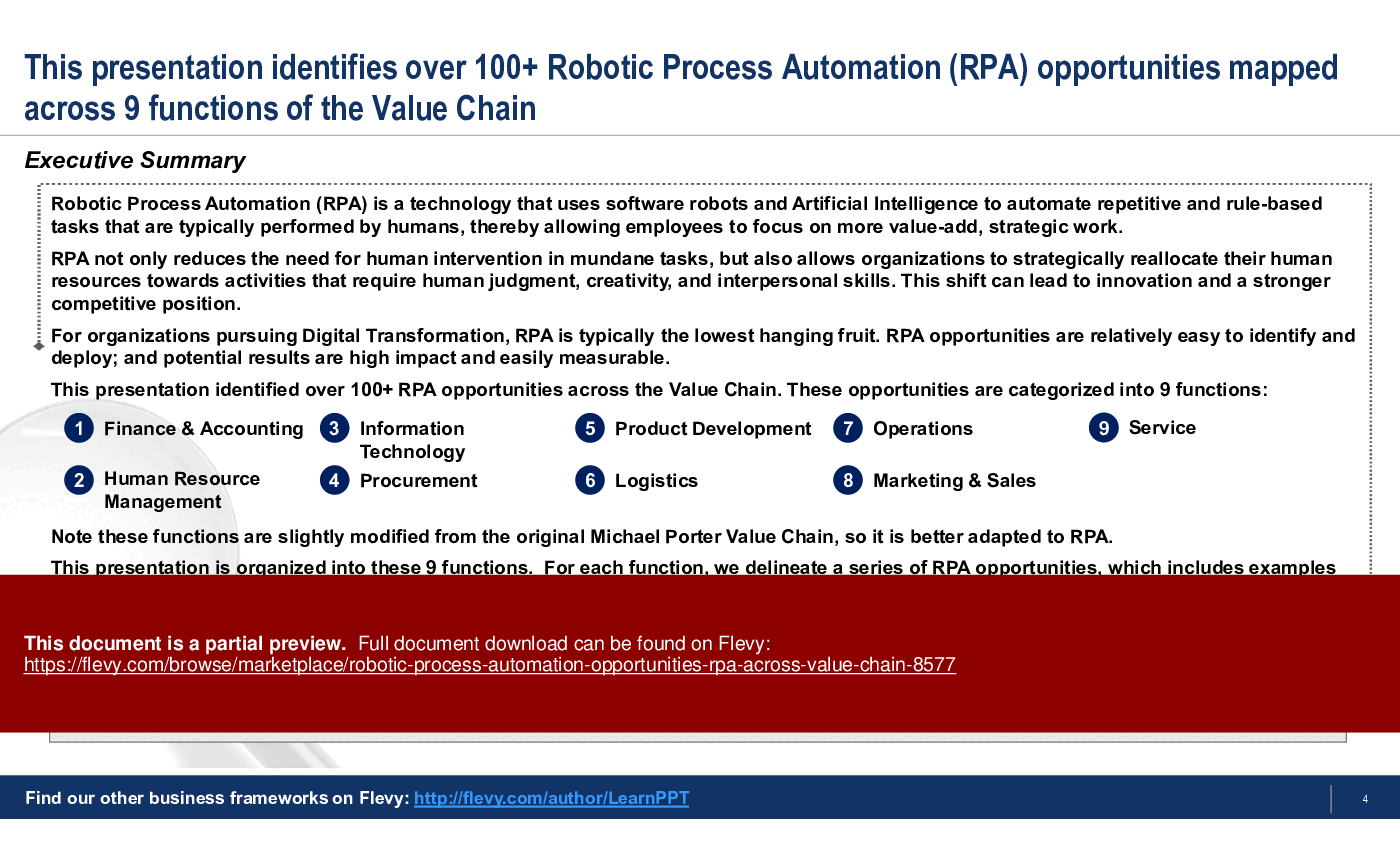
This presentation identified over 100+ RPA opportunities across the Value Chain. These opportunities are categorized into 9 functions:
1. Finance & Accounting
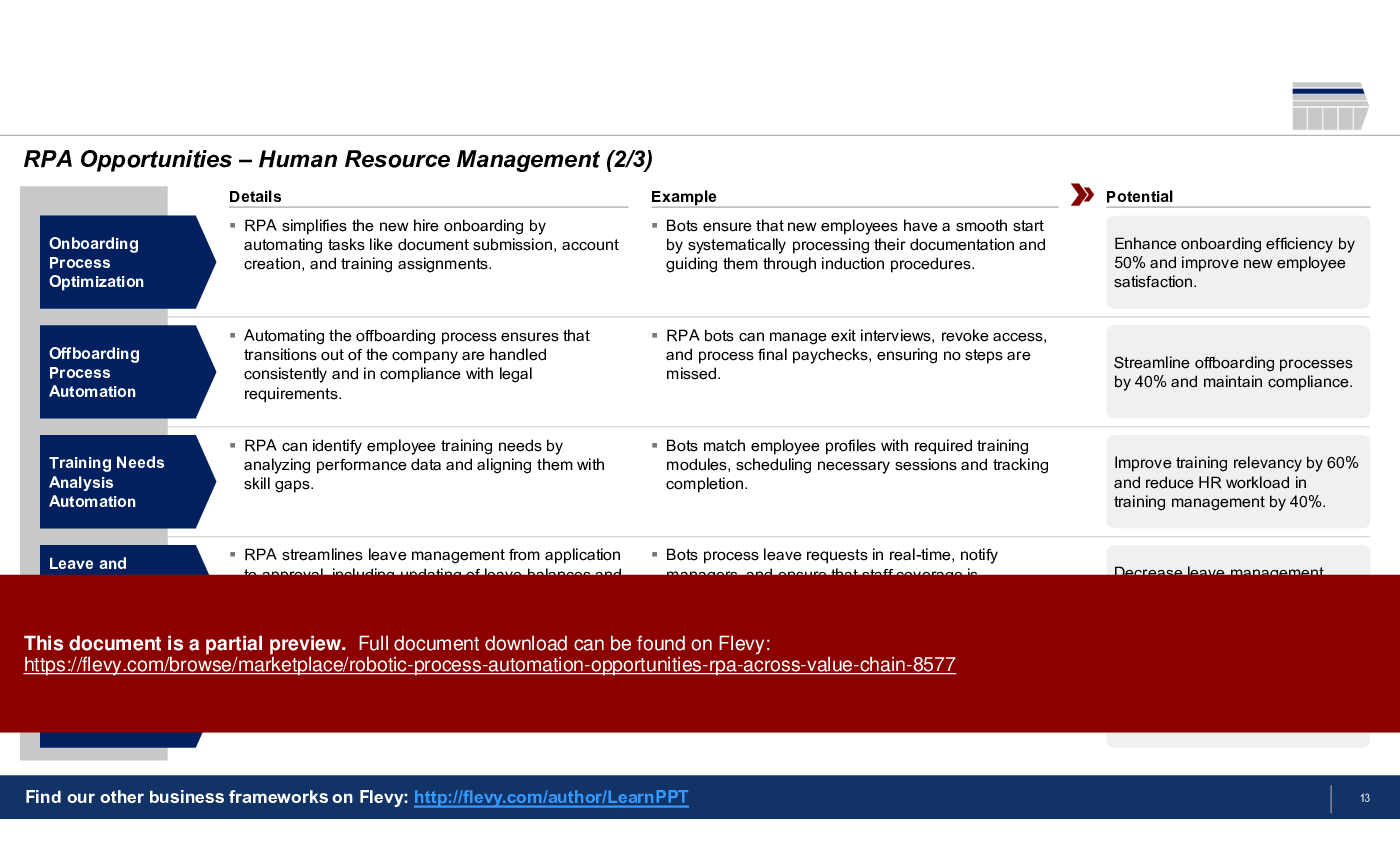
2. Human Resource Management
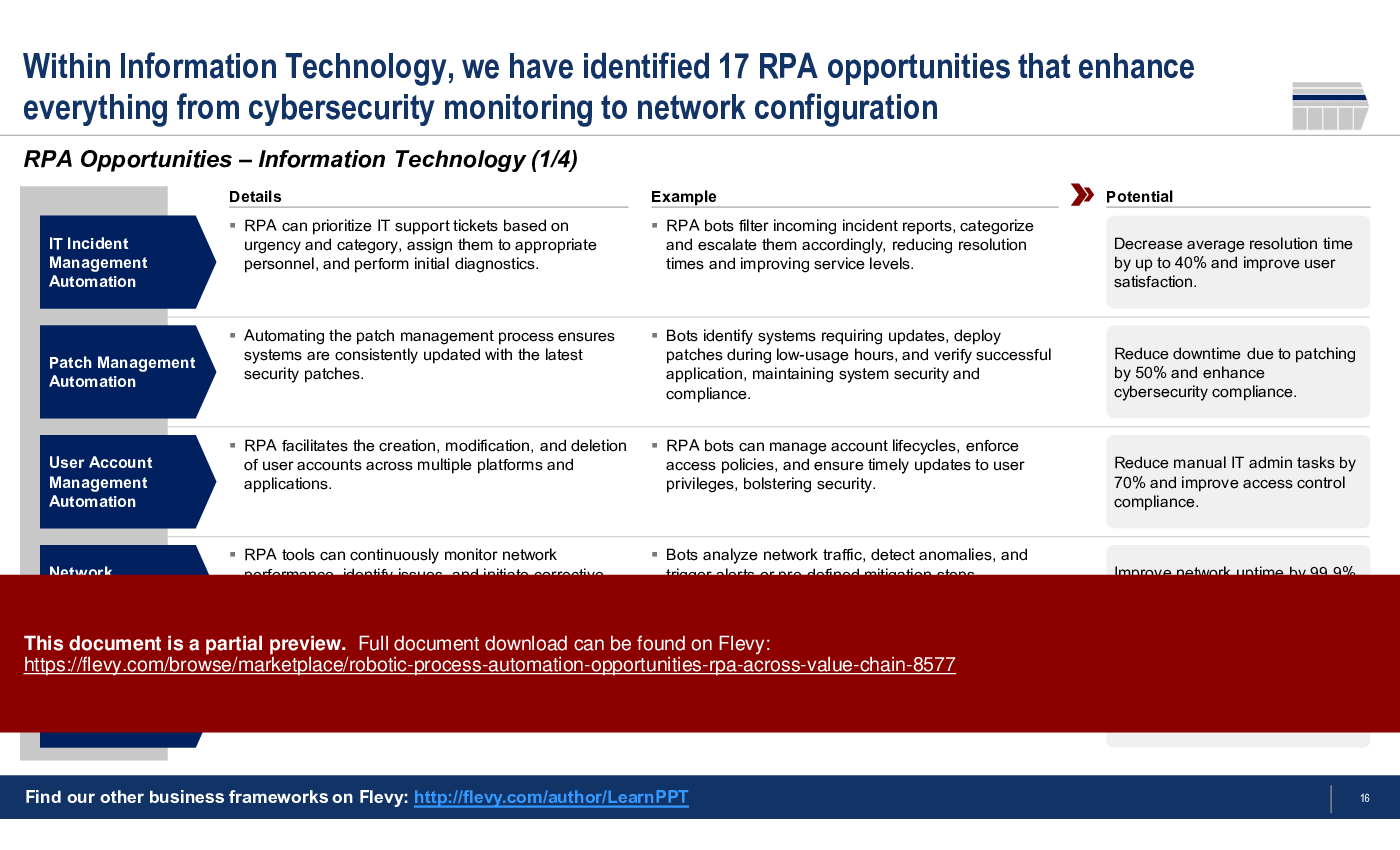
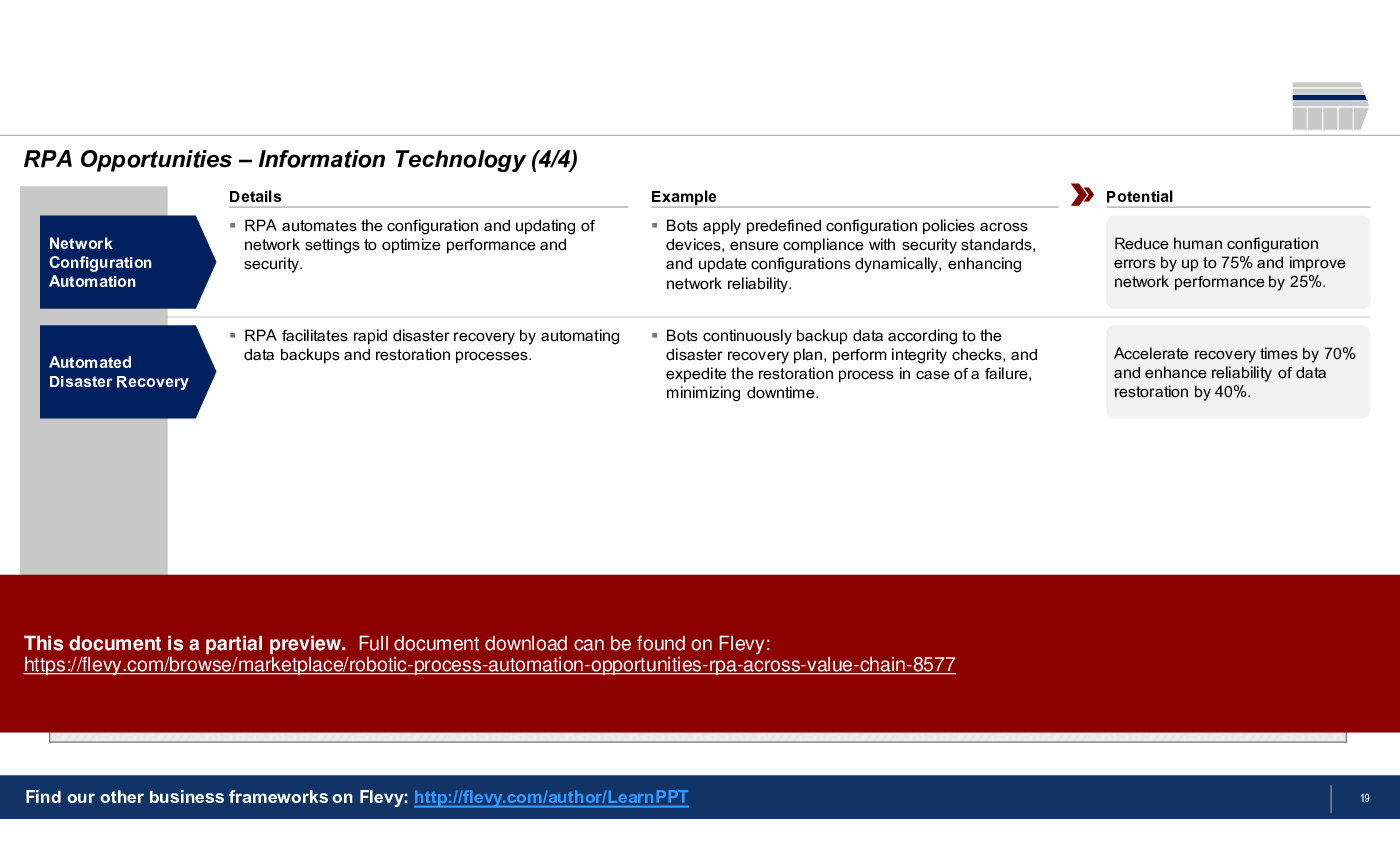
3. Information Technology
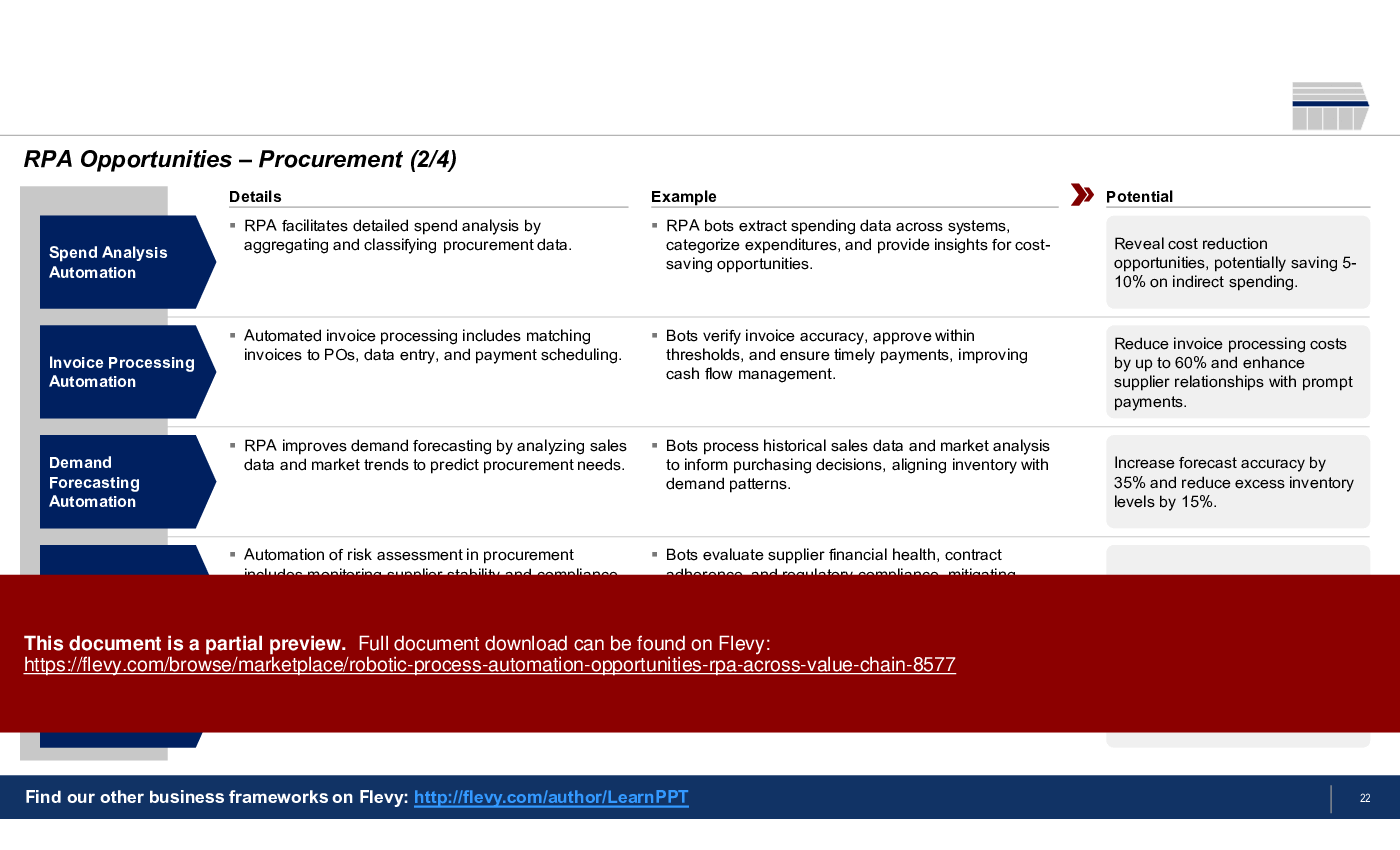
4. Procurement
5. Product Development
6. Logistics
7. Operations
8. Marketing & Sales
9. Service
Note these functions are slightly modified from the original Michael Porter Value Chain, so it is better adapted to RPA.
This PowerPoint presentation is organized into these 9 functions. For each function, we delineate a series of RPA opportunities, which includes examples and a quantification of potential impact for each opportunity.
Got a question about the product? Email us at support@flevy.com or ask the author directly by using the "Ask the Author a Question" form. If you cannot view the preview above this document description, go here to view the large preview instead.
MARCUS OVERVIEW
This synopsis was written by Marcus [?] based on the analysis of the full 44-slide presentation.
Executive Summary
This presentation outlines over 100+ Robotic Process Automation (RPA) opportunities mapped across the value chain, specifically tailored for sectors such as Finance, Human Resources, IT, Procurement, Product Development, Logistics, Operations, Marketing, Sales, and Service. Created by former consultants from top firms like McKinsey and BCG, this consulting-grade framework enables organizations to identify and implement RPA solutions effectively. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA allows employees to focus on higher-value work, enhancing productivity and job satisfaction. This framework serves as a critical resource for organizations pursuing digital transformation, providing measurable impacts and strategic reallocations of human resources.
Who This Is For and When to Use
• Corporate executives looking to enhance operational efficiency through automation
• Integration leaders responsible for implementing RPA solutions across various functions
• Consultants advising organizations on digital transformation strategies
• HR leaders aiming to streamline administrative processes and improve employee experience
• IT managers focused on optimizing service delivery and cybersecurity
Best-fit moments to use this deck:
• During strategic planning sessions for digital transformation initiatives
• When assessing current operational inefficiencies and identifying automation opportunities
• In workshops aimed at training teams on RPA implementation and best practices
• For presentations to stakeholders on the benefits and impacts of RPA across functions
Learning Objectives
• Define the concept of RPA and its relevance across various business functions
• Identify and quantify RPA opportunities within the value chain
• Build a strategic plan for implementing RPA solutions tailored to organizational needs
• Establish metrics for measuring the impact of RPA on operational efficiency and employee satisfaction
• Create a roadmap for integrating RPA into existing processes and systems
• Develop a governance framework for managing RPA initiatives and ensuring compliance
Table of Contents
• Executive Summary (page 3)
• RPA Opportunities across the Value Chain
• Finance & Accounting (page 7)
• Human Resource Management (page 11)
• Information Technology (page 15)
• Procurement (page 20)
• Product Development (page 25)
• Logistics (page 28)
• Operations (page 31)
• Marketing & Sales (page 35)
• Service (page 39)
Primary Topics Covered
• RPA Overview - An introduction to RPA technology and its role in automating repetitive tasks across various functions.
• Value Chain Analysis - Mapping RPA opportunities across the modified Porter Value Chain to enhance operational efficiency.
• Function-Specific Opportunities - Detailed exploration of RPA applications in Finance, HR, IT, Procurement, Product Development, Logistics, Operations, Marketing, Sales, and Service.
• Impact Quantification - Metrics and potential benefits associated with each identified RPA opportunity.
• Implementation Strategies - Best practices for deploying RPA solutions effectively within organizations.
Deliverables, Templates, and Tools
• RPA opportunity assessment templates for each function
• Implementation roadmap for RPA initiatives
• Metrics dashboard for tracking RPA impact
• Governance framework for RPA management
• Case studies illustrating successful RPA deployments
Slide Highlights
• Overview of RPA technology and its benefits
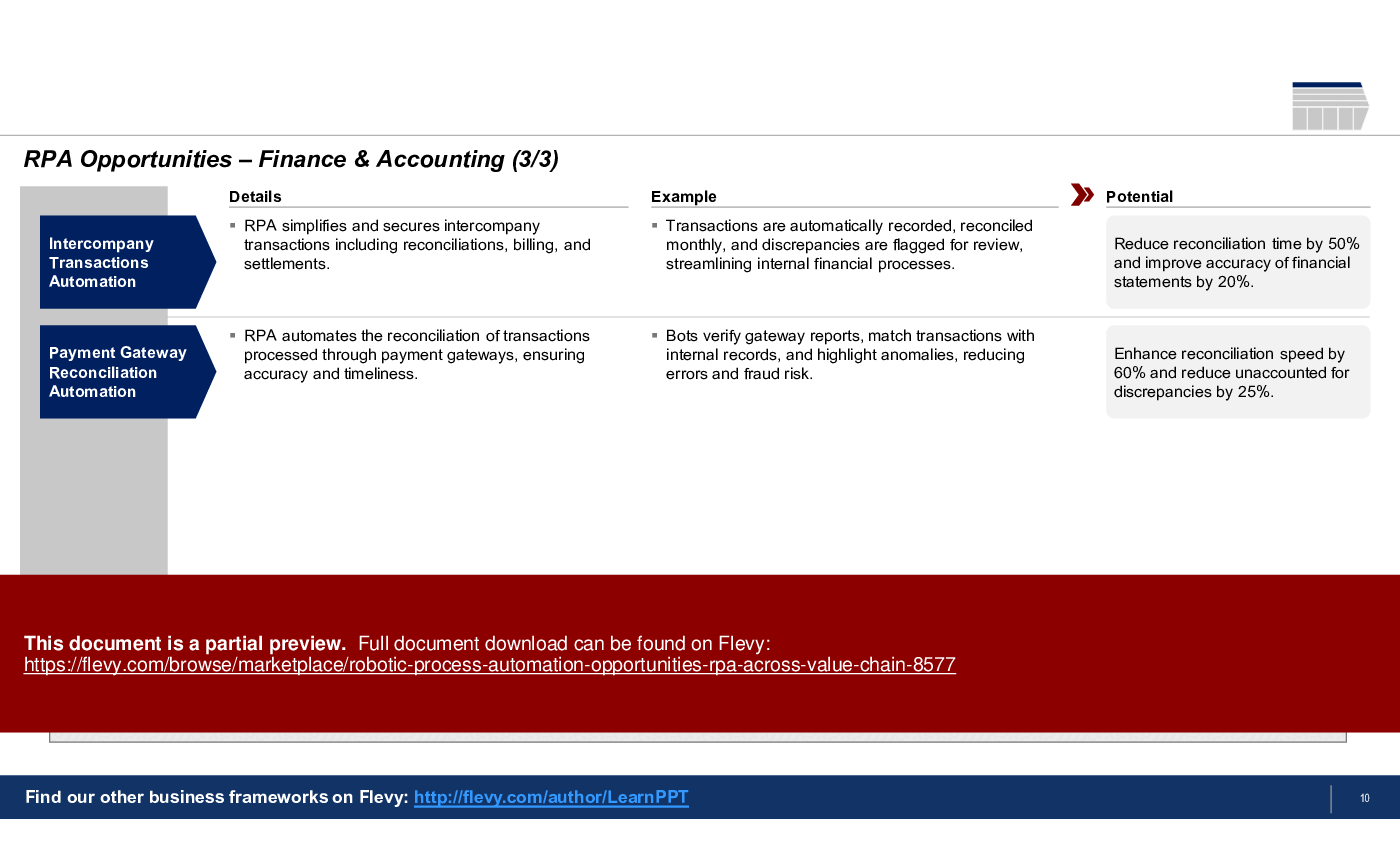
• Detailed breakdown of RPA opportunities in Finance, including accounts receivable and tax compliance automation
• Insights into HR automation, focusing on recruitment and onboarding processes
• IT RPA applications, highlighting incident management and cybersecurity monitoring
• Procurement efficiencies through automated spend analysis and supplier onboarding
• Logistics improvements via demand forecasting and warehouse management automation
Potential Workshop Agenda
RPA Strategy Development Session (90 minutes)
• Discuss current operational challenges and identify potential RPA opportunities
• Review case studies of successful RPA implementations
• Develop a preliminary RPA implementation roadmap
RPA Impact Measurement Workshop (60 minutes)
• Establish key performance indicators for RPA initiatives
• Create a metrics dashboard for tracking RPA effectiveness
RPA Governance Framework Session (60 minutes)
• Define roles and responsibilities for RPA management
• Develop compliance and oversight mechanisms for RPA initiatives
Customization Guidance
• Tailor the RPA opportunity assessment templates to reflect organizational priorities and specific functions
• Adjust the implementation roadmap to align with existing digital transformation strategies
• Incorporate industry-specific metrics for measuring RPA impact
Secondary Topics Covered
• Change management strategies for RPA adoption
• Risk management considerations in RPA implementation
• Integration of RPA with existing IT systems and processes
• Best practices for training employees on RPA tools and technologies
FAQ
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA is a technology that uses software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work.
How can RPA benefit my organization?
RPA can significantly lower operational costs, increase productivity, enhance accuracy, and improve employee satisfaction by freeing them from mundane tasks.
What functions can RPA be applied to?
RPA can be applied across various functions, including Finance, HR, IT, Procurement, Product Development, Logistics, Operations, Marketing, Sales, and Service.
How do I identify RPA opportunities within my organization?
Conduct a thorough assessment of current processes to identify repetitive tasks that can be automated, focusing on areas with high volume and low complexity.
What metrics should I use to measure RPA impact?
Key metrics include cost savings, time reduction, error rates, employee satisfaction, and overall process efficiency.
How do I ensure compliance when implementing RPA?
Establish a governance framework that includes oversight mechanisms, compliance checks, and regular audits of RPA processes.
What are the common challenges in RPA implementation?
Challenges may include resistance to change, integration with legacy systems, and ensuring data security and compliance.
How can I train my team on RPA tools?
Provide training sessions, workshops, and resources that focus on the specific RPA tools being implemented, along with best practices for usage.
Glossary
• Robotic Process Automation (RPA) - Technology that automates repetitive tasks using software robots.
• Value Chain - A model that describes the full range of activities needed to create a product or service.
• Digital Transformation - The integration of digital technology into all areas of a business, fundamentally changing how it operates and delivers value.
• Governance Framework - A structure that outlines roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing RPA initiatives.
• Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) - Metrics used to evaluate the success of an organization or of a particular activity in which it engages.
• Change Management - The approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and organizations to a desired future state.
• Compliance - The act of conforming to laws, regulations, and guidelines relevant to the business.
• Process Efficiency - A measure of how well a process converts inputs into outputs with minimal waste.
• Employee Satisfaction - A measure of how happy and content employees are with their jobs and work environment.
• Integration - The process of combining different systems and processes to work together effectively.
• Automation - The use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention.
• Operational Costs - The expenses associated with the day-to-day functioning of a business.
• Customer Experience - The overall perception of a customer regarding their interactions with a company.
• Data Security - The practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft.
• Supplier Onboarding - The process of integrating a new supplier into a company's supply chain.
• Demand Forecasting - The process of estimating future customer demand for a product or service.
• Inventory Management - The supervision of non-capitalized assets (inventory) and stock items.
• Service Level Agreement (SLA) - A contract that defines the level of service expected from a service provider.
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM) - A technology for managing a company's relationships and interactions with potential customers and clients.
• Feedback Loop - A system where the outputs of a process are circled back and used as inputs.
VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS PPT SLIDES
Source: Best Practices in Value Chain Analysis, RPA PowerPoint Slides: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Opportunities (across Value Chain) PowerPoint (PPTX) Presentation Slide Deck, LearnPPT Consulting